
docling
Get your documents ready for gen AI
Stars: 52925
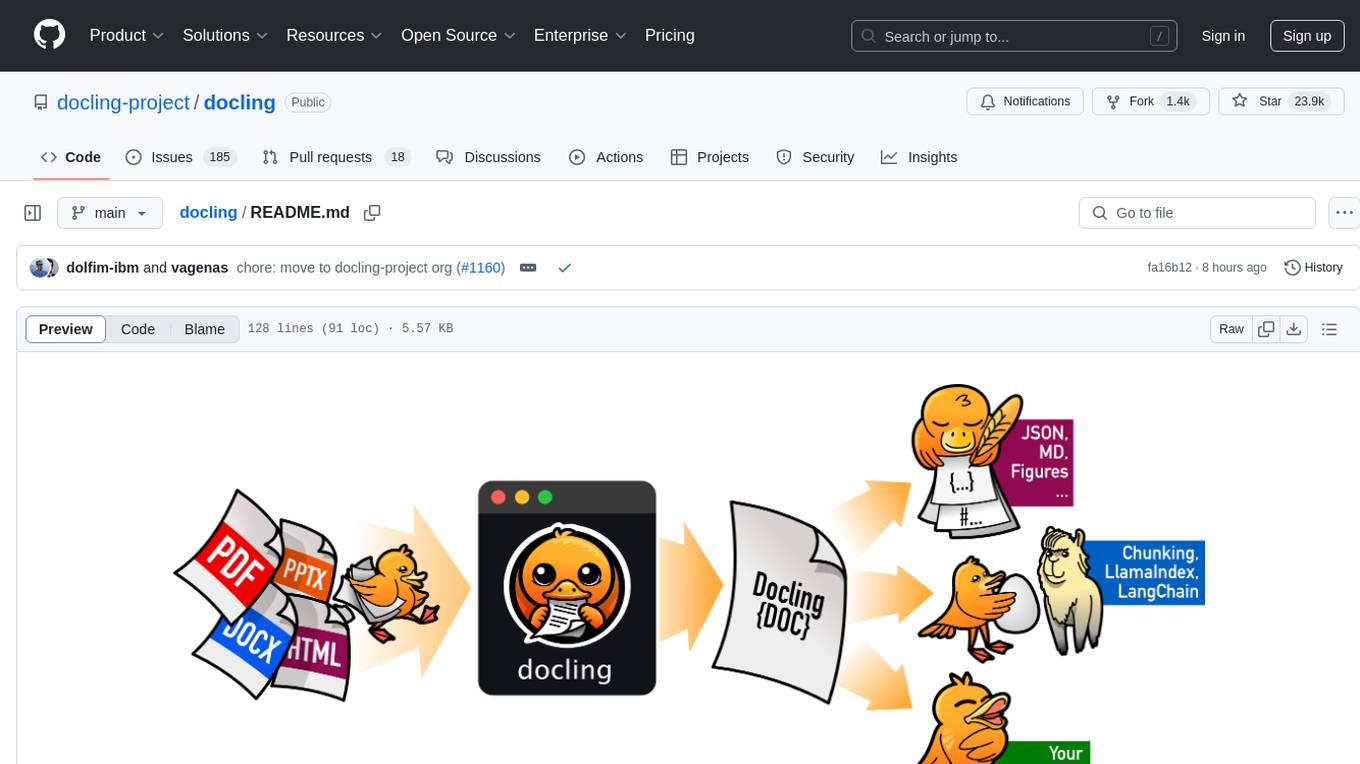
Docling simplifies document processing, parsing diverse formats including advanced PDF understanding, and providing seamless integrations with the general AI ecosystem. It offers features such as parsing multiple document formats, advanced PDF understanding, unified DoclingDocument representation format, various export formats, local execution capabilities, plug-and-play integrations with agentic AI tools, extensive OCR support, and a simple CLI. Coming soon features include metadata extraction, visual language models, chart understanding, and complex chemistry understanding. Docling is installed via pip and works on macOS, Linux, and Windows environments. It provides detailed documentation, examples, integrations with popular frameworks, and support through the discussion section. The codebase is under the MIT license and has been developed by IBM.
README:
Docling simplifies document processing, parsing diverse formats — including advanced PDF understanding — and providing seamless integrations with the gen AI ecosystem.
- 🗂️ Parsing of multiple document formats incl. PDF, DOCX, PPTX, XLSX, HTML, WAV, MP3, WebVTT, images (PNG, TIFF, JPEG, ...), LaTeX, and more
- 📑 Advanced PDF understanding incl. page layout, reading order, table structure, code, formulas, image classification, and more
- 🧬 Unified, expressive DoclingDocument representation format
- ↪️ Various export formats and options, including Markdown, HTML, DocTags and lossless JSON
- 🔒 Local execution capabilities for sensitive data and air-gapped environments
- 🤖 Plug-and-play integrations incl. LangChain, LlamaIndex, Crew AI & Haystack for agentic AI
- 🔍 Extensive OCR support for scanned PDFs and images
- 👓 Support of several Visual Language Models (GraniteDocling)
- 🎙️ Audio support with Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) models
- 🔌 Connect to any agent using the MCP server
- 💻 Simple and convenient CLI
- 📤 Structured information extraction [🧪 beta]
- 📑 New layout model (Heron) by default, for faster PDF parsing
- 🔌 MCP server for agentic applications
- 💬 Parsing of Web Video Text Tracks (WebVTT) files
- 💬 Parsing of LaTeX files
- 📝 Metadata extraction, including title, authors, references & language
- 📝 Chart understanding (Barchart, Piechart, LinePlot, etc)
- 📝 Complex chemistry understanding (Molecular structures)
To use Docling, simply install docling from your package manager, e.g. pip:
pip install doclingNote: Python 3.9 support was dropped in docling version 2.70.0. Please use Python 3.10 or higher.
Works on macOS, Linux and Windows environments. Both x86_64 and arm64 architectures.
More detailed installation instructions are available in the docs.
To convert individual documents with python, use convert(), for example:
from docling.document_converter import DocumentConverter
source = "https://arxiv.org/pdf/2408.09869" # document per local path or URL
converter = DocumentConverter()
result = converter.convert(source)
print(result.document.export_to_markdown()) # output: "## Docling Technical Report[...]"More advanced usage options are available in the docs.
Docling has a built-in CLI to run conversions.
docling https://arxiv.org/pdf/2206.01062You can also use 🥚GraniteDocling and other VLMs via Docling CLI:
docling --pipeline vlm --vlm-model granite_docling https://arxiv.org/pdf/2206.01062This will use MLX acceleration on supported Apple Silicon hardware.
Read more here
Check out Docling's documentation, for details on installation, usage, concepts, recipes, extensions, and more.
Go hands-on with our examples, demonstrating how to address different application use cases with Docling.
To further accelerate your AI application development, check out Docling's native integrations with popular frameworks and tools.
Please feel free to connect with us using the discussion section.
For more details on Docling's inner workings, check out the Docling Technical Report.
Please read Contributing to Docling for details.
If you use Docling in your projects, please consider citing the following:
@techreport{Docling,
author = {Deep Search Team},
month = {8},
title = {Docling Technical Report},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2408.09869},
eprint = {2408.09869},
doi = {10.48550/arXiv.2408.09869},
version = {1.0.0},
year = {2024}
}The Docling codebase is under MIT license. For individual model usage, please refer to the model licenses found in the original packages.
Docling is hosted as a project in the LF AI & Data Foundation.
The project was started by the AI for knowledge team at IBM Research Zurich.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for docling
Similar Open Source Tools

docling
Docling simplifies document processing, parsing diverse formats including advanced PDF understanding, and providing seamless integrations with the general AI ecosystem. It offers features such as parsing multiple document formats, advanced PDF understanding, unified DoclingDocument representation format, various export formats, local execution capabilities, plug-and-play integrations with agentic AI tools, extensive OCR support, and a simple CLI. Coming soon features include metadata extraction, visual language models, chart understanding, and complex chemistry understanding. Docling is installed via pip and works on macOS, Linux, and Windows environments. It provides detailed documentation, examples, integrations with popular frameworks, and support through the discussion section. The codebase is under the MIT license and has been developed by IBM.
docling
Docling is a tool that bundles PDF document conversion to JSON and Markdown in an easy, self-contained package. It can convert any PDF document to JSON or Markdown format, understand detailed page layout, reading order, recover table structures, extract metadata such as title, authors, references, and language, and optionally apply OCR for scanned PDFs. The tool is designed to be stable, lightning fast, and suitable for macOS and Linux environments.

MinerU
MinerU is a tool that converts PDFs into machine-readable formats, allowing for easy extraction into any format. It focuses on solving symbol conversion issues in scientific literature and contributes to technological development. It removes headers, footers, footnotes, and page numbers, preserves document structure, extracts images, tables, and formulas, and supports OCR in 109 languages. MinerU supports various visualization results, runs on CPU/GPU/NPU, and is compatible with Windows, Linux, and Mac platforms.
LMCache
LMCache is a serving engine extension designed to reduce time to first token (TTFT) and increase throughput, particularly in long-context scenarios. It stores key-value caches of reusable texts across different locations like GPU, CPU DRAM, and Local Disk, allowing the reuse of any text in any serving engine instance. By combining LMCache with vLLM, significant delay savings and GPU cycle reduction are achieved in various large language model (LLM) use cases, such as multi-round question answering and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). LMCache provides integration with the latest vLLM version, offering both online serving and offline inference capabilities. It supports sharing key-value caches across multiple vLLM instances and aims to provide stable support for non-prefix key-value caches along with user and developer documentation.

mlflow
MLflow is a platform to streamline machine learning development, including tracking experiments, packaging code into reproducible runs, and sharing and deploying models. MLflow offers a set of lightweight APIs that can be used with any existing machine learning application or library (TensorFlow, PyTorch, XGBoost, etc), wherever you currently run ML code (e.g. in notebooks, standalone applications or the cloud). MLflow's current components are:
* `MLflow Tracking

starwhale
Starwhale is an MLOps/LLMOps platform that brings efficiency and standardization to machine learning operations. It streamlines the model development lifecycle, enabling teams to optimize workflows around key areas like model building, evaluation, release, and fine-tuning. Starwhale abstracts Model, Runtime, and Dataset as first-class citizens, providing tailored capabilities for common workflow scenarios including Models Evaluation, Live Demo, and LLM Fine-tuning. It is an open-source platform designed for clarity and ease of use, empowering developers to build customized MLOps features tailored to their needs.
Kori
Kori is a unified note-taking app with AI capabilities, providing a consistent experience across Android, iOS, Windows, macOS, and Linux. It supports various formats like Drawing, Markdown, TXT, LaTeX, Mermaid diagrams, and Todo.txt lists. Users can benefit from AI co-writing features, note outline generation, find and replace, note templates, local media support, and export options. The app follows Material Design 3 guidelines, offers comprehensive mouse and keyboard support, and is optimized for different screen sizes and orientations.

slideflow
Slideflow is a deep learning library for digital pathology, offering a user-friendly interface for model development. It is designed for medical researchers and AI enthusiasts, providing an accessible platform for developing state-of-the-art pathology models. Slideflow offers customizable training pipelines, robust slide processing and stain normalization toolkit, support for weakly-supervised or strongly-supervised labels, built-in foundation models, multiple-instance learning, self-supervised learning, generative adversarial networks, explainability tools, layer activation analysis tools, uncertainty quantification, interactive user interface for model deployment, and more. It supports both PyTorch and Tensorflow, with optional support for Libvips for slide reading. Slideflow can be installed via pip, Docker container, or from source, and includes non-commercial add-ons for additional tools and pretrained models. It allows users to create projects, extract tiles from slides, train models, and provides evaluation tools like heatmaps and mosaic maps.
easy-dataset
Easy Dataset is a specialized application designed to streamline the creation of fine-tuning datasets for Large Language Models (LLMs). It offers an intuitive interface for uploading domain-specific files, intelligently splitting content, generating questions, and producing high-quality training data for model fine-tuning. With Easy Dataset, users can transform domain knowledge into structured datasets compatible with all OpenAI-format compatible LLM APIs, making the fine-tuning process accessible and efficient.

tidb
TiDB is an open-source distributed SQL database that supports Hybrid Transactional and Analytical Processing (HTAP) workloads. It is MySQL compatible and features horizontal scalability, strong consistency, and high availability.
Kiln
Kiln is an intuitive tool for fine-tuning LLM models, generating synthetic data, and collaborating on datasets. It offers desktop apps for Windows, MacOS, and Linux, zero-code fine-tuning for various models, interactive data generation, and Git-based version control. Users can easily collaborate with QA, PM, and subject matter experts, generate auto-prompts, and work with a wide range of models and providers. The tool is open-source, privacy-first, and supports structured data tasks in JSON format. Kiln is free to use and helps build high-quality AI products with datasets, facilitates collaboration between technical and non-technical teams, allows comparison of models and techniques without code, ensures structured data integrity, and prioritizes user privacy.
smile
Smile (Statistical Machine Intelligence and Learning Engine) is a comprehensive machine learning, NLP, linear algebra, graph, interpolation, and visualization system in Java and Scala. It covers every aspect of machine learning, including classification, regression, clustering, association rule mining, feature selection, manifold learning, multidimensional scaling, genetic algorithms, missing value imputation, efficient nearest neighbor search, etc. Smile implements major machine learning algorithms and provides interactive shells for Java, Scala, and Kotlin. It supports model serialization, data visualization using SmilePlot and declarative approach, and offers a gallery showcasing various algorithms and visualizations.

catalyst
Catalyst is a C# Natural Language Processing library designed for speed, inspired by spaCy's design. It provides pre-trained models, support for training word and document embeddings, and flexible entity recognition models. The library is fast, modern, and pure-C#, supporting .NET standard 2.0. It is cross-platform, running on Windows, Linux, macOS, and ARM. Catalyst offers non-destructive tokenization, named entity recognition, part-of-speech tagging, language detection, and efficient binary serialization. It includes pre-built models for language packages and lemmatization. Users can store and load models using streams. Getting started with Catalyst involves installing its NuGet Package and setting the storage to use the online repository. The library supports lazy loading of models from disk or online. Users can take advantage of C# lazy evaluation and native multi-threading support to process documents in parallel. Training a new FastText word2vec embedding model is straightforward, and Catalyst also provides algorithms for fast embedding search and dimensionality reduction.

sdialog
SDialog is an MIT-licensed open-source toolkit for building, simulating, and evaluating LLM-based conversational agents end-to-end. It aims to bridge agent construction, user simulation, dialog generation, and evaluation in a single reproducible workflow, enabling the generation of reliable, controllable dialog systems or data at scale. The toolkit standardizes a Dialog schema, offers persona-driven multi-agent simulation with LLMs, provides composable orchestration for precise control over behavior and flow, includes built-in evaluation metrics, and offers mechanistic interpretability. It allows for easy creation of user-defined components and interoperability across various AI platforms.
biochatter
Generative AI models have shown tremendous usefulness in increasing accessibility and automation of a wide range of tasks. This repository contains the `biochatter` Python package, a generic backend library for the connection of biomedical applications to conversational AI. It aims to provide a common framework for deploying, testing, and evaluating diverse models and auxiliary technologies in the biomedical domain. BioChatter is part of the BioCypher ecosystem, connecting natively to BioCypher knowledge graphs.
Chat2DB
Chat2DB is an AI-driven data development and analysis platform that enables users to communicate with databases using natural language. It supports a wide range of databases, including MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQLServer, SQLite, MariaDB, ClickHouse, DM, Presto, DB2, OceanBase, Hive, KingBase, MongoDB, Redis, and Snowflake. Chat2DB provides a user-friendly interface that allows users to query databases, generate reports, and explore data using natural language commands. It also offers a variety of features to help users improve their productivity, such as auto-completion, syntax highlighting, and error checking.
For similar tasks
serverless-pdf-chat
The serverless-pdf-chat repository contains a sample application that allows users to ask natural language questions of any PDF document they upload. It leverages serverless services like Amazon Bedrock, AWS Lambda, and Amazon DynamoDB to provide text generation and analysis capabilities. The application architecture involves uploading a PDF document to an S3 bucket, extracting metadata, converting text to vectors, and using a LangChain to search for information related to user prompts. The application is not intended for production use and serves as a demonstration and educational tool.

docling
Docling simplifies document processing, parsing diverse formats including advanced PDF understanding, and providing seamless integrations with the general AI ecosystem. It offers features such as parsing multiple document formats, advanced PDF understanding, unified DoclingDocument representation format, various export formats, local execution capabilities, plug-and-play integrations with agentic AI tools, extensive OCR support, and a simple CLI. Coming soon features include metadata extraction, visual language models, chart understanding, and complex chemistry understanding. Docling is installed via pip and works on macOS, Linux, and Windows environments. It provides detailed documentation, examples, integrations with popular frameworks, and support through the discussion section. The codebase is under the MIT license and has been developed by IBM.

docling
Docling is a tool that bundles PDF document conversion to JSON and Markdown in an easy, self-contained package. It can convert any PDF document to JSON or Markdown format, understand detailed page layout, reading order, recover table structures, extract metadata such as title, authors, references, and language, and optionally apply OCR for scanned PDFs. The tool is designed to be stable, lightning fast, and suitable for macOS and Linux environments.
characterfile
The Characterfile project aims to create a simple format for generating and transmitting character files, compatible with Eliza and other LLM agents. Users can convert their Twitter archive into a character file using the provided scripts. The project also includes examples, JSON schema, and TypeScript types for the character file. Scripts like tweets2character, folder2knowledge, and knowledge2character facilitate the conversion of tweets, documents, and knowledge files into character files for use with AI agents.
markpdfdown
MarkPDFDown is a powerful tool that leverages multimodal large language models to transcribe PDF files into Markdown format. It simplifies the process of converting PDF documents into clean, editable Markdown text by accurately extracting text, preserving formatting, and handling complex document structures including tables, formulas, and diagrams.

datalore-localgen-cli
Datalore is a terminal tool for generating structured datasets from local files like PDFs, Word docs, images, and text. It extracts content, uses semantic search to understand context, applies instructions through a generated schema, and outputs clean, structured data. Perfect for converting raw or unstructured local documents into ready-to-use datasets for training, analysis, or experimentation, all without manual formatting.

skyvern
Skyvern automates browser-based workflows using LLMs and computer vision. It provides a simple API endpoint to fully automate manual workflows, replacing brittle or unreliable automation solutions. Traditional approaches to browser automations required writing custom scripts for websites, often relying on DOM parsing and XPath-based interactions which would break whenever the website layouts changed. Instead of only relying on code-defined XPath interactions, Skyvern adds computer vision and LLMs to the mix to parse items in the viewport in real-time, create a plan for interaction and interact with them. This approach gives us a few advantages: 1. Skyvern can operate on websites it’s never seen before, as it’s able to map visual elements to actions necessary to complete a workflow, without any customized code 2. Skyvern is resistant to website layout changes, as there are no pre-determined XPaths or other selectors our system is looking for while trying to navigate 3. Skyvern leverages LLMs to reason through interactions to ensure we can cover complex situations. Examples include: 1. If you wanted to get an auto insurance quote from Geico, the answer to a common question “Were you eligible to drive at 18?” could be inferred from the driver receiving their license at age 16 2. If you were doing competitor analysis, it’s understanding that an Arnold Palmer 22 oz can at 7/11 is almost definitely the same product as a 23 oz can at Gopuff (even though the sizes are slightly different, which could be a rounding error!) Want to see examples of Skyvern in action? Jump to #real-world-examples-of- skyvern

airbyte-connectors
This repository contains Airbyte connectors used in Faros and Faros Community Edition platforms as well as Airbyte Connector Development Kit (CDK) for JavaScript/TypeScript.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.












