
TTP-Threat-Feeds
Threat feeds designed to extract adversarial TTPs and IOCs, using: ✨AI✨
Stars: 60
TTP-Threat-Feeds is a script-powered threat feed generator that automates the discovery and parsing of threat actor behavior from security research. It scrapes URLs from trusted sources, extracts observable adversary behaviors, and outputs structured YAML files to help detection engineers and threat researchers derive detection opportunities and correlation logic. The tool supports multiple LLM providers for text extraction and includes OCR functionality for extracting content from images. Users can configure URLs, run the extractor, and save results as YAML files. Cloud provider SDKs are optional. Contributions are welcome for improvements and enhancements to the tool.
README:
TTP-Threat-Feeds is a script-powered threat feed generator designed to extract adversarial TTPs and IOCs using ✨AI✨
The purpose of this project is to automate the discovery and parsing of threat actor behavior from published security research. By scraping posts from trusted vendors and blogs listed in urls.txt, the tool identifies relevant content, extracts observable adversary behaviors (TTPs) and then outputs structured, human-readable YAML files. These YAML files are designed to help detection engineers and threat researchers quickly derive detection opportunities and correlation logic.
- Scrapes URLs from vetted threat intel sources (
urls.txt) - Extracts the text of each publication including embedded image OCR for screenshots
- Feeds content into a local LLM with a purpose-built prompt
- Extracts:
- Summary
- Attribution
- Malware families
- MITRE ATT&CK techniques
- Full command lines
- Process relationships
- Persistence and lateral movement artifacts
- IOCs (domains, IPs, hashes and URLs)
- Saves results as structured YAML files, sorted by date and source
- Each file includes a timestamp, source domain, and top malware family name (if found).
This project supports multiple LLM providers, both local and cloud-based.
| Provider | Type | Default Model | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| LM Studio | Local | qwen2.5-coder-32b-instruct |
Default, OpenAI-compatible endpoint |
| Ollama | Local | qwen2.5-coder:32b |
Easy local deployment |
| OpenAI | Cloud | gpt-4o |
Requires API key |
| Claude | Cloud | claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022 |
Requires API key |
| Gemini | Cloud | gemini-2.0-flash-exp |
Requires API key |
Default (LM Studio):
python ttp_extractor.py
# or explicitly
python ttp_extractor.py --lmstudioOllama:
python ttp_extractor.py --ollama
# With custom model
python ttp_extractor.py --ollama --model llama3.1:70bOpenAI:
export OPENAI_API_KEY="your-api-key"
python ttp_extractor.py --openai
# With specific model
python ttp_extractor.py --openai --model gpt-4o-miniClaude:
export ANTHROPIC_API_KEY="your-api-key"
python ttp_extractor.py --claude
# With specific model
python ttp_extractor.py --claude --model claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022Gemini:
export GOOGLE_API_KEY="your-api-key"
python ttp_extractor.py --gemini
# With specific model
python ttp_extractor.py --gemini --model gemini-2.0-flash-expCustom endpoint (for local providers):
python ttp_extractor.py --lmstudio --endpoint http://192.168.1.100:1234/v1/chat/completions
python ttp_extractor.py --ollama --endpoint http://192.168.1.100:11434/api/chatFor local deployment via LM Studio or Ollama:
-
qwen2.5-coder-32b-instructRECOMMENDED gemma-3-12b-it@q8_0phi-4devstral-small-2505llama-3.1-70b-instruct
For cloud providers, set environment variables:
# OpenAI
export OPENAI_API_KEY="sk-..."
# Anthropic Claude
export ANTHROPIC_API_KEY="sk-ant-..."
# Google Gemini
export GOOGLE_API_KEY="..."Or pass directly via command line:
python ttp_extractor.py --openai --api-key "sk-..."Some vendors embed command-line samples or TTPs in screenshots. This tool includes OCR functionality via pytesseract to extract and append this content to the LLM input, ensuring no critical insight is missed.
- Clone and setup:
git clone <repository-url>
cd TTP-Threat-Feeds
python -m venv .venv
source .venv/bin/activate # On Windows: .venv\Scripts\activate
pip install -r requirements.txt- Choose your LLM provider:
Option A: Local (LM Studio) - Default
- Install LM Studio
- Download a model (e.g.,
qwen2.5-coder-32b-instruct) - Start local server
- Run:
python ttp_extractor.py
Option B: Local (Ollama)
- Install Ollama
- Run:
ollama pull qwen2.5-coder:32b - Run:
python ttp_extractor.py --ollama
Option C: Cloud (OpenAI/Claude/Gemini)
- Get API key from your provider
- Run:
export OPENAI_API_KEY="your-key" - Run:
python ttp_extractor.py --openai
-
Configure URLs: Add threat intelligence blog URLs to
urls.txt(one per line) -
Run the extractor:
python ttp_extractor.pyResults will be saved to results/YYYY/MM/ as YAML files.
pip install -r requirements.txtNote: Cloud provider SDKs are optional. Only install if using that provider:
# For OpenAI
pip install openai>=1.0.0
# For Claude
pip install anthropic>=0.18.0
# For Gemini (optional, can use REST API)
pip install google-generativeai>=0.3.0Pull requests are welcome for improvements, especially new URL sources, parser fixes or enhancements to the LLM prompt.
This vibe-coded project generates results via LLM which can be prone to make mistakes. While it produces highly useful results, because of this it is not designed for ingestion into automated pipelines or alerting systems.
Please do not treat these YAMLs as canonical ground truth. Always verify extracted data with the original publication. The LLM is helpful but it is not infallible.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for TTP-Threat-Feeds
Similar Open Source Tools

TTP-Threat-Feeds
TTP-Threat-Feeds is a script-powered threat feed generator that automates the discovery and parsing of threat actor behavior from security research. It scrapes URLs from trusted sources, extracts observable adversary behaviors, and outputs structured YAML files to help detection engineers and threat researchers derive detection opportunities and correlation logic. The tool supports multiple LLM providers for text extraction and includes OCR functionality for extracting content from images. Users can configure URLs, run the extractor, and save results as YAML files. Cloud provider SDKs are optional. Contributions are welcome for improvements and enhancements to the tool.

LEANN
LEANN is an innovative vector database that democratizes personal AI, transforming your laptop into a powerful RAG system that can index and search through millions of documents using 97% less storage than traditional solutions without accuracy loss. It achieves this through graph-based selective recomputation and high-degree preserving pruning, computing embeddings on-demand instead of storing them all. LEANN allows semantic search of file system, emails, browser history, chat history, codebase, or external knowledge bases on your laptop with zero cloud costs and complete privacy. It is a drop-in semantic search MCP service fully compatible with Claude Code, enabling intelligent retrieval without changing your workflow.
docs-mcp-server
The docs-mcp-server repository contains the server-side code for the documentation management system. It provides functionalities for managing, storing, and retrieving documentation files. Users can upload, update, and delete documents through the server. The server also supports user authentication and authorization to ensure secure access to the documentation system. Additionally, the server includes APIs for integrating with other systems and tools, making it a versatile solution for managing documentation in various projects and organizations.
CyberStrikeAI
CyberStrikeAI is an AI-native security testing platform built in Go that integrates 100+ security tools, an intelligent orchestration engine, role-based testing with predefined security roles, a skills system with specialized testing skills, and comprehensive lifecycle management capabilities. It enables end-to-end automation from conversational commands to vulnerability discovery, attack-chain analysis, knowledge retrieval, and result visualization, delivering an auditable, traceable, and collaborative testing environment for security teams. The platform features an AI decision engine with OpenAI-compatible models, native MCP implementation with various transports, prebuilt tool recipes, large-result pagination, attack-chain graph, password-protected web UI, knowledge base with vector search, vulnerability management, batch task management, role-based testing, and skills system.
TermNet
TermNet is an AI-powered terminal assistant that connects a Large Language Model (LLM) with shell command execution, browser search, and dynamically loaded tools. It streams responses in real-time, executes tools one at a time, and maintains conversational memory across steps. The project features terminal integration for safe shell command execution, dynamic tool loading without code changes, browser automation powered by Playwright, WebSocket architecture for real-time communication, a memory system to track planning and actions, streaming LLM output integration, a safety layer to block dangerous commands, dual interface options, a notification system, and scratchpad memory for persistent note-taking. The architecture includes a multi-server setup with servers for WebSocket, browser automation, notifications, and web UI. The project structure consists of core backend files, various tools like web browsing and notification management, and servers for browser automation and notifications. Installation requires Python 3.9+, Ollama, and Chromium, with setup steps provided in the README. The tool can be used via the launcher for managing components or directly by starting individual servers. Additional tools can be added by registering them in `toolregistry.json` and implementing them in Python modules. Safety notes highlight the blocking of dangerous commands, allowed risky commands with warnings, and the importance of monitoring tool execution and setting appropriate timeouts.
oxylabs-mcp
The Oxylabs MCP Server acts as a bridge between AI models and the web, providing clean, structured data from any site. It enables scraping of URLs, rendering JavaScript-heavy pages, content extraction for AI use, bypassing anti-scraping measures, and accessing geo-restricted web data from 195+ countries. The implementation utilizes the Model Context Protocol (MCP) to facilitate secure interactions between AI assistants and web content. Key features include scraping content from any site, automatic data cleaning and conversion, bypassing blocks and geo-restrictions, flexible setup with cross-platform support, and built-in error handling and request management.
mcp-ts-template
The MCP TypeScript Server Template is a production-grade framework for building powerful and scalable Model Context Protocol servers with TypeScript. It features built-in observability, declarative tooling, robust error handling, and a modular, DI-driven architecture. The template is designed to be AI-agent-friendly, providing detailed rules and guidance for developers to adhere to best practices. It enforces architectural principles like 'Logic Throws, Handler Catches' pattern, full-stack observability, declarative components, and dependency injection for decoupling. The project structure includes directories for configuration, container setup, server resources, services, storage, utilities, tests, and more. Configuration is done via environment variables, and key scripts are available for development, testing, and publishing to the MCP Registry.
auto-engineer
Auto Engineer is a tool designed to automate the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) by building production-grade applications with a combination of human and AI agents. It offers a plugin-based architecture that allows users to install only the necessary functionality for their projects. The tool guides users through key stages including Flow Modeling, IA Generation, Deterministic Scaffolding, AI Coding & Testing Loop, and Comprehensive Quality Checks. Auto Engineer follows a command/event-driven architecture and provides a modular plugin system for specific functionalities. It supports TypeScript with strict typing throughout and includes a built-in message bus server with a web dashboard for monitoring commands and events.

MassGen
MassGen is a cutting-edge multi-agent system that leverages the power of collaborative AI to solve complex tasks. It assigns a task to multiple AI agents who work in parallel, observe each other's progress, and refine their approaches to converge on the best solution to deliver a comprehensive and high-quality result. The system operates through an architecture designed for seamless multi-agent collaboration, with key features including cross-model/agent synergy, parallel processing, intelligence sharing, consensus building, and live visualization. Users can install the system, configure API settings, and run MassGen for various tasks such as question answering, creative writing, research, development & coding tasks, and web automation & browser tasks. The roadmap includes plans for advanced agent collaboration, expanded model, tool & agent integration, improved performance & scalability, enhanced developer experience, and a web interface.
forge
Forge is a powerful open-source tool for building modern web applications. It provides a simple and intuitive interface for developers to quickly scaffold and deploy projects. With Forge, you can easily create custom components, manage dependencies, and streamline your development workflow. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced developer, Forge offers a flexible and efficient solution for your web development needs.
text-extract-api
The text-extract-api is a powerful tool that allows users to convert images, PDFs, or Office documents to Markdown text or JSON structured documents with high accuracy. It is built using FastAPI and utilizes Celery for asynchronous task processing, with Redis for caching OCR results. The tool provides features such as PDF/Office to Markdown and JSON conversion, improving OCR results with LLama, removing Personally Identifiable Information from documents, distributed queue processing, caching using Redis, switchable storage strategies, and a CLI tool for task management. Users can run the tool locally or on cloud services, with support for GPU processing. The tool also offers an online demo for testing purposes.
uLoopMCP
uLoopMCP is a Unity integration tool designed to let AI drive your Unity project forward with minimal human intervention. It provides a 'self-hosted development loop' where an AI can compile, run tests, inspect logs, and fix issues using tools like compile, run-tests, get-logs, and clear-console. It also allows AI to operate the Unity Editor itself—creating objects, calling menu items, inspecting scenes, and refining UI layouts from screenshots via tools like execute-dynamic-code, execute-menu-item, and capture-window. The tool enables AI-driven development loops to run autonomously inside existing Unity projects.
RepairAgent
RepairAgent is an autonomous LLM-based agent for automated program repair targeting the Defects4J benchmark. It uses an LLM-driven loop to localize, analyze, and fix Java bugs. The tool requires Docker, VS Code with Dev Containers extension, OpenAI API key, disk space of ~40 GB, and internet access. Users can get started with RepairAgent using either VS Code Dev Container or Docker Image. Running RepairAgent involves checking out the buggy project version, autonomous bug analysis, fix candidate generation, and testing against the project's test suite. Users can configure hyperparameters for budget control, repetition handling, commands limit, and external fix strategy. The tool provides output structure, experiment overview, individual analysis scripts, and data on fixed bugs from the Defects4J dataset.
codemie-code
Unified AI Coding Assistant CLI for managing multiple AI agents like Claude Code, Google Gemini, OpenCode, and custom AI agents. Supports OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, AWS Bedrock, LiteLLM, Ollama, and Enterprise SSO. Features built-in LangGraph agent with file operations, command execution, and planning tools. Cross-platform support for Windows, Linux, and macOS. Ideal for developers seeking a powerful alternative to GitHub Copilot or Cursor.
iloom-cli
iloom is a tool designed to streamline AI-assisted development by focusing on maintaining alignment between human developers and AI agents. It treats context as a first-class concern, persisting AI reasoning in issue comments rather than temporary chats. The tool allows users to collaborate with AI agents in an isolated environment, switch between complex features without losing context, document AI decisions publicly, and capture key insights and lessons learned from AI sessions. iloom is not just a tool for managing git worktrees, but a control plane for maintaining alignment between users and their AI assistants.
Groqqle
Groqqle 2.1 is a revolutionary, free AI web search and API that instantly returns ORIGINAL content derived from source articles, websites, videos, and even foreign language sources, for ANY target market of ANY reading comprehension level! It combines the power of large language models with advanced web and news search capabilities, offering a user-friendly web interface, a robust API, and now a powerful Groqqle_web_tool for seamless integration into your projects. Developers can instantly incorporate Groqqle into their applications, providing a powerful tool for content generation, research, and analysis across various domains and languages.
For similar tasks

TTP-Threat-Feeds
TTP-Threat-Feeds is a script-powered threat feed generator that automates the discovery and parsing of threat actor behavior from security research. It scrapes URLs from trusted sources, extracts observable adversary behaviors, and outputs structured YAML files to help detection engineers and threat researchers derive detection opportunities and correlation logic. The tool supports multiple LLM providers for text extraction and includes OCR functionality for extracting content from images. Users can configure URLs, run the extractor, and save results as YAML files. Cloud provider SDKs are optional. Contributions are welcome for improvements and enhancements to the tool.
dspy.rb
DSPy.rb is a Ruby framework for building reliable LLM applications using composable, type-safe modules. It enables developers to define typed signatures and compose them into pipelines, offering a more structured approach compared to traditional prompting. The framework embraces Ruby conventions and adds innovations like CodeAct agents and enhanced production instrumentation, resulting in scalable LLM applications that are robust and efficient. DSPy.rb is actively developed, with a focus on stability and real-world feedback through the 0.x series before reaching a stable v1.0 API.
tuui
TUUI is a desktop MCP client designed for accelerating AI adoption through the Model Context Protocol (MCP) and enabling cross-vendor LLM API orchestration. It is an LLM chat desktop application based on MCP, created using AI-generated components with strict syntax checks and naming conventions. The tool integrates AI tools via MCP, orchestrates LLM APIs, supports automated application testing, TypeScript, multilingual, layout management, global state management, and offers quick support through the GitHub community and official documentation.
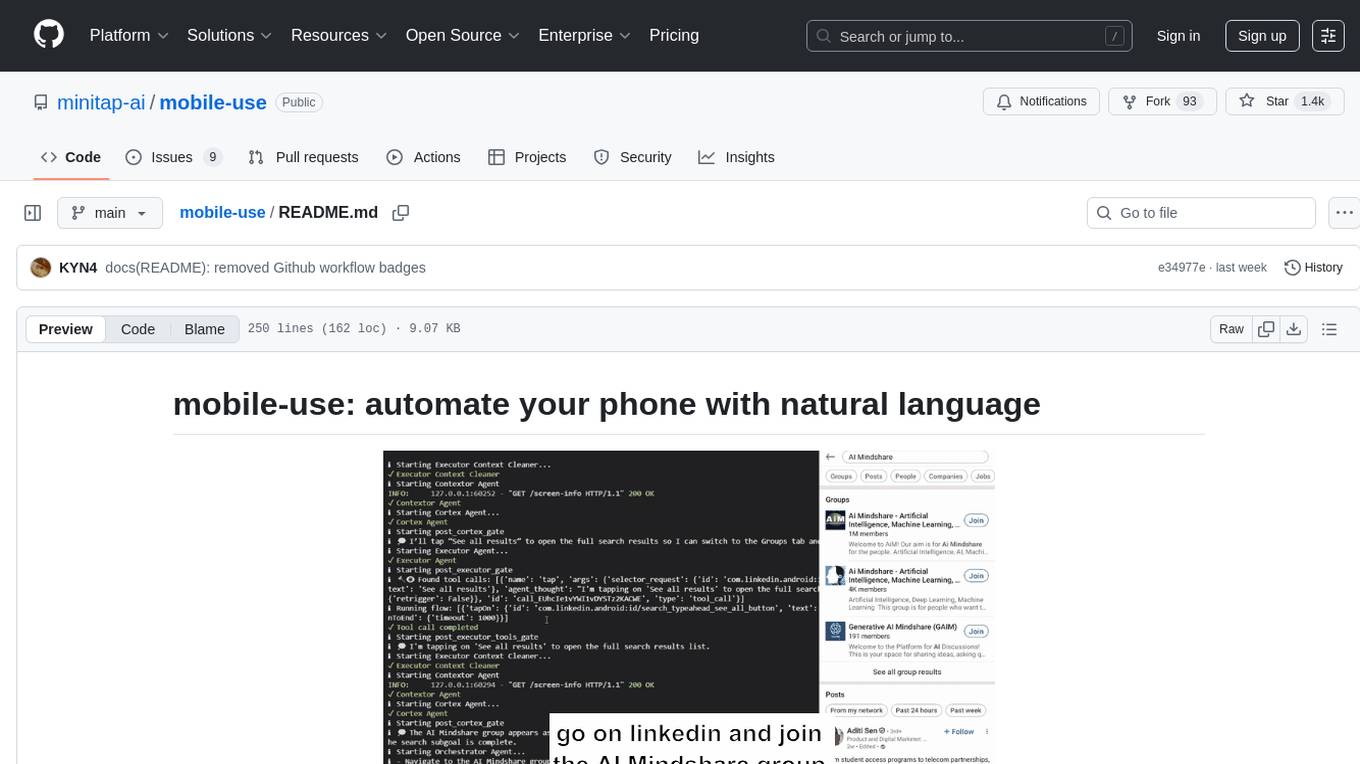
mobile-use
Mobile-use is an open-source AI agent that controls Android or IOS devices using natural language. It understands commands to perform tasks like sending messages and navigating apps. Features include natural language control, UI-aware automation, data scraping, and extensibility. Users can automate their mobile experience by setting up environment variables, customizing LLM configurations, and launching the tool via Docker or manually for development. The tool supports physical Android phones, Android simulators, and iOS simulators. Contributions are welcome, and the project is licensed under MIT.
For similar jobs

TTP-Threat-Feeds
TTP-Threat-Feeds is a script-powered threat feed generator that automates the discovery and parsing of threat actor behavior from security research. It scrapes URLs from trusted sources, extracts observable adversary behaviors, and outputs structured YAML files to help detection engineers and threat researchers derive detection opportunities and correlation logic. The tool supports multiple LLM providers for text extraction and includes OCR functionality for extracting content from images. Users can configure URLs, run the extractor, and save results as YAML files. Cloud provider SDKs are optional. Contributions are welcome for improvements and enhancements to the tool.

tracecat
Tracecat is an open-source automation platform for security teams. It's designed to be simple but powerful, with a focus on AI features and a practitioner-obsessed UI/UX. Tracecat can be used to automate a variety of tasks, including phishing email investigation, evidence collection, and remediation plan generation.
beelzebub
Beelzebub is an advanced honeypot framework designed to provide a highly secure environment for detecting and analyzing cyber attacks. It offers a low code approach for easy implementation and utilizes virtualization techniques powered by OpenAI Generative Pre-trained Transformer. Key features include OpenAI Generative Pre-trained Transformer acting as Linux virtualization, SSH Honeypot, HTTP Honeypot, TCP Honeypot, Prometheus openmetrics integration, Docker integration, RabbitMQ integration, and kubernetes support. Beelzebub allows easy configuration for different services and ports, enabling users to create custom honeypot scenarios. The roadmap includes developing Beelzebub into a robust PaaS platform. The project welcomes contributions and encourages adherence to the Code of Conduct for a supportive and respectful community.
admyral
Admyral is an open-source Cybersecurity Automation & Investigation Assistant that provides a unified console for investigations and incident handling, workflow automation creation, automatic alert investigation, and next step suggestions for analysts. It aims to tackle alert fatigue and automate security workflows effectively by offering features like workflow actions, AI actions, case management, alert handling, and more. Admyral combines security automation and case management to streamline incident response processes and improve overall security posture. The tool is open-source, transparent, and community-driven, allowing users to self-host, contribute, and collaborate on integrations and features.
galah
Galah is an LLM-powered web honeypot designed to mimic various applications and dynamically respond to arbitrary HTTP requests. It supports multiple LLM providers, including OpenAI. Unlike traditional web honeypots, Galah dynamically crafts responses for any HTTP request, caching them to reduce repetitive generation and API costs. The honeypot's configuration is crucial, directing the LLM to produce responses in a specified JSON format. Note that Galah is a weekend project exploring LLM capabilities and not intended for production use, as it may be identifiable through network fingerprinting and non-standard responses.
HaE
HaE is a framework project in the field of network security (data security) that combines artificial intelligence (AI) large models to achieve highlighting and information extraction of HTTP messages (including WebSocket). It aims to reduce testing time, focus on valuable and meaningful messages, and improve vulnerability discovery efficiency. The project provides a clear and visual interface design, simple interface interaction, and centralized data panel for querying and extracting information. It also features built-in color upgrade algorithm, one-click export/import of data, and integration of AI large models API for optimized data processing.
PyWxDump
PyWxDump is a Python tool designed for obtaining WeChat account information, decrypting databases, viewing WeChat chats, and exporting chats as HTML backups. It provides core features such as extracting base address offsets of various WeChat data, decrypting databases, and combining multiple database types for unified viewing. Additionally, it offers extended functions like viewing chat history through the web, exporting chat logs in different formats, and remote viewing of WeChat chat history. The tool also includes document classes for database field descriptions, base address offset methods, and decryption methods for MAC databases. PyWxDump is suitable for network security, daily backup archiving, remote chat history viewing, and more.

quark-engine
Quark Engine is an AI-powered tool designed for analyzing Android APK files. It focuses on enhancing the detection process for auto-suggestion, enabling users to create detection workflows without coding. The tool offers an intuitive drag-and-drop interface for workflow adjustments and updates. Quark Agent, the core component, generates Quark Script code based on natural language input and feedback. The project is committed to providing a user-friendly experience for designing detection workflows through textual and visual methods. Various features are still under development and will be rolled out gradually.
