
LLM-and-Law
This repository is dedicated to summarizing papers related to large language models with the field of law
Stars: 180
This repository is dedicated to summarizing papers related to large language models with the field of law. It includes applications of large language models in legal tasks, legal agents, legal problems of large language models, data resources for large language models in law, law LLMs, and evaluation of large language models in the legal domain.
README:
This repository is dedicated to summarizing papers related to large language models with the field of law
[1] Legal Prompt Engineering for Multilingual Legal Judgement Prediction
[2] Can GPT-3 Perform Statutory Reasoning?
[3] Legal Prompting: Teaching a Language Model to Think Like a Lawyer
[4] Large Language Models as Fiduciaries: A Case Study Toward Robustly Communicating With Artificial Intelligence Through Legal Standards
[5] ChatGPT Goes to Law School
[6] ChatGPT, Professor of Law
[7] ChatGPT & Generative AI Systems as Quasi-Expert Legal Advice Lawyers - Case Study Considering Potential Appeal Against Conviction of Tom Hayes
[8] ‘Words Are Flowing Out Like Endless Rain Into a Paper Cup’: ChatGPT & Law School Assessments
[9] ChatGPT by OpenAI: The End of Litigation Lawyers?
[10] Law Informs Code: A Legal Informatics Approach to Aligning Artificial Intelligence with Humans
[11] ChatGPT may Pass the Bar Exam soon, but has a Long Way to Go for the LexGLUE benchmark paper
[12] How Ready are Pre-trained Abstractive Models and LLMs for Legal Case Judgement Summarization? paper
[13] Explaining Legal Concepts with Augmented Large Language Models (GPT-4) paper
[14] Garbage in, garbage out: Zero-shot detection of crime using Large Language Models paper
[15] Legal Summarisation through LLMs: The PRODIGIT Project paper
[16] Black-Box Analysis: GPTs Across Time in Legal Textual Entailment Task paper
[17] PolicyGPT: Automated Analysis of Privacy Policies with Large Language Models
[18] Reformulating Domain Adaptation of Large Language Models as Adapt-Retrieve-Revise paper
[19] Precedent-Enhanced Legal Judgment Prediction with LLM and Domain-Model Collaboration paper
[20] From Text to Structure: Using Large Language Models to Support the Development of Legal Expert Systems paper
[21] Boosting legal case retrieval by query content selection with large language models paper
[22] LLMediator: GPT-4 Assisted Online Dispute Resolution paper
[23] Employing Label Models on ChatGPT Answers Improves Legal Text Entailment Performance paper
[24] LLaMandement: Large Language Models for Summarization of French Legislative Proposals paper
[25] Logic Rules as Explanations for Legal Case Retrieval paper Our new paper, welcome to pay attention !!!
[26] Enhancing Legal Document Retrieval: A Multi-Phase Approach with Large Language Models paper
[27] BLADE: Enhancing Black-box Large Language Models with Small Domain-Specific Models paper
[28] A Survey on Large Language Models for Critical Societal Domains: Finance, Healthcare, and Law paper
[29] Archimedes-AUEB at SemEval-2024 Task 5: LLM explains Civil Procedure paper
[30] More Than Catastrophic Forgetting: Integrating General Capabilities For Domain-Specific LLMs paper
[31] Legal Documents Drafting with Fine-Tuned Pre-Trained Large Language Model paper
[32] Knowledge-Infused Legal Wisdom: Navigating LLM Consultation through the Lens of Diagnostics and Positive-Unlabeled Reinforcement Learning paper
[33] GOLDCOIN: Grounding Large Language Models in Privacy Laws via Contextual Integrity Theory paper
[34] Enabling Discriminative Reasoning in Large Language Models for Legal Judgment Prediction paper
[35] Large Language Models for Judicial Entity Extraction: A Comparative Study paper
[36] Applicability of Large Language Models and Generative Models for Legal Case Judgement Summarization paper
[37] LawLLM: Law Large Language Model for the US Legal System paper
[38] Legal syllogism prompting: Teaching large language models for legal judgment prediction paper
[39] Optimizing Numerical Estimation and Operational Efficiency in the Legal Domain through Large Language Models paper
[40] Hallucination-Free? Assessing the Reliability of Leading AI Legal Research Tools paper
[41] KRAG Framework for Enhancing LLMs in the Legal Domain paper
[42] Legal Evalutions and Challenges of Large Language Models paper
[43] Analyzing Images of Legal Documents: Toward Multi-Modal LLMs for Access to Justice paper
[44] Automating Legal Concept Interpretation with LLMs: Retrieval, Generation, and Evaluation paper
[45] Domaino1s: Guiding LLM Reasoning for Explainable Answers in High-Stakes Domains paper
[46] RELexED: Retrieval-Enhanced Legal Summarization with Exemplar Diversity paper
[1] SimuCourt: Building Judicial Decision-Making Agents with Real-world Judgement Documents paper
[2] Can Large Language Models Grasp Legal Theories? Enhance Legal Reasoning with Insights from Multi-Agent Collaboration paper
[1] Towards WinoQueer: Developing a Benchmark for Anti-Queer Bias in Large Language Models
[2] Persistent Anti-Muslim Bias in Large Language Models
[3] Understanding the Capabilities, Limitations, and Societal Impact of Large Language Models
[4] The Dark Side of ChatGPT: Legal and Ethical Challenges from Stochastic Parrots and Hallucination
[5] The GPTJudge: Justice in a Generative AI World paper
[6] Is the U.S. Legal System Ready for AI's Challenges to Human Values? paper
[7] Questioning Biases in Case Judgment Summaries: Legal Datasets or Large Language Models? paper
[8] Large Legal Fictions: Profiling Legal Hallucinations in Large Language Models
[9] A Legal Framework for Natural Language Processing Model Training in Portugal paper
[10] LegalBench-RAG: A Benchmark for Retrieval-Augmented Generation in the Legal Domain paper
[11] Bias in Large Language Models: Origin, Evaluation, and Mitigation paper
[12] An Information Theoretic Approach to Operationalize Right to Data Protection paper
[13] Protecting Privacy in Multimodal Large Language Models with MLLMU-Bench paper
[1] CAIL2018: A Large-Scale Legal Dataset for Judgment Prediction
[2] When does pretraining help? assessing self-supervised learning for law and the casehold dataset of 53,000+ legal holdings
[3] LeCaRD: a legal case retrieval dataset for Chinese law system
[4] LeXFiles and LegalLAMA: Facilitating English Multinational Legal Language Model Development
[5] Legal Extractive Summarization of U.S. Court Opinions
[6] Awesome Chinese Legal Resources github
[7] MultiLegalPile: A 689GB Multilingual Legal Corpus paper
[8] The Cambridge Law Corpus: A Corpus for Legal AI Research
[9] TransformLLM: Adapting Large Language Models via LLM-Transformed Reading Comprehension Text paper
[10] Natural Language Processing for the Legal Domain: A Survey of Tasks, Datasets, Models, and Challenges paper
[11] ChineseSafe: A Chinese Benchmark for Evaluating Safety in Large Language Models paper
[12] Augmenting Legal Decision Support Systems with LLM-based NLI for Analyzing Social Media Evidence paper
[13] CaseSumm: A Large-Scale Dataset for Long-Context Summarization from U.S. Supreme Court Opinions paper
[1] LawGPT_zh github
[2] LaWGPT github
[3] Lawyer LLaMA github
[4] LexiLaw github
[5] LexGPT 0.1: pre-trained GPT-J models with Pile of Law paper
[6] TOWARDS THE EXPLOITATION OF LLM-BASED CHATBOT FOR PROVIDING LEGAL SUPPORT TO PALESTINIAN COOPERATIVES paper
[7] ChatLaw: Open-Source Legal Large Language Model with Integrated External Knowledge Bases paper
[8] DISC-LawLLM github
[9] InternLM-Law: An Open Source Chinese Legal Large Language Model paper
[10] SaulLM-54B & SaulLM-141B: Scaling Up Domain Adaptation for the Legal Domain paper
[1] Measuring Massive Multitask Chinese Understanding paper
[2] LawBench: Benchmarking Legal Knowledge of Large Language Models github
[3] Large Language Models are legal but they are not: Making the case for a powerful LegalLLM paper
[4] Better Call GPT, Comparing Large Language Models Against Lawyers paper
[5] Evaluating GPT-3.5's Awareness and Summarization Abilities for European Constitutional Texts with Shared Topics paper
[6] Evaluation Ethics of LLMs in Legal Domain paper
[7] GPTs and Language Barrier: A Cross-Lingual Legal QA Examination paper
[8] LawBench: Benchmarking Legal Knowledge of Large Language Models paper
[9] LexEval: A Comprehensive Chinese Legal Benchmark for Evaluating Large Language Models paper
[10] LegalAgentBench: Evaluating LLM Agents in Legal Domain paper
The survey paper is shown in paper
Please cite the following papers as the references if you use our codes or the processed datasets.
@article{sun2023short,
title={A short survey of viewing large language models in legal aspect},
author={Sun, Zhongxiang},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.09136},
year={2023}
}For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for LLM-and-Law
Similar Open Source Tools

LLM-and-Law
This repository is dedicated to summarizing papers related to large language models with the field of law. It includes applications of large language models in legal tasks, legal agents, legal problems of large language models, data resources for large language models in law, law LLMs, and evaluation of large language models in the legal domain.
Awesome-LLM-Survey
This repository, Awesome-LLM-Survey, serves as a comprehensive collection of surveys related to Large Language Models (LLM). It covers various aspects of LLM, including instruction tuning, human alignment, LLM agents, hallucination, multi-modal capabilities, and more. Researchers are encouraged to contribute by updating information on their papers to benefit the LLM survey community.
Recommendation-Systems-without-Explicit-ID-Features-A-Literature-Review
This repository is a collection of papers and resources related to recommendation systems, focusing on foundation models, transferable recommender systems, large language models, and multimodal recommender systems. It explores questions such as the necessity of ID embeddings, the shift from matching to generating paradigms, and the future of multimodal recommender systems. The papers cover various aspects of recommendation systems, including pretraining, user representation, dataset benchmarks, and evaluation methods. The repository aims to provide insights and advancements in the field of recommendation systems through literature reviews, surveys, and empirical studies.
ChatLaw
ChatLaw is an open-source legal large language model tailored for Chinese legal scenarios. It aims to combine LLM and knowledge bases to provide solutions for legal scenarios. The models include ChatLaw-13B and ChatLaw-33B, trained on various legal texts to construct dialogue data. The project focuses on improving logical reasoning abilities and plans to train models with parameters exceeding 30B for better performance. The dataset consists of forum posts, news, legal texts, judicial interpretations, legal consultations, exam questions, and court judgments, cleaned and enhanced to create dialogue data. The tool is designed to assist in legal tasks requiring complex logical reasoning, with a focus on accuracy and reliability.
Awesome-LLM-in-Social-Science
This repository compiles a list of academic papers that evaluate, align, simulate, and provide surveys or perspectives on the use of Large Language Models (LLMs) in the field of Social Science. The papers cover various aspects of LLM research, including assessing their alignment with human values, evaluating their capabilities in tasks such as opinion formation and moral reasoning, and exploring their potential for simulating social interactions and addressing issues in diverse fields of Social Science. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive resource for researchers and practitioners interested in the intersection of LLMs and Social Science.
Awesome-LLM4RS-Papers
This paper list is about Large Language Model-enhanced Recommender System. It also contains some related works. Keywords: recommendation system, large language models
hallucination-index
LLM Hallucination Index - RAG Special is a comprehensive evaluation of large language models (LLMs) focusing on context length and open vs. closed-source attributes. The index explores the impact of context length on model performance and tests the assumption that closed-source LLMs outperform open-source ones. It also investigates the effectiveness of prompting techniques like Chain-of-Note across different context lengths. The evaluation includes 22 models from various brands, analyzing major trends and declaring overall winners based on short, medium, and long context insights. Methodologies involve rigorous testing with different context lengths and prompting techniques to assess models' abilities in handling extensive texts and detecting hallucinations.

LMOps
LMOps is a research initiative focusing on fundamental research and technology for building AI products with foundation models, particularly enabling AI capabilities with Large Language Models (LLMs) and Generative AI models. The project explores various aspects such as prompt optimization, longer context handling, LLM alignment, acceleration of LLMs, LLM customization, and understanding in-context learning. It also includes tools like Promptist for automatic prompt optimization, Structured Prompting for efficient long-sequence prompts consumption, and X-Prompt for extensible prompts beyond natural language. Additionally, LLMA accelerators are developed to speed up LLM inference by referencing and copying text spans from documents. The project aims to advance technologies that facilitate prompting language models and enhance the performance of LLMs in various scenarios.
LLM_MultiAgents_Survey_Papers
This repository maintains a list of research papers on LLM-based Multi-Agents, categorized into five main streams: Multi-Agents Framework, Multi-Agents Orchestration and Efficiency, Multi-Agents for Problem Solving, Multi-Agents for World Simulation, and Multi-Agents Datasets and Benchmarks. The repository also includes a survey paper on LLM-based Multi-Agents and a table summarizing the key findings of the survey.
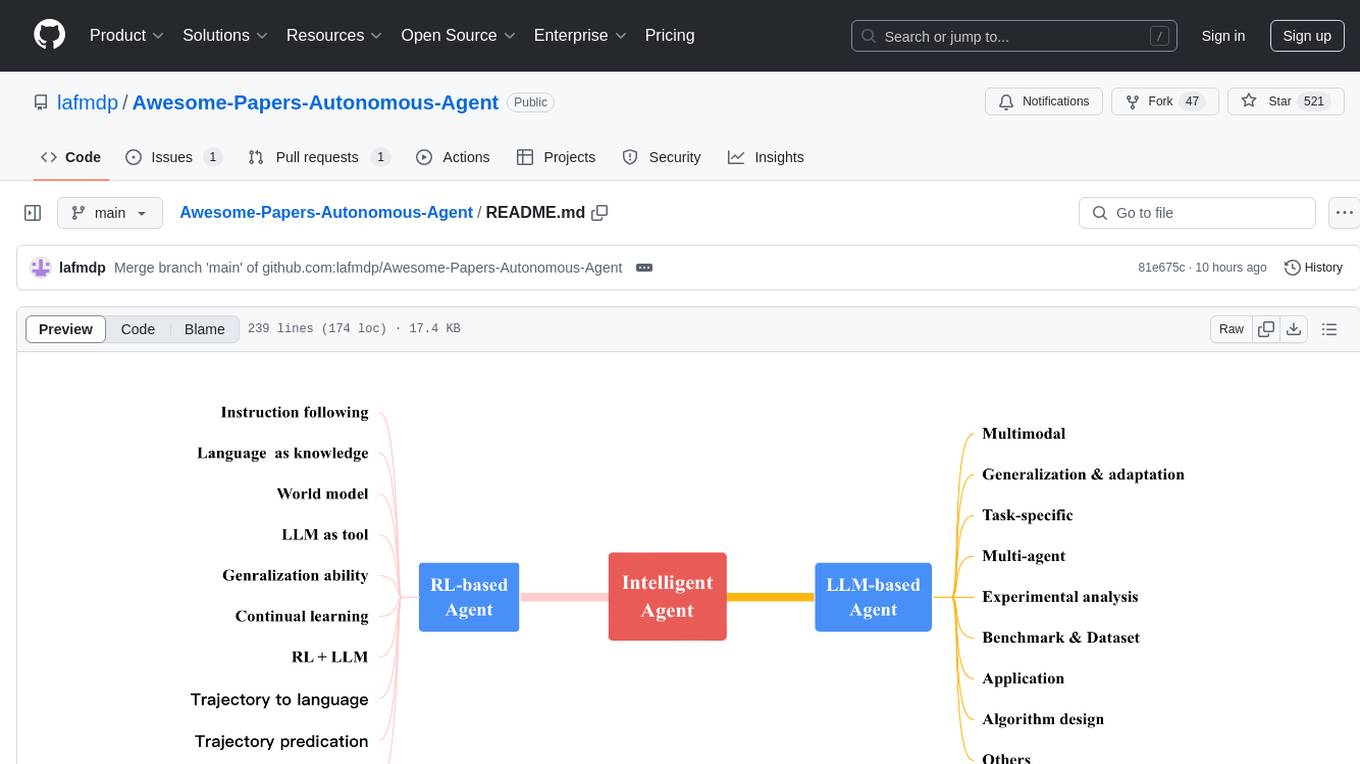
Awesome-Papers-Autonomous-Agent
Awesome-Papers-Autonomous-Agent is a curated collection of recent papers focusing on autonomous agents, specifically interested in RL-based agents and LLM-based agents. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive resource for researchers and practitioners interested in intelligent agents that can achieve goals, acquire knowledge, and continually improve. The collection includes papers on various topics such as instruction following, building agents based on world models, using language as knowledge, leveraging LLMs as a tool, generalization across tasks, continual learning, combining RL and LLM, transformer-based policies, trajectory to language, trajectory prediction, multimodal agents, training LLMs for generalization and adaptation, task-specific designing, multi-agent systems, experimental analysis, benchmarking, applications, algorithm design, and combining with RL.

awesome-generative-ai-guide
This repository serves as a comprehensive hub for updates on generative AI research, interview materials, notebooks, and more. It includes monthly best GenAI papers list, interview resources, free courses, and code repositories/notebooks for developing generative AI applications. The repository is regularly updated with the latest additions to keep users informed and engaged in the field of generative AI.
babilong
BABILong is a generative benchmark designed to evaluate the performance of NLP models in processing long documents with distributed facts. It consists of 20 tasks that simulate interactions between characters and objects in various locations, requiring models to distinguish important information from irrelevant details. The tasks vary in complexity and reasoning aspects, with test samples potentially containing millions of tokens. The benchmark aims to challenge and assess the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) in handling complex, long-context information.
do-not-answer
Do-Not-Answer is an open-source dataset curated to evaluate Large Language Models' safety mechanisms at a low cost. It consists of prompts to which responsible language models do not answer. The dataset includes human annotations and model-based evaluation using a fine-tuned BERT-like evaluator. The dataset covers 61 specific harms and collects 939 instructions across five risk areas and 12 harm types. Response assessment is done for six models, categorizing responses into harmfulness and action categories. Both human and automatic evaluations show the safety of models across different risk areas. The dataset also includes a Chinese version with 1,014 questions for evaluating Chinese LLMs' risk perception and sensitivity to specific words and phrases.
Next-Generation-LLM-based-Recommender-Systems-Survey
The Next-Generation LLM-based Recommender Systems Survey is a comprehensive overview of the latest advancements in recommender systems leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs). The survey covers various paradigms, approaches, and applications of LLMs in recommendation tasks, including generative and non-generative models, multimodal recommendations, personalized explanations, and industrial deployment. It discusses the comparison with existing surveys, different paradigms, and specific works in the field. The survey also addresses challenges and future directions in the domain of LLM-based recommender systems.
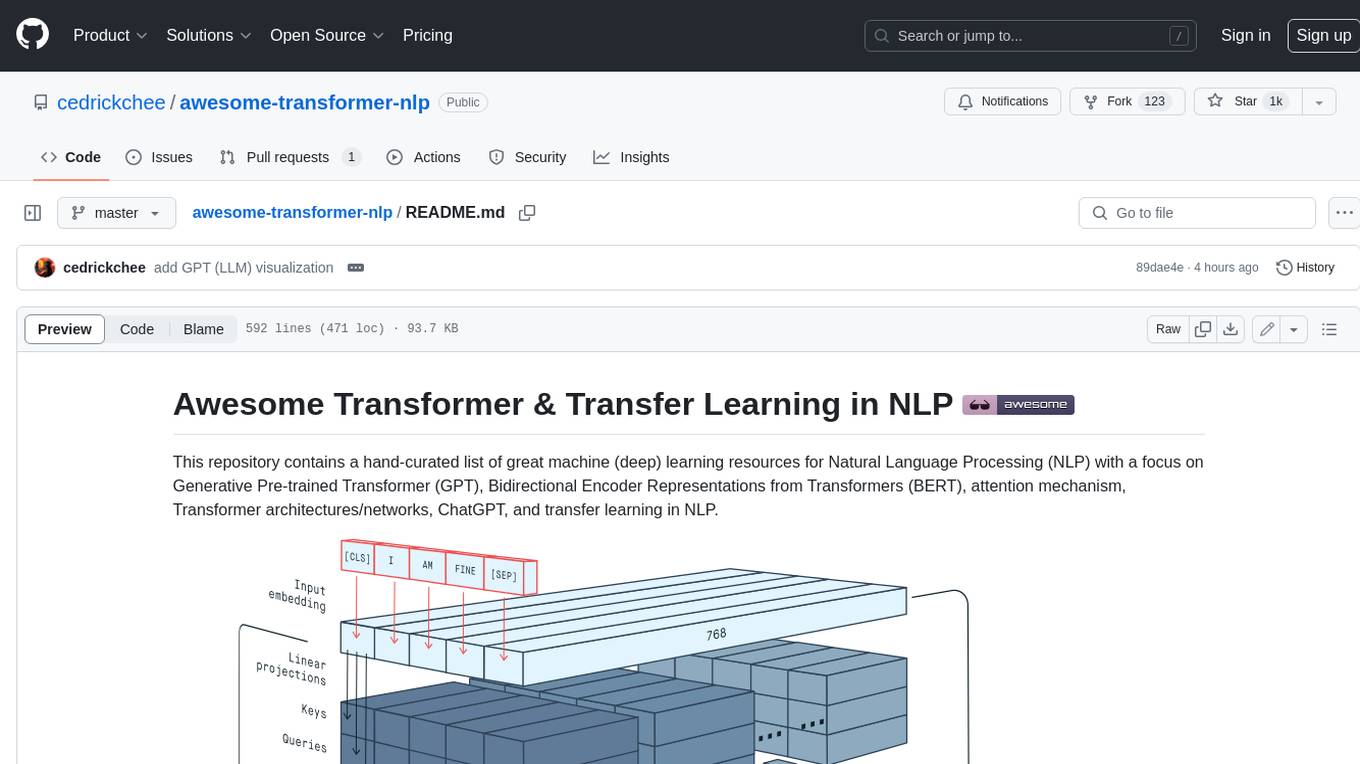
awesome-transformer-nlp
This repository contains a hand-curated list of great machine (deep) learning resources for Natural Language Processing (NLP) with a focus on Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT), Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT), attention mechanism, Transformer architectures/networks, Chatbot, and transfer learning in NLP.
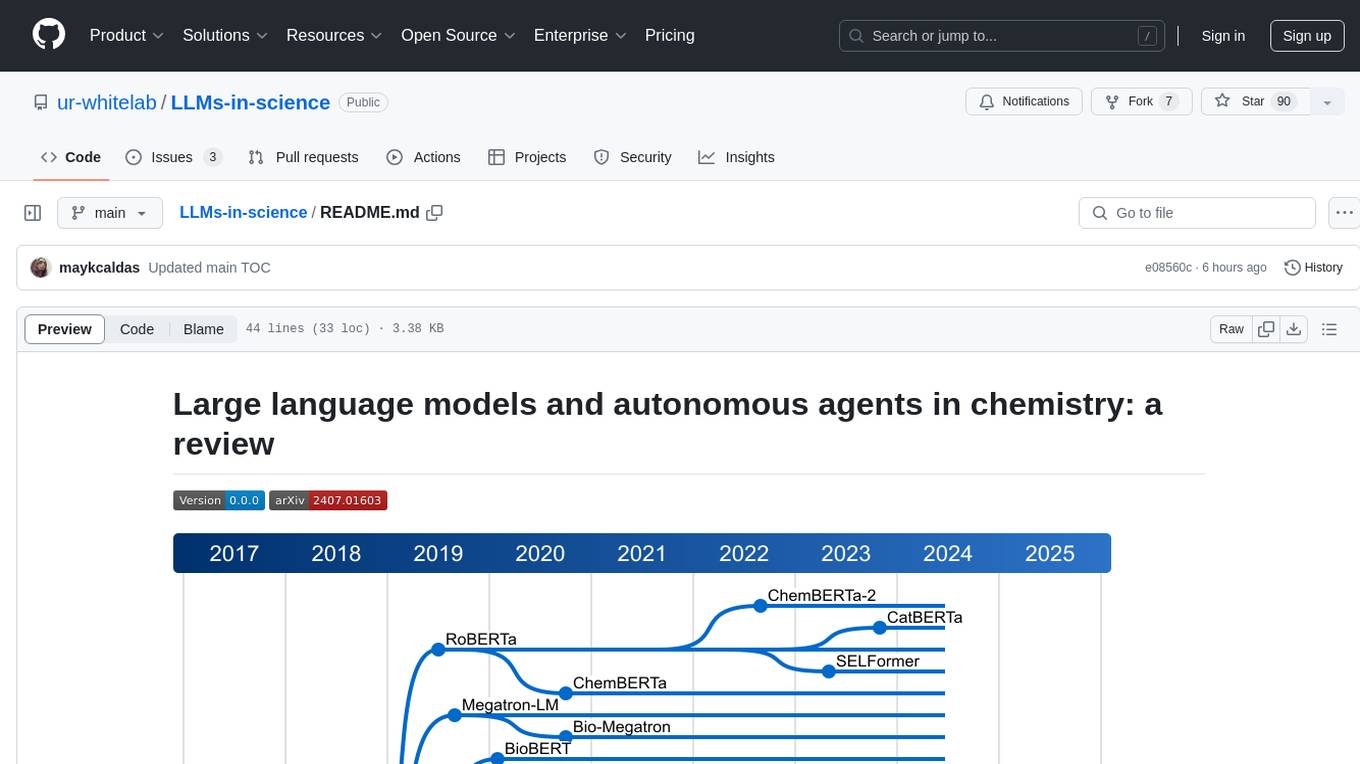
LLMs-in-science
The 'LLMs-in-science' repository is a collaborative environment for organizing papers related to large language models (LLMs) and autonomous agents in the field of chemistry. The goal is to discuss trend topics, challenges, and the potential for supporting scientific discovery in the context of artificial intelligence. The repository aims to maintain a systematic structure of the field and welcomes contributions from the community to keep the content up-to-date and relevant.
For similar tasks

LLM-and-Law
This repository is dedicated to summarizing papers related to large language models with the field of law. It includes applications of large language models in legal tasks, legal agents, legal problems of large language models, data resources for large language models in law, law LLMs, and evaluation of large language models in the legal domain.
For similar jobs

LLM-and-Law
This repository is dedicated to summarizing papers related to large language models with the field of law. It includes applications of large language models in legal tasks, legal agents, legal problems of large language models, data resources for large language models in law, law LLMs, and evaluation of large language models in the legal domain.
start-llms
This repository is a comprehensive guide for individuals looking to start and improve their skills in Large Language Models (LLMs) without an advanced background in the field. It provides free resources, online courses, books, articles, and practical tips to become an expert in machine learning. The guide covers topics such as terminology, transformers, prompting, retrieval augmented generation (RAG), and more. It also includes recommendations for podcasts, YouTube videos, and communities to stay updated with the latest news in AI and LLMs.
aiverify
AI Verify is an AI governance testing framework and software toolkit that validates the performance of AI systems against internationally recognised principles through standardised tests. It offers a new API Connector feature to bypass size limitations, test various AI frameworks, and configure connection settings for batch requests. The toolkit operates within an enterprise environment, conducting technical tests on common supervised learning models for tabular and image datasets. It does not define AI ethical standards or guarantee complete safety from risks or biases.
Awesome-LLM-Watermark
This repository contains a collection of research papers related to watermarking techniques for text and images, specifically focusing on large language models (LLMs). The papers cover various aspects of watermarking LLM-generated content, including robustness, statistical understanding, topic-based watermarks, quality-detection trade-offs, dual watermarks, watermark collision, and more. Researchers have explored different methods and frameworks for watermarking LLMs to protect intellectual property, detect machine-generated text, improve generation quality, and evaluate watermarking techniques. The repository serves as a valuable resource for those interested in the field of watermarking for LLMs.
LLM-LieDetector
This repository contains code for reproducing experiments on lie detection in black-box LLMs by asking unrelated questions. It includes Q/A datasets, prompts, and fine-tuning datasets for generating lies with language models. The lie detectors rely on asking binary 'elicitation questions' to diagnose whether the model has lied. The code covers generating lies from language models, training and testing lie detectors, and generalization experiments. It requires access to GPUs and OpenAI API calls for running experiments with open-source models. Results are stored in the repository for reproducibility.
graphrag
The GraphRAG project is a data pipeline and transformation suite designed to extract meaningful, structured data from unstructured text using LLMs. It enhances LLMs' ability to reason about private data. The repository provides guidance on using knowledge graph memory structures to enhance LLM outputs, with a warning about the potential costs of GraphRAG indexing. It offers contribution guidelines, development resources, and encourages prompt tuning for optimal results. The Responsible AI FAQ addresses GraphRAG's capabilities, intended uses, evaluation metrics, limitations, and operational factors for effective and responsible use.

langtest
LangTest is a comprehensive evaluation library for custom LLM and NLP models. It aims to deliver safe and effective language models by providing tools to test model quality, augment training data, and support popular NLP frameworks. LangTest comes with benchmark datasets to challenge and enhance language models, ensuring peak performance in various linguistic tasks. The tool offers more than 60 distinct types of tests with just one line of code, covering aspects like robustness, bias, representation, fairness, and accuracy. It supports testing LLMS for question answering, toxicity, clinical tests, legal support, factuality, sycophancy, and summarization.
Awesome-Jailbreak-on-LLMs
Awesome-Jailbreak-on-LLMs is a collection of state-of-the-art, novel, and exciting jailbreak methods on Large Language Models (LLMs). The repository contains papers, codes, datasets, evaluations, and analyses related to jailbreak attacks on LLMs. It serves as a comprehensive resource for researchers and practitioners interested in exploring various jailbreak techniques and defenses in the context of LLMs. Contributions such as additional jailbreak-related content, pull requests, and issue reports are welcome, and contributors are acknowledged. For any inquiries or issues, contact [email protected]. If you find this repository useful for your research or work, consider starring it to show appreciation.


