
GraphLLM
None
Stars: 209
GraphLLM is a graph-based framework designed to process data using LLMs. It offers a set of tools including a web scraper, PDF parser, YouTube subtitles downloader, Python sandbox, and TTS engine. The framework provides a GUI for building and debugging graphs with advanced features like loops, conditionals, parallel execution, streaming of results, hierarchical graphs, external tool integration, and dynamic scheduling. GraphLLM is a low-level framework that gives users full control over the raw prompt and output of models, with a steeper learning curve. It is tested with llama70b and qwen 32b, under heavy development with breaking changes expected.
README:
A graph based framework to process data through a LLM or multiple LLMs.
Several examples are available, including an agent capable of answering questions like
"give me a summary of the article on the home page of hacker news that is most likely related to language models."
Here are the features offered by GraphLLM:
- A graph based framework to process data using LLMs.
- A powerful agent capable of performing web searches and running python code
- A set of tools:
- web scraper to scrape web pages and reformat data in a LLM friendly format.
- PDF parser To extract text from PDF files.
- youtube subs downloader to download subtitles from a youtube video.
- Python sandbox for safely executing code generated by a LLM.
- TTS engine using piper.
- GUI for building and debugging graphs with a nice interface
A list of examples is available as a starting point.
This is a very low level framework. You get full control over the raw prompt and you see the raw output of the models. The inner working of the library is not hidden by any abstraction. The disadvantage is a steeper learning curve.
GraphLLM provides a GUI inspired by ComfyUI. The frontend has a similar look but the backend is completely different, so the nodes are not compatible between the project. The reason for this is that I wanted to provide more advanced features and support complex graphs.
Some of the features of GraphLLM's GUI:
- loops: You can have any kind of loop in the graph or even run a graph infinitely
- conditionals: The graph topology can be partially altered by the value going into nodes. This is useful for building state machines
- parallel execution of nodes: More nodes can be executing in parallel, useful for making multiple LLM calls at the same time
- streaming of results: Output of the LLM nodes can be seen in real time while it's produced. Watch nodes can be connected while the graph is running.
- Hierarchical graphs: Graphs can contain other graphs without limits.
- external tools: The graph can call external tools, for example the web scraper, the youtube downloader or the pdf reader
- dynamic scheduling of nodes when they are runnable
Here is an example of graph to generate python code and use it to solve a problem:
https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/486176d6-5bd7-4953-80fb-dbf7edb9af48
More examples:
Expand here to see more examples
This video showcases the File Node and how to make multiple calls to a LLM.
https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/80d5331a-efab-429a-bf51-991feaa64e1d
This screenshot show a Hierarchical graph. The file is downloaded, then summarized using another graph
- Tested mainly with llama70b and qwen 32b, using the llama.cpp server as backend
- Under heavy development, expect breaking changes
Run these commands in a shell to download and start GraphLLM
pip3 install selenium readabilipy html2text pdfminer.six websockets jinja2- (optional)
pip3 install piper-tts git clone https://github.com/matteoserva/GraphLLM.gitcd GraphLLMpython3 server.py
In another terminal, launch the llama.cpp server with Qwen2.5 32b.:
GGML_CUDA_ENABLE_UNIFIED_MEMORY=1 ./llama-server -ngl 99 -t 6 -c 32768 --host 0.0.0.0 -sp -fa -ctk q8_0 -ctv q8_0 -m Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct-Q5_K_M.gguf
Now you can launch the browser and interact with GraphLLM:
- Open http://localhost:8008/ in a web browser
Some tools require further configuration steps, namely the web scraper. Open the detailed setup page below to view the configuration steps.
Expand here to see a more detailed explanation of the setup steps
Required
TBD. When a missing dependency occurs, run pip3 install {dependency}
optional
There are optional dependencies for the extra features:
- pdfminer.six for converting PDF files
- selenium for the web scraping tool
- firefox and its Webdriver, for the web scraping tool
- openai and groq API
Install the python dependencies with
pip3 install selenium readabilipy html2text pdfminer.six openai groq websockets piper-tts
Steps to configure a connection with llama.cpp
llama.cpp server
-
Launch the server with
./llama-server -ngl 99 -t 4 -c 32768 --host 0.0.0.0 -m {your_model} -sp -faRelevant arguments:
-
-host 0.0.0.0if you want to run the server on another machine -
-spTo receive the eom token, this enables llama3.1 tool calling -
-m {your_model}selects the model to use. This project works best with llama 3.1 or qwen2.5
-
client configuration
-
modify
client_config.yml- You can replace the default client by changing the
client_nameparameter in the config file - If needed, setup groq or openai api config
- You can use a list as client_name. In that case if one client fails, the next one will be used. For example you can use this to setup llama.cpp as primary client and a remote API as fallback.
- You can replace the default client by changing the
web scraper
- install firefox and selenium
- open firefox
- open about:profiles
- create a profile named "profile.bot"
- relaunch inside that profile
- install ublock origin and verify that it's working.
- import the ublock filter list I uploaded here
- close firefox
- If needed, download the appropriate geckodriver
- test the tool with
python3 extras/scraper/scrape.py
pdf scraper
- install pdfminer.six
- test it by running
python3 extras/parse_pdf.py {your pdf}
youtube scraper
- test it by running
python3 extras/youtube_subs.py
launching the server
You can launch the server by running this command in a terminal from inside the GraphLLM folder:
python3 server.py
Then you can open the browser at http://localhost:8008/
directly running a graph
This will launch the example summarization prompt:
python3 exec.py examples/graph_summarize.txt test/wikipedia_summary.txt
all the examples
There are more examples in the examples folder You can also open more example from the web gui
GraphLLM supports some inference engines and many models. The suggested combination is llama.cpp with Qwen2.5.
inference engines and API
The llama.cpp server is fully supported. Other engines are available with limited functionality. GraphLLM makes extensive use of advanced features like grammars, assistant response prefilling and using raw prompts. Some engines and API providers support only a subset of these features.
Available engines:
- llama.cpp server: complete support
- llama_swap: full support
- groq API: Grammars and raw prompts not available
- openrouter API: Grammars and raw prompts not available
- OpenAI and compatible API: Grammars and raw prompts not available
- HF transformers: partial support
models
All the popular models are available.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for GraphLLM
Similar Open Source Tools

GraphLLM
GraphLLM is a graph-based framework designed to process data using LLMs. It offers a set of tools including a web scraper, PDF parser, YouTube subtitles downloader, Python sandbox, and TTS engine. The framework provides a GUI for building and debugging graphs with advanced features like loops, conditionals, parallel execution, streaming of results, hierarchical graphs, external tool integration, and dynamic scheduling. GraphLLM is a low-level framework that gives users full control over the raw prompt and output of models, with a steeper learning curve. It is tested with llama70b and qwen 32b, under heavy development with breaking changes expected.
databerry
Chaindesk is a no-code platform that allows users to easily set up a semantic search system for personal data without technical knowledge. It supports loading data from various sources such as raw text, web pages, files (Word, Excel, PowerPoint, PDF, Markdown, Plain Text), and upcoming support for web sites, Notion, and Airtable. The platform offers a user-friendly interface for managing datastores, querying data via a secure API endpoint, and auto-generating ChatGPT Plugins for each datastore. Chaindesk utilizes a Vector Database (Qdrant), Openai's text-embedding-ada-002 for embeddings, and has a chunk size of 1024 tokens. The technology stack includes Next.js, Joy UI, LangchainJS, PostgreSQL, Prisma, and Qdrant, inspired by the ChatGPT Retrieval Plugin.

trafilatura
Trafilatura is a Python package and command-line tool for gathering text on the Web and simplifying the process of turning raw HTML into structured, meaningful data. It includes components for web crawling, downloads, scraping, and extraction of main texts, metadata, and comments. The tool aims to focus on actual content, avoid noise, and make sense of data and metadata. It is robust, fast, and widely used by companies and institutions. Trafilatura outperforms other libraries in text extraction benchmarks and offers various features like support for sitemaps, parallel processing, configurable extraction of key elements, multiple output formats, and optional add-ons. The tool is actively maintained with regular updates and comprehensive documentation.
oramacore
OramaCore is a database designed for AI projects, answer engines, copilots, and search functionalities. It offers features such as a full-text search engine, vector database, LLM interface, and various utilities. The tool is currently under active development and not recommended for production use due to potential API changes. OramaCore aims to provide a comprehensive solution for managing data and enabling advanced search capabilities in AI applications.
AIaW
AIaW is a next-generation LLM client with full functionality, lightweight, and extensible. It supports various basic functions such as streaming transfer, image uploading, and latex formulas. The tool is cross-platform with a responsive interface design. It supports multiple service providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google. Users can modify questions, regenerate in a forked manner, and visualize conversations in a tree structure. Additionally, it offers features like file parsing, video parsing, plugin system, assistant market, local storage with real-time cloud sync, and customizable interface themes. Users can create multiple workspaces, use dynamic prompt word variables, extend plugins, and benefit from detailed design elements like real-time content preview, optimized code pasting, and support for various file types.

traceroot
TraceRoot is a tool that helps engineers debug production issues 10× faster using AI-powered analysis of traces, logs, and code context. It accelerates the debugging process with AI-powered insights, integrates seamlessly into the development workflow, provides real-time trace and log analysis, code context understanding, and intelligent assistance. Features include ease of use, LLM flexibility, distributed services, AI debugging interface, and integration support. Users can get started with TraceRoot Cloud for a 7-day trial or self-host the tool. SDKs are available for Python and JavaScript/TypeScript.
LocalLLMClient
LocalLLMClient is a Swift package designed to interact with local Large Language Models (LLMs) on Apple platforms. It supports GGUF, MLX models, and the FoundationModels framework, providing streaming API, multimodal capabilities, and tool calling functionalities. Users can easily integrate this tool to work with various models for text generation and processing. The package also includes advanced features for low-level API control and multimodal image processing. LocalLLMClient is experimental and subject to API changes, offering support for iOS, macOS, and Linux platforms.
tools
Strands Agents Tools is a community-driven project that provides a powerful set of tools for your agents to use. It bridges the gap between large language models and practical applications by offering ready-to-use tools for file operations, system execution, API interactions, mathematical operations, and more. The tools cover a wide range of functionalities including file operations, shell integration, memory storage, web infrastructure, HTTP client, Slack client, Python execution, mathematical tools, AWS integration, image and video processing, audio output, environment management, task scheduling, advanced reasoning, swarm intelligence, dynamic MCP client, parallel tool execution, browser automation, diagram creation, RSS feed management, and computer automation.
ai21-python
The AI21 Labs Python SDK is a comprehensive tool for interacting with the AI21 API. It provides functionalities for chat completions, conversational RAG, token counting, error handling, and support for various cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Vertex. The SDK offers both synchronous and asynchronous usage, along with detailed examples and documentation. Users can quickly get started with the SDK to leverage AI21's powerful models for various natural language processing tasks.
tunacode
TunaCode CLI is an AI-powered coding assistant that provides a command-line interface for developers to enhance their coding experience. It offers features like model selection, parallel execution for faster file operations, and various commands for code management. The tool aims to improve coding efficiency and provide a seamless coding environment for developers.
llamabot
LlamaBot is a Pythonic bot interface to Large Language Models (LLMs), providing an easy way to experiment with LLMs in Jupyter notebooks and build Python apps utilizing LLMs. It supports all models available in LiteLLM. Users can access LLMs either through local models with Ollama or by using API providers like OpenAI and Mistral. LlamaBot offers different bot interfaces like SimpleBot, ChatBot, QueryBot, and ImageBot for various tasks such as rephrasing text, maintaining chat history, querying documents, and generating images. The tool also includes CLI demos showcasing its capabilities and supports contributions for new features and bug reports from the community.
llm
The 'llm' package for Emacs provides an interface for interacting with Large Language Models (LLMs). It abstracts functionality to a higher level, concealing API variations and ensuring compatibility with various LLMs. Users can set up providers like OpenAI, Gemini, Vertex, Claude, Ollama, GPT4All, and a fake client for testing. The package allows for chat interactions, embeddings, token counting, and function calling. It also offers advanced prompt creation and logging capabilities. Users can handle conversations, create prompts with placeholders, and contribute by creating providers.
DB-GPT
DB-GPT is an open source AI native data app development framework with AWEL(Agentic Workflow Expression Language) and agents. It aims to build infrastructure in the field of large models, through the development of multiple technical capabilities such as multi-model management (SMMF), Text2SQL effect optimization, RAG framework and optimization, Multi-Agents framework collaboration, AWEL (agent workflow orchestration), etc. Which makes large model applications with data simpler and more convenient.

spiceai
Spice is a portable runtime written in Rust that offers developers a unified SQL interface to materialize, accelerate, and query data from any database, data warehouse, or data lake. It connects, fuses, and delivers data to applications, machine-learning models, and AI-backends, functioning as an application-specific, tier-optimized Database CDN. Built with industry-leading technologies such as Apache DataFusion, Apache Arrow, Apache Arrow Flight, SQLite, and DuckDB. Spice makes it fast and easy to query data from one or more sources using SQL, co-locating a managed dataset with applications or machine learning models, and accelerating it with Arrow in-memory, SQLite/DuckDB, or attached PostgreSQL for fast, high-concurrency, low-latency queries.

chatluna
Chatluna is a machine learning model plugin that provides chat services with large language models. It is highly extensible, supports multiple output formats, and offers features like custom conversation presets, rate limiting, and context awareness. Users can deploy Chatluna under Koishi without additional configuration. The plugin supports various models/platforms like OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, Google Gemini, and more. It also provides preset customization using YAML files and allows for easy forking and development within Koishi projects. However, the project lacks web UI, HTTP server, and project documentation, inviting contributions from the community.
simple-ai
Simple AI is a lightweight Python library for implementing basic artificial intelligence algorithms. It provides easy-to-use functions and classes for tasks such as machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision. With Simple AI, users can quickly prototype and deploy AI solutions without the complexity of larger frameworks.
For similar tasks

GraphLLM
GraphLLM is a graph-based framework designed to process data using LLMs. It offers a set of tools including a web scraper, PDF parser, YouTube subtitles downloader, Python sandbox, and TTS engine. The framework provides a GUI for building and debugging graphs with advanced features like loops, conditionals, parallel execution, streaming of results, hierarchical graphs, external tool integration, and dynamic scheduling. GraphLLM is a low-level framework that gives users full control over the raw prompt and output of models, with a steeper learning curve. It is tested with llama70b and qwen 32b, under heavy development with breaking changes expected.

codebox-api
CodeBox is a cloud infrastructure tool designed for running Python code in an isolated environment. It also offers simple file input/output capabilities and will soon support vector database operations. Users can install CodeBox using pip and utilize it by setting up an API key. The tool allows users to execute Python code snippets and interact with the isolated environment. CodeBox is currently in early development stages and requires manual handling for certain operations like refunds and cancellations. The tool is open for contributions through issue reporting and pull requests. It is licensed under MIT and can be contacted via email at [email protected].
OrionChat
Orion is a web-based chat interface that simplifies interactions with multiple AI model providers. It provides a unified platform for chatting and exploring various large language models (LLMs) such as Ollama, OpenAI (GPT model), Cohere (Command-r models), Google (Gemini models), Anthropic (Claude models), Groq Inc., Cerebras, and SambaNova. Users can easily navigate and assess different AI models through an intuitive, user-friendly interface. Orion offers features like browser-based access, code execution with Google Gemini, text-to-speech (TTS), speech-to-text (STT), seamless integration with multiple AI models, customizable system prompts, language translation tasks, document uploads for analysis, and more. API keys are stored locally, and requests are sent directly to official providers' APIs without external proxies.
lyraios
LYRAIOS (LLM-based Your Reliable AI Operating System) is an advanced AI assistant platform built with FastAPI and Streamlit, designed to serve as an operating system for AI applications. It offers core features such as AI process management, memory system, and I/O system. The platform includes built-in tools like Calculator, Web Search, Financial Analysis, File Management, and Research Tools. It also provides specialized assistant teams for Python and research tasks. LYRAIOS is built on a technical architecture comprising FastAPI backend, Streamlit frontend, Vector Database, PostgreSQL storage, and Docker support. It offers features like knowledge management, process control, and security & access control. The roadmap includes enhancements in core platform, AI process management, memory system, tools & integrations, security & access control, open protocol architecture, multi-agent collaboration, and cross-platform support.
langmanus
LangManus is a community-driven AI automation framework that combines language models with specialized tools for tasks like web search, crawling, and Python code execution. It implements a hierarchical multi-agent system with agents like Coordinator, Planner, Supervisor, Researcher, Coder, Browser, and Reporter. The framework supports LLM integration, search and retrieval tools, Python integration, workflow management, and visualization. LangManus aims to give back to the open-source community and welcomes contributions in various forms.
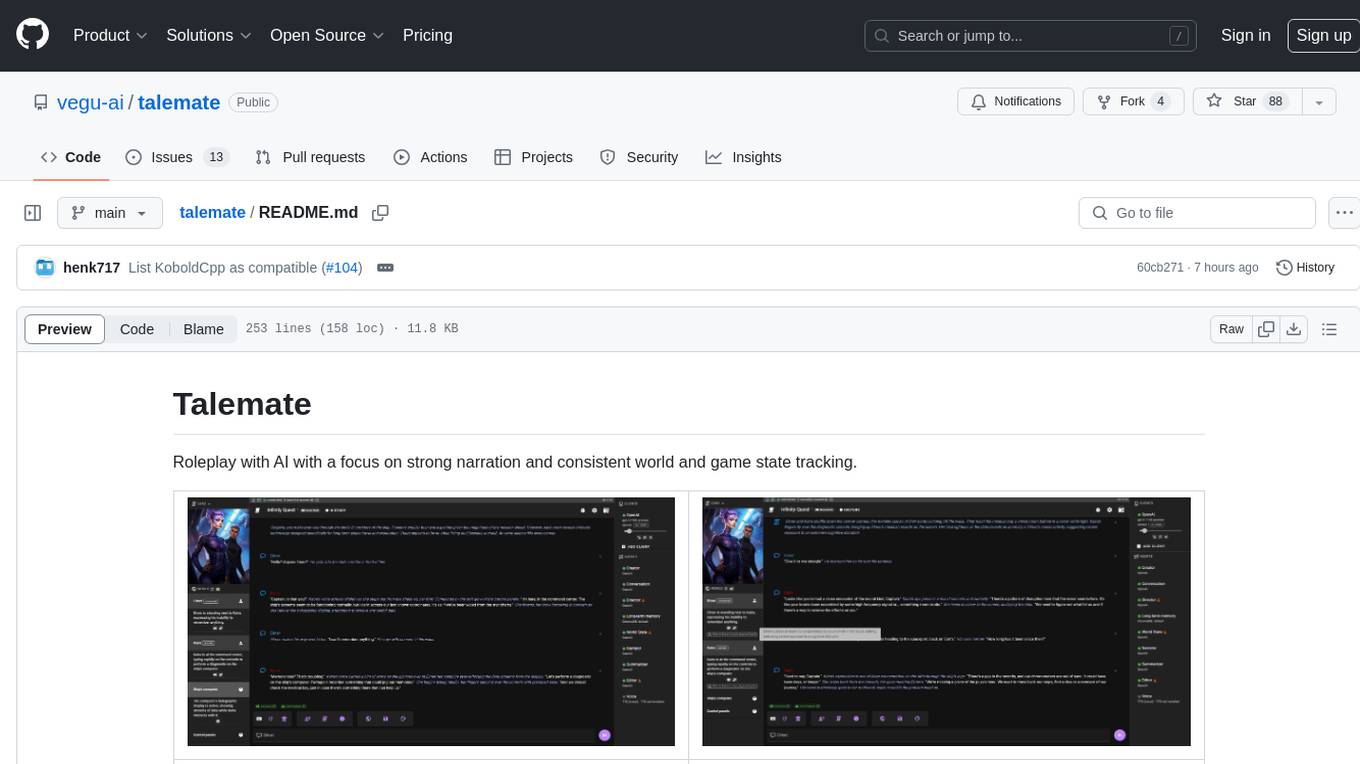
talemate
Talemate is a roleplay tool that allows users to interact with AI agents for dialogue, narration, summarization, direction, editing, world state management, character/scenario creation, text-to-speech, and visual generation. It supports multiple AI clients and APIs, offers long-term memory using ChromaDB, and provides tools for managing NPCs, AI-assisted character creation, and scenario creation. Users can customize prompts using Jinja2 templates and benefit from a modern, responsive UI. The tool also integrates with Runpod for enhanced functionality.
Kuebiko
Kuebiko is a Twitch Chat Bot that reads twitch chat and generates text-to-speech responses using Google Cloud API and OpenAI's GPT-3 text completion model. It allows users to set up their own VTuber AI similar to 'Neuro-Sama'. The project is built with Python and requires setting up various API keys and configurations to enable the bot functionality. Users can customize the voice of their VTuber and route audio using VBAudio Cable. Kuebiko provides a unique way to interact with viewers through chat responses and captions in OBS.
aip-community-registry
AIP Community Registry is a collection of community-built applications and projects leveraging Palantir's AIP Platform. It showcases real-world implementations from developers using AIP in production. The registry features various solutions demonstrating practical implementations and integration patterns across different use cases.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.