AirLine
AirLine: Efficient Learnable Line Detection with Local Edge Voting (IROS 2023)
Stars: 64
AirLine is a learnable edge-based line detection algorithm designed for various robotic tasks such as scene recognition, 3D reconstruction, and SLAM. It offers a novel approach to extracting line segments directly from edges, enhancing generalization ability for unseen environments. The algorithm balances efficiency and accuracy through a region-grow algorithm and local edge voting scheme for line parameterization. AirLine demonstrates state-of-the-art precision with significant runtime acceleration compared to other learning-based methods, making it ideal for low-power robots.
README:
IMPORTANT: MacOS, Linux not supported, only Windows for now
- download unet and dexiNed checkpoints and put it in the checkpoints folder
- specify if using Unet or Dexined using variable usingUnet in AirLine_demo.py, we recommand using dexiNed.
- specify sequencePath which should be a directory containing image sequence to test on.
- run Airline_demo.py in any way you want.
youtube demo video
note: This code may have issue running on MacOS given dependency of dll libraries
*If you wish to run testing, download test set and set up the directory which should look like:
├──AirLine
├── checkpoints
│ ├── unet.pth
│ └── dexi.pth
├── datasets
│ ├── Wireframe
│ │ ├── gt
│ │ │ ├── xxxxx.jpg
│ │ │ └── xxxxx.jpg
│ │ └── data
│ │ ├── xxxxx.jpg
│ │ └── xxxxx.jpg
│ └── YorkUrban
│ ├── gt
│ │ ├── xxxxx.jpg
│ │ └── xxxxx.jpg
│ └── data
│ ├── xxxxx.jpg
│ └── xxxxx.jpg
...
after specifying variable dataset to be "Wireframe" or "YorkUrban" and then run AirLine-test.py.
Line detection is widely used in many robotic tasks such as scene recognition, 3D reconstruction, and simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM). Compared to points, lines can provide both low-level and high-level geometrical information for downstream tasks. In this paper, we propose a novel edge-based line detection algorithm, AirLine, which can be applied to various tasks. In contrast to existing learnable endpoint-based methods which are sensitive to the geometrical condition of environments, AirLine can extract line segments directly from edges, resulting in a better generalization ability for unseen environments. Also to balance efficiency and accuracy, we introduce a region-grow algorithm and local edge voting scheme for line parameterization. To the best of our knowledge, AirLine is one of the first learnable edge-based line detection methods. Our extensive experiments show that it retains state-of-the-art-level precision yet with a $3-80\times$ runtime acceleration compared to other learning-based methods, which is critical for low-power robots.
The figure below provides a qualitative comparison across difference methods on untrained images with overlap detection highlighted in red .The first row is a distant view of city and the second row is street view, while the third to fifth rows are from UMA-VI dataset of subterranean environments. This gif showcases thenstability and great generalization ability of AirLine compared to LSD. In the first screenshot, both LSD and AirLine captured the line circled in red, while LSD lost track in the following frames, which is a good evidence of Airline's stability and robustness. The following video demonstrates a qualitative comparison across difference methods on untrained sequence from UMA_VI. We found that the AirLine and LSD methods performed better than the LETR and LCNN in generating detailed line detections. Moreover, AirLine is preferred over LSD since it is able to merge the two sides of thin lines, while LSD tends to detect both sides. Though LCNN produces lines of high precision, it is not suitable for tasks that require detailed line inputs, as it tends to ignore short lines and connect two unrelated endpoints in complex environments. LETR, which performed the best under the endpoint precision mentioned in its original paper, was found to have the worst line quality in terms of precision, stability, and reasonable geometry. A figure of Airline's pipelineAs shown above, AirLine is a learnable edge-based line detection architecture that is composed of four modules including edge detection, orientation detection, conditional region-grow, and line parameterization. We next present their motivation and detailed process, respectively. We made a video to demonstrate each stage.
By using edge-based learnable line detection approaches, AirLine has achieved state-of-art-level precision and significant efficiency and runtime boost.@inproceedings{lin2023airline,
title = {{AirLine}: Efficient Learnable Line Detection with Local Edge Voting},
author = {Lin, Xiao and Wang, Chen},
booktitle = {IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS)},
year = {2023}
}You may also download this paper.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for AirLine
Similar Open Source Tools

AirLine
AirLine is a learnable edge-based line detection algorithm designed for various robotic tasks such as scene recognition, 3D reconstruction, and SLAM. It offers a novel approach to extracting line segments directly from edges, enhancing generalization ability for unseen environments. The algorithm balances efficiency and accuracy through a region-grow algorithm and local edge voting scheme for line parameterization. AirLine demonstrates state-of-the-art precision with significant runtime acceleration compared to other learning-based methods, making it ideal for low-power robots.
AI4Animation
AI4Animation is a comprehensive framework for data-driven character animation, including data processing, neural network training, and runtime control, developed in Unity3D/PyTorch. It explores deep learning opportunities for character animation, covering biped and quadruped locomotion, character-scene interactions, sports and fighting games, and embodied avatar motions in AR/VR. The research focuses on generative frameworks, codebook matching, periodic autoencoders, animation layering, local motion phases, and neural state machines for character control and animation.
long-context-attention
Long-Context-Attention (YunChang) is a unified sequence parallel approach that combines the strengths of DeepSpeed-Ulysses-Attention and Ring-Attention to provide a versatile and high-performance solution for long context LLM model training and inference. It addresses the limitations of both methods by offering no limitation on the number of heads, compatibility with advanced parallel strategies, and enhanced performance benchmarks. The tool is verified in Megatron-LM and offers best practices for 4D parallelism, making it suitable for various attention mechanisms and parallel computing advancements.
SciMLBenchmarks.jl
SciMLBenchmarks.jl holds webpages, pdfs, and notebooks showing the benchmarks for the SciML Scientific Machine Learning Software ecosystem, including: * Benchmarks of equation solver implementations * Speed and robustness comparisons of methods for parameter estimation / inverse problems * Training universal differential equations (and subsets like neural ODEs) * Training of physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) * Surrogate comparisons, including radial basis functions, neural operators (DeepONets, Fourier Neural Operators), and more The SciML Bench suite is made to be a comprehensive open source benchmark from the ground up, covering the methods of computational science and scientific computing all the way to AI for science.
aligner
Aligner is a model-agnostic alignment tool designed to efficiently correct responses from large language models. It redistributes initial answers to align with human intentions, improving performance across various LLMs. The tool can be applied with minimal training, enhancing upstream models and reducing hallucination. Aligner's 'copy and correct' method preserves the base structure while enhancing responses. It achieves significant performance improvements in helpfulness, harmlessness, and honesty dimensions, with notable success in boosting Win Rates on evaluation leaderboards.
aligner
Aligner is a model-agnostic alignment tool that learns correctional residuals between preferred and dispreferred answers using a small model. It can be directly applied to various open-source and API-based models with only one-off training, suitable for rapid iteration and improving model performance. Aligner has shown significant improvements in helpfulness, harmlessness, and honesty dimensions across different large language models.
Instruct2Act
Instruct2Act is a framework that utilizes Large Language Models to map multi-modal instructions to sequential actions for robotic manipulation tasks. It generates Python programs using the LLM model for perception, planning, and action. The framework leverages foundation models like SAM and CLIP to convert high-level instructions into policy codes, accommodating various instruction modalities and task demands. Instruct2Act has been validated on robotic tasks in tabletop manipulation domains, outperforming learning-based policies in several tasks.
Electronic-Component-Sorter
The Electronic Component Classifier is a project that uses machine learning and artificial intelligence to automate the identification and classification of electrical and electronic components. It features component classification into seven classes, user-friendly design, and integration with Flask for a user-friendly interface. The project aims to reduce human error in component identification, make the process safer and more reliable, and potentially help visually impaired individuals in identifying electronic components.
merlin
Merlin is a groundbreaking model capable of generating natural language responses intricately linked with object trajectories of multiple images. It excels in predicting and reasoning about future events based on initial observations, showcasing unprecedented capability in future prediction and reasoning. Merlin achieves state-of-the-art performance on the Future Reasoning Benchmark and multiple existing multimodal language models benchmarks, demonstrating powerful multi-modal general ability and foresight minds.
bocoel
BoCoEL is a tool that leverages Bayesian Optimization to efficiently evaluate large language models by selecting a subset of the corpus for evaluation. It encodes individual entries into embeddings, uses Bayesian optimization to select queries, retrieves from the corpus, and provides easily managed evaluations. The tool aims to reduce computation costs during evaluation with a dynamic budget, supporting models like GPT2, Pythia, and LLAMA through integration with Hugging Face transformers and datasets. BoCoEL offers a modular design and efficient representation of the corpus to enhance evaluation quality.
llm-course
The LLM course is divided into three parts: 1. 🧩 **LLM Fundamentals** covers essential knowledge about mathematics, Python, and neural networks. 2. 🧑🔬 **The LLM Scientist** focuses on building the best possible LLMs using the latest techniques. 3. 👷 **The LLM Engineer** focuses on creating LLM-based applications and deploying them. For an interactive version of this course, I created two **LLM assistants** that will answer questions and test your knowledge in a personalized way: * 🤗 **HuggingChat Assistant**: Free version using Mixtral-8x7B. * 🤖 **ChatGPT Assistant**: Requires a premium account. ## 📝 Notebooks A list of notebooks and articles related to large language models. ### Tools | Notebook | Description | Notebook | |----------|-------------|----------| | 🧐 LLM AutoEval | Automatically evaluate your LLMs using RunPod |  | | 🥱 LazyMergekit | Easily merge models using MergeKit in one click. |  | | 🦎 LazyAxolotl | Fine-tune models in the cloud using Axolotl in one click. |  | | ⚡ AutoQuant | Quantize LLMs in GGUF, GPTQ, EXL2, AWQ, and HQQ formats in one click. |  | | 🌳 Model Family Tree | Visualize the family tree of merged models. |  | | 🚀 ZeroSpace | Automatically create a Gradio chat interface using a free ZeroGPU. |  |

nesa
Nesa is a tool that allows users to run on-prem AI for a fraction of the cost through a blind API. It provides blind privacy, zero latency on protected inference, wide model coverage, cost savings compared to cloud and on-prem AI, RAG support, and ChatGPT compatibility. Nesa achieves blind AI through Equivariant Encryption (EE), a new security technology that provides complete inference encryption with no additional latency. EE allows users to perform inference on neural networks without exposing the underlying data, preserving data privacy and security.

aitlas
The AiTLAS toolbox (Artificial Intelligence Toolbox for Earth Observation) includes state-of-the-art machine learning methods for exploratory and predictive analysis of satellite imagery as well as a repository of AI-ready Earth Observation (EO) datasets. It can be easily applied for a variety of Earth Observation tasks, such as land use and cover classification, crop type prediction, localization of specific objects (semantic segmentation), etc. The main goal of AiTLAS is to facilitate better usability and adoption of novel AI methods (and models) by EO experts, while offering easy access and standardized format of EO datasets to AI experts which allows benchmarking of various existing and novel AI methods tailored for EO data.
MoBA
MoBA (Mixture of Block Attention) is an innovative approach for long-context language models, enabling efficient processing of long sequences by dividing the full context into blocks and introducing a parameter-less gating mechanism. It allows seamless transitions between full and sparse attention modes, enhancing efficiency without compromising performance. MoBA has been deployed to support long-context requests and demonstrates significant advancements in efficient attention computation for large language models.
Nanoflow
NanoFlow is a throughput-oriented high-performance serving framework for Large Language Models (LLMs) that consistently delivers superior throughput compared to other frameworks by utilizing key techniques such as intra-device parallelism, asynchronous CPU scheduling, and SSD offloading. The framework proposes nano-batching to schedule compute-, memory-, and network-bound operations for simultaneous execution, leading to increased resource utilization. NanoFlow also adopts an asynchronous control flow to optimize CPU overhead and eagerly offloads KV-Cache to SSDs for multi-round conversations. The open-source codebase integrates state-of-the-art kernel libraries and provides necessary scripts for environment setup and experiment reproduction.
For similar tasks

AirLine
AirLine is a learnable edge-based line detection algorithm designed for various robotic tasks such as scene recognition, 3D reconstruction, and SLAM. It offers a novel approach to extracting line segments directly from edges, enhancing generalization ability for unseen environments. The algorithm balances efficiency and accuracy through a region-grow algorithm and local edge voting scheme for line parameterization. AirLine demonstrates state-of-the-art precision with significant runtime acceleration compared to other learning-based methods, making it ideal for low-power robots.
ailia-models
The collection of pre-trained, state-of-the-art AI models. ailia SDK is a self-contained, cross-platform, high-speed inference SDK for AI. The ailia SDK provides a consistent C++ API across Windows, Mac, Linux, iOS, Android, Jetson, and Raspberry Pi platforms. It also supports Unity (C#), Python, Rust, Flutter(Dart) and JNI for efficient AI implementation. The ailia SDK makes extensive use of the GPU through Vulkan and Metal to enable accelerated computing. # Supported models 323 models as of April 8th, 2024

composio
Composio is a production-ready toolset for AI agents that enables users to integrate AI agents with various agentic tools effortlessly. It provides support for over 100 tools across different categories, including popular softwares like GitHub, Notion, Linear, Gmail, Slack, and more. Composio ensures managed authorization with support for six different authentication protocols, offering better agentic accuracy and ease of use. Users can easily extend Composio with additional tools, frameworks, and authorization protocols. The toolset is designed to be embeddable and pluggable, allowing for seamless integration and consistent user experience.
awesome-llm-attributions
This repository focuses on unraveling the sources that large language models tap into for attribution or citation. It delves into the origins of facts, their utilization by the models, the efficacy of attribution methodologies, and challenges tied to ambiguous knowledge reservoirs, biases, and pitfalls of excessive attribution.
Awesome-Model-Merging-Methods-Theories-Applications
A comprehensive repository focusing on 'Model Merging in LLMs, MLLMs, and Beyond', providing an exhaustive overview of model merging methods, theories, applications, and future research directions. The repository covers various advanced methods, applications in foundation models, different machine learning subfields, and tasks like pre-merging methods, architecture transformation, weight alignment, basic merging methods, and more.
For similar jobs

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.
openvino
OpenVINO™ is an open-source toolkit for optimizing and deploying AI inference. It provides a common API to deliver inference solutions on various platforms, including CPU, GPU, NPU, and heterogeneous devices. OpenVINO™ supports pre-trained models from Open Model Zoo and popular frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and ONNX. Key components of OpenVINO™ include the OpenVINO™ Runtime, plugins for different hardware devices, frontends for reading models from native framework formats, and the OpenVINO Model Converter (OVC) for adjusting models for optimal execution on target devices.
peft
PEFT (Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning) is a collection of state-of-the-art methods that enable efficient adaptation of large pretrained models to various downstream applications. By only fine-tuning a small number of extra model parameters instead of all the model's parameters, PEFT significantly decreases the computational and storage costs while achieving performance comparable to fully fine-tuned models.
jetson-generative-ai-playground
This repo hosts tutorial documentation for running generative AI models on NVIDIA Jetson devices. The documentation is auto-generated and hosted on GitHub Pages using their CI/CD feature to automatically generate/update the HTML documentation site upon new commits.
emgucv
Emgu CV is a cross-platform .Net wrapper for the OpenCV image-processing library. It allows OpenCV functions to be called from .NET compatible languages. The wrapper can be compiled by Visual Studio, Unity, and "dotnet" command, and it can run on Windows, Mac OS, Linux, iOS, and Android.
MMStar
MMStar is an elite vision-indispensable multi-modal benchmark comprising 1,500 challenge samples meticulously selected by humans. It addresses two key issues in current LLM evaluation: the unnecessary use of visual content in many samples and the existence of unintentional data leakage in LLM and LVLM training. MMStar evaluates 6 core capabilities across 18 detailed axes, ensuring a balanced distribution of samples across all dimensions.
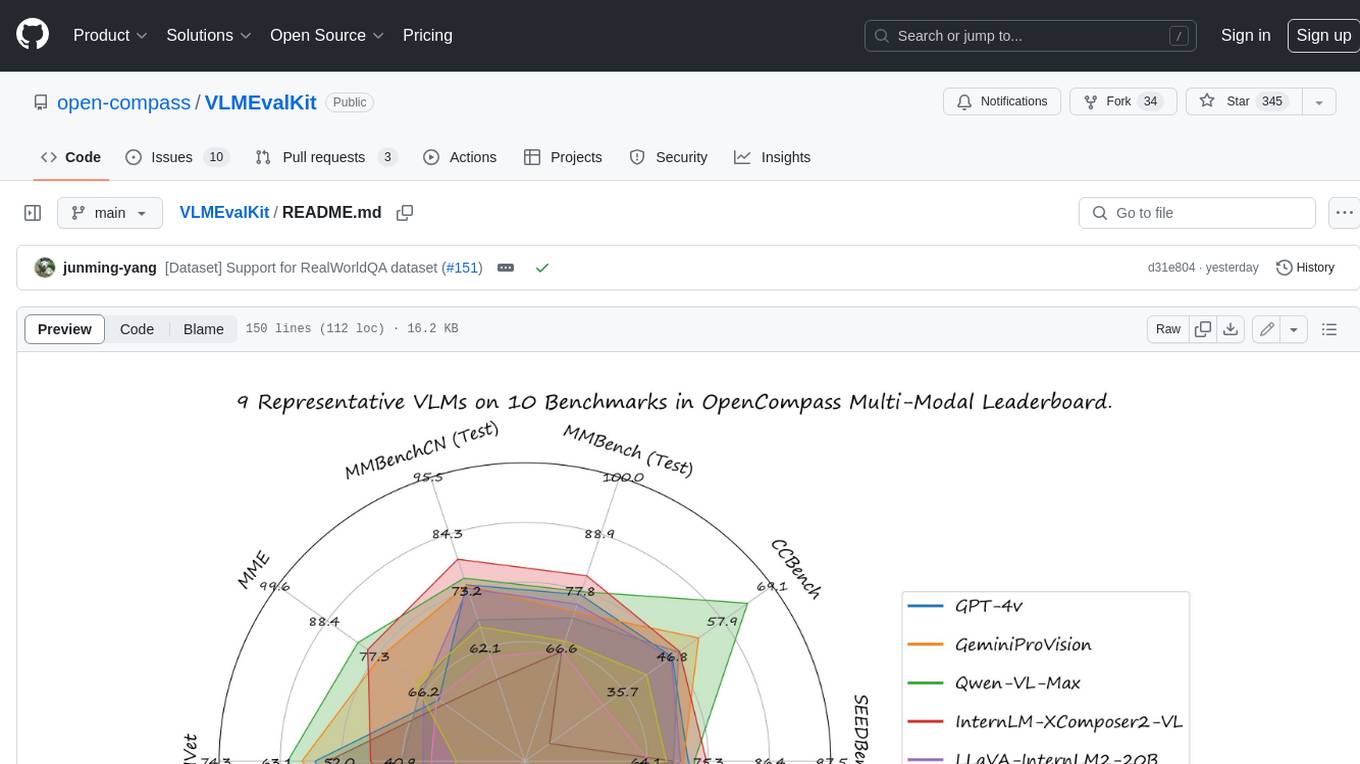
VLMEvalKit
VLMEvalKit is an open-source evaluation toolkit of large vision-language models (LVLMs). It enables one-command evaluation of LVLMs on various benchmarks, without the heavy workload of data preparation under multiple repositories. In VLMEvalKit, we adopt generation-based evaluation for all LVLMs, and provide the evaluation results obtained with both exact matching and LLM-based answer extraction.

llava-docker
This Docker image for LLaVA (Large Language and Vision Assistant) provides a convenient way to run LLaVA locally or on RunPod. LLaVA is a powerful AI tool that combines natural language processing and computer vision capabilities. With this Docker image, you can easily access LLaVA's functionalities for various tasks, including image captioning, visual question answering, text summarization, and more. The image comes pre-installed with LLaVA v1.2.0, Torch 2.1.2, xformers 0.0.23.post1, and other necessary dependencies. You can customize the model used by setting the MODEL environment variable. The image also includes a Jupyter Lab environment for interactive development and exploration. Overall, this Docker image offers a comprehensive and user-friendly platform for leveraging LLaVA's capabilities.