
vllm-mlx
OpenAI and Anthropic compatible server for Apple Silicon. Run LLMs and vision-language models (Llama, Qwen-VL, LLaVA) with continuous batching, MCP tool calling, and multimodal support. Native MLX backend, 400+ tok/s. Works with Claude Code.
Stars: 369
vLLM-MLX is a tool that brings native Apple Silicon GPU acceleration to vLLM by integrating Apple's ML framework with unified memory and Metal kernels. It offers optimized LLM inference with KV cache and quantization, vision-language models for multimodal inference, speech-to-text and text-to-speech with native voices, text embeddings for semantic search and RAG, and more. Users can benefit from features like multimodal support for text, image, video, and audio, native GPU acceleration on Apple Silicon, compatibility with OpenAI API, Anthropic Messages API, reasoning models extraction, integration with external tools via Model Context Protocol, memory-efficient caching, and high throughput for multiple concurrent users.
README:
vLLM-like inference for Apple Silicon - GPU-accelerated Text, Image, Video & Audio on Mac
vllm-mlx brings native Apple Silicon GPU acceleration to vLLM by integrating:
- MLX: Apple's ML framework with unified memory and Metal kernels
- mlx-lm: Optimized LLM inference with KV cache and quantization
- mlx-vlm: Vision-language models for multimodal inference
- mlx-audio: Speech-to-Text and Text-to-Speech with native voices
- mlx-embeddings: Text embeddings for semantic search and RAG
- Multimodal - Text, Image, Video & Audio in one platform
- Native GPU acceleration on Apple Silicon (M1, M2, M3, M4)
- Native TTS voices - Spanish, French, Chinese, Japanese + 5 more languages
- OpenAI API compatible - drop-in replacement for OpenAI client
-
Anthropic Messages API - native
/v1/messagesendpoint for Claude Code and OpenCode -
Embeddings - OpenAI-compatible
/v1/embeddingsendpoint with mlx-embeddings - Reasoning Models - extract thinking process from Qwen3, DeepSeek-R1
- MCP Tool Calling - integrate external tools via Model Context Protocol
- Paged KV Cache - memory-efficient caching with prefix sharing
- Continuous Batching - high throughput for multiple concurrent users
Using uv (recommended):
# Install as CLI tool (system-wide)
uv tool install git+https://github.com/waybarrios/vllm-mlx.git
# Or install in a project/virtual environment
uv pip install git+https://github.com/waybarrios/vllm-mlx.gitUsing pip:
# Install from GitHub
pip install git+https://github.com/waybarrios/vllm-mlx.git
# Or clone and install in development mode
git clone https://github.com/waybarrios/vllm-mlx.git
cd vllm-mlx
pip install -e .# Simple mode (single user, max throughput)
vllm-mlx serve mlx-community/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct-4bit --port 8000
# Continuous batching (multiple users)
vllm-mlx serve mlx-community/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct-4bit --port 8000 --continuous-batching
# With API key authentication
vllm-mlx serve mlx-community/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct-4bit --port 8000 --api-key your-secret-keyfrom openai import OpenAI
# Without API key (local development)
client = OpenAI(base_url="http://localhost:8000/v1", api_key="not-needed")
# With API key (production)
client = OpenAI(base_url="http://localhost:8000/v1", api_key="your-secret-key")
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="default",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "Hello!"}],
)
print(response.choices[0].message.content)vllm-mlx exposes an Anthropic-compatible /v1/messages endpoint, so tools like Claude Code and OpenCode can connect directly.
from anthropic import Anthropic
client = Anthropic(base_url="http://localhost:8000", api_key="not-needed")
response = client.messages.create(
model="default",
max_tokens=256,
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "Hello!"}]
)
print(response.content[0].text)To use with Claude Code:
export ANTHROPIC_BASE_URL=http://localhost:8000
export ANTHROPIC_API_KEY=not-needed
claudeSee Anthropic Messages API docs for streaming, tool calling, system messages, and token counting.
vllm-mlx serve mlx-community/Qwen3-VL-4B-Instruct-3bit --port 8000response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="default",
messages=[{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "text", "text": "What's in this image?"},
{"type": "image_url", "image_url": {"url": "https://example.com/image.jpg"}}
]
}]
)# Install audio dependencies
pip install vllm-mlx[audio]
python -m spacy download en_core_web_sm
brew install espeak-ng # macOS, for non-English languages# Text-to-Speech (English)
python examples/tts_example.py "Hello, how are you?" --play
# Text-to-Speech (Spanish)
python examples/tts_multilingual.py "Hola mundo" --lang es --play
# List available models and languages
python examples/tts_multilingual.py --list-models
python examples/tts_multilingual.py --list-languagesSupported TTS Models:
| Model | Languages | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Kokoro | EN, ES, FR, JA, ZH, IT, PT, HI | Fast, 82M params, 11 voices |
| Chatterbox | 15+ languages | Expressive, voice cloning |
| VibeVoice | EN | Realtime, low latency |
| VoxCPM | ZH, EN | High quality Chinese/English |
Extract the thinking process from reasoning models like Qwen3 and DeepSeek-R1:
# Start server with reasoning parser
vllm-mlx serve mlx-community/Qwen3-8B-4bit --reasoning-parser qwen3response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="default",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "What is 17 × 23?"}]
)
# Access reasoning separately from the answer
print("Thinking:", response.choices[0].message.reasoning)
print("Answer:", response.choices[0].message.content)Supported Parsers:
| Parser | Models | Description |
|---|---|---|
qwen3 |
Qwen3 series | Requires both <think> and </think> tags |
deepseek_r1 |
DeepSeek-R1 | Handles implicit <think> tag |
Generate text embeddings for semantic search, RAG, and similarity:
# Start server with an embedding model pre-loaded
vllm-mlx serve mlx-community/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct-4bit --embedding-model mlx-community/all-MiniLM-L6-v2-4bit# Generate embeddings using the OpenAI SDK
embeddings = client.embeddings.create(
model="mlx-community/all-MiniLM-L6-v2-4bit",
input=["Hello world", "How are you?"]
)
print(f"Dimensions: {len(embeddings.data[0].embedding)}")See Embeddings Guide for details on supported models and lazy loading.
For full documentation, see the docs directory:
-
Getting Started
-
User Guides
-
Reference
-
Benchmarks
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ vLLM API Layer │
│ (OpenAI-compatible interface) │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ MLXPlatform │
│ (vLLM platform plugin for Apple Silicon) │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
│
┌─────────────┬────────────┴────────────┬─────────────┐
▼ ▼ ▼ ▼
┌───────────────┐ ┌───────────────┐ ┌───────────────┐ ┌───────────────┐
│ mlx-lm │ │ mlx-vlm │ │ mlx-audio │ │mlx-embeddings │
│(LLM inference)│ │ (Vision+LLM) │ │ (TTS + STT) │ │ (Embeddings) │
└───────────────┘ └───────────────┘ └───────────────┘ └───────────────┘
│ │ │ │
└─────────────┴─────────────────────────┴─────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ MLX │
│ (Apple ML Framework - Metal kernels) │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
LLM Performance (M4 Max, 128GB):
| Model | Speed | Memory |
|---|---|---|
| Qwen3-0.6B-8bit | 402 tok/s | 0.7 GB |
| Llama-3.2-1B-4bit | 464 tok/s | 0.7 GB |
| Llama-3.2-3B-4bit | 200 tok/s | 1.8 GB |
Continuous Batching (5 concurrent requests):
| Model | Single | Batched | Speedup |
|---|---|---|---|
| Qwen3-0.6B-8bit | 328 tok/s | 1112 tok/s | 3.4x |
| Llama-3.2-1B-4bit | 299 tok/s | 613 tok/s | 2.0x |
Audio - Speech-to-Text (M4 Max, 128GB):
| Model | RTF* | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| whisper-tiny | 197x | Real-time, low latency |
| whisper-large-v3-turbo | 55x | Best quality/speed balance |
| whisper-large-v3 | 24x | Highest accuracy |
*RTF = Real-Time Factor. RTF of 100x means 1 minute transcribes in ~0.6 seconds.
See benchmarks for detailed results.
vllm-mlx includes native support for Gemma 3 vision models. Gemma 3 is automatically detected as MLLM.
# Start server with Gemma 3
vllm-mlx serve mlx-community/gemma-3-27b-it-4bit --port 8000
# Verify it loaded as MLLM (not LLM)
curl http://localhost:8000/health
# Should show: "model_type": "mllm"Gemma 3's default sliding_window=1024 limits context to ~10K tokens on Apple Silicon (Metal GPU timeout at higher context). To enable longer context (up to ~50K tokens), patch mlx-vlm:
Location: ~/.../site-packages/mlx_vlm/models/gemma3/language.py
Find the make_cache method and replace with:
def make_cache(self):
import os
# Set GEMMA3_SLIDING_WINDOW=8192 for ~40K context
# Set GEMMA3_SLIDING_WINDOW=0 for ~50K context (full KVCache)
sliding_window = int(os.environ.get('GEMMA3_SLIDING_WINDOW', self.config.sliding_window))
caches = []
for i in range(self.config.num_hidden_layers):
if (
i % self.config.sliding_window_pattern
== self.config.sliding_window_pattern - 1
):
caches.append(KVCache())
elif sliding_window == 0:
caches.append(KVCache()) # Full context for all layers
else:
caches.append(RotatingKVCache(max_size=sliding_window, keep=0))
return cachesUsage:
# Default (~10K max context)
vllm-mlx serve mlx-community/gemma-3-27b-it-4bit --port 8000
# Extended context (~40K max)
GEMMA3_SLIDING_WINDOW=8192 vllm-mlx serve mlx-community/gemma-3-27b-it-4bit --port 8000
# Maximum context (~50K max)
GEMMA3_SLIDING_WINDOW=0 vllm-mlx serve mlx-community/gemma-3-27b-it-4bit --port 8000Benchmark Results (M4 Max 128GB):
| Setting | Max Context | Memory |
|---|---|---|
| Default (1024) | ~10K tokens | ~16GB |
GEMMA3_SLIDING_WINDOW=8192 |
~40K tokens | ~25GB |
GEMMA3_SLIDING_WINDOW=0 |
~50K tokens | ~35GB |
We welcome contributions! See Contributing Guide for details.
- Bug fixes and improvements
- Performance optimizations
- Documentation improvements
- Benchmarks on different Apple Silicon chips
Submit PRs to: https://github.com/waybarrios/vllm-mlx
Apache 2.0 - see LICENSE for details.
If you use vLLM-MLX in your research or project, please cite:
@software{vllm_mlx2025,
author = {Barrios, Wayner},
title = {vLLM-MLX: Apple Silicon MLX Backend for vLLM},
year = {2025},
url = {https://github.com/waybarrios/vllm-mlx},
note = {Native GPU-accelerated LLM and vision-language model inference on Apple Silicon}
}For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for vllm-mlx
Similar Open Source Tools

vllm-mlx
vLLM-MLX is a tool that brings native Apple Silicon GPU acceleration to vLLM by integrating Apple's ML framework with unified memory and Metal kernels. It offers optimized LLM inference with KV cache and quantization, vision-language models for multimodal inference, speech-to-text and text-to-speech with native voices, text embeddings for semantic search and RAG, and more. Users can benefit from features like multimodal support for text, image, video, and audio, native GPU acceleration on Apple Silicon, compatibility with OpenAI API, Anthropic Messages API, reasoning models extraction, integration with external tools via Model Context Protocol, memory-efficient caching, and high throughput for multiple concurrent users.
memsearch
Memsearch is a tool that allows users to give their AI agents persistent memory in a few lines of code. It enables users to write memories as markdown and search them semantically. Inspired by OpenClaw's markdown-first memory architecture, Memsearch is pluggable into any agent framework. The tool offers features like smart deduplication, live sync, and a ready-made Claude Code plugin for building agent memory.
vibium
Vibium is a browser automation infrastructure designed for AI agents, providing a single binary that manages browser lifecycle, WebDriver BiDi protocol, and an MCP server. It offers zero configuration, AI-native capabilities, and is lightweight with no runtime dependencies. It is suitable for AI agents, test automation, and any tasks requiring browser interaction.
Shannon
Shannon is a battle-tested infrastructure for AI agents that solves problems at scale, such as runaway costs, non-deterministic failures, and security concerns. It offers features like intelligent caching, deterministic replay of workflows, time-travel debugging, WASI sandboxing, and hot-swapping between LLM providers. Shannon allows users to ship faster with zero configuration multi-agent setup, multiple AI patterns, time-travel debugging, and hot configuration changes. It is production-ready with features like WASI sandbox, token budget control, policy engine (OPA), and multi-tenancy. Shannon helps scale without breaking by reducing costs, being provider agnostic, observable by default, and designed for horizontal scaling with Temporal workflow orchestration.
myclaw
myclaw is a personal AI assistant built on agentsdk-go that offers a CLI agent for single message or interactive REPL mode, full orchestration with channels, cron, and heartbeat, support for various messaging channels like Telegram, Feishu, WeCom, WhatsApp, and a web UI, multi-provider support for Anthropic and OpenAI models, image recognition and document processing, scheduled tasks with JSON persistence, long-term and daily memory storage, custom skill loading, and more. It provides a comprehensive solution for interacting with AI models and managing tasks efficiently.
mesh
MCP Mesh is an open-source control plane for MCP traffic that provides a unified layer for authentication, routing, and observability. It replaces multiple integrations with a single production endpoint, simplifying configuration management. Built for multi-tenant organizations, it offers workspace/project scoping for policies, credentials, and logs. With core capabilities like MeshContext, AccessControl, and OpenTelemetry, it ensures fine-grained RBAC, full tracing, and metrics for tools and workflows. Users can define tools with input/output validation, access control checks, audit logging, and OpenTelemetry traces. The project structure includes apps for full-stack MCP Mesh, encryption, observability, and more, with deployment options ranging from Docker to Kubernetes. The tech stack includes Bun/Node runtime, TypeScript, Hono API, React, Kysely ORM, and Better Auth for OAuth and API keys.
solo-server
Solo Server is a lightweight server designed for managing hardware-aware inference. It provides seamless setup through a simple CLI and HTTP servers, an open model registry for pulling models from platforms like Ollama and Hugging Face, cross-platform compatibility for effortless deployment of AI models on hardware, and a configurable framework that auto-detects hardware components (CPU, GPU, RAM) and sets optimal configurations.
pilot
Pilot is an AI tool designed to streamline the process of handling tickets from GitHub, Linear, Jira, or Asana. It plans the implementation, writes the code, runs tests, and opens a PR for you to review and merge. With features like Autopilot, Epic Decomposition, Self-Review, and more, Pilot aims to automate the ticket handling process and reduce the time spent on prioritizing and completing tasks. It integrates with various platforms, offers intelligence features, and provides real-time visibility through a dashboard. Pilot is free to use, with costs associated with Claude API usage. It is designed for bug fixes, small features, refactoring, tests, docs, and dependency updates, but may not be suitable for large architectural changes or security-critical code.
aiohomematic
AIO Homematic (hahomematic) is a lightweight Python 3 library for controlling and monitoring HomeMatic and HomematicIP devices, with support for third-party devices/gateways. It automatically creates entities for device parameters, offers custom entity classes for complex behavior, and includes features like caching paramsets for faster restarts. Designed to integrate with Home Assistant, it requires specific firmware versions for HomematicIP devices. The public API is defined in modules like central, client, model, exceptions, and const, with example usage provided. Useful links include changelog, data point definitions, troubleshooting, and developer resources for architecture, data flow, model extension, and Home Assistant lifecycle.
distill
Distill is a reliability layer for LLM context that provides deterministic deduplication to remove redundancy before reaching the model. It aims to reduce redundant data, lower costs, provide faster responses, and offer more efficient and deterministic results. The tool works by deduplicating, compressing, summarizing, and caching context to ensure reliable outputs. It offers various installation methods, including binary download, Go install, Docker usage, and building from source. Distill can be used for tasks like deduplicating chunks, connecting to vector databases, integrating with AI assistants, analyzing files for duplicates, syncing vectors to Pinecone, querying from the command line, and managing configuration files. The tool supports self-hosting via Docker, Docker Compose, building from source, Fly.io deployment, Render deployment, and Railway integration. Distill also provides monitoring capabilities with Prometheus-compatible metrics, Grafana dashboard, and OpenTelemetry tracing.
boxlite
BoxLite is an embedded, lightweight micro-VM runtime designed for AI agents running OCI containers with hardware-level isolation. It is built for high concurrency with no daemon required, offering features like lightweight VMs, high concurrency, hardware isolation, embeddability, and OCI compatibility. Users can spin up 'Boxes' to run containers for AI agent sandboxes and multi-tenant code execution scenarios where Docker alone is insufficient and full VM infrastructure is too heavy. BoxLite supports Python, Node.js, and Rust with quick start guides for each, along with features like CPU/memory limits, storage options, networking capabilities, security layers, and image registry configuration. The tool provides SDKs for Python and Node.js, with Go support coming soon. It offers detailed documentation, examples, and architecture insights for users to understand how BoxLite works under the hood.
osmedeus
Osmedeus is a security-focused declarative orchestration engine that simplifies complex workflow automation into auditable YAML definitions. It provides powerful automation capabilities without compromising infrastructure integrity and safety. With features like declarative YAML workflows, multiple runners, event-driven triggers, template engine, utility functions, REST API server, distributed execution, notifications, cloud storage, AI integration, SAST integration, language detection, and preset installations, Osmedeus offers a comprehensive solution for security automation tasks.
giztoy
Giztoy is a multi-language framework designed for building AI toys and intelligent applications. It provides a unified abstraction layer that spans from resource-constrained embedded systems to powerful cloud services. With features like native support for ESP32 and other MCUs, cross-platform app development, a unified build system with Bazel, an agent framework for AI agents, audio processing capabilities, support for various Large Language Models, real-time models with WebSocket streaming, secure transport protocols, and multi-language implementations in Go, Rust, Zig, and C/C++, Giztoy serves as a versatile tool for developing AI-powered applications across different platforms and devices.
tinyclaw
TinyClaw is a lightweight wrapper around Claude Code that connects WhatsApp via QR code, processes messages sequentially, maintains conversation context, runs 24/7 in tmux, and is ready for multi-channel support. Its key innovation is the file-based queue system that prevents race conditions and enables multi-channel support. TinyClaw consists of components like whatsapp-client.js for WhatsApp I/O, queue-processor.js for message processing, heartbeat-cron.sh for health checks, and tinyclaw.sh as the main orchestrator with a CLI interface. It ensures no race conditions, is multi-channel ready, provides clean responses using claude -c -p, and supports persistent sessions. Security measures include local storage of WhatsApp session and queue files, channel-specific authentication, and running Claude with user permissions.
AgentX
AgentX is a next-generation open-source AI agent development framework and runtime platform. It provides an event-driven runtime with a simple framework and minimal UI. The platform is ready-to-use and offers features like multi-user support, session persistence, real-time streaming, and Docker readiness. Users can build AI Agent applications with event-driven architecture using TypeScript for server-side (Node.js) and client-side (Browser/React) development. AgentX also includes comprehensive documentation, core concepts, guides, API references, and various packages for different functionalities. The architecture follows an event-driven design with layered components for server-side and client-side interactions.
helix
HelixML is a private GenAI platform that allows users to deploy the best of open AI in their own data center or VPC while retaining complete data security and control. It includes support for fine-tuning models with drag-and-drop functionality. HelixML brings the best of open source AI to businesses in an ergonomic and scalable way, optimizing the tradeoff between GPU memory and latency.
For similar tasks

HPT
Hyper-Pretrained Transformers (HPT) is a novel multimodal LLM framework from HyperGAI, trained for vision-language models capable of understanding both textual and visual inputs. The repository contains the open-source implementation of inference code to reproduce the evaluation results of HPT Air on different benchmarks. HPT has achieved competitive results with state-of-the-art models on various multimodal LLM benchmarks. It offers models like HPT 1.5 Air and HPT 1.0 Air, providing efficient solutions for vision-and-language tasks.
learnopencv
LearnOpenCV is a repository containing code for Computer Vision, Deep learning, and AI research articles shared on the blog LearnOpenCV.com. It serves as a resource for individuals looking to enhance their expertise in AI through various courses offered by OpenCV. The repository includes a wide range of topics such as image inpainting, instance segmentation, robotics, deep learning models, and more, providing practical implementations and code examples for readers to explore and learn from.
spark-free-api
Spark AI Free 服务 provides high-speed streaming output, multi-turn dialogue support, AI drawing support, long document interpretation, and image parsing. It offers zero-configuration deployment, multi-token support, and automatic session trace cleaning. It is fully compatible with the ChatGPT interface. The repository includes multiple free-api projects for various AI services. Users can access the API for tasks such as chat completions, AI drawing, document interpretation, image analysis, and ssoSessionId live checking. The project also provides guidelines for deployment using Docker, Docker-compose, Render, Vercel, and native deployment methods. It recommends using custom clients for faster and simpler access to the free-api series projects.
mlx-vlm
MLX-VLM is a package designed for running Vision LLMs on Mac systems using MLX. It provides a convenient way to install and utilize the package for processing large language models related to vision tasks. The tool simplifies the process of running LLMs on Mac computers, offering a seamless experience for users interested in leveraging MLX for vision-related projects.
clarifai-python-grpc
This is the official Clarifai gRPC Python client for interacting with their recognition API. Clarifai offers a platform for data scientists, developers, researchers, and enterprises to utilize artificial intelligence for image, video, and text analysis through computer vision and natural language processing. The client allows users to authenticate, predict concepts in images, and access various functionalities provided by the Clarifai API. It follows a versioning scheme that aligns with the backend API updates and includes specific instructions for installation and troubleshooting. Users can explore the Clarifai demo, sign up for an account, and refer to the documentation for detailed information.
horde-worker-reGen
This repository provides the latest implementation for the AI Horde Worker, allowing users to utilize their graphics card(s) to generate, post-process, or analyze images for others. It offers a platform where users can create images and earn 'kudos' in return, granting priority for their own image generations. The repository includes important details for setup, recommendations for system configurations, instructions for installation on Windows and Linux, basic usage guidelines, and information on updating the AI Horde Worker. Users can also run the worker with multiple GPUs and receive notifications for updates through Discord. Additionally, the repository contains models that are licensed under the CreativeML OpenRAIL License.
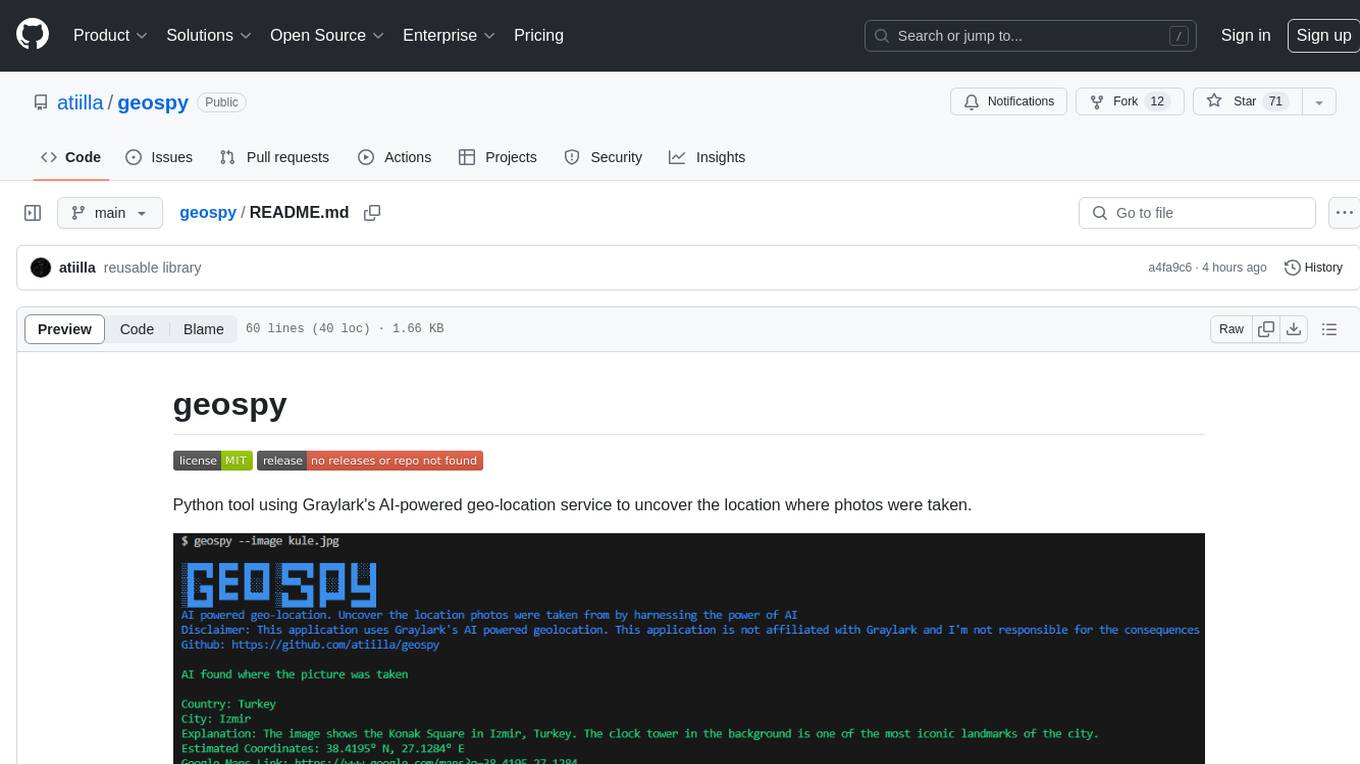
geospy
Geospy is a Python tool that utilizes Graylark's AI-powered geolocation service to determine the location where photos were taken. It allows users to analyze images and retrieve information such as country, city, explanation, coordinates, and Google Maps links. The tool provides a seamless way to integrate geolocation services into various projects and applications.
Awesome-Colorful-LLM
Awesome-Colorful-LLM is a meticulously assembled anthology of vibrant multimodal research focusing on advancements propelled by large language models (LLMs) in domains such as Vision, Audio, Agent, Robotics, and Fundamental Sciences like Mathematics. The repository contains curated collections of works, datasets, benchmarks, projects, and tools related to LLMs and multimodal learning. It serves as a comprehensive resource for researchers and practitioners interested in exploring the intersection of language models and various modalities for tasks like image understanding, video pretraining, 3D modeling, document understanding, audio analysis, agent learning, robotic applications, and mathematical research.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.


