IG-LLM
Code for "Re-Thinking Inverse Graphics With Large Language Models"; TMLR 2024
Stars: 52
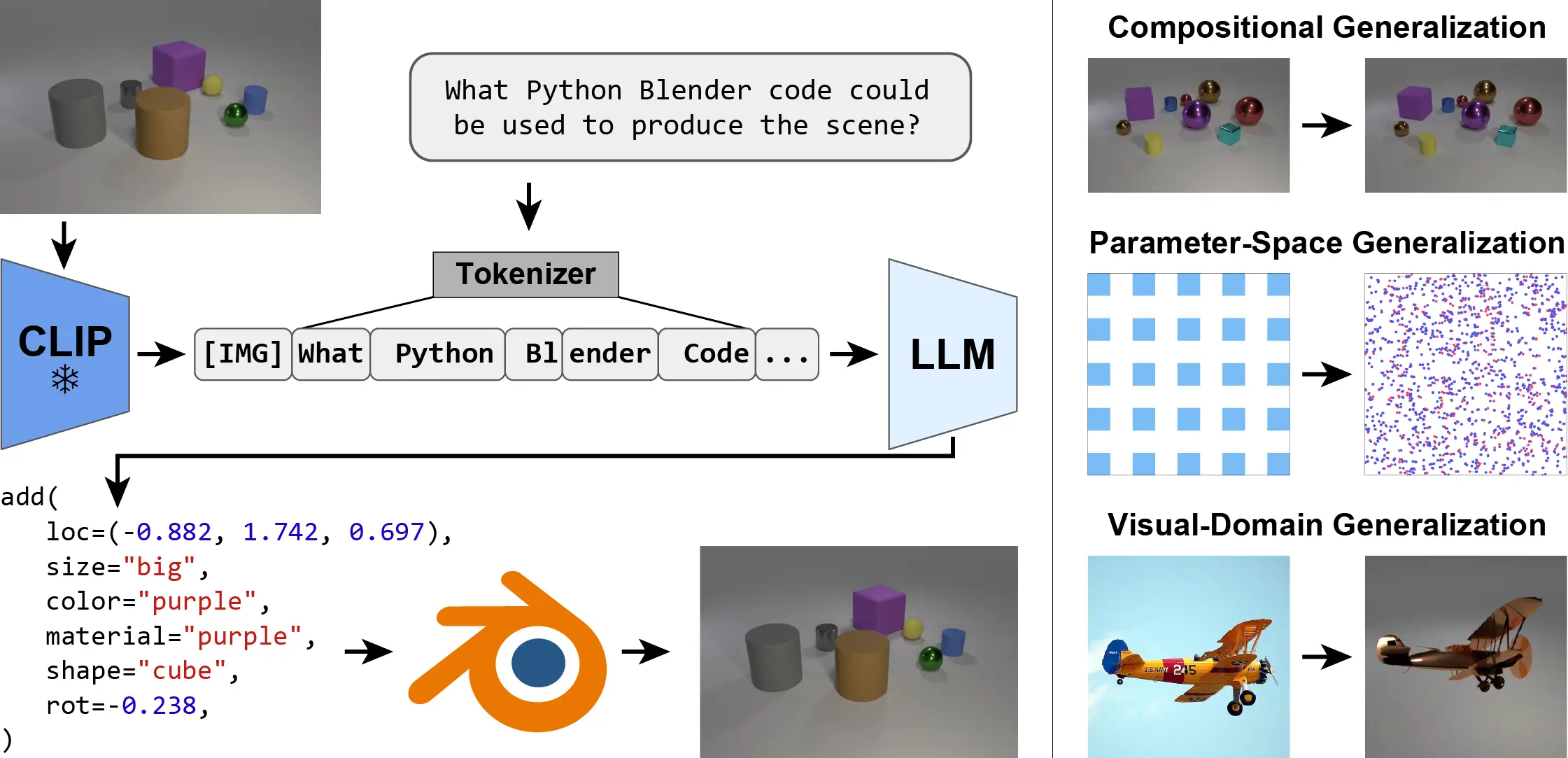
IG-LLM is a framework for solving inverse-graphics problems by instruction-tuning a Large Language Model (LLM) to decode visual embeddings into graphics code. The framework demonstrates natural generalization across distribution shifts without special inductive biases. It provides training and evaluation data for various scenarios like CLEVR, 2D, SO(3), 6-DoF, and ShapeNet. The environment setup can be done using conda/micromamba or Dockerfile. Training can be initiated for each scenario with specific commands, and inference can be performed using the provided script.
README:
Peter Kulits*, Haiwen Feng*, Weiyang Liu, Victoria Abrevaya, Michael J. Black
We present the Inverse-Graphics Large Language Model (IG-LLM) framework, a general approach to solving inverse-graphics problems. We instruction-tune an LLM to decode a visual (CLIP) embedding into graphics code that can be used to reproduce the observed scene using a standard graphics engine. Leveraging the broad reasoning abilities of LLMs, we demonstrate that our framework exhibits natural generalization across a variety of distribution shifts without the use of special inductive biases.Training and evaluation data can be found at https://ig-llm.is.tue.mpg.de/download.php after registering on the project page. The following is an outline of the data available:
├── CLEVR
│ ├── images
│ │ ├── train.tar
│ │ ├── val_ID.tar
│ │ └── val_OOD.tar
│ └── labels
│ ├── train.json
│ ├── val_ID.json
│ └── val_OOD.json
├── 2D
│ └── 2d.npz
├── SO3
│ ├── images
│ │ ├── train.tar
│ │ ├── val_ID.tar
│ │ └── val_OOD.tar
│ └── labels
│ ├── train.json
│ ├── val_ID.json
│ └── val_OOD.json
├── 6DoF
│ ├── images
│ │ ├── train.tar
│ │ └── val_ID.tar
│ └── labels
│ ├── train.json
│ └── val_ID.json
└── ShapeNet
├── images
│ ├── train.tar
│ ├── val_ID.tar
│ ├── val_OOD_texture.tar
│ └── val_OOD_shape.tar
└── labels
├── train.json
├── val_ID.json
├── val_OOD_texture.json
└── val_OOD_shape.jsonconda/micromamba from environment.yml or using the Dockerfile.
After the data has been downloaded, training can be initiated with the following:
-
CLEVR
python train.py \ --images_tar data/CLEVR/images/train.tar \ --data_path data/CLEVR/images/train.json \ --images_val_tar data/CLEVR/images/val_OOD.tar \ --data_path_val data/CLEVR/labels/val_OOD.json \ --per_device_train_batch_size X \ --output_dir ./checkpoints/clevr-Y \ --max_steps 40000 \ --float_head_type (none|tanh_mlp_gelu) \ --image_aspect_ratio pad \ --num_samples 4000 -
2D
2d.npzis expected to be atdata/2d.npzprior to runningtrain.py.python train.py \ --data_path checkerboard_sparse \ --data_path_val random \ --per_device_train_batch_size X \ --output_dir ./checkpoints/2d-Y \ --max_steps 40000 \ --float_head_type (none|tanh_mlp_gelu) \ --image_aspect_ratio pad \ --is_2d True -
SO(3)
python train.py \ --images_tar data/SO3/images/train.tar \ --data_path data/SO3/images/train.json \ --images_val_tar data/SO3/images/val_OOD.tar \ --data_path_val data/SO3/labels/val_OOD.json \ --per_device_train_batch_size X \ --output_dir ./checkpoints/so3-Y \ --max_steps 40000 \ --float_head_type (none|tanh_mlp_gelu) \ --image_aspect_ratio pad \ --rotation_rep (euler_int|euler|aa|6d) -
6-DoF
python train.py \ --images_tar data/6DoF/images/train.tar \ --data_path data/6DoF/images/train.json \ --images_val_tar data/6DoF/images/val_ID.tar \ --data_path_val data/6DoF/labels/val_ID.json \ --per_device_train_batch_size X \ --output_dir ./checkpoints/6dof-Y \ --max_steps 200000 \ --float_head_type (none|tanh_mlp_gelu) \ --image_aspect_ratio pad \ --rotation_rep (euler_int|euler|aa|6d) -
ShapeNet
python train.py \ --images_tar data/ShapeNet/images/train.tar \ --data_path data/ShapeNet/images/train.json \ --images_val_tar data/ShapeNet/images/val_OOD_texture.tar \ --data_path_val data/ShapeNet/labels/val_OOD_texture.json \ --per_device_train_batch_size X \ --output_dir ./checkpoints/shapenet-Y \ --max_steps 500000 \ --float_head_type (none|tanh_mlp_gelu) \ --image_aspect_ratio pad \ --rotation_rep (euler_int|euler|aa|6d)
python inference.py \
--model-path ./checkpoints/clevr-Y \
--images_tar data/CLEVR/images/val_OOD.tar \
--out_path ./out/clevr-Y-val_OOD.json \
--image_aspect_ratio padLICENSE.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for IG-LLM
Similar Open Source Tools

IG-LLM
IG-LLM is a framework for solving inverse-graphics problems by instruction-tuning a Large Language Model (LLM) to decode visual embeddings into graphics code. The framework demonstrates natural generalization across distribution shifts without special inductive biases. It provides training and evaluation data for various scenarios like CLEVR, 2D, SO(3), 6-DoF, and ShapeNet. The environment setup can be done using conda/micromamba or Dockerfile. Training can be initiated for each scenario with specific commands, and inference can be performed using the provided script.
morgana-form
MorGana Form is a full-stack form builder project developed using Next.js, React, TypeScript, Ant Design, PostgreSQL, and other technologies. It allows users to quickly create and collect data through survey forms. The project structure includes components, hooks, utilities, pages, constants, Redux store, themes, types, server-side code, and component packages. Environment variables are required for database settings, NextAuth login configuration, and file upload services. Additionally, the project integrates an AI model for form generation using the Ali Qianwen model API.
DeepTutor
DeepTutor is an AI-powered personalized learning assistant that offers a suite of modules for massive document knowledge Q&A, interactive learning visualization, knowledge reinforcement with practice exercise generation, deep research, and idea generation. The tool supports multi-agent collaboration, dynamic topic queues, and structured outputs for various tasks. It provides a unified system entry for activity tracking, knowledge base management, and system status monitoring. DeepTutor is designed to streamline learning and research processes by leveraging AI technologies and interactive features.
mcp-ts-template
The MCP TypeScript Server Template is a production-grade framework for building powerful and scalable Model Context Protocol servers with TypeScript. It features built-in observability, declarative tooling, robust error handling, and a modular, DI-driven architecture. The template is designed to be AI-agent-friendly, providing detailed rules and guidance for developers to adhere to best practices. It enforces architectural principles like 'Logic Throws, Handler Catches' pattern, full-stack observability, declarative components, and dependency injection for decoupling. The project structure includes directories for configuration, container setup, server resources, services, storage, utilities, tests, and more. Configuration is done via environment variables, and key scripts are available for development, testing, and publishing to the MCP Registry.
VT.ai
VT.ai is a multimodal AI platform that offers dynamic conversation routing with SemanticRouter, multi-modal interactions (text/image/audio), an assistant framework with code interpretation, real-time response streaming, cross-provider model switching, and local model support with Ollama integration. It supports various AI providers such as OpenAI, Anthropic, Google Gemini, Groq, Cohere, and OpenRouter, providing a wide range of core capabilities for AI orchestration.
sandbox
AIO Sandbox is an all-in-one agent sandbox environment that combines Browser, Shell, File, MCP operations, and VSCode Server in a single Docker container. It provides a unified, secure execution environment for AI agents and developers, with features like unified file system, multiple interfaces, secure execution, zero configuration, and agent-ready MCP-compatible APIs. The tool allows users to run shell commands, perform file operations, automate browser tasks, and integrate with various development tools and services.
lihil
Lihil is a performant, productive, and professional web framework designed to make Python the mainstream programming language for web development. It is 100% test covered and strictly typed, offering fast performance, ergonomic API, and built-in solutions for common problems. Lihil is suitable for enterprise web development, delivering robust and scalable solutions with best practices in microservice architecture and related patterns. It features dependency injection, OpenAPI docs generation, error response generation, data validation, message system, testability, and strong support for AI features. Lihil is ASGI compatible and uses starlette as its ASGI toolkit, ensuring compatibility with starlette classes and middlewares. The framework follows semantic versioning and has a roadmap for future enhancements and features.
distill
Distill is a reliability layer for LLM context that provides deterministic deduplication to remove redundancy before reaching the model. It aims to reduce redundant data, lower costs, provide faster responses, and offer more efficient and deterministic results. The tool works by deduplicating, compressing, summarizing, and caching context to ensure reliable outputs. It offers various installation methods, including binary download, Go install, Docker usage, and building from source. Distill can be used for tasks like deduplicating chunks, connecting to vector databases, integrating with AI assistants, analyzing files for duplicates, syncing vectors to Pinecone, querying from the command line, and managing configuration files. The tool supports self-hosting via Docker, Docker Compose, building from source, Fly.io deployment, Render deployment, and Railway integration. Distill also provides monitoring capabilities with Prometheus-compatible metrics, Grafana dashboard, and OpenTelemetry tracing.
httpjail
httpjail is a cross-platform tool designed for monitoring and restricting HTTP/HTTPS requests from processes using network isolation and transparent proxy interception. It provides process-level network isolation, HTTP/HTTPS interception with TLS certificate injection, script-based and JavaScript evaluation for custom request logic, request logging, default deny behavior, and zero-configuration setup. The tool operates on Linux and macOS, creating an isolated network environment for target processes and intercepting all HTTP/HTTPS traffic through a transparent proxy enforcing user-defined rules.
fluid.sh
fluid.sh is a tool designed to manage and debug VMs using AI agents in isolated environments before applying changes to production. It provides a workflow where AI agents work autonomously in sandbox VMs, and human approval is required before any changes are made to production. The tool offers features like autonomous execution, full VM isolation, human-in-the-loop approval workflow, Ansible export, and a Python SDK for building autonomous agents.
simple-data-analysis
Simple data analysis (SDA) is an easy-to-use and high-performance TypeScript library for data analysis. It can be used with tabular and geospatial data. The library is maintained by Nael Shiab, a computational journalist and senior data producer for CBC News. SDA is based on DuckDB, a fast in-process analytical database, and it sends SQL queries to be executed by DuckDB. The library provides methods inspired by Pandas (Python) and the Tidyverse (R), and it also supports writing custom SQL queries and processing data with JavaScript. Additionally, SDA offers methods for leveraging large language models (LLMs) for data cleaning, extraction, categorization, and natural language interaction, as well as for embeddings and semantic search.
mimiclaw
MimiClaw is a pocket AI assistant that runs on a $5 chip, specifically designed for the ESP32-S3 board. It operates without Linux or Node.js, using pure C language. Users can interact with MimiClaw through Telegram, enabling it to handle various tasks and learn from local memory. The tool is energy-efficient, running on USB power 24/7. With MimiClaw, users can have a personal AI assistant on a chip the size of a thumb, making it convenient and accessible for everyday use.
AiToEarn
AiToEarn is a one-click publishing tool for multiple self-media platforms such as Douyin, Xiaohongshu, Video Number, and Kuaishou. It allows users to publish videos with ease, observe popular content across the web, and view rankings of explosive articles on Xiaohongshu. The tool is also capable of providing daily and weekly rankings of popular content on Xiaohongshu, Douyin, Video Number, and Kuaishou. In progress features include expanding publishing parameters to support short video e-commerce, adding an AI tool ranking list, enabling AI automatic comments, and AI comment search.
agentboard
Agentboard is a Web GUI for tmux optimized for agent TUI's like claude and codex. It provides a shared workspace across devices with features such as paste support, touch scrolling, virtual arrow keys, log tracking, and session pinning. Users can interact with tmux sessions from any device through a live terminal stream. The tool allows session discovery, status inference, and terminal I/O streaming for efficient agent management.

hub
Hub is an open-source, high-performance LLM gateway written in Rust. It serves as a smart proxy for LLM applications, centralizing control and tracing of all LLM calls and traces. Built for efficiency, it provides a single API to connect to any LLM provider. The tool is designed to be fast, efficient, and completely open-source under the Apache 2.0 license.
mcp-prompts
mcp-prompts is a Python library that provides a collection of prompts for generating creative writing ideas. It includes a variety of prompts such as story starters, character development, plot twists, and more. The library is designed to inspire writers and help them overcome writer's block by offering unique and engaging prompts to spark creativity. With mcp-prompts, users can access a wide range of writing prompts to kickstart their imagination and enhance their storytelling skills.
For similar tasks

IG-LLM
IG-LLM is a framework for solving inverse-graphics problems by instruction-tuning a Large Language Model (LLM) to decode visual embeddings into graphics code. The framework demonstrates natural generalization across distribution shifts without special inductive biases. It provides training and evaluation data for various scenarios like CLEVR, 2D, SO(3), 6-DoF, and ShapeNet. The environment setup can be done using conda/micromamba or Dockerfile. Training can be initiated for each scenario with specific commands, and inference can be performed using the provided script.
model_server
OpenVINO™ Model Server (OVMS) is a high-performance system for serving models. Implemented in C++ for scalability and optimized for deployment on Intel architectures, the model server uses the same architecture and API as TensorFlow Serving and KServe while applying OpenVINO for inference execution. Inference service is provided via gRPC or REST API, making deploying new algorithms and AI experiments easy.
TaskingAI
TaskingAI brings Firebase's simplicity to **AI-native app development**. The platform enables the creation of GPTs-like multi-tenant applications using a wide range of LLMs from various providers. It features distinct, modular functions such as Inference, Retrieval, Assistant, and Tool, seamlessly integrated to enhance the development process. TaskingAI’s cohesive design ensures an efficient, intelligent, and user-friendly experience in AI application development.
MathCoder
MathCoder is a repository focused on enhancing mathematical reasoning by fine-tuning open-source language models to use code for modeling and deriving math equations. It introduces MathCodeInstruct dataset with solutions interleaving natural language, code, and execution results. The repository provides MathCoder models capable of generating code-based solutions for challenging math problems, achieving state-of-the-art scores on MATH and GSM8K datasets. It offers tools for model deployment, inference, and evaluation, along with a citation for referencing the work.
llm_qlora
LLM_QLoRA is a repository for fine-tuning Large Language Models (LLMs) using QLoRA methodology. It provides scripts for training LLMs on custom datasets, pushing models to HuggingFace Hub, and performing inference. Additionally, it includes models trained on HuggingFace Hub, a blog post detailing the QLoRA fine-tuning process, and instructions for converting and quantizing models. The repository also addresses troubleshooting issues related to Python versions and dependencies.
instruct-ner
Instruct NER is a solution for complex Named Entity Recognition tasks, including Nested NER, based on modern Large Language Models (LLMs). It provides tools for dataset creation, training, automatic metric calculation, inference, error analysis, and model implementation. Users can create instructions for LLM, build dictionaries with labels, and generate model input templates. The tool supports various entity types and datasets, such as RuDReC, NEREL-BIO, CoNLL-2003, and MultiCoNER II. It offers training scripts for LLMs and metric calculation functions. Instruct NER models like Llama, Mistral, T5, and RWKV are implemented, with HuggingFace models available for adaptation and merging.
rknn-llm
RKLLM software stack is a toolkit designed to help users quickly deploy AI models to Rockchip chips. It consists of RKLLM-Toolkit for model conversion and quantization, RKLLM Runtime for deploying models on Rockchip NPU platform, and RKNPU kernel driver for hardware interaction. The toolkit supports RK3588 and RK3576 series chips and various models like TinyLLAMA, Qwen, Phi, ChatGLM3, Gemma, InternLM2, and MiniCPM. Users can download packages, docker images, examples, and docs from RKLLM_SDK. Additionally, RKNN-Toolkit2 SDK is available for deploying additional AI models.

booster
Booster is a powerful inference accelerator designed for scaling large language models within production environments or for experimental purposes. It is built with performance and scaling in mind, supporting various CPUs and GPUs, including Nvidia CUDA, Apple Metal, and OpenCL cards. The tool can split large models across multiple GPUs, offering fast inference on machines with beefy GPUs. It supports both regular FP16/FP32 models and quantised versions, along with popular LLM architectures. Additionally, Booster features proprietary Janus Sampling for code generation and non-English languages.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.