
gwq
🌳 Git worktree manager with fuzzy finder - Work on multiple branches simultaneously, perfect for parallel AI coding workflows 🍋
Stars: 351
gwq is a CLI tool for efficiently managing Git worktrees, providing intuitive operations for creating, switching, and deleting worktrees using a fuzzy finder interface. It allows users to work on multiple features simultaneously, run parallel AI coding agents on different tasks, review code while developing new features, and test changes without disrupting the main workspace. The tool is ideal for enabling parallel AI coding workflows, independent tasks, parallel migrations, and code review workflows.
README:
gwq is a CLI tool for efficiently managing Git worktrees. Like how ghq manages repository clones, gwq provides intuitive operations for creating, switching, and deleting worktrees using a fuzzy finder interface.
Git worktrees allow you to check out multiple branches from the same repository into separate directories. This is particularly powerful when:
- Working on multiple features simultaneously
- Running parallel AI coding agents on different tasks
- Reviewing code while developing new features
- Testing changes without disrupting your main workspace
One of the most powerful applications of gwq is enabling parallel AI coding workflows. Instead of having a single AI agent work sequentially through tasks, you can leverage multiple worktrees to have multiple AI agents work on different parts of your project simultaneously:
# Create worktrees for parallel development
gwq add -b feature/authentication
gwq add -b feature/data-visualization
gwq add -b bugfix/login-issue
# Each AI agent can work in its own worktree
cd $(gwq get authentication) && claude
cd $(gwq get visualization) && claude
cd $(gwq get login) && claude
# Monitor all agent activity in real-time
gwq status --watchSince each worktree has its own working directory with isolated files, AI agents can work at full speed without merge conflicts. This approach is ideal for independent tasks, parallel migrations, and code review workflows.
brew install d-kuro/tap/gwqgo install github.com/d-kuro/gwq/cmd/gwq@latestgit clone https://github.com/d-kuro/gwq.git
cd gwq
go build -o gwq ./cmd/gwq# Create a new worktree with new branch
gwq add -b feature/new-ui
# List all worktrees
gwq list
# Check status of all worktrees
gwq status
# Get worktree path (for cd)
cd $(gwq get feature)
# Execute command in worktree
gwq exec feature -- npm test
# Remove a worktree
gwq remove feature/old-ui- Fuzzy Finder Interface: Built-in fuzzy finder for intuitive branch and worktree selection
- Global Worktree Management: Access all your worktrees across repositories from anywhere
- Status Dashboard: Monitor all worktrees' git status, changes, and activity at a glance
- Tmux Integration: Run and manage long-running processes in persistent tmux sessions
- Tab Completion: Full shell completion support for branches, worktrees, and configuration
Create a new worktree.
# Create worktree with new branch
gwq add -b feature/new-ui
# Create from existing branch
gwq add main
# Interactive branch selection
gwq add -i
# Stay in worktree directory after creation
gwq add -s feature/new-uiFlags: -b (new branch), -i (interactive), -s (stay), -f (force)
Display all worktrees.
# Simple list
gwq list
gwq ls
# Detailed information
gwq list -v
# JSON format
gwq list --json
# Show all worktrees globally
gwq list -gFlags: -v (verbose), -g (global), --json
Get worktree path. Useful for shell command substitution.
# Get path and change directory
cd $(gwq get feature)
# Get from global worktrees
gwq get -g myapp:featureFlags: -g (global), -0 (null-terminated)
Change to worktree directory by launching a new shell.
# Change to a worktree
gwq cd feature
# Interactive selection
gwq cdFlags: -g (global)
Note: By default,
gwq cdlaunches a new shell. Setcd.launch_shell = falseto change directory in the current shell instead. This requires shell integration — see Shell Integration for setup. PowerShell is currently not supported for shell integration.
Execute command in worktree directory.
# Run tests in feature branch
gwq exec feature -- npm test
# Stay in directory after command
gwq exec -s feature -- npm installFlags: -g (global), -s (stay)
Delete a worktree.
# Interactive selection
gwq remove
# Delete by pattern
gwq remove feature/old
# Also delete the branch
gwq remove -b feature/completed
# Force delete unmerged branch
gwq remove -b --force-delete-branch feature/abandoned
# Preview deletion
gwq remove --dry-run feature/oldFlags: -f (force), -b (delete branch), --force-delete-branch, -g (global), --dry-run
Monitor the status of all worktrees.
# Table view
gwq status
# Watch mode (auto-refresh)
gwq status --watch
# Filter by status
gwq status --filter changed
# Sort by activity
gwq status --sort activity
# Output formats
gwq status --json
gwq status --csvFlags: -w (watch), -f (filter), -s (sort), -v (verbose), -g (global), --json, --csv
Manage tmux sessions for long-running processes.
# List sessions
gwq tmux list
# Run command in new session
gwq tmux run "npm run dev"
# Run with custom ID
gwq tmux run --id dev-server "npm run dev"
# Attach to session
gwq tmux attach dev-server
# Kill session
gwq tmux kill dev-serverManage configuration.
# Show configuration
gwq config list
# Set global value (default)
gwq config set worktree.basedir ~/worktrees
# Set local value (writes to .gwq.toml in current directory)
gwq config set --local finder.preview false
# Get value
gwq config get worktree.basedirFlags: --local (write to local config instead of global)
Clean up deleted worktree information.
gwq prunegwq automatically discovers all worktrees in your configured base directory:
- Outside Git Repositories: Shows all worktrees in the base directory
-
Inside Git Repositories: Shows only worktrees for the current repository (use
-gto see all) - No Registry Required: Uses filesystem scanning instead of maintaining a separate registry
The completion scripts provide both tab completion and gwq cd shell integration. When cd.launch_shell is set to false, the completion script includes a shell wrapper that allows gwq cd to change the directory in the current shell without launching a new shell. PowerShell is currently not supported for shell integration.
Bash:
source <(gwq completion bash)Zsh:
source <(gwq completion zsh)Fish:
gwq completion fish > ~/.config/fish/completions/gwq.fishPowerShell:
gwq completion powershell | Out-String | Invoke-Expressiongwq uses two configuration files:
| File | Location | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Global | ~/.config/gwq/config.toml |
Default settings for all projects |
| Local |
.gwq.toml (current directory) |
Project-specific overrides |
Local configuration takes precedence over global settings.
Example global config (~/.config/gwq/config.toml):
[worktree]
basedir = "~/worktrees"
auto_mkdir = true
[finder]
preview = true
[naming]
template = "{{.Host}}/{{.Owner}}/{{.Repository}}/{{.Branch}}"
sanitize_chars = { "/" = "-", ":" = "-" }
[cd]
launch_shell = false # Use shell integration instead of launching a new shell
[ui]
icons = true
tilde_home = true
[[repository_settings]]
repository = "~/src/myproject"
copy_files = ["templates/.env.example"]
setup_commands = ["npm install"]| Setting | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
worktree.basedir |
Base directory for worktrees | ~/worktrees |
naming.template |
Directory naming template | {{.Host}}/{{.Owner}}/{{.Repository}}/{{.Branch}} |
ui.tilde_home |
Display ~ instead of full home path |
true |
cd.launch_shell |
Launch a new shell for gwq cd (set false for shell integration) |
true |
ui.icons |
Show icons in output | true |
Configure automatic file copying and setup commands per repository. These settings can be defined in both global and local configuration files.
[[repository_settings]]
repository = "~/src/myproject"
copy_files = ["templates/.env.example", "config/*.json"]
setup_commands = ["npm install", "npm run setup"]When both global and local configs define repository_settings, they are merged using the repository field as the key:
- Same repository: Local settings completely override global
- Different repositories: Both are kept
Example:
Global config (~/.config/gwq/config.toml):
[[repository_settings]]
repository = "~/src/project-a"
setup_commands = ["npm install"]
[[repository_settings]]
repository = "~/src/project-b"
setup_commands = ["go mod download"]Local config (.gwq.toml):
[[repository_settings]]
repository = "~/src/project-a"
setup_commands = ["yarn install", "yarn build"]
[[repository_settings]]
repository = "~/src/project-c"
setup_commands = ["make setup"]Merged result:
| Repository | Source | Commands |
|---|---|---|
project-a |
Local (override) |
yarn install, yarn build
|
project-b |
Global | go mod download |
project-c |
Local (new) | make setup |
For a powerful development workflow, you can integrate gwq with ghq (repository manager) and fzf (fuzzy finder). This combination is particularly effective for parallel AI coding agent workflows.
The key idea is to place worktrees alongside your cloned repositories under the same root directory, enabling unified fuzzy search across both. This consolidates all your development directories into a single searchable location.
For detailed configuration and shell function setup, see: A Coding-Agent-Friendly Environment Is Friendly to Humans Too: ghq x gwq x fzf
gwq organizes worktrees using a URL-based hierarchy:
~/worktrees/
├── github.com/
│ └── user/
│ └── myapp/
│ ├── feature-auth/
│ └── feature-api/
└── gitlab.com/
└── company/
└── project/
└── feature-x/
This structure prevents naming conflicts and preserves context about which repository a worktree belongs to.
- Git 2.5+ (for worktree support)
- Go 1.24+ (for building from source)
Apache License 2.0 - see LICENSE file for details.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for gwq
Similar Open Source Tools

gwq
gwq is a CLI tool for efficiently managing Git worktrees, providing intuitive operations for creating, switching, and deleting worktrees using a fuzzy finder interface. It allows users to work on multiple features simultaneously, run parallel AI coding agents on different tasks, review code while developing new features, and test changes without disrupting the main workspace. The tool is ideal for enabling parallel AI coding workflows, independent tasks, parallel migrations, and code review workflows.
ruler
Ruler is a tool designed to centralize AI coding assistant instructions, providing a single source of truth for managing instructions across multiple AI coding tools. It helps in avoiding inconsistent guidance, duplicated effort, context drift, onboarding friction, and complex project structures by automatically distributing instructions to the right configuration files. With support for nested rule loading, Ruler can handle complex project structures with context-specific instructions for different components. It offers features like centralised rule management, nested rule loading, automatic distribution, targeted agent configuration, MCP server propagation, .gitignore automation, and a simple CLI for easy configuration management.
localgpt
LocalGPT is a local device focused AI assistant built in Rust, providing persistent memory and autonomous tasks. It runs entirely on your machine, ensuring your memory data stays private. The tool offers a markdown-based knowledge store with full-text and semantic search capabilities, hybrid web search, and multiple interfaces including CLI, web UI, desktop GUI, and Telegram bot. It supports multiple LLM providers, is OpenClaw compatible, and offers defense-in-depth security features such as signed policy files, kernel-enforced sandbox, and prompt injection defenses. Users can configure web search providers, use OAuth subscription plans, and access the tool from Telegram for chat, tool use, and memory support.
aicommit2
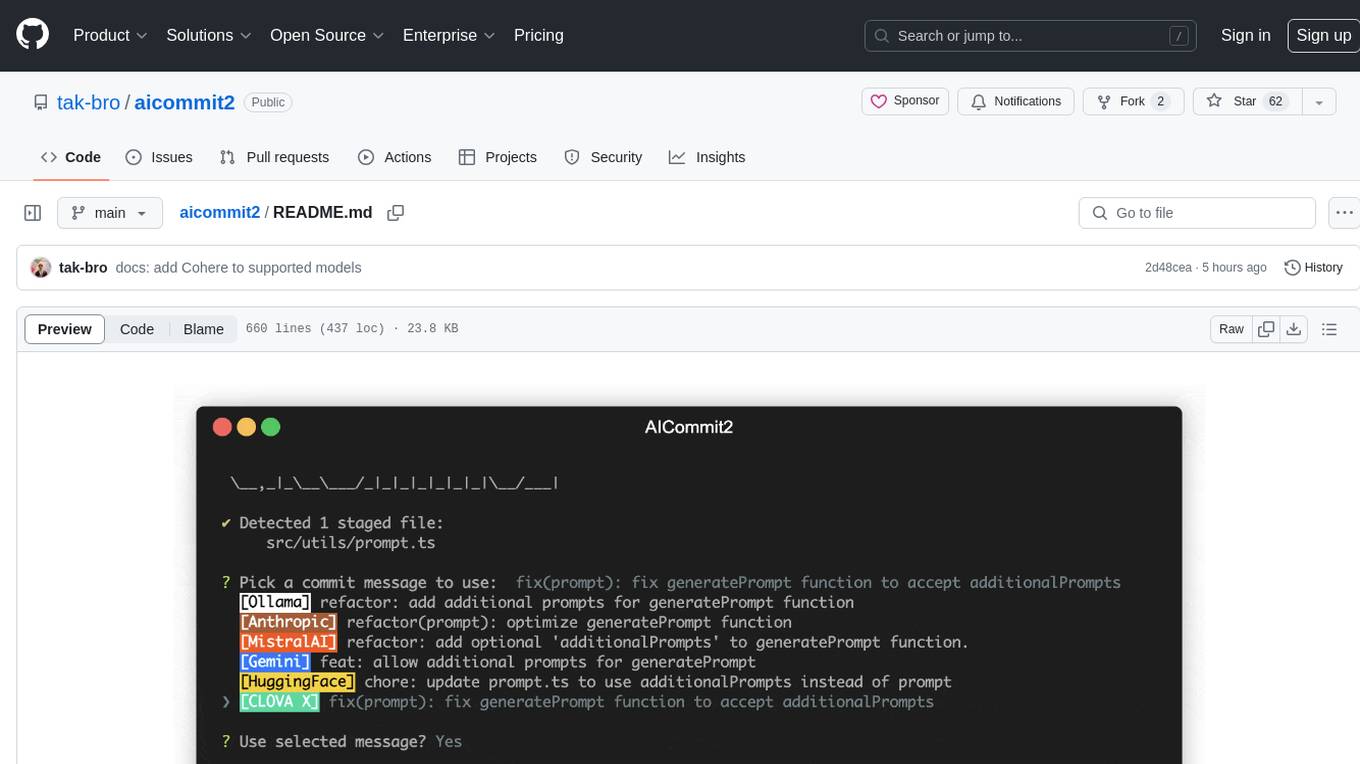
AICommit2 is a Reactive CLI tool that streamlines interactions with various AI providers such as OpenAI, Anthropic Claude, Gemini, Mistral AI, Cohere, and unofficial providers like Huggingface and Clova X. Users can request multiple AI simultaneously to generate git commit messages without waiting for all AI responses. The tool runs 'git diff' to grab code changes, sends them to configured AI, and returns the AI-generated commit message. Users can set API keys or Cookies for different providers and configure options like locale, generate number of messages, commit type, proxy, timeout, max-length, and more. AICommit2 can be used both locally with Ollama and remotely with supported providers, offering flexibility and efficiency in generating commit messages.
ocode
OCode is a sophisticated terminal-native AI coding assistant that provides deep codebase intelligence and autonomous task execution. It seamlessly works with local Ollama models, bringing enterprise-grade AI assistance directly to your development workflow. OCode offers core capabilities such as terminal-native workflow, deep codebase intelligence, autonomous task execution, direct Ollama integration, and an extensible plugin layer. It can perform tasks like code generation & modification, project understanding, development automation, data processing, system operations, and interactive operations. The tool includes specialized tools for file operations, text processing, data processing, system operations, development tools, and integration. OCode enhances conversation parsing, offers smart tool selection, and provides performance improvements for coding tasks.
tokscale
Tokscale is a high-performance CLI tool and visualization dashboard for tracking token usage and costs across multiple AI coding agents. It helps monitor and analyze token consumption from various AI coding tools, providing real-time pricing calculations using LiteLLM's pricing data. Inspired by the Kardashev scale, Tokscale measures token consumption as users scale the ranks of AI-augmented development. It offers interactive TUI mode, multi-platform support, real-time pricing, detailed breakdowns, web visualization, flexible filtering, and social platform features.
zeroclaw
ZeroClaw is a fast, small, and fully autonomous AI assistant infrastructure built with Rust. It features a lean runtime, cost-efficient deployment, fast cold starts, and a portable architecture. It is secure by design, fully swappable, and supports OpenAI-compatible provider support. The tool is designed for low-cost boards and small cloud instances, with a memory footprint of less than 5MB. It is suitable for tasks like deploying AI assistants, swapping providers/channels/tools, and pluggable everything.
nosia
Nosia is a self-hosted AI RAG + MCP platform that allows users to run AI models on their own data with complete privacy and control. It integrates the Model Context Protocol (MCP) to connect AI models with external tools, services, and data sources. The platform is designed to be easy to install and use, providing OpenAI-compatible APIs that work seamlessly with existing AI applications. Users can augment AI responses with their documents, perform real-time streaming, support multi-format data, enable semantic search, and achieve easy deployment with Docker Compose. Nosia also offers multi-tenancy for secure data separation.
git-mcp-server
A secure and scalable Git MCP server providing AI agents with powerful version control capabilities for local and serverless environments. It offers 28 comprehensive Git operations organized into seven functional categories, resources for contextual information about the Git environment, and structured prompt templates for guiding AI agents through complex workflows. The server features declarative tools, robust error handling, pluggable authentication, abstracted storage, full-stack observability, dependency injection, and edge-ready architecture. It also includes specialized features for Git integration such as cross-runtime compatibility, provider-based architecture, optimized Git execution, working directory management, configurable Git identity, safety features, and commit signing.
mediasoup-client-aiortc
mediasoup-client-aiortc is a handler for the aiortc Python library, allowing Node.js applications to connect to a mediasoup server using WebRTC for real-time audio, video, and DataChannel communication. It facilitates the creation of Worker instances to manage Python subprocesses, obtain audio/video tracks, and create mediasoup-client handlers. The tool supports features like getUserMedia, handlerFactory creation, and event handling for subprocess closure and unexpected termination. It provides custom classes for media stream and track constraints, enabling diverse audio/video sources like devices, files, or URLs. The tool enhances WebRTC capabilities in Node.js applications through seamless Python subprocess communication.
repomix
Repomix is a powerful tool that packs your entire repository into a single, AI-friendly file. It is designed to format your codebase for easy understanding by AI tools like Large Language Models (LLMs), Claude, ChatGPT, and Gemini. Repomix offers features such as AI optimization, token counting, simplicity in usage, customization options, Git awareness, and security-focused checks using Secretlint. It allows users to pack their entire repository or specific directories/files using glob patterns, and even supports processing remote Git repositories. The tool generates output in plain text, XML, or Markdown formats, with options for including/excluding files, removing comments, and performing security checks. Repomix also provides a global configuration option, custom instructions for AI context, and a security check feature to detect sensitive information in files.
RepairAgent
RepairAgent is an autonomous LLM-based agent for automated program repair targeting the Defects4J benchmark. It uses an LLM-driven loop to localize, analyze, and fix Java bugs. The tool requires Docker, VS Code with Dev Containers extension, OpenAI API key, disk space of ~40 GB, and internet access. Users can get started with RepairAgent using either VS Code Dev Container or Docker Image. Running RepairAgent involves checking out the buggy project version, autonomous bug analysis, fix candidate generation, and testing against the project's test suite. Users can configure hyperparameters for budget control, repetition handling, commands limit, and external fix strategy. The tool provides output structure, experiment overview, individual analysis scripts, and data on fixed bugs from the Defects4J dataset.
sonarqube-mcp-server
The SonarQube MCP Server is a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server that enables seamless integration with SonarQube Server or Cloud for code quality and security. It supports the analysis of code snippets directly within the agent context. The server provides various tools for analyzing code, managing issues, accessing metrics, and interacting with SonarQube projects. It also supports advanced features like dependency risk analysis, enterprise portfolio management, and system health checks. The server can be configured for different transport modes, proxy settings, and custom certificates. Telemetry data collection can be disabled if needed.
docutranslate
Docutranslate is a versatile tool for translating documents efficiently. It supports multiple file formats and languages, making it ideal for businesses and individuals needing quick and accurate translations. The tool uses advanced algorithms to ensure high-quality translations while maintaining the original document's formatting. With its user-friendly interface, Docutranslate simplifies the translation process and saves time for users. Whether you need to translate legal documents, technical manuals, or personal letters, Docutranslate is the go-to solution for all your document translation needs.
FDAbench
FDABench is a benchmark tool designed for evaluating data agents' reasoning ability over heterogeneous data in analytical scenarios. It offers 2,007 tasks across various data sources, domains, difficulty levels, and task types. The tool provides ready-to-use data agent implementations, a DAG-based evaluation system, and a framework for agent-expert collaboration in dataset generation. Key features include data agent implementations, comprehensive evaluation metrics, multi-database support, different task types, extensible framework for custom agent integration, and cost tracking. Users can set up the environment using Python 3.10+ on Linux, macOS, or Windows. FDABench can be installed with a one-command setup or manually. The tool supports API configuration for LLM access and offers quick start guides for database download, dataset loading, and running examples. It also includes features like dataset generation using the PUDDING framework, custom agent integration, evaluation metrics like accuracy and rubric score, and a directory structure for easy navigation.
nanocoder
Nanocoder is a versatile code editor designed for beginners and experienced programmers alike. It provides a user-friendly interface with features such as syntax highlighting, code completion, and error checking. With Nanocoder, you can easily write and debug code in various programming languages, making it an ideal tool for learning, practicing, and developing software projects. Whether you are a student, hobbyist, or professional developer, Nanocoder offers a seamless coding experience to boost your productivity and creativity.
For similar tasks

Gito
Gito is a lightweight and user-friendly tool for managing and organizing your GitHub repositories. It provides a simple and intuitive interface for users to easily view, clone, and manage their repositories. With Gito, you can quickly access important information about your repositories, such as commit history, branches, and pull requests. The tool also allows you to perform common Git operations, such as pushing changes and creating new branches, directly from the interface. Gito is designed to streamline your GitHub workflow and make repository management more efficient and convenient.

gwq
gwq is a CLI tool for efficiently managing Git worktrees, providing intuitive operations for creating, switching, and deleting worktrees using a fuzzy finder interface. It allows users to work on multiple features simultaneously, run parallel AI coding agents on different tasks, review code while developing new features, and test changes without disrupting the main workspace. The tool is ideal for enabling parallel AI coding workflows, independent tasks, parallel migrations, and code review workflows.
worktrunk
Worktrunk is a CLI tool designed for managing git worktrees efficiently, especially for running AI agents in parallel. It simplifies the process of creating, switching, and managing worktrees, providing quality-of-life features like workflow automation through hooks. Worktrunk aims to streamline the experience of working with multiple parallel changes in a git repository, making it easier for users to handle tasks involving AI agents and git worktree management.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.

oss-fuzz-gen
This framework generates fuzz targets for real-world `C`/`C++` projects with various Large Language Models (LLM) and benchmarks them via the `OSS-Fuzz` platform. It manages to successfully leverage LLMs to generate valid fuzz targets (which generate non-zero coverage increase) for 160 C/C++ projects. The maximum line coverage increase is 29% from the existing human-written targets.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.
