
friendly-stable-audio-tools
Refactored / updated version of `stable-audio-tools` which is an open-source code for audio/music generative models originally by Stability AI.
Stars: 63
This repository is a refactored and updated version of `stable-audio-tools`, an open-source code for audio/music generative models originally by Stability AI. It contains refactored codes for improved readability and usability, useful scripts for evaluating and playing with trained models, and instructions on how to train models such as `Stable Audio 2.0`. The repository does not contain any pretrained checkpoints. Requirements include PyTorch 2.0 or later for Flash Attention support and Python 3.8.10 or later for development. The repository provides guidance on installing, building a training environment using Docker or Singularity, logging with Weights & Biases, training configurations, and stages for VAE-GAN and Diffusion Transformer (DiT) training.
README:
This repository is a refactored / updated version of stable-audio-tools
which is an open-source code for audio/music generative models
originally by Stability AI.
This repository contains the following additional features:
- 🔥 Refactored codes of
stable-audio-toolsfor improved readability and usability. - 🔥 Useful scripts for evaluating and playing with your own trained models.
- 🔥 Instruction on how to train models such as
Stable Audio 2.0.
and does NOT contain:
- Any pretrained checkpoints
- PyTorch 2.0 or later for Flash Attention support
- Development for the repo is done in Python 3.8.10 or later
To run the training scripts or inference code, you'll need to clone this repository, navigate to the root directory, and then execute the pip command as follow:
$ git clone https://github.com/yukara-ikemiya/friendly-stable-audio-tools.git
$ cd friendly-stable-audio-tools
$ pip install .
$ # you may need to execute this to avoid Accelerate import error
$ pip uninstall -y transformer-engineTo simplify setting up the training environment, I recommend to use container systems like Docker or Singularity instead of installing dependencies on each GPU machine. Below are the steps for creating Docker and Singularity containers.
All example scripts are stored at the container folder.
Please be sure that Docker and Singularity are installed in advance.
$ # create a Docker image
$ NAME=friendly-stable-audio-tools
$ docker build -t ${NAME} -f ./container/${NAME}.Dockerfile .$ # convert a Docker image to a Singularity container
$ singularity build friendly-stable-audio-tools.sif docker-daemon://friendly-stable-audio-toolsBy running the above script, friendly-stable-audio-tools.sif should be created in the working directory.
The training code also requires a Weights & Biases account to log the training outputs and demos. Create an account and log in with:
$ wandb loginOr you can also pass an API key as an environment variable WANDB_API_KEY.
(You can obtain the API key from https://wandb.ai/authorize after logging in to your account.)
$ WANDB_API_KEY="12345x6789y..."This method is convenient when you want to execute the code using containers such as Docker or Singularity.
Before starting your training run, you have to prepare the following two configuration files.
- model config file
- dataset config file
For more information about those, refer to the Configuration section below.
To start a training run, run the train.py script in the repo root with:
$ python3 train.py --dataset-config /path/to/dataset/config --model-config /path/to/model/config --name my_experimentThe --name parameter will set the project name for your Weights and Biases run.
Fine-tuning involves resuming a training run from a pre-trained checkpoint.
- To resume training from a wrapped checkpoint, you can pass in the checkpoint path (.ckpt) to
train.pywith the--ckpt-pathflag. - To start fresh training from a pre-trained unwrapped model, you can pass in the unwrapped checkpoint path (.ckpt) to
train.pywith the--pretrained-ckpt-pathflag.
stable-audio-tools uses PyTorch Lightning to facilitate multi-GPU and multi-node training.
When a model is being trained, it is wrapped in a "training wrapper", which is a pl.LightningModule that contains all of the relevant objects needed only for training. That includes things like discriminators for autoencoders, EMA copies of models, and all of the optimizer states.
The checkpoint files created during training include this training wrapper, which greatly increases the size of the checkpoint file.
unwrap_model.py takes in a wrapped model checkpoint and save a new checkpoint file including only the model itself.
That can be run with from the repo root with:
$ python3 unwrap_model.py --model-config /path/to/model/config --ckpt-path /path/to/wrapped/ckpt.ckpt --name /new/path/to/new_ckpt_nameUnwrapped model checkpoints are required for:
- Inference scripts
- Using a model as a pretransform for another model (e.g. using an autoencoder model for latent diffusion)
- Fine-tuning a pre-trained model with a modified configuration (i.e. partial initialization)
Training and inference code for stable-audio-tools is based around JSON configuration files that define model hyperparameters, training settings, and information about your training dataset.
The model config file defines all of the information needed to load a model for training or inference. It also contains the training configuration needed to fine-tune a model or train from scratch.
The following properties are defined in the top level of the model configuration:
-
model_type- The type of model being defined, currently limited to one of
"autoencoder", "diffusion_uncond", "diffusion_cond", "diffusion_cond_inpaint", "diffusion_autoencoder", "lm".
- The type of model being defined, currently limited to one of
-
sample_size- The length of the audio provided to the model during training, in samples. For diffusion models, this is also the raw audio sample length used for inference.
-
sample_rate- The sample rate of the audio provided to the model during training, and generated during inference, in Hz.
-
audio_channels- The number of channels of audio provided to the model during training, and generated during inference. Defaults to 2. Set to 1 for mono.
-
model- The specific configuration for the model being defined, varies based on
model_type
- The specific configuration for the model being defined, varies based on
-
training- The training configuration for the model, varies based on
model_type. Provides parameters for training as well as demos.
- The training configuration for the model, varies based on
stable-audio-tools currently supports two kinds of data sources: local directories of audio files, and WebDataset datasets stored in Amazon S3. More information can be found in the dataset config documentation
Additional optional flags for train.py include:
-
--config-file- The path to the defaults.ini file in the repo root, required if running
train.pyfrom a directory other than the repo root
- The path to the defaults.ini file in the repo root, required if running
-
--pretransform-ckpt-path- Used in various model types such as latent diffusion models to load a pre-trained autoencoder. Requires an unwrapped model checkpoint.
-
--save-dir- The directory in which to save the model checkpoints
-
--checkpoint-every- The number of steps between saved checkpoints.
- Default: 10000
-
--batch-size- Number of samples per-GPU during training. Should be set as large as your GPU VRAM will allow.
- Default: 8
-
--num-gpus- Number of GPUs per-node to use for training
- Default: 1
-
--num-nodes- Number of GPU nodes being used for training
- Default: 1
-
--accum-batches- Enables and sets the number of batches for gradient batch accumulation. Useful for increasing effective batch size when training on smaller GPUs.
-
--strategy- Multi-GPU strategy for distributed training. Setting to
deepspeedwill enable DeepSpeed ZeRO Stage 2. -
Default:
ddpif--num_gpus> 1, else None
- Multi-GPU strategy for distributed training. Setting to
-
--precision- floating-point precision to use during training
- Default: 16
-
--num-workers- Number of CPU workers used by the data loader
-
--seed- RNG seed for PyTorch, helps with deterministic training
To use CLAP encoder for conditioning music generation, you have to prepare a pretrained checkpoint file of CLAP.
- Download a pretrained CLAP checkpoint trained with music dataset (
music_audioset_epoch_15_esc_90.14.pt) from the LAION CLAP repository. - Store the checkpoint file to a directory of your choice.
- Edit a
model configfile of Stable Audio 2.0 as follows
= stable_audio_2_0.json =
...
"model": {
...
"conditioning": {
"configs": [
{
...
"config": {
...
"clap_ckpt_path": "ckpt/clap/music_audioset_epoch_15_esc_90.14.pt",
...Since Stable Audio uses text prompts as condition for music generation, you have to prepare them as metadata in addition to audio data.
When using a dataset in a local environment, I support the use of metadata in JSON format as follows.
- You can include any information as metadata in a JSON file, but you must always include the text data named
promptrequired for training of Stable Audio.
= music_2.json =
{
"prompt": "This is an electronic song sending positive vibes."
}
- The metadata files must be placed in the same directory as corresponding audio files. And the file names must also be the same.
.
└── dataset/
├── music_1.wav
├── music_1.json
├── music_2.wav
├── music_2.json
└── ...
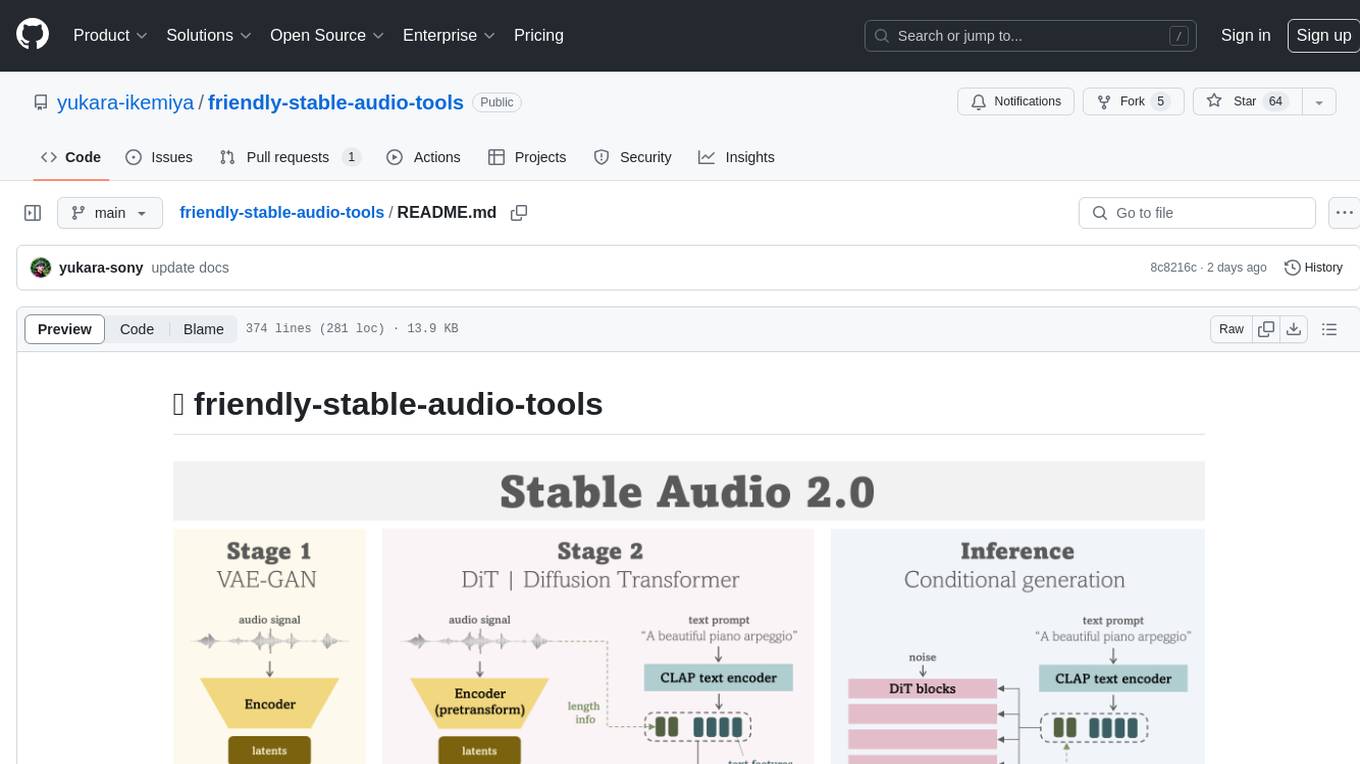
As the 1st stage of Stable Audio 2.0, you'll train a VAE-GAN which is a compression model for audio signal.
The model config file for a VAE-GAN is place in the configs directory. Regarding dataset configuration, please prepare a dataset config file corresponding to your own datasets.
Once you prepare configuration files, you can execute a training job like this:
CONTAINER_PATH="/path/to/sif/friendly-stable-audio-tools.sif"
ROOT_DIR="/path/to/friendly-stable-audio-tools/"
DATASET_DIR="/path/to/your/dataset/"
OUTPUT_DIR="/path/to/output/directory/"
MODEL_CONFIG="stable_audio_tools/configs/model_configs/autoencoders/stable_audio_2_0_vae.json"
DATASET_CONFIG="stable_audio_tools/configs/dataset_configs/local_training_example.json"
BATCH_SIZE=10 # WARNING : This is batch size per GPU
WANDB_API_KEY="12345x6789y..."
PORT=12345
# Singularity container case
# NOTE: Please change each configuration as you like
singularity exec --nv --pwd $ROOT_DIR -B $ROOT_DIR -B $DATASET_DIR \
--env WANDB_API_KEY=$WANDB_API_KEY \
${CONTAINER_PATH} \
torchrun --nproc_per_node gpu --master_port ${PORT} \
${ROOT_DIR}/train.py \
--dataset-config ${DATASET_CONFIG} \
--model-config ${MODEL_CONFIG} \
--name "vae_training" \
--num-gpus 8 \
--batch-size ${BATCH_SIZE} \
--num-workers 8 \
--save-dir ${OUTPUT_DIR}As described in the unwrapping-a-model section, after completing the training of VAE, you need to unwrap the model checkpoint for using the next stage training.
CKPT_PATH="/path/to/wrapped_ckpt/last.ckpt"
# NOTE: file extension ".ckpt" will be automatically added to the end of OUTPOUT_DIR name
OUTPUT_PATH="/path/to/output_name/unwrapped_last"
singularity exec --nv --pwd $ROOT_DIR -B $ROOT_DIR \
--env WANDB_API_KEY=$WANDB_API_KEY \
${CONTAINER_PATH} \
torchrun --nproc_per_node gpu --master_port ${PORT} \
${ROOT_DIR}/unwrap_model.py \
--model-config ${MODEL_CONFIG} \
--ckpt-path ${CKPT_PATH} \
--name ${OUTPUT_PATH}Once you finished the VAE training, you might want to test and evaluate reconstruction quality of the trained model.
I support reconstruction of audio files in a directory with reconstruct_audios.py,
and you can use the reconstructed audios for your evaluation.
AUDIO_DIR="/path/to/original_audio/"
OUTPUT_DIR="/path/to/output_audio/"
FRAME_DURATION=1.0 # [sec]
OVERLAP_RATE=0.01
BATCH_SIZE=50
singularity exec --nv --pwd $ROOT_DIR -B $ROOT_DIR -B $DATASET_DIR \
--env WANDB_API_KEY=$WANDB_API_KEY \
${CONTAINER_PATH} \
torchrun --nproc_per_node gpu --master_port ${PORT} \
${ROOT_DIR}/reconstruct_audios.py \
--model-config ${MODEL_CONFIG} \
--ckpt-path ${UNWRAP_CKPT_PATH} \
--audio-dir ${AUDIO_DIR} \
--output-dir ${OUTPUT_DIR} \
--frame-duration ${FRAME_DURATION} \
--overlap-rate ${OVERLAP_RATE} \
--batch-size ${BATCH_SIZE}As the 2nd stage of Stable Audio 2.0, you'll train a DiT which is a generative model in latent domain.
Before this part, please make sure that
- you have met all of the prerequisites
- you have trained the VAE model and created an unwrapped checkpoints file (See the VAE section.)
Now, you can train a DiT model as follows:
CONTAINER_PATH="/path/to/sif/friendly-stable-audio-tools.sif"
ROOT_DIR="/path/to/friendly-stable-audio-tools/"
DATASET_DIR="/path/to/your/dataset/"
OUTPUT_DIR="/path/to/output/directory/"
MODEL_CONFIG="stable_audio_tools/configs/model_configs/txt2audio/stable_audio_2_0.json"
DATASET_CONFIG="stable_audio_tools/configs/dataset_configs/local_training_example.json"
# Pretrained checkpoint of VAE (Stage-1) model
PRETRANSFORM_CKPT="/path/to/vae_ckpt/unwrapped_last.ckpt"
BATCH_SIZE=10 # WARNING : This is batch size per GPU
WANDB_API_KEY="12345x6789y..."
PORT=12345
singularity exec --nv --pwd $ROOT_DIR -B $ROOT_DIR -B $DATASET_DIR \
--env WANDB_API_KEY=$WANDB_API_KEY \
${CONTAINER_PATH} \
torchrun --nproc_per_node gpu --master_port ${PORT} \
${ROOT_DIR}/train.py \
--dataset-config ${DATASET_CONFIG} \
--model-config ${MODEL_CONFIG} \
--pretransform-ckpt-path ${PRETRANSFORM_CKPT} \
--name "dit_training" \
--num-gpus ${NUM_GPUS} \
--batch-size ${BATCH_SIZE} \
--save-dir ${OUTPUT_DIR}- [ ] Add convenient scripts for sampling
- [ ] Add documentation for Gradio interface
- [ ] Add troubleshooting section
- [ ] Add contribution guidelines
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for friendly-stable-audio-tools
Similar Open Source Tools

friendly-stable-audio-tools
This repository is a refactored and updated version of `stable-audio-tools`, an open-source code for audio/music generative models originally by Stability AI. It contains refactored codes for improved readability and usability, useful scripts for evaluating and playing with trained models, and instructions on how to train models such as `Stable Audio 2.0`. The repository does not contain any pretrained checkpoints. Requirements include PyTorch 2.0 or later for Flash Attention support and Python 3.8.10 or later for development. The repository provides guidance on installing, building a training environment using Docker or Singularity, logging with Weights & Biases, training configurations, and stages for VAE-GAN and Diffusion Transformer (DiT) training.
paxml
Pax is a framework to configure and run machine learning experiments on top of Jax.

raglite
RAGLite is a Python toolkit for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) with PostgreSQL or SQLite. It offers configurable options for choosing LLM providers, database types, and rerankers. The toolkit is fast and permissive, utilizing lightweight dependencies and hardware acceleration. RAGLite provides features like PDF to Markdown conversion, multi-vector chunk embedding, optimal semantic chunking, hybrid search capabilities, adaptive retrieval, and improved output quality. It is extensible with a built-in Model Context Protocol server, customizable ChatGPT-like frontend, document conversion to Markdown, and evaluation tools. Users can configure RAGLite for various tasks like configuring, inserting documents, running RAG pipelines, computing query adapters, evaluating performance, running MCP servers, and serving frontends.

shellChatGPT
ShellChatGPT is a shell wrapper for OpenAI's ChatGPT, DALL-E, Whisper, and TTS, featuring integration with LocalAI, Ollama, Gemini, Mistral, Groq, and GitHub Models. It provides text and chat completions, vision, reasoning, and audio models, voice-in and voice-out chatting mode, text editor interface, markdown rendering support, session management, instruction prompt manager, integration with various service providers, command line completion, file picker dialogs, color scheme personalization, stdin and text file input support, and compatibility with Linux, FreeBSD, MacOS, and Termux for a responsive experience.
chatgpt-cli
ChatGPT CLI provides a powerful command-line interface for seamless interaction with ChatGPT models via OpenAI and Azure. It features streaming capabilities, extensive configuration options, and supports various modes like streaming, query, and interactive mode. Users can manage thread-based context, sliding window history, and provide custom context from any source. The CLI also offers model and thread listing, advanced configuration options, and supports GPT-4, GPT-3.5-turbo, and Perplexity's models. Installation is available via Homebrew or direct download, and users can configure settings through default values, a config.yaml file, or environment variables.
llama_index
LlamaIndex is a data framework for building LLM applications. It provides tools for ingesting, structuring, and querying data, as well as integrating with LLMs and other tools. LlamaIndex is designed to be easy to use for both beginner and advanced users, and it provides a comprehensive set of features for building LLM applications.
aidermacs
Aidermacs is an AI pair programming tool for Emacs that integrates Aider, a powerful open-source AI pair programming tool. It provides top performance on the SWE Bench, support for multi-file edits, real-time file synchronization, and broad language support. Aidermacs delivers an Emacs-centric experience with features like intelligent model selection, flexible terminal backend support, smarter syntax highlighting, enhanced file management, and streamlined transient menus. It thrives on community involvement, encouraging contributions, issue reporting, idea sharing, and documentation improvement.
co-llm
Co-LLM (Collaborative Language Models) is a tool for learning to decode collaboratively with multiple language models. It provides a method for data processing, training, and inference using a collaborative approach. The tool involves steps such as formatting/tokenization, scoring logits, initializing Z vector, deferral training, and generating results using multiple models. Co-LLM supports training with different collaboration pairs and provides baseline training scripts for various models. In inference, it uses 'vllm' services to orchestrate models and generate results through API-like services. The tool is inspired by allenai/open-instruct and aims to improve decoding performance through collaborative learning.
llm-vscode
llm-vscode is an extension designed for all things LLM, utilizing llm-ls as its backend. It offers features such as code completion with 'ghost-text' suggestions, the ability to choose models for code generation via HTTP requests, ensuring prompt size fits within the context window, and code attribution checks. Users can configure the backend, suggestion behavior, keybindings, llm-ls settings, and tokenization options. Additionally, the extension supports testing models like Code Llama 13B, Phind/Phind-CodeLlama-34B-v2, and WizardLM/WizardCoder-Python-34B-V1.0. Development involves cloning llm-ls, building it, and setting up the llm-vscode extension for use.
ChatSim
ChatSim is a tool designed for editable scene simulation for autonomous driving via LLM-Agent collaboration. It provides functionalities for setting up the environment, installing necessary dependencies like McNeRF and Inpainting tools, and preparing data for simulation. Users can train models, simulate scenes, and track trajectories for smoother and more realistic results. The tool integrates with Blender software and offers options for training McNeRF models and McLight's skydome estimation network. It also includes a trajectory tracking module for improved trajectory tracking. ChatSim aims to facilitate the simulation of autonomous driving scenarios with collaborative LLM-Agents.
ethereum-etl-airflow
This repository contains Airflow DAGs for extracting, transforming, and loading (ETL) data from the Ethereum blockchain into BigQuery. The DAGs use the Google Cloud Platform (GCP) services, including BigQuery, Cloud Storage, and Cloud Composer, to automate the ETL process. The repository also includes scripts for setting up the GCP environment and running the DAGs locally.

Fabric
Fabric is an open-source framework designed to augment humans using AI by organizing prompts by real-world tasks. It addresses the integration problem of AI by creating and organizing prompts for various tasks. Users can create, collect, and organize AI solutions in a single place for use in their favorite tools. Fabric also serves as a command-line interface for those focused on the terminal. It offers a wide range of features and capabilities, including support for multiple AI providers, internationalization, speech-to-text, AI reasoning, model management, web search, text-to-speech, desktop notifications, and more. The project aims to help humans flourish by leveraging AI technology to solve human problems and enhance creativity.
Agentless
Agentless is an open-source tool designed for automatically solving software development problems. It follows a two-phase process of localization and repair to identify faults in specific files, classes, and functions, and generate candidate patches for fixing issues. The tool is aimed at simplifying the software development process by automating issue resolution and patch generation.
ML-Bench
ML-Bench is a tool designed to evaluate large language models and agents for machine learning tasks on repository-level code. It provides functionalities for data preparation, environment setup, usage, API calling, open source model fine-tuning, and inference. Users can clone the repository, load datasets, run ML-LLM-Bench, prepare data, fine-tune models, and perform inference tasks. The tool aims to facilitate the evaluation of language models and agents in the context of machine learning tasks on code repositories.
vector-inference
This repository provides an easy-to-use solution for running inference servers on Slurm-managed computing clusters using vLLM. All scripts in this repository run natively on the Vector Institute cluster environment. Users can deploy models as Slurm jobs, check server status and performance metrics, and shut down models. The repository also supports launching custom models with specific configurations. Additionally, users can send inference requests and set up an SSH tunnel to run inference from a local device.
consult-llm-mcp
Consult LLM MCP is an MCP server that enables users to consult powerful AI models like GPT-5.2, Gemini 3.0 Pro, and DeepSeek Reasoner for complex problem-solving. It supports multi-turn conversations, direct queries with optional file context, git changes inclusion for code review, comprehensive logging with cost estimation, and various CLI modes for Gemini and Codex. The tool is designed to simplify the process of querying AI models for assistance in resolving coding issues and improving code quality.
For similar tasks

friendly-stable-audio-tools
This repository is a refactored and updated version of `stable-audio-tools`, an open-source code for audio/music generative models originally by Stability AI. It contains refactored codes for improved readability and usability, useful scripts for evaluating and playing with trained models, and instructions on how to train models such as `Stable Audio 2.0`. The repository does not contain any pretrained checkpoints. Requirements include PyTorch 2.0 or later for Flash Attention support and Python 3.8.10 or later for development. The repository provides guidance on installing, building a training environment using Docker or Singularity, logging with Weights & Biases, training configurations, and stages for VAE-GAN and Diffusion Transformer (DiT) training.
For similar jobs

promptflow
**Prompt flow** is a suite of development tools designed to streamline the end-to-end development cycle of LLM-based AI applications, from ideation, prototyping, testing, evaluation to production deployment and monitoring. It makes prompt engineering much easier and enables you to build LLM apps with production quality.

deepeval
DeepEval is a simple-to-use, open-source LLM evaluation framework specialized for unit testing LLM outputs. It incorporates various metrics such as G-Eval, hallucination, answer relevancy, RAGAS, etc., and runs locally on your machine for evaluation. It provides a wide range of ready-to-use evaluation metrics, allows for creating custom metrics, integrates with any CI/CD environment, and enables benchmarking LLMs on popular benchmarks. DeepEval is designed for evaluating RAG and fine-tuning applications, helping users optimize hyperparameters, prevent prompt drifting, and transition from OpenAI to hosting their own Llama2 with confidence.

MegaDetector
MegaDetector is an AI model that identifies animals, people, and vehicles in camera trap images (which also makes it useful for eliminating blank images). This model is trained on several million images from a variety of ecosystems. MegaDetector is just one of many tools that aims to make conservation biologists more efficient with AI. If you want to learn about other ways to use AI to accelerate camera trap workflows, check out our of the field, affectionately titled "Everything I know about machine learning and camera traps".

leapfrogai
LeapfrogAI is a self-hosted AI platform designed to be deployed in air-gapped resource-constrained environments. It brings sophisticated AI solutions to these environments by hosting all the necessary components of an AI stack, including vector databases, model backends, API, and UI. LeapfrogAI's API closely matches that of OpenAI, allowing tools built for OpenAI/ChatGPT to function seamlessly with a LeapfrogAI backend. It provides several backends for various use cases, including llama-cpp-python, whisper, text-embeddings, and vllm. LeapfrogAI leverages Chainguard's apko to harden base python images, ensuring the latest supported Python versions are used by the other components of the stack. The LeapfrogAI SDK provides a standard set of protobuffs and python utilities for implementing backends and gRPC. LeapfrogAI offers UI options for common use-cases like chat, summarization, and transcription. It can be deployed and run locally via UDS and Kubernetes, built out using Zarf packages. LeapfrogAI is supported by a community of users and contributors, including Defense Unicorns, Beast Code, Chainguard, Exovera, Hypergiant, Pulze, SOSi, United States Navy, United States Air Force, and United States Space Force.

llava-docker
This Docker image for LLaVA (Large Language and Vision Assistant) provides a convenient way to run LLaVA locally or on RunPod. LLaVA is a powerful AI tool that combines natural language processing and computer vision capabilities. With this Docker image, you can easily access LLaVA's functionalities for various tasks, including image captioning, visual question answering, text summarization, and more. The image comes pre-installed with LLaVA v1.2.0, Torch 2.1.2, xformers 0.0.23.post1, and other necessary dependencies. You can customize the model used by setting the MODEL environment variable. The image also includes a Jupyter Lab environment for interactive development and exploration. Overall, this Docker image offers a comprehensive and user-friendly platform for leveraging LLaVA's capabilities.

carrot
The 'carrot' repository on GitHub provides a list of free and user-friendly ChatGPT mirror sites for easy access. The repository includes sponsored sites offering various GPT models and services. Users can find and share sites, report errors, and access stable and recommended sites for ChatGPT usage. The repository also includes a detailed list of ChatGPT sites, their features, and accessibility options, making it a valuable resource for ChatGPT users seeking free and unlimited GPT services.

TrustLLM
TrustLLM is a comprehensive study of trustworthiness in LLMs, including principles for different dimensions of trustworthiness, established benchmark, evaluation, and analysis of trustworthiness for mainstream LLMs, and discussion of open challenges and future directions. Specifically, we first propose a set of principles for trustworthy LLMs that span eight different dimensions. Based on these principles, we further establish a benchmark across six dimensions including truthfulness, safety, fairness, robustness, privacy, and machine ethics. We then present a study evaluating 16 mainstream LLMs in TrustLLM, consisting of over 30 datasets. The document explains how to use the trustllm python package to help you assess the performance of your LLM in trustworthiness more quickly. For more details about TrustLLM, please refer to project website.

AI-YinMei
AI-YinMei is an AI virtual anchor Vtuber development tool (N card version). It supports fastgpt knowledge base chat dialogue, a complete set of solutions for LLM large language models: [fastgpt] + [one-api] + [Xinference], supports docking bilibili live broadcast barrage reply and entering live broadcast welcome speech, supports Microsoft edge-tts speech synthesis, supports Bert-VITS2 speech synthesis, supports GPT-SoVITS speech synthesis, supports expression control Vtuber Studio, supports painting stable-diffusion-webui output OBS live broadcast room, supports painting picture pornography public-NSFW-y-distinguish, supports search and image search service duckduckgo (requires magic Internet access), supports image search service Baidu image search (no magic Internet access), supports AI reply chat box [html plug-in], supports AI singing Auto-Convert-Music, supports playlist [html plug-in], supports dancing function, supports expression video playback, supports head touching action, supports gift smashing action, supports singing automatic start dancing function, chat and singing automatic cycle swing action, supports multi scene switching, background music switching, day and night automatic switching scene, supports open singing and painting, let AI automatically judge the content.
