
neural-speed
An innovative library for efficient LLM inference via low-bit quantization
Stars: 327
Neural Speed is an innovative library designed to support the efficient inference of large language models (LLMs) on Intel platforms through the state-of-the-art (SOTA) low-bit quantization powered by Intel Neural Compressor. The work is inspired by llama.cpp and further optimized for Intel platforms with our innovations in NeurIPS' 2023
README:
Neural Speed is an innovative library designed to support the efficient inference of large language models (LLMs) on Intel platforms through the state-of-the-art (SOTA) low-bit quantization powered by Intel Neural Compressor. The work is inspired by llama.cpp and further optimized for Intel platforms with our innovations in NeurIPS' 2023
- Highly optimized kernels on CPUs with ISAs (AMX, VNNI, AVX512F, AVX_VNNI and AVX2) for N-bit weight (int1, int2, int3, int4, int5, int6, int7 and int8). See details
- Up to 40x performance speedup on popular LLMs compared with llama.cpp. See details
- Tensor parallelism across sockets/nodes on CPUs. See details
Neural Speed is under active development so APIs are subject to change.
| Hardware | Supported |
|---|---|
| Intel Xeon Scalable Processors | ✔ |
| Intel Xeon CPU Max Series | ✔ |
| Intel Core Processors | ✔ |
Support almost all the LLMs in PyTorch format from Hugging Face such as Llama2, ChatGLM2, Baichuan2, Qwen, Mistral, Whisper, etc. File an issue if your favorite LLM does not work.
Support typical LLMs in GGUF format such as Llama2, Falcon, MPT, Bloom etc. More are coming. Check out the details.
pip install -r requirements.txt
pip install neural-speedpip install .Note: GCC requires version 10+
Install Intel Extension for Transformers to use Transformer-like APIs.
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, TextStreamer
from intel_extension_for_transformers.transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
model_name = "Intel/neural-chat-7b-v3-1" # Hugging Face model_id or local model
prompt = "Once upon a time, there existed a little girl,"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name, trust_remote_code=True)
inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt").input_ids
streamer = TextStreamer(tokenizer)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name, load_in_4bit=True)
outputs = model.generate(inputs, streamer=streamer, max_new_tokens=300)from transformers import AutoTokenizer, TextStreamer
from intel_extension_for_transformers.transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
# Specify the GGUF repo on the Hugginface
model_name = "TheBloke/Llama-2-7B-Chat-GGUF"
# Download the the specific gguf model file from the above repo
gguf_file = "llama-2-7b-chat.Q4_0.gguf"
# make sure you are granted to access this model on the Huggingface.
tokenizer_name = "meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hf"
prompt = "Once upon a time"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(tokenizer_name, trust_remote_code=True)
inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt").input_ids
streamer = TextStreamer(tokenizer)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name, gguf_file = gguf_file)
outputs = model.generate(inputs, streamer=streamer, max_new_tokens=300)from transformers import TextStreamer
from modelscope import AutoTokenizer
from intel_extension_for_transformers.transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
model_name = "qwen/Qwen-7B" # Modelscope model_id or local model
prompt = "Once upon a time, there existed a little girl,"
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name, load_in_4bit=True, model_hub="modelscope")
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name, trust_remote_code=True)
inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt").input_ids
streamer = TextStreamer(tokenizer)
outputs = model.generate(inputs, streamer=streamer, max_new_tokens=300)Neural Speed can be used in Neural Chat Server of Intel Extension for Transformers. You can choose to enable it by adding use_neural_speed: true in config.yaml.
- add
optimizationkey section to useNeural Speedand its RTN quantization (example).
device: "cpu"
# itrex int4 llm runtime optimization
optimization:
use_neural_speed: true
optimization_type: "weight_only"
compute_dtype: "fp32"
weight_dtype: "int4"- add key
use_neural_speedand keyuse_gptqto useNeural Speedand loadGPT-Qmodel (example).
device: "cpu"
use_neural_speed: true
use_gptq: trueMore details please refer to Neural Chat.
python scripts/run.py model-path --weight_dtype int4 -p "She opened the door and see"
# skip the step if GGUF model is from Hugging Face or generated by llama.cpp
python scripts/convert.py --outtype f32 --outfile ne-f32.bin EleutherAI/gpt-j-6b
# Using the quantize script requires a binary installation of Neural Speed
mkdir build&&cd build
cmake ..&&make -j
cd ..
python scripts/quantize.py --model_name gptj --model_file ne-f32.bin --out_file ne-q4_j.bin --build_dir ./build --weight_dtype int4 --alg sym# Linux and WSL
OMP_NUM_THREADS=<physic_cores> numactl -m 0 -C 0-<physic_cores-1> python scripts/inference.py --model_name llama -m ne-q4_j.bin -c 512 -b 1024 -n 256 -t <physic_cores> --color -p "She opened the door and see"# Windows
python scripts/inference.py --model_name llama -m ne-q4_j.bin -c 512 -b 1024 -n 256 -t <physic_cores|P-cores> --color -p "She opened the door and see"Please refer to Advanced Usage for more details.
You can consider adding your own models, please follow the document: graph developer document.
Enable NEURAL_SPEED_VERBOSE environment variable for performance profiling.
Available modes:
- 0: Print full information: evaluation time and operator profiling. Need to set
NS_PROFILINGto ON and recompile. - 1: Print evaluation time. Time taken for each evaluation.
- 2: Profile individual operator. Identify performance bottleneck within the model. Need to set
NS_PROFILINGto ON and recompile.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for neural-speed
Similar Open Source Tools

neural-speed
Neural Speed is an innovative library designed to support the efficient inference of large language models (LLMs) on Intel platforms through the state-of-the-art (SOTA) low-bit quantization powered by Intel Neural Compressor. The work is inspired by llama.cpp and further optimized for Intel platforms with our innovations in NeurIPS' 2023
hqq
HQQ is a fast and accurate model quantizer that skips the need for calibration data. It's super simple to implement (just a few lines of code for the optimizer). It can crunch through quantizing the Llama2-70B model in only 4 minutes! 🚀
Phi-3-Vision-MLX
Phi-3-MLX is a versatile AI framework that leverages both the Phi-3-Vision multimodal model and the Phi-3-Mini-128K language model optimized for Apple Silicon using the MLX framework. It provides an easy-to-use interface for a wide range of AI tasks, from advanced text generation to visual question answering and code execution. The project features support for batched generation, flexible agent system, custom toolchains, model quantization, LoRA fine-tuning capabilities, and API integration for extended functionality.
paxml
Pax is a framework to configure and run machine learning experiments on top of Jax.
SimplerLLM
SimplerLLM is an open-source Python library that simplifies interactions with Large Language Models (LLMs) for researchers and beginners. It provides a unified interface for different LLM providers, tools for enhancing language model capabilities, and easy development of AI-powered tools and apps. The library offers features like unified LLM interface, generic text loader, RapidAPI connector, SERP integration, prompt template builder, and more. Users can easily set up environment variables, create LLM instances, use tools like SERP, generic text loader, calling RapidAPI APIs, and prompt template builder. Additionally, the library includes chunking functions to split texts into manageable chunks based on different criteria. Future updates will bring more tools, interactions with local LLMs, prompt optimization, response evaluation, GPT Trainer, document chunker, advanced document loader, integration with more providers, Simple RAG with SimplerVectors, integration with vector databases, agent builder, and LLM server.
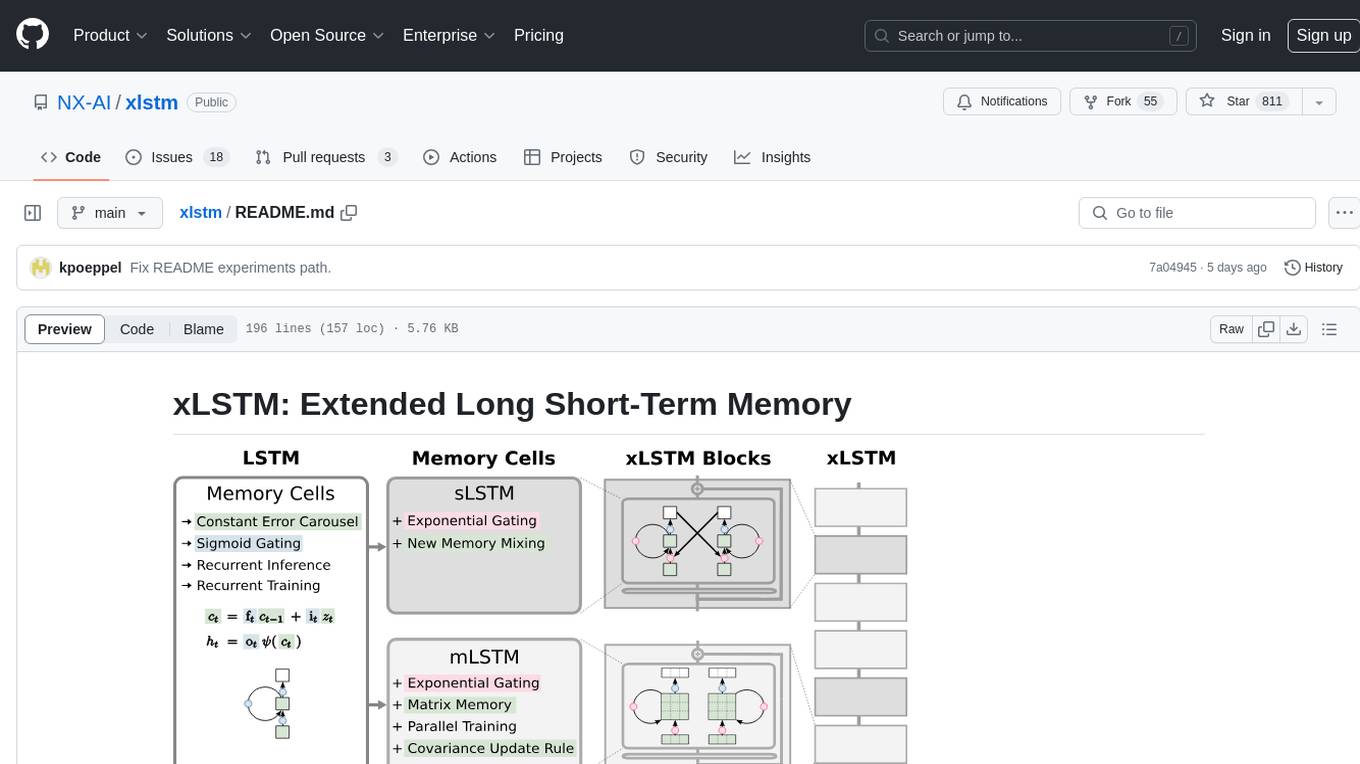
xlstm
xLSTM is a new Recurrent Neural Network architecture based on ideas of the original LSTM. Through Exponential Gating with appropriate normalization and stabilization techniques and a new Matrix Memory it overcomes the limitations of the original LSTM and shows promising performance on Language Modeling when compared to Transformers or State Space Models. The package is based on PyTorch and was tested for versions >=1.8. For the CUDA version of xLSTM, you need Compute Capability >= 8.0. The xLSTM tool provides two main components: xLSTMBlockStack for non-language applications or integrating in other architectures, and xLSTMLMModel for language modeling or other token-based applications.
WordLlama
WordLlama is a fast, lightweight NLP toolkit optimized for CPU hardware. It recycles components from large language models to create efficient word representations. It offers features like Matryoshka Representations, low resource requirements, binarization, and numpy-only inference. The tool is suitable for tasks like semantic matching, fuzzy deduplication, ranking, and clustering, making it a good option for NLP-lite tasks and exploratory analysis.
lionagi
LionAGI is a robust framework for orchestrating multi-step AI operations with precise control. It allows users to bring together multiple models, advanced reasoning, tool integrations, and custom validations in a single coherent pipeline. The framework is structured, expandable, controlled, and transparent, offering features like real-time logging, message introspection, and tool usage tracking. LionAGI supports advanced multi-step reasoning with ReAct, integrates with Anthropic's Model Context Protocol, and provides observability and debugging tools. Users can seamlessly orchestrate multiple models, integrate with Claude Code CLI SDK, and leverage a fan-out fan-in pattern for orchestration. The framework also offers optional dependencies for additional functionalities like reader tools, local inference support, rich output formatting, database support, and graph visualization.
aigverse
aigverse is a Python infrastructure framework that bridges the gap between logic synthesis and AI/ML applications. It allows efficient representation and manipulation of logic circuits, making it easier to integrate logic synthesis and optimization tasks into machine learning pipelines. Built upon EPFL Logic Synthesis Libraries, particularly mockturtle, aigverse provides a high-level Python interface to state-of-the-art algorithms for And-Inverter Graph (AIG) manipulation and logic synthesis, widely used in formal verification, hardware design, and optimization tasks.
DeepPavlov
DeepPavlov is an open-source conversational AI library built on PyTorch. It is designed for the development of production-ready chatbots and complex conversational systems, as well as for research in the area of NLP and dialog systems. The library offers a wide range of models for tasks such as Named Entity Recognition, Intent/Sentence Classification, Question Answering, Sentence Similarity/Ranking, Syntactic Parsing, and more. DeepPavlov also provides embeddings like BERT, ELMo, and FastText for various languages, along with AutoML capabilities and integrations with REST API, Socket API, and Amazon AWS.
tensorrtllm_backend
The TensorRT-LLM Backend is a Triton backend designed to serve TensorRT-LLM models with Triton Inference Server. It supports features like inflight batching, paged attention, and more. Users can access the backend through pre-built Docker containers or build it using scripts provided in the repository. The backend can be used to create models for tasks like tokenizing, inferencing, de-tokenizing, ensemble modeling, and more. Users can interact with the backend using provided client scripts and query the server for metrics related to request handling, memory usage, KV cache blocks, and more. Testing for the backend can be done following the instructions in the 'ci/README.md' file.
aicsimageio
AICSImageIO is a Python tool for Image Reading, Metadata Conversion, and Image Writing for Microscopy Images. It supports various file formats like OME-TIFF, TIFF, ND2, DV, CZI, LIF, PNG, GIF, and Bio-Formats. Users can read and write metadata and imaging data, work with different file systems like local paths, HTTP URLs, s3fs, and gcsfs. The tool provides functionalities for full image reading, delayed image reading, mosaic image reading, metadata reading, xarray coordinate plane attachment, cloud IO support, and saving to OME-TIFF. It also offers benchmarking and developer resources.

zeta
Zeta is a tool designed to build state-of-the-art AI models faster by providing modular, high-performance, and scalable building blocks. It addresses the common issues faced while working with neural nets, such as chaotic codebases, lack of modularity, and low performance modules. Zeta emphasizes usability, modularity, and performance, and is currently used in hundreds of models across various GitHub repositories. It enables users to prototype, train, optimize, and deploy the latest SOTA neural nets into production. The tool offers various modules like FlashAttention, SwiGLUStacked, RelativePositionBias, FeedForward, BitLinear, PalmE, Unet, VisionEmbeddings, niva, FusedDenseGELUDense, FusedDropoutLayerNorm, MambaBlock, Film, hyper_optimize, DPO, and ZetaCloud for different tasks in AI model development.
KVCache-Factory
KVCache-Factory is a unified framework for KV Cache compression of diverse models. It supports multi-GPUs inference with big LLMs and various attention implementations. The tool enables KV cache compression without Flash Attention v2, multi-GPU inference, and specific models like Mistral. It also provides functions for KV cache budget allocation and batch inference. The visualization tools help in understanding the attention patterns of models.
FlexFlow
FlexFlow Serve is an open-source compiler and distributed system for **low latency**, **high performance** LLM serving. FlexFlow Serve outperforms existing systems by 1.3-2.0x for single-node, multi-GPU inference and by 1.4-2.4x for multi-node, multi-GPU inference.
LLMDebugger
This repository contains the code and dataset for LDB, a novel debugging framework that enables Large Language Models (LLMs) to refine their generated programs by tracking the values of intermediate variables throughout the runtime execution. LDB segments programs into basic blocks, allowing LLMs to concentrate on simpler code units, verify correctness block by block, and pinpoint errors efficiently. The tool provides APIs for debugging and generating code with debugging messages, mimicking how human developers debug programs.
For similar tasks

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

onnxruntime-genai
ONNX Runtime Generative AI is a library that provides the generative AI loop for ONNX models, including inference with ONNX Runtime, logits processing, search and sampling, and KV cache management. Users can call a high level `generate()` method, or run each iteration of the model in a loop. It supports greedy/beam search and TopP, TopK sampling to generate token sequences, has built in logits processing like repetition penalties, and allows for easy custom scoring.

jupyter-ai
Jupyter AI connects generative AI with Jupyter notebooks. It provides a user-friendly and powerful way to explore generative AI models in notebooks and improve your productivity in JupyterLab and the Jupyter Notebook. Specifically, Jupyter AI offers: * An `%%ai` magic that turns the Jupyter notebook into a reproducible generative AI playground. This works anywhere the IPython kernel runs (JupyterLab, Jupyter Notebook, Google Colab, Kaggle, VSCode, etc.). * A native chat UI in JupyterLab that enables you to work with generative AI as a conversational assistant. * Support for a wide range of generative model providers, including AI21, Anthropic, AWS, Cohere, Gemini, Hugging Face, NVIDIA, and OpenAI. * Local model support through GPT4All, enabling use of generative AI models on consumer grade machines with ease and privacy.

khoj
Khoj is an open-source, personal AI assistant that extends your capabilities by creating always-available AI agents. You can share your notes and documents to extend your digital brain, and your AI agents have access to the internet, allowing you to incorporate real-time information. Khoj is accessible on Desktop, Emacs, Obsidian, Web, and Whatsapp, and you can share PDF, markdown, org-mode, notion files, and GitHub repositories. You'll get fast, accurate semantic search on top of your docs, and your agents can create deeply personal images and understand your speech. Khoj is self-hostable and always will be.

langchain_dart
LangChain.dart is a Dart port of the popular LangChain Python framework created by Harrison Chase. LangChain provides a set of ready-to-use components for working with language models and a standard interface for chaining them together to formulate more advanced use cases (e.g. chatbots, Q&A with RAG, agents, summarization, extraction, etc.). The components can be grouped into a few core modules: * **Model I/O:** LangChain offers a unified API for interacting with various LLM providers (e.g. OpenAI, Google, Mistral, Ollama, etc.), allowing developers to switch between them with ease. Additionally, it provides tools for managing model inputs (prompt templates and example selectors) and parsing the resulting model outputs (output parsers). * **Retrieval:** assists in loading user data (via document loaders), transforming it (with text splitters), extracting its meaning (using embedding models), storing (in vector stores) and retrieving it (through retrievers) so that it can be used to ground the model's responses (i.e. Retrieval-Augmented Generation or RAG). * **Agents:** "bots" that leverage LLMs to make informed decisions about which available tools (such as web search, calculators, database lookup, etc.) to use to accomplish the designated task. The different components can be composed together using the LangChain Expression Language (LCEL).

danswer
Danswer is an open-source Gen-AI Chat and Unified Search tool that connects to your company's docs, apps, and people. It provides a Chat interface and plugs into any LLM of your choice. Danswer can be deployed anywhere and for any scale - on a laptop, on-premise, or to cloud. Since you own the deployment, your user data and chats are fully in your own control. Danswer is MIT licensed and designed to be modular and easily extensible. The system also comes fully ready for production usage with user authentication, role management (admin/basic users), chat persistence, and a UI for configuring Personas (AI Assistants) and their Prompts. Danswer also serves as a Unified Search across all common workplace tools such as Slack, Google Drive, Confluence, etc. By combining LLMs and team specific knowledge, Danswer becomes a subject matter expert for the team. Imagine ChatGPT if it had access to your team's unique knowledge! It enables questions such as "A customer wants feature X, is this already supported?" or "Where's the pull request for feature Y?"

infinity
Infinity is an AI-native database designed for LLM applications, providing incredibly fast full-text and vector search capabilities. It supports a wide range of data types, including vectors, full-text, and structured data, and offers a fused search feature that combines multiple embeddings and full text. Infinity is easy to use, with an intuitive Python API and a single-binary architecture that simplifies deployment. It achieves high performance, with 0.1 milliseconds query latency on million-scale vector datasets and up to 15K QPS.
For similar jobs
h2ogpt
h2oGPT is an Apache V2 open-source project that allows users to query and summarize documents or chat with local private GPT LLMs. It features a private offline database of any documents (PDFs, Excel, Word, Images, Video Frames, Youtube, Audio, Code, Text, MarkDown, etc.), a persistent database (Chroma, Weaviate, or in-memory FAISS) using accurate embeddings (instructor-large, all-MiniLM-L6-v2, etc.), and efficient use of context using instruct-tuned LLMs (no need for LangChain's few-shot approach). h2oGPT also offers parallel summarization and extraction, reaching an output of 80 tokens per second with the 13B LLaMa2 model, HYDE (Hypothetical Document Embeddings) for enhanced retrieval based upon LLM responses, a variety of models supported (LLaMa2, Mistral, Falcon, Vicuna, WizardLM. With AutoGPTQ, 4-bit/8-bit, LORA, etc.), GPU support from HF and LLaMa.cpp GGML models, and CPU support using HF, LLaMa.cpp, and GPT4ALL models. Additionally, h2oGPT provides Attention Sinks for arbitrarily long generation (LLaMa-2, Mistral, MPT, Pythia, Falcon, etc.), a UI or CLI with streaming of all models, the ability to upload and view documents through the UI (control multiple collaborative or personal collections), Vision Models LLaVa, Claude-3, Gemini-Pro-Vision, GPT-4-Vision, Image Generation Stable Diffusion (sdxl-turbo, sdxl) and PlaygroundAI (playv2), Voice STT using Whisper with streaming audio conversion, Voice TTS using MIT-Licensed Microsoft Speech T5 with multiple voices and Streaming audio conversion, Voice TTS using MPL2-Licensed TTS including Voice Cloning and Streaming audio conversion, AI Assistant Voice Control Mode for hands-free control of h2oGPT chat, Bake-off UI mode against many models at the same time, Easy Download of model artifacts and control over models like LLaMa.cpp through the UI, Authentication in the UI by user/password via Native or Google OAuth, State Preservation in the UI by user/password, Linux, Docker, macOS, and Windows support, Easy Windows Installer for Windows 10 64-bit (CPU/CUDA), Easy macOS Installer for macOS (CPU/M1/M2), Inference Servers support (oLLaMa, HF TGI server, vLLM, Gradio, ExLLaMa, Replicate, OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, Anthropic), OpenAI-compliant, Server Proxy API (h2oGPT acts as drop-in-replacement to OpenAI server), Python client API (to talk to Gradio server), JSON Mode with any model via code block extraction. Also supports MistralAI JSON mode, Claude-3 via function calling with strict Schema, OpenAI via JSON mode, and vLLM via guided_json with strict Schema, Web-Search integration with Chat and Document Q/A, Agents for Search, Document Q/A, Python Code, CSV frames (Experimental, best with OpenAI currently), Evaluate performance using reward models, and Quality maintained with over 1000 unit and integration tests taking over 4 GPU-hours.

mistral.rs
Mistral.rs is a fast LLM inference platform written in Rust. We support inference on a variety of devices, quantization, and easy-to-use application with an Open-AI API compatible HTTP server and Python bindings.
ollama
Ollama is a lightweight, extensible framework for building and running language models on the local machine. It provides a simple API for creating, running, and managing models, as well as a library of pre-built models that can be easily used in a variety of applications. Ollama is designed to be easy to use and accessible to developers of all levels. It is open source and available for free on GitHub.
llama-cpp-agent
The llama-cpp-agent framework is a tool designed for easy interaction with Large Language Models (LLMs). Allowing users to chat with LLM models, execute structured function calls and get structured output (objects). It provides a simple yet robust interface and supports llama-cpp-python and OpenAI endpoints with GBNF grammar support (like the llama-cpp-python server) and the llama.cpp backend server. It works by generating a formal GGML-BNF grammar of the user defined structures and functions, which is then used by llama.cpp to generate text valid to that grammar. In contrast to most GBNF grammar generators it also supports nested objects, dictionaries, enums and lists of them.
llama_ros
This repository provides a set of ROS 2 packages to integrate llama.cpp into ROS 2. By using the llama_ros packages, you can easily incorporate the powerful optimization capabilities of llama.cpp into your ROS 2 projects by running GGUF-based LLMs and VLMs.
MITSUHA
OneReality is a virtual waifu/assistant that you can speak to through your mic and it'll speak back to you! It has many features such as: * You can speak to her with a mic * It can speak back to you * Has short-term memory and long-term memory * Can open apps * Smarter than you * Fluent in English, Japanese, Korean, and Chinese * Can control your smart home like Alexa if you set up Tuya (more info in Prerequisites) It is built with Python, Llama-cpp-python, Whisper, SpeechRecognition, PocketSphinx, VITS-fast-fine-tuning, VITS-simple-api, HyperDB, Sentence Transformers, and Tuya Cloud IoT.
wenxin-starter
WenXin-Starter is a spring-boot-starter for Baidu's "Wenxin Qianfan WENXINWORKSHOP" large model, which can help you quickly access Baidu's AI capabilities. It fully integrates the official API documentation of Wenxin Qianfan. Supports text-to-image generation, built-in dialogue memory, and supports streaming return of dialogue. Supports QPS control of a single model and supports queuing mechanism. Plugins will be added soon.

FlexFlow
FlexFlow Serve is an open-source compiler and distributed system for **low latency**, **high performance** LLM serving. FlexFlow Serve outperforms existing systems by 1.3-2.0x for single-node, multi-GPU inference and by 1.4-2.4x for multi-node, multi-GPU inference.