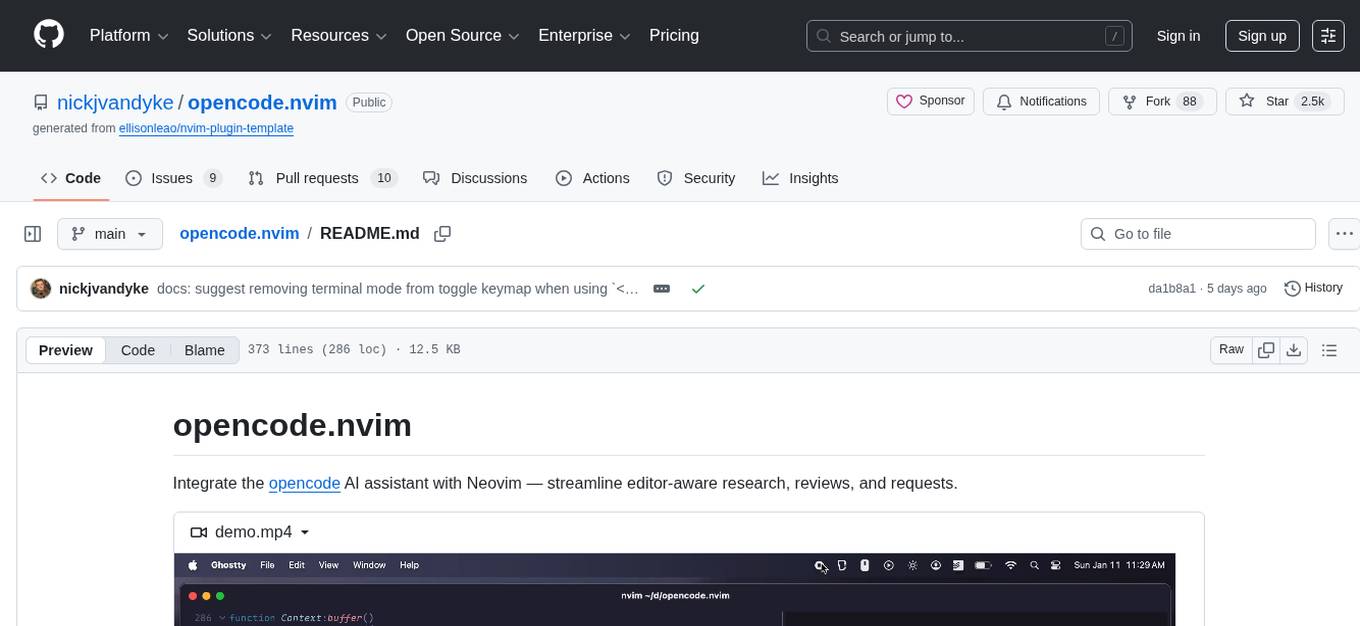
opencode.nvim
Integrate the opencode AI assistant with Neovim — streamline editor-aware research, reviews, and requests.
Stars: 2527
opencode.nvim is a tool that integrates the opencode AI assistant with Neovim, allowing users to streamline editor-aware research, reviews, and requests. It provides features such as connecting to opencode instances, sharing editor context, input prompts with completions, executing commands, and monitoring state via statusline component. Users can define their own prompts, reload edited buffers in real-time, and forward Server-Sent-Events for automation. The tool offers sensible defaults with flexible configuration and API to fit various workflows, supporting ranges and dot-repeat in a Vim-like manner.
README:
Integrate the opencode AI assistant with Neovim — streamline editor-aware research, reviews, and requests.
https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/077daa78-d401-4b8b-98d1-9ba9f94c2330
- Connect to any
opencodes running in Neovim's CWD, or provide an integrated instance. - Share editor context (buffer, cursor, selection, diagnostics, etc.).
- Input prompts with completions, highlights, and normal-mode support.
- Select prompts from a library and define your own.
- Execute commands.
- Respond to permission requests.
- Reload edited buffers in real-time.
- Monitor state via statusline component.
- Forward Server-Sent-Events as autocmds for automation.
- Sensible defaults with well-documented, flexible configuration and API to fit your workflow.
- Vim-y — supports ranges and dot-repeat.
{
"nickjvandyke/opencode.nvim",
dependencies = {
-- Recommended for `ask()` and `select()`.
-- Required for `snacks` provider.
---@module 'snacks' <- Loads `snacks.nvim` types for configuration intellisense.
{ "folke/snacks.nvim", opts = { input = {}, picker = {}, terminal = {} } },
},
config = function()
---@type opencode.Opts
vim.g.opencode_opts = {
-- Your configuration, if any — see `lua/opencode/config.lua`, or "goto definition" on the type or field.
}
-- Required for `opts.events.reload`.
vim.o.autoread = true
-- Recommended/example keymaps.
vim.keymap.set({ "n", "x" }, "<C-a>", function() require("opencode").ask("@this: ", { submit = true }) end, { desc = "Ask opencode…" })
vim.keymap.set({ "n", "x" }, "<C-x>", function() require("opencode").select() end, { desc = "Execute opencode action…" })
vim.keymap.set({ "n", "t" }, "<C-.>", function() require("opencode").toggle() end, { desc = "Toggle opencode" })
vim.keymap.set({ "n", "x" }, "go", function() return require("opencode").operator("@this ") end, { desc = "Add range to opencode", expr = true })
vim.keymap.set("n", "goo", function() return require("opencode").operator("@this ") .. "_" end, { desc = "Add line to opencode", expr = true })
vim.keymap.set("n", "<S-C-u>", function() require("opencode").command("session.half.page.up") end, { desc = "Scroll opencode up" })
vim.keymap.set("n", "<S-C-d>", function() require("opencode").command("session.half.page.down") end, { desc = "Scroll opencode down" })
-- You may want these if you use the opinionated `<C-a>` and `<C-x>` keymaps above — otherwise consider `<leader>o…` (and remove terminal mode from the `toggle` keymap).
vim.keymap.set("n", "+", "<C-a>", { desc = "Increment under cursor", noremap = true })
vim.keymap.set("n", "-", "<C-x>", { desc = "Decrement under cursor", noremap = true })
end,
}programs.nixvim = {
extraPlugins = [
pkgs.vimPlugins.opencode-nvim
];
};[!TIP] Run
:checkhealth opencodeafter setup.
opencode.nvim provides a rich and reliable default experience — see all available options and their defaults here.
opencode.nvim replaces placeholders in prompts with the corresponding context:
| Placeholder | Context |
|---|---|
@this |
Operator range or visual selection if any, else cursor position |
@buffer |
Current buffer |
@buffers |
Open buffers |
@visible |
Visible text |
@diagnostics |
Current buffer diagnostics |
@quickfix |
Quickfix list |
@diff |
Git diff |
@marks |
Global marks |
@grapple |
grapple.nvim tags |
Select or reference prompts to review, explain, and improve your code:
| Name | Prompt |
|---|---|
diagnostics |
Explain @diagnostics
|
diff |
Review the following git diff for correctness and readability: @diff
|
document |
Add comments documenting @this
|
explain |
Explain @this and its context |
fix |
Fix @diagnostics
|
implement |
Implement @this
|
optimize |
Optimize @this for performance and readability |
review |
Review @this for correctness and readability |
test |
Add tests for @this
|
You can manually run opencodes in Neovim's CWD however you like and opencode.nvim will find them!
If opencode.nvim can't find an existing opencode, it uses the configured provider (defaulting based on availability) to manage one for you.
[!IMPORTANT] You must run
opencodewith the--portflag to expose its server. Providers do so by default.
Neovim terminal
vim.g.opencode_opts = {
provider = {
enabled = "terminal",
terminal = {
-- ...
}
}
}snacks.terminal
vim.g.opencode_opts = {
provider = {
enabled = "snacks",
snacks = {
-- ...
}
}
}kitty
vim.g.opencode_opts = {
provider = {
enabled = "kitty",
kitty = {
-- ...
}
}
}The kitty provider requires remote control via a socket to be enabled.
You can do this either by running Kitty with the following command:
# For Linux only:
kitty -o allow_remote_control=yes --single-instance --listen-on unix:@mykitty
# Other UNIX systems:
kitty -o allow_remote_control=yes --single-instance --listen-on unix:/tmp/mykittyOR, by adding the following to your kitty.conf:
# For Linux only:
allow_remote_control yes
listen_on unix:@mykitty
# Other UNIX systems:
allow_remote_control yes
listen_on unix:/tmp/kitty
wezterm
vim.g.opencode_opts = {
provider = {
enabled = "wezterm",
wezterm = {
-- ...
}
}
}tmux
vim.g.opencode_opts = {
provider = {
enabled = "tmux",
tmux = {
-- ...
}
}
}custom
Integrate your custom method for convenience!
vim.g.opencode_opts = {
provider = {
toggle = function(self)
-- ...
end,
start = function(self)
-- ...
end,
stop = function(self)
-- ...
end,
}
}Please submit PRs adding new providers! 🙂
opencode.nvim sets these buffer-local keymaps in provider terminals for Neovim-like message navigation:
| Keymap | Command | Description |
|---|---|---|
<C-u> |
session.half.page.up |
Scroll up half page |
<C-d> |
session.half.page.down |
Scroll down half page |
<Esc> |
session.interrupt |
Interrupt |
gg |
session.first |
Go to first message |
G |
session.last |
Go to last message |
Input a prompt for opencode.
- Press
<Up>to browse recent asks. - Highlights and completes contexts and
opencodesubagents.- Press
<Tab>to trigger built-in completion. - Registers
opts.ask.blink_cmp_sourceswhen usingsnacks.inputandblink.cmp.
- Press
Select from all opencode.nvim functionality.
- Prompts
- Commands
- Fetches custom commands from
opencode
- Fetches custom commands from
- Provider controls
Highlights and previews items when using snacks.picker.
Prompt opencode.
- Resolves named references to configured prompts.
- Injects configured contexts.
-
opencodewill interpret@references to files or subagents.
Wraps prompt as an operator, supporting ranges and dot-repeat.
Command opencode:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
session.list |
List sessions |
session.new |
Start a new session |
session.select |
Select a session |
session.share |
Share the current session |
session.interrupt |
Interrupt the current session |
session.compact |
Compact the current session (reduce context size) |
session.page.up |
Scroll messages up by one page |
session.page.down |
Scroll messages down by one page |
session.half.page.up |
Scroll messages up by half a page |
session.half.page.down |
Scroll messages down by half a page |
session.first |
Jump to the first message in the session |
session.last |
Jump to the last message in the session |
session.undo |
Undo the last action in the current session |
session.redo |
Redo the last undone action in the current session |
prompt.submit |
Submit the TUI input |
prompt.clear |
Clear the TUI input |
agent.cycle |
Cycle the selected agent |
opencode.nvim forwards opencode's Server-Sent-Events as an OpencodeEvent autocmd:
-- Handle `opencode` events
vim.api.nvim_create_autocmd("User", {
pattern = "OpencodeEvent:*", -- Optionally filter event types
callback = function(args)
---@type opencode.cli.client.Event
local event = args.data.event
---@type number
local port = args.data.port
-- See the available event types and their properties
vim.notify(vim.inspect(event))
-- Do something useful
if event.type == "session.idle" then
vim.notify("`opencode` finished responding")
end
end,
})When opencode edits a file, opencode.nvim automatically reloads the corresponding buffer.
When opencode requests a permission, opencode.nvim waits for idle to ask you to approve or deny it.
lualine
require("lualine").setup({
sections = {
lualine_z = {
{
require("opencode").statusline,
},
}
}
})- Inspired by nvim-aider, neopencode.nvim, and sidekick.nvim.
- Uses
opencode's TUI for simplicity — see sudo-tee/opencode.nvim for a Neovim frontend. - mcp-neovim-server may better suit you, but it lacks customization and tool calls are slow and unreliable.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for opencode.nvim
Similar Open Source Tools

opencode.nvim
opencode.nvim is a tool that integrates the opencode AI assistant with Neovim, allowing users to streamline editor-aware research, reviews, and requests. It provides features such as connecting to opencode instances, sharing editor context, input prompts with completions, executing commands, and monitoring state via statusline component. Users can define their own prompts, reload edited buffers in real-time, and forward Server-Sent-Events for automation. The tool offers sensible defaults with flexible configuration and API to fit various workflows, supporting ranges and dot-repeat in a Vim-like manner.
fittencode.nvim
Fitten Code AI Programming Assistant for Neovim provides fast completion using AI, asynchronous I/O, and support for various actions like document code, edit code, explain code, find bugs, generate unit test, implement features, optimize code, refactor code, start chat, and more. It offers features like accepting suggestions with Tab, accepting line with Ctrl + Down, accepting word with Ctrl + Right, undoing accepted text, automatic scrolling, and multiple HTTP/REST backends. It can run as a coc.nvim source or nvim-cmp source.
opencode.nvim
Opencode.nvim is a neovim frontend for Opencode, a terminal-based AI coding agent. It provides a chat interface between neovim and the Opencode AI agent, capturing editor context to enhance prompts. The plugin maintains persistent sessions for continuous conversations with the AI assistant, similar to Cursor AI.
worker-vllm
The worker-vLLM repository provides a serverless endpoint for deploying OpenAI-compatible vLLM models with blazing-fast performance. It supports deploying various model architectures, such as Aquila, Baichuan, BLOOM, ChatGLM, Command-R, DBRX, DeciLM, Falcon, Gemma, GPT-2, GPT BigCode, GPT-J, GPT-NeoX, InternLM, Jais, LLaMA, MiniCPM, Mistral, Mixtral, MPT, OLMo, OPT, Orion, Phi, Phi-3, Qwen, Qwen2, Qwen2MoE, StableLM, Starcoder2, Xverse, and Yi. Users can deploy models using pre-built Docker images or build custom images with specified arguments. The repository also supports OpenAI compatibility for chat completions, completions, and models, with customizable input parameters. Users can modify their OpenAI codebase to use the deployed vLLM worker and access a list of available models for deployment.
avante.nvim
avante.nvim is a Neovim plugin that emulates the behavior of the Cursor AI IDE, providing AI-driven code suggestions and enabling users to apply recommendations to their source files effortlessly. It offers AI-powered code assistance and one-click application of suggested changes, streamlining the editing process and saving time. The plugin is still in early development, with functionalities like setting API keys, querying AI about code, reviewing suggestions, and applying changes. Key bindings are available for various actions, and the roadmap includes enhancing AI interactions, stability improvements, and introducing new features for coding tasks.
opencode.nvim
Opencode.nvim is a Neovim plugin that provides a simple and efficient way to browse, search, and open files in a project. It enhances the file navigation experience by offering features like fuzzy finding, file preview, and quick access to frequently used files. With Opencode.nvim, users can easily navigate through their project files, jump to specific locations, and manage their workflow more effectively. The plugin is designed to improve productivity and streamline the development process by simplifying file handling tasks within Neovim.
code-cli
Autohand Code CLI is an autonomous coding agent in CLI form that uses the ReAct pattern to understand, plan, and execute code changes. It is designed for seamless coding experience without context switching or copy-pasting. The tool is fast, intuitive, and extensible with modular skills. It can be used to automate coding tasks, enforce code quality, and speed up development. Autohand can be integrated into team workflows and CI/CD pipelines to enhance productivity and efficiency.
llm.nvim
llm.nvim is a universal plugin for a large language model (LLM) designed to enable users to interact with LLM within neovim. Users can customize various LLMs such as gpt, glm, kimi, and local LLM. The plugin provides tools for optimizing code, comparing code, translating text, and more. It also supports integration with free models from Cloudflare, Github models, siliconflow, and others. Users can customize tools, chat with LLM, quickly translate text, and explain code snippets. The plugin offers a flexible window interface for easy interaction and customization.
ax
Ax is a Typescript library that allows users to build intelligent agents inspired by agentic workflows and the Stanford DSP paper. It seamlessly integrates with multiple Large Language Models (LLMs) and VectorDBs to create RAG pipelines or collaborative agents capable of solving complex problems. The library offers advanced features such as streaming validation, multi-modal DSP, and automatic prompt tuning using optimizers. Users can easily convert documents of any format to text, perform smart chunking, embedding, and querying, and ensure output validation while streaming. Ax is production-ready, written in Typescript, and has zero dependencies.
SwiftAgent
A type-safe, declarative framework for building AI agents in Swift, SwiftAgent is built on Apple FoundationModels. It allows users to compose agents by combining Steps in a declarative syntax similar to SwiftUI. The framework ensures compile-time checked input/output types, native Apple AI integration, structured output generation, and built-in security features like permission, sandbox, and guardrail systems. SwiftAgent is extensible with MCP integration, distributed agents, and a skills system. Users can install SwiftAgent with Swift 6.2+ on iOS 26+, macOS 26+, or Xcode 26+ using Swift Package Manager.
nextlint
Nextlint is a rich text editor (WYSIWYG) written in Svelte, using MeltUI headless UI and tailwindcss CSS framework. It is built on top of tiptap editor (headless editor) and prosemirror. Nextlint is easy to use, develop, and maintain. It has a prompt engine that helps to integrate with any AI API and enhance the writing experience. Dark/Light theme is supported and customizable.
LocalAGI
LocalAGI is a powerful, self-hostable AI Agent platform that allows you to design AI automations without writing code. It provides a complete drop-in replacement for OpenAI's Responses APIs with advanced agentic capabilities. With LocalAGI, you can create customizable AI assistants, automations, chat bots, and agents that run 100% locally, without the need for cloud services or API keys. The platform offers features like no-code agents, web-based interface, advanced agent teaming, connectors for various platforms, comprehensive REST API, short & long-term memory capabilities, planning & reasoning, periodic tasks scheduling, memory management, multimodal support, extensible custom actions, fully customizable models, observability, and more.
capsule
Capsule is a secure and durable runtime for AI agents, designed to coordinate tasks in isolated environments. It allows for long-running workflows, large-scale processing, autonomous decision-making, and multi-agent systems. Tasks run in WebAssembly sandboxes with isolated execution, resource limits, automatic retries, and lifecycle tracking. It enables safe execution of untrusted code within AI agent systems.
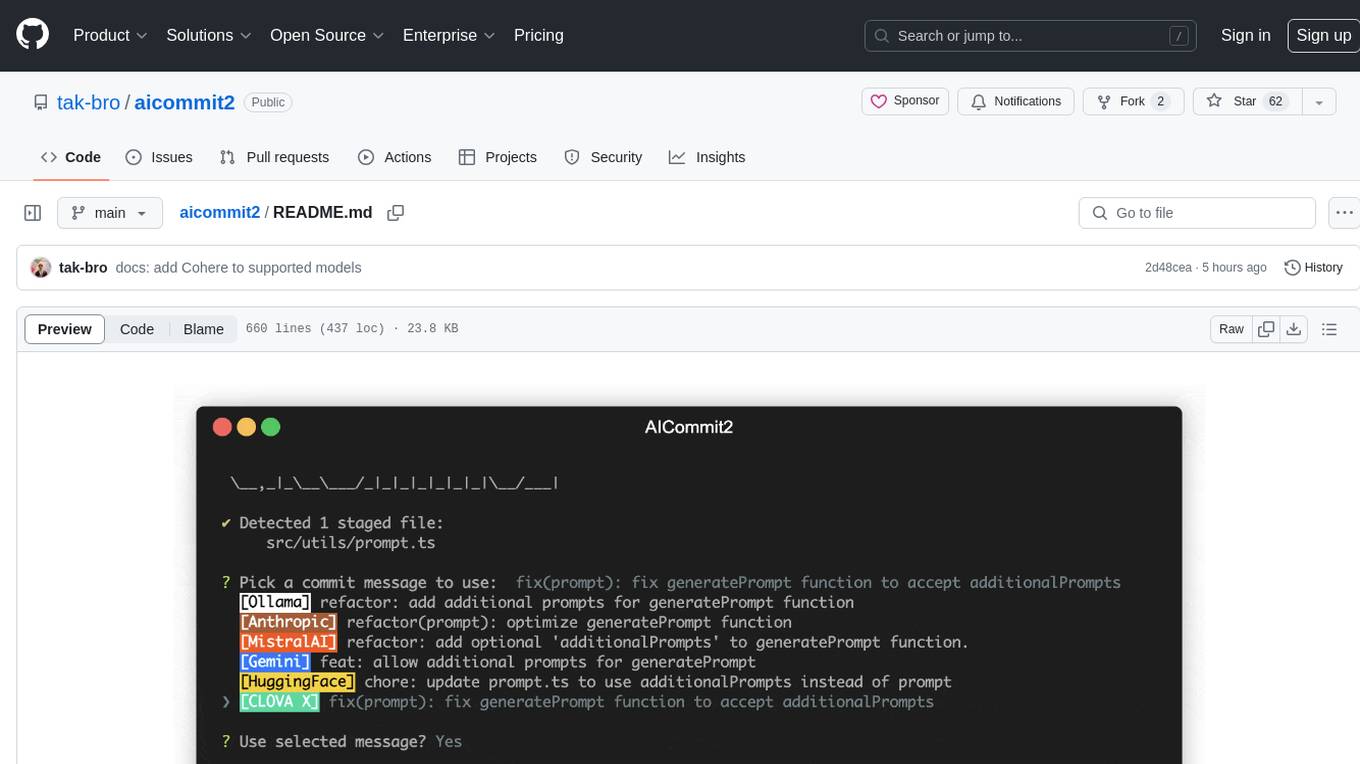
aicommit2
AICommit2 is a Reactive CLI tool that streamlines interactions with various AI providers such as OpenAI, Anthropic Claude, Gemini, Mistral AI, Cohere, and unofficial providers like Huggingface and Clova X. Users can request multiple AI simultaneously to generate git commit messages without waiting for all AI responses. The tool runs 'git diff' to grab code changes, sends them to configured AI, and returns the AI-generated commit message. Users can set API keys or Cookies for different providers and configure options like locale, generate number of messages, commit type, proxy, timeout, max-length, and more. AICommit2 can be used both locally with Ollama and remotely with supported providers, offering flexibility and efficiency in generating commit messages.
ai-coders-context
The @ai-coders/context repository provides the Ultimate MCP for AI Agent Orchestration, Context Engineering, and Spec-Driven Development. It simplifies context engineering for AI by offering a universal process called PREVC, which consists of Planning, Review, Execution, Validation, and Confirmation steps. The tool aims to address the problem of context fragmentation by introducing a single `.context/` directory that works universally across different tools. It enables users to create structured documentation, generate agent playbooks, manage workflows, provide on-demand expertise, and sync across various AI tools. The tool follows a structured, spec-driven development approach to improve AI output quality and ensure reproducible results across projects.
For similar tasks
HiNote
HiNote is an AI-programmed Obsidian plugin that allows users to extract highlighted text from notes, add comments, generate AI comments, and engage in dialogue with the highlighted text. Users can highlight text in various formats, export it as knowledge card images, create new notes, and enjoy extended features in the main view. The plugin supports features like highlighted text retrieval, highlight comments, export as image, export as note, AI comment generation, AI chat, and premium features like a Flashcard system for effective memorization.

opencode.nvim
opencode.nvim is a tool that integrates the opencode AI assistant with Neovim, allowing users to streamline editor-aware research, reviews, and requests. It provides features such as connecting to opencode instances, sharing editor context, input prompts with completions, executing commands, and monitoring state via statusline component. Users can define their own prompts, reload edited buffers in real-time, and forward Server-Sent-Events for automation. The tool offers sensible defaults with flexible configuration and API to fit various workflows, supporting ranges and dot-repeat in a Vim-like manner.
aichat
Aichat is an AI-powered CLI chat and copilot tool that seamlessly integrates with over 10 leading AI platforms, providing a powerful combination of chat-based interaction, context-aware conversations, and AI-assisted shell capabilities, all within a customizable and user-friendly environment.
wingman-ai
Wingman AI allows you to use your voice to talk to various AI providers and LLMs, process your conversations, and ultimately trigger actions such as pressing buttons or reading answers. Our _Wingmen_ are like characters and your interface to this world, and you can easily control their behavior and characteristics, even if you're not a developer. AI is complex and it scares people. It's also **not just ChatGPT**. We want to make it as easy as possible for you to get started. That's what _Wingman AI_ is all about. It's a **framework** that allows you to build your own Wingmen and use them in your games and programs. The idea is simple, but the possibilities are endless. For example, you could: * **Role play** with an AI while playing for more immersion. Have air traffic control (ATC) in _Star Citizen_ or _Flight Simulator_. Talk to Shadowheart in Baldur's Gate 3 and have her respond in her own (cloned) voice. * Get live data such as trade information, build guides, or wiki content and have it read to you in-game by a _character_ and voice you control. * Execute keystrokes in games/applications and create complex macros. Trigger them in natural conversations with **no need for exact phrases.** The AI understands the context of your dialog and is quite _smart_ in recognizing your intent. Say _"It's raining! I can't see a thing!"_ and have it trigger a command you simply named _WipeVisors_. * Automate tasks on your computer * improve accessibility * ... and much more
letmedoit
LetMeDoIt AI is a virtual assistant designed to revolutionize the way you work. It goes beyond being a mere chatbot by offering a unique and powerful capability - the ability to execute commands and perform computing tasks on your behalf. With LetMeDoIt AI, you can access OpenAI ChatGPT-4, Google Gemini Pro, and Microsoft AutoGen, local LLMs, all in one place, to enhance your productivity.
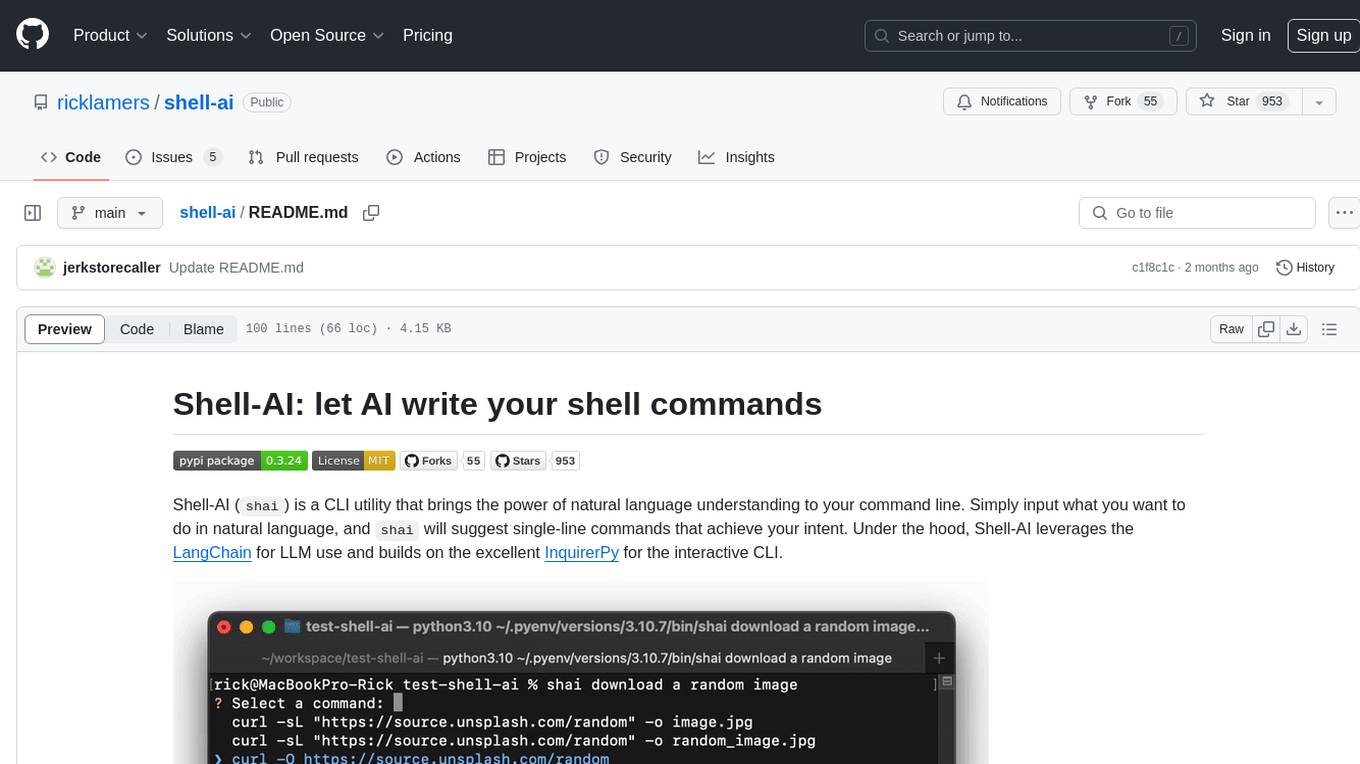
shell-ai
Shell-AI (`shai`) is a CLI utility that enables users to input commands in natural language and receive single-line command suggestions. It leverages natural language understanding and interactive CLI tools to enhance command line interactions. Users can describe tasks in plain English and receive corresponding command suggestions, making it easier to execute commands efficiently. Shell-AI supports cross-platform usage and is compatible with Azure OpenAI deployments, offering a user-friendly and efficient way to interact with the command line.
AIRAVAT
AIRAVAT is a multifunctional Android Remote Access Tool (RAT) with a GUI-based Web Panel that does not require port forwarding. It allows users to access various features on the victim's device, such as reading files, downloading media, retrieving system information, managing applications, SMS, call logs, contacts, notifications, keylogging, admin permissions, phishing, audio recording, music playback, device control (vibration, torch light, wallpaper), executing shell commands, clipboard text retrieval, URL launching, and background operation. The tool requires a Firebase account and tools like ApkEasy Tool or ApkTool M for building. Users can set up Firebase, host the web panel, modify Instagram.apk for RAT functionality, and connect the victim's device to the web panel. The tool is intended for educational purposes only, and users are solely responsible for its use.
chatflow
Chatflow is a tool that provides a chat interface for users to interact with systems using natural language. The engine understands user intent and executes commands for tasks, allowing easy navigation of complex websites/products. This approach enhances user experience, reduces training costs, and boosts productivity.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.

oss-fuzz-gen
This framework generates fuzz targets for real-world `C`/`C++` projects with various Large Language Models (LLM) and benchmarks them via the `OSS-Fuzz` platform. It manages to successfully leverage LLMs to generate valid fuzz targets (which generate non-zero coverage increase) for 160 C/C++ projects. The maximum line coverage increase is 29% from the existing human-written targets.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.