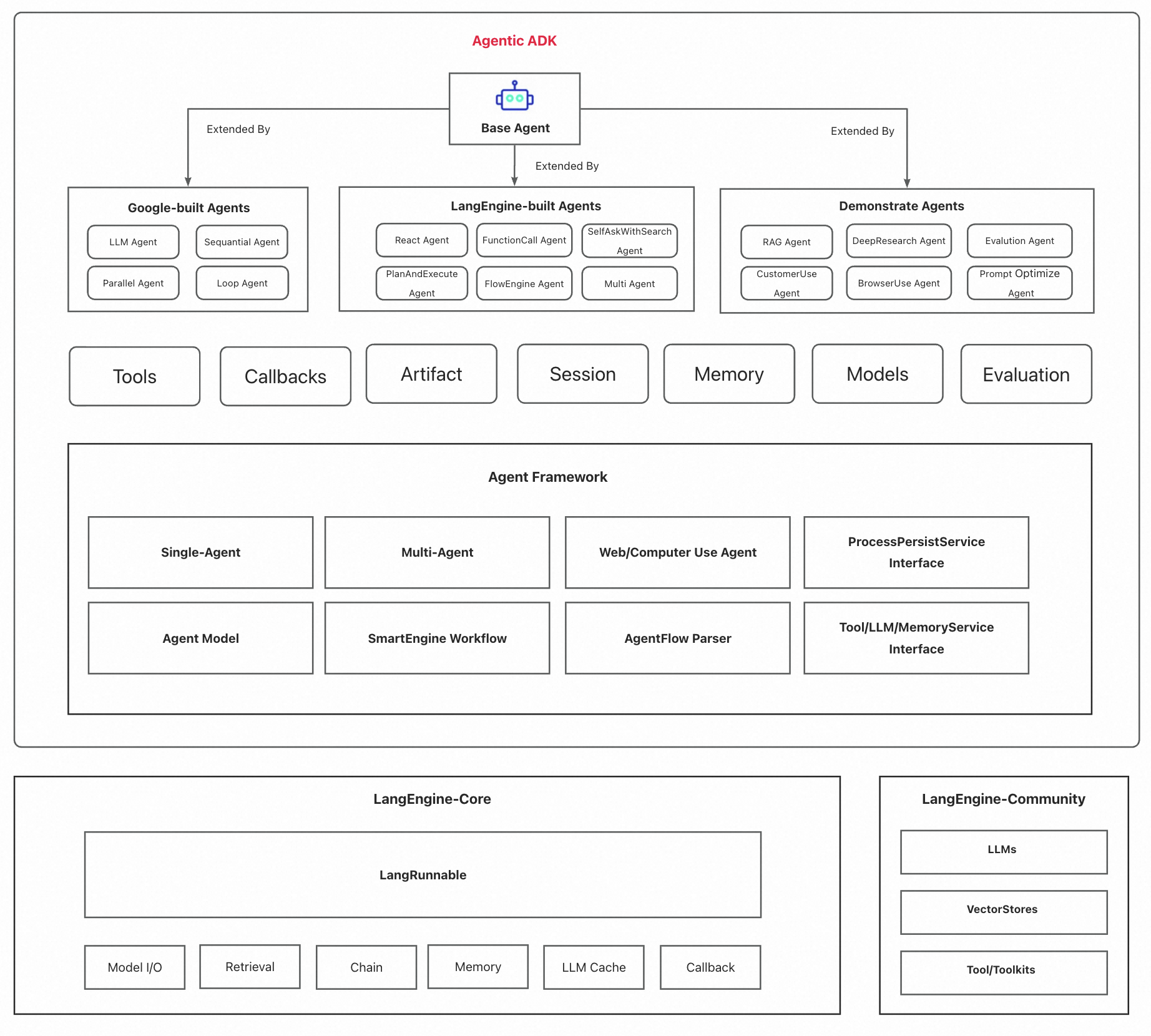
Agentic-ADK
Agentic ADK is an Agent application development framework launched by Alibaba International AI Business, based on Google-ADK and Ali-LangEngine.
Stars: 508
Agentic ADK is an Agent application development framework launched by Alibaba International AI Business, based on Google-ADK and Ali-LangEngine. It is used for developing, constructing, evaluating, and deploying powerful, flexible, and controllable complex AI Agents. ADK aims to make Agent development simpler and more user-friendly, enabling developers to more easily build, deploy, and orchestrate various Agent applications ranging from simple tasks to complex collaborations.
README:
Agentic ADK is an Agent application development framework launched by Alibaba International AI Business, based on Google-ADK and Ali-LangEngine.
Agentic ADK is an Agent application development framework launched by Alibaba International AI Business, based on Google-ADK and Ali-LangEngine. It is used for developing, constructing, evaluating, and deploying powerful, flexible, and controllable complex AI Agents. ADK aims to make Agent development simpler and more user-friendly, enabling developers to more easily build, deploy, and orchestrate various Agent applications ranging from simple tasks to complex collaborations.
Features Overview
- Based on the Google ADK interface, it strengthens core execution pathways such as streaming interaction and visualization debugging tools, enabling developers to efficiently develop Agent applications.
-
Seamlessly integrates with Alibaba's International Multimodal Large Language Model, Ovis, to achieve deep alignment and fusion of visual and textual information. This model is characterized by high performance and lightweight design, offering the following advantages for efficient development and deployment of multimodal Agents:
- Outstanding Logical Reasoning: By combining instruction fine-tuning and preference learning, the model's Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning abilities are significantly enhanced, enabling it to better understand and execute complex instructions.
- Precise Cross-Language Understanding and Recognition: Beyond just Chinese and English, the model has improved text recognition (OCR) capabilities in multilingual environments and optimized the accuracy of structured data extraction from complex visual elements such as tables and charts.
- Flexible multi-agent framework, supporting various execution modes such as synchronous, asynchronous, streaming, and parallel, and naturally integrating the A2A protocol.
- A high-performance workflow engine combined with agents, built on top of Alibaba's SmartEngine workflow engine, utilizes RxJava3 to implement a reactive programming model. It employs a node-based process system to define agent behaviors, supporting synchronous, asynchronous, and bidirectional communication modes, providing a flexible foundation for building complex AI applications.
- Offers hundreds of API tools and introduces the MCP integration gateway.
- DeepResearch/RAG, ComputerUse, BrowserUse, Sandbox, and other best practices for Agentic AI.
- Implementation of context extension for agent conversations, including Session, Memory, Artifact, and more, with built-in short and long-term memory plugins.
- Provides prompt automation tuning and security risk control-related agent examples.
Agentic ADK inherits the excellent design of google-adk and supports the following key features:
Rich large model selection. Natively compatible with the use of models/vendors including OpenAI, Bailian/Qwen, OpenRouter, Claude, etc.
| Component Abstraction | Description |
|---|---|
| LangEngine | This component supports all compatible third-party Model/WorkSpace integrations under the LangEngine ecosystem into the Agent system, including OpenAI, Bailian/Qwen, Idealab, OpenRouter, etc. |
| DashScopeLlm | Supports integration with OpenAPI interfaces on Alibaba Cloud Bailian |
Highly abstracted Agent definition and flexible Agent orchestration. The framework has built-in LLM/sequential/parallel/loop Agent definitions; supports single Agent and multi-Agent (MAS) architecture design, facilitating the expansion of your agent design patterns and architecture.
| Component Abstraction | Description |
|---|---|
| LlmAgent | A core component in ADK that acts as the "thinking" part of the application. It leverages the powerful capabilities of large language models (LLMs) for reasoning, understanding natural language, making decisions, generating responses, and interacting with tools. |
| SequentialAgent | A WorkflowAgent that executes its child Agents in the order specified in the list. |
| LoopAgent | A WorkflowAgent that executes its child Agents in a loop (i.e., iterative) manner. It repeatedly runs a set of agents until a specified iteration count is reached or a termination condition is met. |
| ParallelAgent | A WorkflowAgent that can execute its child Agents concurrently, significantly speeding up the entire workflow when subtasks can be executed independently. |
| Other Advanced Concepts |
CustomAgents: Custom Agent processing flows can be implemented by inheriting google.adk.agents.BaseAgent. Multi-Agent Systems: Multiple different Agent instances can be combined into a multi-agent system (MAS), supporting the construction of more complex applications |
Rich tool assembly. Easy integration of Function/MCP and any third-party tools.
| Component Abstraction | Description |
|---|---|
| Function Tool |
FunctionTool: Function as a tool, any method can be converted into a Tool for Agent to call. LongRunningFunctionTool: Designed for tasks that require significant processing time without blocking Agent execution. AgentTool: By orchestrating other Agents as tools, their capabilities in the system can be fully utilized. This tool allows the current Agent to call another Agent to perform specific tasks, effectively delegating responsibilities. |
| DashScopeTool | Integration with Alibaba Cloud Bailian tool applications |
| MCPTool | ADK built-in MCP tool |
| GoogleSearchTool | ADK built-in Google search tool |
| GUITaskExecuteTool | ADK built-in GUI task execution tool |
Flexible Callback mechanism. Provides hooks at multiple timing points during Agent execution, making it convenient to implement custom logic before and after LLM/Tool/Agent calls.
Reference: https://google.github.io/adk-docs/callbacks
Best Practices: https://google.github.io/adk-docs/callbacks/design-patterns-and-best-practices/
Out-of-the-box debugging and evaluation capabilities. Provides a white-screen Debug page for quick Agent debugging whether locally or remotely.
Built on Alibaba's SmartEngine workflow engine, it utilizes RxJava3 to implement reactive programming patterns, employs a node-based process system to define agent behavior, and supports synchronous, asynchronous, and bidirectional communication modes, providing a flexible foundation for building complex AI applications.
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ User Application Layer │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ Runner (Execution Entry) │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ Pipeline Processing Layer │
│ ┌─────────────┐ ┌────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Agent │ │ ... │ │ Custom Processing │ │
│ │ Execution │ │ │ │ Pipeline │ │
│ │ Pipe │ │ │ │ │ │
│ └─────────────┘ └────────────────┘ └─────────────────────────┘ │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ Flow Engine Layer │
│ ┌─────────────┐ ┌────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ FlowCanvas │ │ │ │ │ │
│ │ (Flow │ │ FlowNode │ │ DelegationExecutor │ │
│ │ Container) │ │ │ │ │ │
│ └─────────────┘ └────────────────┘ └─────────────────────────┘ │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ AI Capability Abstraction Layer │
│ ┌─────────────┐ ┌────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ BasicLlm │ │ BaseTool │ │ BaseCondition │ │
│ │ (LLM Model) │ │ (Tool Set) │ │ (Conditional Judgment) │ │
│ └─────────────┘ └────────────────┘ └─────────────────────────┘ │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ Infrastructure Layer │
│ ┌─────────────┐ ┌────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ SmartEngine │ │ RxJava3 │ │ Spring Framework │ │
│ │ (Workflow │ │ (Reactive │ │ (Dependency Injection │ │
│ │ Engine) │ │ Programming │ │ Framework) │ │
│ │ │ │ Framework) │ │ │ │
│ └─────────────┘ └────────────────┘ └─────────────────────────┘ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
- FlowCanvas: The main container for flow definition, used to build and deploy workflows
- FlowNode: The base class for all flow nodes, defining the basic behavior of nodes
-
Node Types:
-
LlmFlowNode: Used for interacting with large language models -
ToolFlowNode: Used for executing external tools -
ConditionalContainer: Used for conditional branching -
ParallelFlowNode: Used for parallel execution -
ReferenceFlowNode: Used for referencing other flows
-
- Runner: The main entry point for flow execution
- DelegationExecutor: Handles the execution of delegated tasks
- SystemContext: Contains execution context and configuration information
- Request/Result: Data structures for requests and responses
-
BasicLlm Interface and Implementations (e.g.,
DashScopeLlm): Defines and implements interactions with large language models - LlmRequest/LlmResponse: Data structures for large language model interactions
-
BaseTool Interface and Implementations (e.g.,
DashScopeTools): Defines and implements external tool calls
- PipeInterface: Interface for pipeline components
- AgentExecutePipe: Main implementation of the execution pipeline
- PipelineUtil: Utility class for pipeline execution
The framework supports three execution modes:
- SYNC (Synchronous Mode): Sequential execution, waiting for each node to complete before executing the next
- ASYNC (Asynchronous Mode): Asynchronous execution, can process multiple tasks in parallel
- BIDI (Bidirectional Mode): Supports bidirectional communication, can dynamically receive input
This project is licensed under Apache License Version 2 (https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0.txt, SPDX-License-identifier: Apache-2.0).
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Agentic-ADK
Similar Open Source Tools

Agentic-ADK
Agentic ADK is an Agent application development framework launched by Alibaba International AI Business, based on Google-ADK and Ali-LangEngine. It is used for developing, constructing, evaluating, and deploying powerful, flexible, and controllable complex AI Agents. ADK aims to make Agent development simpler and more user-friendly, enabling developers to more easily build, deploy, and orchestrate various Agent applications ranging from simple tasks to complex collaborations.
kweaver
KWeaver is an open-source ecosystem for building, deploying, and running decision intelligence AI applications. It adopts ontology as the core methodology for business knowledge networks, with DIP as the core platform, aiming to provide elastic, agile, and reliable enterprise-grade decision intelligence to further unleash productivity. The DIP platform includes key subsystems such as ADP, Decision Agent, DIP Studio, and AI Store.
chronicle
Chronicle is a self-hostable AI system that captures audio/video data from OMI devices and other sources to generate memories, action items, and contextual insights about conversations and daily interactions. It includes a mobile app for OMI devices, backend services with AI features, a web dashboard for conversation and memory management, and optional services like speaker recognition and offline ASR. The project aims to provide a system that records personal spoken context and visual context to generate memories, action items, and enable home automation.
giztoy
Giztoy is a multi-language framework designed for building AI toys and intelligent applications. It provides a unified abstraction layer that spans from resource-constrained embedded systems to powerful cloud services. With features like native support for ESP32 and other MCUs, cross-platform app development, a unified build system with Bazel, an agent framework for AI agents, audio processing capabilities, support for various Large Language Models, real-time models with WebSocket streaming, secure transport protocols, and multi-language implementations in Go, Rust, Zig, and C/C++, Giztoy serves as a versatile tool for developing AI-powered applications across different platforms and devices.
observers
Observers is a lightweight library for AI observability that provides support for various generative AI APIs and storage backends. It allows users to track interactions with AI models and sync observations to different storage systems. The library supports OpenAI, Hugging Face transformers, AISuite, Litellm, and Docling for document parsing and export. Users can configure different stores such as Hugging Face Datasets, DuckDB, Argilla, and OpenTelemetry to manage and query their observations. Observers is designed to enhance AI model monitoring and observability in a user-friendly manner.
aiohomematic
AIO Homematic (hahomematic) is a lightweight Python 3 library for controlling and monitoring HomeMatic and HomematicIP devices, with support for third-party devices/gateways. It automatically creates entities for device parameters, offers custom entity classes for complex behavior, and includes features like caching paramsets for faster restarts. Designed to integrate with Home Assistant, it requires specific firmware versions for HomematicIP devices. The public API is defined in modules like central, client, model, exceptions, and const, with example usage provided. Useful links include changelog, data point definitions, troubleshooting, and developer resources for architecture, data flow, model extension, and Home Assistant lifecycle.
osmedeus
Osmedeus is a security-focused declarative orchestration engine that simplifies complex workflow automation into auditable YAML definitions. It provides powerful automation capabilities without compromising infrastructure integrity and safety. With features like declarative YAML workflows, multiple runners, event-driven triggers, template engine, utility functions, REST API server, distributed execution, notifications, cloud storage, AI integration, SAST integration, language detection, and preset installations, Osmedeus offers a comprehensive solution for security automation tasks.
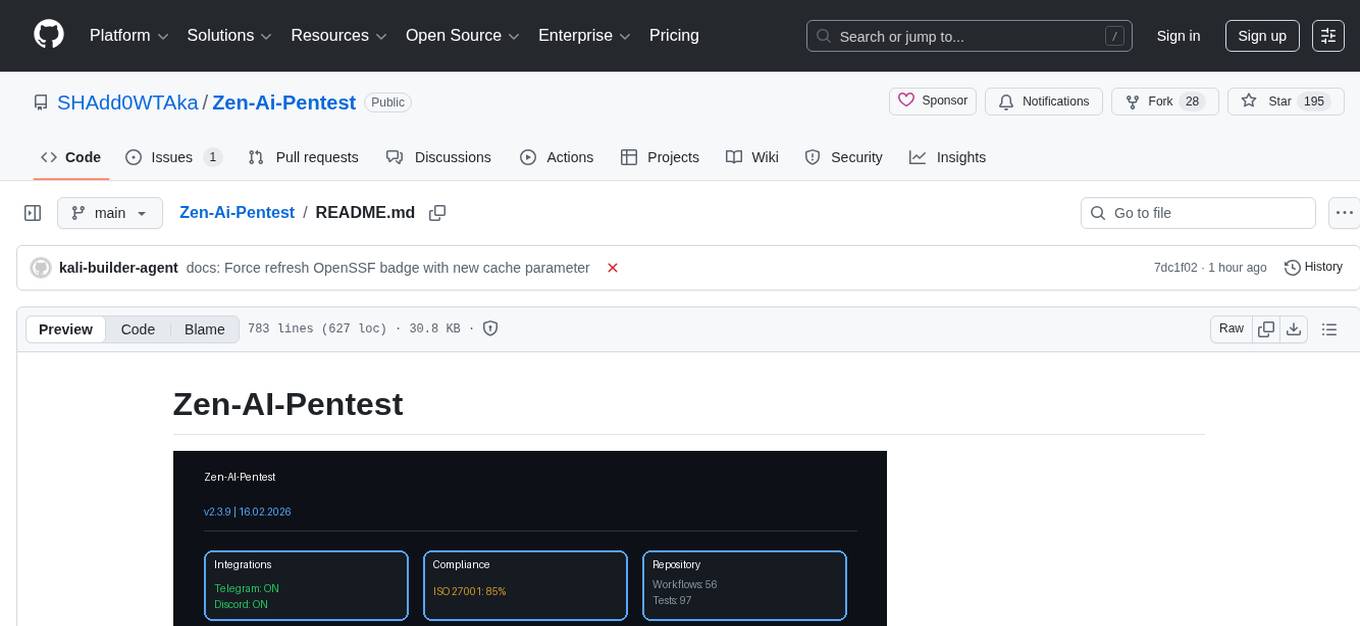
Zen-Ai-Pentest
Zen-AI-Pentest is a professional AI-powered penetration testing framework designed for security professionals, bug bounty hunters, and enterprise security teams. It combines cutting-edge language models with 20+ integrated security tools, offering comprehensive security assessments. The framework is security-first with multiple safety controls, extensible with a plugin system, cloud-native for deployment on AWS, Azure, or GCP, and production-ready with CI/CD, monitoring, and support. It features autonomous AI agents, risk analysis, exploit validation, benchmarking, CI/CD integration, AI persona system, subdomain scanning, and multi-cloud & virtualization support.
bumpgen
bumpgen is a tool designed to automatically upgrade TypeScript / TSX dependencies and make necessary code changes to handle any breaking issues that may arise. It uses an abstract syntax tree to analyze code relationships, type definitions for external methods, and a plan graph DAG to execute changes in the correct order. The tool is currently limited to TypeScript and TSX but plans to support other strongly typed languages in the future. It aims to simplify the process of upgrading dependencies and handling code changes caused by updates.

ai-on-gke
This repository contains assets related to AI/ML workloads on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). Run optimized AI/ML workloads with Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) platform orchestration capabilities. A robust AI/ML platform considers the following layers: Infrastructure orchestration that support GPUs and TPUs for training and serving workloads at scale Flexible integration with distributed computing and data processing frameworks Support for multiple teams on the same infrastructure to maximize utilization of resources
memsearch
Memsearch is a tool that allows users to give their AI agents persistent memory in a few lines of code. It enables users to write memories as markdown and search them semantically. Inspired by OpenClaw's markdown-first memory architecture, Memsearch is pluggable into any agent framework. The tool offers features like smart deduplication, live sync, and a ready-made Claude Code plugin for building agent memory.
vibium
Vibium is a browser automation infrastructure designed for AI agents, providing a single binary that manages browser lifecycle, WebDriver BiDi protocol, and an MCP server. It offers zero configuration, AI-native capabilities, and is lightweight with no runtime dependencies. It is suitable for AI agents, test automation, and any tasks requiring browser interaction.
helix
HelixML is a private GenAI platform that allows users to deploy the best of open AI in their own data center or VPC while retaining complete data security and control. It includes support for fine-tuning models with drag-and-drop functionality. HelixML brings the best of open source AI to businesses in an ergonomic and scalable way, optimizing the tradeoff between GPU memory and latency.
FinMem-LLM-StockTrading
This repository contains the Python source code for FINMEM, a Performance-Enhanced Large Language Model Trading Agent with Layered Memory and Character Design. It introduces FinMem, a novel LLM-based agent framework devised for financial decision-making, encompassing three core modules: Profiling, Memory with layered processing, and Decision-making. FinMem's memory module aligns closely with the cognitive structure of human traders, offering robust interpretability and real-time tuning. The framework enables the agent to self-evolve its professional knowledge, react agilely to new investment cues, and continuously refine trading decisions in the volatile financial environment. It presents a cutting-edge LLM agent framework for automated trading, boosting cumulative investment returns.
jat
JAT is a complete, self-contained environment for agentic development, offering task management, agent orchestration, code editor, git integration, and terminal access all in a single IDE. It allows users to connect various external sources like RSS, Slack, Telegram, and Gmail to create tasks and spawn agents automatically. JAT supports hands-on supervision of agents or autonomous operation. The tool provides features such as multi-agent management, task management, smart question UI, epic swarm for parallel agent spawning, autonomous triggers, task scheduling, error recovery, and a skill marketplace. JAT is designed to be a control tower for managing a swarm of agents, whether actively supervised or running autonomously.
open-computer-use
Open Computer Use is an open-source platform that enables AI agents to control computers through browser automation, terminal access, and desktop interaction. It is designed for developers to create autonomous AI workflows. The platform allows agents to browse the web, run terminal commands, control desktop applications, orchestrate multi-agents, stream execution, and is 100% open-source and self-hostable. It provides capabilities similar to Anthropic's Claude Computer Use but is fully open-source and extensible.
For similar tasks
OpenAGI
OpenAGI is an AI agent creation package designed for researchers and developers to create intelligent agents using advanced machine learning techniques. The package provides tools and resources for building and training AI models, enabling users to develop sophisticated AI applications. With a focus on collaboration and community engagement, OpenAGI aims to facilitate the integration of AI technologies into various domains, fostering innovation and knowledge sharing among experts and enthusiasts.
GPTSwarm
GPTSwarm is a graph-based framework for LLM-based agents that enables the creation of LLM-based agents from graphs and facilitates the customized and automatic self-organization of agent swarms with self-improvement capabilities. The library includes components for domain-specific operations, graph-related functions, LLM backend selection, memory management, and optimization algorithms to enhance agent performance and swarm efficiency. Users can quickly run predefined swarms or utilize tools like the file analyzer. GPTSwarm supports local LM inference via LM Studio, allowing users to run with a local LLM model. The framework has been accepted by ICML2024 and offers advanced features for experimentation and customization.
AgentForge
AgentForge is a low-code framework tailored for the rapid development, testing, and iteration of AI-powered autonomous agents and Cognitive Architectures. It is compatible with a range of LLM models and offers flexibility to run different models for different agents based on specific needs. The framework is designed for seamless extensibility and database-flexibility, making it an ideal playground for various AI projects. AgentForge is a beta-testing ground and future-proof hub for crafting intelligent, model-agnostic autonomous agents.
atomic_agents
Atomic Agents is a modular and extensible framework designed for creating powerful applications. It follows the principles of Atomic Design, emphasizing small and single-purpose components. Leveraging Pydantic for data validation and serialization, the framework offers a set of tools and agents that can be combined to build AI applications. It depends on the Instructor package and supports various APIs like OpenAI, Cohere, Anthropic, and Gemini. Atomic Agents is suitable for developers looking to create AI agents with a focus on modularity and flexibility.
LongRoPE
LongRoPE is a method to extend the context window of large language models (LLMs) beyond 2 million tokens. It identifies and exploits non-uniformities in positional embeddings to enable 8x context extension without fine-tuning. The method utilizes a progressive extension strategy with 256k fine-tuning to reach a 2048k context. It adjusts embeddings for shorter contexts to maintain performance within the original window size. LongRoPE has been shown to be effective in maintaining performance across various tasks from 4k to 2048k context lengths.
ax
Ax is a Typescript library that allows users to build intelligent agents inspired by agentic workflows and the Stanford DSP paper. It seamlessly integrates with multiple Large Language Models (LLMs) and VectorDBs to create RAG pipelines or collaborative agents capable of solving complex problems. The library offers advanced features such as streaming validation, multi-modal DSP, and automatic prompt tuning using optimizers. Users can easily convert documents of any format to text, perform smart chunking, embedding, and querying, and ensure output validation while streaming. Ax is production-ready, written in Typescript, and has zero dependencies.
Awesome-AI-Agents
Awesome-AI-Agents is a curated list of projects, frameworks, benchmarks, platforms, and related resources focused on autonomous AI agents powered by Large Language Models (LLMs). The repository showcases a wide range of applications, multi-agent task solver projects, agent society simulations, and advanced components for building and customizing AI agents. It also includes frameworks for orchestrating role-playing, evaluating LLM-as-Agent performance, and connecting LLMs with real-world applications through platforms and APIs. Additionally, the repository features surveys, paper lists, and blogs related to LLM-based autonomous agents, making it a valuable resource for researchers, developers, and enthusiasts in the field of AI.
CodeFuse-muAgent
CodeFuse-muAgent is a Multi-Agent framework designed to streamline Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) orchestration for agents. It integrates toolkits, code libraries, knowledge bases, and sandbox environments for rapid construction of complex Multi-Agent interactive applications. The framework enables efficient execution and handling of multi-layered and multi-dimensional tasks.
For similar jobs

promptflow
**Prompt flow** is a suite of development tools designed to streamline the end-to-end development cycle of LLM-based AI applications, from ideation, prototyping, testing, evaluation to production deployment and monitoring. It makes prompt engineering much easier and enables you to build LLM apps with production quality.

deepeval
DeepEval is a simple-to-use, open-source LLM evaluation framework specialized for unit testing LLM outputs. It incorporates various metrics such as G-Eval, hallucination, answer relevancy, RAGAS, etc., and runs locally on your machine for evaluation. It provides a wide range of ready-to-use evaluation metrics, allows for creating custom metrics, integrates with any CI/CD environment, and enables benchmarking LLMs on popular benchmarks. DeepEval is designed for evaluating RAG and fine-tuning applications, helping users optimize hyperparameters, prevent prompt drifting, and transition from OpenAI to hosting their own Llama2 with confidence.

MegaDetector
MegaDetector is an AI model that identifies animals, people, and vehicles in camera trap images (which also makes it useful for eliminating blank images). This model is trained on several million images from a variety of ecosystems. MegaDetector is just one of many tools that aims to make conservation biologists more efficient with AI. If you want to learn about other ways to use AI to accelerate camera trap workflows, check out our of the field, affectionately titled "Everything I know about machine learning and camera traps".

leapfrogai
LeapfrogAI is a self-hosted AI platform designed to be deployed in air-gapped resource-constrained environments. It brings sophisticated AI solutions to these environments by hosting all the necessary components of an AI stack, including vector databases, model backends, API, and UI. LeapfrogAI's API closely matches that of OpenAI, allowing tools built for OpenAI/ChatGPT to function seamlessly with a LeapfrogAI backend. It provides several backends for various use cases, including llama-cpp-python, whisper, text-embeddings, and vllm. LeapfrogAI leverages Chainguard's apko to harden base python images, ensuring the latest supported Python versions are used by the other components of the stack. The LeapfrogAI SDK provides a standard set of protobuffs and python utilities for implementing backends and gRPC. LeapfrogAI offers UI options for common use-cases like chat, summarization, and transcription. It can be deployed and run locally via UDS and Kubernetes, built out using Zarf packages. LeapfrogAI is supported by a community of users and contributors, including Defense Unicorns, Beast Code, Chainguard, Exovera, Hypergiant, Pulze, SOSi, United States Navy, United States Air Force, and United States Space Force.

llava-docker
This Docker image for LLaVA (Large Language and Vision Assistant) provides a convenient way to run LLaVA locally or on RunPod. LLaVA is a powerful AI tool that combines natural language processing and computer vision capabilities. With this Docker image, you can easily access LLaVA's functionalities for various tasks, including image captioning, visual question answering, text summarization, and more. The image comes pre-installed with LLaVA v1.2.0, Torch 2.1.2, xformers 0.0.23.post1, and other necessary dependencies. You can customize the model used by setting the MODEL environment variable. The image also includes a Jupyter Lab environment for interactive development and exploration. Overall, this Docker image offers a comprehensive and user-friendly platform for leveraging LLaVA's capabilities.

carrot
The 'carrot' repository on GitHub provides a list of free and user-friendly ChatGPT mirror sites for easy access. The repository includes sponsored sites offering various GPT models and services. Users can find and share sites, report errors, and access stable and recommended sites for ChatGPT usage. The repository also includes a detailed list of ChatGPT sites, their features, and accessibility options, making it a valuable resource for ChatGPT users seeking free and unlimited GPT services.

TrustLLM
TrustLLM is a comprehensive study of trustworthiness in LLMs, including principles for different dimensions of trustworthiness, established benchmark, evaluation, and analysis of trustworthiness for mainstream LLMs, and discussion of open challenges and future directions. Specifically, we first propose a set of principles for trustworthy LLMs that span eight different dimensions. Based on these principles, we further establish a benchmark across six dimensions including truthfulness, safety, fairness, robustness, privacy, and machine ethics. We then present a study evaluating 16 mainstream LLMs in TrustLLM, consisting of over 30 datasets. The document explains how to use the trustllm python package to help you assess the performance of your LLM in trustworthiness more quickly. For more details about TrustLLM, please refer to project website.

AI-YinMei
AI-YinMei is an AI virtual anchor Vtuber development tool (N card version). It supports fastgpt knowledge base chat dialogue, a complete set of solutions for LLM large language models: [fastgpt] + [one-api] + [Xinference], supports docking bilibili live broadcast barrage reply and entering live broadcast welcome speech, supports Microsoft edge-tts speech synthesis, supports Bert-VITS2 speech synthesis, supports GPT-SoVITS speech synthesis, supports expression control Vtuber Studio, supports painting stable-diffusion-webui output OBS live broadcast room, supports painting picture pornography public-NSFW-y-distinguish, supports search and image search service duckduckgo (requires magic Internet access), supports image search service Baidu image search (no magic Internet access), supports AI reply chat box [html plug-in], supports AI singing Auto-Convert-Music, supports playlist [html plug-in], supports dancing function, supports expression video playback, supports head touching action, supports gift smashing action, supports singing automatic start dancing function, chat and singing automatic cycle swing action, supports multi scene switching, background music switching, day and night automatic switching scene, supports open singing and painting, let AI automatically judge the content.