
mcpproxy-go
Supercharge AI Agents, Safely
Stars: 125
MCPProxy is an open-source desktop application that enhances AI agents by enabling intelligent tool discovery, reducing token usage, and providing security against malicious servers. It allows users to federate multiple servers, save tokens, and improve accuracy. The tool works offline and is compatible with various platforms. It offers features like Docker isolation, secrets management, OAuth authentication support, and HTTPS setup. Users can easily install, run, and manage servers using CLI commands. The tool provides detailed documentation and supports various tasks like adding servers, connecting to IDEs, and managing secrets.
README:
MCPProxy is an open-source desktop application that super-charges AI agents with intelligent tool discovery, massive token savings, and built-in security quarantine against malicious MCP servers.
- Scale beyond API limits – Federate hundreds of MCP servers while bypassing Cursor's 40-tool limit and OpenAI's 128-function cap.
-
Save tokens & accelerate responses – Agents load just one
retrieve_toolsfunction instead of hundreds of schemas. Research shows ~99 % token reduction with 43 % accuracy improvement. - Advanced security protection – Automatic quarantine blocks Tool Poisoning Attacks until you manually approve new servers.
- Works offline & cross-platform – Native binaries for macOS (Intel & Apple Silicon), Windows (x64 & ARM64), and Linux (x64 & ARM64) with system-tray UI.
macOS (Recommended - DMG Installer):
Download the latest DMG installer for your architecture:
-
Apple Silicon (M1/M2): Download DMG →
mcpproxy-*-darwin-arm64.dmg -
Intel Mac: Download DMG →
mcpproxy-*-darwin-amd64.dmg
Windows (Recommended - Installer):
Download the latest Windows installer for your architecture:
-
x64 (64-bit): Download Installer →
mcpproxy-setup-*-amd64.exe -
ARM64: Download Installer →
mcpproxy-setup-*-arm64.exe
The installer automatically:
- Installs both
mcpproxy.exe(core server) andmcpproxy-tray.exe(system tray app) to Program Files - Adds MCPProxy to your system PATH for command-line access
- Creates Start Menu shortcuts
- Supports silent installation:
.\mcpproxy-setup.exe /VERYSILENT
Alternative install methods:
macOS (Homebrew):
brew install smart-mcp-proxy/mcpproxy/mcpproxyManual download (all platforms):
Prerelease Builds (Latest Features):
Want to try the newest features? Download prerelease builds from the next branch:
- Go to GitHub Actions
- Click the latest successful "Prerelease" workflow run
- Download from Artifacts:
-
dmg-darwin-arm64(Apple Silicon Macs) -
dmg-darwin-amd64(Intel Macs) -
versioned-linux-amd64,versioned-windows-amd64(other platforms)
-
Note: Prerelease builds are signed and notarized for macOS but contain cutting-edge features that may be unstable.
- macOS: Intel | Apple Silicon
Anywhere with Go 1.22+:
go install github.com/smart-mcp-proxy/mcpproxy-go/cmd/mcpproxy@latestmcpproxy serve # starts HTTP server on :8080 and shows trayEdit mcp_config.json (see below). Or ask LLM to add servers (see doc).
📖 Complete Setup Guide - Detailed instructions for Cursor, VS Code, Claude Desktop, and Goose
- Open Cursor Settings
- Click "Tools & Integrations"
- Add MCP server
"MCPProxy": {
"type": "http",
"url": "http://localhost:8080/mcp/"
}| Field | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
listen |
Address the proxy listens on | 127.0.0.1:8080 |
data_dir |
Folder for config, DB & logs | ~/.mcpproxy |
enable_tray |
Show native system-tray UI | true |
top_k |
Tools returned by retrieve_tools
|
5 |
tools_limit |
Max tools returned to client | 15 |
tool_response_limit |
Auto-truncate responses above N chars (0 disables) |
20000 |
tls.enabled |
Enable HTTPS with local CA certificates | false |
tls.require_client_cert |
Enable mutual TLS (mTLS) for client authentication | false |
tls.certs_dir |
Custom directory for TLS certificates | {data_dir}/certs |
tls.hsts |
Send HTTP Strict Transport Security headers | true |
docker_isolation |
Docker security isolation settings (see below) | enabled: false |
Main Commands:
mcpproxy serve # Start proxy server with system tray
mcpproxy tools list --server=NAME # Debug tool discovery for specific server
mcpproxy trust-cert # Install CA certificate as trusted (for HTTPS)Management Commands:
# Single-server operations
mcpproxy upstream list # List all servers with status
mcpproxy upstream restart <name> # Restart specific server
mcpproxy upstream enable <name> # Enable specific server
mcpproxy upstream disable <name> # Disable specific server
mcpproxy upstream logs <name> # View server logs (--tail, --follow)
# Bulk operations (multiple servers)
mcpproxy upstream restart --all # Restart all configured servers
mcpproxy upstream enable --all # Enable all servers
mcpproxy upstream disable --all # Disable all servers
# Health diagnostics
mcpproxy doctor # Run comprehensive health checksManagement Service Architecture:
All management operations (CLI, REST API, and MCP protocol) share a unified service layer that provides:
-
Configuration gates: Respects
disable_managementandread_only_modesettings - Event integration: Real-time updates to system tray and web UI
- Bulk operations: Efficient multi-server management with partial failure handling
- Consistent behavior: Same validation and error handling across all interfaces
Serve Command Flags:
mcpproxy serve --help
-c, --config <file> path to mcp_config.json
-l, --listen <addr> listen address for HTTP mode
-d, --data-dir <dir> custom data directory
--log-level <level> trace|debug|info|warn|error
--log-to-file enable logging to file in standard OS location
--read-only enable read-only mode
--disable-management disable management features
--allow-server-add allow adding new servers (default true)
--allow-server-remove allow removing existing servers (default true)
--enable-prompts enable prompts for user input (default true)
--tool-response-limit <num> tool response limit in characters (0 = disabled)
Tools Command Flags:
mcpproxy tools list --help
-s, --server <name> upstream server name (required)
-l, --log-level <level> trace|debug|info|warn|error (default: info)
-t, --timeout <duration> connection timeout (default: 30s)
-o, --output <format> output format: table|json|yaml (default: table)
-c, --config <file> path to mcp_config.json
Debug Examples:
# List tools with trace logging to see all JSON-RPC frames
mcpproxy tools list --server=github-server --log-level=trace
# List tools with custom timeout for slow servers
mcpproxy tools list --server=slow-server --timeout=60s
# Output tools in JSON format for scripting
mcpproxy tools list --server=weather-api --output=jsonMCPProxy provides secure secrets management using your operating system's native keyring to store sensitive information like API keys, tokens, and credentials.
- OS-native security: Uses macOS Keychain, Linux Secret Service, or Windows Credential Manager
-
Placeholder expansion: Automatically resolves
${keyring:secret_name}placeholders in config files - Global access: Secrets are shared across all MCPProxy configurations and data directories
- CLI management: Full command-line interface for storing, retrieving, and managing secrets
Store a secret:
# Interactive prompt (recommended for sensitive values)
mcpproxy secrets set github_token
# From command line (less secure - visible in shell history)
mcpproxy secrets set github_token "ghp_abcd1234..."
# From environment variable
mcpproxy secrets set github_token --from-env GITHUB_TOKENList all secrets:
mcpproxy secrets list
# Output: Found 3 secrets in keyring:
# github_token
# openai_api_key
# database_passwordRetrieve a secret:
mcpproxy secrets get github_tokenDelete a secret:
mcpproxy secrets delete github_tokenUse ${keyring:secret_name} placeholders in your mcp_config.json:
{
"mcpServers": [
{
"name": "github-mcp",
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["mcp-server-github"],
"protocol": "stdio",
"env": {
"GITHUB_TOKEN": "${keyring:github_token}",
"OPENAI_API_KEY": "${keyring:openai_api_key}"
},
"enabled": true
},
{
"name": "database-server",
"command": "python",
"args": ["-m", "my_db_server", "--password", "${keyring:database_password}"],
"protocol": "stdio",
"enabled": true
}
]
}Placeholder expansion works in:
- ✅ Environment variables (
envfield) - ✅ Command arguments (
argsfield) - ❌ Server names, commands, URLs (static fields)
Storage Location:
-
macOS: Keychain Access (
/Applications/Utilities/Keychain Access.app) - Linux: Secret Service (GNOME Keyring, KDE Wallet, etc.)
- Windows: Windows Credential Manager
Service Name: All secrets are stored under the service name "mcpproxy"
Global Scope:
- ✅ Secrets are shared across all MCPProxy instances regardless of:
- Configuration file location (
--configflag) - Data directory (
--data-dirflag) - Working directory
- Configuration file location (
- ✅ Same secrets work across different projects and setups
⚠️ No isolation - all MCPProxy instances access the same keyring
If you use MCPProxy with multiple projects or environments, use descriptive secret names:
# Environment-specific secrets
mcpproxy secrets set prod_database_url
mcpproxy secrets set dev_database_url
mcpproxy secrets set staging_api_key
# Project-specific secrets
mcpproxy secrets set work_github_token
mcpproxy secrets set personal_github_token
mcpproxy secrets set client_a_api_keyThen reference them in your configs:
{
"mcpServers": [
{
"name": "work-github",
"env": {
"GITHUB_TOKEN": "${keyring:work_github_token}"
}
},
{
"name": "personal-github",
"env": {
"GITHUB_TOKEN": "${keyring:personal_github_token}"
}
}
]
}- Encrypted storage: Secrets are encrypted by the OS keyring
- Process isolation: Other applications cannot access MCPProxy secrets without appropriate permissions
- No file storage: Secrets are never written to config files or logs
- Audit trail: OS keyring may provide access logs (varies by platform)
Secret not found:
# Verify secret exists
mcpproxy secrets list
# Check the exact secret name (case-sensitive)
mcpproxy secrets get your_secret_nameKeyring access denied:
-
macOS: Grant MCPProxy access in
System Preferences > Security & Privacy > Privacy > Accessibility - Linux: Ensure your desktop session has an active keyring service
- Windows: Run MCPProxy with appropriate user permissions
Placeholder not resolving:
# Test secret resolution
mcpproxy secrets get your_secret_name
# Check logs for secret resolution errors
mcpproxy serve --log-level=debugMCPProxy provides Docker isolation for stdio MCP servers to enhance security by running each server in its own isolated container:
- Process Isolation: Each MCP server runs in a separate Docker container
- File System Isolation: Servers cannot access host file system outside their container
- Network Isolation: Configurable network modes for additional security
- Resource Limits: Memory and CPU limits prevent resource exhaustion
- Automatic Runtime Detection: Detects Python, Node.js, Go, Rust environments automatically
- Runtime Detection: Automatically detects server type (uvx→Python, npx→Node.js, etc.)
- Container Selection: Maps to appropriate Docker images with required tools
- Environment Passing: Passes API keys and config via secure environment variables
- Git Support: Uses full Docker images with Git for package installations from repositories
Add to your mcp_config.json:
{
"docker_isolation": {
"enabled": true,
"memory_limit": "512m",
"cpu_limit": "1.0",
"timeout": "60s",
"network_mode": "bridge",
"default_images": {
"python": "python:3.11",
"uvx": "python:3.11",
"node": "node:20",
"npx": "node:20",
"go": "golang:1.21-alpine"
}
},
"mcpServers": [
{
"name": "isolated-python-server",
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["some-python-package"],
"env": {
"API_KEY": "your-api-key"
},
"enabled": true
// Docker isolation applied automatically
},
{
"name": "custom-isolation-server",
"command": "python",
"args": ["-m", "my_server"],
"isolation": {
"enabled": true,
"image": "custom-python:latest",
"working_dir": "/app"
},
"enabled": true
}
]
}| Command | Detected Runtime | Docker Image |
|---|---|---|
uvx |
Python with UV package manager | python:3.11 |
npx |
Node.js with npm | node:20 |
python, python3
|
Python | python:3.11 |
node |
Node.js | node:20 |
go |
Go language | golang:1.21-alpine |
cargo |
Rust | rust:1.75-slim |
- Environment Variables: API keys and secrets are passed securely to containers
- Git Support: Full images include Git for installing packages from repositories
- No Docker-in-Docker: Existing Docker servers are automatically excluded from isolation
- Resource Limits: Prevents runaway processes from consuming system resources
- Network Isolation: Containers run in isolated network environments
# Check which servers are using Docker isolation
mcpproxy serve --log-level=debug --tray=false | grep -i "docker isolation"
# Monitor Docker containers created by MCPProxy
docker ps --format "table {{.Names}}\t{{.Image}}\t{{.Status}}"
# View container logs for a specific server
docker logs <container-id>MCPProxy includes intelligent Docker recovery that automatically detects and handles Docker engine outages:
- Automatic Detection: Monitors Docker health every 2-60 seconds with exponential backoff
- Graceful Reconnection: Automatically reconnects all Docker-based servers when Docker recovers
- System Notifications: Native notifications keep you informed of recovery progress
- Container Cleanup: Removes orphaned containers on shutdown
- Zero Configuration: Works out-of-the-box with sensible defaults
- Health Monitoring: Continuously checks Docker engine availability
- Failure Detection: Detects when Docker becomes unavailable (paused, stopped, crashed)
- Exponential Backoff: Starts with 2-second checks, backs off to 60 seconds to save resources
- Automatic Reconnection: When Docker recovers, all affected servers are reconnected
- User Notification: System notifications inform you of recovery status
MCPProxy shows native system notifications during Docker recovery:
| Event | Notification |
|---|---|
| Recovery Started | "Docker engine detected offline. Reconnecting servers..." |
| Recovery Success | "Successfully reconnected X server(s)" |
| Recovery Failed | "Unable to reconnect servers. Check Docker status." |
| Retry Attempts | "Retry attempt X. Next check in Y" |
Servers don't reconnect after Docker recovery:
# 1. Check Docker is running
docker ps
# 2. Check mcpproxy logs
cat ~/.mcpproxy/logs/main.log | grep -i "docker recovery"
# 3. Verify container labels
docker ps -a --filter label=com.mcpproxy.managed
# 4. Force reconnect via system tray
# System Tray → Force Reconnect All ServersContainers not cleaned up on shutdown:
# Check for orphaned containers
docker ps -a --filter label=com.mcpproxy.managed=true
# Manual cleanup if needed
docker ps -a --filter label=com.mcpproxy.managed=true -q | xargs docker rm -fDocker recovery taking too long:
- Docker recovery uses exponential backoff (2s → 60s intervals)
- This is intentional to avoid wasting resources while Docker is offline
- You can force an immediate reconnect via the system tray menu
MCPProxy provides seamless OAuth 2.1 authentication for MCP servers that require user authorization (like Cloudflare AutoRAG, Runlayer, GitHub, etc.):
- Zero-Config OAuth: Automatic detection and configuration for most OAuth servers
- RFC 8707 Resource Auto-Detection: Automatically discovers resource parameters from server metadata
- RFC 8252 Compliant: Dynamic port allocation for secure callback handling
- PKCE Security: Proof Key for Code Exchange for enhanced security
- Auto Browser Launch: Opens your default browser for authentication
- Dynamic Client Registration: Automatic client registration with OAuth servers
- Token Management: Automatic token refresh and storage
- Add OAuth Server: Configure an OAuth-enabled MCP server in your config
- Auto Detection: MCPProxy detects OAuth requirements and auto-configures parameters
- Browser Opens: Your default browser opens to the OAuth provider's login page
- Dynamic Callback: MCPProxy starts a local callback server on a random port
- Token Exchange: Authorization code is automatically exchanged for access tokens
- Ready to Use: Server becomes available for tool calls immediately
For most OAuth servers (including Runlayer, Cloudflare, etc.), no OAuth configuration is needed. MCPProxy automatically:
- Detects OAuth requirements via 401 responses
- Discovers Protected Resource Metadata (RFC 9728)
- Injects the RFC 8707
resourceparameter automatically
{
"mcpServers": [
{
"name": "runlayer-slack",
"url": "https://oauth.runlayer.com/api/v1/proxy/YOUR-UUID/mcp"
},
{
"name": "cloudflare_autorag",
"url": "https://autorag.mcp.cloudflare.com/mcp",
"protocol": "streamable-http"
}
]
}That's it - no oauth block needed. MCPProxy handles everything automatically.
Use explicit configuration when you need to:
- Customize OAuth scopes
- Override auto-detected parameters
- Use pre-registered client credentials
- Support providers with non-standard requirements
{
"mcpServers": [
{
"name": "github-enterprise",
"url": "https://github.example.com/mcp",
"protocol": "http",
"oauth": {
"scopes": ["repo", "user:email", "read:org"],
"pkce_enabled": true,
"client_id": "your-registered-client-id",
"extra_params": {
"resource": "https://api.github.example.com",
"audience": "github-enterprise-api"
}
}
}
]
}OAuth Configuration Options (all optional):
-
scopes: OAuth scopes to request (auto-discovered if not specified) -
pkce_enabled: Enable PKCE for security (default:true, recommended) -
client_id: Pre-registered client ID (uses Dynamic Client Registration if empty) -
client_secret: Client secret (optional, for confidential clients) -
extra_params: Additional OAuth parameters (override auto-detected values)
Check OAuth status and auto-detected parameters:
# View OAuth status for a specific server
mcpproxy auth status --server=runlayer-slack
# View all OAuth-enabled servers
mcpproxy auth status --all
# Run health diagnostics including OAuth issues
mcpproxy doctorEnable debug logging to see the complete OAuth flow:
mcpproxy serve --log-level=debug --tray=falseCheck logs for OAuth flow details:
tail -f ~/Library/Logs/mcpproxy/main.log | grep -E "(oauth|OAuth)"Solve project context issues by specifying working directories for stdio MCP servers:
{
"mcpServers": [
{
"name": "ast-grep-project-a",
"command": "npx",
"args": ["ast-grep-mcp"],
"working_dir": "/home/user/projects/project-a",
"enabled": true
},
{
"name": "git-work-repo",
"command": "npx",
"args": ["@modelcontextprotocol/server-git"],
"working_dir": "/home/user/work/company-repo",
"enabled": true
}
]
}Benefits:
- Project isolation: File-based servers operate in correct directory context
- Multiple projects: Same MCP server type for different projects
- Context separation: Work and personal project isolation
Tool-based Management:
# Add server with working directory
mcpproxy call tool --tool-name=upstream_servers \
--json_args='{"operation":"add","name":"git-myproject","command":"npx","args_json":"[\"@modelcontextprotocol/server-git\"]","working_dir":"/home/user/projects/myproject","enabled":true}'
# Update existing server working directory
mcpproxy call tool --tool-name=upstream_servers \
--json_args='{"operation":"update","name":"git-myproject","working_dir":"/new/project/path"}'MCPProxy works with HTTP by default for easy setup. HTTPS is optional and primarily useful for production environments or when stricter security is required.
💡 Note: Most users can stick with HTTP (the default) as it works perfectly with all supported clients including Claude Desktop, Cursor, and VS Code.
1. Enable HTTPS (choose one method):
# Method 1: Environment variable
export MCPPROXY_TLS_ENABLED=true
mcpproxy serve
# Method 2: Config file
# Edit ~/.mcpproxy/mcp_config.json and set "tls.enabled": true2. Trust the certificate (one-time setup):
mcpproxy trust-cert3. Use HTTPS URLs:
- MCP endpoint:
https://localhost:8080/mcp - Web UI:
https://localhost:8080/ui/
For Claude Desktop, add this to your claude_desktop_config.json:
HTTP (Default - Recommended):
{
"mcpServers": {
"mcpproxy": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"-y",
"mcp-remote",
"http://localhost:8080/mcp"
]
}
}
}HTTPS (With Certificate Trust):
{
"mcpServers": {
"mcpproxy": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"-y",
"mcp-remote",
"https://localhost:8080/mcp"
],
"env": {
"NODE_EXTRA_CA_CERTS": "~/.mcpproxy/certs/ca.pem"
}
}
}
}- Automatic generation: Certificates created on first HTTPS startup
-
Multi-domain support: Works with
localhost,127.0.0.1,::1 -
Trust installation: Use
mcpproxy trust-certto add to system keychain -
Certificate location:
~/.mcpproxy/certs/(ca.pem, server.pem, server-key.pem)
Certificate trust issues:
# Re-trust certificate
mcpproxy trust-cert --force
# Check certificate location
ls ~/.mcpproxy/certs/
# Test HTTPS connection
curl -k https://localhost:8080/api/v1/statusClaude Desktop connection issues:
- Ensure
NODE_EXTRA_CA_CERTSpoints to the correct ca.pem file - Restart Claude Desktop after config changes
- Verify HTTPS is enabled:
mcpproxy serve --log-level=debug
- Documentation: Configuration, Features, Usage
- Website: https://mcpproxy.app
- Releases: https://github.com/smart-mcp-proxy/mcpproxy-go/releases
We welcome issues, feature ideas, and PRs! Fork the repo, create a feature branch, and open a pull request. See CONTRIBUTING.md (coming soon) for guidelines.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for mcpproxy-go
Similar Open Source Tools

mcpproxy-go
MCPProxy is an open-source desktop application that enhances AI agents by enabling intelligent tool discovery, reducing token usage, and providing security against malicious servers. It allows users to federate multiple servers, save tokens, and improve accuracy. The tool works offline and is compatible with various platforms. It offers features like Docker isolation, secrets management, OAuth authentication support, and HTTPS setup. Users can easily install, run, and manage servers using CLI commands. The tool provides detailed documentation and supports various tasks like adding servers, connecting to IDEs, and managing secrets.
superagent
Superagent is an open-source AI assistant framework and API that allows developers to add powerful AI assistants to their applications. These assistants use large language models (LLMs), retrieval augmented generation (RAG), and generative AI to help users with a variety of tasks, including question answering, chatbot development, content generation, data aggregation, and workflow automation. Superagent is backed by Y Combinator and is part of YC W24.
zeroclaw
ZeroClaw is a fast, small, and fully autonomous AI assistant infrastructure built with Rust. It features a lean runtime, cost-efficient deployment, fast cold starts, and a portable architecture. It is secure by design, fully swappable, and supports OpenAI-compatible provider support. The tool is designed for low-cost boards and small cloud instances, with a memory footprint of less than 5MB. It is suitable for tasks like deploying AI assistants, swapping providers/channels/tools, and pluggable everything.
supergateway
Supergateway is a tool that allows running MCP stdio-based servers over SSE (Server-Sent Events) with one command. It is useful for remote access, debugging, or connecting to SSE-based clients when your MCP server only speaks stdio. The tool supports running in SSE to Stdio mode as well, where it connects to a remote SSE server and exposes a local stdio interface for downstream clients. Supergateway can be used with ngrok to share local MCP servers with remote clients and can also be run in a Docker containerized deployment. It is designed with modularity in mind, ensuring compatibility and ease of use for AI tools exchanging data.
ai-counsel
AI Counsel is a true deliberative consensus MCP server where AI models engage in actual debate, refine positions across multiple rounds, and converge with voting and confidence levels. It features two modes (quick and conference), mixed adapters (CLI tools and HTTP services), auto-convergence, structured voting, semantic grouping, model-controlled stopping, evidence-based deliberation, local model support, data privacy, context injection, semantic search, fault tolerance, and full transcripts. Users can run local and cloud models to deliberate on various questions, ground decisions in reality by querying code and files, and query past decisions for analysis. The tool is designed for critical technical decisions requiring multi-model deliberation and consensus building.
z-ai-sdk-python
Z.ai Open Platform Python SDK is the official Python SDK for Z.ai's large model open interface, providing developers with easy access to Z.ai's open APIs. The SDK offers core features like chat completions, embeddings, video generation, audio processing, assistant API, and advanced tools. It supports various functionalities such as speech transcription, text-to-video generation, image understanding, and structured conversation handling. Developers can customize client behavior, configure API keys, and handle errors efficiently. The SDK is designed to simplify AI interactions and enhance AI capabilities for developers.
claude_code_bridge
Claude Code Bridge (ccb) is a new multi-model collaboration tool that enables effective collaboration among multiple AI models in a split-pane CLI environment. It offers features like visual and controllable interface, persistent context maintenance, token savings, and native workflow integration. The tool allows users to unleash the full power of CLI by avoiding model bias, cognitive blind spots, and context limitations. It provides a new WYSIWYG solution for multi-model collaboration, making it easier to control and visualize multiple AI models simultaneously.
LocalAGI
LocalAGI is a powerful, self-hostable AI Agent platform that allows you to design AI automations without writing code. It provides a complete drop-in replacement for OpenAI's Responses APIs with advanced agentic capabilities. With LocalAGI, you can create customizable AI assistants, automations, chat bots, and agents that run 100% locally, without the need for cloud services or API keys. The platform offers features like no-code agents, web-based interface, advanced agent teaming, connectors for various platforms, comprehensive REST API, short & long-term memory capabilities, planning & reasoning, periodic tasks scheduling, memory management, multimodal support, extensible custom actions, fully customizable models, observability, and more.
mcp-context-forge
MCP Context Forge is a powerful tool for generating context-aware data for machine learning models. It provides functionalities to create diverse datasets with contextual information, enhancing the performance of AI algorithms. The tool supports various data formats and allows users to customize the context generation process easily. With MCP Context Forge, users can efficiently prepare training data for tasks requiring contextual understanding, such as sentiment analysis, recommendation systems, and natural language processing.
mcp-devtools
MCP DevTools is a high-performance server written in Go that replaces multiple Node.js and Python-based servers. It provides access to essential developer tools through a unified, modular interface. The server is efficient, with minimal memory footprint and fast response times. It offers a comprehensive tool suite for agentic coding, including 20+ essential developer agent tools. The tool registry allows for easy addition of new tools. The server supports multiple transport modes, including STDIO, HTTP, and SSE. It includes a security framework for multi-layered protection and a plugin system for adding new tools.
git-mcp-server
A secure and scalable Git MCP server providing AI agents with powerful version control capabilities for local and serverless environments. It offers 28 comprehensive Git operations organized into seven functional categories, resources for contextual information about the Git environment, and structured prompt templates for guiding AI agents through complex workflows. The server features declarative tools, robust error handling, pluggable authentication, abstracted storage, full-stack observability, dependency injection, and edge-ready architecture. It also includes specialized features for Git integration such as cross-runtime compatibility, provider-based architecture, optimized Git execution, working directory management, configurable Git identity, safety features, and commit signing.
tokscale
Tokscale is a high-performance CLI tool and visualization dashboard for tracking token usage and costs across multiple AI coding agents. It helps monitor and analyze token consumption from various AI coding tools, providing real-time pricing calculations using LiteLLM's pricing data. Inspired by the Kardashev scale, Tokscale measures token consumption as users scale the ranks of AI-augmented development. It offers interactive TUI mode, multi-platform support, real-time pricing, detailed breakdowns, web visualization, flexible filtering, and social platform features.
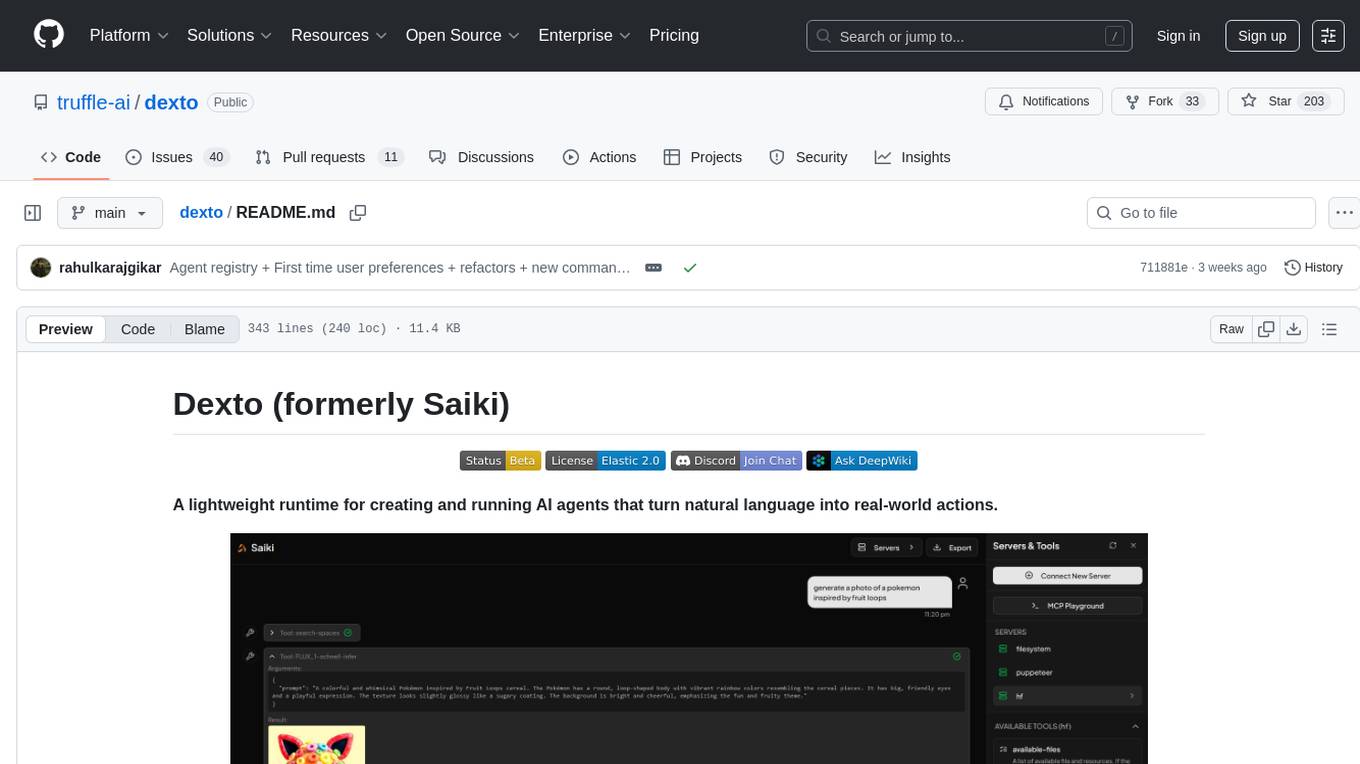
dexto
Dexto is a lightweight runtime for creating and running AI agents that turn natural language into real-world actions. It serves as the missing intelligence layer for building AI applications, standalone chatbots, or as the reasoning engine inside larger products. Dexto features a powerful CLI and Web UI for running AI agents, supports multiple interfaces, allows hot-swapping of LLMs from various providers, connects to remote tool servers via the Model Context Protocol, is config-driven with version-controlled YAML, offers production-ready core features, extensibility for custom services, and enables multi-agent collaboration via MCP and A2A.
alphora
Alphora is a full-stack framework for building production AI agents, providing agent orchestration, prompt engineering, tool execution, memory management, streaming, and deployment with an async-first, OpenAI-compatible design. It offers features like agent derivation, reasoning-action loop, async streaming, visual debugger, OpenAI compatibility, multimodal support, tool system with zero-config tools and type safety, prompt engine with dynamic prompts, memory and storage management, sandbox for secure execution, deployment as API, and more. Alphora allows users to build sophisticated AI agents easily and efficiently.
OpenMemory
OpenMemory is a cognitive memory engine for AI agents, providing real long-term memory capabilities beyond simple embeddings. It is self-hosted and supports Python + Node SDKs, with integrations for various tools like LangChain, CrewAI, AutoGen, and more. Users can ingest data from sources like GitHub, Notion, Google Drive, and others directly into memory. OpenMemory offers explainable traces for recalled information and supports multi-sector memory, temporal reasoning, decay engine, waypoint graph, and more. It aims to provide a true memory system rather than just a vector database with marketing copy, enabling users to build agents, copilots, journaling systems, and coding assistants that can remember and reason effectively.
llamafarm
LlamaFarm is a comprehensive AI framework that empowers users to build powerful AI applications locally, with full control over costs and deployment options. It provides modular components for RAG systems, vector databases, model management, prompt engineering, and fine-tuning. Users can create differentiated AI products without needing extensive ML expertise, using simple CLI commands and YAML configs. The framework supports local-first development, production-ready components, strategy-based configuration, and deployment anywhere from laptops to the cloud.
For similar tasks

mcpproxy-go
MCPProxy is an open-source desktop application that enhances AI agents by enabling intelligent tool discovery, reducing token usage, and providing security against malicious servers. It allows users to federate multiple servers, save tokens, and improve accuracy. The tool works offline and is compatible with various platforms. It offers features like Docker isolation, secrets management, OAuth authentication support, and HTTPS setup. Users can easily install, run, and manage servers using CLI commands. The tool provides detailed documentation and supports various tasks like adding servers, connecting to IDEs, and managing secrets.
PyAirbyte
PyAirbyte brings the power of Airbyte to every Python developer by providing a set of utilities to use Airbyte connectors in Python. It enables users to easily manage secrets, work with various connectors like GitHub, Shopify, and Postgres, and contribute to the project. PyAirbyte is not a replacement for Airbyte but complements it, supporting data orchestration frameworks like Airflow and Snowpark. Users can develop ETL pipelines and import connectors from local directories. The tool simplifies data integration tasks for Python developers.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.
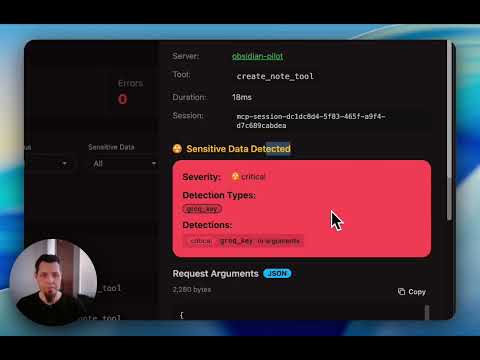



{ "listen": "127.0.0.1:8080", // Localhost-only by default for security "data_dir": "~/.mcpproxy", "enable_tray": true, // Search & tool limits "top_k": 5, "tools_limit": 15, "tool_response_limit": 20000, // Optional HTTPS configuration (disabled by default) "tls": { "enabled": false, // Set to true to enable HTTPS "require_client_cert": false, "hsts": true }, "mcpServers": [ { "name": "local-python", "command": "python", "args": ["-m", "my_server"], "protocol": "stdio", "enabled": true }, { "name": "remote-http", "url": "http://localhost:3001", "protocol": "http", "enabled": true } ] }