mcp-context-forge
A Model Context Protocol (MCP) Gateway & Registry. Serves as a central management point for tools, resources, and prompts that can be accessed by MCP-compatible LLM applications. Converts REST API endpoints to MCP, composes virtual MCP servers with added security and observability, and converts between protocols (stdio, SSE, Streamable HTTP).
Stars: 3287
MCP Context Forge is a powerful tool for generating context-aware data for machine learning models. It provides functionalities to create diverse datasets with contextual information, enhancing the performance of AI algorithms. The tool supports various data formats and allows users to customize the context generation process easily. With MCP Context Forge, users can efficiently prepare training data for tasks requiring contextual understanding, such as sentiment analysis, recommendation systems, and natural language processing.
README:
Model Context Protocol gateway & proxy - unify REST, MCP, and A2A with federation, virtual servers, retries, security, and an optional admin UI.
ContextForge MCP Gateway is a feature-rich gateway, proxy and MCP Registry that federates MCP and REST services - unifying discovery, auth, rate-limiting, observability, virtual servers, multi-transport protocols, and an optional Admin UI into one clean endpoint for your AI clients. It runs as a fully compliant MCP server, deployable via PyPI or Docker, and scales to multi-cluster environments on Kubernetes with Redis-backed federation and caching.
- Overview & Goals
- Quick Start - PyPI
- Quick Start - Containers
- VS Code Dev Container
- Installation
- Upgrading
- Configuration
- Running
- Cloud Deployment
- API Reference
- Testing
- Project Structure
- Development
- Troubleshooting
- Contributing
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| 5-Minute Setup | Get started fast — uvx, Docker, Compose, or local dev |
| Getting Help | Support options, FAQ, community channels |
| Issue Guide | How to file bugs, request features, contribute |
| Full Documentation | Complete guides, tutorials, API reference |
ContextForge is a gateway, registry, and proxy that sits in front of any Model Context Protocol (MCP) server, A2A server or REST API-exposing a unified endpoint for all your AI clients. See the project roadmap for more details.
It currently supports:
- Federation across multiple MCP and REST services
- A2A (Agent-to-Agent) integration for external AI agents (OpenAI, Anthropic, custom)
- gRPC-to-MCP translation via automatic reflection-based service discovery
- Virtualization of legacy APIs as MCP-compliant tools and servers
- Transport over HTTP, JSON-RPC, WebSocket, SSE (with configurable keepalive), stdio and streamable-HTTP
- An Admin UI for real-time management, configuration, and log monitoring (with airgapped deployment support)
- Built-in auth, retries, and rate-limiting with user-scoped OAuth tokens and unconditional X-Upstream-Authorization header support
- OpenTelemetry observability with Phoenix, Jaeger, Zipkin, and other OTLP backends
- Scalable deployments via Docker or PyPI, Redis-backed caching, and multi-cluster federation
For a list of upcoming features, check out the ContextForge Roadmap
🔌 Gateway Layer with Protocol Flexibility
- Sits in front of any MCP server or REST API
- Lets you choose your MCP protocol version (e.g.,
2025-06-18) - Exposes a single, unified interface for diverse backends
🧩 Virtualization of REST/gRPC Services
- Wraps non-MCP services as virtual MCP servers
- Registers tools, prompts, and resources with minimal configuration
- gRPC-to-MCP translation via server reflection protocol
- Automatic service discovery and method introspection
🔁 REST-to-MCP Tool Adapter
-
Adapts REST APIs into tools with:
- Automatic JSON Schema extraction
- Support for headers, tokens, and custom auth
- Retry, timeout, and rate-limit policies
🧠 Unified Registries
- Prompts: Jinja2 templates, multimodal support, rollback/versioning
- Resources: URI-based access, MIME detection, caching, SSE updates
- Tools: Native or adapted, with input validation and concurrency controls
📈 Admin UI, Observability & Dev Experience
- Admin UI built with HTMX + Alpine.js
- Real-time log viewer with filtering, search, and export capabilities
- Auth: Basic, JWT, or custom schemes
- Structured logs, health endpoints, metrics
- 400+ tests, Makefile targets, live reload, pre-commit hooks
🔍 OpenTelemetry Observability
- Vendor-agnostic tracing with OpenTelemetry (OTLP) protocol support
- Multiple backend support: Phoenix (LLM-focused), Jaeger, Zipkin, Tempo, DataDog, New Relic
- Distributed tracing across federated gateways and services
- Automatic instrumentation of tools, prompts, resources, and gateway operations
- LLM-specific metrics: Token usage, costs, model performance
- Zero-overhead when disabled with graceful degradation
See Observability Documentation for setup guides with Phoenix, Jaeger, and other backends.
ContextForge is published on PyPI as mcp-contextforge-gateway.
TLDR;: (single command using uv)
# Quick start with environment variables
BASIC_AUTH_PASSWORD=pass \
MCPGATEWAY_UI_ENABLED=true \
MCPGATEWAY_ADMIN_API_ENABLED=true \
[email protected] \
PLATFORM_ADMIN_PASSWORD=changeme \
PLATFORM_ADMIN_FULL_NAME="Platform Administrator" \
uvx --from mcp-contextforge-gateway mcpgateway --host 0.0.0.0 --port 4444
# Or better: use the provided .env.example
cp .env.example .env
# Edit .env to customize your settings
uvx --from mcp-contextforge-gateway mcpgateway --host 0.0.0.0 --port 4444📋 Prerequisites
- Python ≥ 3.10 (3.11 recommended)
- curl + jq - only for the last smoke-test step
# 1️⃣ Isolated env + install from pypi
mkdir mcpgateway && cd mcpgateway
python3 -m venv .venv && source .venv/bin/activate
pip install --upgrade pip
pip install mcp-contextforge-gateway
# 2️⃣ Copy and customize the configuration
# Download the example environment file
curl -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/IBM/mcp-context-forge/main/.env.example
cp .env.example .env
# Edit .env to customize your settings (especially passwords!)
# Or set environment variables directly:
export MCPGATEWAY_UI_ENABLED=true
export MCPGATEWAY_ADMIN_API_ENABLED=true
export [email protected]
export PLATFORM_ADMIN_PASSWORD=changeme
export PLATFORM_ADMIN_FULL_NAME="Platform Administrator"
BASIC_AUTH_PASSWORD=pass JWT_SECRET_KEY=my-test-key \
mcpgateway --host 0.0.0.0 --port 4444 & # admin/pass
# 3️⃣ Generate a bearer token & smoke-test the API
export MCPGATEWAY_BEARER_TOKEN=$(python3 -m mcpgateway.utils.create_jwt_token \
--username [email protected] --exp 10080 --secret my-test-key)
curl -s -H "Authorization: Bearer $MCPGATEWAY_BEARER_TOKEN" \
http://127.0.0.1:4444/version | jqWindows (PowerShell) quick-start
# 1️⃣ Isolated env + install from PyPI
mkdir mcpgateway ; cd mcpgateway
python3 -m venv .venv ; .\.venv\Scripts\Activate.ps1
pip install --upgrade pip
pip install mcp-contextforge-gateway
# 2️⃣ Copy and customize the configuration
# Download the example environment file
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/IBM/mcp-context-forge/main/.env.example" -OutFile ".env.example"
Copy-Item .env.example .env
# Edit .env to customize your settings
# Or set environment variables (session-only)
$Env:MCPGATEWAY_UI_ENABLED = "true"
$Env:MCPGATEWAY_ADMIN_API_ENABLED = "true"
# Note: Basic auth for API is disabled by default (API_ALLOW_BASIC_AUTH=false)
$Env:JWT_SECRET_KEY = "my-test-key"
$Env:PLATFORM_ADMIN_EMAIL = "[email protected]"
$Env:PLATFORM_ADMIN_PASSWORD = "changeme"
$Env:PLATFORM_ADMIN_FULL_NAME = "Platform Administrator"
# 3️⃣ Launch the gateway
mcpgateway.exe --host 0.0.0.0 --port 4444
# Optional: background it
# Start-Process -FilePath "mcpgateway.exe" -ArgumentList "--host 0.0.0.0 --port 4444"
# 4️⃣ Bearer token and smoke-test
$Env:MCPGATEWAY_BEARER_TOKEN = python3 -m mcpgateway.utils.create_jwt_token `
--username admin@example.com --exp 10080 --secret my-test-key
curl -s -H "Authorization: Bearer $Env:MCPGATEWAY_BEARER_TOKEN" `
http://127.0.0.1:4444/version | jq⚡ Alternative: uv (faster)
# 1️⃣ Isolated env + install from PyPI using uv
mkdir mcpgateway ; cd mcpgateway
uv venv
.\.venv\Scripts\activate
uv pip install mcp-contextforge-gateway
# Continue with steps 2️⃣-4️⃣ above...More configuration
Copy .env.example to .env and tweak any of the settings (or use them as env variables).
🚀 End-to-end demo (register a local MCP server)
# 1️⃣ Spin up the sample GO MCP time server using mcpgateway.translate & docker (replace docker with podman if needed)
python3 -m mcpgateway.translate \
--stdio "docker run --rm -i ghcr.io/ibm/fast-time-server:latest -transport=stdio" \
--expose-sse \
--port 8003
# Or using the official mcp-server-git using uvx:
pip install uv # to install uvx, if not already installed
python3 -m mcpgateway.translate --stdio "uvx mcp-server-git" --expose-sse --port 9000
# Alternative: running the local binary
# cd mcp-servers/go/fast-time-server; make build
# python3 -m mcpgateway.translate --stdio "./dist/fast-time-server -transport=stdio" --expose-sse --port 8002
# NEW: Expose via multiple protocols simultaneously!
python3 -m mcpgateway.translate \
--stdio "uvx mcp-server-git" \
--expose-sse \
--expose-streamable-http \
--port 9000
# Now accessible via both /sse (SSE) and /mcp (streamable HTTP) endpoints
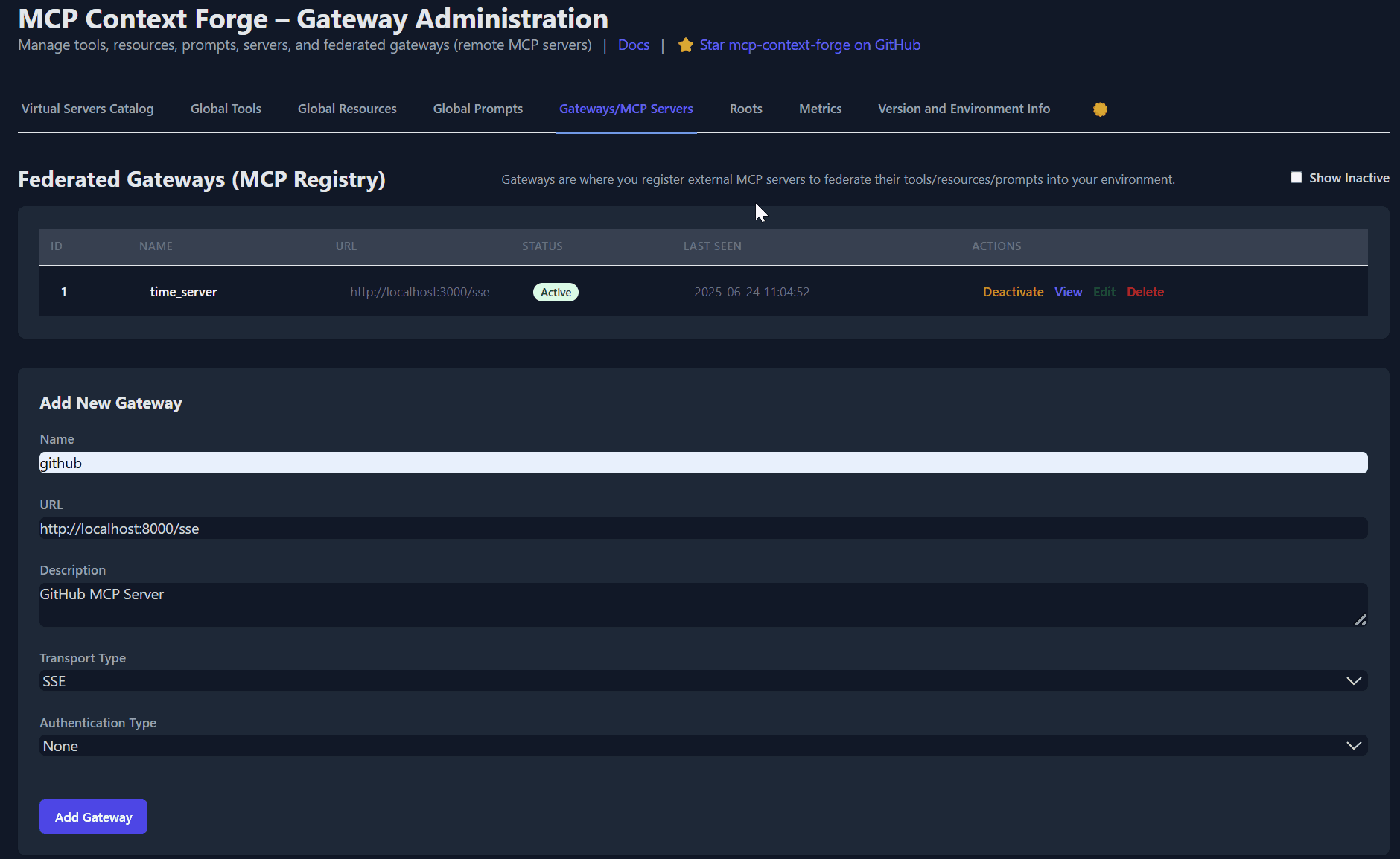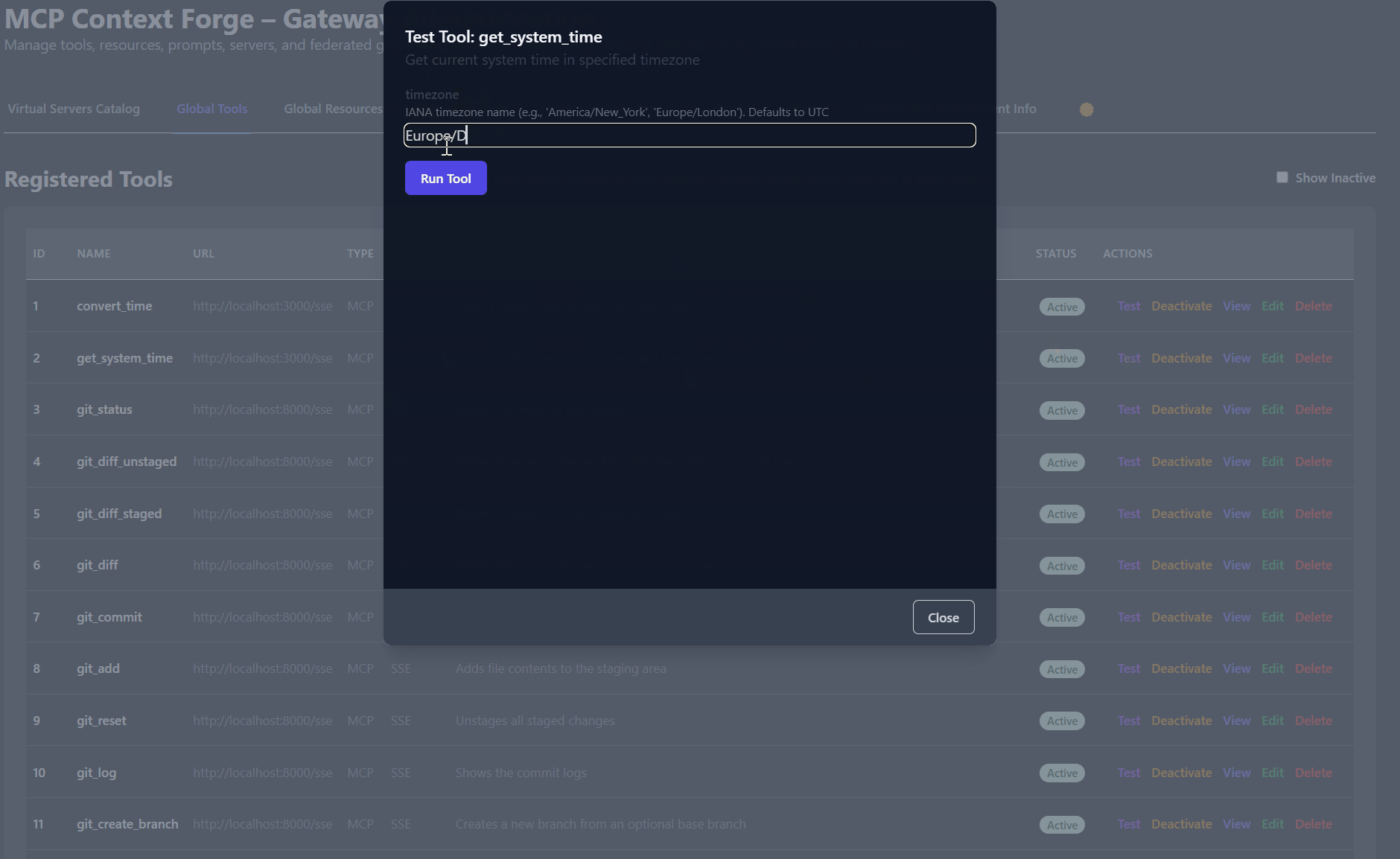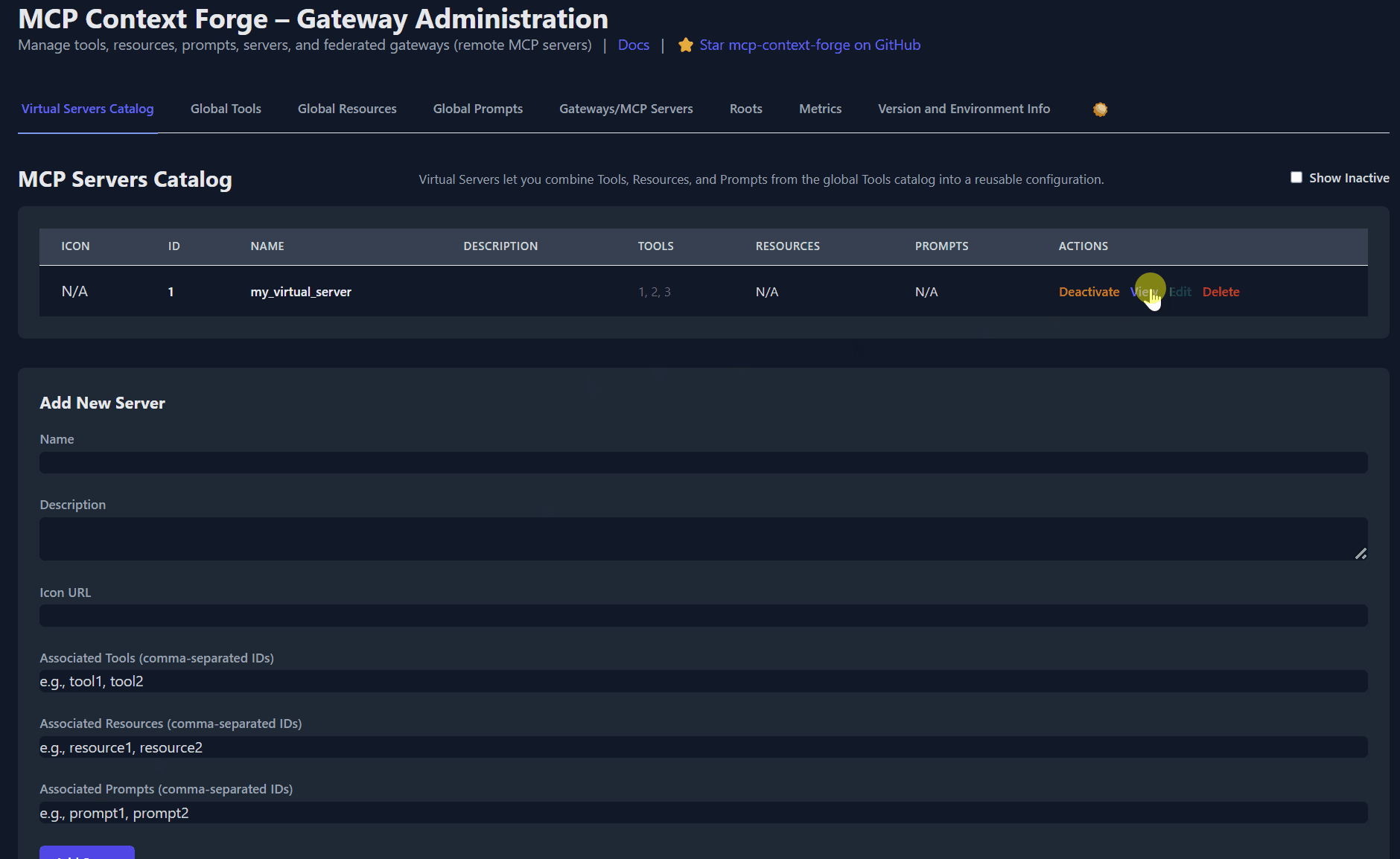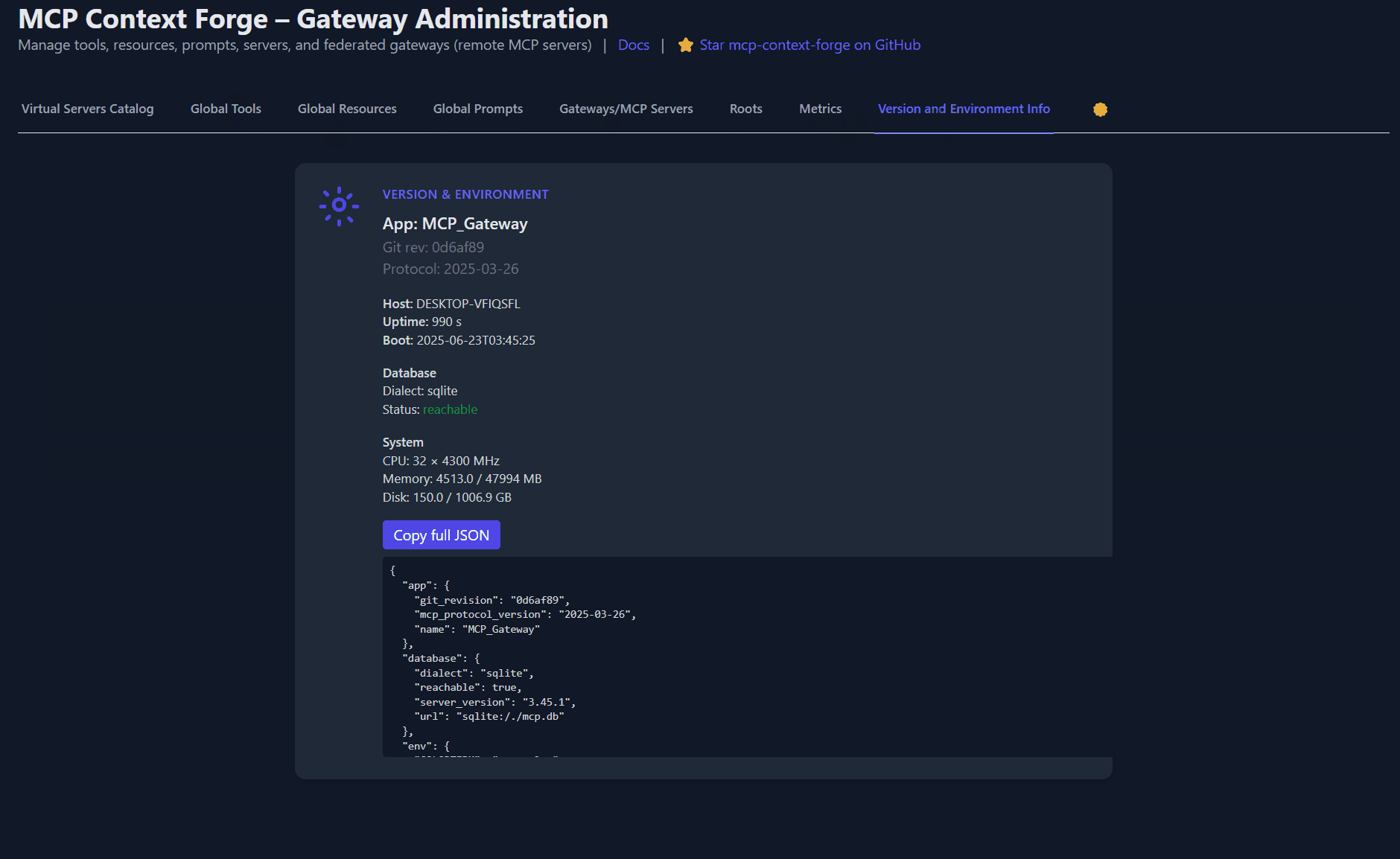
# 2️⃣ Register it with the gateway
curl -s -X POST -H "Authorization: Bearer $MCPGATEWAY_BEARER_TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"name":"fast_time","url":"http://localhost:8003/sse"}' \
http://localhost:4444/gateways
# 3️⃣ Verify tool catalog
curl -s -H "Authorization: Bearer $MCPGATEWAY_BEARER_TOKEN" http://localhost:4444/tools | jq
# 4️⃣ Create a *virtual server* bundling those tools. Use the ID of tools from the tool catalog (Step #3) and pass them in the associatedTools list.
curl -s -X POST -H "Authorization: Bearer $MCPGATEWAY_BEARER_TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"server":{"name":"time_server","description":"Fast time tools","associated_tools":[<ID_OF_TOOLS>]}}' \
http://localhost:4444/servers | jq
# Example curl
curl -s -X POST -H "Authorization: Bearer $MCPGATEWAY_BEARER_TOKEN"
-H "Content-Type: application/json"
-d '{"server":{"name":"time_server","description":"Fast time tools","associated_tools":["6018ca46d32a4ac6b4c054c13a1726a2"]}}' \
http://localhost:4444/servers | jq
# 5️⃣ List servers (should now include the UUID of the newly created virtual server)
curl -s -H "Authorization: Bearer $MCPGATEWAY_BEARER_TOKEN" http://localhost:4444/servers | jq
# 6️⃣ Client HTTP endpoint. Inspect it interactively with the MCP Inspector CLI (or use any MCP client)
npx -y @modelcontextprotocol/inspector
# Transport Type: Streamable HTTP, URL: http://localhost:4444/servers/UUID_OF_SERVER_1/mcp, Header Name: "Authorization", Bearer Token🖧 Using the stdio wrapper (mcpgateway-wrapper)
export MCP_AUTH="Bearer ${MCPGATEWAY_BEARER_TOKEN}"
export MCP_SERVER_URL=http://localhost:4444/servers/UUID_OF_SERVER_1/mcp
python3 -m mcpgateway.wrapper # Ctrl-C to exitYou can also run it with uv or inside Docker/Podman - see the Containers section above.
In MCP Inspector, define MCP_AUTH and MCP_SERVER_URL env variables, and select python3 as the Command, and -m mcpgateway.wrapper as Arguments.
echo $PWD/.venv/bin/python3 # Using the Python3 full path ensures you have a working venv
export MCP_SERVER_URL='http://localhost:4444/servers/UUID_OF_SERVER_1/mcp'
export MCP_AUTH="Bearer ${MCPGATEWAY_BEARER_TOKEN}"
npx -y @modelcontextprotocol/inspectoror
Pass the url and auth as arguments (no need to set environment variables)
npx -y @modelcontextprotocol/inspector
command as `python`
Arguments as `-m mcpgateway.wrapper --url "http://localhost:4444/servers/UUID_OF_SERVER_1/mcp" --auth "Bearer <your token>"`When using a MCP Client such as Claude with stdio:
{
"mcpServers": {
"mcpgateway-wrapper": {
"command": "python",
"args": ["-m", "mcpgateway.wrapper"],
"env": {
"MCP_AUTH": "Bearer your-token-here",
"MCP_SERVER_URL": "http://localhost:4444/servers/UUID_OF_SERVER_1",
"MCP_TOOL_CALL_TIMEOUT": "120"
}
}
}
}Use the official OCI image from GHCR with Docker or Podman. Please note: Currently, arm64 is not supported on production. If you are e.g. running on MacOS with Apple Silicon chips (M1, M2, etc), you can run the containers using Rosetta or install via PyPi instead.
Get a full stack running with MariaDB and Redis in under 30 seconds:
# Clone and start the stack
git clone https://github.com/IBM/mcp-context-forge.git
cd mcp-context-forge
# Start with MariaDB (recommended for production)
docker compose up -d
# Or start with PostgreSQL
# Uncomment postgres in docker-compose.yml and comment mariadb section
# docker compose up -d
# Check status
docker compose ps
# View logs
docker compose logs -f gateway
# Access Admin UI: http://localhost:4444/admin (login with PLATFORM_ADMIN_EMAIL/PASSWORD)
# Generate API token
docker compose exec gateway python3 -m mcpgateway.utils.create_jwt_token \
--username [email protected] --exp 10080 --secret my-test-keyWhat you get:
- 🗄️ MariaDB 10.6 - Production-ready database with 36+ tables
- 🚀 MCP Gateway - Full-featured gateway with Admin UI
- 📊 Redis - High-performance caching and session storage
- 🔧 Admin Tools - pgAdmin, Redis Insight for database management
- 🌐 Nginx Proxy - Caching reverse proxy (optional)
Enable HTTPS (optional):
# Start with TLS enabled (auto-generates self-signed certs)
make compose-tls
# Access via HTTPS: https://localhost:8443/admin
# Or bring your own certificates:
# Unencrypted key:
mkdir -p certs
cp your-cert.pem certs/cert.pem && cp your-key.pem certs/key.pem
make compose-tls
# Passphrase-protected key:
mkdir -p certs
cp your-cert.pem certs/cert.pem && cp your-encrypted-key.pem certs/key-encrypted.pem
echo "KEY_FILE_PASSWORD=your-passphrase" >> .env
make compose-tlsDeploy to Kubernetes with enterprise-grade features:
# Add Helm repository (when available)
# helm repo add mcp-context-forge https://ibm.github.io/mcp-context-forge
# helm repo update
# For now, use local chart
git clone https://github.com/IBM/mcp-context-forge.git
cd mcp-context-forge/charts/mcp-stack
# Install with MariaDB
helm install mcp-gateway . \
--set mcpContextForge.secret.PLATFORM_ADMIN_EMAIL=admin@yourcompany.com \
--set mcpContextForge.secret.PLATFORM_ADMIN_PASSWORD=changeme \
--set mcpContextForge.secret.JWT_SECRET_KEY=your-secret-key \
--set postgres.enabled=false \
--set mariadb.enabled=true
# Or install with PostgreSQL (default)
helm install mcp-gateway . \
--set mcpContextForge.secret.PLATFORM_ADMIN_EMAIL=admin@yourcompany.com \
--set mcpContextForge.secret.PLATFORM_ADMIN_PASSWORD=changeme \
--set mcpContextForge.secret.JWT_SECRET_KEY=your-secret-key
# Check deployment status
kubectl get pods -l app.kubernetes.io/name=mcp-context-forge
# Port forward to access Admin UI
kubectl port-forward svc/mcp-gateway-mcp-context-forge 4444:80
# Access: http://localhost:4444/admin
# Generate API token
kubectl exec deployment/mcp-gateway-mcp-context-forge -- \
python3 -m mcpgateway.utils.create_jwt_token \
--username [email protected] --exp 10080 --secret your-secret-keyEnterprise Features:
- 🔄 Auto-scaling - HPA with CPU/memory targets
- 🗄️ Database Choice - PostgreSQL, MariaDB, or MySQL
- 📊 Observability - Prometheus metrics, OpenTelemetry tracing
- 🔒 Security - RBAC, network policies, secret management
- 🚀 High Availability - Multi-replica deployments with Redis clustering
- 📈 Monitoring - Built-in Grafana dashboards and alerting
docker run -d --name mcpgateway \
-p 4444:4444 \
-e MCPGATEWAY_UI_ENABLED=true \
-e MCPGATEWAY_ADMIN_API_ENABLED=true \
-e HOST=0.0.0.0 \
-e JWT_SECRET_KEY=my-test-key \
-e AUTH_REQUIRED=true \
-e [email protected] \
-e PLATFORM_ADMIN_PASSWORD=changeme \
-e PLATFORM_ADMIN_FULL_NAME="Platform Administrator" \
-e DATABASE_URL=sqlite:///./mcp.db \
-e SECURE_COOKIES=false \
ghcr.io/ibm/mcp-context-forge:1.0.0-RC-1
# Tail logs and generate API key
docker logs -f mcpgateway
docker run --rm -it ghcr.io/ibm/mcp-context-forge:1.0.0-RC-1 \
python3 -m mcpgateway.utils.create_jwt_token --username [email protected] --exp 10080 --secret my-test-keyBrowse to http://localhost:4444/admin and login with PLATFORM_ADMIN_EMAIL / PLATFORM_ADMIN_PASSWORD.
Advanced: Persistent storage, host networking, airgapped
Persist SQLite database:
mkdir -p $(pwd)/data && touch $(pwd)/data/mcp.db && chmod 777 $(pwd)/data
docker run -d --name mcpgateway --restart unless-stopped \
-p 4444:4444 -v $(pwd)/data:/data \
-e DATABASE_URL=sqlite:////data/mcp.db \
-e MCPGATEWAY_UI_ENABLED=true -e MCPGATEWAY_ADMIN_API_ENABLED=true \
-e HOST=0.0.0.0 -e JWT_SECRET_KEY=my-test-key \
-e [email protected] -e PLATFORM_ADMIN_PASSWORD=changeme \
ghcr.io/ibm/mcp-context-forge:1.0.0-RC-1Host networking (access local MCP servers):
docker run -d --name mcpgateway --network=host \
-v $(pwd)/data:/data -e DATABASE_URL=sqlite:////data/mcp.db \
-e MCPGATEWAY_UI_ENABLED=true -e HOST=0.0.0.0 -e PORT=4444 \
ghcr.io/ibm/mcp-context-forge:1.0.0-RC-1Airgapped deployment (no internet):
docker build -f Containerfile.lite -t mcpgateway:airgapped .
docker run -d --name mcpgateway -p 4444:4444 \
-e MCPGATEWAY_UI_AIRGAPPED=true -e MCPGATEWAY_UI_ENABLED=true \
-e HOST=0.0.0.0 -e JWT_SECRET_KEY=my-test-key \
mcpgateway:airgappedpodman run -d --name mcpgateway \
-p 4444:4444 -e HOST=0.0.0.0 -e DATABASE_URL=sqlite:///./mcp.db \
ghcr.io/ibm/mcp-context-forge:1.0.0-RC-1Advanced: Persistent storage, host networking
Persist SQLite:
mkdir -p $(pwd)/data && chmod 777 $(pwd)/data
podman run -d --name mcpgateway --restart=on-failure \
-p 4444:4444 -v $(pwd)/data:/data \
-e DATABASE_URL=sqlite:////data/mcp.db \
ghcr.io/ibm/mcp-context-forge:1.0.0-RC-1Host networking:
podman run -d --name mcpgateway --network=host \
-v $(pwd)/data:/data -e DATABASE_URL=sqlite:////data/mcp.db \
ghcr.io/ibm/mcp-context-forge:1.0.0-RC-1✏️ Docker/Podman tips
-
.env files - Put all the
-e FOO=lines into a file and replace them with--env-file .env. See the provided .env.example for reference. -
Pinned tags - Use an explicit version (e.g.
1.0.0-RC-1) instead oflatestfor reproducible builds. -
JWT tokens - Generate one in the running container:
docker exec mcpgateway python3 -m mcpgateway.utils.create_jwt_token --username [email protected] --exp 10080 --secret my-test-key
-
Upgrades - Stop, remove, and rerun with the same
-v $(pwd)/data:/datamount; your DB and config stay intact.
🚑 Smoke-test the running container
curl -s -H "Authorization: Bearer $MCPGATEWAY_BEARER_TOKEN" \
http://localhost:4444/health | jq
curl -s -H "Authorization: Bearer $MCPGATEWAY_BEARER_TOKEN" \
http://localhost:4444/tools | jq
curl -s -H "Authorization: Bearer $MCPGATEWAY_BEARER_TOKEN" \
http://localhost:4444/version | jq🖧 Running the MCP Gateway stdio wrapper
The mcpgateway.wrapper lets you connect to the gateway over stdio while keeping JWT authentication. You should run this from the MCP Client. The example below is just for testing.
# Set environment variables
export MCPGATEWAY_BEARER_TOKEN=$(python3 -m mcpgateway.utils.create_jwt_token --username [email protected] --exp 10080 --secret my-test-key)
export MCP_AUTH="Bearer ${MCPGATEWAY_BEARER_TOKEN}"
export MCP_SERVER_URL='http://localhost:4444/servers/UUID_OF_SERVER_1/mcp'
export MCP_TOOL_CALL_TIMEOUT=120
export MCP_WRAPPER_LOG_LEVEL=DEBUG # or OFF to disable logging
docker run --rm -i \
-e MCP_AUTH=$MCP_AUTH \
-e MCP_SERVER_URL=http://host.docker.internal:4444/servers/UUID_OF_SERVER_1/mcp \
-e MCP_TOOL_CALL_TIMEOUT=120 \
-e MCP_WRAPPER_LOG_LEVEL=DEBUG \
ghcr.io/ibm/mcp-context-forge:1.0.0-RC-1 \
python3 -m mcpgateway.wrapperClone the repo and open in VS Code—it will detect .devcontainer and prompt to "Reopen in Container". The container includes Python 3.11, Docker CLI, and all project dependencies.
For detailed setup, workflows, and GitHub Codespaces instructions, see Developer Onboarding.
make venv install # create .venv + install deps
make serve # gunicorn on :4444Alternative: UV or pip
# UV (faster)
uv venv && source .venv/bin/activate
uv pip install -e '.[dev]'
# pip
python3 -m venv .venv && source .venv/bin/activate
pip install -e ".[dev]"PostgreSQL adapter setup
Install the psycopg driver for PostgreSQL:
# Install system dependencies first
# Debian/Ubuntu: sudo apt-get install libpq-dev
# macOS: brew install libpq
uv pip install 'psycopg[binary]' # dev (pre-built wheels)
# or: uv pip install 'psycopg[c]' # production (requires compiler)Connection URL format:
DATABASE_URL=postgresql+psycopg://user:password@localhost:5432/mcpQuick Postgres container:
docker run --name mcp-postgres \
-e POSTGRES_USER=postgres -e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=mysecretpassword \
-e POSTGRES_DB=mcp -p 5432:5432 -d postgresFor upgrade instructions, migration guides, and rollback procedures, see:
- Upgrade Guide — General upgrade procedures
- CHANGELOG.md — Version history and breaking changes
- MIGRATION-0.7.0.md — Multi-tenancy migration (v0.6.x → v0.7.x)
⚠️ If any required.envvariable is missing or invalid, the gateway will fail fast at startup with a validation error via Pydantic.
Copy the provided .env.example to .env and update the security-sensitive values below.
These variables have insecure defaults and must be changed before production deployment:
| Variable | Description | Default | Action Required |
|---|---|---|---|
JWT_SECRET_KEY |
Secret key for signing JWT tokens (32+ chars) | my-test-key |
Generate with openssl rand -hex 32
|
AUTH_ENCRYPTION_SECRET |
Passphrase for encrypting stored credentials | my-test-salt |
Generate with openssl rand -hex 32
|
BASIC_AUTH_USER |
Username for HTTP Basic auth | admin |
Change for production |
BASIC_AUTH_PASSWORD |
Password for HTTP Basic auth | changeme |
Set a strong password |
PLATFORM_ADMIN_EMAIL |
Email for bootstrap admin user | [email protected] |
Use real admin email |
PLATFORM_ADMIN_PASSWORD |
Password for bootstrap admin user | changeme |
Set a strong password |
PLATFORM_ADMIN_FULL_NAME |
Display name for bootstrap admin | Admin User |
Set admin name |
These settings are enabled by default for security—only disable for backward compatibility:
| Variable | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
REQUIRE_JTI |
Require JTI claim in tokens for revocation support | true |
REQUIRE_TOKEN_EXPIRATION |
Require exp claim in tokens | true |
PUBLIC_REGISTRATION_ENABLED |
Allow public user self-registration | false |
These values differ from code defaults to provide a working local/dev setup:
| Variable | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
HOST |
Bind address | 0.0.0.0 |
MCPGATEWAY_UI_ENABLED |
Enable Admin UI dashboard | true |
MCPGATEWAY_ADMIN_API_ENABLED |
Enable Admin API endpoints | true |
DATABASE_URL |
SQLAlchemy connection URL | sqlite:///./mcp.db |
SECURE_COOKIES |
Set false for HTTP (non-HTTPS) dev |
true |
For the complete list of 300+ environment variables organized by category (authentication, caching, SSO, observability, etc.), see the Configuration Reference.
| Command | Server | Port | Database | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
make dev |
Uvicorn | 8000 | SQLite | Development (single instance, auto-reload) |
make serve |
Gunicorn | 4444 | SQLite | Production single-node (multi-worker) |
make serve-ssl |
Gunicorn | 4444 | SQLite | Production single-node with HTTPS |
make compose-up |
Docker Compose + Nginx | 8080 | PostgreSQL + Redis | Full stack (3 replicas, load-balanced) |
make compose-sso |
Docker Compose + Keycloak | 8080 / 8180 | PostgreSQL + Redis | Local SSO testing (Keycloak profile) |
make testing-up |
Docker Compose + Nginx | 8080 | PostgreSQL + Redis | Testing environment |
make dev # Uvicorn on :8000 with auto-reload and SQLite
# or
./run.sh --reload --log debug --workers 2
run.shis a wrapper arounduvicornthat loads.env, supports reload, and passes arguments to the server.
Key flags:
| Flag | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
-e, --env FILE |
load env-file | --env prod.env |
-H, --host |
bind address | --host 127.0.0.1 |
-p, --port |
listen port | --port 8080 |
-w, --workers |
gunicorn workers | --workers 4 |
-r, --reload |
auto-reload | --reload |
make serve # Gunicorn on :4444 with multiple workers
make serve-ssl # Gunicorn behind HTTPS on :4444 (uses ./certs)make compose-up # Start full stack: PostgreSQL, Redis, 3 gateway replicas, Nginx on :8080
make compose-sso # Start SSO stack with Keycloak on :8180
make sso-test-login # Run SSO smoke checks (providers + login URL + test users)
make compose-logs # Tail logs from all services
make compose-down # Stop the stackuvicorn mcpgateway.main:app --host 0.0.0.0 --port 4444 --workers 4MCP Gateway can be deployed to any major cloud platform:
| Platform | Guide |
|---|---|
| AWS | ECS/EKS Deployment |
| Azure | AKS Deployment |
| Google Cloud | Cloud Run |
| IBM Cloud | Code Engine |
| Kubernetes | Helm Charts |
| OpenShift | OpenShift Deployment |
For comprehensive deployment guides, see Deployment Documentation.
Interactive API documentation is available when the server is running:
- Swagger UI — Try API calls directly in your browser
- ReDoc — Browse the complete endpoint reference
Quick Authentication:
# Generate a JWT token
export TOKEN=$(python3 -m mcpgateway.utils.create_jwt_token \
--username [email protected] --exp 10080 --secret my-test-key)
# Test API access
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" http://localhost:4444/healthFor comprehensive curl examples covering all endpoints, see the API Usage Guide.
make test # Run unit tests
make lint # Run all linters
make doctest # Run doctests
make coverage # Generate coverage reportSee Doctest Coverage Guide for documentation testing details.
mcpgateway/ # Core FastAPI application
├── main.py # Entry point
├── config.py # Pydantic Settings configuration
├── db.py # SQLAlchemy ORM models
├── schemas.py # Pydantic validation schemas
├── services/ # Business logic layer (50+ services)
├── routers/ # HTTP endpoint definitions
├── middleware/ # Cross-cutting concerns
└── transports/ # SSE, WebSocket, stdio, streamable HTTP
tests/ # Test suite (400+ tests)
docs/docs/ # Full documentation (MkDocs)
charts/ # Kubernetes/Helm charts
plugins/ # Plugin framework and implementations
For complete structure, see CONTRIBUTING.md or run tree -L 2.
make dev # Dev server with auto-reload (:8000)
make test # Run test suite
make lint # Run all linters
make coverage # Generate coverage reportRun make to see all 75+ available targets.
For development workflows, see:
Common issues and solutions:
| Issue | Quick Fix |
|---|---|
| SQLite "disk I/O error" on macOS | Avoid iCloud-synced directories; use ~/mcp-context-forge/data
|
| Port 4444 not accessible on WSL2 | Configure WSL integration in Docker Desktop |
| Gateway exits immediately | Copy .env.example to .env and configure required vars |
ModuleNotFoundError |
Run make install-dev
|
For detailed troubleshooting guides, see Troubleshooting Documentation.
- Fork the repo, create a feature branch.
- Run
make lintand fix any issues. - Keep
make testgreen. - Open a PR with signed commits (
git commit -s).
See CONTRIBUTING.md for full guidelines and Issue Guide #2502 for how to file bugs, request features, and find issues to work on.
A complete changelog can be found here: CHANGELOG.md
Licensed under the Apache License 2.0 - see LICENSE
- Mihai Criveti - Distinguished Engineer, Agentic AI
Special thanks to our contributors for helping us improve ContextForge:
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for mcp-context-forge
Similar Open Source Tools

mcp-context-forge
MCP Context Forge is a powerful tool for generating context-aware data for machine learning models. It provides functionalities to create diverse datasets with contextual information, enhancing the performance of AI algorithms. The tool supports various data formats and allows users to customize the context generation process easily. With MCP Context Forge, users can efficiently prepare training data for tasks requiring contextual understanding, such as sentiment analysis, recommendation systems, and natural language processing.

oh-my-pi
oh-my-pi is an AI coding agent for the terminal, providing tools for interactive coding, AI-powered git commits, Python code execution, LSP integration, time-traveling streamed rules, interactive code review, task management, interactive questioning, custom TypeScript slash commands, universal config discovery, MCP & plugin system, web search & fetch, SSH tool, Cursor provider integration, multi-credential support, image generation, TUI overhaul, edit fuzzy matching, and more. It offers a modern terminal interface with smart session management, supports multiple AI providers, and includes various tools for coding, task management, code review, and interactive questioning.
dexto
Dexto is a lightweight runtime for creating and running AI agents that turn natural language into real-world actions. It serves as the missing intelligence layer for building AI applications, standalone chatbots, or as the reasoning engine inside larger products. Dexto features a powerful CLI and Web UI for running AI agents, supports multiple interfaces, allows hot-swapping of LLMs from various providers, connects to remote tool servers via the Model Context Protocol, is config-driven with version-controlled YAML, offers production-ready core features, extensibility for custom services, and enables multi-agent collaboration via MCP and A2A.
tokscale
Tokscale is a high-performance CLI tool and visualization dashboard for tracking token usage and costs across multiple AI coding agents. It helps monitor and analyze token consumption from various AI coding tools, providing real-time pricing calculations using LiteLLM's pricing data. Inspired by the Kardashev scale, Tokscale measures token consumption as users scale the ranks of AI-augmented development. It offers interactive TUI mode, multi-platform support, real-time pricing, detailed breakdowns, web visualization, flexible filtering, and social platform features.
9router
9Router is a free AI router tool designed to help developers maximize their AI subscriptions, auto-route to free and cheap AI models with smart fallback, and avoid hitting limits and wasting money. It offers features like real-time quota tracking, format translation between OpenAI, Claude, and Gemini, multi-account support, auto token refresh, custom model combinations, request logging, cloud sync, usage analytics, and flexible deployment options. The tool supports various providers like Claude Code, Codex, Gemini CLI, GitHub Copilot, GLM, MiniMax, iFlow, Qwen, and Kiro, and allows users to create combos for different scenarios. Users can connect to the tool via CLI tools like Cursor, Claude Code, Codex, OpenClaw, and Cline, and deploy it on VPS, Docker, or Cloudflare Workers.
ai-real-estate-assistant
AI Real Estate Assistant is a modern platform that uses AI to assist real estate agencies in helping buyers and renters find their ideal properties. It features multiple AI model providers, intelligent query processing, advanced search and retrieval capabilities, and enhanced user experience. The tool is built with a FastAPI backend and Next.js frontend, offering semantic search, hybrid agent routing, and real-time analytics.
onnxruntime-server
ONNX Runtime Server is a server that provides TCP and HTTP/HTTPS REST APIs for ONNX inference. It aims to offer simple, high-performance ML inference and a good developer experience. Users can provide inference APIs for ONNX models without writing additional code by placing the models in the directory structure. Each session can choose between CPU or CUDA, analyze input/output, and provide Swagger API documentation for easy testing. Ready-to-run Docker images are available, making it convenient to deploy the server.
inspector
A developer tool for testing and debugging Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers. It allows users to test the compliance of their MCP servers with the latest MCP specs, supports various transports like STDIO, SSE, and Streamable HTTP, features an LLM Playground for testing server behavior against different models, provides comprehensive logging and error reporting for MCP server development, and offers a modern developer experience with multiple server connections and saved configurations. The tool is built using Next.js and integrates MCP capabilities, AI SDKs from OpenAI, Anthropic, and Ollama, and various technologies like Node.js, TypeScript, and Next.js.
llamafarm
LlamaFarm is a comprehensive AI framework that empowers users to build powerful AI applications locally, with full control over costs and deployment options. It provides modular components for RAG systems, vector databases, model management, prompt engineering, and fine-tuning. Users can create differentiated AI products without needing extensive ML expertise, using simple CLI commands and YAML configs. The framework supports local-first development, production-ready components, strategy-based configuration, and deployment anywhere from laptops to the cloud.
claude_code_bridge
Claude Code Bridge (ccb) is a new multi-model collaboration tool that enables effective collaboration among multiple AI models in a split-pane CLI environment. It offers features like visual and controllable interface, persistent context maintenance, token savings, and native workflow integration. The tool allows users to unleash the full power of CLI by avoiding model bias, cognitive blind spots, and context limitations. It provides a new WYSIWYG solution for multi-model collaboration, making it easier to control and visualize multiple AI models simultaneously.
gpt-load
GPT-Load is a high-performance, enterprise-grade AI API transparent proxy service designed for enterprises and developers needing to integrate multiple AI services. Built with Go, it features intelligent key management, load balancing, and comprehensive monitoring capabilities for high-concurrency production environments. The tool serves as a transparent proxy service, preserving native API formats of various AI service providers like OpenAI, Google Gemini, and Anthropic Claude. It supports dynamic configuration, distributed leader-follower deployment, and a Vue 3-based web management interface. GPT-Load is production-ready with features like dual authentication, graceful shutdown, and error recovery.
shadcn-ui-mcp-server
A Model Context Protocol (MCP) server that provides AI assistants with comprehensive access to shadcn/ui v4 components, blocks, demos, and metadata. It allows users to seamlessly retrieve React, Svelte, Vue, and React Native implementations for AI-powered development workflows. The server supports multi-frameworks, component source code, demos, blocks, metadata access, directory browsing, smart caching, SSE transport, and Docker containerization. Users can quickly start the server, integrate with Claude Desktop, deploy with SSE transport or Docker, and access documentation for installation, configuration, integration, usage, frameworks, troubleshooting, and API reference. The server supports React, Svelte, Vue, and React Native implementations, with options for UI library selection. It enables AI-powered development, multi-client deployments, production environments, component discovery, multi-framework learning, rapid prototyping, and code generation.
readme-ai
README-AI is a developer tool that auto-generates README.md files using a combination of data extraction and generative AI. It streamlines documentation creation and maintenance, enhancing developer productivity. This project aims to enable all skill levels, across all domains, to better understand, use, and contribute to open-source software. It offers flexible README generation, supports multiple large language models (LLMs), provides customizable output options, works with various programming languages and project types, and includes an offline mode for generating boilerplate README files without external API calls.

ProxyPilot
ProxyPilot is a powerful local API proxy tool built in Go that eliminates the need for separate API keys when using Claude Code, Codex, Gemini, Kiro, and Qwen subscriptions with any AI coding tool. It handles OAuth authentication, token management, and API translation automatically, providing a single server to route requests. The tool supports multiple authentication providers, universal API translation, tool calling repair, extended thinking models, OAuth integration, multi-account support, quota auto-switching, usage statistics tracking, context compression, agentic harness for coding agents, session memory, system tray app, auto-updates, rollback support, and over 60 management APIs. ProxyPilot also includes caching layers for response and prompt caching to reduce latency and token usage.
flyte-sdk
Flyte 2 SDK is a pure Python tool for type-safe, distributed orchestration of agents, ML pipelines, and more. It allows users to write data pipelines, ML training jobs, and distributed compute in Python without any DSL constraints. With features like async-first parallelism and fine-grained observability, Flyte 2 offers a seamless workflow experience. Users can leverage core concepts like TaskEnvironments for container configuration, pure Python workflows for flexibility, and async parallelism for distributed execution. Advanced features include sub-task observability with tracing and remote task execution. The tool also provides native Jupyter integration for running and monitoring workflows directly from notebooks. Configuration and deployment are made easy with configuration files and commands for deploying and running workflows. Flyte 2 is licensed under the Apache 2.0 License.
botserver
General Bots is a self-hosted AI automation platform and LLM conversational platform focused on convention over configuration and code-less approaches. It serves as the core API server handling LLM orchestration, business logic, database operations, and multi-channel communication. The platform offers features like multi-vendor LLM API, MCP + LLM Tools Generation, Semantic Caching, Web Automation Engine, Enterprise Data Connectors, and Git-like Version Control. It enforces a ZERO TOLERANCE POLICY for code quality and security, with strict guidelines for error handling, performance optimization, and code patterns. The project structure includes modules for core functionalities like Rhai BASIC interpreter, security, shared types, tasks, auto task system, file operations, learning system, and LLM assistance.
For similar tasks
nlp-llms-resources
The 'nlp-llms-resources' repository is a comprehensive resource list for Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Large Language Models (LLMs). It covers a wide range of topics including traditional NLP datasets, data acquisition, libraries for NLP, neural networks, sentiment analysis, optical character recognition, information extraction, semantics, topic modeling, multilingual NLP, domain-specific LLMs, vector databases, ethics, costing, books, courses, surveys, aggregators, newsletters, papers, conferences, and societies. The repository provides valuable information and resources for individuals interested in NLP and LLMs.

adata
AData is a free and open-source A-share database that focuses on transaction-related data. It provides comprehensive data on stocks, including basic information, market data, and sentiment analysis. AData is designed to be easy to use and integrate with other applications, making it a valuable tool for quantitative trading and AI training.

PIXIU
PIXIU is a project designed to support the development, fine-tuning, and evaluation of Large Language Models (LLMs) in the financial domain. It includes components like FinBen, a Financial Language Understanding and Prediction Evaluation Benchmark, FIT, a Financial Instruction Dataset, and FinMA, a Financial Large Language Model. The project provides open resources, multi-task and multi-modal financial data, and diverse financial tasks for training and evaluation. It aims to encourage open research and transparency in the financial NLP field.

hezar
Hezar is an all-in-one AI library designed specifically for the Persian community. It brings together various AI models and tools, making it easy to use AI with just a few lines of code. The library seamlessly integrates with Hugging Face Hub, offering a developer-friendly interface and task-based model interface. In addition to models, Hezar provides tools like word embeddings, tokenizers, feature extractors, and more. It also includes supplementary ML tools for deployment, benchmarking, and optimization.
text-embeddings-inference
Text Embeddings Inference (TEI) is a toolkit for deploying and serving open source text embeddings and sequence classification models. TEI enables high-performance extraction for popular models like FlagEmbedding, Ember, GTE, and E5. It implements features such as no model graph compilation step, Metal support for local execution on Macs, small docker images with fast boot times, token-based dynamic batching, optimized transformers code for inference using Flash Attention, Candle, and cuBLASLt, Safetensors weight loading, and production-ready features like distributed tracing with Open Telemetry and Prometheus metrics.
CodeProject.AI-Server
CodeProject.AI Server is a standalone, self-hosted, fast, free, and open-source Artificial Intelligence microserver designed for any platform and language. It can be installed locally without the need for off-device or out-of-network data transfer, providing an easy-to-use solution for developers interested in AI programming. The server includes a HTTP REST API server, backend analysis services, and the source code, enabling users to perform various AI tasks locally without relying on external services or cloud computing. Current capabilities include object detection, face detection, scene recognition, sentiment analysis, and more, with ongoing feature expansions planned. The project aims to promote AI development, simplify AI implementation, focus on core use-cases, and leverage the expertise of the developer community.
spark-nlp
Spark NLP is a state-of-the-art Natural Language Processing library built on top of Apache Spark. It provides simple, performant, and accurate NLP annotations for machine learning pipelines that scale easily in a distributed environment. Spark NLP comes with 36000+ pretrained pipelines and models in more than 200+ languages. It offers tasks such as Tokenization, Word Segmentation, Part-of-Speech Tagging, Named Entity Recognition, Dependency Parsing, Spell Checking, Text Classification, Sentiment Analysis, Token Classification, Machine Translation, Summarization, Question Answering, Table Question Answering, Text Generation, Image Classification, Image to Text (captioning), Automatic Speech Recognition, Zero-Shot Learning, and many more NLP tasks. Spark NLP is the only open-source NLP library in production that offers state-of-the-art transformers such as BERT, CamemBERT, ALBERT, ELECTRA, XLNet, DistilBERT, RoBERTa, DeBERTa, XLM-RoBERTa, Longformer, ELMO, Universal Sentence Encoder, Llama-2, M2M100, BART, Instructor, E5, Google T5, MarianMT, OpenAI GPT2, Vision Transformers (ViT), OpenAI Whisper, and many more not only to Python and R, but also to JVM ecosystem (Java, Scala, and Kotlin) at scale by extending Apache Spark natively.
scikit-llm
Scikit-LLM is a tool that seamlessly integrates powerful language models like ChatGPT into scikit-learn for enhanced text analysis tasks. It allows users to leverage large language models for various text analysis applications within the familiar scikit-learn framework. The tool simplifies the process of incorporating advanced language processing capabilities into machine learning pipelines, enabling users to benefit from the latest advancements in natural language processing.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.