
swe-rl
Official codebase for "SWE-RL: Advancing LLM Reasoning via Reinforcement Learning on Open Software Evolution"
Stars: 244
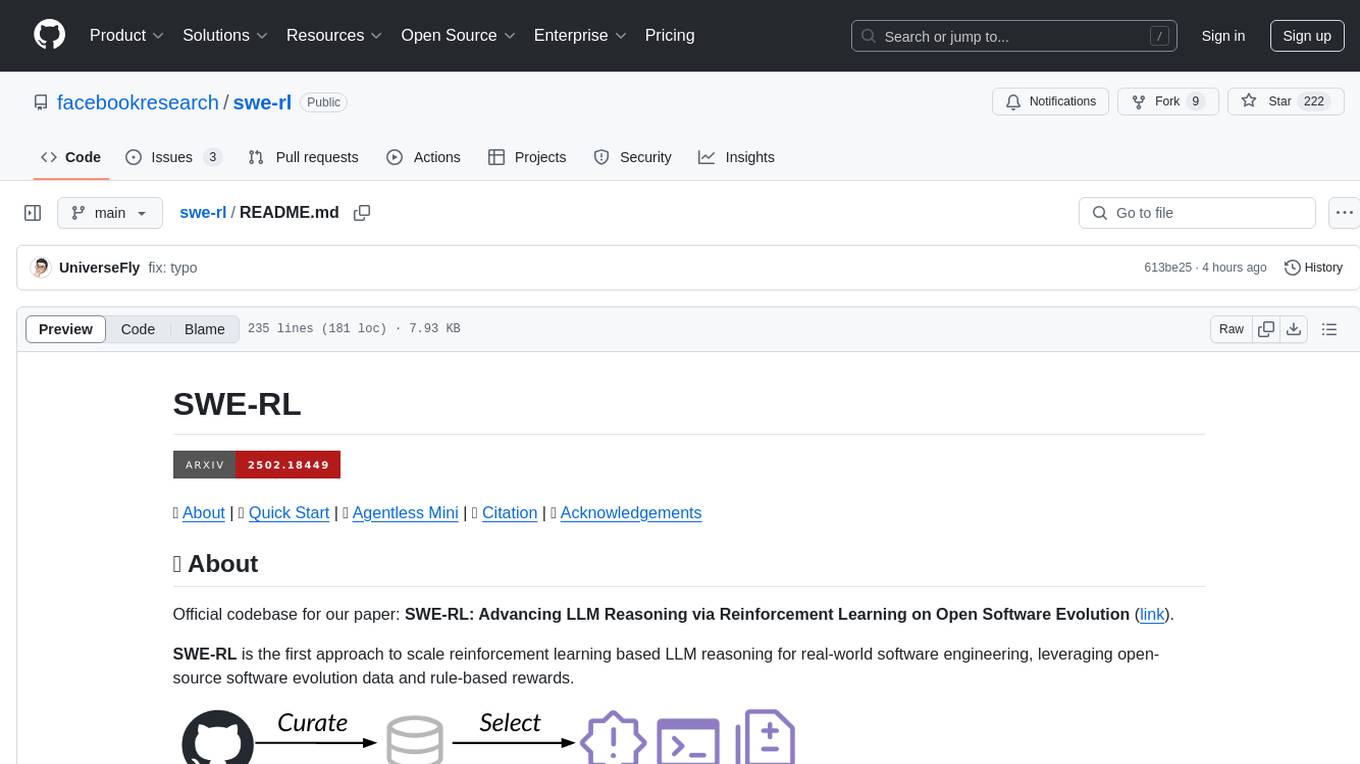
SWE-RL is the official codebase for the paper 'SWE-RL: Advancing LLM Reasoning via Reinforcement Learning on Open Software Evolution'. It is the first approach to scale reinforcement learning based LLM reasoning for real-world software engineering, leveraging open-source software evolution data and rule-based rewards. The code provides prompt templates and the implementation of the reward function based on sequence similarity. Agentless Mini, a part of SWE-RL, builds on top of Agentless with improvements like fast async inference, code refactoring for scalability, and support for using multiple reproduction tests for reranking. The tool can be used for localization, repair, and reproduction test generation in software engineering tasks.
README:
🧐 About | 🚀 Quick Start | 🐣 Agentless Mini | 📝 Citation | 🙏 Acknowledgements
Official codebase for our paper: SWE-RL: Advancing LLM Reasoning via Reinforcement Learning on Open Software Evolution (link).
SWE-RL is the first approach to scale reinforcement learning based LLM reasoning for real-world software engineering, leveraging open-source software evolution data and rule-based rewards.
[!NOTE] We have undertaken significant code refactoring to enhance quality and accessibility. However, this may introduce potential inconsistencies with our internal implementation. If you encounter a bug, please file an issue. We are also gradually updating the repo to include additional information.
git clone https://github.com/facebookresearch/swe-rl && cd swe-rl
pip install -e ".[dev]"
pytestThe code currently provides our prompt templates and the implementation of the reward function based on sequence similarity. You can find them in src/swerl/core/prompts.py and src/swerl/core/reward.py respectively.
A toy example on how you can use the reward function in your own project:
import swerl
file = """
def sort_list(lst):
return sorted(lst)
""".strip()
oracle_file = """
def sort_list(lst: list[int]) -> list[int]:
return sorted(lst)
""".strip()
context = {"example.py": file}
oracle = {"example.py": oracle_file}
output = """
<think>
...thoughts by LLM
</think>
<solution>
```python
### example.py
<<<<<<< SEARCH
def sort_list(lst):
=======
def sort_list(lst: list[int]) -> list[int]:
>>>>>>> REPLACE
```
</solution>
""".strip()
reward, metadata = swerl.core.reward.calculate_search_replace_reward(context, oracle, output)
assert reward == 1.0
print(metadata)You can also check swerl.core.reward.calculate_reward, which is more general and can be paired with any editing format.
Agentless Mini builds on top of Agentless with the following key improvements and functionality changes:
- Fast async inference with openai-python.
- Code refactoring for better scalability, parallelization, and accessibility.
- Only performing file-level localization, and entire file content will be used for repair.
- Support of using multiple reproduction tests for reranking.
To get started, run the following command to install the dependencies:
git clone https://github.com/facebookresearch/swe-rl && cd swe-rl
pip install -e ".[agentless]"Agentless Mini works with any OpenAI-compatible endpoint. If you want to host your own Hugging Face models, popular choices are vLLM and SGLang. Taking vLLM as an example:
# Host Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct with vLLM
pip install vllm
vllm serve meta-llama/Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct --tensor-parallel-size 4 --port 8000
# The endpointn url will be http://localhost:8000/v1Finally, you would need to set up some environment variables required by Agentless Mini:
# Assume you're doing the above vLLM setup
# Otherwise, just adjust them accordingly
export OPENAI_API_KEY="Empty"
export OPENAI_BASE_URL="http://localhost:8000/v1"
# Whether "thinking" is in model output (yes/no). If so, we need to extract the answer block during parsing
# and ignore the thinking. We assume the answer is enclosed with "<solution>" and "</solution>".
# Check src/swerl/agentless_mini/utils/envs.py to learn how to adjust them.
export THINKING=no
# A temporary directory used to process patches
export PLAYGROUND_DIR="tmp_agentless"
# Please download it from https://github.com/OpenAutoCoder/Agentless/releases/download/v1.5.0/swebench_repo_structure.txt
export PROJECT_FILE_LOC="/path/to/swebench/repo_structures"
# The tokenizer model. Can be either huggingface or tiktoken model name
export TOKENIZER_MODEL="meta-llama/Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct"Now you can run Agentless Mini if the environment variables are properly configured. Below is the simplest setup where oracle files are provided for repair. This can be a good proxy for end to end result:
# Make sure your are in the root directory of swe-rl
#
# Agentless Mini supports sharding. If you are using a compute cluster, then you can run
# different shards with different compute nodes to parallelize the evaluation.
# Below, we set num_shards to 125, so each shard will have (500 / 125) instances, where
# 500 is the number of problems in SWE-bench Verified.
python -m swerl.agentless_mini.repair \
--loc_file resources/sweb_verified_gt_loc.jsonl \
--output_folder demo_gt_repair \
--shard 0 \
--num_shards 125 \
--num_samples 1 \
--temperature 0.0 \
--model "meta-llama/Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct"
# Get your all_preds.jsonl
python -m swerl.agentless_mini.rerank \
--patch_folder ${REPAIR_DIR} \
--num_samples ${NUM_SAMPLES} \
--output_file demo_gt_repair/all_preds.jsonl \
--deduplicateYou can also run the full pipeline. We show a greedy-decoding demo below:
NUM_SAMPLES=1
COMMON_ARGS=(
--shard 0
--num_shards 125
--num_samples ${NUM_SAMPLES}
--temperature 0.0
--model "meta-llama/Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct"
# Check --max_concurrent_requests on how to control the concurrency
)
ROOT=demo_agentless
LOC_FILE=${ROOT}/loc.jsonl
REPAIR_DIR=${ROOT}/repair
PRED_FILE=${ROOT}/all_preds.jsonl
# Localization
python -m swerl.agentless_mini.localize \
--output_file ${LOC_FILE} \
${COMMON_ARGS[@]}
# Optionally, check localization performance
python -m swerl.agentless_mini.tools.check_loc_perf --locfile ${LOC_FILE}
# Repair
python -m swerl.agentless_mini.repair \
--loc_file ${LOC_FILE} \
--output_folder ${REPAIR_DIR} \
${COMMON_ARGS[@]}
# Rerank
python -m swerl.agentless_mini.rerank \
--patch_folder ${REPAIR_DIR} \
--num_samples ${NUM_SAMPLES} \
--output_file ${PRED_FILE} \
--deduplicate
# Now the ${PRED_FILE} will be ready. If you get all empty outputs, it means
# the model isn't generating correctly formatted edits. Then you should consider
# changing your base model or sampling more locations & repairs.[!NOTE] Reproduction test generation, regression test selection, and test execution are WIP due to refactoring and infra difference. They will be updated shortly.
@article{wei2025swerl,
title={SWE-RL: Advancing LLM Reasoning via Reinforcement Learning on Open Software Evolution},
author={Yuxiang Wei and Olivier Duchenne and Jade Copet and Quentin Carbonneaux and Lingming Zhang and Daniel Fried and Gabriel Synnaeve and Rishabh Singh and Sida I. Wang},
year={2025},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2502.18449}
}Agentless, SWE-Gym, SWE-Fixer, SWE-bench, Moatless EvalTools, Nebius SWE-agent.
The majority of SWE-RL is licensed under CC BY-NC 4.0, however portions of the project are available under separate license terms: Agentless Mini is licensed under the MIT license.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for swe-rl
Similar Open Source Tools

swe-rl
SWE-RL is the official codebase for the paper 'SWE-RL: Advancing LLM Reasoning via Reinforcement Learning on Open Software Evolution'. It is the first approach to scale reinforcement learning based LLM reasoning for real-world software engineering, leveraging open-source software evolution data and rule-based rewards. The code provides prompt templates and the implementation of the reward function based on sequence similarity. Agentless Mini, a part of SWE-RL, builds on top of Agentless with improvements like fast async inference, code refactoring for scalability, and support for using multiple reproduction tests for reranking. The tool can be used for localization, repair, and reproduction test generation in software engineering tasks.

raglite
RAGLite is a Python toolkit for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) with PostgreSQL or SQLite. It offers configurable options for choosing LLM providers, database types, and rerankers. The toolkit is fast and permissive, utilizing lightweight dependencies and hardware acceleration. RAGLite provides features like PDF to Markdown conversion, multi-vector chunk embedding, optimal semantic chunking, hybrid search capabilities, adaptive retrieval, and improved output quality. It is extensible with a built-in Model Context Protocol server, customizable ChatGPT-like frontend, document conversion to Markdown, and evaluation tools. Users can configure RAGLite for various tasks like configuring, inserting documents, running RAG pipelines, computing query adapters, evaluating performance, running MCP servers, and serving frontends.
suno-api
Suno AI API is an open-source project that allows developers to integrate the music generation capabilities of Suno.ai into their own applications. The API provides a simple and convenient way to generate music, lyrics, and other audio content using Suno.ai's powerful AI models. With Suno AI API, developers can easily add music generation functionality to their apps, websites, and other projects.
consult-llm-mcp
Consult LLM MCP is an MCP server that enables users to consult powerful AI models like GPT-5.2, Gemini 3.0 Pro, and DeepSeek Reasoner for complex problem-solving. It supports multi-turn conversations, direct queries with optional file context, git changes inclusion for code review, comprehensive logging with cost estimation, and various CLI modes for Gemini and Codex. The tool is designed to simplify the process of querying AI models for assistance in resolving coding issues and improving code quality.
metis
Metis is an open-source, AI-driven tool for deep security code review, created by Arm's Product Security Team. It helps engineers detect subtle vulnerabilities, improve secure coding practices, and reduce review fatigue. Metis uses LLMs for semantic understanding and reasoning, RAG for context-aware reviews, and supports multiple languages and vector store backends. It provides a plugin-friendly and extensible architecture, named after the Greek goddess of wisdom, Metis. The tool is designed for large, complex, or legacy codebases where traditional tooling falls short.
plexe
Plexe is a tool that allows users to create machine learning models by describing them in plain language. Users can explain their requirements, provide a dataset, and the AI-powered system will build a fully functional model through an automated agentic approach. It supports multiple AI agents and model building frameworks like XGBoost, CatBoost, and Keras. Plexe also provides Docker images with pre-configured environments, YAML configuration for customization, and support for multiple LiteLLM providers. Users can visualize experiment results using the built-in Streamlit dashboard and extend Plexe's functionality through custom integrations.
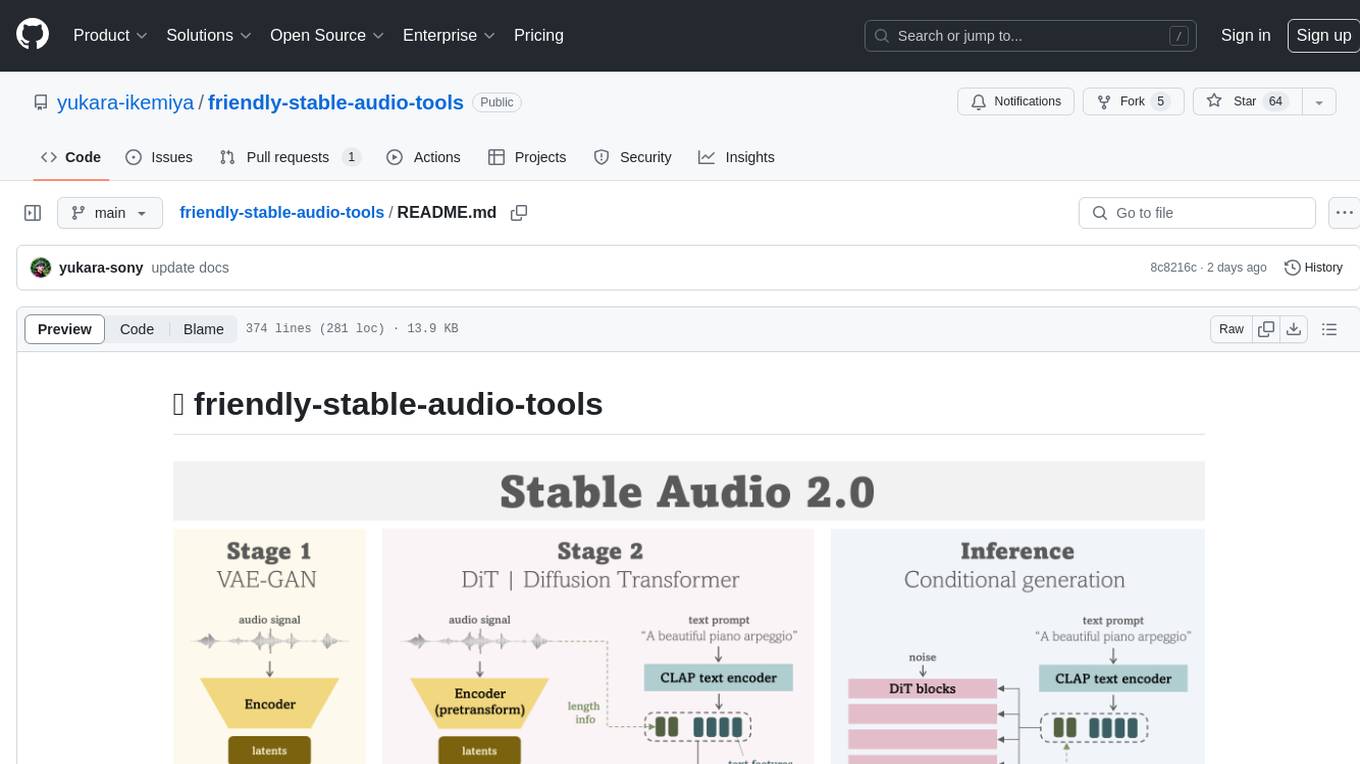
friendly-stable-audio-tools
This repository is a refactored and updated version of `stable-audio-tools`, an open-source code for audio/music generative models originally by Stability AI. It contains refactored codes for improved readability and usability, useful scripts for evaluating and playing with trained models, and instructions on how to train models such as `Stable Audio 2.0`. The repository does not contain any pretrained checkpoints. Requirements include PyTorch 2.0 or later for Flash Attention support and Python 3.8.10 or later for development. The repository provides guidance on installing, building a training environment using Docker or Singularity, logging with Weights & Biases, training configurations, and stages for VAE-GAN and Diffusion Transformer (DiT) training.
OpenMusic
OpenMusic is a repository providing an implementation of QA-MDT, a Quality-Aware Masked Diffusion Transformer for music generation. The code integrates state-of-the-art models and offers training strategies for music generation. The repository includes implementations of AudioLDM, PixArt-alpha, MDT, AudioMAE, and Open-Sora. Users can train or fine-tune the model using different strategies and datasets. The model is well-pretrained and can be used for music generation tasks. The repository also includes instructions for preparing datasets, training the model, and performing inference. Contact information is provided for any questions or suggestions regarding the project.

langserve
LangServe helps developers deploy `LangChain` runnables and chains as a REST API. This library is integrated with FastAPI and uses pydantic for data validation. In addition, it provides a client that can be used to call into runnables deployed on a server. A JavaScript client is available in LangChain.js.

wllama
Wllama is a WebAssembly binding for llama.cpp, a high-performance and lightweight language model library. It enables you to run inference directly on the browser without the need for a backend or GPU. Wllama provides both high-level and low-level APIs, allowing you to perform various tasks such as completions, embeddings, tokenization, and more. It also supports model splitting, enabling you to load large models in parallel for faster download. With its Typescript support and pre-built npm package, Wllama is easy to integrate into your React Typescript projects.
paxml
Pax is a framework to configure and run machine learning experiments on top of Jax.
qa-mdt
This repository provides an implementation of QA-MDT, integrating state-of-the-art models for music generation. It offers a Quality-Aware Masked Diffusion Transformer for enhanced music generation. The code is based on various repositories like AudioLDM, PixArt-alpha, MDT, AudioMAE, and Open-Sora. The implementation allows for training and fine-tuning the model with different strategies and datasets. The repository also includes instructions for preparing datasets in LMDB format and provides a script for creating a toy LMDB dataset. The model can be used for music generation tasks, with a focus on quality injection to enhance the musicality of generated music.
zml
ZML is a high-performance AI inference stack built for production, using Zig language, MLIR, and Bazel. It allows users to create exciting AI projects, run pre-packaged models like MNIST, TinyLlama, OpenLLama, and Meta Llama, and compile models for accelerator runtimes. Users can also run tests, explore examples, and contribute to the project. ZML is licensed under the Apache 2.0 license.
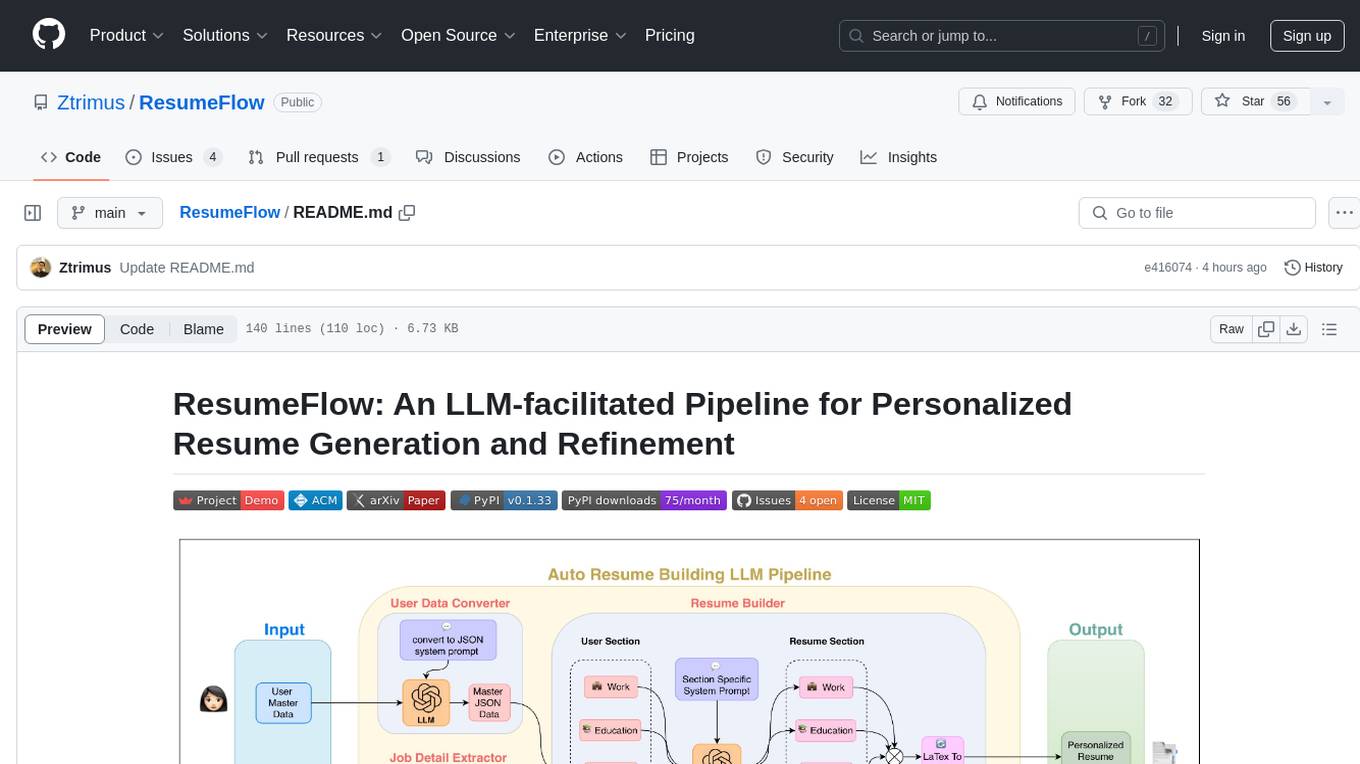
ResumeFlow
ResumeFlow is an automated system that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to streamline the job application process. By integrating LLM technology, the tool aims to automate various stages of job hunting, making it easier for users to apply for jobs. Users can access ResumeFlow as a web tool, install it as a Python package, or download the source code from GitHub. The tool requires Python 3.11.6 or above and an LLM API key from OpenAI or Gemini Pro for usage. ResumeFlow offers functionalities such as generating curated resumes and cover letters based on job URLs and user's master resume data.

xFasterTransformer
xFasterTransformer is an optimized solution for Large Language Models (LLMs) on the X86 platform, providing high performance and scalability for inference on mainstream LLM models. It offers C++ and Python APIs for easy integration, along with example codes and benchmark scripts. Users can prepare models in a different format, convert them, and use the APIs for tasks like encoding input prompts, generating token ids, and serving inference requests. The tool supports various data types and models, and can run in single or multi-rank modes using MPI. A web demo based on Gradio is available for popular LLM models like ChatGLM and Llama2. Benchmark scripts help evaluate model inference performance quickly, and MLServer enables serving with REST and gRPC interfaces.
TokenFormer
TokenFormer is a fully attention-based neural network architecture that leverages tokenized model parameters to enhance architectural flexibility. It aims to maximize the flexibility of neural networks by unifying token-token and token-parameter interactions through the attention mechanism. The architecture allows for incremental model scaling and has shown promising results in language modeling and visual modeling tasks. The codebase is clean, concise, easily readable, state-of-the-art, and relies on minimal dependencies.
For similar tasks

swe-rl
SWE-RL is the official codebase for the paper 'SWE-RL: Advancing LLM Reasoning via Reinforcement Learning on Open Software Evolution'. It is the first approach to scale reinforcement learning based LLM reasoning for real-world software engineering, leveraging open-source software evolution data and rule-based rewards. The code provides prompt templates and the implementation of the reward function based on sequence similarity. Agentless Mini, a part of SWE-RL, builds on top of Agentless with improvements like fast async inference, code refactoring for scalability, and support for using multiple reproduction tests for reranking. The tool can be used for localization, repair, and reproduction test generation in software engineering tasks.
AI-Office-Translator
AI-Office-Translator is a free, fully localized, user-friendly translation tool that helps you translate Office files (Word, PowerPoint, and Excel) between different languages. It supports .docx, .pptx, and .xlsx files and allows translation between English, Chinese, and Japanese. Users can run the tool after installing CUDA, downloading Ollama dependencies and models, setting up a virtual environment (optional), and installing requirements. The tool provides a UI where users can select languages, models, upload files for translation, start translation, and download translated files. It also supports an online mode with API key integration. The software is open-source under GPL-3.0 license and only provides AI translation services, with users expected to engage in legal translation activities.

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

sourcegraph
Sourcegraph is a code search and navigation tool that helps developers read, write, and fix code in large, complex codebases. It provides features such as code search across all repositories and branches, code intelligence for navigation and refactoring, and the ability to fix and refactor code across multiple repositories at once.
continue
Continue is an open-source autopilot for VS Code and JetBrains that allows you to code with any LLM. With Continue, you can ask coding questions, edit code in natural language, generate files from scratch, and more. Continue is easy to use and can help you save time and improve your coding skills.
cody
Cody is a free, open-source AI coding assistant that can write and fix code, provide AI-generated autocomplete, and answer your coding questions. Cody fetches relevant code context from across your entire codebase to write better code that uses more of your codebase's APIs, impls, and idioms, with less hallucination.
awesome-code-ai
A curated list of AI coding tools, including code completion, refactoring, and assistants. This list includes both open-source and commercial tools, as well as tools that are still in development. Some of the most popular AI coding tools include GitHub Copilot, CodiumAI, Codeium, Tabnine, and Replit Ghostwriter.
commanddash
Dash AI is an open-source coding assistant for Flutter developers. It is designed to not only write code but also run and debug it, allowing it to assist beyond code completion and automate routine tasks. Dash AI is powered by Gemini, integrated with the Dart Analyzer, and specifically tailored for Flutter engineers. The vision for Dash AI is to create a single-command assistant that can automate tedious development tasks, enabling developers to focus on creativity and innovation. It aims to assist with the entire process of engineering a feature for an app, from breaking down the task into steps to generating exploratory tests and iterating on the code until the feature is complete. To achieve this vision, Dash AI is working on providing LLMs with the same access and information that human developers have, including full contextual knowledge, the latest syntax and dependencies data, and the ability to write, run, and debug code. Dash AI welcomes contributions from the community, including feature requests, issue fixes, and participation in discussions. The project is committed to building a coding assistant that empowers all Flutter developers.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.
