
Remote-MCP
A type-safe solution to remote MCP communication, enabling effortless integration for centralized management of Model Context.
Stars: 83
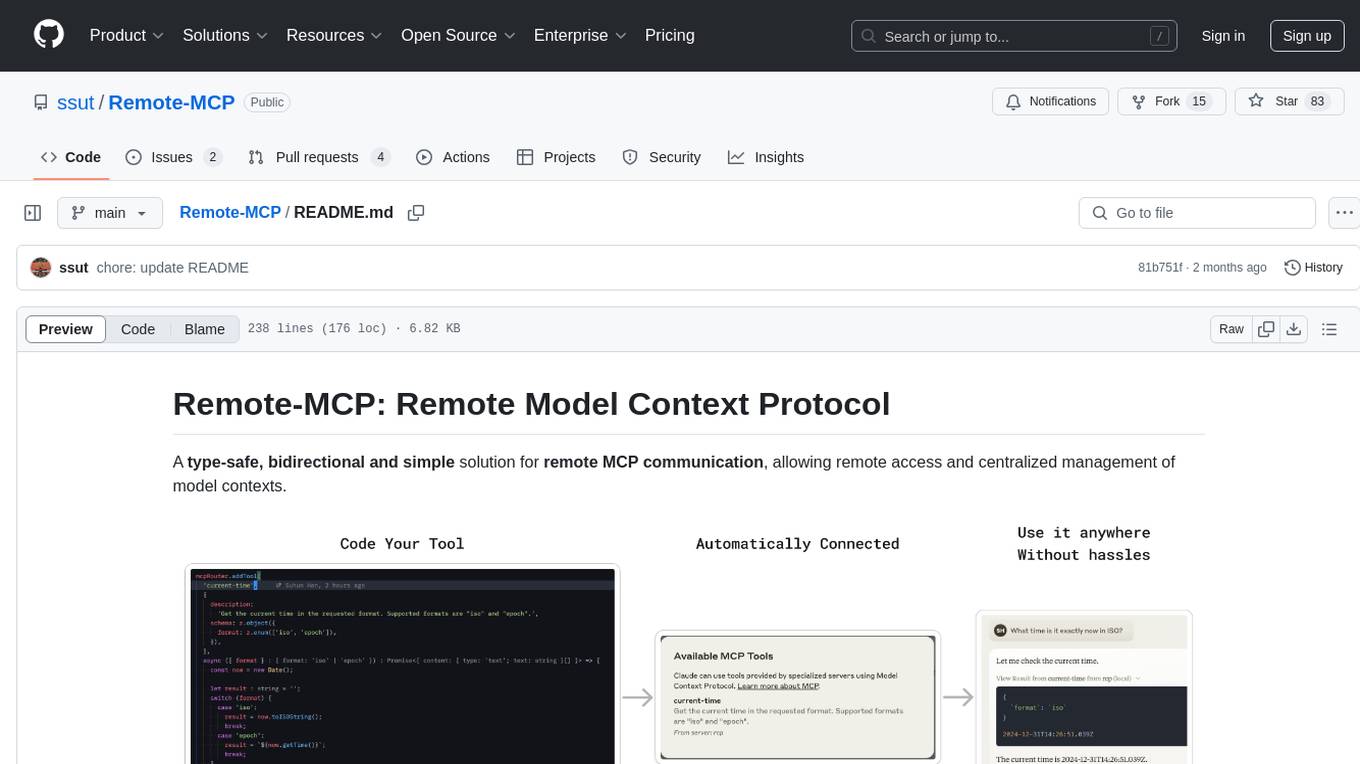
Remote-MCP is a type-safe, bidirectional, and simple solution for remote MCP communication, enabling remote access and centralized management of model contexts. It provides a bridge for immediate remote access to a remote MCP server from a local MCP client, without waiting for future official implementations. The repository contains client and server libraries for creating and connecting to remotely accessible MCP services. The core features include basic type-safe client/server communication, MCP command/tool/prompt support, custom headers, and ongoing work on crash-safe handling and event subscription system.
README:
A type-safe, bidirectional and simple solution for remote MCP communication, allowing remote access and centralized management of model contexts.
%%{init: {"flowchart": {"htmlLabels": false}} }%%
graph TD
%% Modern, Bright Color Styling with white text
classDef client fill:#22c55e,stroke:#059669,stroke-width:2px,color:#ffffff
classDef gateway fill:#06b6d4,stroke:#0891b2,stroke-width:2px,color:#ffffff
classDef backend fill:#f97316,stroke:#ea580c,stroke-width:2px,color:#ffffff
classDef resource fill:#8b5cf6,stroke:#7c3aed,stroke-width:2px,color:#ffffff
classDef server fill:#06b6d4,stroke:#0891b2,stroke-width:2px,color:#ffffff
linkStyle default stroke:#64748b,stroke-width:1.5px,stroke-dasharray: 5 5
%% Current MCP Setup (Multiple Local Servers)
subgraph Current["Current Setup (Local)"]
direction LR
subgraph ClientGroup["Client"]
A[Client]:::client
end
subgraph Servers["Local MCP Servers"]
direction TB
B1["Local MCP Server (DB)"]:::server -->|"DB Access"| C1[DB]:::resource
B2["Local MCP Server (API 1)"]:::server -->|"API Access"| C2["Web API 1"]:::resource
B3["Local MCP Server (API 2)"]:::server -->|"API Access"| C3["Web API 2"]:::resource
end
A -->|"MCP Protocol"| B1
A -->|"MCP Protocol"| B2
A -->|"MCP Protocol"| B3
end
%% Vertical separator
Current --> Proposed
%% Proposed MCP Architecture (Decoupled)
subgraph Proposed["Proposed Architecture (Remote)"]
direction LR
D[Client/Host]:::client -->|"MCP Protocol"| E["Local MCP Server (@remote-mcp/client)"]:::server
E <-->|"tRPC(HTTP)"| F["Remote MCP Server (@remote-mcp/server)"]:::backend
%% Separated Resources
F -->|"DB Access"| G1[DB]:::resource
F -->|"API Access"| G2["Web API 1"]:::resource
F -->|"API Access"| G3["Web API 2"]:::resource
endYes, I know that the official MCP roadmap includes remote MCP support in the first quarter of 2025. However, the need for remote access was immediate for me, and likely for many others. This library was created to bridge that gap, providing a way to connect to a remote MCP server from a local MCP client right now, without waiting for future official implementations.
Note: I don't want this to be a sophisticated or overcomplicated thing. This way just works right now.
Note: This project is currently under active development and is considered experimental. Expect breaking changes and potential issues.
Just put the following code in your MCP client settings, in here I'm using Claude as an example:
{
"mcpServers": {
"remote-mcp": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "@remote-mcp/client"],
"env": {
"REMOTE_MCP_URL": "http://localhost:9512",
"HTTP_HEADER__Authorization": "Bearer <token>"
}
}
}
}Install requirements:
$ npm install @remote-mcp/client @trpc/client@next zodthen write your own code like the following:
import { RemoteMCPClient } from "@remote-mcp/client";
const client = new RemoteMCPClient({
remoteUrl: "http://localhost:9512",
onError: (method, error) => console.error(`Error in ${method}:`, error)
});
void client.start();You can see some examples in the examples directory.
After npm install @remote-mcp/server, you can your own remote MCP server like the following:
import { MCPRouter, LogLevel } from "@remote-mcp/server";
import { createHTTPServer } from '@trpc/server/adapters/standalone';
import { z } from "zod";
// Create router instance
const mcpRouter = new MCPRouter({
logLevel: LogLevel.DEBUG,
name: "example-server",
version: "1.0.0",
capabilities: {
logging: {},
},
});
// Add example tool
mcpRouter.addTool(
"calculator",
{
description:
"Perform basic calculations. Add, subtract, multiply, divide. Invoke this every time you need to perform a calculation.",
schema: z.object({
operation: z.enum(["add", "subtract", "multiply", "divide"]),
a: z.string(),
b: z.string(),
}),
},
async (args) => {
const a = Number(args.a);
const b = Number(args.b);
let result: number;
switch (args.operation) {
case "add":
result = Number(a) + b;
break;
case "subtract":
result = a - b;
break;
case "multiply":
result = a * b;
break;
case "divide":
if (b === 0) throw new Error("Division by zero");
result = a / b;
break;
}
return {
content: [{ type: "text", text: `${result}` }],
};
},
);
const appRouter = mcpRouter.createTRPCRouter();
void createHTTPServer({
router: appRouter,
createContext: () => ({}),
}).listen(Number(process.env.PORT || 9512));Then you can see like the following in your MCP client:
This repository contains:
-
@remote-mcp/client: Client library acting as a local MCP server, connecting to a remote implementation. -
@remote-mcp/server: Server library for creating remotely accessible MCP services (used as the remote implementation).
- [x] Basic Type-safe Client/Server Communication
- [x] Basic MCP Command Support
- [x] Basic MCP Tool Support
- [x] Basic MCP Prompt Support
- [ ] Crash-Safe Handling (WIP, top priority)
- [ ] Complete Event Subscription System
- [ ] Resource change notifications
- [ ] Tool/Prompt list change notifications
- [ ] HTTP Header Support
- [x] Custom Headers
- [ ] Authentication Middleware
- [ ] Basic error handling improvements
- [ ] Basic middleware support
- [ ] Nest.js Integration (
@remote-mcp/nestjs)
- [ ] Bidirectional communication
- [ ] Server-to-client requests
- [ ] Resource sharing between server/client
- [ ] Basic monitoring & logging
Contributions are welcome. See CONTRIBUTING.md for details.
This library is a complementary extension, not part of the official MCP specification, built upon existing MCP concepts.
This project is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for details.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Remote-MCP
Similar Open Source Tools

Remote-MCP
Remote-MCP is a type-safe, bidirectional, and simple solution for remote MCP communication, enabling remote access and centralized management of model contexts. It provides a bridge for immediate remote access to a remote MCP server from a local MCP client, without waiting for future official implementations. The repository contains client and server libraries for creating and connecting to remotely accessible MCP services. The core features include basic type-safe client/server communication, MCP command/tool/prompt support, custom headers, and ongoing work on crash-safe handling and event subscription system.
mcphub.nvim
MCPHub.nvim is a powerful Neovim plugin that integrates MCP (Model Context Protocol) servers into your workflow. It offers a centralized config file for managing servers and tools, with an intuitive UI for testing resources. Ideal for LLM integration, it provides programmatic API access and interactive testing through the `:MCPHub` command.
klavis
Klavis AI is a production-ready solution for managing Multiple Communication Protocol (MCP) servers. It offers self-hosted solutions and a hosted service with enterprise OAuth support. With Klavis AI, users can easily deploy and manage over 50 MCP servers for various services like GitHub, Gmail, Google Sheets, YouTube, Slack, and more. The tool provides instant access to MCP servers, seamless authentication, and integration with AI frameworks, making it ideal for individuals and businesses looking to streamline their communication and data management workflows.
ruby_llm-mcp
RubyLLM::MCP is a Ruby client for the Model Context Protocol (MCP), designed to seamlessly integrate with RubyLLM. It provides a Ruby-first API for using MCP tools, resources, and prompts directly in RubyLLM chat workflows. The tool supports the stable MCP spec `2025-06-18` and offers draft spec `2026-01-26` compatibility. It includes features like notification and response handlers, OAuth 2.1 authentication support, integration paths for Rails apps and CLI flows, and straightforward integration for any Ruby app or Rails project using RubyLLM. The tool allows users to work with MCP tools, resources, and prompts over `stdio`, streamable HTTP, or SSE transports.
ai-sdk-cpp
The AI SDK CPP is a modern C++ toolkit that provides a unified, easy-to-use API for building AI-powered applications with popular model providers like OpenAI and Anthropic. It bridges the gap for C++ developers by offering a clean, expressive codebase with minimal dependencies. The toolkit supports text generation, streaming content, multi-turn conversations, error handling, tool calling, async tool execution, and configurable retries. Future updates will include additional providers, text embeddings, and image generation models. The project also includes a patched version of nlohmann/json for improved thread safety and consistent behavior in multi-threaded environments.
mcp-go
MCP Go is a Go implementation of the Model Context Protocol (MCP), facilitating seamless integration between LLM applications and external data sources and tools. It handles complex protocol details and server management, allowing developers to focus on building tools. The tool is designed to be fast, simple, and complete, aiming to provide a high-level and easy-to-use interface for developing MCP servers. MCP Go is currently under active development, with core features working and advanced capabilities in progress.
x
Ant Design X is a tool for crafting AI-driven interfaces effortlessly. It is built on the best practices of enterprise-level AI products, offering flexible and diverse atomic components for various AI dialogue scenarios. The tool provides out-of-the-box model integration with inference services compatible with OpenAI standards. It also enables efficient management of conversation data flows, supports rich template options, complete TypeScript support, and advanced theme customization. Ant Design X is designed to enhance development efficiency and deliver exceptional AI interaction experiences.
aioshelly
Aioshelly is an asynchronous library designed to control Shelly devices. It is currently under development and requires Python version 3.11 or higher, along with dependencies like bluetooth-data-tools, aiohttp, and orjson. The library provides examples for interacting with Gen1 devices using CoAP protocol and Gen2/Gen3 devices using RPC and WebSocket protocols. Users can easily connect to Shelly devices, retrieve status information, and perform various actions through the provided APIs. The repository also includes example scripts for quick testing and usage guidelines for contributors to maintain consistency with the Shelly API.
aiosonic
Aiosonic is a lightweight Python asyncio HTTP/WebSocket client that offers fast and efficient communication with HTTP/1.1, HTTP/2, and WebSocket protocols. It supports keepalive, connection pooling, multipart file uploads, chunked responses, timeouts, automatic decompression, redirect following, type annotations, WebSocket communication, HTTP proxy, cookie sessions, elegant cookies, and nearly 100% test coverage. It requires Python version 3.10 or higher for installation and provides a simple API for making HTTP requests and WebSocket connections. Additionally, it allows API wrapping for customizing response handling and includes a performance benchmark script for comparing its speed with other HTTP clients.

mcp
Semgrep MCP Server is a beta server under active development for using Semgrep to scan code for security vulnerabilities. It provides a Model Context Protocol (MCP) for various coding tools to get specialized help in tasks. Users can connect to Semgrep AppSec Platform, scan code for vulnerabilities, customize Semgrep rules, analyze and filter scan results, and compare results. The tool is published on PyPI as semgrep-mcp and can be installed using pip, pipx, uv, poetry, or other methods. It supports CLI and Docker environments for running the server. Integration with VS Code is also available for quick installation. The project welcomes contributions and is inspired by core technologies like Semgrep and MCP, as well as related community projects and tools.
instructor
Instructor is a tool that provides structured outputs from Large Language Models (LLMs) in a reliable manner. It simplifies the process of extracting structured data by utilizing Pydantic for validation, type safety, and IDE support. With Instructor, users can define models and easily obtain structured data without the need for complex JSON parsing, error handling, or retries. The tool supports automatic retries, streaming support, and extraction of nested objects, making it production-ready for various AI applications. Trusted by a large community of developers and companies, Instructor is used by teams at OpenAI, Google, Microsoft, AWS, and YC startups.
UnrealGenAISupport
The Unreal Engine Generative AI Support Plugin is a tool designed to integrate various cutting-edge LLM/GenAI models into Unreal Engine for game development. It aims to simplify the process of using AI models for game development tasks, such as controlling scene objects, generating blueprints, running Python scripts, and more. The plugin currently supports models from organizations like OpenAI, Anthropic, XAI, Google Gemini, Meta AI, Deepseek, and Baidu. It provides features like API support, model control, generative AI capabilities, UI generation, project file management, and more. The plugin is still under development but offers a promising solution for integrating AI models into game development workflows.
aio-pika
Aio-pika is a wrapper around aiormq for asyncio and humans. It provides a completely asynchronous API, object-oriented API, transparent auto-reconnects with complete state recovery, Python 3.7+ compatibility, transparent publisher confirms support, transactions support, and complete type-hints coverage.
mcp-framework
MCP-Framework is a TypeScript framework for building Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers with automatic directory-based discovery for tools, resources, and prompts. It provides powerful abstractions, simple server setup, and a CLI for rapid development and project scaffolding.
llm-sandbox
LLM Sandbox is a lightweight and portable sandbox environment designed to securely execute large language model (LLM) generated code in a safe and isolated manner using Docker containers. It provides an easy-to-use interface for setting up, managing, and executing code in a controlled Docker environment, simplifying the process of running code generated by LLMs. The tool supports multiple programming languages, offers flexibility with predefined Docker images or custom Dockerfiles, and allows scalability with support for Kubernetes and remote Docker hosts.
volga
Volga is a general purpose real-time data processing engine in Python for modern AI/ML systems. It aims to be a Python-native alternative to Flink/Spark Streaming with extended functionality for real-time AI/ML workloads. It provides a hybrid push+pull architecture, Entity API for defining data entities and feature pipelines, DataStream API for general data processing, and customizable data connectors. Volga can run on a laptop or a distributed cluster, making it suitable for building custom real-time AI/ML feature platforms or general data pipelines without relying on third-party platforms.
For similar tasks

Remote-MCP
Remote-MCP is a type-safe, bidirectional, and simple solution for remote MCP communication, enabling remote access and centralized management of model contexts. It provides a bridge for immediate remote access to a remote MCP server from a local MCP client, without waiting for future official implementations. The repository contains client and server libraries for creating and connecting to remotely accessible MCP services. The core features include basic type-safe client/server communication, MCP command/tool/prompt support, custom headers, and ongoing work on crash-safe handling and event subscription system.
For similar jobs
aiomcache
aiomcache is a Python library that provides an asyncio (PEP 3156) interface to work with memcached. It allows users to interact with memcached servers asynchronously, making it suitable for high-performance applications that require non-blocking I/O operations. The library offers similar functionality to other memcache clients and includes features like setting and getting values, multi-get operations, and deleting keys. Version 0.8 introduces the `FlagClient` class, which enables users to register callbacks for setting or processing flags, providing additional flexibility and customization options for working with memcached servers.
aiolimiter
An efficient implementation of a rate limiter for asyncio using the Leaky bucket algorithm, providing precise control over the rate a code section can be entered. It allows for limiting the number of concurrent entries within a specified time window, ensuring that a section of code is executed a maximum number of times in that period.
bee
Bee is an easy and high efficiency ORM framework that simplifies database operations by providing a simple interface and eliminating the need to write separate DAO code. It supports various features such as automatic filtering of properties, partial field queries, native statement pagination, JSON format results, sharding, multiple database support, and more. Bee also offers powerful functionalities like dynamic query conditions, transactions, complex queries, MongoDB ORM, cache management, and additional tools for generating distributed primary keys, reading Excel files, and more. The newest versions introduce enhancements like placeholder precompilation, default date sharding, ElasticSearch ORM support, and improved query capabilities.
claude-api
claude-api is a web conversation library for ClaudeAI implemented in GoLang. It provides functionalities to interact with ClaudeAI for web-based conversations. Users can easily integrate this library into their Go projects to enable chatbot capabilities and handle conversations with ClaudeAI. The library includes features for sending messages, receiving responses, and managing chat sessions, making it a valuable tool for developers looking to incorporate AI-powered chatbots into their applications.
aide
Aide is a code-first API documentation and utility library for Rust, along with other related utility crates for web-servers. It provides tools for creating API documentation and handling JSON request validation. The repository contains multiple crates that offer drop-in replacements for existing libraries, ensuring compatibility with Aide. Contributions are welcome, and the code is dual licensed under MIT and Apache-2.0. If Aide does not meet your requirements, you can explore similar libraries like paperclip, utoipa, and okapi.
amadeus-java
Amadeus Java SDK provides a rich set of APIs for the travel industry, allowing developers to access various functionalities such as flight search, booking, airport information, and more. The SDK simplifies interaction with the Amadeus API by providing self-contained code examples and detailed documentation. Developers can easily make API calls, handle responses, and utilize features like pagination and logging. The SDK supports various endpoints for tasks like flight search, booking management, airport information retrieval, and travel analytics. It also offers functionalities for hotel search, booking, and sentiment analysis. Overall, the Amadeus Java SDK is a comprehensive tool for integrating Amadeus APIs into Java applications.
rig
Rig is a Rust library designed for building scalable, modular, and user-friendly applications powered by large language models (LLMs). It provides full support for LLM completion and embedding workflows, offers simple yet powerful abstractions for LLM providers like OpenAI and Cohere, as well as vector stores such as MongoDB and in-memory storage. With Rig, users can easily integrate LLMs into their applications with minimal boilerplate code.
celery-aio-pool
Celery AsyncIO Pool is a free software tool licensed under GNU Affero General Public License v3+. It provides an AsyncIO worker pool for Celery, enabling users to leverage the power of AsyncIO in their Celery applications. The tool allows for easy installation using Poetry, pip, or directly from GitHub. Users can configure Celery to use the AsyncIO pool provided by celery-aio-pool, or they can wait for the upcoming support for out-of-tree worker pools in Celery 5.3. The tool is actively maintained and welcomes contributions from the community.