
InfiniStore
A distributed KV store for disaggregated LLM inference
Stars: 52
InfiniStore is an open-source high-performance KV store designed to support LLM Inference clusters. It provides high-performance and low-latency KV cache transfer and reuse among inference nodes. In addition to inference clusters, it can be used as a standalone KV store for integration with LLM training or inference services. InfiniStore is currently integrated with vLLM via LMCache and is in progress for integration with SGLang and other inference engines.
README:
InfiniStore is an open-source high-performance KV store. It's designed to support LLM Inference clusters, whether the cluster is in prefill-decoding disaggregation mode or not. InfiniStore provides high-performance and low-latency KV cache transfer and KV cache reuse among inference nodes in the cluster.
In addition to inference clusters, InfiniStore can also be used as a standalone KV store to integrate with any other LLM training or inference services.
There are two major scenarios how InfiniStore supports :
- Prefill-Decoding disaggregation clusters: in such mode inference workloads are separated into two node pools: prefill nodes and decoding nodes. InfiniStore enables KV cache transfer among these two types of nodes, and also KV cache reuse.
- Non-disaggregated clusters: in such mode prefill and decoding workloads are mixed on every node. Infinistore serves as an extra large KV cache pool in addition to GPU cache and local CPU cache, and also enables cross-node KV cache reuse.
Currently InfiniStore has been integrated with vLLM. The integration is done via LMCache for the flexibility purpose.
Integration with SGLang and other inference engines are in progress.
Most users just need to deploy and run InfiniStore, and they don't need to understand how InfiniStore works internally. For these users, PIP is the recommended way to install:
pip install InfiniStore
For users who need to understand how InfiniStore code works or make code contributions to InfiniStore, it's recommended to install from source code:
apt install libuv1-dev
apt install libflatbuffers-dev
apt install libspdlog-dev libfmt-dev
apt install ibverbs-utils libibverbs-dev
apt install libboost-dev libboost-stacktrace-dev
pip install -e .
pip install pre-commit
pre-commit install
After installation, either from PIP or from source code, run the following command to verify your installation is successful:
InfiniStore --manage-port 8088
curl http://127.0.0.1:8088/selftest
- Start InfiniStore Server
The first step is to start an InfiniStore server. The server can be running on a GPU machine or a CPU machine.
Your server machine may be equipped with TCP network or RDMA network. The command line to start a server varies depending on the network configurations:
For TCP/IP Network:
InfiniStore --service-port 12345
For RDMA(RoCE):
InfiniStore --service-port 12345 --dev-name mlx5_0 --link-type Ethernet
For RDMA(Infiniband):
InfiniStore --service-port 12345 --dev-name mlx5_0 --link-type IB
- Run InfiniStore Client
Check the following example code to run an InfiniStore client:
InfiniStore/example/client.pyInfiniStore/example/client_async.pyInfiniStore/example/client_async_single.py
As illustrated in the previous section, InfiniStore enables different functionalities in a vLLM cluster: KV cache transfer between prefill nodes and decoding nodes, extended KV cache pool, cross-node KV cache reuse, etc.
The setup will varies depending on the specific vLLM cluster configurations. But usually it requires the following installations:
- Install vLLM on all nodes
- Install LMCache on all nodes
- Install InfiniStore on all nodes
Because this setup is a complicated process, we've made a separate demo repo for the PD disaggregation setup.
Please refer to the repo for the details: https://github.com/bytedance-iaas/splitwise-demos
InfiniStore is an open-source project and community. We welcome anyone who is interested in helping improve InfiniStore, whether code contributions, document contributions or any other contributions.
If you are submitting a code change, run the following unit test and pre-commit check to ensure your code change doesn't break existing features before submitting the PR:
-
Make your code changes
Just clone this repo, make code changes according to your feature design.
-
Run Unit Tests
pytest InfiniStore/test_InfiniStore.py
- Run Pre-commit Checks
pre-commit run --all-files
- Submit PR
If you code change passes both unit tests and pre-commit checks, submit the PR.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for InfiniStore
Similar Open Source Tools

InfiniStore
InfiniStore is an open-source high-performance KV store designed to support LLM Inference clusters. It provides high-performance and low-latency KV cache transfer and reuse among inference nodes. In addition to inference clusters, it can be used as a standalone KV store for integration with LLM training or inference services. InfiniStore is currently integrated with vLLM via LMCache and is in progress for integration with SGLang and other inference engines.
uwazi
Uwazi is a flexible database application designed for capturing and organizing collections of information, with a focus on document management. It is developed and supported by HURIDOCS, benefiting human rights organizations globally. The tool requires NodeJs, ElasticSearch, ICU Analysis Plugin, MongoDB, Yarn, and pdftotext for installation. It offers production and development installation guides, including Docker setup. Uwazi supports hot reloading, unit and integration testing with JEST, and end-to-end testing with Nightmare or Puppeteer. The system requirements include RAM, CPU, and disk space recommendations for on-premises and development usage.
trinityX
TrinityX is an open-source HPC, AI, and cloud platform designed to provide all services required in a modern system, with full customization options. It includes default services like Luna node provisioner, OpenLDAP, SLURM or OpenPBS, Prometheus, Grafana, OpenOndemand, and more. TrinityX also sets up NFS-shared directories, OpenHPC applications, environment modules, HA, and more. Users can install TrinityX on Enterprise Linux, configure network interfaces, set up passwordless authentication, and customize the installation using Ansible playbooks. The platform supports HA, OpenHPC integration, and provides detailed documentation for users to contribute to the project.
gpustack
GPUStack is an open-source GPU cluster manager designed for running large language models (LLMs). It supports a wide variety of hardware, scales with GPU inventory, offers lightweight Python package with minimal dependencies, provides OpenAI-compatible APIs, simplifies user and API key management, enables GPU metrics monitoring, and facilitates token usage and rate metrics tracking. The tool is suitable for managing GPU clusters efficiently and effectively.
LARS
LARS is an application that enables users to run Large Language Models (LLMs) locally on their devices, upload their own documents, and engage in conversations where the LLM grounds its responses with the uploaded content. The application focuses on Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) to increase accuracy and reduce AI-generated inaccuracies. LARS provides advanced citations, supports various file formats, allows follow-up questions, provides full chat history, and offers customization options for LLM settings. Users can force enable or disable RAG, change system prompts, and tweak advanced LLM settings. The application also supports GPU-accelerated inferencing, multiple embedding models, and text extraction methods. LARS is open-source and aims to be the ultimate RAG-centric LLM application.
OSWorld
OSWorld is a benchmarking tool designed to evaluate multimodal agents for open-ended tasks in real computer environments. It provides a platform for running experiments, setting up virtual machines, and interacting with the environment using Python scripts. Users can install the tool on their desktop or server, manage dependencies with Conda, and run benchmark tasks. The tool supports actions like executing commands, checking for specific results, and evaluating agent performance. OSWorld aims to facilitate research in AI by providing a standardized environment for testing and comparing different agent baselines.

minio
MinIO is a High Performance Object Storage released under GNU Affero General Public License v3.0. It is API compatible with Amazon S3 cloud storage service. Use MinIO to build high performance infrastructure for machine learning, analytics and application data workloads.
LlamaEdge
The LlamaEdge project makes it easy to run LLM inference apps and create OpenAI-compatible API services for the Llama2 series of LLMs locally. It provides a Rust+Wasm stack for fast, portable, and secure LLM inference on heterogeneous edge devices. The project includes source code for text generation, chatbot, and API server applications, supporting all LLMs based on the llama2 framework in the GGUF format. LlamaEdge is committed to continuously testing and validating new open-source models and offers a list of supported models with download links and startup commands. It is cross-platform, supporting various OSes, CPUs, and GPUs, and provides troubleshooting tips for common errors.
Open_Data_QnA
Open Data QnA is a Python library that allows users to interact with their PostgreSQL or BigQuery databases in a conversational manner, without needing to write SQL queries. The library leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to bridge the gap between human language and database queries, enabling users to ask questions in natural language and receive informative responses. It offers features such as conversational querying with multiturn support, table grouping, multi schema/dataset support, SQL generation, query refinement, natural language responses, visualizations, and extensibility. The library is built on a modular design and supports various components like Database Connectors, Vector Stores, and Agents for SQL generation, validation, debugging, descriptions, embeddings, responses, and visualizations.
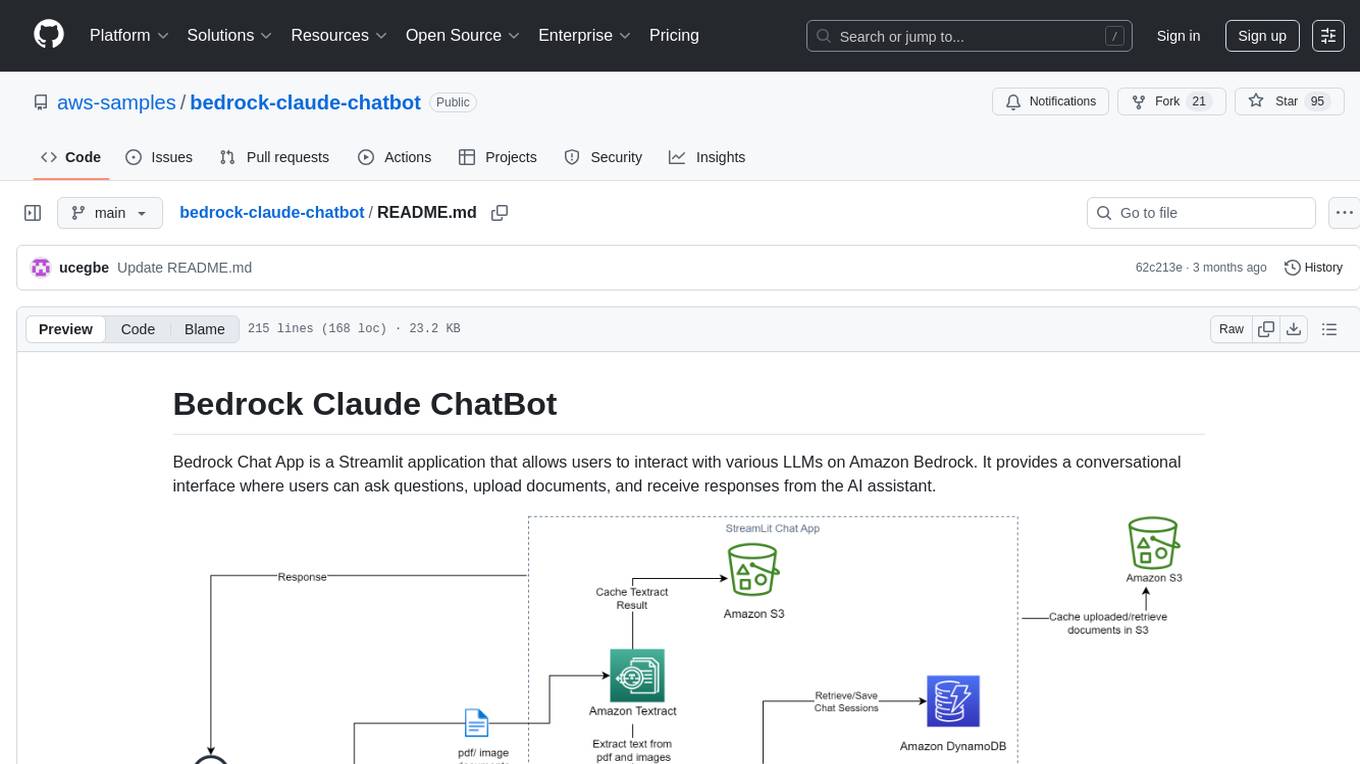
bedrock-claude-chatbot
Bedrock Claude ChatBot is a Streamlit application that provides a conversational interface for users to interact with various Large Language Models (LLMs) on Amazon Bedrock. Users can ask questions, upload documents, and receive responses from the AI assistant. The app features conversational UI, document upload, caching, chat history storage, session management, model selection, cost tracking, logging, and advanced data analytics tool integration. It can be customized using a config file and is extensible for implementing specialized tools using Docker containers and AWS Lambda. The app requires access to Amazon Bedrock Anthropic Claude Model, S3 bucket, Amazon DynamoDB, Amazon Textract, and optionally Amazon Elastic Container Registry and Amazon Athena for advanced analytics features.

airnode
Airnode is a fully-serverless oracle node that is designed specifically for API providers to operate their own oracles.
holohub
Holohub is a central repository for the NVIDIA Holoscan AI sensor processing community to share reference applications, operators, tutorials, and benchmarks. It includes example applications, community components, package configurations, and tutorials. Users and developers of the Holoscan platform are invited to reuse and contribute to this repository. The repository provides detailed instructions on prerequisites, building, running applications, contributing, and glossary terms. It also offers a searchable catalog of available components on the Holoscan SDK User Guide website.
RepoAgent
RepoAgent is an LLM-powered framework designed for repository-level code documentation generation. It automates the process of detecting changes in Git repositories, analyzing code structure through AST, identifying inter-object relationships, replacing Markdown content, and executing multi-threaded operations. The tool aims to assist developers in understanding and maintaining codebases by providing comprehensive documentation, ultimately improving efficiency and saving time.
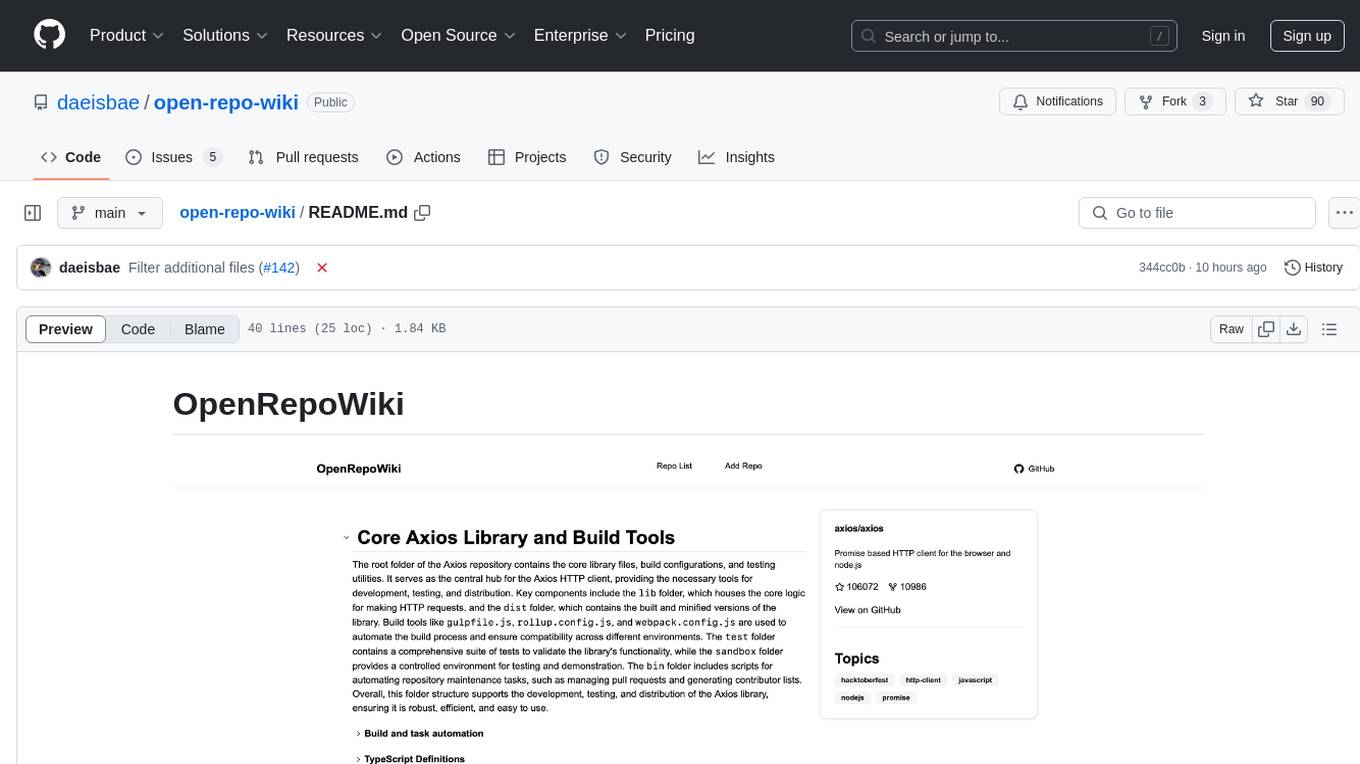
open-repo-wiki
OpenRepoWiki is a tool designed to automatically generate a comprehensive wiki page for any GitHub repository. It simplifies the process of understanding the purpose, functionality, and core components of a repository by analyzing its code structure, identifying key files and functions, and providing explanations. The tool aims to assist individuals who want to learn how to build various projects by providing a summarized overview of the repository's contents. OpenRepoWiki requires certain dependencies such as Google AI Studio or Deepseek API Key, PostgreSQL for storing repository information, Github API Key for accessing repository data, and Amazon S3 for optional usage. Users can configure the tool by setting up environment variables, installing dependencies, building the server, and running the application. It is recommended to consider the token usage and opt for cost-effective options when utilizing the tool.
lmql
LMQL is a programming language designed for large language models (LLMs) that offers a unique way of integrating traditional programming with LLM interaction. It allows users to write programs that combine algorithmic logic with LLM calls, enabling model reasoning capabilities within the context of the program. LMQL provides features such as Python syntax integration, rich control-flow options, advanced decoding techniques, powerful constraints via logit masking, runtime optimization, sync and async API support, multi-model compatibility, and extensive applications like JSON decoding and interactive chat interfaces. The tool also offers library integration, flexible tooling, and output streaming options for easy model output handling.

cognita
Cognita is an open-source framework to organize your RAG codebase along with a frontend to play around with different RAG customizations. It provides a simple way to organize your codebase so that it becomes easy to test it locally while also being able to deploy it in a production ready environment. The key issues that arise while productionizing RAG system from a Jupyter Notebook are: 1. **Chunking and Embedding Job** : The chunking and embedding code usually needs to be abstracted out and deployed as a job. Sometimes the job will need to run on a schedule or be trigerred via an event to keep the data updated. 2. **Query Service** : The code that generates the answer from the query needs to be wrapped up in a api server like FastAPI and should be deployed as a service. This service should be able to handle multiple queries at the same time and also autoscale with higher traffic. 3. **LLM / Embedding Model Deployment** : Often times, if we are using open-source models, we load the model in the Jupyter notebook. This will need to be hosted as a separate service in production and model will need to be called as an API. 4. **Vector DB deployment** : Most testing happens on vector DBs in memory or on disk. However, in production, the DBs need to be deployed in a more scalable and reliable way. Cognita makes it really easy to customize and experiment everything about a RAG system and still be able to deploy it in a good way. It also ships with a UI that makes it easier to try out different RAG configurations and see the results in real time. You can use it locally or with/without using any Truefoundry components. However, using Truefoundry components makes it easier to test different models and deploy the system in a scalable way. Cognita allows you to host multiple RAG systems using one app. ### Advantages of using Cognita are: 1. A central reusable repository of parsers, loaders, embedders and retrievers. 2. Ability for non-technical users to play with UI - Upload documents and perform QnA using modules built by the development team. 3. Fully API driven - which allows integration with other systems. > If you use Cognita with Truefoundry AI Gateway, you can get logging, metrics and feedback mechanism for your user queries. ### Features: 1. Support for multiple document retrievers that use `Similarity Search`, `Query Decompostion`, `Document Reranking`, etc 2. Support for SOTA OpenSource embeddings and reranking from `mixedbread-ai` 3. Support for using LLMs using `Ollama` 4. Support for incremental indexing that ingests entire documents in batches (reduces compute burden), keeps track of already indexed documents and prevents re-indexing of those docs.
For similar tasks

InfiniStore
InfiniStore is an open-source high-performance KV store designed to support LLM Inference clusters. It provides high-performance and low-latency KV cache transfer and reuse among inference nodes. In addition to inference clusters, it can be used as a standalone KV store for integration with LLM training or inference services. InfiniStore is currently integrated with vLLM via LMCache and is in progress for integration with SGLang and other inference engines.
For similar jobs
db2rest
DB2Rest is a modern low-code REST DATA API platform that simplifies the development of intelligent applications. It seamlessly integrates existing and new databases with language models (LMs/LLMs) and vector stores, enabling the rapid delivery of context-aware, reasoning applications without vendor lock-in.

mage-ai
Mage is an open-source data pipeline tool for transforming and integrating data. It offers an easy developer experience, engineering best practices built-in, and data as a first-class citizen. Mage makes it easy to build, preview, and launch data pipelines, and provides observability and scaling capabilities. It supports data integrations, streaming pipelines, and dbt integration.

airbyte
Airbyte is an open-source data integration platform that makes it easy to move data from any source to any destination. With Airbyte, you can build and manage data pipelines without writing any code. Airbyte provides a library of pre-built connectors that make it easy to connect to popular data sources and destinations. You can also create your own connectors using Airbyte's no-code Connector Builder or low-code CDK. Airbyte is used by data engineers and analysts at companies of all sizes to build and manage their data pipelines.

labelbox-python
Labelbox is a data-centric AI platform for enterprises to develop, optimize, and use AI to solve problems and power new products and services. Enterprises use Labelbox to curate data, generate high-quality human feedback data for computer vision and LLMs, evaluate model performance, and automate tasks by combining AI and human-centric workflows. The academic & research community uses Labelbox for cutting-edge AI research.

telemetry-airflow
This repository codifies the Airflow cluster that is deployed at workflow.telemetry.mozilla.org (behind SSO) and commonly referred to as "WTMO" or simply "Airflow". Some links relevant to users and developers of WTMO: * The `dags` directory in this repository contains some custom DAG definitions * Many of the DAGs registered with WTMO don't live in this repository, but are instead generated from ETL task definitions in bigquery-etl * The Data SRE team maintains a WTMO Developer Guide (behind SSO)

airflow
Apache Airflow (or simply Airflow) is a platform to programmatically author, schedule, and monitor workflows. When workflows are defined as code, they become more maintainable, versionable, testable, and collaborative. Use Airflow to author workflows as directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) of tasks. The Airflow scheduler executes your tasks on an array of workers while following the specified dependencies. Rich command line utilities make performing complex surgeries on DAGs a snap. The rich user interface makes it easy to visualize pipelines running in production, monitor progress, and troubleshoot issues when needed.

airbyte-platform
Airbyte is an open-source data integration platform that makes it easy to move data from any source to any destination. With Airbyte, you can build and manage data pipelines without writing any code. Airbyte provides a library of pre-built connectors that make it easy to connect to popular data sources and destinations. You can also create your own connectors using Airbyte's low-code Connector Development Kit (CDK). Airbyte is used by data engineers and analysts at companies of all sizes to move data for a variety of purposes, including data warehousing, data analysis, and machine learning.
chronon
Chronon is a platform that simplifies and improves ML workflows by providing a central place to define features, ensuring point-in-time correctness for backfills, simplifying orchestration for batch and streaming pipelines, offering easy endpoints for feature fetching, and guaranteeing and measuring consistency. It offers benefits over other approaches by enabling the use of a broad set of data for training, handling large aggregations and other computationally intensive transformations, and abstracting away the infrastructure complexity of data plumbing.


