cleanlab
The standard data-centric AI package for data quality and machine learning with messy, real-world data and labels.
Stars: 10204

Cleanlab helps you **clean** data and **lab** els by automatically detecting issues in a ML dataset. To facilitate **machine learning with messy, real-world data** , this data-centric AI package uses your _existing_ models to estimate dataset problems that can be fixed to train even _better_ models.
README:
Documentation | Examples | Blog | Research | Cleanlab Studio | Community
cleanlab helps you clean data and labels by automatically detecting issues in a ML dataset. To facilitate machine learning with messy, real-world data, this data-centric AI package uses your existing models to estimate dataset problems that can be fixed to train even better models. Improve reliability across supervised learning, LLM, and RAG applications.
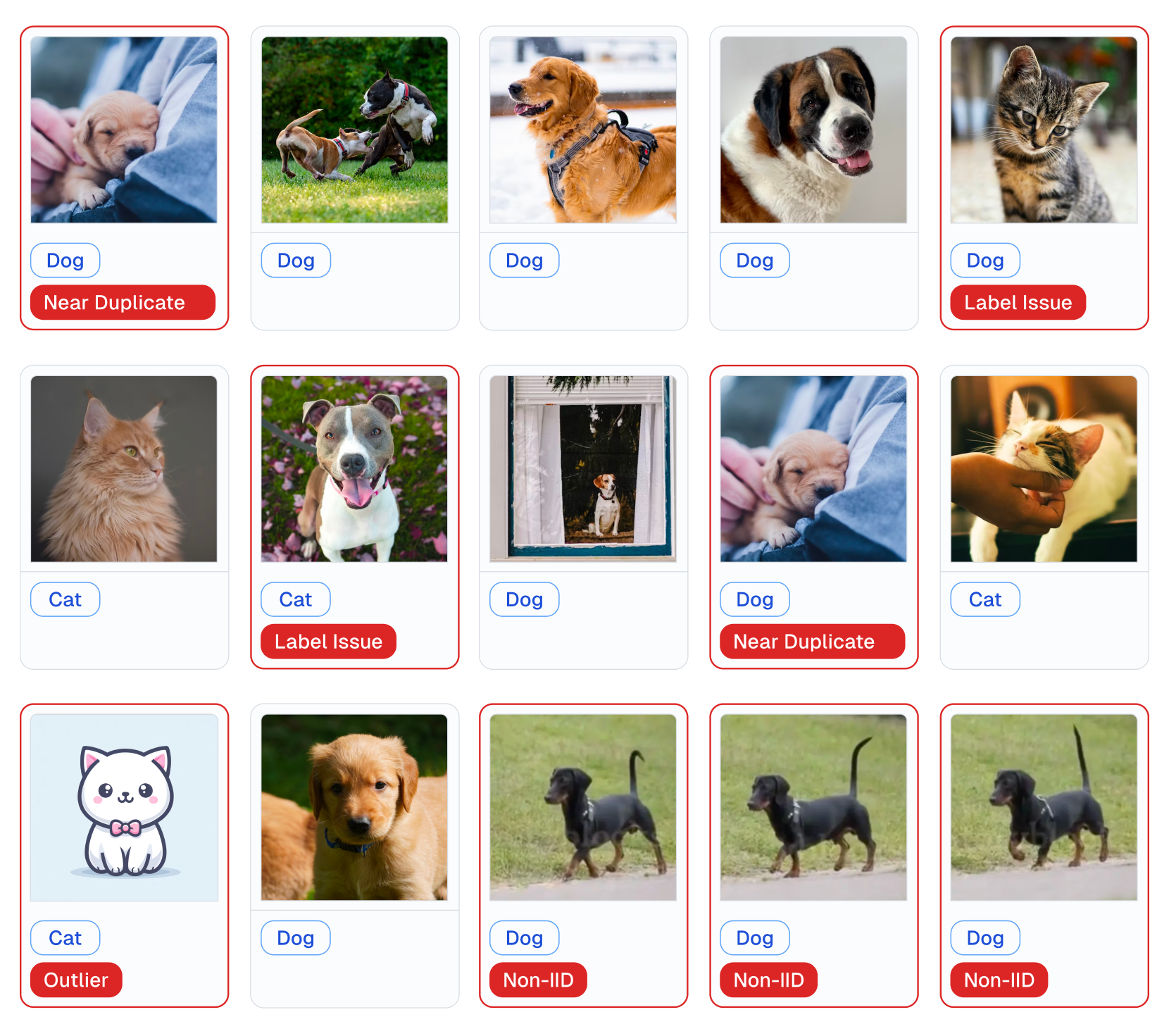
Examples of various issues in Cat/Dog dataset automatically detected by cleanlab via this code:
lab = cleanlab.Datalab(data=dataset, label="column_name_for_labels")
# Fit any ML model, get its feature_embeddings & pred_probs for your data
lab.find_issues(features=feature_embeddings, pred_probs=pred_probs)
lab.report()- Use cleanlab to automatically check every: text, audio, image, or tabular dataset.
- Use cleanlab to automatically: detect data issues (outliers, duplicates, label errors, etc), train robust models, infer consensus + annotator-quality for multi-annotator data, suggest data to (re)label next (active learning).
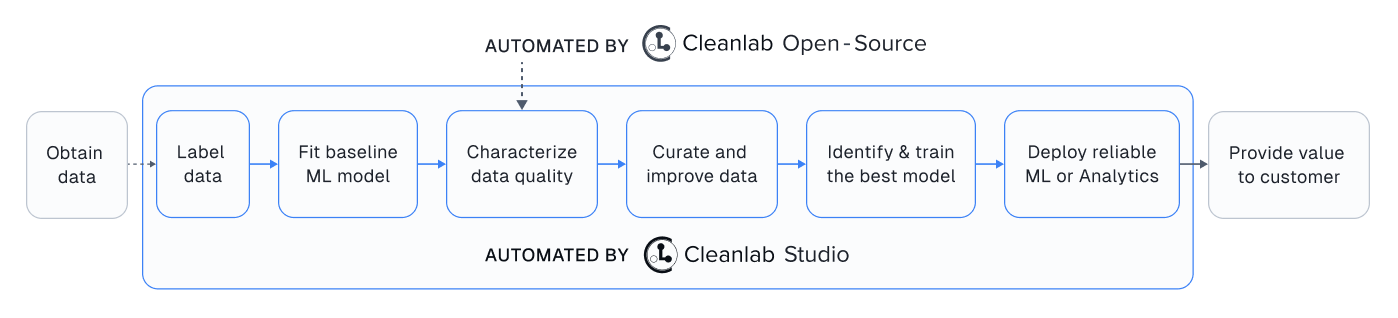
While this open-source package finds data issues, its utility depends on you having: a good existing ML model + an interface to efficiently fix these issues in your dataset. Providing all these pieces, Cleanlab Studio is a Data Curation platform to find and fix problems in any {text, image, tabular} dataset. Cleanlab Studio automatically runs optimized algorithms from this package on top of AutoML & Foundation models fit to your data, and presents detected issues (+ AI-suggested fixes) in an intelligent data correction interface.
Try it for free! Adopting Cleanlab Studio enables users of this package to:
- Work 100x faster (1 min to analyze your raw data with zero code or ML work; optionally use Python API)
- Produce better-quality data (10x more types of issues auto detected & corrected via built-in AI)
- Accomplish more (auto-label data, deploy ML instantly, audit LLM inputs/outputs, moderate content, ...)
- Monitor incoming data and detect issues in real-time (integrate your data pipeline on an Enterprise plan)
This cleanlab package runs on Python 3.8+ and supports Linux, macOS, as well as Windows.
- Get started here! Install via
piporconda. - Developers who install the bleeding-edge from source should refer to this master branch documentation.
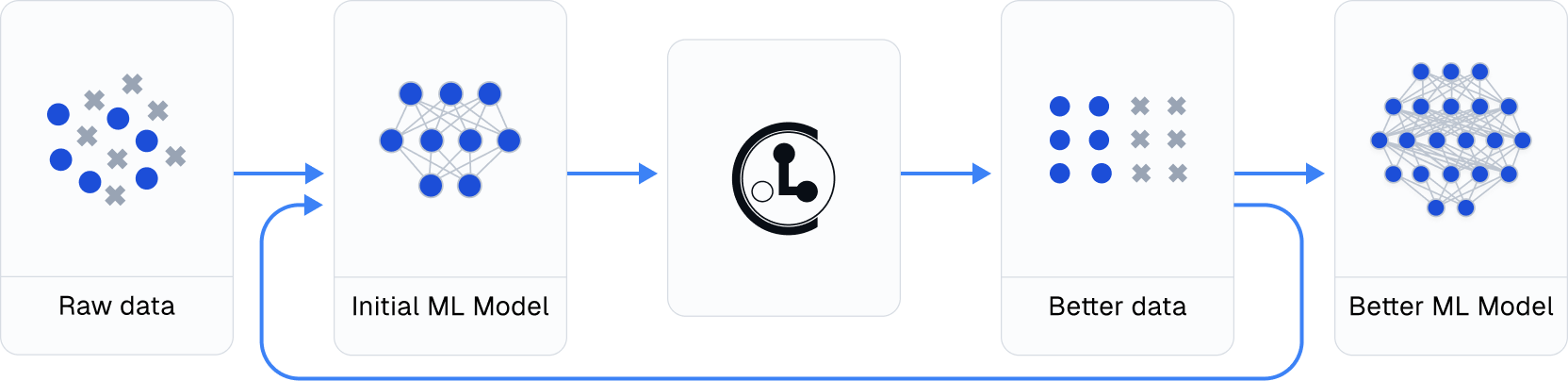
Practicing data-centric AI can look like this:
- Train initial ML model on original dataset.
- Utilize this model to diagnose data issues (via cleanlab methods) and improve the dataset.
- Train the same model on the improved dataset.
- Try various modeling techniques to further improve performance.
Most folks jump from Step 1 → 4, but you may achieve big gains without any change to your modeling code by using cleanlab! Continuously boost performance by iterating Steps 2 → 4 (and try to evaluate with cleaned data).
All features of cleanlab work with any dataset and any model. Yes, any model: PyTorch, Tensorflow, Keras, JAX, HuggingFace, OpenAI, XGBoost, scikit-learn, etc.
cleanlab is useful across a wide variety of Machine Learning tasks. Specific tasks this data-centric AI package offers dedicated functionality for include:
- Binary and multi-class classification
- Multi-label classification (e.g. image/document tagging)
- Token classification (e.g. entity recognition in text)
- Regression (predicting numerical column in a dataset)
- Image segmentation (images with per-pixel annotations)
- Object detection (images with bounding box annotations)
- Classification with data labeled by multiple annotators
- Active learning with multiple annotators (suggest which data to label or re-label to improve model most)
- Outlier detection (identify atypical data that appears out of distribution)
For other ML tasks, cleanlab can still help you improve your dataset if appropriately applied. See our Example Notebooks and Blog.
Beyond automatically catching all sorts of issues lurking in your data, this data-centric AI package helps you deal with noisy labels and train more robust ML models. Here's an example:
# cleanlab works with **any classifier**. Yup, you can use PyTorch/TensorFlow/OpenAI/XGBoost/etc.
cl = cleanlab.classification.CleanLearning(sklearn.YourFavoriteClassifier())
# cleanlab finds data and label issues in **any dataset**... in ONE line of code!
label_issues = cl.find_label_issues(data, labels)
# cleanlab trains a robust version of your model that works more reliably with noisy data.
cl.fit(data, labels)
# cleanlab estimates the predictions you would have gotten if you had trained with *no* label issues.
cl.predict(test_data)
# A universal data-centric AI tool, cleanlab quantifies class-level issues and overall data quality, for any dataset.
cleanlab.dataset.health_summary(labels, confident_joint=cl.confident_joint)cleanlab cleans your data's labels via state-of-the-art confident learning algorithms, published in this paper and blog. See some of the datasets cleaned with cleanlab at labelerrors.com.
cleanlab is:
- backed by theory -- with provable guarantees of exact label noise estimation, even with imperfect models.
- fast -- code is parallelized and scalable.
- easy to use -- one line of code to find mislabeled data, bad annotators, outliers, or train noise-robust models.
- general -- works with any dataset (text, image, tabular, audio,...) + any model (PyTorch, OpenAI, XGBoost,...)
Examples of incorrect given labels in various image datasets found and corrected using cleanlab. While these examples are from image datasets, this also works for text, audio, tabular data.
cleanlab is based on peer-reviewed research. Here are relevant papers to cite if you use this package:
Confident Learning (JAIR '21) (click to show bibtex)
@article{northcutt2021confidentlearning,
title={Confident Learning: Estimating Uncertainty in Dataset Labels},
author={Curtis G. Northcutt and Lu Jiang and Isaac L. Chuang},
journal={Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research (JAIR)},
volume={70},
pages={1373--1411},
year={2021}
}
Rank Pruning (UAI '17) (click to show bibtex)
@inproceedings{northcutt2017rankpruning,
author={Northcutt, Curtis G. and Wu, Tailin and Chuang, Isaac L.},
title={Learning with Confident Examples: Rank Pruning for Robust Classification with Noisy Labels},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Thirty-Third Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence},
series = {UAI'17},
year = {2017},
location = {Sydney, Australia},
numpages = {10},
url = {http://auai.org/uai2017/proceedings/papers/35.pdf},
publisher = {AUAI Press},
}
Label Quality Scoring (ICML '22) (click to show bibtex)
@inproceedings{kuan2022labelquality,
title={Model-agnostic label quality scoring to detect real-world label errors},
author={Kuan, Johnson and Mueller, Jonas},
booktitle={ICML DataPerf Workshop},
year={2022}
}
Out-of-Distribution Detection (ICML '22) (click to show bibtex)
@inproceedings{kuan2022ood,
title={Back to the Basics: Revisiting Out-of-Distribution Detection Baselines},
author={Kuan, Johnson and Mueller, Jonas},
booktitle={ICML Workshop on Principles of Distribution Shift},
year={2022}
}
Token Classification Label Errors (NeurIPS '22) (click to show bibtex)
@inproceedings{wang2022tokenerrors,
title={Detecting label errors in token classification data},
author={Wang, Wei-Chen and Mueller, Jonas},
booktitle={NeurIPS Workshop on Interactive Learning for Natural Language Processing (InterNLP)},
year={2022}
}
CROWDLAB for Data with Multiple Annotators (NeurIPS '22) (click to show bibtex)
@inproceedings{goh2022crowdlab,
title={CROWDLAB: Supervised learning to infer consensus labels and quality scores for data with multiple annotators},
author={Goh, Hui Wen and Tkachenko, Ulyana and Mueller, Jonas},
booktitle={NeurIPS Human in the Loop Learning Workshop},
year={2022}
}
ActiveLab: Active learning with data re-labeling (ICLR '23) (click to show bibtex)
@inproceedings{goh2023activelab,
title={ActiveLab: Active Learning with Re-Labeling by Multiple Annotators},
author={Goh, Hui Wen and Mueller, Jonas},
booktitle={ICLR Workshop on Trustworthy ML},
year={2023}
}
Incorrect Annotations in Multi-Label Classification (ICLR '23) (click to show bibtex)
@inproceedings{thyagarajan2023multilabel,
title={Identifying Incorrect Annotations in Multi-Label Classification Data},
author={Thyagarajan, Aditya and Snorrason, Elías and Northcutt, Curtis and Mueller, Jonas},
booktitle={ICLR Workshop on Trustworthy ML},
year={2023}
}
Detecting Dataset Drift and Non-IID Sampling (ICML '23) (click to show bibtex)
@inproceedings{cummings2023drift,
title={Detecting Dataset Drift and Non-IID Sampling via k-Nearest Neighbors},
author={Cummings, Jesse and Snorrason, Elías and Mueller, Jonas},
booktitle={ICML Workshop on Data-centric Machine Learning Research},
year={2023}
}
Detecting Errors in Numerical Data (ICML '23) (click to show bibtex)
@inproceedings{zhou2023errors,
title={Detecting Errors in Numerical Data via any Regression Model},
author={Zhou, Hang and Mueller, Jonas and Kumar, Mayank and Wang, Jane-Ling and Lei, Jing},
booktitle={ICML Workshop on Data-centric Machine Learning Research},
year={2023}
}
ObjectLab: Mislabeled Images in Object Detection Data (ICML '23) (click to show bibtex)
@inproceedings{tkachenko2023objectlab,
title={ObjectLab: Automated Diagnosis of Mislabeled Images in Object Detection Data},
author={Tkachenko, Ulyana and Thyagarajan, Aditya and Mueller, Jonas},
booktitle={ICML Workshop on Data-centric Machine Learning Research},
year={2023}
}
Label Errors in Segmentation Data (ICML '23) (click to show bibtex)
@inproceedings{lad2023segmentation,
title={Estimating label quality and errors in semantic segmentation data via any model},
author={Lad, Vedang and Mueller, Jonas},
booktitle={ICML Workshop on Data-centric Machine Learning Research},
year={2023}
}
To understand/cite other cleanlab functionality not described above, check out our additional publications.
-
Example Notebooks demonstrating practical applications of this package
-
NeurIPS 2021 paper: Pervasive Label Errors in Test Sets Destabilize Machine Learning Benchmarks
-
Learn, discuss, and shape the future of cleanlab in our 1000+ member Slack community.
-
Interested in contributing? See the contributing guide, development guide, and ideas on useful contributions. We welcome your help building a standard open-source platform for data-centric AI!
-
Have questions? Check out our FAQ, Github Issues, or Slack.
-
Need professional help with your Data/AI project? Email us: [email protected]
For instance, we can help you monitor incoming data and detect issues in real-time.
Copyright (c) 2017 Cleanlab Inc.
cleanlab is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU Affero General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
cleanlab is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
See GNU Affero General Public LICENSE for details. You can email us to discuss licensing: [email protected]
Commercial licensing is available for teams and enterprises that want to use cleanlab in production workflows, but are unable to open-source their code as is required by the current license. Please email us: [email protected]
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for cleanlab
Similar Open Source Tools

cleanlab
Cleanlab helps you **clean** data and **lab** els by automatically detecting issues in a ML dataset. To facilitate **machine learning with messy, real-world data** , this data-centric AI package uses your _existing_ models to estimate dataset problems that can be fixed to train even _better_ models.

sdialog
SDialog is an MIT-licensed open-source toolkit for building, simulating, and evaluating LLM-based conversational agents end-to-end. It aims to bridge agent construction, user simulation, dialog generation, and evaluation in a single reproducible workflow, enabling the generation of reliable, controllable dialog systems or data at scale. The toolkit standardizes a Dialog schema, offers persona-driven multi-agent simulation with LLMs, provides composable orchestration for precise control over behavior and flow, includes built-in evaluation metrics, and offers mechanistic interpretability. It allows for easy creation of user-defined components and interoperability across various AI platforms.
unify
The Unify Python Package provides access to the Unify REST API, allowing users to query Large Language Models (LLMs) from any Python 3.7.1+ application. It includes Synchronous and Asynchronous clients with Streaming responses support. Users can easily use any endpoint with a single key, route to the best endpoint for optimal throughput, cost, or latency, and customize prompts to interact with the models. The package also supports dynamic routing to automatically direct requests to the top-performing provider. Additionally, users can enable streaming responses and interact with the models asynchronously for handling multiple user requests simultaneously.

MInference
MInference is a tool designed to accelerate pre-filling for long-context Language Models (LLMs) by leveraging dynamic sparse attention. It achieves up to a 10x speedup for pre-filling on an A100 while maintaining accuracy. The tool supports various decoding LLMs, including LLaMA-style models and Phi models, and provides custom kernels for attention computation. MInference is useful for researchers and developers working with large-scale language models who aim to improve efficiency without compromising accuracy.
pytorch-forecasting
PyTorch Forecasting is a PyTorch-based package designed for state-of-the-art timeseries forecasting using deep learning architectures. It offers a high-level API and leverages PyTorch Lightning for efficient training on GPU or CPU with automatic logging. The package aims to simplify timeseries forecasting tasks by providing a flexible API for professionals and user-friendly defaults for beginners. It includes features such as a timeseries dataset class for handling data transformations, missing values, and subsampling, various neural network architectures optimized for real-world deployment, multi-horizon timeseries metrics, and hyperparameter tuning with optuna. Built on pytorch-lightning, it supports training on CPUs, single GPUs, and multiple GPUs out-of-the-box.
MathVerse
MathVerse is an all-around visual math benchmark designed to evaluate the capabilities of Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) in visual math problem-solving. It collects high-quality math problems with diagrams to assess how well MLLMs can understand visual diagrams for mathematical reasoning. The benchmark includes 2,612 problems transformed into six versions each, contributing to 15K test samples. It also introduces a Chain-of-Thought (CoT) Evaluation strategy for fine-grained assessment of output answers.
MathCoder
MathCoder is a repository focused on enhancing mathematical reasoning by fine-tuning open-source language models to use code for modeling and deriving math equations. It introduces MathCodeInstruct dataset with solutions interleaving natural language, code, and execution results. The repository provides MathCoder models capable of generating code-based solutions for challenging math problems, achieving state-of-the-art scores on MATH and GSM8K datasets. It offers tools for model deployment, inference, and evaluation, along with a citation for referencing the work.
mobius
Mobius is an AI infra platform including realtime computing and training. It is built on Ray, a distributed computing framework, and provides a number of features that make it well-suited for online machine learning tasks. These features include: * **Cross Language**: Mobius can run in multiple languages (only Python and Java are supported currently) with high efficiency. You can implement your operator in different languages and run them in one job. * **Single Node Failover**: Mobius has a special failover mechanism that only needs to rollback the failed node itself, in most cases, to recover the job. This is a huge benefit if your job is sensitive about failure recovery time. * **AutoScaling**: Mobius can generate a new graph with different configurations in runtime without stopping the job. * **Fusion Training**: Mobius can combine TensorFlow/Pytorch and streaming, then building an e2e online machine learning pipeline. Mobius is still under development, but it has already been used to power a number of real-world applications, including: * A real-time recommendation system for a major e-commerce company * A fraud detection system for a large financial institution * A personalized news feed for a major news organization If you are interested in using Mobius for your own online machine learning projects, you can find more information in the documentation.

rl
TorchRL is an open-source Reinforcement Learning (RL) library for PyTorch. It provides pytorch and **python-first** , low and high level abstractions for RL that are intended to be **efficient** , **modular** , **documented** and properly **tested**. The code is aimed at supporting research in RL. Most of it is written in python in a highly modular way, such that researchers can easily swap components, transform them or write new ones with little effort.
qa-mdt
This repository provides an implementation of QA-MDT, integrating state-of-the-art models for music generation. It offers a Quality-Aware Masked Diffusion Transformer for enhanced music generation. The code is based on various repositories like AudioLDM, PixArt-alpha, MDT, AudioMAE, and Open-Sora. The implementation allows for training and fine-tuning the model with different strategies and datasets. The repository also includes instructions for preparing datasets in LMDB format and provides a script for creating a toy LMDB dataset. The model can be used for music generation tasks, with a focus on quality injection to enhance the musicality of generated music.
crawl4ai
Crawl4AI is a powerful and free web crawling service that extracts valuable data from websites and provides LLM-friendly output formats. It supports crawling multiple URLs simultaneously, replaces media tags with ALT, and is completely free to use and open-source. Users can integrate Crawl4AI into Python projects as a library or run it as a standalone local server. The tool allows users to crawl and extract data from specified URLs using different providers and models, with options to include raw HTML content, force fresh crawls, and extract meaningful text blocks. Configuration settings can be adjusted in the `crawler/config.py` file to customize providers, API keys, chunk processing, and word thresholds. Contributions to Crawl4AI are welcome from the open-source community to enhance its value for AI enthusiasts and developers.
OpenMusic
OpenMusic is a repository providing an implementation of QA-MDT, a Quality-Aware Masked Diffusion Transformer for music generation. The code integrates state-of-the-art models and offers training strategies for music generation. The repository includes implementations of AudioLDM, PixArt-alpha, MDT, AudioMAE, and Open-Sora. Users can train or fine-tune the model using different strategies and datasets. The model is well-pretrained and can be used for music generation tasks. The repository also includes instructions for preparing datasets, training the model, and performing inference. Contact information is provided for any questions or suggestions regarding the project.
Eco2AI
Eco2AI is a python library for CO2 emission tracking that monitors energy consumption of CPU & GPU devices and estimates equivalent carbon emissions based on regional emission coefficients. Users can easily integrate Eco2AI into their Python scripts by adding a few lines of code. The library records emissions data and device information in a local file, providing detailed session logs with project names, experiment descriptions, start times, durations, power consumption, CO2 emissions, CPU and GPU names, operating systems, and countries.

catalyst
Catalyst is a C# Natural Language Processing library designed for speed, inspired by spaCy's design. It provides pre-trained models, support for training word and document embeddings, and flexible entity recognition models. The library is fast, modern, and pure-C#, supporting .NET standard 2.0. It is cross-platform, running on Windows, Linux, macOS, and ARM. Catalyst offers non-destructive tokenization, named entity recognition, part-of-speech tagging, language detection, and efficient binary serialization. It includes pre-built models for language packages and lemmatization. Users can store and load models using streams. Getting started with Catalyst involves installing its NuGet Package and setting the storage to use the online repository. The library supports lazy loading of models from disk or online. Users can take advantage of C# lazy evaluation and native multi-threading support to process documents in parallel. Training a new FastText word2vec embedding model is straightforward, and Catalyst also provides algorithms for fast embedding search and dimensionality reduction.
Adaptive-MT-LLM-Fine-tuning
The repository Adaptive-MT-LLM-Fine-tuning contains code and data for the paper 'Fine-tuning Large Language Models for Adaptive Machine Translation'. It focuses on enhancing Mistral 7B, a large language model, for real-time adaptive machine translation in the medical domain. The fine-tuning process involves using zero-shot and one-shot translation prompts to improve terminology and style adherence. The repository includes training and test data, data processing code, fuzzy match retrieval techniques, fine-tuning methods, conversion to CTranslate2 format, tokenizers, translation codes, and evaluation metrics.
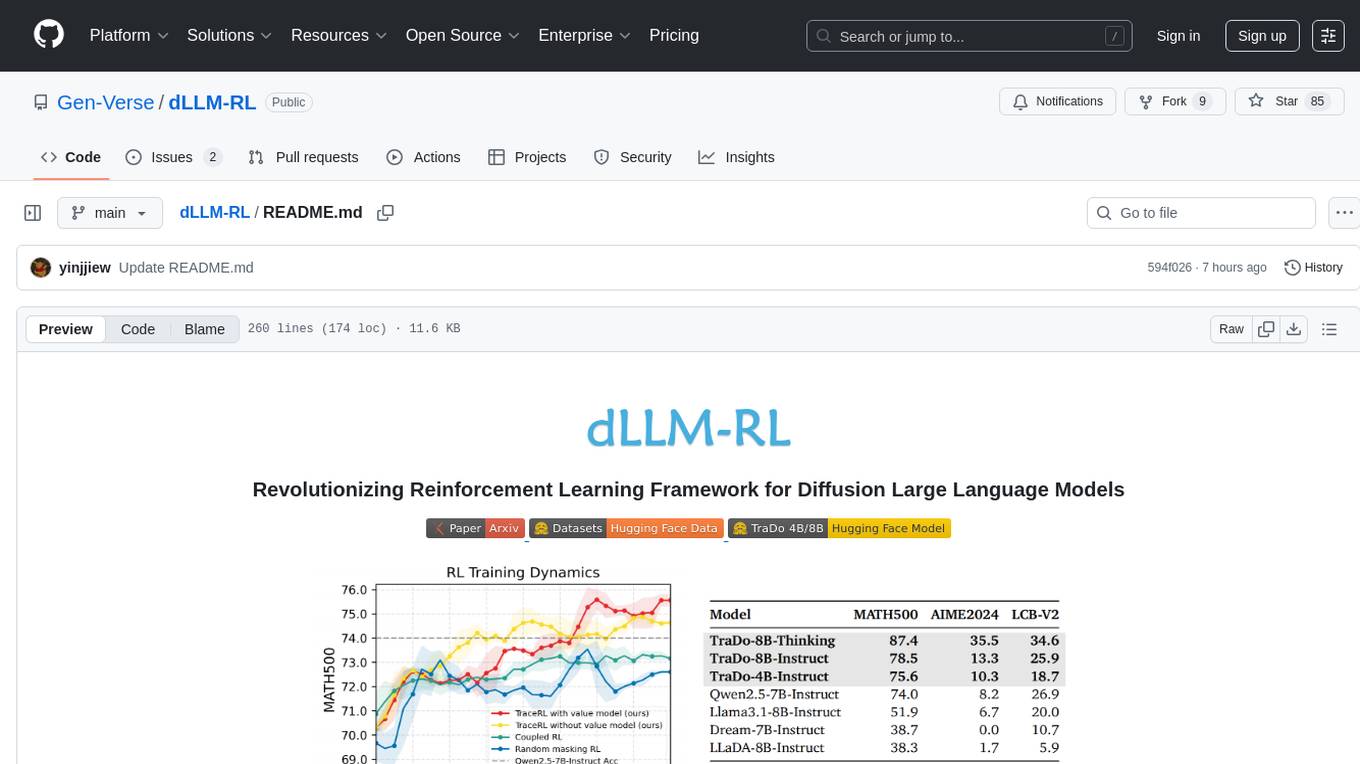
dLLM-RL
dLLM-RL is a revolutionary reinforcement learning framework designed for Diffusion Large Language Models. It supports various models with diverse structures, offers inference acceleration, RL training capabilities, and SFT functionalities. The tool introduces TraceRL for trajectory-aware RL and diffusion-based value models for optimization stability. Users can download and try models like TraDo-4B-Instruct and TraDo-8B-Instruct. The tool also provides support for multi-node setups and easy building of reinforcement learning methods. Additionally, it offers supervised fine-tuning strategies for different models and tasks.
For similar tasks

cleanlab
Cleanlab helps you **clean** data and **lab** els by automatically detecting issues in a ML dataset. To facilitate **machine learning with messy, real-world data** , this data-centric AI package uses your _existing_ models to estimate dataset problems that can be fixed to train even _better_ models.
For similar jobs

lollms-webui
LoLLMs WebUI (Lord of Large Language Multimodal Systems: One tool to rule them all) is a user-friendly interface to access and utilize various LLM (Large Language Models) and other AI models for a wide range of tasks. With over 500 AI expert conditionings across diverse domains and more than 2500 fine tuned models over multiple domains, LoLLMs WebUI provides an immediate resource for any problem, from car repair to coding assistance, legal matters, medical diagnosis, entertainment, and more. The easy-to-use UI with light and dark mode options, integration with GitHub repository, support for different personalities, and features like thumb up/down rating, copy, edit, and remove messages, local database storage, search, export, and delete multiple discussions, make LoLLMs WebUI a powerful and versatile tool.

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.

minio
MinIO is a High Performance Object Storage released under GNU Affero General Public License v3.0. It is API compatible with Amazon S3 cloud storage service. Use MinIO to build high performance infrastructure for machine learning, analytics and application data workloads.

mage-ai
Mage is an open-source data pipeline tool for transforming and integrating data. It offers an easy developer experience, engineering best practices built-in, and data as a first-class citizen. Mage makes it easy to build, preview, and launch data pipelines, and provides observability and scaling capabilities. It supports data integrations, streaming pipelines, and dbt integration.

AiTreasureBox
AiTreasureBox is a versatile AI tool that provides a collection of pre-trained models and algorithms for various machine learning tasks. It simplifies the process of implementing AI solutions by offering ready-to-use components that can be easily integrated into projects. With AiTreasureBox, users can quickly prototype and deploy AI applications without the need for extensive knowledge in machine learning or deep learning. The tool covers a wide range of tasks such as image classification, text generation, sentiment analysis, object detection, and more. It is designed to be user-friendly and accessible to both beginners and experienced developers, making AI development more efficient and accessible to a wider audience.

tidb
TiDB is an open-source distributed SQL database that supports Hybrid Transactional and Analytical Processing (HTAP) workloads. It is MySQL compatible and features horizontal scalability, strong consistency, and high availability.

airbyte
Airbyte is an open-source data integration platform that makes it easy to move data from any source to any destination. With Airbyte, you can build and manage data pipelines without writing any code. Airbyte provides a library of pre-built connectors that make it easy to connect to popular data sources and destinations. You can also create your own connectors using Airbyte's no-code Connector Builder or low-code CDK. Airbyte is used by data engineers and analysts at companies of all sizes to build and manage their data pipelines.

labelbox-python
Labelbox is a data-centric AI platform for enterprises to develop, optimize, and use AI to solve problems and power new products and services. Enterprises use Labelbox to curate data, generate high-quality human feedback data for computer vision and LLMs, evaluate model performance, and automate tasks by combining AI and human-centric workflows. The academic & research community uses Labelbox for cutting-edge AI research.