driverlessai-recipes
Recipes for Driverless AI
Stars: 246
This repository contains custom recipes for H2O Driverless AI, which is an Automatic Machine Learning platform for the Enterprise. Custom recipes are Python code snippets that can be uploaded into Driverless AI at runtime to automate feature engineering, model building, visualization, and interpretability. Users can gain control over the optimization choices made by Driverless AI by providing their own custom recipes. The repository includes recipes for various tasks such as data manipulation, data preprocessing, feature selection, data augmentation, model building, scoring, and more. Best practices for creating and using recipes are also provided, including security considerations, performance tips, and safety measures.
README:
H2O Driverless AI is Automatic Machine Learning for the Enterprise. Driverless AI automates feature engineering, model building, visualization and interpretability.
- Learn more about Driverless AI from the H2O.ai website
- Take the test drive
- Go to the Driverless AI community Slack channel and ask your BYOR related questions in #general
BYOR stands for Bring Your Own Recipe and is a key feature of Driverless AI. It allows domain scientists to solve their problems faster and with more precision.
Custom recipes are Python code snippets that can be uploaded into Driverless AI at runtime, like plugins. No need to restart Driverless AI. Custom recipes can be provided for transformers, models and scorers. During training of a supervised machine learning modeling pipeline (aka experiment), Driverless AI can then use these code snippets as building blocks, in combination with all built-in code pieces (or instead of). By providing your own custom recipes, you can gain control over the optimization choices that Driverless AI makes to best solve your machine learning problems.
-
Recipes are meant to be built by people you trust and each recipe should be code-reviewed before going to production.
-
Assume that a user with access to Driverless AI has access to the data inside that instance.
- Apart from securing access to the instance via private networks, various methods of authentication are possible. Local authentication provides the most control over which users have access to Driverless AI.
- Unless the
config.tomlsettingenable_dataset_downloading=falseis set, an authenticated user can download all imported datasets as .csv via direct APIs.
-
When recipes are enabled (
enable_custom_recipes=true, the default), be aware that:- The code for the recipes runs as the same native Linux user that runs the Driverless AI application.
- Recipes have explicit access to all data passing through the transformer/model/scorer API
- Recipes have implicit access to system resources such as disk, memory, CPUs, GPUs, network, etc.
- An H2O-3 Java process is started in the background, for use by all recipes using H2O-3. Anyone with access to the Driverless AI instance can browse the file system, see models and data through the H2O-3 interface.
- The code for the recipes runs as the same native Linux user that runs the Driverless AI application.
-
Enable automatic detection of forbidden or dangerous code constructs in a custom recipe with
custom_recipe_security_analysis_enabled = tr ue. Note the following:- When
custom_recipe_security_analysis_enabledis enabled, do not use modules specified in the banlist. Specify the banlist with thecu stom_recipe_import_banlistconfig option.- For example:
custom_recipe_import_banlist = ["shlex", "plumbum", "pexpect", "envoy", "commands", "fabric", "subprocess", "os.system", "system"](default)
- For example:
- When
custom_recipe_security_analysis_enabledis enabled, code is also checked for dangerous calls likeeval(),exec()and other in secure calls (regex patterns) defined incustom_recipe_method_call_banlist. Code is also checked for other dangerous constructs defined as regex patterns in thecustom_recipe_dangerous_patternsconfig setting. - Security analysis is only performed on recipes that are uploaded after the
custom_recipe_security_analysis_enabledconfig option is en abled. - To specify a list of modules that can be imported in custom recipes, use the
custom_recipe_import_allowlistconfig option. - The
custom_recipe_security_analysis_enabledconfig option is disabled by default.
- When
-
Best ways to control access to Driverless AI and custom recipes:
- Control access to the Driverless AI instance
- Use local authentication to specify exactly which users are allowed to access Driverless AI
- Run Driverless AI in a Docker container, as a certain user, with only certain ports exposed, and only certain mount points mapped
- To disable all recipes: Set
enable_custom_recipes=falsein the config.toml, or add the environment variableDRIVERLESS_AI_ENABLE_CUSTOM_RECIPES=0at startup of Driverless AI. This will disable all custom transformers, models and scorers. - To disable new recipes: To keep all previously uploaded recipes enabled and disable the upload of any new recipes, set
enable_custom_recipes_upload=falseorDRIVERLESS_AI_ENABLE_CUSTOM_RECIPES_UPLOAD=0at startup of Driverless AI.
- Driverless AI automatically performs basic acceptance tests for all custom recipes unless disabled
- More information in the FAQ
- Use fast and efficient data manipulation tools like
datatable,sklearn,numpyorpandasinstead of Python lists, for-loops etc. - Use disk sparingly, delete temporary files as soon as possible
- Use memory sparingly, delete objects when no longer needed
Go to Recipes for Driverless 1.7.0 1.7.1 1.8.0 1.8.1 1.8.2 1.8.3 1.8.4 1.8.5 1.8.6 1.8.7 1.8.8 1.8.9 1.8.10 1.9.0 1.9.1 1.9.2 1.9.3 1.10.0 1.10.1 1.10.2 1.10.3 1.10.4 1.10.4.1 1.10.4.2 1.10.4.3 1.10.5
-
AIR-GAPPED_INSTALLATIONS
- load_custom_recipe.py [Load custom recipes on air-gapped installations.]
-
DATA
- GroupAgg.py [Aggregation features on numeric columns across multiple categorical columns]
- airlines.py [Create airlines dataset]
- airlines_joined_data_flights_in_out.py [Create augmented airlines datasets]
- airlines_joined_data_flights_in_out_regression.py [Create augmented airlines datasets for regression]
- airlines_multiple.py [Create airlines dataset]
- any_env.py [Modify dataset with arbitrary env]
- any_env2.py [Modify dataset with arbitrary env]
- any_env3.py [Modify dataset with arbitrary env]
- any_env4.py [Modify dataset with arbitrary env]
- audio_to_image.py [Data recipe to transform input audio to Mel spectrograms]
- bigquery_sharded_data_pull.py [Pull data >1Gb from GCP Bigquery using sharding functionality.Based on: https://cloud.google.com/bigquery/docs/exporting-data#exporting_table_data https://cloud.google.com/storage/docs/reference/libraries#using_the_client_libraryAuthor: Travis CoutureCreated: 03/18/2020Last Updated: 03/18/2020]
- catchallenge.py [Create cat challenge dataset]
- covidtracking_daily_by_states.py [Upload daily Covid Tracking (https://covidtracking.com) US States cases, hospitalization, recovery, test and death data ]
- create_transactional_data_or_convert_to_iid.py [Example code to generate and convert transactional data to i.i.d. data.]
- creditcard.py [Modify credit card dataset]
- data_template.py [Custom data recipe base class]
- data_test.py [Create test dataset]
- data_test_multiple.py [Create multiple dataset test]
- elasticsearch_dataset.py [Create a datasets off a scroll search query from ElasticSearch]
- feature_selection.py [Perform feature selection by using target perturbation technique]
- feature_selection_backward.py [Backward Feature Selection using an sklearn estimator.]
- feature_selection_bidirectional.py [Bidirectional Feature Selection using an sklearn estimator.]
- feature_selection_exhaustive.py [Exhaustive Feature Selection using an sklearn estimator.]
- feature_selection_forward.py [Forward Feature Selection using an sklearn estimator.]
- generate_random_int_columns.py [Data recipe to add one or more columns containing random integers.]
- ieee_data_puddle.py [Data recipe to prepare data for Kaggle IEEE-CIS Fraud Detection https://www.kaggle.com/c/ieee-fraud-detection]
- image_cropper.py [ Data Recipe to Crop the Cheque Image (or any Image) in a fixed dimension ]
- imdb_datasets.py [Create titles and episodes datasets from IMDB tables]
- kaggle_bosch.py [Create Bosch competition datasets with leak]
- kaggle_ieee_fraud.py [Data recipe to prepare data for Kaggle IEEE-CIS Fraud Detection https://www.kaggle.com/c/ieee-fraud-detection]
- kaggle_m5.py [Prepare data for m5 Kaggle Time-Series Forecast competition]
- keywords_data.py [Check and match a list of words from a specific string column]
- load_json_from_zip.py [Data Recipe to load JSON datasets from a zip file. Just include this script inside the zip and upload it as a data recipe.]
- load_sas7bdat.py [Data Recipe to load a single sas file]
- load_sas7bdat_from_zip.py [Data Recipe to load sas7bdat datasets from a zip file. Just include this script inside the zip and upload it as a data recipe.]
- load_xml_from_zip.py [Data Recipe to load XML datasets from a zip file. Just include this script inside the zip and upload it as a data recipe. ]
- marketbasketanalysis.py [Market basket analysis]
- mnist.py [Prep and upload the MNIST datasset]
- mozilla_deepspeech_wav2txt.py [Speech to text using Mozilla's DeepSpeechSettings for this recipe:Assing MODEL_PATH global variable prior to usageAssign WAV_COLNAME global variable with proper column name from your dataset.This colums should contain absolute paths to .wav file which needs to be converted to text.General requirements to .wav's:1 channel (mono)16 bit16000 frequency]
- nytimes_covid19_cases_deaths_by_counties.py [Upload daily COVID-19 cases and deaths in US by counties - NY Times github Source: nytimes/covid-19-data Coronavirus (Covid-19) Data in the United States https://github.com/nytimes/covid-19-data]
- nytimes_covid19_cases_deaths_by_states.py [Upload daily COVID-19 cases and deaths in US by states from NY Times github]
- nytimes_covid19_cases_deaths_us.py [Upload daily COVID-19 cases and deaths in US total from NY Times github]
- owid_covid19_cases_deaths_by_countries.py [Upload daily COVID-19 cases and deaths by countries Source: Our World in Data. It is updated daily and includes data on confirmed cases, deaths, and testing. https://ourworldindata.org/coronavirus-source-data]
- rowwise_aggregates_by_column_groups.py [Augments dataset by computing rowwise aggregates by column groups]
- seattle_rain_modify.py [Transpose the Monthly Seattle Rain Inches data set for Time Series use cases]
- seattle_rain_upload.py [Upload Monthly Seattle Rain Inches data set from data provided by the City of Seattle]
- ts_fill_n_cluster.py [Data Recipe to fill missing values in TS data and then create new data sets from TS Clustering]
- two_sigma_rental.py [Download and preprocess datasets from the Two Sigma Rental competition on Kaggle]
- video_to_image.py [Data recipe to transform input video to the images]
- wav2txt.py [Speech to text using Azure Cognitive ServicesSettings for this recipe:Assing AZURE_SERVICE_KEY and AZURE_SERVICE_REGION global variable prior to usageAssign WAV_COLNAME global variable with proper column name from your dataset.This colums should contain absolute paths to .wav file which needs to be converted to text.]
-
DATABASES
- create_dataset_from_mongodb_collection.py [Create dataset from MonogDB]
-
NLP
- sentiment_score.py [Data recipe to get sentiment score using textblob]
- sentiment_score_vader.py [Data recipe to get sentiment score using vader]
- text_summarization.py [Data recipe to get summary of text using gensim]
- tokenize_chinese.py [Chinese text tokenization using jieba package - https://github.com/fxsjy/jieba]
- tokenize_japanese.py [Japanese text tokenization using janome package - https://mocobeta.github.io/janome/en/]
- topic_modeling.py [Data recipe to perform topic modeling]
- twitter_preprocessing_recipe.py [Preprocess the tweets by normalising username, removing unnecessary punctuations, expanding the hashtags]
-
UNSUPERVISED
- DBScanClustering.py [Data Recipe to perform DBScan Clustering.]
- IsolationForestRecipe.py [Data Recipe to perform Isolation Forest Clustering on a dataset.]
- KMeansClustering.py [Data Recipe to perform KMeans Clustering on a dataset.]
- Kmeans_with_adjusted_mutual_info_score.py [Kmeans Clustering with Adjusted Mutual Info Score to evaluate cluster quality.]
- Kmeans_with_fowlkes_mallows_score.py [Data Recipe to perform KMeans Clustering with Fowlkes Mallows Score.]
- Kmeans_with_homogeneity_score.py [Data Recipe to perform KMeans Clustering on a dataset with homogenity score to evaluate cluster quality.]
- KmodesRecipe.py [Data Recipe to perform KModes Clustering on a dataset.]
-
EXPLAINERS
- DOC
-
EXPLAINERS
- ale_explainer.py [Accumulated Local Effects (ALE) explainerNote:This example repurposes the Partial Dependence format render data. As such, the label"Average Prediction of {response}" is used for the y-axis instead of "ALE of {response}".]
- morris_sensitivity_explainer.py [Morris Sensitivity Analysis Explainer]
-
EXAMPLES
- example_compatibility_check_explainer.py [Runs compatibility check for MLI recipe.]
- example_custom_explanation_explainer.py [Example of how to define custom MLI explanations.]
- example_dai_metadata_explainer.py [Example of how to print MLI explainer metadata.]
- example_eda_explainer.py [Example of MLI explainer for Exploratory Data Analysis]
- example_hello_world_explainer.py [Hello World! explainer example.]
- example_logging_explainer.py [Example of how to use logging on MLI explainers.]
- example_params_explainer.py [Example of how to define MLI explainer parameters.]
- example_persistence_explainer.py [Example of how to use the persistence object inside an MLI explainer to access FS directories.]
- example_score_explainer.py [Example of how to use a model's predict method inside an MLI explainer.]
-
TEMPLATES
- template_dt_explainer.py [Decision Tree explainer which can be used to create explainer with global and local decision tree explanations.]
- template_featimp_explainer.py [Feature importance explainer template which can be used create explainer with global and local feature importance explanations.]
- template_md_explainer.py [Markdown report with raster image chart explainer template which can be used to create explainer with global report explanations.]
- template_md_featimp_summary_explainer.py [Markdown report with summary feature importance chart explainer template which can be used to create explainer with global report explanations.]
- template_md_vega_explainer.py [Markdown report with Vega chart explainer template which can be used to create explainer which creates global report explanations.]
- template_pd_explainer.py [PD and ICE explainer template which can be used to create example with partial dependence (global) and individual conditional explanations (local) explanations.]
- template_scatter_plot_explainer.py [Scatter plot explainer template which can be used to create explainer with global and local explanations.]
- NOTEBOOKS
-
HOW_TO_WRITE_A_RECIPE
- ExampleLogTransformer.py [Apply log transform to any single numeric column.]
-
INDIVIDUALS
- credit_card.py [Custom Final Individual 0 from Experiment test_credit_card_9f03b_f55d_pawisaco ]
- indiv_test1.py [Test individual 1]
- indiv_test2.py [Test individual 2]
- individual_template.py [Template base class for a custom individual recipe.]
- paribas_basemodel0.py [Custom Individual 0 from Experiment satocemi ]
- walmart_lags.py [Custom Final Individual 0 from Experiment test_time_series_walmart_nolimits_3f587_2993_miduhoge ]
-
MODELS
- mock_gpu_test_model.py [For GPU usage testing purposes.]
- mock_tf2_test.py [For GPU usage testing purposes.]
- mock_tf_test.py [For GPU usage testing purposes.]
- model_template.py [Template base class for a custom model recipe.]
-
ALGORITHMS
- adaboost.py [Adaboost model from sklearn]
- autogluon.py [AutoGluon + RAPIDS]
- calibratedClassifier.py [ Calibrated Classifier Model: To calibrate predictions using Platt's scaling, Isotonic Regression or Splines] ✓ MOJO Enabled
- catboost.py [CatBoost gradient boosting by Yandex. Currently supports regression and binary classification.]
- catboost_regression_uncertanity.py [please add description]
- daal_trees.py [Binary Classification and Regression for Decision Forest and Gradient Boosting based on Intel DAAL]
- datatable_glm.py [datatable Linear Model]
- extra_trees.py [Extremely Randomized Trees (ExtraTrees) model from sklearn]
- extremeClassifier.py [ Extreme Classifier Model: To speed up train of multiclass model (100s of classes) for lightGBM. Caution: can only be used for AUC (or GINI) and accuracy metrics. Based on: Extreme Classification in Log Memory using Count-Min Sketch: https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.13830]
- h2o-3-gbm-poisson.py [H2O-3 Distributed Scalable Machine Learning Models: Poisson GBM]
- h2o-3-models.py [H2O-3 Distributed Scalable Machine Learning Models (DL/GLM/GBM/DRF/NB/AutoML)]
- h2o-glm-poisson.py [H2O-3 Distributed Scalable Machine Learning Models: Poisson GLM]
- kernel_naive_bayes.py [Kernel Naive Bayes implementation by sklearn. For small data (< 200k rows).]
- knearestneighbour.py [K-Nearest Neighbor implementation by sklearn. For small data (< 200k rows).]
- lda.py [Linear/Quadratic Discriminant Analysis (LDA/QDA) model from sklearn]
- libfm_fastfm.py [LibFM implementation of fastFM ]
- linear_svm.py [Linear Support Vector Machine (SVM) implementation by sklearn. For small data.]
- logistic_regression.py [Logistic Regression based upon sklearn.]
- nusvm.py [Nu-SVM implementation by sklearn. For small data.]
- quantile_forest.py [Quantile Random Forest Regression model from skgarden]
- random_forest.py [Random Forest (RandomForest) model from sklearn]
-
CUSTOM_LOSS
- lightgbm_quantile_regression.py [Modified version of Driverless AI's internal LightGBM implementation with for quantile regression] ✓ MOJO Enabled
- lightgbm_train_valid_score_gap.py [Modified version of Driverless AI's internal LightGBM implementation with a custom objective function (used for tree split finding).] ✓ MOJO Enabled
- lightgbm_tweedie.py [Modified version of Driverless AI's internal LightGBM implementation with tweedie distribution] ✓ MOJO Enabled
- lightgbm_with_custom_loss.py [Modified version of Driverless AI's internal LightGBM implementation with a custom objective function (used for tree split finding).] ✓ MOJO Enabled
- xgboost_with_custom_loss.py [Modified version of Driverless AI's internal XGBoost implementation with a custom objective function (used for tree split finding).] ✓ MOJO Enabled
-
MLI
- model_decision_tree_linear_combo.py [Decision tree plus linear model]
- model_ebm.py [Explainable Boosting Machines (EBM), implementation of GA2M with option for user-defined interaction between features. ]
- model_gam.py [Generalized Additive Model]
- model_skopes_rules.py [Skopes rules ]
- model_xnn.py [ Explainable neural net ]
-
FAIRNESS
- model_fairxgb.py [Fair XGB ]
- reweighing_recipe.py [Debiasing using reweighing]
-
MONOTONIC
- monotonic_models.py [LightGBM/XGBoostGBM/DecisionTree with user-given monotonicity constraints (1/-1/0) for original numeric features]
-
NLP
- portuguese_bert.py [Custom Bert model pretrained on Portuguese.]
- text_binary_count_logistic.py [Text classification model using binary count of words]
- text_tfidf_model.py [Text classification / regression model using TFIDF]
- text_tfidf_model_continuous.py [Text classification model using TFIDF]
-
TIMESERIES
- autoarima_parallel.py [autoarima for TimeSeries with an example of parameter mutation.]
- exponential_smoothing.py [Linear Model on top of Exponential Weighted Moving Average Lags for Time-Series. Provide appropriate lags and past outcomes during batch scoring for best results.]
- fb_prophet.py [Prophet by Facebook for TimeSeries with an example of parameter mutation.]
- fb_prophet_parallel.py [Prophet by Facebook for TimeSeries with an example of parameter mutation.]
- historic_mean.py [Historic Mean for Time-Series problems. Predicts the mean of the target for each timegroup for regression problems.]
- nixtla_arimax.py [AutoARIMA for TimeSeries Forecasting Uses AutoARIMA implemented in https://github.com/Nixtla/statsforecastCurrent limitations:(1) No handling for prediction "gap"(2) Enable user to pass in seasonality length to run AutoARIMA with seasonality. NOTE: Not passing any seasonality parameter will result in ARIMA (current default)]
- nixtla_ces.py [AutoCES for TimeSeries Forecasting Uses AutoCES implemented in https://github.com/Nixtla/statsforecastCurrent limitations:(1) No handling for prediction "gap"(2) Enable user to pass in seasonality length to run AutoCES with seasonality. NOTE: The seasonality will be infered based on the temporal column.]
- nixtla_ets.py [AutoETS for TimeSeries Forecasting Uses AutoETS implemented in https://github.com/Nixtla/statsforecastCurrent limitations:(1) No handling for prediction "gap"(2) Enable user to pass in seasonality length to run AutoETS with seasonality. NOTE: The seasonality will be infered based on the temporal column.]
- nixtla_theta.py [AutoTheta for TimeSeries Forecasting Uses AutoTheta implemented in https://github.com/Nixtla/statsforecastCurrent limitations:(1) No handling for prediction "gap"(2) Enable user to pass in seasonality length to run AutoTheta with seasonality. NOTE: The seasonality will be infered based on the temporal column.]
- ts_rnn.py [Recurrent Neural Networks with Convolution for Time-series problems using LSTM, GRU or Elman cells.]
-
UNSUPERVISED
- TextKMeansIsolationForest.py [Variety of unsupervised models that mimic internal versions but includes text handling via text embedding using custom transformer]
- TextSentiment.py [Extract sentiment from text using pretrained models from TextBlob]
- aggregator.py [Unsupervised Aggregator algorithm (by Leland Wilkinson) to segment data into user-given number of exemplars]
- dbscan.py [Clustering using DBScan]
- isolation_forest_custom_scorer.py [Custom Anomaly Score for Isolation Forest]
- lda.py [Unsupervised way to extract topic information from one text column]
- local_outlier_factor.py [Outlier detection with Local Outlier Factor]
- pytod_lof.py [Local Outlier Factor method for outlier detection, based on PyTOD library.]
- rapids_kmeans.py [KMeans clustering using RAPIDS.ai]
-
UPLIFT
- GLMTransformedOutcome.py [GLM for uplift modeling] ✓ MOJO Enabled
- LightGBMTransformedOutcome.py [LightGBM for uplift modeling] ✓ MOJO Enabled
- XGBoostTransformedOutcome.py [XGBoost for uplift modeling] ✓ MOJO Enabled
-
RECIPES
- amazon.py [Recipe for Kaggle Competition: Amazon.com - Employee Access Challenge]
- REFERENCE
-
SCORERS
- huber_loss.py [Huber Loss for Regression or Binary Classification. Robust loss, combination of quadratic loss and linear loss.]
- scorer_template.py [Template base class for a custom scorer recipe.]
-
CLASSIFICATION
- f3_score.py [F3 Score]
- f4_score.py [F4 Score]
- probF.py [Probabilistic F Score with optimized threshold]
-
BINARY
- average_mcc.py [Averaged Matthews Correlation Coefficient (averaged over several thresholds, for imbalanced problems). Example how to use Driverless AI's internal scorer.]
- balanced_accuracy.py [balanced_accuracy_score]
- brier_loss.py [Brier Loss]
-
cost.py [Using hard-coded dollar amounts x for false positives and y for false negatives, calculate the cost of a model using:
(x * FP + y * FN) / N] - cost_access_to_data.py [Same as CostBinary, but provides access to full Data]
-
cost_smooth.py [Using hard-coded dollar amounts x for false positives and y for false negatives, calculate the cost of a model using:
(1 - y_true) * y_pred * fp_cost + y_true * (1 - y_pred) * fn_cost] - fair_auc.py [Custom scorer for detecting and reducing bias in machine learning models.]
- kolmogorov_smirnov.py [Kolmogorov-Smirnov scorer recipe.If you need to print debug messages into DAI log, uncomment lines with logger and loggerinfo.Starting 1.10.2 - DAI handles exceptions raised by custom scorers.Default DAI behavior is to continue experiment in case of Scorer failure.To enable forcing experiment to fail, in case of scorer error, set following parameters in DAI: - skip_scorer_failures=false (Disabled) - skip_model_failures=false (Disabled)]
- logloss_with_costs.py [Logloss with costs associated with each type of 4 outcomes - typically applicable to fraud use case]
- marketing_campaign.py [Computes the mean profit per outbound marketing letter, given a fraction of the population addressed, and fixed cost and reward]
- profit.py [Profit Scorer for binary classification]
-
MULTICLASS
- hamming_loss.py [Hamming Loss - Misclassification Rate (1 - Accuracy)]
- linear_weighted_kappa.py [Cohen’s Kappa with linear weights]
- [email protected] [Mean Average Precision @ k (MAP@k)]
- quadratic_weighted_kappa.py [Qudratic Weighted Kappa]
-
REGRESSION
- WAPE_scorer.py [Weighted Absoluted Percent Error]
- asymmetric_mae.py [MAE with a penalty that differs for positive and negative errors]
- auuc.py [Area under uplift curve]
- cosh_loss.py [Hyperbolic Cosine Loss]
- explained_variance.py [Explained Variance. Fraction of variance that is explained by the model.]
- gamma_deviance.py [Gamma Deviance scorer recipe.This is same as Tweedie Deviance scorer with power=2If you need to print debug messages into DAI log, uncomment lines with logger and loggerinfo.Starting 1.10.2 - DAI handles exceptions raised by custom scorers.Default DAI behavior is to continue experiment in case of Scorer failure.To enable forcing experiment to fail, in case of scorer error, set following parameters in DAI: - skip_scorer_failures=false (Disabled) - skip_model_failures=false (Disabled)]
- largest_error.py [Largest error for regression problems. Highly sensitive to outliers.]
- log_mae.py [Log Mean Absolute Error for regression]
- mean_absolute_scaled_error.py [Mean Absolute Scaled Error for time-series regression]
- mean_squared_log_error.py [Mean Squared Log Error for regression]
- median_absolute_error.py [Median Absolute Error for regression]
- pearson_correlation.py [Pearson Correlation Coefficient for regression]
- poisson_deviance.py [Poisson Deviance scorer recipe.]
- quantile_loss.py [Quantile Loss regression]
- r2_by_tgc.py [Custom R2 scorer computes R2 on each time series, then averages them out for the final score.]
- rmse_with_x.py [Custom RMSE Scorer that also gets X (original features) - for demo/testing purposes only]
- top_decile.py [Median Absolute Error for predictions in the top decile]
- tweedie_deviance.py [Tweedie Deviance scorer recipe.User inputs can be provided through recipe_dict in config.To pass power parameterrecipe_dict = "{'power':2.0}"The default value is 1.5If you need to print debug messages into DAI log, uncomment lines with logger and loggerinfo.Starting 1.10.2 - DAI handles exceptions raised by custom scorers.Default DAI behavior is to continue experiment in case of Scorer failure.To enable forcing experiment to fail, in case of scorer error, set following parameters in DAI: - skip_scorer_failures=false (Disabled) - skip_model_failures=false (Disabled)]
-
TRANSFORMERS
- how_to_debug_transformer.py [Example how to debug a transformer outside of Driverless AI (optional)]
- how_to_test_from_py_client.py [Testing a BYOR Transformer the PyClient - works on 1.7.0 & 1.7.1-17]
- transformer_template.py [Template base class for a custom transformer recipe.]
-
ANOMALY
- [isolation_forest.py](./transformers/anomaly /isolation_forest.py) [H2O-3 Distributed Scalable Machine Learning Transformers (IF)]
-
AUGMENTATION
- germany_landers_holidays.py [Returns a flag for whether a date falls on a holiday for each of Germany's Bundeslaender. ]
- holidays_this_week.py [Returns the amount of US holidays for a given week]
- ipaddress_features.py [Parses IP addresses and networks and extracts its properties.]
- is_ramadan.py [Returns a flag for whether a date falls on Ramadan in Saudi Arabia]
- singapore_public_holidays.py [Flag for whether a date falls on a public holiday in Singapore.]
- usairportcode_origin_dest.py [Transformer to parse and augment US airport codes with geolocation info.]
- usairportcode_origin_dest_geo_features.py [Transformer to augment US airport codes with geolocation info.]
- uszipcode_features_database.py [Transformer to parse and augment US zipcodes with info from zipcode database.]
- uszipcode_features_light.py [Lightweight transformer to parse and augment US zipcodes with info from zipcode database.]
-
DATETIME
- datetime_diff_transformer.py [Difference in time between two datetime columns]
- datetime_encoder_transformer.py [Converts datetime column into an integer (milliseconds since 1970)]
- days_until_dec2020.py [Creates new feature for any date columns, by computing the difference in days between the date value and 31st Dec 2020]
-
EXECUTABLES
- pe_data_directory_features.py [Extract LIEF features from PE files]
- pe_exports_features.py [Extract LIEF features from PE files]
- pe_general_features.py [Extract LIEF features from PE files]
- pe_header_features.py [Extract LIEF features from PE files]
- pe_imports_features.py [Extract LIEF features from PE files]
- pe_normalized_byte_count.py [Extract LIEF features from PE files]
- pe_section_characteristics.py [Extract LIEF features from PE files]
- DATA
-
GENERIC
- count_missing_values_transformer.py [Count of missing values per row]
- missing_flag_transformer.py [Returns 1 if a value is missing, or 0 otherwise]
- specific_column_transformer.py [Example of a transformer that operates on the entire original frame, and hence on any column(s) desired.]
-
GEOSPATIAL
- geodesic.py [Calculates the distance in miles between two latitude/longitude points in space]
- myhaversine.py [Computes miles between first two *_latitude and *_longitude named columns in the data set]
-
HIERARCHICAL
- firstNCharCVTE.py [Target-encode high cardinality categorical text by their first few characters in the string ]
- log_scale_target_encoding.py [Target-encode numbers by their logarithm]
-
IMAGE
- image_ocr_transformer.py [Convert a path to an image to text using OCR based on tesseract]
- image_url_transformer.py [Convert a path to an image (JPG/JPEG/PNG) to a vector of class probabilities created by a pretrained ImageNet deeplearning model (Keras, TensorFlow).]
-
NLP
- continuous_TextTransformer.py [Creates a TF-IDF based text transformation that can be continuously updated with new data and vocabulary.] ✓ MOJO Enabled
- fuzzy_text_similarity_transformers.py [Row-by-row similarity between two text columns based on FuzzyWuzzy]
- text_binary_count_transformer.py [Explainable Text transformer that uses binary counts of words using sklearn's CountVectorizer]
- text_char_tfidf_count_transformers.py [Character level TFIDF and Count followed by Truncated SVD on text columns]
- text_embedding_similarity_transformers.py [Row-by-row similarity between two text columns based on pretrained Deep Learning embedding space]
- text_lang_detect_transformer.py [Detect the language for a text value using Google's 'langdetect' package]
- text_meta_transformers.py [Extract common meta features from text]
- text_named_entities_transformer.py [Extract the counts of different named entities in the text (e.g. Person, Organization, Location)]
- text_pos_tagging_transformer.py [Extract the count of nouns, verbs, adjectives and adverbs in the text]
- text_preprocessing_transformer.py [Preprocess the text column by stemming, lemmatization and stop word removal]
- text_readability_transformers.py [ Custom Recipe to extract Readability features from the text data]
- text_sentiment_transformer.py [Extract sentiment from text using pretrained models from TextBlob]
- text_similarity_transformers.py [Row-by-row similarity between two text columns based on common N-grams, Jaccard similarity, Dice similarity and edit distance.]
- text_spelling_correction_transformers.py [Correct the spelling of text column]
- text_topic_modeling_transformer.py [Extract topics from text column using LDA]
- text_url_summary_transformer.py [Extract text from URL and summarizes it]
- vader_text_sentiment_transformer.py [Extract sentiment from text using lexicon and rule-based sentiment analysis tool called VADER]
-
NUMERIC
- boxcox_transformer.py [Box-Cox Transform]
- clusterdist_all.py [Cluster Distance for all columns]
- count_negative_values_transformer.py [Count of negative values per row]
- count_positive_values_transformer.py [Count of positive values per row]
- exp_diff_transformer.py [Exponentiated difference of two numbers]
- factor_analysis_transformer.py [Factor Analysis Transformer]
- log_transformer.py [Converts numbers to their Logarithm] ✓ MOJO Enabled
- ohe.py [One-Hot Encoding for categorical columns]
- pca_transformer.py [Principal Component Analysis (PCA) Transformer]
- product.py [Products together 3 or more numeric features]
- random_transformer.py [Creates random numbers]
- round_transformer.py [Rounds numbers to 1, 2 or 3 decimals]
- square_root_transformer.py [Converts numbers to the square root, preserving the sign of the original numbers]
- sum.py [Adds together 3 or more numeric features]
- truncated_svd_all.py [Truncated SVD for all columns]
- yeojohnson_transformer.py [Yeo-Johnson Power Transformer]
-
OUTLIERS
- h2o3-dl-anomaly.py [Anomaly score for each row based on reconstruction error of an H2O-3 deep learning autoencoder]
- quantile_winsorizer.py [Winsorizes (truncates) univariate outliers outside of a given quantile threshold]
- twosigma_winsorizer.py [Winsorizes (truncates) univariate outliers outside of two standard deviations from the mean.]
-
RECOMMENDATIONS
- matrixfactorization.py [Collaborative filtering features using various techniques of Matrix Factorization for recommendations.Recommended for large data]
-
SIGNAL_PROCESSING
- signal_processing.py [This custom transformer processes signal files to create features used by DriverlessAI to solve a regression problem]
-
SPEECH
- audio_MFCC_transformer.py [Extract MFCC and spectrogram features from audio files]
- azure_speech_to_text.py [An example of integration with Azure Speech Recognition Service]
-
STRING
- simple_grok_parser.py [Extract column data using grok patterns]
- strlen_transformer.py [Returns the string length of categorical values]
- to_string_transformer.py [Converts numbers to strings]
- user_agent_transformer.py [A best effort transformer to determine browser device characteristics from a user-agent string]
-
SURVIVAL
- dummy-pretransformer.py [Dummy Pre-Transformer to use as a template for custom pre-transformer recipes. This transformer consumes all features at once, adds 'pre:' to the names and passes them down to transformer level and GA as-is.]
- h2o-3-coxph-pretransformer.py [Pre-transformer utilizing survival analysis modeling using CoxPH (Cox proportional hazard) using H2O-3 CoxPH function. It adds risk score produced by CoxPH model and drops stop_column feature used for survival modeling along with actual target as event.]
-
TARGETENCODING
- ExpandingMean.py [CatBoost-style target encoding. See https://youtu.be/d6UMEmeXB6o?t=818 for short explanation]
- leaky_mean_target_encoder.py [Example implementation of a out-of-fold target encoder (leaky, not recommended)]
-
TIMESERIES
- auto_arima_forecast.py [Auto ARIMA transformer is a time series transformer that predicts target using ARIMA models.]
- general_time_series_transformer.py [Demonstrates the API for custom time-series transformers.]
- parallel_auto_arima_forecast.py [Parallel Auto ARIMA transformer is a time series transformer that predicts target using ARIMA models.In this implementation, Time Group Models are fitted in parallel]
- parallel_prophet_forecast.py [Parallel FB Prophet transformer is a time series transformer that predicts target using FBProphet models.]
- parallel_prophet_forecast_using_individual_groups.py [Parallel FB Prophet transformer is a time series transformer that predicts target using FBProphet models.This transformer fits one model for each time group column values and is significantly fasterthan the implementation available in parallel_prophet_forecast.py.]
- serial_prophet_forecast.py [Transformer that uses FB Prophet for time series prediction.Please see the parallel implementation for more information]
- time_encoder_transformer.py [converts the Time Column to an ordered integer]
- trading_volatility.py [Calculates Historical Volatility for numeric features (makes assumptions on the data)]
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for driverlessai-recipes
Similar Open Source Tools

driverlessai-recipes
This repository contains custom recipes for H2O Driverless AI, which is an Automatic Machine Learning platform for the Enterprise. Custom recipes are Python code snippets that can be uploaded into Driverless AI at runtime to automate feature engineering, model building, visualization, and interpretability. Users can gain control over the optimization choices made by Driverless AI by providing their own custom recipes. The repository includes recipes for various tasks such as data manipulation, data preprocessing, feature selection, data augmentation, model building, scoring, and more. Best practices for creating and using recipes are also provided, including security considerations, performance tips, and safety measures.
MathVerse
MathVerse is an all-around visual math benchmark designed to evaluate the capabilities of Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) in visual math problem-solving. It collects high-quality math problems with diagrams to assess how well MLLMs can understand visual diagrams for mathematical reasoning. The benchmark includes 2,612 problems transformed into six versions each, contributing to 15K test samples. It also introduces a Chain-of-Thought (CoT) Evaluation strategy for fine-grained assessment of output answers.
llmfarm_core.swift
LLMFarm_core.swift is a Swift library designed to work with large language models (LLM). It enables users to load different LLMs with specific parameters. The library supports MacOS (13+) and iOS (16+), offering various inferences and sampling methods. It includes features such as Metal support (not compatible with Intel Mac), model setting templates, LoRA adapters support, and LoRA train support. The library is based on ggml and llama.cpp by Georgi Gerganov, with additional sources from rwkv.cpp by saharNooby and Mia by byroneverson.

fuse-med-ml
FuseMedML is a Python framework designed to accelerate machine learning-based discovery in the medical field by promoting code reuse. It provides a flexible design concept where data is stored in a nested dictionary, allowing easy handling of multi-modality information. The framework includes components for creating custom models, loss functions, metrics, and data processing operators. Additionally, FuseMedML offers 'batteries included' key components such as fuse.data for data processing, fuse.eval for model evaluation, and fuse.dl for reusable deep learning components. It supports PyTorch and PyTorch Lightning libraries and encourages the creation of domain extensions for specific medical domains.
opencompass
OpenCompass is a one-stop platform for large model evaluation, aiming to provide a fair, open, and reproducible benchmark for large model evaluation. Its main features include: * Comprehensive support for models and datasets: Pre-support for 20+ HuggingFace and API models, a model evaluation scheme of 70+ datasets with about 400,000 questions, comprehensively evaluating the capabilities of the models in five dimensions. * Efficient distributed evaluation: One line command to implement task division and distributed evaluation, completing the full evaluation of billion-scale models in just a few hours. * Diversified evaluation paradigms: Support for zero-shot, few-shot, and chain-of-thought evaluations, combined with standard or dialogue-type prompt templates, to easily stimulate the maximum performance of various models. * Modular design with high extensibility: Want to add new models or datasets, customize an advanced task division strategy, or even support a new cluster management system? Everything about OpenCompass can be easily expanded! * Experiment management and reporting mechanism: Use config files to fully record each experiment, and support real-time reporting of results.
pytorch-forecasting
PyTorch Forecasting is a PyTorch-based package designed for state-of-the-art timeseries forecasting using deep learning architectures. It offers a high-level API and leverages PyTorch Lightning for efficient training on GPU or CPU with automatic logging. The package aims to simplify timeseries forecasting tasks by providing a flexible API for professionals and user-friendly defaults for beginners. It includes features such as a timeseries dataset class for handling data transformations, missing values, and subsampling, various neural network architectures optimized for real-world deployment, multi-horizon timeseries metrics, and hyperparameter tuning with optuna. Built on pytorch-lightning, it supports training on CPUs, single GPUs, and multiple GPUs out-of-the-box.
stability-sdk
The stability-sdk is a Python package that provides a client implementation for interacting with the Stability API. This API allows users to generate images, upscale images, and animate images using a variety of different models and settings. The stability-sdk makes it easy to use the Stability API from Python code, and it provides a number of helpful features such as command line usage, support for multiple models, and the ability to filter artifacts by type.
MiniCheck
MiniCheck is an efficient fact-checking tool designed to verify claims against grounding documents using large language models. It provides a sentence-level fact-checking model that can be used to evaluate the consistency of claims with the provided documents. MiniCheck offers different models, including Bespoke-MiniCheck-7B, which is the state-of-the-art and commercially usable. The tool enables users to fact-check multi-sentence claims by breaking them down into individual sentences for optimal performance. It also supports automatic prefix caching for faster inference when repeatedly fact-checking the same document with different claims.
create-million-parameter-llm-from-scratch
The 'create-million-parameter-llm-from-scratch' repository provides a detailed guide on creating a Large Language Model (LLM) with 2.3 million parameters from scratch. The blog replicates the LLaMA approach, incorporating concepts like RMSNorm for pre-normalization, SwiGLU activation function, and Rotary Embeddings. The model is trained on a basic dataset to demonstrate the ease of creating a million-parameter LLM without the need for a high-end GPU.
Quantus
Quantus is a toolkit designed for the evaluation of neural network explanations. It offers more than 30 metrics in 6 categories for eXplainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) evaluation. The toolkit supports different data types (image, time-series, tabular, NLP) and models (PyTorch, TensorFlow). It provides built-in support for explanation methods like captum, tf-explain, and zennit. Quantus is under active development and aims to provide a comprehensive set of quantitative evaluation metrics for XAI methods.
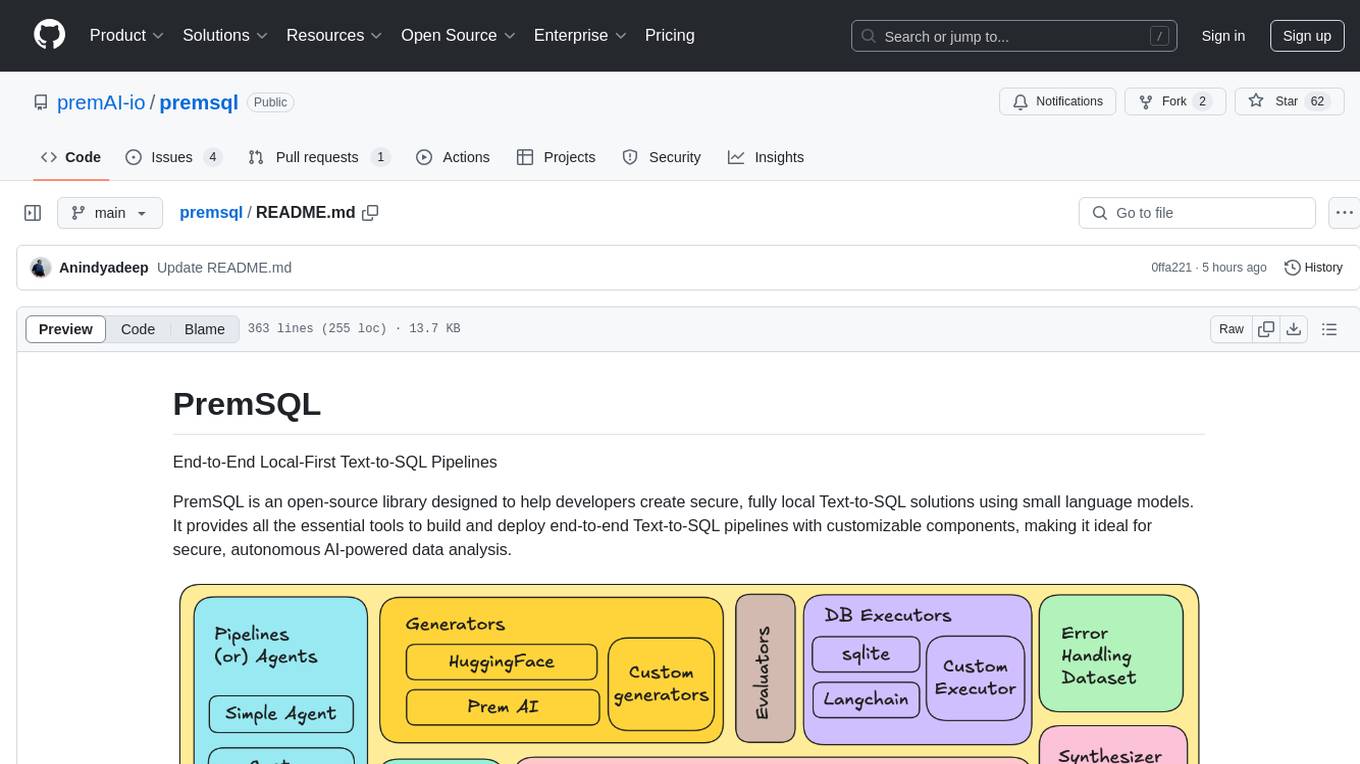
premsql
PremSQL is an open-source library designed to help developers create secure, fully local Text-to-SQL solutions using small language models. It provides essential tools for building and deploying end-to-end Text-to-SQL pipelines with customizable components, ideal for secure, autonomous AI-powered data analysis. The library offers features like Local-First approach, Customizable Datasets, Robust Executors and Evaluators, Advanced Generators, Error Handling and Self-Correction, Fine-Tuning Support, and End-to-End Pipelines. Users can fine-tune models, generate SQL queries from natural language inputs, handle errors, and evaluate model performance against predefined metrics. PremSQL is extendible for customization and private data usage.

AIL-framework
AIL framework is a modular framework to analyze potential information leaks from unstructured data sources like pastes from Pastebin or similar services or unstructured data streams. AIL framework is flexible and can be extended to support other functionalities to mine or process sensitive information (e.g. data leak prevention).

ail-framework
AIL framework is a modular framework to analyze potential information leaks from unstructured data sources like pastes from Pastebin or similar services or unstructured data streams. AIL framework is flexible and can be extended to support other functionalities to mine or process sensitive information (e.g. data leak prevention).
codellm-devkit
Codellm-devkit (CLDK) is a Python library that serves as a multilingual program analysis framework bridging traditional static analysis tools and Large Language Models (LLMs) specialized for code (CodeLLMs). It simplifies the process of analyzing codebases across multiple programming languages, enabling the extraction of meaningful insights and facilitating LLM-based code analysis. The library provides a unified interface for integrating outputs from various analysis tools and preparing them for effective use by CodeLLMs. Codellm-devkit aims to enable the development and experimentation of robust analysis pipelines that combine traditional program analysis tools and CodeLLMs, reducing friction in multi-language code analysis and ensuring compatibility across different tools and LLM platforms. It is designed to seamlessly integrate with popular analysis tools like WALA, Tree-sitter, LLVM, and CodeQL, acting as a crucial intermediary layer for efficient communication between these tools and CodeLLMs. The project is continuously evolving to include new tools and frameworks, maintaining its versatility for code analysis and LLM integration.
venice
Venice is a derived data storage platform, providing the following characteristics: 1. High throughput asynchronous ingestion from batch and streaming sources (e.g. Hadoop and Samza). 2. Low latency online reads via remote queries or in-process caching. 3. Active-active replication between regions with CRDT-based conflict resolution. 4. Multi-cluster support within each region with operator-driven cluster assignment. 5. Multi-tenancy, horizontal scalability and elasticity within each cluster. The above makes Venice particularly suitable as the stateful component backing a Feature Store, such as Feathr. AI applications feed the output of their ML training jobs into Venice and then query the data for use during online inference workloads.
For similar tasks

driverlessai-recipes
This repository contains custom recipes for H2O Driverless AI, which is an Automatic Machine Learning platform for the Enterprise. Custom recipes are Python code snippets that can be uploaded into Driverless AI at runtime to automate feature engineering, model building, visualization, and interpretability. Users can gain control over the optimization choices made by Driverless AI by providing their own custom recipes. The repository includes recipes for various tasks such as data manipulation, data preprocessing, feature selection, data augmentation, model building, scoring, and more. Best practices for creating and using recipes are also provided, including security considerations, performance tips, and safety measures.
whatsapp-ai-bot
The WhatsApp AI Bot is a chatbot that utilizes various AI models APIs to generate responses to user input. Users can interact with the bot using commands to access different AI models such as Gemini, Gemini-Vision, CHAT-GPT, DALL-E, and Stability AI. Additionally, users have the flexibility to create their own custom models to personalize the bot's behavior. The bot operates on WhatsApp Web through Puppeteer and requires API keys for Gemini, OpenAI, and StabilityAI. It provides a range of functionalities and customization options for users interested in AI-powered chatbots.

lhotse
Lhotse is a Python library designed to make speech and audio data preparation flexible and accessible. It aims to attract a wider community to speech processing tasks by providing a Python-centric design and an expressive command-line interface. Lhotse offers standard data preparation recipes, PyTorch Dataset classes for speech tasks, and efficient data preparation for model training with audio cuts. It supports data augmentation, feature extraction, and feature-space cut mixing. The tool extends Kaldi's data preparation recipes with seamless PyTorch integration, human-readable text manifests, and convenient Python classes.
amber-data-prep
This repository contains the code to prepare the data for the Amber 7B language model. The final training data comes from three sources: RedPajama V1, RefinedWeb, and StarCoderData. The data preparation involves downloading untokenized data, tokenizing the data using the Huggingface tokenizer, concatenating tokens into 2048 token sequences, merging datasets, and splitting the merged dataset into 360 chunks. Each tokenized data chunk is a jsonl file containing samples with 2049 tokens. The repository provides scripts for downloading datasets, tokenizing and concatenating sequences, validating data, and merging subsets into chunks.
LESS
This repository contains the code for the paper 'LESS: Selecting Influential Data for Targeted Instruction Tuning'. The work proposes a data selection method to choose influential data for inducing a target capability. It includes steps for warmup training, building the gradient datastore, selecting data for a task, and training with the selected data. The repository provides tools for data preparation, data selection pipeline, and evaluation of the model trained on the selected data.
aws-machine-learning-university-responsible-ai
This repository contains slides, notebooks, and data for the Machine Learning University (MLU) Responsible AI class. The mission is to make Machine Learning accessible to everyone, covering widely used ML techniques and applying them to real-world problems. The class includes lectures, final projects, and interactive visuals to help users learn about Responsible AI and core ML concepts.
TempCompass
TempCompass is a benchmark designed to evaluate the temporal perception ability of Video LLMs. It encompasses a diverse set of temporal aspects and task formats to comprehensively assess the capability of Video LLMs in understanding videos. The benchmark includes conflicting videos to prevent models from relying on single-frame bias and language priors. Users can clone the repository, install required packages, prepare data, run inference using examples like Video-LLaVA and Gemini, and evaluate the performance of their models across different tasks such as Multi-Choice QA, Yes/No QA, Caption Matching, and Caption Generation.
ML-Bench
ML-Bench is a tool designed to evaluate large language models and agents for machine learning tasks on repository-level code. It provides functionalities for data preparation, environment setup, usage, API calling, open source model fine-tuning, and inference. Users can clone the repository, load datasets, run ML-LLM-Bench, prepare data, fine-tune models, and perform inference tasks. The tool aims to facilitate the evaluation of language models and agents in the context of machine learning tasks on code repositories.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.