
CodeLLMPaper
A continuously updated collection of CodeLLM papers maintained by PurCL group @ Purdue
Stars: 356
CodeLLM Paper repository provides a curated list of research papers focused on Large Language Models (LLMs) for code. It aims to facilitate researchers and practitioners in exploring the rapidly growing body of literature on this topic. The papers are systematically collected from various top-tier venues, categorized, and labeled for easier navigation. The selection strategy involves abstract extraction, keyword matching, relevance check using LLMs, and manual labeling. The papers are categorized based on Application, Principle, and Research Paradigm dimensions. Contributions to expand the repository are welcome through PR submission, issue submission, or request for batch updates. The repository is intended solely for research purposes, with raw data sourced from publicly available information on ACM, IEEE, and corresponding conference websites.
README:
This repository provides a curated list of research papers focused on Large Language Models (LLMs) for code. It aims to facilitate researchers and practitioners in exploring the rapidly growing body of literature on this topic. The papers are systematically collected from various top-tier venues, categorized, and labeled for easier navigation.
We have systematically selected papers from the following venues, which are top-tier conferences and journals in SE/PL/Sec/NLP communities.
-
Software Engineering (SE)
-
Programming Languages (PL)
-
Security (Sec)
-
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Due to the large volume, we do not systematically collect the papers published in top-tier ML conferences (ICML, NeurIPS, and ICLR) and arXiv. However, we are keeping manually adding important works published in these venues. We plan to expand the collection over time, and contributions are welcome. For details, see the section How to Contribute.
-
Abstract Extraction: Extract the abstracts from bib files or HTML files. The bib and HTML files of the above listed venues are stored in the directory
data/rawdata. -
Keyword Matching: Filter abstracts that meet both of the following conditions:
-
Contains at least one keyword from:
{"pretrain", "LLM", "large language model", "transformer", "code model"}. -
Contains the keyword
"code"or"program".
-
-
Relevance Check Using LLMs: Use LLMs to verify if the papers obtained in Step 2 are related to LLMs for code.
-
Manual Labeling: Manually assign labels to the papers based on domain knowledge.
All the selected papers along with the labels are maintained in the json file data/labeldata/labeldata.json. src/process.py is the python script used for selecting and labeling papers.
The papers in this repository are categorized along three dimensions: Application, Principle, and Research Paradigm. Each paper is assigned multiple labels based on these categories. Note that categories are not necessarily disjoint.
This category focuses on typical tasks in Software Engineering (SE) and Programming Languages (PL).
- General Coding Task (32)
-
Code Generation (199)
- Program Synthesis (83)
- Code Completion (23)
- Program Repair (41)
- Program Transformation (32)
-
Program Testing (55)
- General Testing (1)
- Fuzzing (24)
- Library Testing (1)
- DBMS Testing (1)
- Compiler Testing (4)
- Protocol Fuzzing (1)
- Mutation Testing (2)
- Unit Testing (7)
- Differential Testing (2)
- Debugging (9)
- Bug Reproduction (2)
- Vulnerability Exploitation (6)
-
Static Analysis (149)
- Syntactic Analysis (1)
- Pointer Analysis (3)
- Call Graph Analysis (2)
- Data-flow Analysis (8)
- Type Inference (3)
- Specification Inference (17)
- Equivalence Checking (1)
- Code Similarity Analysis (5)
- Bug Detection (77)
- Program Verification (20)
- Program Optimization (4)
- Program Decompilation (9)
- Code Summarization (10)
- Code Search (5)
- Software Composition Analysis (3)
- Software Maintenance and Deployment (18)
This category concentrates on the LLMs' ability in understanding different forms of code and the non-functional properties of the LLMs (e.g., security and robustness). We also consider how to utilize the LLMs for general reasoning problems, such as typical agent-centric designs and specific PL designs for LLMs.
-
Code Model (112)
-
Code Model Training (84)
- Source Code Model (64)
- IR Code Model (5)
- Binary Code Model (15)
- Code Model Security (23)
- Code Model Robustness (4)
-
Code Model Training (84)
- Hallucination In Reasoning (12)
- PL Design For LLMs (3)
-
Agent Design (58)
- Prompt Strategy (39)
- Planning (9)
This category includes studies on benchmarks, empirical evaluations, and surveys. The papers that do not belong to the following three categories are purely technical papers.
- Benchmark (47)
- Empirical Study (79)
- Survey (18)
We welcome contributions to expand this repository. If you want to add new papers to the list, please follow these steps:
-
Prepare a JSON File: Format the file like
data/labeldata/patch/example.json. Each paper should include:-
title,authors,abstract,url,venue, andlabels(aligned with the taxonomy indata/labeldata/patch).
-
-
Upload the File: Place the JSON file in the
data/labeldata/patchdirectory. -
Update Markdown Files: Run the following command to update the repository:
cd src && python patch.py
If you want to add new labels and change the current taxonomy, please post an issue first and suggest your taxonomy (See below).
Another option is to post the papers you wish to add in an issue. Please include a permanently valid link to the paper and specify the venue. If you'd like, you can also categorize the paper based on your understanding of the work by attaching appropriate labels from the existing options in data/category.json or by creating new ones. We will add the paper to our repository very soon.
To facilitate timely batch updates to the paper repository, we prefer to utilize the proceedings of various conferences and journals. Here are several examples: ASE2024, OOPSLA2023, S&P2023, and ACL2024. By parsing and extracting information from bib files and HTML files (See data/rawdata), including abstracts, we can semi-automatically classify papers based on the aforementioned selection strategy. If the conference or journal you are following has recently released its complete proceedings, please notify us by submitting an issue. We will prioritize the batch update and add the corresponding conference or journal name to the venue list.
This paper repository is intended solely for research purposes. All raw data is sourced from publicly available information on ACM, IEEE, and corresponding conference websites. Any content involving additional copyright information, including full PDF versions of the papers, is not disclosed in this repository.
For any questions or suggestions, please contact [email protected] or [email protected]
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for CodeLLMPaper
Similar Open Source Tools

CodeLLMPaper
CodeLLM Paper repository provides a curated list of research papers focused on Large Language Models (LLMs) for code. It aims to facilitate researchers and practitioners in exploring the rapidly growing body of literature on this topic. The papers are systematically collected from various top-tier venues, categorized, and labeled for easier navigation. The selection strategy involves abstract extraction, keyword matching, relevance check using LLMs, and manual labeling. The papers are categorized based on Application, Principle, and Research Paradigm dimensions. Contributions to expand the repository are welcome through PR submission, issue submission, or request for batch updates. The repository is intended solely for research purposes, with raw data sourced from publicly available information on ACM, IEEE, and corresponding conference websites.

cleanlab
Cleanlab helps you **clean** data and **lab** els by automatically detecting issues in a ML dataset. To facilitate **machine learning with messy, real-world data** , this data-centric AI package uses your _existing_ models to estimate dataset problems that can be fixed to train even _better_ models.
codellm-devkit
Codellm-devkit (CLDK) is a Python library that serves as a multilingual program analysis framework bridging traditional static analysis tools and Large Language Models (LLMs) specialized for code (CodeLLMs). It simplifies the process of analyzing codebases across multiple programming languages, enabling the extraction of meaningful insights and facilitating LLM-based code analysis. The library provides a unified interface for integrating outputs from various analysis tools and preparing them for effective use by CodeLLMs. Codellm-devkit aims to enable the development and experimentation of robust analysis pipelines that combine traditional program analysis tools and CodeLLMs, reducing friction in multi-language code analysis and ensuring compatibility across different tools and LLM platforms. It is designed to seamlessly integrate with popular analysis tools like WALA, Tree-sitter, LLVM, and CodeQL, acting as a crucial intermediary layer for efficient communication between these tools and CodeLLMs. The project is continuously evolving to include new tools and frameworks, maintaining its versatility for code analysis and LLM integration.
SheetCopilot
SheetCopilot is an assistant agent that manipulates spreadsheets by following user commands. It leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to interact with spreadsheets like a human expert, enabling non-expert users to complete tasks on complex software such as Google Sheets and Excel via a language interface. The tool observes spreadsheet states, polishes generated solutions based on external action documents and error feedback, and aims to improve success rate and efficiency. SheetCopilot offers a dataset with diverse task categories and operations, supporting operations like entry & manipulation, management, formatting, charts, and pivot tables. Users can interact with SheetCopilot in Excel or Google Sheets, executing tasks like calculating revenue, creating pivot tables, and plotting charts. The tool's evaluation includes performance comparisons with leading LLMs and VBA-based methods on specific datasets, showcasing its capabilities in controlling various aspects of a spreadsheet.
MicroLens
MicroLens is a content-driven micro-video recommendation dataset at scale. It provides a large dataset with multimodal data, including raw text, images, audio, video, and video comments, for tasks such as multi-modal recommendation, foundation model building, and fairness recommendation. The dataset is available in two versions: MicroLens-50K and MicroLens-100K, with extracted features for multimodal recommendation tasks. Researchers can access the dataset through provided links and reach out to the corresponding author for the complete dataset. The repository also includes codes for various algorithms like VideoRec, IDRec, and VIDRec, each implementing different video models and baselines.
ag2
Ag2 is a lightweight and efficient tool for generating automated reports from data sources. It simplifies the process of creating reports by allowing users to define templates and automate the data extraction and formatting. With Ag2, users can easily generate reports in various formats such as PDF, Excel, and CSV, saving time and effort in manual report generation tasks.
swiftide
Swiftide is a fast, streaming indexing and query library tailored for Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) in AI applications. It is built in Rust, utilizing parallel, asynchronous streams for blazingly fast performance. With Swiftide, users can easily build AI applications from idea to production in just a few lines of code. The tool addresses frustrations around performance, stability, and ease of use encountered while working with Python-based tooling. It offers features like fast streaming indexing pipeline, experimental query pipeline, integrations with various platforms, loaders, transformers, chunkers, embedders, and more. Swiftide aims to provide a platform for data indexing and querying to advance the development of automated Large Language Model (LLM) applications.
Video-MME
Video-MME is the first-ever comprehensive evaluation benchmark of Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) in Video Analysis. It assesses the capabilities of MLLMs in processing video data, covering a wide range of visual domains, temporal durations, and data modalities. The dataset comprises 900 videos with 256 hours and 2,700 human-annotated question-answer pairs. It distinguishes itself through features like duration variety, diversity in video types, breadth in data modalities, and quality in annotations.

sdialog
SDialog is an MIT-licensed open-source toolkit for building, simulating, and evaluating LLM-based conversational agents end-to-end. It aims to bridge agent construction, user simulation, dialog generation, and evaluation in a single reproducible workflow, enabling the generation of reliable, controllable dialog systems or data at scale. The toolkit standardizes a Dialog schema, offers persona-driven multi-agent simulation with LLMs, provides composable orchestration for precise control over behavior and flow, includes built-in evaluation metrics, and offers mechanistic interpretability. It allows for easy creation of user-defined components and interoperability across various AI platforms.
ExtractThinker
ExtractThinker is a library designed for extracting data from files and documents using Language Model Models (LLMs). It offers ORM-style interaction between files and LLMs, supporting multiple document loaders such as Tesseract OCR, Azure Form Recognizer, AWS TextExtract, and Google Document AI. Users can customize extraction using contract definitions, process documents asynchronously, handle various document formats efficiently, and split and process documents. The project is inspired by the LangChain ecosystem and focuses on Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) using LLMs to achieve high accuracy in document extraction tasks.
sec-parser
The `sec-parser` project simplifies extracting meaningful information from SEC EDGAR HTML documents by organizing them into semantic elements and a tree structure. It helps in parsing SEC filings for financial and regulatory analysis, analytics and data science, AI and machine learning, causal AI, and large language models. The tool is especially beneficial for AI, ML, and LLM applications by streamlining data pre-processing and feature extraction.

fuse-med-ml
FuseMedML is a Python framework designed to accelerate machine learning-based discovery in the medical field by promoting code reuse. It provides a flexible design concept where data is stored in a nested dictionary, allowing easy handling of multi-modality information. The framework includes components for creating custom models, loss functions, metrics, and data processing operators. Additionally, FuseMedML offers 'batteries included' key components such as fuse.data for data processing, fuse.eval for model evaluation, and fuse.dl for reusable deep learning components. It supports PyTorch and PyTorch Lightning libraries and encourages the creation of domain extensions for specific medical domains.

zshot
Zshot is a highly customizable framework for performing Zero and Few shot named entity and relationships recognition. It can be used for mentions extraction, wikification, zero and few shot named entity recognition, zero and few shot named relationship recognition, and visualization of zero-shot NER and RE extraction. The framework consists of two main components: the mentions extractor and the linker. There are multiple mentions extractors and linkers available, each serving a specific purpose. Zshot also includes a relations extractor and a knowledge extractor for extracting relations among entities and performing entity classification. The tool requires Python 3.6+ and dependencies like spacy, torch, transformers, evaluate, and datasets for evaluation over datasets like OntoNotes. Optional dependencies include flair and blink for additional functionalities. Zshot provides examples, tutorials, and evaluation methods to assess the performance of the components.
MME-RealWorld
MME-RealWorld is a benchmark designed to address real-world applications with practical relevance, featuring 13,366 high-resolution images and 29,429 annotations across 43 tasks. It aims to provide substantial recognition challenges and overcome common barriers in existing Multimodal Large Language Model benchmarks, such as small data scale, restricted data quality, and insufficient task difficulty. The dataset offers advantages in data scale, data quality, task difficulty, and real-world utility compared to existing benchmarks. It also includes a Chinese version with additional images and QA pairs focused on Chinese scenarios.
glossAPI
The glossAPI project aims to develop a Greek language model as open-source software, with code licensed under EUPL and data under Creative Commons BY-SA. The project focuses on collecting and evaluating open text sources in Greek, with efforts to prioritize and gather textual data sets. The project encourages contributions through the CONTRIBUTING.md file and provides resources in the wiki for viewing and modifying recorded sources. It also welcomes ideas and corrections through issue submissions. The project emphasizes the importance of open standards, ethically secured data, privacy protection, and addressing digital divides in the context of artificial intelligence and advanced language technologies.

AIL-framework
AIL framework is a modular framework to analyze potential information leaks from unstructured data sources like pastes from Pastebin or similar services or unstructured data streams. AIL framework is flexible and can be extended to support other functionalities to mine or process sensitive information (e.g. data leak prevention).
For similar tasks

CodeLLMPaper
CodeLLM Paper repository provides a curated list of research papers focused on Large Language Models (LLMs) for code. It aims to facilitate researchers and practitioners in exploring the rapidly growing body of literature on this topic. The papers are systematically collected from various top-tier venues, categorized, and labeled for easier navigation. The selection strategy involves abstract extraction, keyword matching, relevance check using LLMs, and manual labeling. The papers are categorized based on Application, Principle, and Research Paradigm dimensions. Contributions to expand the repository are welcome through PR submission, issue submission, or request for batch updates. The repository is intended solely for research purposes, with raw data sourced from publicly available information on ACM, IEEE, and corresponding conference websites.
For similar jobs

asreview
The ASReview project implements active learning for systematic reviews, utilizing AI-aided pipelines to assist in finding relevant texts for search tasks. It accelerates the screening of textual data with minimal human input, saving time and increasing output quality. The software offers three modes: Oracle for interactive screening, Exploration for teaching purposes, and Simulation for evaluating active learning models. ASReview LAB is designed to support decision-making in any discipline or industry by improving efficiency and transparency in screening large amounts of textual data.
NewEraAI-Papers
The NewEraAI-Papers repository provides links to collections of influential and interesting research papers from top AI conferences, along with open-source code to promote reproducibility and provide detailed implementation insights beyond the scope of the article. Users can stay up to date with the latest advances in AI research by exploring this repository. Contributions to improve the completeness of the list are welcomed, and users can create pull requests, open issues, or contact the repository owner via email to enhance the repository further.
cltk
The Classical Language Toolkit (CLTK) is a Python library that provides natural language processing (NLP) capabilities for pre-modern languages. It offers a modular processing pipeline with pre-configured defaults and supports almost 20 languages. Users can install the latest version using pip and access detailed documentation on the official website. The toolkit is designed to meet the unique needs of researchers working with historical languages, filling a void in the NLP landscape that often neglects non-spoken languages and different research goals.
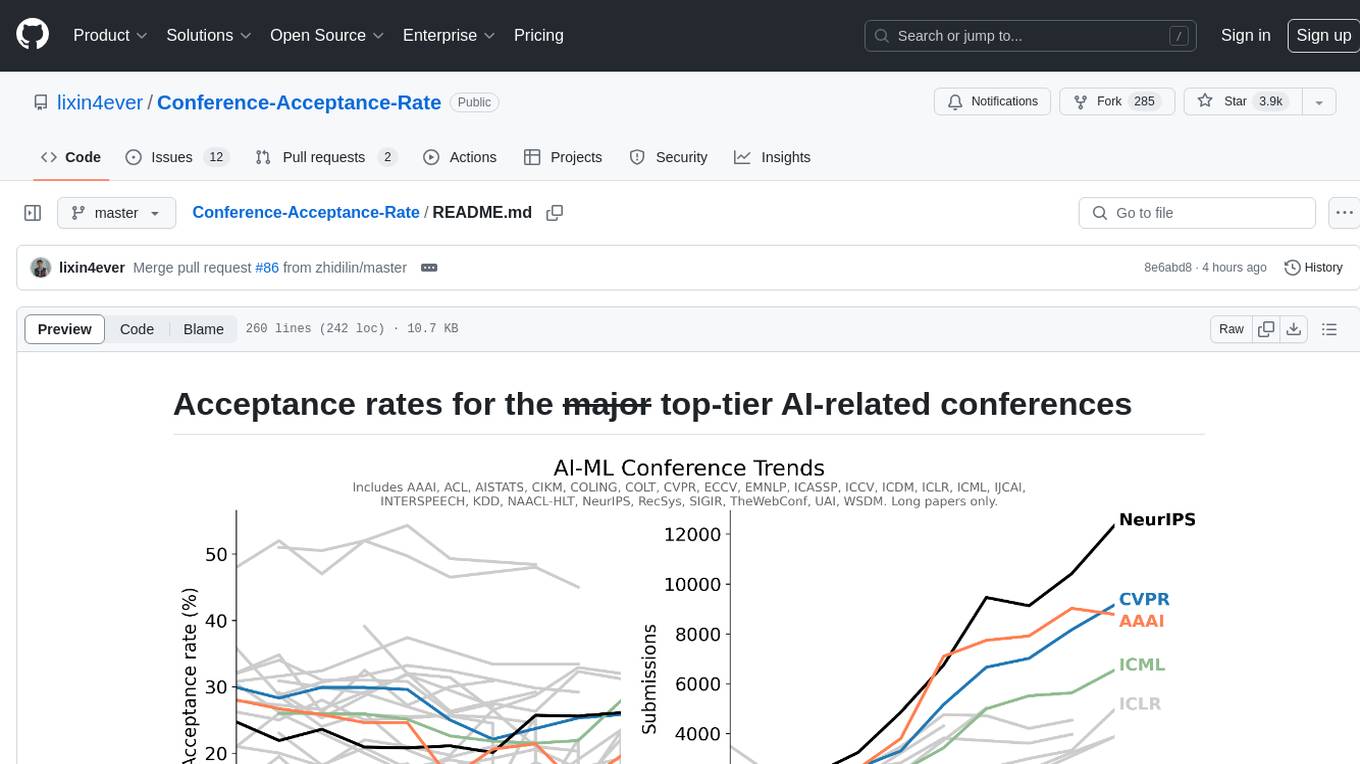
Conference-Acceptance-Rate
The 'Conference-Acceptance-Rate' repository provides acceptance rates for top-tier AI-related conferences in the fields of Natural Language Processing, Computational Linguistics, Computer Vision, Pattern Recognition, Machine Learning, Learning Theory, Artificial Intelligence, Data Mining, Information Retrieval, Speech Processing, and Signal Processing. The data includes acceptance rates for long papers and short papers over several years for each conference, allowing researchers to track trends and make informed decisions about where to submit their work.
pdftochat
PDFToChat is a tool that allows users to chat with their PDF documents in seconds. It is powered by Together AI and Pinecone, utilizing a tech stack including Next.js, Mixtral, M2 Bert, LangChain.js, MongoDB Atlas, Bytescale, Vercel, Clerk, and Tailwind CSS. Users can deploy the tool to Vercel or any other host by setting up Together.ai, MongoDB Atlas database, Bytescale, Clerk, and Vercel. The tool enables users to interact with PDFs through chat, with future tasks including adding features like trash icon for deleting PDFs, exploring different embedding models, implementing auto scrolling, improving replies, benchmarking accuracy, researching chunking and retrieval best practices, adding demo video, upgrading to Next.js 14, adding analytics, customizing tailwind prose, saving chats in postgres DB, compressing large PDFs, implementing custom uploader, session tracking, error handling, and support for images in PDFs.
tods-arxiv-daily-paper
This repository provides a tool for fetching and summarizing daily papers from the arXiv repository. It allows users to stay updated with the latest research in various fields by automatically retrieving and summarizing papers on a daily basis. The tool simplifies the process of accessing and digesting academic papers, making it easier for researchers and enthusiasts to keep track of new developments in their areas of interest.
Awesome-LLM-Strawberry
Awesome LLM Strawberry is a collection of research papers and blogs related to OpenAI Strawberry(o1) and Reasoning. The repository is continuously updated to track the frontier of LLM Reasoning.
Call-for-Reviewers
The `Call-for-Reviewers` repository aims to collect the latest 'call for reviewers' links from various top CS/ML/AI conferences/journals. It provides an opportunity for individuals in the computer/ machine learning/ artificial intelligence fields to gain review experience for applying for NIW/H1B/EB1 or enhancing their CV. The repository helps users stay updated with the latest research trends and engage with the academic community.