
dotnet-slopwatch
Catch naughty LLM reward-hacking and bad behavior for .NET coding
Stars: 61
Slopwatch is a .NET tool designed to detect LLM 'reward hacking' behaviors in code changes. It runs as a Claude Code hook or in CI/CD pipelines to catch when AI coding assistants take shortcuts instead of properly fixing issues. Slopwatch identifies patterns such as disabling tests, suppressing warnings, swallowing exceptions, adding delays, project-level warning suppression, and bypassing central package management. By analyzing code changes, Slopwatch helps prevent these shortcuts from making it into the codebase, ensuring code quality and adherence to best practices.
README:
// LLM anti-cheat
A .NET tool that detects LLM "reward hacking" behaviors in code changes.
Runs as a Claude Code hook or in CI/CD pipelines to catch when AI coding assistants take shortcuts instead of properly fixing issues.
When LLMs generate code, they sometimes take shortcuts that make tests pass or builds succeed without actually solving the underlying problem. These patterns include:
-
Disabling tests instead of fixing them (
[Fact(Skip="flaky")]) -
Suppressing warnings instead of addressing them (
#pragma warning disable) - Swallowing exceptions with empty catch blocks
-
Adding arbitrary delays to mask timing issues (
Task.Delay(1000)) -
Project-level warning suppression (
<NoWarn>,<TreatWarningsAsErrors>false</TreatWarningsAsErrors>) -
Bypassing Central Package Management with
VersionOverrideor inlineVersionattributes - And more...
Slopwatch catches these patterns before they make it into your codebase.
# Install as a global tool
dotnet tool install --global Slopwatch.Cmd
# Or install locally
dotnet tool install Slopwatch.Cmd# 1. Install slopwatch
dotnet tool install --global Slopwatch.Cmd
# 2. Initialize in your project (creates baseline from existing code)
cd your-project
slopwatch init
# 3. Commit the baseline to your repository
git add .slopwatch/baseline.json
git commit -m "Add slopwatch baseline"
# 4. From now on, only NEW slop is detected
slopwatch analyzeThe baseline approach ensures slopwatch catches new slop being introduced without flagging legacy code. Your CI/CD pipeline will fail if someone introduces new slop patterns.
# Create baseline from existing code
slopwatch init
# Force overwrite existing baseline
slopwatch init --forceThis creates .slopwatch/baseline.json containing all existing detections. Commit this file to your repository.
# Analyze current directory (requires baseline by default)
slopwatch analyze
# Analyze specific directory
slopwatch analyze -d src/
# Skip baseline and report ALL issues (not recommended for CI)
slopwatch analyze --no-baselineWhen you intentionally add code that triggers slopwatch (with proper justification):
# Add new detections to existing baseline
slopwatch analyze --update-baseline# Human-readable console output (default)
slopwatch analyze
# JSON for programmatic use
slopwatch analyze --output json# Fail if errors found (default)
slopwatch analyze --fail-on error
# Fail on warnings too
slopwatch analyze --fail-on warningIf you're concerned about performance on large projects, use --stats to see how many files are being analyzed and how long it takes:
slopwatch analyze --stats
# Output: Stats: 44 files analyzed in 1.64s| Rule | Severity | Description |
|---|---|---|
| SW001 | Error | Disabled tests via Skip, Ignore, or #if false |
| SW002 | Warning | Warning suppression via pragma or SuppressMessage |
| SW003 | Error | Empty catch blocks that swallow exceptions |
| SW004 | Warning | Arbitrary delays in test code (Task.Delay, Thread.Sleep) |
| SW005 | Warning | Project file slop (NoWarn, TreatWarningsAsErrors=false) |
| SW006 | Warning | CPM bypass via VersionOverride or inline Version attributes |
Add slopwatch as a hook to catch slop patterns during AI-assisted coding. Add the following to your project's .claude/settings.json:
{
"hooks": {
"PostToolUse": [
{
"matcher": "Write|Edit|MultiEdit",
"hooks": [
{
"type": "command",
"command": "slopwatch analyze -d . --hook",
"timeout": 60000
}
]
}
]
}
}The --hook flag enables Claude Code integration mode which:
-
Uses
git statusto only analyze dirty files - makes hooks near-instant even on large repos - Outputs errors to stderr in a readable format
- Suppresses all other output
- Blocks on warnings and errors
- Exits with code 2 on failure (blocking the edit)
Claude will see the formatted error message and can then fix the issue properly.
Note: Hook mode requires git. If git is unavailable, it falls back to full analysis.
- name: Install Slopwatch
run: dotnet tool install --global Slopwatch.Cmd
- name: Run Slopwatch
run: slopwatch analyze -d . --output json --fail-on errorNote: The baseline file (.slopwatch/baseline.json) should be committed to your repository. Run slopwatch init locally first.
- task: DotNetCoreCLI@2
displayName: 'Install Slopwatch'
inputs:
command: 'custom'
custom: 'tool'
arguments: 'install --global Slopwatch.Cmd'
- script: slopwatch analyze -d . --fail-on error
displayName: 'Run Slopwatch'Create a .slopwatch/slopwatch.json configuration file to customize behavior:
{
"minSeverity": "warning",
"rules": {
"SW001": { "enabled": true, "severity": "error" },
"SW002": { "enabled": true, "severity": "warning" },
"SW003": { "enabled": true, "severity": "error" },
"SW004": { "enabled": true, "severity": "warning" },
"SW005": { "enabled": true, "severity": "warning" },
"SW006": { "enabled": true, "severity": "warning" }
},
"exclude": ["**/Generated/**", "**/obj/**", "**/bin/**"]
}Use the -c or --config option to specify a custom configuration file location:
slopwatch analyze -d . --config path/to/config.jsondotnet build
dotnet test
dotnet pack- Fork and create a feature branch
- Make changes and add tests
- Submit a pull request
Note: This project uses slopwatch on itself - your PR will be analyzed for slop patterns!
Apache 2.0 - see LICENSE for details.
- Slopometry - Python equivalent for Claude Code
- Incrementalist - Git diff analysis patterns
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for dotnet-slopwatch
Similar Open Source Tools

dotnet-slopwatch
Slopwatch is a .NET tool designed to detect LLM 'reward hacking' behaviors in code changes. It runs as a Claude Code hook or in CI/CD pipelines to catch when AI coding assistants take shortcuts instead of properly fixing issues. Slopwatch identifies patterns such as disabling tests, suppressing warnings, swallowing exceptions, adding delays, project-level warning suppression, and bypassing central package management. By analyzing code changes, Slopwatch helps prevent these shortcuts from making it into the codebase, ensuring code quality and adherence to best practices.
lumen
Lumen is a command-line tool that leverages AI to enhance your git workflow. It assists in generating commit messages, understanding changes, interactive searching, and analyzing impacts without the need for an API key. With smart commit messages, git history insights, interactive search, change analysis, and rich markdown output, Lumen offers a seamless and flexible experience for users across various git workflows.
open-edison
OpenEdison is a secure MCP control panel that connects AI to data/software with additional security controls to reduce data exfiltration risks. It helps address the lethal trifecta problem by providing visibility, monitoring potential threats, and alerting on data interactions. The tool offers features like data leak monitoring, controlled execution, easy configuration, visibility into agent interactions, a simple API, and Docker support. It integrates with LangGraph, LangChain, and plain Python agents for observability and policy enforcement. OpenEdison helps gain observability, control, and policy enforcement for AI interactions with systems of records, existing company software, and data to reduce risks of AI-caused data leakage.
sonarqube-mcp-server
The SonarQube MCP Server is a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server that enables seamless integration with SonarQube Server or Cloud for code quality and security. It supports the analysis of code snippets directly within the agent context. The server provides various tools for analyzing code, managing issues, accessing metrics, and interacting with SonarQube projects. It also supports advanced features like dependency risk analysis, enterprise portfolio management, and system health checks. The server can be configured for different transport modes, proxy settings, and custom certificates. Telemetry data collection can be disabled if needed.
aiavatarkit
AIAvatarKit is a tool for building AI-based conversational avatars quickly. It supports various platforms like VRChat and cluster, along with real-world devices. The tool is extensible, allowing unlimited capabilities based on user needs. It requires VOICEVOX API, Google or Azure Speech Services API keys, and Python 3.10. Users can start conversations out of the box and enjoy seamless interactions with the avatars.
instructor
Instructor is a popular Python library for managing structured outputs from large language models (LLMs). It offers a user-friendly API for validation, retries, and streaming responses. With support for various LLM providers and multiple languages, Instructor simplifies working with LLM outputs. The library includes features like response models, retry management, validation, streaming support, and flexible backends. It also provides hooks for logging and monitoring LLM interactions, and supports integration with Anthropic, Cohere, Gemini, Litellm, and Google AI models. Instructor facilitates tasks such as extracting user data from natural language, creating fine-tuned models, managing uploaded files, and monitoring usage of OpenAI models.

mcp
Semgrep MCP Server is a beta server under active development for using Semgrep to scan code for security vulnerabilities. It provides a Model Context Protocol (MCP) for various coding tools to get specialized help in tasks. Users can connect to Semgrep AppSec Platform, scan code for vulnerabilities, customize Semgrep rules, analyze and filter scan results, and compare results. The tool is published on PyPI as semgrep-mcp and can be installed using pip, pipx, uv, poetry, or other methods. It supports CLI and Docker environments for running the server. Integration with VS Code is also available for quick installation. The project welcomes contributions and is inspired by core technologies like Semgrep and MCP, as well as related community projects and tools.
langchainrb
Langchain.rb is a Ruby library that makes it easy to build LLM-powered applications. It provides a unified interface to a variety of LLMs, vector search databases, and other tools, making it easy to build and deploy RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation) systems and assistants. Langchain.rb is open source and available under the MIT License.
gitleaks
Gitleaks is a tool for detecting secrets like passwords, API keys, and tokens in git repos, files, and whatever else you wanna throw at it via stdin. It can be installed using Homebrew, Docker, or Go, and is available in binary form for many popular platforms and OS types. Gitleaks can be implemented as a pre-commit hook directly in your repo or as a GitHub action. It offers scanning modes for git repositories, directories, and stdin, and allows creating baselines for ignoring old findings. Gitleaks also provides configuration options for custom secret detection rules and supports features like decoding encoded text and generating reports in various formats.
swarmzero
SwarmZero SDK is a library that simplifies the creation and execution of AI Agents and Swarms of Agents. It supports various LLM Providers such as OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, Anthropic, MistralAI, Gemini, Nebius, and Ollama. Users can easily install the library using pip or poetry, set up the environment and configuration, create and run Agents, collaborate with Swarms, add tools for complex tasks, and utilize retriever tools for semantic information retrieval. Sample prompts are provided to help users explore the capabilities of the agents and swarms. The SDK also includes detailed examples and documentation for reference.
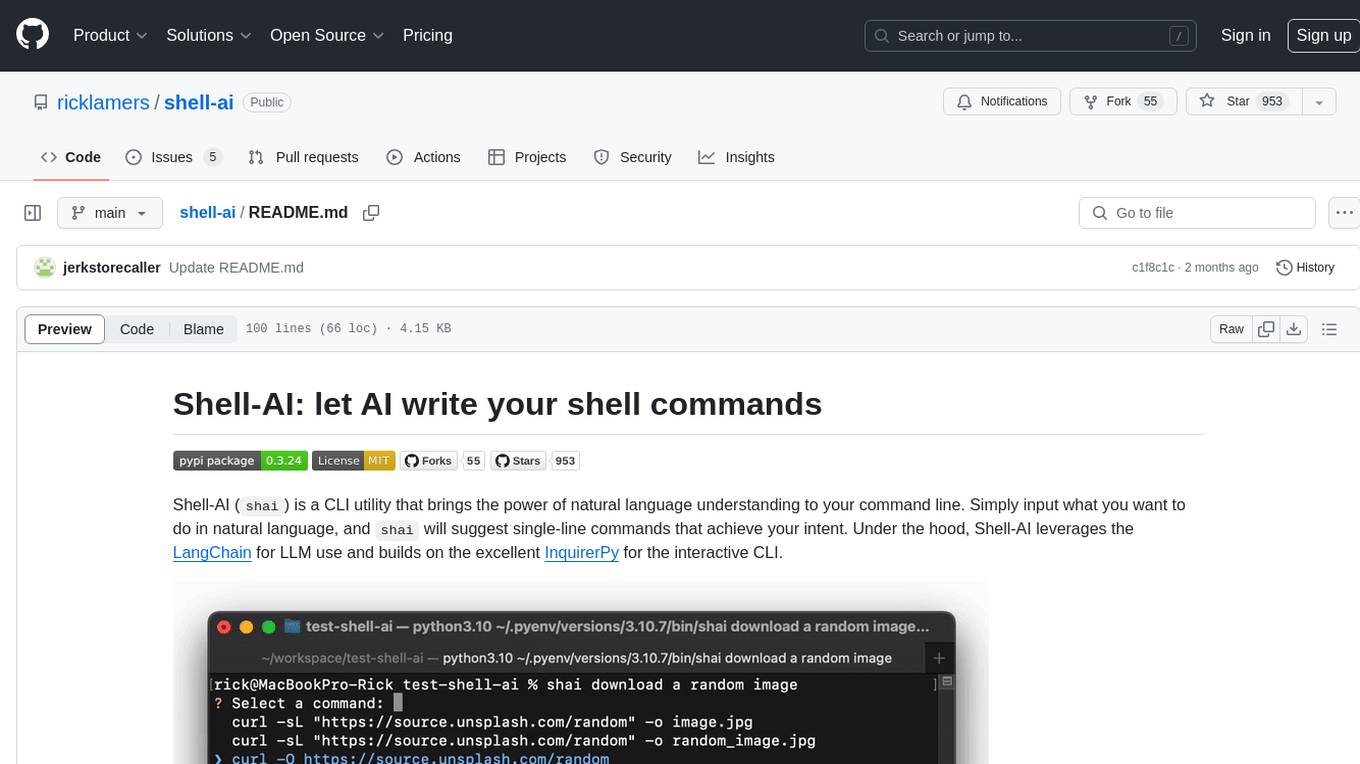
shell-ai
Shell-AI (`shai`) is a CLI utility that enables users to input commands in natural language and receive single-line command suggestions. It leverages natural language understanding and interactive CLI tools to enhance command line interactions. Users can describe tasks in plain English and receive corresponding command suggestions, making it easier to execute commands efficiently. Shell-AI supports cross-platform usage and is compatible with Azure OpenAI deployments, offering a user-friendly and efficient way to interact with the command line.
json-repair
JSON Repair is a toolkit designed to address JSON anomalies that can arise from Large Language Models (LLMs). It offers a comprehensive solution for repairing JSON strings, ensuring accuracy and reliability in your data processing. With its user-friendly interface and extensive capabilities, JSON Repair empowers developers to seamlessly integrate JSON repair into their workflows.
flapi
flAPI is a powerful service that automatically generates read-only APIs for datasets by utilizing SQL templates. Built on top of DuckDB, it offers features like automatic API generation, support for Model Context Protocol (MCP), connecting to multiple data sources, caching, security implementation, and easy deployment. The tool allows users to create APIs without coding and enables the creation of AI tools alongside REST endpoints using SQL templates. It supports unified configuration for REST endpoints and MCP tools/resources, concurrent servers for REST API and MCP server, and automatic tool discovery. The tool also provides DuckLake-backed caching for modern, snapshot-based caching with features like full refresh, incremental sync, retention, compaction, and audit logs.
ruby_llm-monitoring
RubyLLM::Monitoring is a tool designed to monitor the LLM (Live-Link Monitoring) usage within a Rails application. It provides a dashboard to display metrics such as Throughput, Cost, Response Time, and Error Rate. Users can customize the displayed metrics and add their own custom metrics. The tool also supports setting up alerts based on predefined conditions, such as monitoring cost and errors. Authentication and authorization are left to the user, allowing for flexibility in securing the monitoring dashboard. Overall, RubyLLM::Monitoring aims to provide a comprehensive solution for monitoring and analyzing the performance of a Rails application.
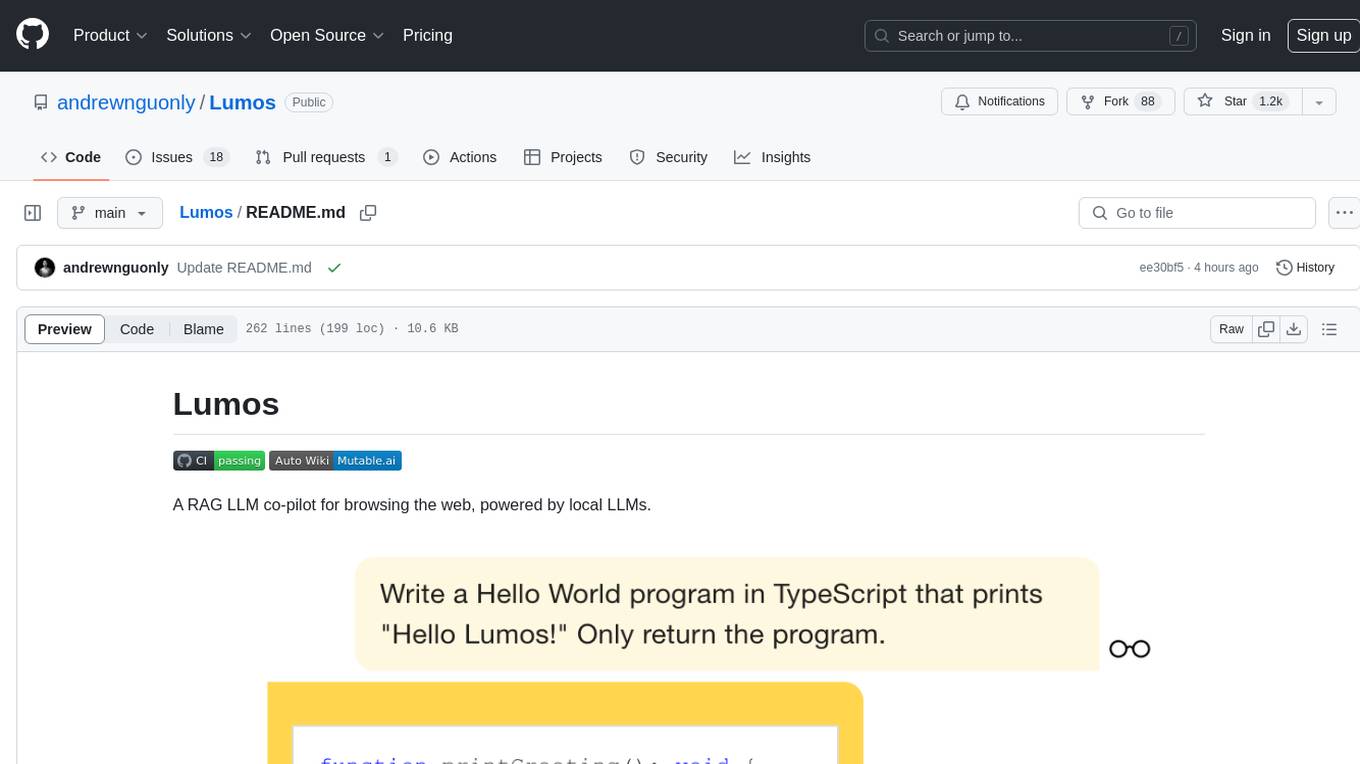
Lumos
Lumos is a Chrome extension powered by a local LLM co-pilot for browsing the web. It allows users to summarize long threads, news articles, and technical documentation. Users can ask questions about reviews and product pages. The tool requires a local Ollama server for LLM inference and embedding database. Lumos supports multimodal models and file attachments for processing text and image content. It also provides options to customize models, hosts, and content parsers. The extension can be easily accessed through keyboard shortcuts and offers tools for automatic invocation based on prompts.
claude-task-master
Claude Task Master is a task management system designed for AI-driven development with Claude, seamlessly integrating with Cursor AI. It allows users to configure tasks through environment variables, parse PRD documents, generate structured tasks with dependencies and priorities, and manage task status. The tool supports task expansion, complexity analysis, and smart task recommendations. Users can interact with the system through CLI commands for task discovery, implementation, verification, and completion. It offers features like task breakdown, dependency management, and AI-driven task generation, providing a structured workflow for efficient development.
For similar tasks

gemini-ai-code-reviewer
Gemini AI Code Reviewer is a GitHub Action that automatically reviews pull requests using Google's Gemini AI. It analyzes code changes, consults the Gemini model, provides feedback, and delivers review comments directly to pull requests on GitHub. Users need a Gemini API key and can trigger the workflow by commenting '/gemini-review' in the PR. The tool helps improve source code quality by giving suggestions and comments for enhancement.
CR-Mentor
CR-Mentor is a project that leverages Knowledge Base + LLM to improve development efficiency in Code Review. It provides comprehensive code context understanding, customizable code standards, global code analysis, and risk code identification. The tool aims to enhance code review processes by automating tracking of related files, supporting custom code review standards, generating comprehensive review reports, and identifying potentially risky changes with improvement suggestions.

dotnet-slopwatch
Slopwatch is a .NET tool designed to detect LLM 'reward hacking' behaviors in code changes. It runs as a Claude Code hook or in CI/CD pipelines to catch when AI coding assistants take shortcuts instead of properly fixing issues. Slopwatch identifies patterns such as disabling tests, suppressing warnings, swallowing exceptions, adding delays, project-level warning suppression, and bypassing central package management. By analyzing code changes, Slopwatch helps prevent these shortcuts from making it into the codebase, ensuring code quality and adherence to best practices.
code-review-gpt
Code Review GPT uses Large Language Models to review code in your CI/CD pipeline. It helps streamline the code review process by providing feedback on code that may have issues or areas for improvement. It should pick up on common issues such as exposed secrets, slow or inefficient code, and unreadable code. It can also be run locally in your command line to review staged files. Code Review GPT is in alpha and should be used for fun only. It may provide useful feedback but please check any suggestions thoroughly.
digma
Digma is a Continuous Feedback platform that provides code-level insights related to performance, errors, and usage during development. It empowers developers to own their code all the way to production, improving code quality and preventing critical issues. Digma integrates with OpenTelemetry traces and metrics to generate insights in the IDE, helping developers analyze code scalability, bottlenecks, errors, and usage patterns.
ai-codereviewer
AI Code Reviewer is a GitHub Action that utilizes OpenAI's GPT-4 API to provide intelligent feedback and suggestions on pull requests. It helps enhance code quality and streamline the code review process by offering insightful comments and filtering out specified files. The tool is easy to set up and integrate into GitHub workflows.
sourcery
Sourcery is an automated code reviewer tool that provides instant feedback on pull requests, helping to speed up the code review process, improve code quality, and accelerate development velocity. It offers high-level feedback, line-by-line suggestions, and aims to mimic the type of code review one would expect from a colleague. Sourcery can also be used as an IDE coding assistant to understand existing code, add unit tests, optimize code, and improve code quality with instant suggestions. It is free for public repos/open source projects and offers a 14-day trial for private repos.
RTL-Coder
RTL-Coder is a tool designed to outperform GPT-3.5 in RTL code generation by providing a fully open-source dataset and a lightweight solution. It targets Verilog code generation and offers an automated flow to generate a large labeled dataset with over 27,000 diverse Verilog design problems and answers. The tool addresses the data availability challenge in IC design-related tasks and can be used for various applications beyond LLMs. The tool includes four RTL code generation models available on the HuggingFace platform, each with specific features and performance characteristics. Additionally, RTL-Coder introduces a new LLM training scheme based on code quality feedback to further enhance model performance and reduce GPU memory consumption.
For similar jobs

sourcegraph
Sourcegraph is a code search and navigation tool that helps developers read, write, and fix code in large, complex codebases. It provides features such as code search across all repositories and branches, code intelligence for navigation and refactoring, and the ability to fix and refactor code across multiple repositories at once.
pr-agent
PR-Agent is a tool that helps to efficiently review and handle pull requests by providing AI feedbacks and suggestions. It supports various commands such as generating PR descriptions, providing code suggestions, answering questions about the PR, and updating the CHANGELOG.md file. PR-Agent can be used via CLI, GitHub Action, GitHub App, Docker, and supports multiple git providers and models. It emphasizes real-life practical usage, with each tool having a single GPT-4 call for quick and affordable responses. The PR Compression strategy enables effective handling of both short and long PRs, while the JSON prompting strategy allows for modular and customizable tools. PR-Agent Pro, the hosted version by CodiumAI, provides additional benefits such as full management, improved privacy, priority support, and extra features.

code-review-gpt
Code Review GPT uses Large Language Models to review code in your CI/CD pipeline. It helps streamline the code review process by providing feedback on code that may have issues or areas for improvement. It should pick up on common issues such as exposed secrets, slow or inefficient code, and unreadable code. It can also be run locally in your command line to review staged files. Code Review GPT is in alpha and should be used for fun only. It may provide useful feedback but please check any suggestions thoroughly.
DevoxxGenieIDEAPlugin
Devoxx Genie is a Java-based IntelliJ IDEA plugin that integrates with local and cloud-based LLM providers to aid in reviewing, testing, and explaining project code. It supports features like code highlighting, chat conversations, and adding files/code snippets to context. Users can modify REST endpoints and LLM parameters in settings, including support for cloud-based LLMs. The plugin requires IntelliJ version 2023.3.4 and JDK 17. Building and publishing the plugin is done using Gradle tasks. Users can select an LLM provider, choose code, and use commands like review, explain, or generate unit tests for code analysis.
code2prompt
code2prompt is a command-line tool that converts your codebase into a single LLM prompt with a source tree, prompt templating, and token counting. It automates generating LLM prompts from codebases of any size, customizing prompt generation with Handlebars templates, respecting .gitignore, filtering and excluding files using glob patterns, displaying token count, including Git diff output, copying prompt to clipboard, saving prompt to an output file, excluding files and folders, adding line numbers to source code blocks, and more. It helps streamline the process of creating LLM prompts for code analysis, generation, and other tasks.

ai-codereviewer
AI Code Reviewer is a GitHub Action that utilizes OpenAI's GPT-4 API to provide intelligent feedback and suggestions on pull requests. It helps enhance code quality and streamline the code review process by offering insightful comments and filtering out specified files. The tool is easy to set up and integrate into GitHub workflows.
github-pr-summary
github-pr-summary is a bot designed to summarize GitHub Pull Requests, helping open source contributors make faster decisions. It automatically summarizes commits and changed files in PRs, triggered by new commits or a magic trigger phrase. Users can deploy their own code review bot in 3 steps: create a bot from their GitHub repo, configure it to review PRs, and connect to GitHub for access to the target repo. The bot runs on flows.network using Rust and WasmEdge Runtimes. It utilizes ChatGPT/4 to review and summarize PR content, posting the result back as a comment on the PR. The bot can be used on multiple repos by creating new flows and importing the source code repo, specifying the target repo using flow config. Users can also change the magic phrase to trigger a review from a PR comment.
fittencode.nvim
Fitten Code AI Programming Assistant for Neovim provides fast completion using AI, asynchronous I/O, and support for various actions like document code, edit code, explain code, find bugs, generate unit test, implement features, optimize code, refactor code, start chat, and more. It offers features like accepting suggestions with Tab, accepting line with Ctrl + Down, accepting word with Ctrl + Right, undoing accepted text, automatic scrolling, and multiple HTTP/REST backends. It can run as a coc.nvim source or nvim-cmp source.


