
ForAINet
official source code for paper entitled "Automated forest inventory: analysis of high-density airborne LiDAR point clouds with 3D deep learning"
Stars: 52
This repository contains the official code for the paper 'Automated forest inventory: analysis of high-density airborne LiDAR point clouds with 3D deep learning'. It provides tools for point cloud segmentation experiments based on different settings, tree parameters extraction, handling large point clouds through tiling, predicting, and merging workflows. Additionally, it includes commands for training, testing, and evaluating the models, along with the necessary datasets and pretrained models.
README:
Automated forest inventory: analysis of high-density airborne LiDAR point clouds with 3D deep learning
This repository represents the official code for paper entitled "Automated forest inventory: analysis of high-density airborne LiDAR point clouds with 3D deep learning".
Please refer to our previous repo:
https://github.com/prs-eth/PanopticSegForLargeScalePointCloud
It includes the detailed steps and issues that might happen but already resolved.
Please replace the old raw files with our new raw files:
For example, data_set1_5classes contains the data for "basic setting" in Table 4 in our paper.
- dataset for settings "basic setting", "+ binary semantic loss", "+ class weights", "+ height weights", "+ region weights", "+ elastic distortion and subsampling", "+ TreeMix"
- For other setting to be added here.
cd /$YOURPATH$/ForAINet/PointCloudSegmentation- Experiment for "basic setting" in the paper.
# Command for training
python train.py task=panoptic data=panoptic/treeins_set1 models=panoptic/FORpartseg_3heads model_name=PointGroup-PAPER training=treeins_set1 job_name=#YOUR_JOB_NAME#- Experiment for "+ binary semantic loss" setting in the paper
# Command for training
python train.py task=panoptic data=panoptic/treeins_set1 models=panoptic/FORpartseg_3heads_BiLoss model_name=PointGroup-PAPER training=treeins_set1_addBiLoss job_name=#YOUR_JOB_NAME#- Experiment for "+ class weights" setting in the paper
# Command for training
python train.py task=panoptic data=panoptic/treeins_set1_classweight models=panoptic/FORpartseg_3heads model_name=PointGroup-PAPER training=treeins_set1_nw8_classweight job_name=#YOUR_JOB_NAME#- Experiment for "+ height weights" setting in the paper
# Command for training
python train.py task=panoptic data=panoptic/treeins_set1_classweight models=panoptic/FORpartseg_3heads_heightweight model_name=PointGroup-PAPER training=treeins_set1_heightweight job_name=#YOUR_JOB_NAME#- Experiment for "+ region weights" setting in the paper
# Command for training
# To be added- Experiment for "+ intensity" setting in the paper
# Command for training
python train.py task=panoptic data=panoptic/treeins_set1_add_intensity models=panoptic/FORpartseg_3heads model_name=PointGroup-PAPER training=treeins_set1_intensity job_name=#YOUR_JOB_NAME#- Experiment for "+ return number" setting in the paper
# Command for training
python train.py task=panoptic data=panoptic/treeins_set1_add_return_num models=panoptic/FORpartseg_3heads model_name=PointGroup-PAPER training=treeins_set1_return_num job_name=#YOUR_JOB_NAME#- Experiment for "+ scan angle rank" setting in the paper
# Command for training
python train.py task=panoptic data=panoptic/treeins_set1_add_scan_angle_rank models=panoptic/FORpartseg_3heads model_name=PointGroup-PAPER training=treeins_set1_scan_angle_rank job_name=#YOUR_JOB_NAME#- Experiment for "+ hand-crafted features" setting in the paper
# Command for training
python train.py task=panoptic data=panoptic/treeins_set1_add_all_20010 models=panoptic/FORpartseg_3heads model_name=PointGroup-PAPER training=treeins_set1_addallFea_20010 job_name=#YOUR_JOB_NAME#- Experiment for "+ elastic distortion and subsampling" setting in the paper
# Command for training
python train.py task=panoptic data=panoptic/treeins_set1_curved_subsam models=panoptic/FORpartseg_3heads model_name=PointGroup-PAPER training=treeins_set1_addCurvedSubsample job_name=#YOUR_JOB_NAME#- Experiment for "+ TreeMix" setting in the paper
# Command for training
python train.py task=panoptic data=panoptic/treeins_set1_treemix3d models=panoptic/FORpartseg_3heads model_name=PointGroup-PAPER training=treeins_set1_mixtree job_name=#YOUR_JOB_NAME#- Experiments for data with different point density
# Command for training
python train.py task=panoptic data=panoptic/treeins_set1_treemix3d_pd#POINT_DENSITY# models=panoptic/FORpartseg_3heads model_name=PointGroup-PAPER training=mixtree_#POINT_DENSITY# job_name=#YOUR_JOB_NAME#
# take point density=10 as an example
python train.py task=panoptic data=panoptic/treeins_set1_treemix3d_pd10 models=panoptic/FORpartseg_3heads model_name=PointGroup-PAPER training=mixtree_10 job_name=#YOUR_JOB_NAME#- Commands for testing. Remember to change "checkpoint_dir" parameter to your path.
Our pretrained model could be download here: https://www.dropbox.com/scl/fi/mv4nxe60cco86fd2u9f3z/PointGroup-PAPER.pt?rlkey=ua6093kehk0youpo8g3a6g0nm&st=wiqv3a0u&dl=0
# Command for test
# remember to change the following 2 parameters in eval.yaml:
# 1. "checkpoint_dir" to your log files path
# 2. "data" is the paths for your test files
python eval.py
# Command for output the final evaluation file
# replace parameter "test_sem_path" by your path
python evaluation_stats_FOR.pycd /$YOURPATH$/ForAINet/tree_metrics
# remember to adjust parameters based on your dataset
python measurement.py# Please note that our code is based on the Superpoint Graphs repository, which can be found at https://github.com/loicland/superpoint_graph. We have included our custom partition_FORdata.py file.
cd /$YOURPATH$/ForAINet/superpoint_graph/partition
python partition_FORdata.pyFor large point clouds, we provide the code to process them seamlessly. The workflow involves the following steps:
- Splitting the point cloud: use split_largePC_to_tiles.py to divide the large point cloud into fixed-size tiles (default: 50m tiles with 5m overlap).
- Predicting for each tile: run predictions on each tile using generate_eval_command.py.
- Merging results: combine the results of all tiles back into the original point cloud using merge_tiles.py. All these operations can be easily executed with the large_PC_predict.sh command:
# modify parameters in large_PC_predict.sh:
# base_path: your project directory
# tile_size and overlap
# src_dir: specify the directory where your model is stored
# modify parameters in exampleeval.yaml:
# checkpoint_dir: the location of your model checkpoint
# data.fold: the paths of the point cloud files you want to test
bash large_PC_predict.shIf you find our work useful, please do not hesitate to cite it:
@article{
xiang2024automated,
title={Automated forest inventory: analysis of high-density airborne LiDAR point clouds with 3D deep learning},
author={Binbin Xiang, Maciej Wielgosz, Theodora Kontogianni, Torben Peters, Stefano Puliti, Rasmus Astrup, Konrad Schindler},
journal={Remote Sensing of Environment},
volume={305},
pages={114078},
year={2024},
publisher={Elsevier}
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for ForAINet
Similar Open Source Tools

ForAINet
This repository contains the official code for the paper 'Automated forest inventory: analysis of high-density airborne LiDAR point clouds with 3D deep learning'. It provides tools for point cloud segmentation experiments based on different settings, tree parameters extraction, handling large point clouds through tiling, predicting, and merging workflows. Additionally, it includes commands for training, testing, and evaluating the models, along with the necessary datasets and pretrained models.
paxml
Pax is a framework to configure and run machine learning experiments on top of Jax.
Pixel-Reasoner
Pixel Reasoner is a framework that introduces reasoning in the pixel-space for Vision-Language Models (VLMs), enabling them to directly inspect, interrogate, and infer from visual evidences. This enhances reasoning fidelity for visual tasks by equipping VLMs with visual reasoning operations like zoom-in and select-frame. The framework addresses challenges like model's imbalanced competence and reluctance to adopt pixel-space operations through a two-phase training approach involving instruction tuning and curiosity-driven reinforcement learning. With these visual operations, VLMs can interact with complex visual inputs such as images or videos to gather necessary information, leading to improved performance across visual reasoning benchmarks.
llama.vim
llama.vim is a plugin that provides local LLM-assisted text completion for Vim users. It offers features such as auto-suggest on cursor movement, manual suggestion toggling, suggestion acceptance with Tab and Shift+Tab, control over text generation time, context configuration, ring context with chunks from open and edited files, and performance stats display. The plugin requires a llama.cpp server instance to be running and supports FIM-compatible models. It aims to be simple, lightweight, and provide high-quality and performant local FIM completions even on consumer-grade hardware.
mergekit
Mergekit is a toolkit for merging pre-trained language models. It uses an out-of-core approach to perform unreasonably elaborate merges in resource-constrained situations. Merges can be run entirely on CPU or accelerated with as little as 8 GB of VRAM. Many merging algorithms are supported, with more coming as they catch my attention.
react-native-fast-tflite
A high-performance TensorFlow Lite library for React Native that utilizes JSI for power, zero-copy ArrayBuffers for efficiency, and low-level C/C++ TensorFlow Lite core API for direct memory access. It supports swapping out TensorFlow Models at runtime and GPU-accelerated delegates like CoreML/Metal/OpenGL. Easy VisionCamera integration allows for seamless usage. Users can load TensorFlow Lite models, interpret input and output data, and utilize GPU Delegates for faster computation. The library is suitable for real-time object detection, image classification, and other machine learning tasks in React Native applications.
suno-api
Suno AI API is an open-source project that allows developers to integrate the music generation capabilities of Suno.ai into their own applications. The API provides a simple and convenient way to generate music, lyrics, and other audio content using Suno.ai's powerful AI models. With Suno AI API, developers can easily add music generation functionality to their apps, websites, and other projects.
model_baseline
This repository contains code for testing model baselines on ARC-AGI tasks. Users can test model baselines on ARC-AGI-1 and ARC-AGI-2 tasks, run single tasks, run tasks with concurrency, score submissions, and view historical results. Contributors can add more model adapters to the `src/adapters` folder. The repository also provides CLI usage for validation, uploading model outputs, bulk uploading, and Hugging Face integration for model submissions. Contributors can test new providers using the `test_providers.sh` script before submitting pull requests.
swe-rl
SWE-RL is the official codebase for the paper 'SWE-RL: Advancing LLM Reasoning via Reinforcement Learning on Open Software Evolution'. It is the first approach to scale reinforcement learning based LLM reasoning for real-world software engineering, leveraging open-source software evolution data and rule-based rewards. The code provides prompt templates and the implementation of the reward function based on sequence similarity. Agentless Mini, a part of SWE-RL, builds on top of Agentless with improvements like fast async inference, code refactoring for scalability, and support for using multiple reproduction tests for reranking. The tool can be used for localization, repair, and reproduction test generation in software engineering tasks.
llm-detect-ai
This repository contains code and configurations for the LLM - Detect AI Generated Text competition. It includes setup instructions for hardware, software, dependencies, and datasets. The training section covers scripts and configurations for training LLM models, DeBERTa ranking models, and an embedding model. Text generation section details fine-tuning LLMs using the CLM objective on the PERSUADE corpus to generate student-like essays.
aicsimageio
AICSImageIO is a Python tool for Image Reading, Metadata Conversion, and Image Writing for Microscopy Images. It supports various file formats like OME-TIFF, TIFF, ND2, DV, CZI, LIF, PNG, GIF, and Bio-Formats. Users can read and write metadata and imaging data, work with different file systems like local paths, HTTP URLs, s3fs, and gcsfs. The tool provides functionalities for full image reading, delayed image reading, mosaic image reading, metadata reading, xarray coordinate plane attachment, cloud IO support, and saving to OME-TIFF. It also offers benchmarking and developer resources.
gemini-srt-translator
Gemini SRT Translator is a tool that utilizes Google Generative AI to provide accurate and efficient translations for subtitle files. Users can customize translation settings, such as model name and batch size, and list available models from the Gemini API. The tool requires a free API key from Google AI Studio for setup and offers features like translating subtitles to a specified target language and resuming partial translations. Users can further customize translation settings with optional parameters like gemini_api_key2, output_file, start_line, model_name, batch_size, and more.

svelte-bench
SvelteBench is an LLM benchmark tool for evaluating Svelte components generated by large language models. It supports multiple LLM providers such as OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, and OpenRouter. Users can run predefined test suites to verify the functionality of the generated components. The tool allows configuration of API keys for different providers and offers debug mode for faster development. Users can provide a context file to improve component generation. Benchmark results are saved in JSON format for analysis and visualization.
ethereum-etl-airflow
This repository contains Airflow DAGs for extracting, transforming, and loading (ETL) data from the Ethereum blockchain into BigQuery. The DAGs use the Google Cloud Platform (GCP) services, including BigQuery, Cloud Storage, and Cloud Composer, to automate the ETL process. The repository also includes scripts for setting up the GCP environment and running the DAGs locally.
detoxify
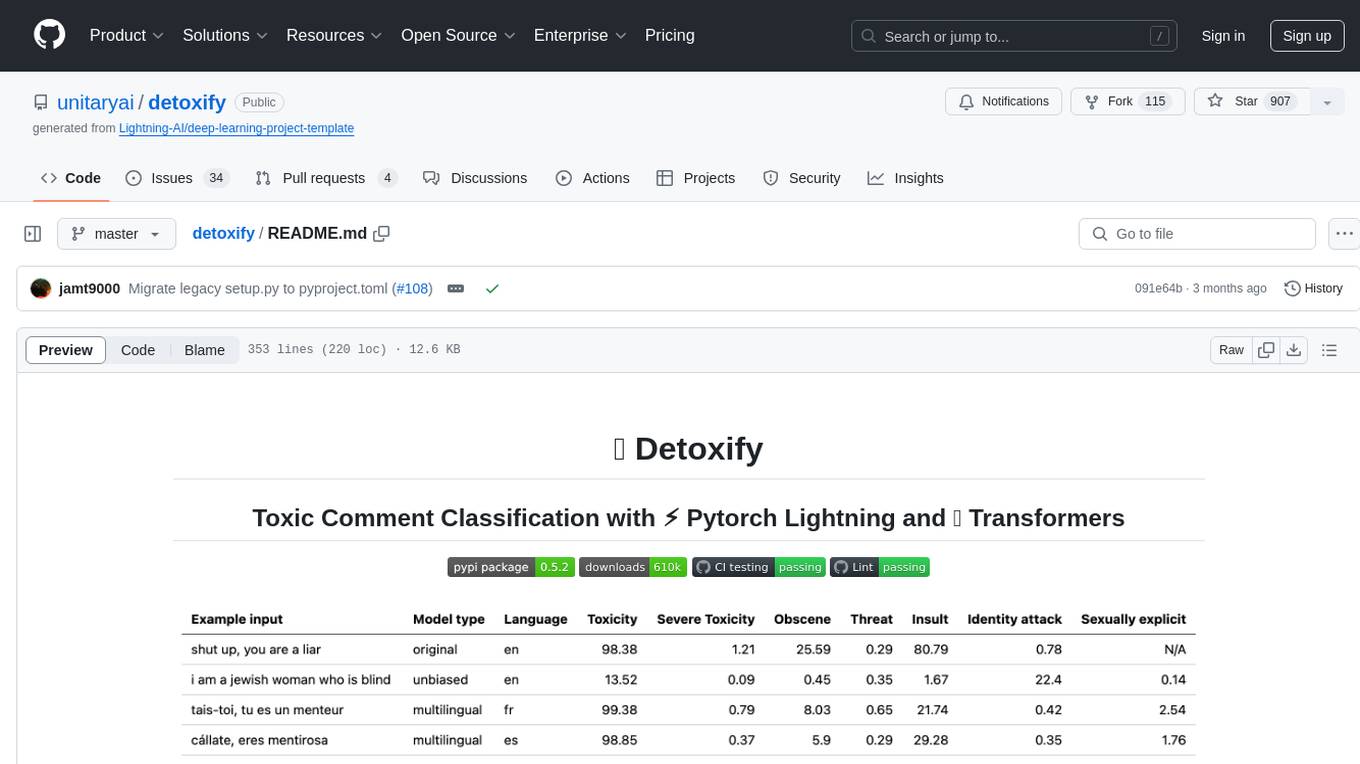
Detoxify is a library that provides trained models and code to predict toxic comments on 3 Jigsaw challenges: Toxic comment classification, Unintended Bias in Toxic comments, Multilingual toxic comment classification. It includes models like 'original', 'unbiased', and 'multilingual' trained on different datasets to detect toxicity and minimize bias. The library aims to help in stopping harmful content online by interpreting visual content in context. Users can fine-tune the models on carefully constructed datasets for research purposes or to aid content moderators in flagging out harmful content quicker. The library is built to be user-friendly and straightforward to use.
llmgraph
llmgraph is a tool that enables users to create knowledge graphs in GraphML, GEXF, and HTML formats by extracting world knowledge from large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT. It supports various entity types and relationships, offers cache support for efficient graph growth, and provides insights into LLM costs. Users can customize the model used and interact with different LLM providers. The tool allows users to generate interactive graphs based on a specified entity type and Wikipedia link, making it a valuable resource for knowledge graph creation and exploration.
For similar tasks

ForAINet
This repository contains the official code for the paper 'Automated forest inventory: analysis of high-density airborne LiDAR point clouds with 3D deep learning'. It provides tools for point cloud segmentation experiments based on different settings, tree parameters extraction, handling large point clouds through tiling, predicting, and merging workflows. Additionally, it includes commands for training, testing, and evaluating the models, along with the necessary datasets and pretrained models.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.

oss-fuzz-gen
This framework generates fuzz targets for real-world `C`/`C++` projects with various Large Language Models (LLM) and benchmarks them via the `OSS-Fuzz` platform. It manages to successfully leverage LLMs to generate valid fuzz targets (which generate non-zero coverage increase) for 160 C/C++ projects. The maximum line coverage increase is 29% from the existing human-written targets.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.