diagram-of-thought
Official implementation of paper "On the Diagram of Thought" (https://arxiv.org/abs/2409.10038)
Stars: 65
The Diagram of Thought is a tool designed to visualize and analyze complex thought processes. It provides a graphical representation of reasoning and decision-making, allowing users to map out their ideas and explore different paths of thinking. By using this tool, individuals can gain insights into their cognitive processes and enhance their problem-solving skills. The Diagram of Thought aims to facilitate a deeper understanding of how thoughts are interconnected and how they influence our actions and perceptions.
README:
On the Diagram of Thought, https://arxiv.org/abs/2409.10038
As Huggingface Daily Paper: https://huggingface.co/papers/2409.10038
Demo: https://chatgpt.com/g/g-oPWt6oqF0-iterative-reasoner
Chat history: https://chatgpt.com/g/g-oPWt6oqF0-iterative-reasoner/c/66e6c96c-1fbc-800e-98bb-44c8e11561a4
Please cite the paper and star this repo if you use Diagram of Thought (DoT) and find it interesting/useful, thanks! Feel free to contact [email protected] or open an issue if you have any questions.
@article{zhang2024diagram,
title={On the Diagram of Thought},
author={Zhang, Yifan and Yuan, Yang and Yao, Andrew Chi-Chih},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2409.10038},
year={2024}
}For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for diagram-of-thought
Similar Open Source Tools

diagram-of-thought
The Diagram of Thought is a tool designed to visualize and analyze complex thought processes. It provides a graphical representation of reasoning and decision-making, allowing users to map out their ideas and explore different paths of thinking. By using this tool, individuals can gain insights into their cognitive processes and enhance their problem-solving skills. The Diagram of Thought aims to facilitate a deeper understanding of how thoughts are interconnected and how they influence our actions and perceptions.
awesome-RLAIF
Reinforcement Learning from AI Feedback (RLAIF) is a concept that describes a type of machine learning approach where **an AI agent learns by receiving feedback or guidance from another AI system**. This concept is closely related to the field of Reinforcement Learning (RL), which is a type of machine learning where an agent learns to make a sequence of decisions in an environment to maximize a cumulative reward. In traditional RL, an agent interacts with an environment and receives feedback in the form of rewards or penalties based on the actions it takes. It learns to improve its decision-making over time to achieve its goals. In the context of Reinforcement Learning from AI Feedback, the AI agent still aims to learn optimal behavior through interactions, but **the feedback comes from another AI system rather than from the environment or human evaluators**. This can be **particularly useful in situations where it may be challenging to define clear reward functions or when it is more efficient to use another AI system to provide guidance**. The feedback from the AI system can take various forms, such as: - **Demonstrations** : The AI system provides demonstrations of desired behavior, and the learning agent tries to imitate these demonstrations. - **Comparison Data** : The AI system ranks or compares different actions taken by the learning agent, helping it to understand which actions are better or worse. - **Reward Shaping** : The AI system provides additional reward signals to guide the learning agent's behavior, supplementing the rewards from the environment. This approach is often used in scenarios where the RL agent needs to learn from **limited human or expert feedback or when the reward signal from the environment is sparse or unclear**. It can also be used to **accelerate the learning process and make RL more sample-efficient**. Reinforcement Learning from AI Feedback is an area of ongoing research and has applications in various domains, including robotics, autonomous vehicles, and game playing, among others.
hallucination-index
LLM Hallucination Index - RAG Special is a comprehensive evaluation of large language models (LLMs) focusing on context length and open vs. closed-source attributes. The index explores the impact of context length on model performance and tests the assumption that closed-source LLMs outperform open-source ones. It also investigates the effectiveness of prompting techniques like Chain-of-Note across different context lengths. The evaluation includes 22 models from various brands, analyzing major trends and declaring overall winners based on short, medium, and long context insights. Methodologies involve rigorous testing with different context lengths and prompting techniques to assess models' abilities in handling extensive texts and detecting hallucinations.
awesome-transformer-nlp
This repository contains a hand-curated list of great machine (deep) learning resources for Natural Language Processing (NLP) with a focus on Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT), Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT), attention mechanism, Transformer architectures/networks, Chatbot, and transfer learning in NLP.
MediaAI
MediaAI is a repository containing lectures and materials for Aalto University's AI for Media, Art & Design course. The course is a hands-on, project-based crash course focusing on deep learning and AI techniques for artists and designers. It covers common AI algorithms & tools, their applications in art, media, and design, and provides hands-on practice in designing, implementing, and using these tools. The course includes lectures, exercises, and a final project based on students' interests. Students can complete the course without programming by creatively utilizing existing tools like ChatGPT and DALL-E. The course emphasizes collaboration, peer-to-peer tutoring, and project-based learning. It covers topics such as text generation, image generation, optimization, and game AI.
Nucleoid
Nucleoid is a declarative (logic) runtime environment that manages both data and logic under the same runtime. It uses a declarative programming paradigm, which allows developers to focus on the business logic of the application, while the runtime manages the technical details. This allows for faster development and reduces the amount of code that needs to be written. Additionally, the sharding feature can help to distribute the load across multiple instances, which can further improve the performance of the system.
Self-Iterative-Agent-System-for-Complex-Problem-Solving
The Self-Iterative Agent System for Complex Problem Solving is a solution developed for the Alibaba Mathematical Competition (AI Challenge). It involves multiple LLMs engaging in multi-round 'self-questioning' to iteratively refine the problem-solving process and select optimal solutions. The system consists of main and evaluation models, with a process that includes detailed problem-solving steps, feedback loops, and iterative improvements. The approach emphasizes communication and reasoning between sub-agents, knowledge extraction, and the importance of Agent-like architectures in complex tasks. While effective, there is room for improvement in model capabilities and error prevention mechanisms.
catwalk
Catwalk is a lightweight and user-friendly tool for visualizing and analyzing data. It provides a simple interface for users to explore and understand their datasets through interactive charts and graphs. With Catwalk, users can easily upload their data, customize visualizations, and gain insights from their data without the need for complex coding or technical skills.
ManipVQA
ManipVQA is a framework that enhances Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) with manipulation-centric knowledge through a Visual Question-Answering (VQA) format. It addresses the deficiency of conventional MLLMs in understanding affordances and physical concepts crucial for manipulation tasks. By infusing robotics-specific knowledge, including tool detection, affordance recognition, and physical concept comprehension, ManipVQA improves the performance of robots in manipulation tasks. The framework involves fine-tuning MLLMs with a curated dataset of interactive objects, enabling robots to understand and execute natural language instructions more effectively.
LLMs-in-science
The 'LLMs-in-science' repository is a collaborative environment for organizing papers related to large language models (LLMs) and autonomous agents in the field of chemistry. The goal is to discuss trend topics, challenges, and the potential for supporting scientific discovery in the context of artificial intelligence. The repository aims to maintain a systematic structure of the field and welcomes contributions from the community to keep the content up-to-date and relevant.
AutoWebGLM
AutoWebGLM is a project focused on developing a language model-driven automated web navigation agent. It extends the capabilities of the ChatGLM3-6B model to navigate the web more efficiently and address real-world browsing challenges. The project includes features such as an HTML simplification algorithm, hybrid human-AI training, reinforcement learning, rejection sampling, and a bilingual web navigation benchmark for testing AI web navigation agents.
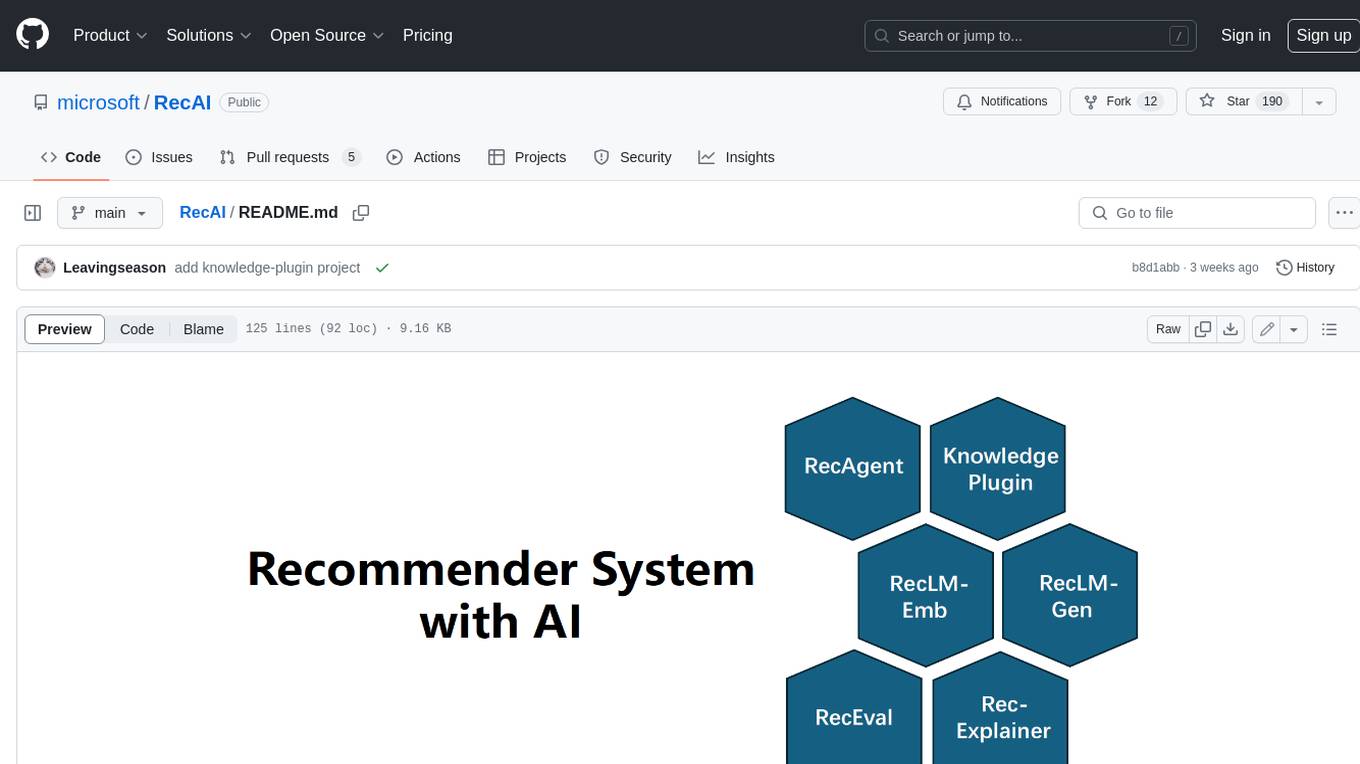
RecAI
RecAI is a project that explores the integration of Large Language Models (LLMs) into recommender systems, addressing the challenges of interactivity, explainability, and controllability. It aims to bridge the gap between general-purpose LLMs and domain-specific recommender systems, providing a holistic perspective on the practical requirements of LLM4Rec. The project investigates various techniques, including Recommender AI agents, selective knowledge injection, fine-tuning language models, evaluation, and LLMs as model explainers, to create more sophisticated, interactive, and user-centric recommender systems.
SuperKnowa
SuperKnowa is a fast framework to build Enterprise RAG (Retriever Augmented Generation) Pipelines at Scale, powered by watsonx. It accelerates Enterprise Generative AI applications to get prod-ready solutions quickly on private data. The framework provides pluggable components for tackling various Generative AI use cases using Large Language Models (LLMs), allowing users to assemble building blocks to address challenges in AI-driven text generation. SuperKnowa is battle-tested from 1M to 200M private knowledge base & scaled to billions of retriever tokens.
mlforpublicpolicylab
The Machine Learning for Public Policy Lab is a project-based course focused on solving real-world problems using machine learning in the context of public policy and social good. Students will gain hands-on experience building end-to-end machine learning systems, developing skills in problem formulation, working with messy data, communicating with non-technical stakeholders, model interpretability, and understanding algorithmic bias & disparities. The course covers topics such as project scoping, data acquisition, feature engineering, model evaluation, bias and fairness, and model interpretability. Students will work in small groups on policy projects, with graded components including project proposals, presentations, and final reports.

Raspberry
Raspberry is an open source project aimed at creating a toy dataset for finetuning Large Language Models (LLMs) with reasoning abilities. The project involves synthesizing complex user queries across various domains, generating CoT and Self-Critique data, cleaning and rectifying samples, finetuning an LLM with the dataset, and seeking funding for scalability. The ultimate goal is to develop a dataset that challenges models with tasks requiring math, coding, logic, reasoning, and planning skills, spanning different sectors like medicine, science, and software development.
For similar tasks

diagram-of-thought
The Diagram of Thought is a tool designed to visualize and analyze complex thought processes. It provides a graphical representation of reasoning and decision-making, allowing users to map out their ideas and explore different paths of thinking. By using this tool, individuals can gain insights into their cognitive processes and enhance their problem-solving skills. The Diagram of Thought aims to facilitate a deeper understanding of how thoughts are interconnected and how they influence our actions and perceptions.
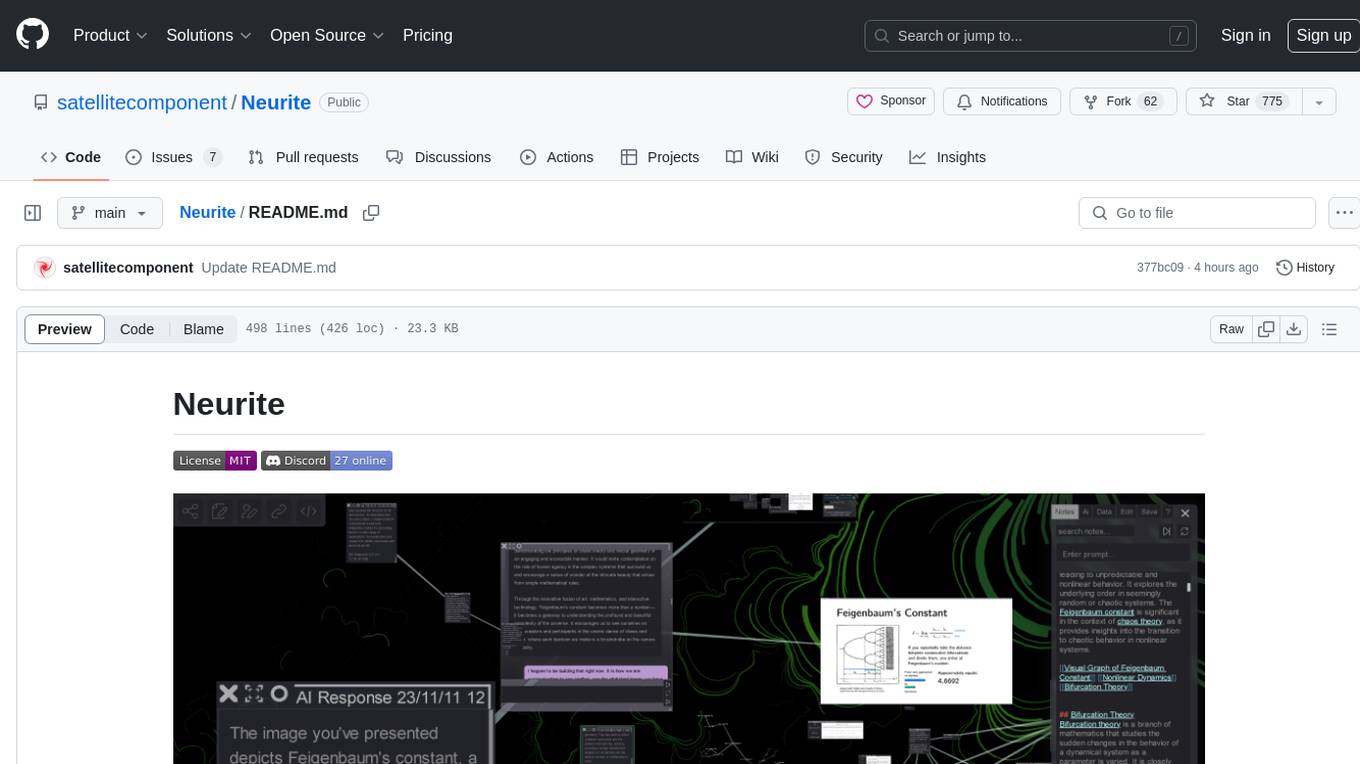
Neurite
Neurite is an innovative project that combines chaos theory and graph theory to create a digital interface that explores hidden patterns and connections for creative thinking. It offers a unique workspace blending fractals with mind mapping techniques, allowing users to navigate the Mandelbrot set in real-time. Nodes in Neurite represent various content types like text, images, videos, code, and AI agents, enabling users to create personalized microcosms of thoughts and inspirations. The tool supports synchronized knowledge management through bi-directional synchronization between mind-mapping and text-based hyperlinking. Neurite also features FractalGPT for modular conversation with AI, local AI capabilities for multi-agent chat networks, and a Neural API for executing code and sequencing animations. The project is actively developed with plans for deeper fractal zoom, advanced control over node placement, and experimental features.
For similar jobs
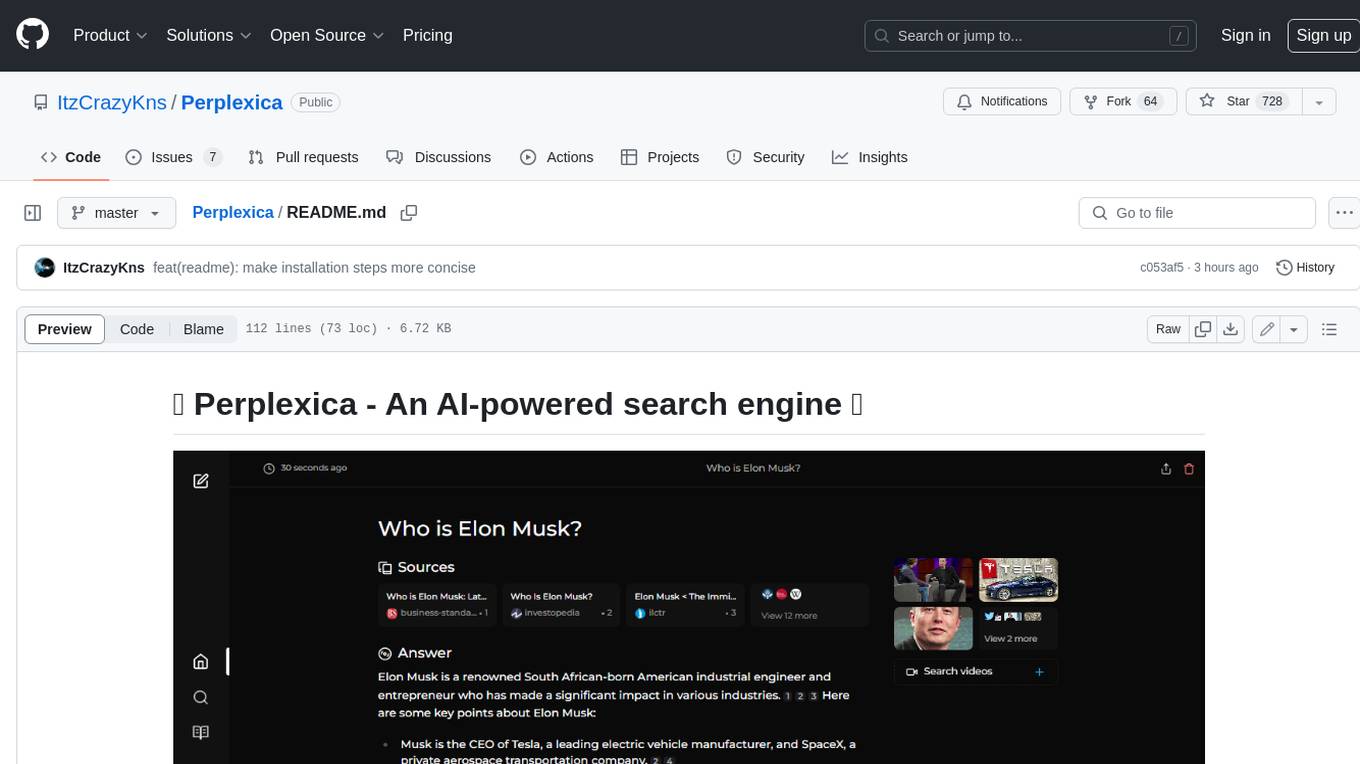
Perplexica
Perplexica is an open-source AI-powered search engine that utilizes advanced machine learning algorithms to provide clear answers with sources cited. It offers various modes like Copilot Mode, Normal Mode, and Focus Modes for specific types of questions. Perplexica ensures up-to-date information by using SearxNG metasearch engine. It also features image and video search capabilities and upcoming features include finalizing Copilot Mode and adding Discover and History Saving features.

KULLM
KULLM (구름) is a Korean Large Language Model developed by Korea University NLP & AI Lab and HIAI Research Institute. It is based on the upstage/SOLAR-10.7B-v1.0 model and has been fine-tuned for instruction. The model has been trained on 8×A100 GPUs and is capable of generating responses in Korean language. KULLM exhibits hallucination and repetition phenomena due to its decoding strategy. Users should be cautious as the model may produce inaccurate or harmful results. Performance may vary in benchmarks without a fixed system prompt.
MMMU
MMMU is a benchmark designed to evaluate multimodal models on college-level subject knowledge tasks, covering 30 subjects and 183 subfields with 11.5K questions. It focuses on advanced perception and reasoning with domain-specific knowledge, challenging models to perform tasks akin to those faced by experts. The evaluation of various models highlights substantial challenges, with room for improvement to stimulate the community towards expert artificial general intelligence (AGI).
1filellm
1filellm is a command-line data aggregation tool designed for LLM ingestion. It aggregates and preprocesses data from various sources into a single text file, facilitating the creation of information-dense prompts for large language models. The tool supports automatic source type detection, handling of multiple file formats, web crawling functionality, integration with Sci-Hub for research paper downloads, text preprocessing, and token count reporting. Users can input local files, directories, GitHub repositories, pull requests, issues, ArXiv papers, YouTube transcripts, web pages, Sci-Hub papers via DOI or PMID. The tool provides uncompressed and compressed text outputs, with the uncompressed text automatically copied to the clipboard for easy pasting into LLMs.
gpt-researcher
GPT Researcher is an autonomous agent designed for comprehensive online research on a variety of tasks. It can produce detailed, factual, and unbiased research reports with customization options. The tool addresses issues of speed, determinism, and reliability by leveraging parallelized agent work. The main idea involves running 'planner' and 'execution' agents to generate research questions, seek related information, and create research reports. GPT Researcher optimizes costs and completes tasks in around 3 minutes. Features include generating long research reports, aggregating web sources, an easy-to-use web interface, scraping web sources, and exporting reports to various formats.
ChatTTS
ChatTTS is a generative speech model optimized for dialogue scenarios, providing natural and expressive speech synthesis with fine-grained control over prosodic features. It supports multiple speakers and surpasses most open-source TTS models in terms of prosody. The model is trained with 100,000+ hours of Chinese and English audio data, and the open-source version on HuggingFace is a 40,000-hour pre-trained model without SFT. The roadmap includes open-sourcing additional features like VQ encoder, multi-emotion control, and streaming audio generation. The tool is intended for academic and research use only, with precautions taken to limit potential misuse.
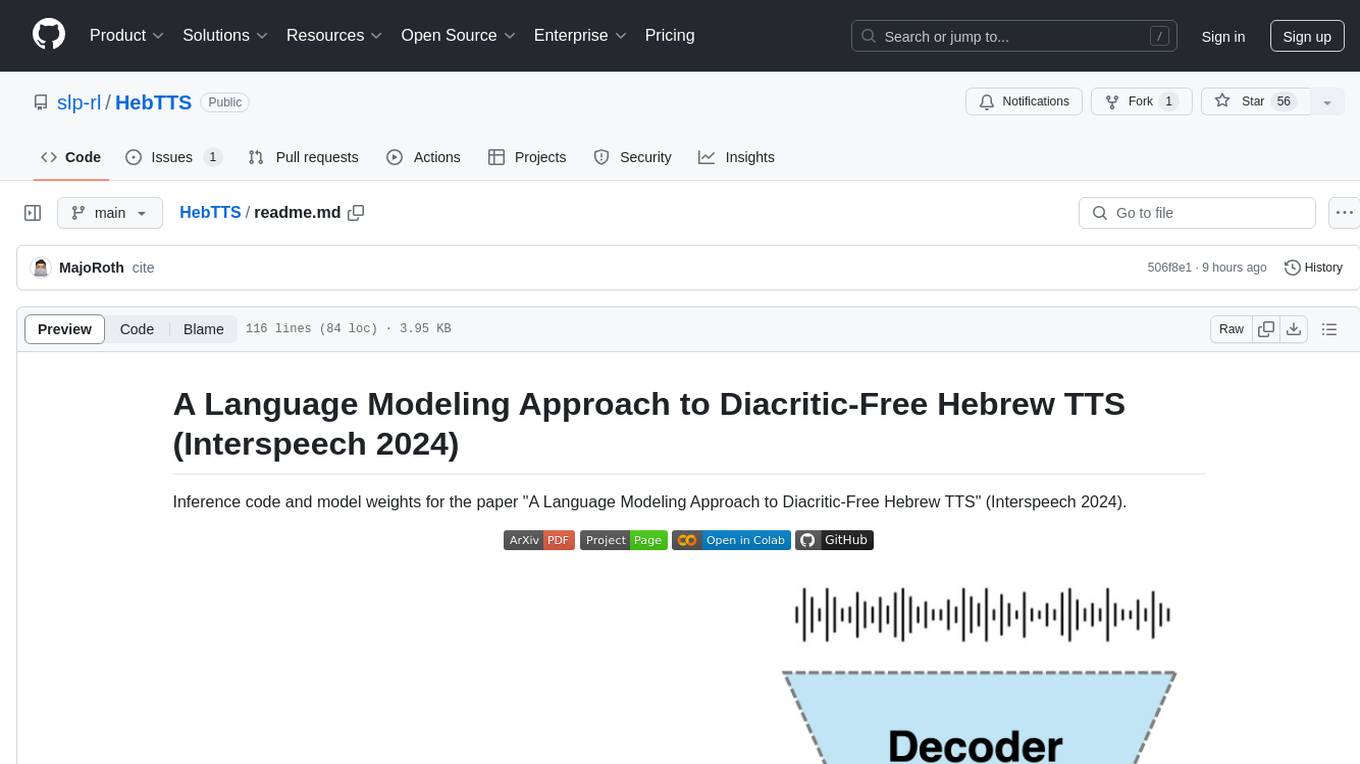
HebTTS
HebTTS is a language modeling approach to diacritic-free Hebrew text-to-speech (TTS) system. It addresses the challenge of accurately mapping text to speech in Hebrew by proposing a language model that operates on discrete speech representations and is conditioned on a word-piece tokenizer. The system is optimized using weakly supervised recordings and outperforms diacritic-based Hebrew TTS systems in terms of content preservation and naturalness of generated speech.
do-research-in-AI
This repository is a collection of research lectures and experience sharing posts from frontline researchers in the field of AI. It aims to help individuals upgrade their research skills and knowledge through insightful talks and experiences shared by experts. The content covers various topics such as evaluating research papers, choosing research directions, research methodologies, and tips for writing high-quality scientific papers. The repository also includes discussions on academic career paths, research ethics, and the emotional aspects of research work. Overall, it serves as a valuable resource for individuals interested in advancing their research capabilities in the field of AI.