PaddleOCR
Turn any PDF or image document into structured data for your AI. A powerful, lightweight OCR toolkit that bridges the gap between images/PDFs and LLMs. Supports 80+ languages.
Stars: 55381
PaddleOCR is an easy-to-use and scalable OCR toolkit based on PaddlePaddle. It provides a series of text detection and recognition models, supporting multiple languages and various scenarios. With PaddleOCR, users can perform accurate and efficient text extraction from images and videos, making it suitable for tasks such as document scanning, text recognition, and information extraction.
README:
English | 简体中文 | 繁體中文 | 日本語 | 한국어 | Français | Русский | Español | العربية
PaddleOCR is an industry-leading, production-ready OCR and document AI engine, offering end-to-end solutions from text extraction to intelligent document understanding
[!TIP] PaddleOCR now provides an MCP server that supports integration with Agent applications like Claude Desktop. For details, please refer to PaddleOCR MCP Server.
The PaddleOCR 3.0 Technical Report is now available. See details at: PaddleOCR 3.0 Technical Report
PaddleOCR converts documents and images into structured, AI-friendly data (like JSON and Markdown) with industry-leading accuracy—powering AI applications for everyone from indie developers and startups to large enterprises worldwide. With over 50,000 stars and deep integration into leading projects like MinerU, RAGFlow, and OmniParser, PaddleOCR has become the premier solution for developers building intelligent document applications in the AI era.
-
PP-OCRv5 — Universal Scene Text Recognition
Single model supports five text types (Simplified Chinese, Traditional Chinese, English, Japanese, and Pinyin) with 13% accuracy improvement. Solves multilingual mixed document recognition challenges. -
PP-StructureV3 — Complex Document Parsing
Intelligently converts complex PDFs and document images into Markdown and JSON files that preserve original structure. Outperforms numerous commercial solutions in public benchmarks. Perfectly maintains document layout and hierarchical structure. -
PP-ChatOCRv4 — Intelligent Information Extraction
Natively integrates ERNIE 4.5 to precisely extract key information from massive documents, with 15% accuracy improvement over previous generation. Makes documents "understand" your questions and provide accurate answers.
In addition to providing an outstanding model library, PaddleOCR 3.0 also offers user-friendly tools covering model training, inference, and service deployment, so developers can rapidly bring AI applications to production.
Special Note: PaddleOCR 3.x introduces several significant interface changes. Old code written based on PaddleOCR 2.x is likely incompatible with PaddleOCR 3.x. Please ensure that the documentation you are reading matches the version of PaddleOCR you are using. This document explains the reasons for the upgrade and the major changes from PaddleOCR 2.x to 3.x.
-
Significant Model Additions:
- Introduced training, inference, and deployment for PP-OCRv5 recognition models in English, Thai, and Greek. The PP-OCRv5 English model delivers an 11% improvement in English scenarios compared to the main PP-OCRv5 model, with the Thai and Greek recognition models achieving accuracies of 82.68% and 89.28%, respectively.
-
Deployment Capability Upgrades:
- Full support for PaddlePaddle framework versions 3.1.0 and 3.1.1.
- Comprehensive upgrade of the PP-OCRv5 C++ local deployment solution, now supporting both Linux and Windows, with feature parity and identical accuracy to the Python implementation.
- High-performance inference now supports CUDA 12, and inference can be performed using either the Paddle Inference or ONNX Runtime backends.
- The high-stability service-oriented deployment solution is now fully open-sourced, allowing users to customize Docker images and SDKs as required.
- The high-stability service-oriented deployment solution also supports invocation via manually constructed HTTP requests, enabling client-side code development in any programming language.
-
Benchmark Support:
- All production lines now support fine-grained benchmarking, enabling measurement of end-to-end inference time as well as per-layer and per-module latency data to assist with performance analysis. Here's how to set up and use the benchmark feature.
- Documentation has been updated to include key metrics for commonly used configurations on mainstream hardware, such as inference latency and memory usage, providing deployment references for users.
-
Bug Fixes:
- Resolved the issue of failed log saving during model training.
- Upgraded the data augmentation component for formula models for compatibility with newer versions of the albumentations dependency, and fixed deadlock warnings when using the tokenizers package in multi-process scenarios.
- Fixed inconsistencies in switch behaviors (e.g.,
use_chart_parsing) in the PP-StructureV3 configuration files compared to other pipelines.
-
Other Enhancements:
- Separated core and optional dependencies. Only minimal core dependencies are required for basic text recognition; additional dependencies for document parsing and information extraction can be installed as needed.
- Enabled support for NVIDIA RTX 50 series graphics cards on Windows; users can refer to the installation guide for the corresponding PaddlePaddle framework versions.
- PP-OCR series models now support returning single-character coordinates.
- Added AIStudio, ModelScope, and other model download sources, allowing users to specify the source for model downloads.
- Added support for chart-to-table conversion via the PP-Chart2Table module.
- Optimized documentation descriptions to improve usability.
2025.08.15: PaddleOCR 3.1.1 Released
-
Bug Fixes:
- Added the missing methods
save_vector,save_visual_info_list,load_vector, andload_visual_info_listin thePP-ChatOCRv4class. - Added the missing parameters
glossaryandllm_request_intervalto thetranslatemethod in thePPDocTranslationclass.
- Added the missing methods
-
Documentation Improvements:
- Added a demo to the MCP documentation.
- Added information about the PaddlePaddle and PaddleOCR version used for performance metrics testing in the documentation.
- Fixed errors and omissions in the production line document translation.
-
Others:
- Changed the MCP server dependency to use the pure Python library
puremagicinstead ofpython-magicto reduce installation issues. - Retested PP-OCRv5 performance metrics with PaddleOCR version 3.1.0 and updated the documentation.
- Changed the MCP server dependency to use the pure Python library
2025.06.29: PaddleOCR 3.1.0 Released
-
Key Models and Pipelines:
- Added PP-OCRv5 Multilingual Text Recognition Model, which supports the training and inference process for text recognition models in 37 languages, including French, Spanish, Portuguese, Russian, Korean, etc. Average accuracy improved by over 30%. Details
- Upgraded the PP-Chart2Table model in PP-StructureV3, further enhancing the capability of converting charts to tables. On internal custom evaluation sets, the metric (RMS-F1) increased by 9.36 percentage points (71.24% -> 80.60%).
- Newly launched document translation pipeline, PP-DocTranslation, based on PP-StructureV3 and ERNIE 4.5, which supports the translation of Markdown format documents, various complex-layout PDF documents, and document images, with the results saved as Markdown format documents. Details
-
New MCP server: Details
- Supports both OCR and PP-StructureV3 pipelines.
- Supports three working modes: local Python library, AIStudio Community Cloud Service, and self-hosted service.
- Supports invoking local services via stdio and remote services via Streamable HTTP.
-
Documentation Optimization: Improved the descriptions in some user guides for a smoother reading experience.
2025.06.26: PaddleOCR 3.0.3 Released
- Bug Fix: Resolved the issue where the `enable_mkldnn` parameter was not effective, restoring the default behavior of using MKL-DNN for CPU inference.2025.06.19: PaddleOCR 3.0.2 Released
- **New Features:**-
The default download source has been changed from
BOStoHuggingFace. Users can also change the environment variablePADDLE_PDX_MODEL_SOURCEtoBOSto set the model download source back to Baidu Object Storage (BOS). -
Added service invocation examples for six languages—C++, Java, Go, C#, Node.js, and PHP—for pipelines like PP-OCRv5, PP-StructureV3, and PP-ChatOCRv4.
-
Improved the layout partition sorting algorithm in the PP-StructureV3 pipeline, enhancing the sorting logic for complex vertical layouts to deliver better results.
-
Enhanced model selection logic: when a language is specified but a model version is not, the system will automatically select the latest model version supporting that language.
-
Set a default upper limit for MKL-DNN cache size to prevent unlimited growth, while also allowing users to configure cache capacity.
-
Updated default configurations for high-performance inference to support Paddle MKL-DNN acceleration and optimized the logic for automatic configuration selection for smarter choices.
-
Adjusted the logic for obtaining the default device to consider the actual support for computing devices by the installed Paddle framework, making program behavior more intuitive.
-
Added Android example for PP-OCRv5. Details.
-
Bug Fixes:
- Fixed an issue with some CLI parameters in PP-StructureV3 not taking effect.
- Resolved an issue where
export_paddlex_config_to_yamlwould not function correctly in certain cases. - Corrected the discrepancy between the actual behavior of
save_pathand its documentation description. - Fixed potential multithreading errors when using MKL-DNN in basic service deployment.
- Corrected channel order errors in image preprocessing for the Latex-OCR model.
- Fixed channel order errors in saving visualized images within the text recognition module.
- Resolved channel order errors in visualized table results within PP-StructureV3 pipeline.
- Fixed an overflow issue in the calculation of
overlap_ratiounder extremely special circumstances in the PP-StructureV3 pipeline.
-
Documentation Improvements:
- Updated the description of the
enable_mkldnnparameter in the documentation to accurately reflect the program's actual behavior. - Fixed errors in the documentation regarding the
langandocr_versionparameters. - Added instructions for exporting pipeline configuration files via CLI.
- Fixed missing columns in the performance data table for PP-OCRv5.
- Refined benchmark metrics for PP-StructureV3 across different configurations.
- Updated the description of the
-
Others:
- Relaxed version restrictions on dependencies like numpy and pandas, restoring support for Python 3.12.
History Log
2025.06.05: PaddleOCR 3.0.1 Released, includes:
-
Optimisation of certain models and model configurations:
- Updated the default model configuration for PP-OCRv5, changing both detection and recognition from mobile to server models. To improve default performance in most scenarios, the parameter
limit_side_lenin the configuration has been changed from 736 to 64. - Added a new text line orientation classification model
PP-LCNet_x1_0_textline_oriwith an accuracy of 99.42%. The default text line orientation classifier for OCR, PP-StructureV3, and PP-ChatOCRv4 pipelines has been updated to this model. - Optimized the text line orientation classification model
PP-LCNet_x0_25_textline_ori, improving accuracy by 3.3 percentage points to a current accuracy of 98.85%.
- Updated the default model configuration for PP-OCRv5, changing both detection and recognition from mobile to server models. To improve default performance in most scenarios, the parameter
- Optimizations and fixes for some issues in version 3.0.0, details
🔥🔥2025.05.20: Official Release of PaddleOCR v3.0, including:
-
PP-OCRv5: High-Accuracy Text Recognition Model for All Scenarios - Instant Text from Images/PDFs.
- 🌐 Single-model support for five text types - Seamlessly process Simplified Chinese, Traditional Chinese, Simplified Chinese Pinyin, English and Japanese within a single model.
- ✍️ Improved handwriting recognition: Significantly better at complex cursive scripts and non-standard handwriting.
- 🎯 13-point accuracy gain over PP-OCRv4, achieving state-of-the-art performance across a variety of real-world scenarios.
-
PP-StructureV3: General-Purpose Document Parsing – Unleash SOTA Images/PDFs Parsing for Real-World Scenarios!
- 🧮 High-Accuracy multi-scene PDF parsing, leading both open- and closed-source solutions on the OmniDocBench benchmark.
- 🧠 Specialized capabilities include seal recognition, chart-to-table conversion, table recognition with nested formulas/images, vertical text document parsing, and complex table structure analysis.
-
PP-ChatOCRv4: Intelligent Document Understanding – Extract Key Information, not just text from Images/PDFs.
- 🔥 15-point accuracy gain in key-information extraction on PDF/PNG/JPG files over the previous generation.
- 💻 Native support for ERNIE 4.5, with compatibility for large-model deployments via PaddleNLP, Ollama, vLLM, and more.
- 🤝 Integrated PP-DocBee2, enabling extraction and understanding of printed text, handwriting, seals, tables, charts, and other common elements in complex documents.
Install PaddlePaddle refer to Installation Guide, after then, install the PaddleOCR toolkit.
# If you only want to use the basic text recognition feature (returns text position coordinates and content), including the PP-OCR series
python -m pip install paddleocr
# If you want to use all features such as document parsing, document understanding, document translation, key information extraction, etc.
# python -m pip install "paddleocr[all]"Starting from version 3.2.0, in addition to the all dependency group demonstrated above, PaddleOCR also supports installing partial optional features by specifying other dependency groups. All dependency groups provided by PaddleOCR are as follows:
| Dependency Group Name | Corresponding Functionality |
|---|---|
doc-parser |
Document parsing: can be used to extract layout elements such as tables, formulas, stamps, images, etc. from documents; includes models like PP-StructureV3 |
ie |
Information extraction: can be used to extract key information from documents, such as names, dates, addresses, amounts, etc.; includes models like PP-ChatOCRv4 |
trans |
Document translation: can be used to translate documents from one language to another; includes models like PP-DocTranslation |
all |
Complete functionality |
# Run PP-OCRv5 inference
paddleocr ocr -i https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/imgs/demo_image/general_ocr_002.png --use_doc_orientation_classify False --use_doc_unwarping False --use_textline_orientation False
# Run PP-StructureV3 inference
paddleocr pp_structurev3 -i https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/imgs/demo_image/pp_structure_v3_demo.png --use_doc_orientation_classify False --use_doc_unwarping False
# Get the Qianfan API Key at first, and then run PP-ChatOCRv4 inference
paddleocr pp_chatocrv4_doc -i https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/imgs/demo_image/vehicle_certificate-1.png -k 驾驶室准乘人数 --qianfan_api_key your_api_key --use_doc_orientation_classify False --use_doc_unwarping False
# Get more information about "paddleocr ocr"
paddleocr ocr --help4.1 PP-OCRv5 Example
# Initialize PaddleOCR instance
from paddleocr import PaddleOCR
ocr = PaddleOCR(
use_doc_orientation_classify=False,
use_doc_unwarping=False,
use_textline_orientation=False)
# Run OCR inference on a sample image
result = ocr.predict(
input="https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/imgs/demo_image/general_ocr_002.png")
# Visualize the results and save the JSON results
for res in result:
res.print()
res.save_to_img("output")
res.save_to_json("output")4.2 PP-StructureV3 Example
from pathlib import Path
from paddleocr import PPStructureV3
pipeline = PPStructureV3(
use_doc_orientation_classify=False,
use_doc_unwarping=False
)
# For Image
output = pipeline.predict(
input="https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/imgs/demo_image/pp_structure_v3_demo.png",
)
# Visualize the results and save the JSON results
for res in output:
res.print()
res.save_to_json(save_path="output")
res.save_to_markdown(save_path="output") 4.3 PP-ChatOCRv4 Example
from paddleocr import PPChatOCRv4Doc
chat_bot_config = {
"module_name": "chat_bot",
"model_name": "ernie-3.5-8k",
"base_url": "https://qianfan.baidubce.com/v2",
"api_type": "openai",
"api_key": "api_key", # your api_key
}
retriever_config = {
"module_name": "retriever",
"model_name": "embedding-v1",
"base_url": "https://qianfan.baidubce.com/v2",
"api_type": "qianfan",
"api_key": "api_key", # your api_key
}
pipeline = PPChatOCRv4Doc(
use_doc_orientation_classify=False,
use_doc_unwarping=False
)
visual_predict_res = pipeline.visual_predict(
input="https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/imgs/demo_image/vehicle_certificate-1.png",
use_common_ocr=True,
use_seal_recognition=True,
use_table_recognition=True,
)
mllm_predict_info = None
use_mllm = False
# If a multimodal large model is used, the local mllm service needs to be started. You can refer to the documentation: https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleX/blob/release/3.0/docs/pipeline_usage/tutorials/vlm_pipelines/doc_understanding.en.md performs deployment and updates the mllm_chat_bot_config configuration.
if use_mllm:
mllm_chat_bot_config = {
"module_name": "chat_bot",
"model_name": "PP-DocBee",
"base_url": "http://127.0.0.1:8080/", # your local mllm service url
"api_type": "openai",
"api_key": "api_key", # your api_key
}
mllm_predict_res = pipeline.mllm_pred(
input="https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/imgs/demo_image/vehicle_certificate-1.png",
key_list=["驾驶室准乘人数"],
mllm_chat_bot_config=mllm_chat_bot_config,
)
mllm_predict_info = mllm_predict_res["mllm_res"]
visual_info_list = []
for res in visual_predict_res:
visual_info_list.append(res["visual_info"])
layout_parsing_result = res["layout_parsing_result"]
vector_info = pipeline.build_vector(
visual_info_list, flag_save_bytes_vector=True, retriever_config=retriever_config
)
chat_result = pipeline.chat(
key_list=["驾驶室准乘人数"],
visual_info=visual_info_list,
vector_info=vector_info,
mllm_predict_info=mllm_predict_info,
chat_bot_config=chat_bot_config,
retriever_config=retriever_config,
)
print(chat_result)- Convert models to ONNX format: Obtaining ONNX Models.
- Accelerate inference using engines like OpenVINO, ONNX Runtime, TensorRT, or perform inference using ONNX format models: High-Performance Inference.
- Accelerate inference using multi-GPU and multi-process: Parallel Inference for Pipelines.
- Integrate PaddleOCR into applications written in C++, C#, Java, etc.: Serving.
⭐ Star this repository to keep up with exciting updates and new releases, including powerful OCR and document parsing capabilities! ⭐
PaddleOCR wouldn't be where it is today without its incredible community! 💗 A massive thank you to all our longtime partners, new collaborators, and everyone who's poured their passion into PaddleOCR — whether we've named you or not. Your support fuels our fire!
| Project Name | Description |
|---|---|
RAGFlow 
|
RAG engine based on deep document understanding. |
MinerU 
|
Multi-type Document to Markdown Conversion Tool |
Umi-OCR 
|
Free, Open-source, Batch Offline OCR Software. |
OmniParser
|
OmniParser: Screen Parsing tool for Pure Vision Based GUI Agent. |
QAnything
|
Question and Answer based on Anything. |
PDF-Extract-Kit 
|
A powerful open-source toolkit designed to efficiently extract high-quality content from complex and diverse PDF documents. |
Dango-Translator
|
Recognize text on the screen, translate it and show the translation results in real time. |
| Learn more projects | More projects based on PaddleOCR |
This project is released under the Apache 2.0 license.
@misc{cui2025paddleocr30technicalreport,
title={PaddleOCR 3.0 Technical Report},
author={Cheng Cui and Ting Sun and Manhui Lin and Tingquan Gao and Yubo Zhang and Jiaxuan Liu and Xueqing Wang and Zelun Zhang and Changda Zhou and Hongen Liu and Yue Zhang and Wenyu Lv and Kui Huang and Yichao Zhang and Jing Zhang and Jun Zhang and Yi Liu and Dianhai Yu and Yanjun Ma},
year={2025},
eprint={2507.05595},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.05595},
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for PaddleOCR
Similar Open Source Tools

PaddleOCR
PaddleOCR is an easy-to-use and scalable OCR toolkit based on PaddlePaddle. It provides a series of text detection and recognition models, supporting multiple languages and various scenarios. With PaddleOCR, users can perform accurate and efficient text extraction from images and videos, making it suitable for tasks such as document scanning, text recognition, and information extraction.

trafilatura
Trafilatura is a Python package and command-line tool for gathering text on the Web and simplifying the process of turning raw HTML into structured, meaningful data. It includes components for web crawling, downloads, scraping, and extraction of main texts, metadata, and comments. The tool aims to focus on actual content, avoid noise, and make sense of data and metadata. It is robust, fast, and widely used by companies and institutions. Trafilatura outperforms other libraries in text extraction benchmarks and offers various features like support for sitemaps, parallel processing, configurable extraction of key elements, multiple output formats, and optional add-ons. The tool is actively maintained with regular updates and comprehensive documentation.
cellm
Cellm is an Excel extension that allows users to leverage Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT within cell formulas. It enables users to extract AI responses to text ranges, making it useful for automating repetitive tasks that involve data processing and analysis. Cellm supports various models from Anthropic, Mistral, OpenAI, and Google, as well as locally hosted models via Llamafiles, Ollama, or vLLM. The tool is designed to simplify the integration of AI capabilities into Excel for tasks such as text classification, data cleaning, content summarization, entity extraction, and more.
mcp-use
MCP-Use is a Python library for analyzing and processing text data using Markov Chains. It provides functionalities for generating text based on input data, calculating transition probabilities, and simulating text sequences. The library is designed to be user-friendly and efficient, making it suitable for natural language processing tasks.
databerry
Chaindesk is a no-code platform that allows users to easily set up a semantic search system for personal data without technical knowledge. It supports loading data from various sources such as raw text, web pages, files (Word, Excel, PowerPoint, PDF, Markdown, Plain Text), and upcoming support for web sites, Notion, and Airtable. The platform offers a user-friendly interface for managing datastores, querying data via a secure API endpoint, and auto-generating ChatGPT Plugins for each datastore. Chaindesk utilizes a Vector Database (Qdrant), Openai's text-embedding-ada-002 for embeddings, and has a chunk size of 1024 tokens. The technology stack includes Next.js, Joy UI, LangchainJS, PostgreSQL, Prisma, and Qdrant, inspired by the ChatGPT Retrieval Plugin.
awesome-VLLMs
This repository contains a collection of pre-trained Very Large Language Models (VLLMs) that can be used for various natural language processing tasks. The models are fine-tuned on large text corpora and can be easily integrated into existing NLP pipelines for tasks such as text generation, sentiment analysis, and language translation. The repository also provides code examples and tutorials to help users get started with using these powerful language models in their projects.

CogVideo
CogVideo is a Python library for analyzing and processing video data. It provides functionalities for video segmentation, object detection, and tracking. With CogVideo, users can extract meaningful information from video streams, enabling applications in computer vision, surveillance, and video analytics. The library is designed to be user-friendly and efficient, making it suitable for both research and industrial projects.
PerforatedAI
PerforatedAI is a machine learning tool designed to automate the process of analyzing and extracting information from perforated documents. It uses advanced OCR technology to accurately identify and extract data from documents with perforations, such as surveys, questionnaires, and forms. The tool can handle various types of perforations and is capable of processing large volumes of documents quickly and efficiently. PerforatedAI streamlines the data extraction process, saving time and reducing errors associated with manual data entry. It is a valuable tool for businesses and organizations that deal with large amounts of perforated documents on a regular basis.
onlook
Onlook is a web scraping tool that allows users to extract data from websites easily and efficiently. It provides a user-friendly interface for creating web scraping scripts and supports various data formats for exporting the extracted data. With Onlook, users can automate the process of collecting information from multiple websites, saving time and effort. The tool is designed to be flexible and customizable, making it suitable for a wide range of web scraping tasks.
llm
The 'llm' package for Emacs provides an interface for interacting with Large Language Models (LLMs). It abstracts functionality to a higher level, concealing API variations and ensuring compatibility with various LLMs. Users can set up providers like OpenAI, Gemini, Vertex, Claude, Ollama, GPT4All, and a fake client for testing. The package allows for chat interactions, embeddings, token counting, and function calling. It also offers advanced prompt creation and logging capabilities. Users can handle conversations, create prompts with placeholders, and contribute by creating providers.
enterprise-h2ogpte
Enterprise h2oGPTe - GenAI RAG is a repository containing code examples, notebooks, and benchmarks for the enterprise version of h2oGPTe, a powerful AI tool for generating text based on the RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) architecture. The repository provides resources for leveraging h2oGPTe in enterprise settings, including implementation guides, performance evaluations, and best practices. Users can explore various applications of h2oGPTe in natural language processing tasks, such as text generation, content creation, and conversational AI.
GraphLLM
GraphLLM is a graph-based framework designed to process data using LLMs. It offers a set of tools including a web scraper, PDF parser, YouTube subtitles downloader, Python sandbox, and TTS engine. The framework provides a GUI for building and debugging graphs with advanced features like loops, conditionals, parallel execution, streaming of results, hierarchical graphs, external tool integration, and dynamic scheduling. GraphLLM is a low-level framework that gives users full control over the raw prompt and output of models, with a steeper learning curve. It is tested with llama70b and qwen 32b, under heavy development with breaking changes expected.
open-webui-tools
Open WebUI Tools Collection is a set of tools for structured planning, arXiv paper search, Hugging Face text-to-image generation, prompt enhancement, and multi-model conversations. It enhances LLM interactions with academic research, image generation, and conversation management. Tools include arXiv Search Tool and Hugging Face Image Generator. Function Pipes like Planner Agent offer autonomous plan generation and execution. Filters like Prompt Enhancer improve prompt quality. Installation and configuration instructions are provided for each tool and pipe.

turftopic
Turftopic is a Python library that provides tools for sentiment analysis and topic modeling of text data. It allows users to analyze large volumes of text data to extract insights on sentiment and topics. The library includes functions for preprocessing text data, performing sentiment analysis using machine learning models, and conducting topic modeling using algorithms such as Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA). Turftopic is designed to be user-friendly and efficient, making it suitable for both beginners and experienced data analysts.
LocalLLMClient
LocalLLMClient is a Swift package designed to interact with local Large Language Models (LLMs) on Apple platforms. It supports GGUF, MLX models, and the FoundationModels framework, providing streaming API, multimodal capabilities, and tool calling functionalities. Users can easily integrate this tool to work with various models for text generation and processing. The package also includes advanced features for low-level API control and multimodal image processing. LocalLLMClient is experimental and subject to API changes, offering support for iOS, macOS, and Linux platforms.

waidrin
Waidrin is a powerful web scraping tool that allows users to easily extract data from websites. It provides a user-friendly interface for creating custom web scraping scripts and supports various data formats for exporting the extracted data. With Waidrin, users can automate the process of collecting information from multiple websites, saving time and effort. The tool is designed to be flexible and scalable, making it suitable for both beginners and advanced users in the field of web scraping.
For similar tasks

langchain_dart
LangChain.dart is a Dart port of the popular LangChain Python framework created by Harrison Chase. LangChain provides a set of ready-to-use components for working with language models and a standard interface for chaining them together to formulate more advanced use cases (e.g. chatbots, Q&A with RAG, agents, summarization, extraction, etc.). The components can be grouped into a few core modules: * **Model I/O:** LangChain offers a unified API for interacting with various LLM providers (e.g. OpenAI, Google, Mistral, Ollama, etc.), allowing developers to switch between them with ease. Additionally, it provides tools for managing model inputs (prompt templates and example selectors) and parsing the resulting model outputs (output parsers). * **Retrieval:** assists in loading user data (via document loaders), transforming it (with text splitters), extracting its meaning (using embedding models), storing (in vector stores) and retrieving it (through retrievers) so that it can be used to ground the model's responses (i.e. Retrieval-Augmented Generation or RAG). * **Agents:** "bots" that leverage LLMs to make informed decisions about which available tools (such as web search, calculators, database lookup, etc.) to use to accomplish the designated task. The different components can be composed together using the LangChain Expression Language (LCEL).
x-crawl
x-crawl is a flexible Node.js AI-assisted crawler library that offers powerful AI assistance functions to make crawler work more efficient, intelligent, and convenient. It consists of a crawler API and various functions that can work normally even without relying on AI. The AI component is currently based on a large AI model provided by OpenAI, simplifying many tedious operations. The library supports crawling dynamic pages, static pages, interface data, and file data, with features like control page operations, device fingerprinting, asynchronous sync, interval crawling, failed retry handling, rotation proxy, priority queue, crawl information control, and TypeScript support.
nlp-llms-resources
The 'nlp-llms-resources' repository is a comprehensive resource list for Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Large Language Models (LLMs). It covers a wide range of topics including traditional NLP datasets, data acquisition, libraries for NLP, neural networks, sentiment analysis, optical character recognition, information extraction, semantics, topic modeling, multilingual NLP, domain-specific LLMs, vector databases, ethics, costing, books, courses, surveys, aggregators, newsletters, papers, conferences, and societies. The repository provides valuable information and resources for individuals interested in NLP and LLMs.

sycamore
Sycamore is a conversational search and analytics platform for complex unstructured data, such as documents, presentations, transcripts, embedded tables, and internal knowledge repositories. It retrieves and synthesizes high-quality answers through bringing AI to data preparation, indexing, and retrieval. Sycamore makes it easy to prepare unstructured data for search and analytics, providing a toolkit for data cleaning, information extraction, enrichment, summarization, and generation of vector embeddings that encapsulate the semantics of data. Sycamore uses your choice of generative AI models to make these operations simple and effective, and it enables quick experimentation and iteration. Additionally, Sycamore uses OpenSearch for indexing, enabling hybrid (vector + keyword) search, retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) pipelining, filtering, analytical functions, conversational memory, and other features to improve information retrieval.
langroid
Langroid is a Python framework that makes it easy to build LLM-powered applications. It uses a multi-agent paradigm inspired by the Actor Framework, where you set up Agents, equip them with optional components (LLM, vector-store and tools/functions), assign them tasks, and have them collaboratively solve a problem by exchanging messages. Langroid is a fresh take on LLM app-development, where considerable thought has gone into simplifying the developer experience; it does not use Langchain.

ontogpt
OntoGPT is a Python package for extracting structured information from text using large language models, instruction prompts, and ontology-based grounding. It provides a command line interface and a minimal web app for easy usage. The tool has been evaluated on test data and is used in related projects like TALISMAN for gene set analysis. OntoGPT enables users to extract information from text by specifying relevant terms and provides the extracted objects as output.
document-ai-samples
The Google Cloud Document AI Samples repository contains code samples and Community Samples demonstrating how to analyze, classify, and search documents using Google Cloud Document AI. It includes various projects showcasing different functionalities such as integrating with Google Drive, processing documents using Python, content moderation with Dialogflow CX, fraud detection, language extraction, paper summarization, tax processing pipeline, and more. The repository also provides access to test document files stored in a publicly-accessible Google Cloud Storage Bucket. Additionally, there are codelabs available for optical character recognition (OCR), form parsing, specialized processors, and managing Document AI processors. Community samples, like the PDF Annotator Sample, are also included. Contributions are welcome, and users can seek help or report issues through the repository's issues page. Please note that this repository is not an officially supported Google product and is intended for demonstrative purposes only.
llm-graph-builder
Knowledge Graph Builder App is a tool designed to convert PDF documents into a structured knowledge graph stored in Neo4j. It utilizes OpenAI's GPT/Diffbot LLM to extract nodes, relationships, and properties from PDF text content. Users can upload files from local machine or S3 bucket, choose LLM model, and create a knowledge graph. The app integrates with Neo4j for easy visualization and querying of extracted information.
For similar jobs

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.
daily-poetry-image
Daily Chinese ancient poetry and AI-generated images powered by Bing DALL-E-3. GitHub Action triggers the process automatically. Poetry is provided by Today's Poem API. The website is built with Astro.
exif-photo-blog
EXIF Photo Blog is a full-stack photo blog application built with Next.js, Vercel, and Postgres. It features built-in authentication, photo upload with EXIF extraction, photo organization by tag, infinite scroll, light/dark mode, automatic OG image generation, a CMD-K menu with photo search, experimental support for AI-generated descriptions, and support for Fujifilm simulations. The application is easy to deploy to Vercel with just a few clicks and can be customized with a variety of environment variables.
SillyTavern
SillyTavern is a user interface you can install on your computer (and Android phones) that allows you to interact with text generation AIs and chat/roleplay with characters you or the community create. SillyTavern is a fork of TavernAI 1.2.8 which is under more active development and has added many major features. At this point, they can be thought of as completely independent programs.
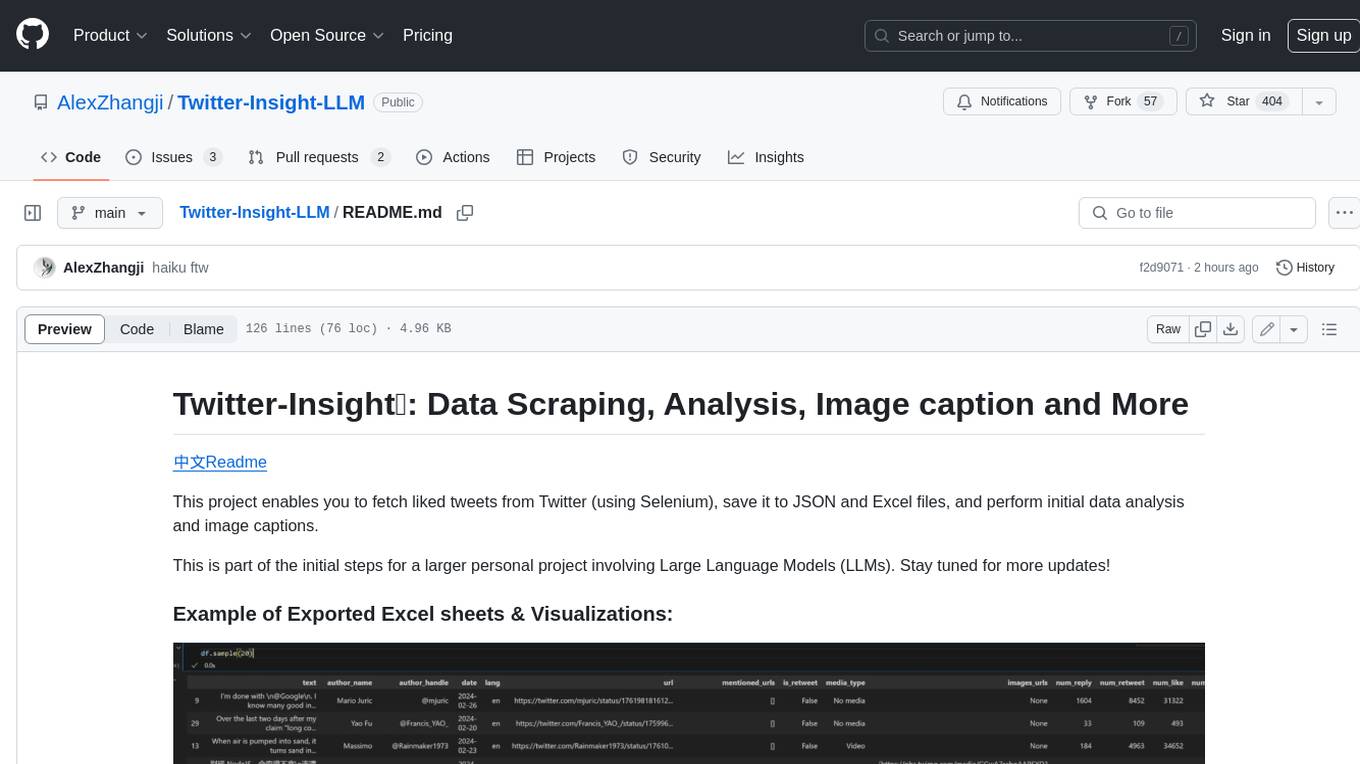
Twitter-Insight-LLM
This project enables you to fetch liked tweets from Twitter (using Selenium), save it to JSON and Excel files, and perform initial data analysis and image captions. This is part of the initial steps for a larger personal project involving Large Language Models (LLMs).
AISuperDomain
Aila Desktop Application is a powerful tool that integrates multiple leading AI models into a single desktop application. It allows users to interact with various AI models simultaneously, providing diverse responses and insights to their inquiries. With its user-friendly interface and customizable features, Aila empowers users to engage with AI seamlessly and efficiently. Whether you're a researcher, student, or professional, Aila can enhance your AI interactions and streamline your workflow.
ChatGPT-On-CS
This project is an intelligent dialogue customer service tool based on a large model, which supports access to platforms such as WeChat, Qianniu, Bilibili, Douyin Enterprise, Douyin, Doudian, Weibo chat, Xiaohongshu professional account operation, Xiaohongshu, Zhihu, etc. You can choose GPT3.5/GPT4.0/ Lazy Treasure Box (more platforms will be supported in the future), which can process text, voice and pictures, and access external resources such as operating systems and the Internet through plug-ins, and support enterprise AI applications customized based on their own knowledge base.
obs-localvocal
LocalVocal is a live-streaming AI assistant plugin for OBS that allows you to transcribe audio speech into text and perform various language processing functions on the text using AI / LLMs (Large Language Models). It's privacy-first, with all data staying on your machine, and requires no GPU, cloud costs, network, or downtime.