
rtk
CLI proxy that reduces LLM token consumption by 60-90% on common dev commands. Single Rust binary, zero dependencies
Stars: 452
RTK is a lightweight and flexible tool for real-time kinematic positioning. It provides accurate positioning data by combining data from GPS satellites with a reference station. RTK is commonly used in surveying, agriculture, construction, and drone navigation. The tool offers real-time corrections to improve the accuracy of GPS data, making it ideal for applications requiring precise location information. With RTK, users can achieve centimeter-level accuracy in their positioning data, enabling them to perform tasks that demand high precision and reliability.
README:
High-performance CLI proxy to minimize LLM token consumption.
rtk filters and compresses command outputs before they reach your LLM context, saving 60-90% of tokens on common operations.
There are TWO different projects named "rtk":
-
✅ This project (Rust Token Killer) - LLM token optimizer
- Repos:
rtk-ai/rtk - Purpose: Reduce Claude Code token consumption
- Repos:
-
❌ reachingforthejack/rtk - Rust Type Kit (DIFFERENT PROJECT)
- Purpose: Query Rust codebase and generate types
- DO NOT install this one if you want token optimization
How to verify you have the correct rtk:
rtk --version # Should show "rtk X.Y.Z"
rtk gain # Should show token savings statsIf rtk gain doesn't exist, you installed the wrong package. See installation instructions below.
Typical session without rtk: ~150,000 tokens With rtk: ~45,000 tokens → 70% reduction
| Operation | Frequency | Standard | rtk | Savings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
ls / tree
|
10× | 2,000 | 400 | -80% |
cat / read
|
20× | 40,000 | 12,000 | -70% |
grep / rg
|
8× | 16,000 | 3,200 | -80% |
git status |
10× | 3,000 | 600 | -80% |
git diff |
5× | 10,000 | 2,500 | -75% |
git log |
5× | 2,500 | 500 | -80% |
git add/commit/push |
8× | 1,600 | 120 | -92% |
npm test / cargo test
|
5× | 25,000 | 2,500 | -90% |
docker ps |
3× | 900 | 180 | -80% |
| Total | ~101,000 | ~22,000 | -78% |
Estimates based on medium-sized TypeScript/Rust projects. Actual savings vary by project size.
ALWAYS verify if rtk is already installed before installing:
rtk --version # Check if installed
rtk gain # Verify it's the Token Killer (not Type Kit)
which rtk # Check installation pathIf already installed and rtk gain works, DO NOT reinstall. Skip to Quick Start.
curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rtk-ai/rtk/refs/heads/master/install.sh | shAfter installation, verify you have the correct rtk:
rtk gain # Must show token savings stats (not "command not found")# From rtk-ai upstream (maintained by pszymkowiak)
cargo install --git https://github.com/rtk-ai/rtk
# OR if published to crates.io
cargo install rtkcargo install rtk from crates.io might install the wrong package (Type Kit instead of Token Killer). Always verify with rtk gain after installation.
Download from rtk-ai/releases:
- macOS:
rtk-x86_64-apple-darwin.tar.gz/rtk-aarch64-apple-darwin.tar.gz - Linux:
rtk-x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu.tar.gz/rtk-aarch64-unknown-linux-gnu.tar.gz - Windows:
rtk-x86_64-pc-windows-msvc.zip
# 1. Verify installation
rtk gain # Must show token stats, not "command not found"
# 2. Initialize for Claude Code (RECOMMENDED: hook-first mode)
rtk init --global
# → Installs hook + creates slim RTK.md (10 lines, 99.5% token savings)
# → Follow printed instructions to add hook to ~/.claude/settings.json
# 3. Test it works
rtk git status # Should show ultra-compact output
rtk init --show # Verify hook is installed and executable
# Alternative modes:
# rtk init --global --claude-md # Legacy: full injection (137 lines)
# rtk init # Local project only (./CLAUDE.md)New in v0.9.5: Hook-first installation eliminates ~2000 tokens from Claude's context while maintaining full RTK functionality through transparent command rewriting.
-u, --ultra-compact # ASCII icons, inline format (extra token savings)
-v, --verbose # Increase verbosity (-v, -vv, -vvv)rtk ls . # Token-optimized directory tree
rtk read file.rs # Smart file reading
rtk read file.rs -l aggressive # Signatures only (strips bodies)
rtk smart file.rs # 2-line heuristic code summary
rtk find "*.rs" . # Compact find results
rtk grep "pattern" . # Grouped search resultsrtk git status # Compact status
rtk git log -n 10 # One-line commits
rtk git diff # Condensed diff
rtk git add # → "ok ✓"
rtk git commit -m "msg" # → "ok ✓ abc1234"
rtk git push # → "ok ✓ main"
rtk git pull # → "ok ✓ 3 files +10 -2"rtk test cargo test # Show failures only (-90% tokens)
rtk err npm run build # Errors/warnings only
rtk summary <long command> # Heuristic summary
rtk log app.log # Deduplicated logs
rtk gh pr list # Compact PR listing
rtk gh pr view 42 # PR details + checks summary
rtk gh issue list # Compact issue listing
rtk gh run list # Workflow run status
rtk wget https://example.com # Download, strip progress bars
rtk config # Show config (--create to generate)rtk json config.json # Structure without values
rtk deps # Dependencies summary
rtk env -f AWS # Filtered env vars
# Token Savings Analytics (includes execution time metrics)
rtk gain # Summary stats with total exec time
rtk gain --graph # With ASCII graph of last 30 days
rtk gain --history # With recent command history (10)
rtk gain --quota --tier 20x # Monthly quota analysis (pro/5x/20x)
# Temporal Breakdowns (includes time metrics per period)
rtk gain --daily # Day-by-day with avg execution time
rtk gain --weekly # Week-by-week breakdown
rtk gain --monthly # Month-by-month breakdown
rtk gain --all # All breakdowns combined
# Export Formats (includes total_time_ms and avg_time_ms fields)
rtk gain --all --format json # JSON export for APIs/dashboards
rtk gain --all --format csv # CSV export for Excel/analysis📖 API Documentation: For programmatic access to tracking data (Rust library usage, CI/CD integration, custom dashboards), see docs/tracking.md.
Scans your Claude Code session history to find commands where rtk would have saved tokens. Use it to:
- Measure what you're missing — see exactly how many tokens you could save
- Identify habits — find which commands you keep running without rtk
- Spot new opportunities — see unhandled commands that could become rtk features
rtk discover # Current project, last 30 days
rtk discover --all # All Claude Code projects
rtk discover --all --since 7 # Last 7 days across all projects
rtk discover -p aristote # Filter by project name (substring)
rtk discover --format json # Machine-readable outputExample output:
RTK Discover -- Savings Opportunities
====================================================
Scanned: 142 sessions (last 30 days), 1786 Bash commands
Already using RTK: 108 commands (6%)
MISSED SAVINGS -- Commands RTK already handles
----------------------------------------------------
Command Count RTK Equivalent Est. Savings
git log 434 rtk git ~55.9K tokens
cargo test 203 rtk cargo ~49.9K tokens
ls -la 107 rtk ls ~11.8K tokens
gh pr 80 rtk gh ~10.4K tokens
----------------------------------------------------
Total: 986 commands -> ~143.9K tokens saveable
TOP UNHANDLED COMMANDS -- open an issue?
----------------------------------------------------
Command Count Example
git checkout 84 git checkout feature/my-branch
cargo run 32 cargo run -- gain --help
----------------------------------------------------
-> github.com/rtk-ai/rtk/issues
rtk docker ps # Compact container list
rtk docker images # Compact image list
rtk docker logs <container> # Deduplicated logs
rtk kubectl pods # Compact pod list
rtk kubectl logs <pod> # Deduplicated logs
rtk kubectl services # Compact service listrtk lint # ESLint grouped by rule/file
rtk lint biome # Supports other linters too
rtk tsc # TypeScript errors grouped by file
rtk next build # Next.js build compact output
rtk prettier --check . # Files needing formatting
rtk vitest run # Test failures only
rtk playwright test # E2E results (failures only)
rtk prisma generate # Schema generation (no ASCII art)
rtk prisma migrate dev --name x # Migration summary
rtk prisma db-push # Schema push summaryDirectory listing:
# ls -la (45 lines, ~800 tokens)
drwxr-xr-x 15 user staff 480 Jan 23 10:00 .
drwxr-xr-x 5 user staff 160 Jan 23 09:00 ..
-rw-r--r-- 1 user staff 1234 Jan 23 10:00 Cargo.toml
...
# rtk ls (12 lines, ~150 tokens)
📁 my-project/
├── src/ (8 files)
│ ├── main.rs
│ └── lib.rs
├── Cargo.toml
└── README.md
Git operations:
# git push (15 lines, ~200 tokens)
Enumerating objects: 5, done.
Counting objects: 100% (5/5), done.
Delta compression using up to 8 threads
...
# rtk git push (1 line, ~10 tokens)
ok ✓ main
Test output:
# cargo test (200+ lines on failure)
running 15 tests
test utils::test_parse ... ok
test utils::test_format ... ok
...
# rtk test cargo test (only failures, ~20 lines)
FAILED: 2/15 tests
✗ test_edge_case: assertion failed at src/lib.rs:42
✗ test_overflow: panic at src/utils.rs:18
- Smart Filtering: Removes noise (comments, whitespace, boilerplate)
- Grouping: Aggregates similar items (files by directory, errors by type)
- Truncation: Keeps relevant context, cuts redundancy
- Deduplication: Collapses repeated log lines with counts
| Command | Scope | Hook | RTK.md | CLAUDE.md | Tokens in Context | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
rtk init -g |
Global | ✅ | ✅ (10 lines) | @RTK.md | ~10 | Recommended: All projects, automatic |
rtk init -g --claude-md |
Global | ❌ | ❌ | Full (137 lines) | ~2000 | Legacy compatibility |
rtk init -g --hook-only |
Global | ✅ | ❌ | Nothing | 0 | Minimal setup, hook-only |
rtk init |
Local | ❌ | ❌ | Full (137 lines) | ~2000 | Single project, no hook |
rtk init --show # Show current configuration
rtk init -g # Install hook + RTK.md (recommended)
rtk init -g --claude-md # Legacy: full injection into CLAUDE.md
rtk init # Local project: full injection into ./CLAUDE.mdSettings.json Control:
rtk init -g # Default: prompt to patch [y/N]
rtk init -g --auto-patch # Patch settings.json without prompting
rtk init -g --no-patch # Skip patching, show manual instructionsMode Control:
rtk init -g --claude-md # Legacy: full 137-line injection (no hook)
rtk init -g --hook-only # Hook only, no RTK.mdUninstall:
rtk init -g --uninstall # Remove all RTK artifactsWhat is settings.json?
Claude Code configuration file that registers the RTK hook. The hook transparently rewrites commands (e.g., git status → rtk git status) before execution. Without this registration, Claude won't use the hook.
Backup Behavior:
RTK creates ~/.claude/settings.json.bak before making changes. If something breaks, restore with:
cp ~/.claude/settings.json.bak ~/.claude/settings.jsonMigration: If you previously used rtk init -g with the old system (137-line injection), simply re-run rtk init -g to automatically migrate to the new hook-first approach.
example of 3 days session:
📊 RTK Token Savings
════════════════════════════════════════
Total commands: 133
Input tokens: 30.5K
Output tokens: 10.7K
Tokens saved: 25.3K (83.0%)
By Command:
────────────────────────────────────────
Command Count Saved Avg%
rtk git status 41 17.4K 82.9%
rtk git push 54 3.4K 91.6%
rtk grep 15 3.2K 26.5%
rtk ls 23 1.4K 37.2%
Daily Savings (last 30 days):
────────────────────────────────────────
01-23 │███████████████████ 6.4K
01-24 │██████████████████ 5.9K
01-25 │ 18
01-26 │████████████████████████████████████████ 13.0KBy default, RTK stores tracking data in ~/.local/share/rtk/history.db. You can override this:
Environment variable (highest priority):
export RTK_DB_PATH="/path/to/custom.db"Config file (~/.config/rtk/config.toml):
[tracking]
database_path = "/path/to/custom.db"Priority: RTK_DB_PATH env var > config.toml > default location.
The most effective way to use rtk is with the auto-rewrite hook for Claude Code. Instead of relying on CLAUDE.md instructions (which subagents may ignore), this hook transparently intercepts Bash commands and rewrites them to their rtk equivalents before execution.
Result: 100% rtk adoption across all conversations and subagents, zero token overhead in Claude's context.
For Beginners:
Claude Code hooks are scripts that run before/after Claude executes commands. RTK uses a PreToolUse hook that intercepts Bash commands and rewrites them (e.g., git status → rtk git status) before execution. This is transparent - Claude never sees the rewrite, it just gets optimized output.
Why settings.json?
Claude Code reads ~/.claude/settings.json to find registered hooks. Without this file, Claude doesn't know the RTK hook exists. Think of it as the hook registry.
Is it safe?
Yes. RTK creates a backup (settings.json.bak) before changes. The hook is read-only (it only modifies command strings, never deletes files or accesses secrets). Review the hook script at ~/.claude/hooks/rtk-rewrite.sh anytime.
The hook runs as a Claude Code PreToolUse hook. When Claude Code is about to execute a Bash command like git status, the hook rewrites it to rtk git status before the command reaches the shell. Claude Code never sees the rewrite — it's transparent.
rtk init -g
# → Installs hook to ~/.claude/hooks/rtk-rewrite.sh (with executable permissions)
# → Creates ~/.claude/RTK.md (10 lines, minimal context footprint)
# → Adds @RTK.md reference to ~/.claude/CLAUDE.md
# → Prompts: "Patch settings.json? [y/N]"
# → If yes: creates backup (~/.claude/settings.json.bak), patches file
# Verify installation
rtk init --show # Shows hook status, settings.json registrationSettings.json Patching Options:
rtk init -g # Default: prompts for consent [y/N]
rtk init -g --auto-patch # Patch immediately without prompting (CI/CD)
rtk init -g --no-patch # Skip patching, print manual JSON snippetWhat is settings.json?
Claude Code's configuration file that registers the RTK hook. Without this, Claude won't use the hook. RTK backs up the file before changes (settings.json.bak).
Restart Required: After installation, restart Claude Code, then test with git status.
If automatic patching fails or you prefer manual control:
# 1. Install hook and RTK.md
rtk init -g --no-patch # Prints JSON snippet
# 2. Manually edit ~/.claude/settings.json (add the printed snippet)
# 3. Restart Claude CodeAlternative: Full manual setup
# 1. Copy the hook script
mkdir -p ~/.claude/hooks
cp .claude/hooks/rtk-rewrite.sh ~/.claude/hooks/rtk-rewrite.sh
chmod +x ~/.claude/hooks/rtk-rewrite.sh
# 2. Add to ~/.claude/settings.json under hooks.PreToolUse:Add this entry to the PreToolUse array in ~/.claude/settings.json:
{
"hooks": {
"PreToolUse": [
{
"matcher": "Bash",
"hooks": [
{
"type": "command",
"command": "~/.claude/hooks/rtk-rewrite.sh"
}
]
}
]
}
}The hook is included in this repository at .claude/hooks/rtk-rewrite.sh. To use it in another project, copy the hook and add the same settings.json entry using a relative path or project-level .claude/settings.json.
| Raw Command | Rewritten To |
|---|---|
git status/diff/log/add/commit/push/pull/branch/fetch/stash |
rtk git ... |
gh pr/issue/run |
rtk gh ... |
cargo test/build/clippy |
rtk cargo ... |
cat <file> |
rtk read <file> |
rg/grep <pattern> |
rtk grep <pattern> |
ls |
rtk ls |
vitest/pnpm test |
rtk vitest run |
tsc/pnpm tsc |
rtk tsc |
eslint/pnpm lint |
rtk lint |
prettier |
rtk prettier |
playwright |
rtk playwright |
prisma |
rtk prisma |
docker ps/images/logs |
rtk docker ... |
kubectl get/logs |
rtk kubectl ... |
curl |
rtk curl |
pnpm list/ls/outdated |
rtk pnpm ... |
Commands already using rtk, heredocs (<<), and unrecognized commands pass through unchanged.
If you prefer Claude Code to suggest rtk usage rather than automatically rewriting commands, use the suggest hook pattern instead. This emits a system reminder when rtk-compatible commands are detected, without modifying the command execution.
Comparison:
| Aspect | Auto-Rewrite Hook | Suggest Hook |
|---|---|---|
| Strategy | Intercepts and modifies command before execution | Emits system reminder when rtk-compatible command detected |
| Effect | Claude Code never sees the original command | Claude Code receives hint to use rtk, decides autonomously |
| Adoption | 100% (forced) | ~70-85% (depends on Claude Code's adherence to instructions) |
| Use Case | Production workflows, guaranteed savings | Learning mode, auditing, user preference for explicit control |
| Overhead | Zero (transparent rewrite) | Minimal (reminder message in context) |
When to use suggest over rewrite:
- You want to audit which commands Claude Code chooses to run
- You're learning rtk patterns and want visibility into the rewrite logic
- You prefer Claude Code to make explicit decisions rather than transparent rewrites
- You want to preserve exact command execution for debugging
1. Create the suggest hook script
mkdir -p ~/.claude/hooks
cp .claude/hooks/rtk-suggest.sh ~/.claude/hooks/rtk-suggest.sh
chmod +x ~/.claude/hooks/rtk-suggest.sh2. Add to ~/.claude/settings.json
{
"hooks": {
"PreToolUse": [
{
"matcher": "Bash",
"hooks": [
{
"type": "command",
"command": "~/.claude/hooks/rtk-suggest.sh"
}
]
}
]
}
}The suggest hook detects the same commands as the rewrite hook but outputs a systemMessage instead of updatedInput, informing Claude Code that an rtk alternative exists.
Complete Removal (Global Only):
rtk init -g --uninstall
# Removes:
# - ~/.claude/hooks/rtk-rewrite.sh
# - ~/.claude/RTK.md
# - @RTK.md reference from ~/.claude/CLAUDE.md
# - RTK hook entry from ~/.claude/settings.json
# Restart Claude Code after uninstallRestore from Backup (if needed):
cp ~/.claude/settings.json.bak ~/.claude/settings.jsonLocal Projects: Manually remove RTK instructions from ./CLAUDE.md
Binary Removal:
# If installed via cargo
cargo uninstall rtk
# If installed via package manager
brew uninstall rtk # macOS Homebrew
sudo apt remove rtk # Debian/Ubuntu
sudo dnf remove rtk # Fedora/RHEL-
TROUBLESHOOTING.md -
⚠️ Fix common issues (wrong rtk installed, missing commands, PATH issues) - INSTALL.md - Detailed installation guide with verification steps
- AUDIT_GUIDE.md - Complete guide to token savings analytics, temporal breakdowns, and data export
- CLAUDE.md - Claude Code integration instructions and project context
- ARCHITECTURE.md - Technical architecture and development guide
- SECURITY.md - Security policy, vulnerability reporting, and PR review process
Problem: rtk init -g fails to patch settings.json
Solutions:
# Check if settings.json is valid JSON
cat ~/.claude/settings.json | python3 -m json.tool
# Use manual patching
rtk init -g --no-patch # Prints JSON snippet
# Restore from backup
cp ~/.claude/settings.json.bak ~/.claude/settings.json
# Check permissions
ls -la ~/.claude/settings.json
chmod 644 ~/.claude/settings.jsonProblem: Commands still not using RTK after rtk init -g
Solutions:
# Verify hook is registered
rtk init --show
# Check settings.json manually
cat ~/.claude/settings.json | grep rtk-rewrite
# Restart Claude Code (critical step!)
# Test with a command
git status # Should use rtk automaticallyProblem: RTK traces remain after rtk init -g --uninstall
Manual Cleanup:
# Remove hook
rm ~/.claude/hooks/rtk-rewrite.sh
# Remove RTK.md
rm ~/.claude/RTK.md
# Remove @RTK.md reference
nano ~/.claude/CLAUDE.md # Delete @RTK.md line
# Remove from settings.json
nano ~/.claude/settings.json # Remove RTK hook entry
# Restore from backup
cp ~/.claude/settings.json.bak ~/.claude/settings.jsonSee TROUBLESHOOTING.md for more issues and solutions.
RTK implements a comprehensive 3-layer security review process for external PRs:
Every PR triggers .github/workflows/security-check.yml:
- Cargo audit: CVE detection in dependencies
- Critical files alert: Flags modifications to high-risk files (runner.rs, tracking.rs, Cargo.toml, workflows)
- Dangerous pattern scanning: Shell injection, network operations, unsafe code, panic risks
- Dependency auditing: Supply chain verification for new crates
- Clippy security lints: Enforces Rust safety best practices
Results appear in the PR's GitHub Actions summary.
For comprehensive manual review, maintainers with Claude Code can use:
/rtk-pr-security <PR_NUMBER>The skill performs:
- Critical files analysis: Detects modifications to shell execution, validation, or CI/CD files
- Dangerous pattern detection: Identifies shell injection, environment manipulation, exfiltration vectors
- Supply chain audit: Verifies new dependencies on crates.io (downloads, maintainer, license)
- Semantic analysis: Checks intent vs reality, logic bombs, code quality red flags
- Structured report generation: Produces security assessment with risk level and verdict
Skill installation (maintainers only):
# The skill is bundled in the rtk-pr-security directory
# Copy to your Claude skills directory:
cp -r ~/.claude/skills/rtk-pr-security ~/.claude/skills/The skill includes:
-
SKILL.md- Workflow automation and usage guide -
critical-files.md- RTK-specific file risk tiers with attack scenarios -
dangerous-patterns.md- Regex patterns with exploitation examples -
checklist.md- Manual review template
For PRs touching critical files or adding dependencies:
- 2 maintainers required for Cargo.toml, workflows, or Tier 1 files
- Isolated testing recommended for high-risk changes
- Follow the checklist in SECURITY.md
See SECURITY.md for complete security policy and review guidelines.
MIT License - see LICENSE for details.
Contributions welcome! Please open an issue or PR on GitHub.
For external contributors: Your PR will undergo automated security review (see SECURITY.md). This protects RTK's shell execution capabilities against injection attacks and supply chain vulnerabilities.
- Website: https://www.rtk-ai.app
- Email: [email protected]
- Issues: https://github.com/rtk-ai/rtk/issues
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for rtk
Similar Open Source Tools

rtk
RTK is a lightweight and flexible tool for real-time kinematic positioning. It provides accurate positioning data by combining data from GPS satellites with a reference station. RTK is commonly used in surveying, agriculture, construction, and drone navigation. The tool offers real-time corrections to improve the accuracy of GPS data, making it ideal for applications requiring precise location information. With RTK, users can achieve centimeter-level accuracy in their positioning data, enabling them to perform tasks that demand high precision and reliability.
botserver
General Bots is a self-hosted AI automation platform and LLM conversational platform focused on convention over configuration and code-less approaches. It serves as the core API server handling LLM orchestration, business logic, database operations, and multi-channel communication. The platform offers features like multi-vendor LLM API, MCP + LLM Tools Generation, Semantic Caching, Web Automation Engine, Enterprise Data Connectors, and Git-like Version Control. It enforces a ZERO TOLERANCE POLICY for code quality and security, with strict guidelines for error handling, performance optimization, and code patterns. The project structure includes modules for core functionalities like Rhai BASIC interpreter, security, shared types, tasks, auto task system, file operations, learning system, and LLM assistance.
mcp-context-forge
MCP Context Forge is a powerful tool for generating context-aware data for machine learning models. It provides functionalities to create diverse datasets with contextual information, enhancing the performance of AI algorithms. The tool supports various data formats and allows users to customize the context generation process easily. With MCP Context Forge, users can efficiently prepare training data for tasks requiring contextual understanding, such as sentiment analysis, recommendation systems, and natural language processing.
claude-code-mastery
Claude Code Mastery is a comprehensive tool for maximizing Claude Code, offering a production-ready project template with 16 slash commands, deterministic hook enforcement, MongoDB wrapper, live AI monitoring, and three-layer security. It provides a security gatekeeper, project scaffolding blueprint, MCP server integration, workflow automation through custom commands, and emphasizes the importance of single-purpose chats to avoid performance degradation.
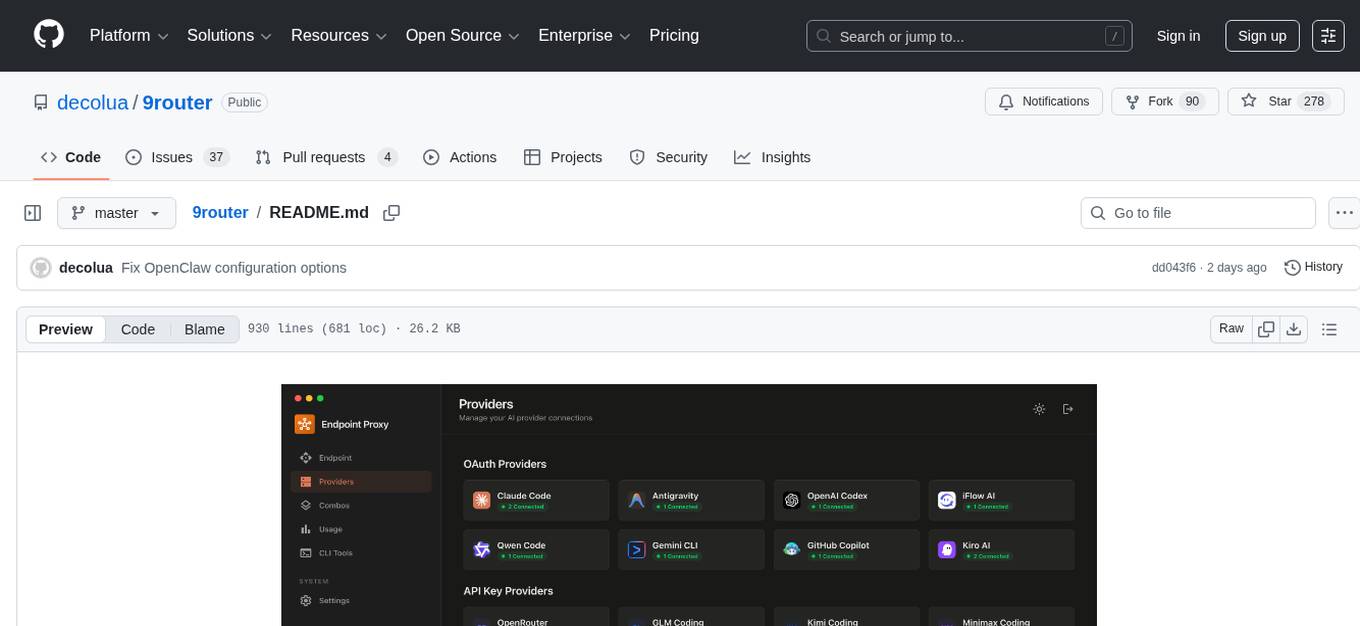
9router
9Router is a free AI router tool designed to help developers maximize their AI subscriptions, auto-route to free and cheap AI models with smart fallback, and avoid hitting limits and wasting money. It offers features like real-time quota tracking, format translation between OpenAI, Claude, and Gemini, multi-account support, auto token refresh, custom model combinations, request logging, cloud sync, usage analytics, and flexible deployment options. The tool supports various providers like Claude Code, Codex, Gemini CLI, GitHub Copilot, GLM, MiniMax, iFlow, Qwen, and Kiro, and allows users to create combos for different scenarios. Users can connect to the tool via CLI tools like Cursor, Claude Code, Codex, OpenClaw, and Cline, and deploy it on VPS, Docker, or Cloudflare Workers.
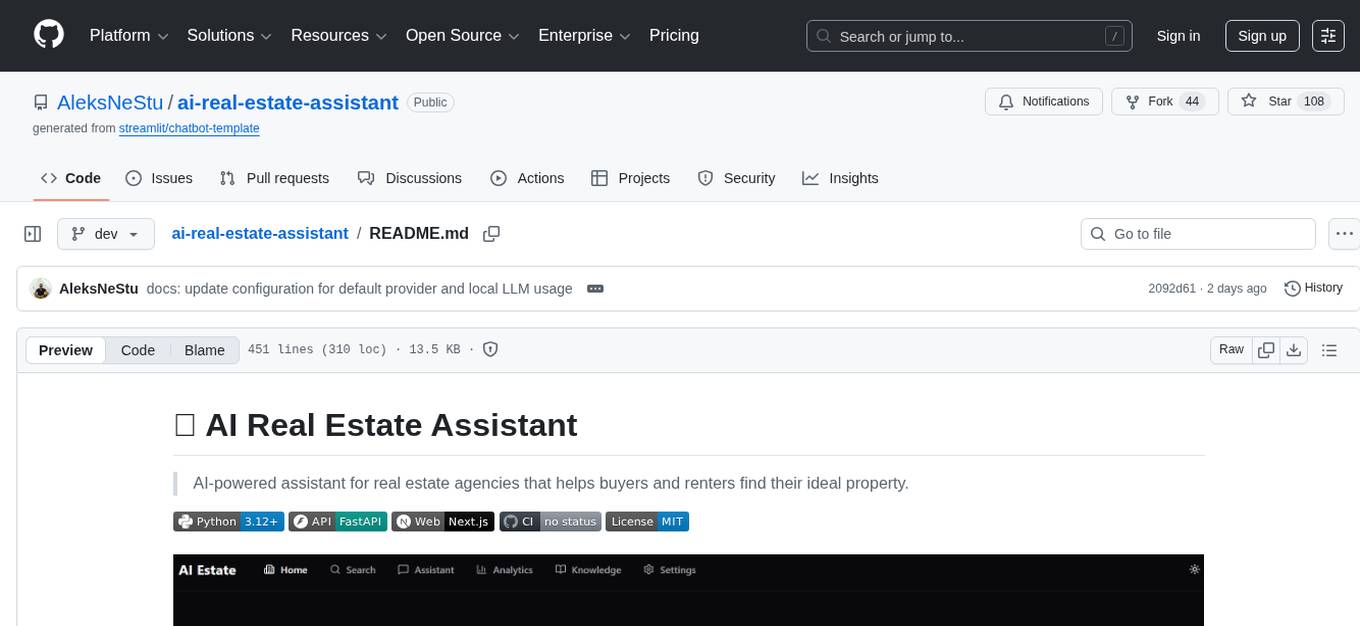
ai-real-estate-assistant
AI Real Estate Assistant is a modern platform that uses AI to assist real estate agencies in helping buyers and renters find their ideal properties. It features multiple AI model providers, intelligent query processing, advanced search and retrieval capabilities, and enhanced user experience. The tool is built with a FastAPI backend and Next.js frontend, offering semantic search, hybrid agent routing, and real-time analytics.
VimLM
VimLM is an AI-powered coding assistant for Vim that integrates AI for code generation, refactoring, and documentation directly into your Vim workflow. It offers native Vim integration with split-window responses and intuitive keybindings, offline first execution with MLX-compatible models, contextual awareness with seamless integration with codebase and external resources, conversational workflow for iterating on responses, project scaffolding for generating and deploying code blocks, and extensibility for creating custom LLM workflows with command chains.
flyte-sdk
Flyte 2 SDK is a pure Python tool for type-safe, distributed orchestration of agents, ML pipelines, and more. It allows users to write data pipelines, ML training jobs, and distributed compute in Python without any DSL constraints. With features like async-first parallelism and fine-grained observability, Flyte 2 offers a seamless workflow experience. Users can leverage core concepts like TaskEnvironments for container configuration, pure Python workflows for flexibility, and async parallelism for distributed execution. Advanced features include sub-task observability with tracing and remote task execution. The tool also provides native Jupyter integration for running and monitoring workflows directly from notebooks. Configuration and deployment are made easy with configuration files and commands for deploying and running workflows. Flyte 2 is licensed under the Apache 2.0 License.
pipelock
Pipelock is an all-in-one security harness designed for AI agents, offering control over network egress, detection of credential exfiltration, scanning for prompt injection, and monitoring workspace integrity. It utilizes capability separation to restrict the agent process with secrets and employs a separate fetch proxy for web browsing. The tool runs a 7-layer scanner pipeline on every request to ensure security. Pipelock is suitable for users running AI agents like Claude Code, OpenHands, or any AI agent with shell access and API keys.
readme-ai
README-AI is a developer tool that auto-generates README.md files using a combination of data extraction and generative AI. It streamlines documentation creation and maintenance, enhancing developer productivity. This project aims to enable all skill levels, across all domains, to better understand, use, and contribute to open-source software. It offers flexible README generation, supports multiple large language models (LLMs), provides customizable output options, works with various programming languages and project types, and includes an offline mode for generating boilerplate README files without external API calls.

Callytics
Callytics is an advanced call analytics solution that leverages speech recognition and large language models (LLMs) technologies to analyze phone conversations from customer service and call centers. By processing both the audio and text of each call, it provides insights such as sentiment analysis, topic detection, conflict detection, profanity word detection, and summary. These cutting-edge techniques help businesses optimize customer interactions, identify areas for improvement, and enhance overall service quality. When an audio file is placed in the .data/input directory, the entire pipeline automatically starts running, and the resulting data is inserted into the database. This is only a v1.1.0 version; many new features will be added, models will be fine-tuned or trained from scratch, and various optimization efforts will be applied.

vibe-remote
Vibe Remote is a tool that allows developers to code using AI agents through Slack or Discord, eliminating the need for a laptop or IDE. It provides a seamless experience for coding tasks, enabling users to interact with AI agents in real-time, delegate tasks, and monitor progress. The tool supports multiple coding agents, offers a setup wizard for easy installation, and ensures security by running locally on the user's machine. Vibe Remote enhances productivity by reducing context-switching and enabling parallel task execution within isolated workspaces.
ChordMiniApp
ChordMini is an advanced music analysis platform with AI-powered chord recognition, beat detection, and synchronized lyrics. It features a clean and intuitive interface for YouTube search, chord progression visualization, interactive guitar diagrams with accurate fingering patterns, lead sheet with AI assistant for synchronized lyrics transcription, and various add-on features like Roman Numeral Analysis, Key Modulation Signals, Simplified Chord Notation, and Enhanced Chord Correction. The tool requires Node.js, Python 3.9+, and a Firebase account for setup. It offers a hybrid backend architecture for local development and production deployments, with features like beat detection, chord recognition, lyrics processing, rate limiting, and audio processing supporting MP3, WAV, and FLAC formats. ChordMini provides a comprehensive music analysis workflow from user input to visualization, including dual input support, environment-aware processing, intelligent caching, advanced ML pipeline, and rich visualization options.
kubectl-mcp-server
Control your entire Kubernetes infrastructure through natural language conversations with AI. Talk to your clusters like you talk to a DevOps expert. Debug crashed pods, optimize costs, deploy applications, audit security, manage Helm charts, and visualize dashboards—all through natural language. The tool provides 253 powerful tools, 8 workflow prompts, 8 data resources, and works with all major AI assistants. It offers AI-powered diagnostics, built-in cost optimization, enterprise-ready features, zero learning curve, universal compatibility, visual insights, and production-grade deployment options. From debugging crashed pods to optimizing cluster costs, kubectl-mcp-server is your AI-powered DevOps companion.

ProxyPilot
ProxyPilot is a powerful local API proxy tool built in Go that eliminates the need for separate API keys when using Claude Code, Codex, Gemini, Kiro, and Qwen subscriptions with any AI coding tool. It handles OAuth authentication, token management, and API translation automatically, providing a single server to route requests. The tool supports multiple authentication providers, universal API translation, tool calling repair, extended thinking models, OAuth integration, multi-account support, quota auto-switching, usage statistics tracking, context compression, agentic harness for coding agents, session memory, system tray app, auto-updates, rollback support, and over 60 management APIs. ProxyPilot also includes caching layers for response and prompt caching to reduce latency and token usage.
Edit-Banana
Edit Banana is a universal content re-editor that allows users to transform fixed content into fully manipulatable assets. Powered by SAM 3 and multimodal large models, it enables high-fidelity reconstruction while preserving original diagram details and logical relationships. The platform offers advanced segmentation, fixed multi-round VLM scanning, high-quality OCR, user system with credits, multi-user concurrency, and a web interface. Users can upload images or PDFs to get editable DrawIO (XML) or PPTX files in seconds. The project structure includes components for segmentation, text extraction, frontend, models, and scripts, with detailed installation and setup instructions provided. The tool is open-source under the Apache License 2.0, allowing commercial use and secondary development.
For similar tasks

rtk
RTK is a lightweight and flexible tool for real-time kinematic positioning. It provides accurate positioning data by combining data from GPS satellites with a reference station. RTK is commonly used in surveying, agriculture, construction, and drone navigation. The tool offers real-time corrections to improve the accuracy of GPS data, making it ideal for applications requiring precise location information. With RTK, users can achieve centimeter-level accuracy in their positioning data, enabling them to perform tasks that demand high precision and reliability.
For similar jobs
AgriTech
AgriTech is an AI-powered smart agriculture platform designed to assist farmers with crop recommendations, yield prediction, plant disease detection, and community-driven collaboration—enabling sustainable and data-driven farming practices. It offers AI-driven decision support for modern agriculture, early-stage plant disease detection, crop yield forecasting using machine learning models, and a collaborative ecosystem for farmers and stakeholders. The platform includes features like crop recommendation, yield prediction, disease detection, an AI chatbot for platform guidance and agriculture support, a farmer community, and shopkeeper listings. AgriTech's AI chatbot provides comprehensive support for farmers with features like platform guidance, agriculture support, decision making, image analysis, and 24/7 support. The tech stack includes frontend technologies like HTML5, CSS3, JavaScript, backend technologies like Python (Flask) and optional Node.js, machine learning libraries like TensorFlow, Scikit-learn, OpenCV, and database & DevOps tools like MySQL, MongoDB, Firebase, Docker, and GitHub Actions.

rtk
RTK is a lightweight and flexible tool for real-time kinematic positioning. It provides accurate positioning data by combining data from GPS satellites with a reference station. RTK is commonly used in surveying, agriculture, construction, and drone navigation. The tool offers real-time corrections to improve the accuracy of GPS data, making it ideal for applications requiring precise location information. With RTK, users can achieve centimeter-level accuracy in their positioning data, enabling them to perform tasks that demand high precision and reliability.
Construction-Hazard-Detection
Construction-Hazard-Detection is an AI-driven tool focused on improving safety at construction sites by utilizing the YOLOv8 model for object detection. The system identifies potential hazards like overhead heavy loads and steel pipes, providing real-time analysis and warnings. Users can configure the system via a YAML file and run it using Docker. The primary dataset used for training is the Construction Site Safety Image Dataset enriched with additional annotations. The system logs are accessible within the Docker container for debugging, and notifications are sent through the LINE messaging API when hazards are detected.
Geoweaver
Geoweaver is an in-browser software that enables users to easily compose and execute full-stack data processing workflows using online spatial data facilities, high-performance computation platforms, and open-source deep learning libraries. It provides server management, code repository, workflow orchestration software, and history recording capabilities. Users can run it from both local and remote machines. Geoweaver aims to make data processing workflows manageable for non-coder scientists and preserve model run history. It offers features like progress storage, organization, SSH connection to external servers, and a web UI with Python support.
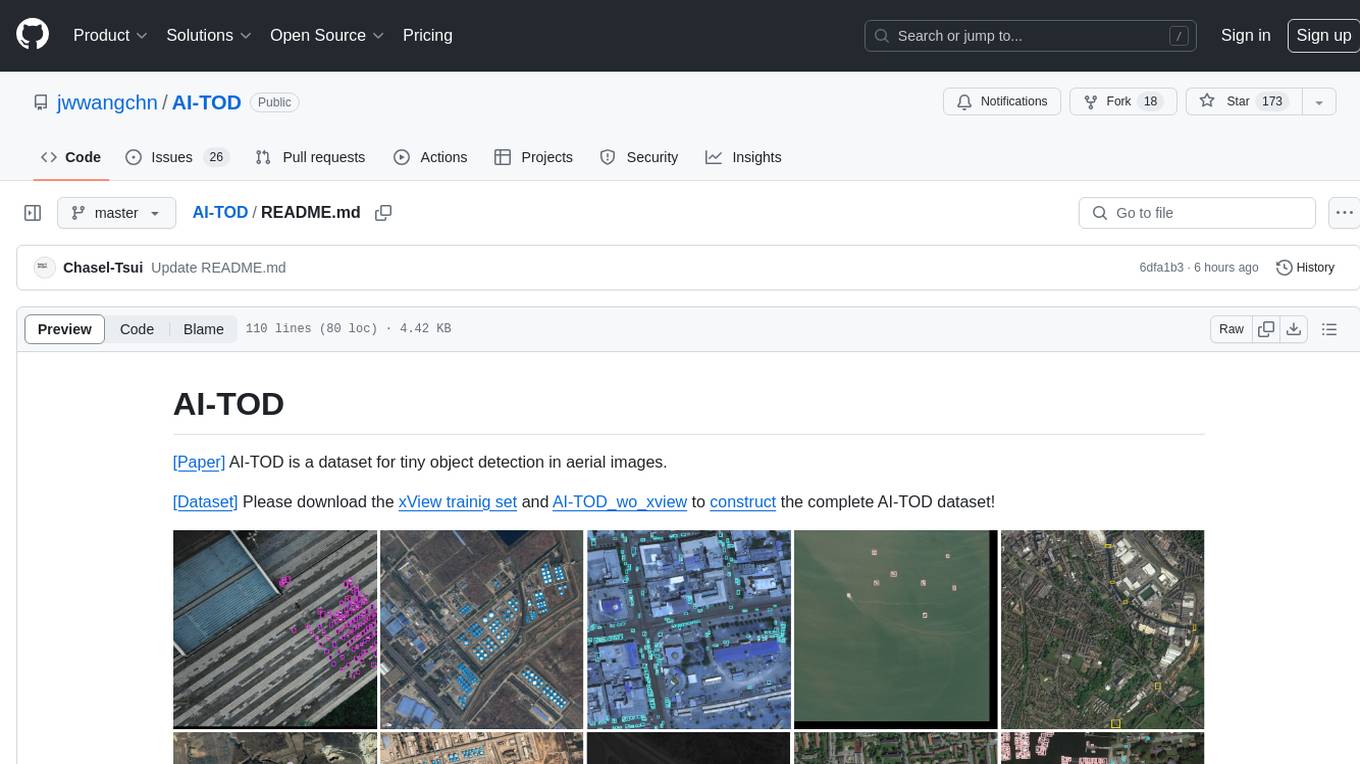
AI-TOD
AI-TOD is a dataset for tiny object detection in aerial images, containing 700,621 object instances across 28,036 images. Objects in AI-TOD are smaller with a mean size of 12.8 pixels compared to other aerial image datasets. To use AI-TOD, download xView training set and AI-TOD_wo_xview, then generate the complete dataset using the provided synthesis tool. The dataset is publicly available for academic and research purposes under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.

aitlas
The AiTLAS toolbox (Artificial Intelligence Toolbox for Earth Observation) includes state-of-the-art machine learning methods for exploratory and predictive analysis of satellite imagery as well as a repository of AI-ready Earth Observation (EO) datasets. It can be easily applied for a variety of Earth Observation tasks, such as land use and cover classification, crop type prediction, localization of specific objects (semantic segmentation), etc. The main goal of AiTLAS is to facilitate better usability and adoption of novel AI methods (and models) by EO experts, while offering easy access and standardized format of EO datasets to AI experts which allows benchmarking of various existing and novel AI methods tailored for EO data.
farmvibes-ai
FarmVibes.AI is a repository focused on developing multi-modal geospatial machine learning models for agriculture and sustainability. It enables users to fuse various geospatial and spatiotemporal datasets, such as satellite imagery, drone imagery, and weather data, to generate robust insights for agriculture-related problems. The repository provides fusion workflows, data preparation tools, model training notebooks, and an inference engine to facilitate the creation of geospatial models tailored for agriculture and farming. Users can interact with the tools via a local cluster, REST API, or a Python client, and the repository includes documentation and notebook examples to guide users in utilizing FarmVibes.AI for tasks like harvest date detection, climate impact estimation, micro climate prediction, and crop identification.
fAIr
fAIr is an open AI-assisted mapping service developed by the Humanitarian OpenStreetMap Team (HOT) to improve mapping efficiency and accuracy for humanitarian purposes. It uses AI models, specifically computer vision techniques, to detect objects like buildings, roads, waterways, and trees from satellite and UAV imagery. The service allows OSM community members to create and train their own AI models for mapping in their region of interest and ensures models are relevant to local communities. Constant feedback loop with local communities helps eliminate model biases and improve model accuracy.
