
docs
TiDB database documentation. TiDB is an open-source, cloud-native, distributed, MySQL-Compatible database for elastic scale and real-time analytics. Try AI-powered Chat2Query free at : https://www.pingcap.com/tidb-serverless/
Stars: 601
The TiDB Documentation repository contains the source files for TiDB Docs in English and Chinese. Users can contribute by creating issues or pull requests to improve the documentation. It also provides guidance on customizing and generating PDF versions of the documentation. The repository maintains various versions of TiDB documentation in different branches, including development milestone releases and long-term support versions. Contributors can refer to the Contributing Guide to become a part of the project. The documentation is licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0.
README:
Welcome to TiDB documentation!
This repository stores all the source files of TiDB Docs at the PingCAP website, while the pingcap/docs-cn repository stores all the source files of TiDB Documentation in Chinese.
If you find documentation issues, feel free to create an Issue to let us know or directly create a Pull Request to help fix or update it.
If you want to locally customize and output TiDB documentation in PDF format to meet the needs of specific scenarios, such as freely sorting or deleting certain contents in TiDB documentation, please refer to TiDB Documentation PDF Generation Tutorial.
Currently, the official documentation supports two languages:
You can use Google Translate to view the documentation in different languages. For example:
-
fr: documentation in French -
ja: documentation in Japanese -
ko: documentation in Korean -
de: documentation in German -
es: documentation in Spanish
Currently, we maintain the following versions of TiDB documentation in different branches:
| Branch name | TiDB docs version |
|---|---|
master |
The latest development version |
release-8.5 |
8.5 LTS (Long-Term Support) |
release-8.4 |
8.4 Development Milestone Release |
release-8.3 |
8.3 Development Milestone Release |
release-8.2 |
8.2 Development Milestone Release (Archived documentation, no longer updated) |
release-8.1 |
8.1 LTS (Long-Term Support) |
release-8.0 |
8.0 Development Milestone Release (Archived documentation, no longer updated) |
release-7.6 |
7.6 Development Milestone Release (Archived documentation, no longer updated) |
release-7.5 |
7.5 LTS (Long-Term Support) |
release-7.4 |
7.4 Development Milestone Release (Archived documentation, no longer updated) |
release-7.3 |
7.3 Development Milestone Release (Archived documentation, no longer updated) |
release-7.2 |
7.2 Development Milestone Release (Archived documentation, no longer updated) |
release-7.1 |
7.1 LTS (Long-Term Support) version |
release-7.0 |
7.0 Development Milestone Release (Archived documentation, no longer updated) |
release-6.6 |
6.6 Development Milestone Release (Archived documentation, no longer updated) |
release-6.5 |
6.5 LTS (Long-Term Support) version |
release-6.4 |
6.4 Development Milestone Release (Archived documentation, no longer updated) |
release-6.3 |
6.3 Development Milestone Release (Archived documentation, no longer updated) |
release-6.2 |
6.2 Development Milestone Release (Archived documentation, no longer updated) |
release-6.1 |
6.1 LTS (Long-Term Support) version |
release-6.0 |
6.0 Development Milestone Release (Archived documentation, no longer updated) |
release-5.4 |
5.4 stable version |
release-5.3 |
5.3 stable version (Archived documentation, no longer updated) |
release-5.2 |
5.2 stable version (Archived documentation, no longer updated) |
release-5.1 |
5.1 stable version (Archived documentation, no longer updated) |
release-5.0 |
5.0 stable version (Archived documentation, no longer updated) |
release-4.0 |
4.0 stable version (Archived documentation, no longer updated) |
release-3.1 |
3.1 stable version (Archived documentation, no longer updated) |
release-3.0 |
3.0 stable version (Archived documentation, no longer updated) |
release-2.1 |
2.1 stable version (Archived documentation, no longer updated) |
See TiDB Documentation Contributing Guide to become a contributor! 🤓

All documentation starting from TiDB v7.0 is available under the terms of CC BY-SA 3.0.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for docs
Similar Open Source Tools

docs
The TiDB Documentation repository contains the source files for TiDB Docs in English and Chinese. Users can contribute by creating issues or pull requests to improve the documentation. It also provides guidance on customizing and generating PDF versions of the documentation. The repository maintains various versions of TiDB documentation in different branches, including development milestone releases and long-term support versions. Contributors can refer to the Contributing Guide to become a part of the project. The documentation is licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0.
airswap-protocols
AirSwap Protocols is a repository containing smart contracts for developers and traders on the AirSwap peer-to-peer trading network. It includes various packages for functionalities like server registry, atomic token swap, staking, rewards pool, batch token and order calls, libraries, and utils. The repository follows a branching and release process for contracts and tools, with steps for regular development process and individual package features or patches. Users can deploy and verify contracts using specific commands with network flags.
flowgen
FlowGen is a tool built for AutoGen, a great agent framework from Microsoft and a lot of contributors. It provides intuitive visual tools that streamline the construction and oversight of complex agent-based workflows, simplifying the process for creators and developers. Users can create Autoflows, chat with agents, and share flow templates. The tool is fully dockerized and supports deployment on Railway.app. Contributions to the project are welcome, and the platform uses semantic-release for versioning and releases.

vscode-unify-chat-provider
The 'vscode-unify-chat-provider' repository is a tool that integrates multiple LLM API providers into VS Code's GitHub Copilot Chat using the Language Model API. It offers free tier access to mainstream models, perfect compatibility with major LLM API formats, deep adaptation to API features, best performance with built-in parameters, out-of-the-box configuration, import/export support, great UX, and one-click use of various models. The tool simplifies model setup, migration, and configuration for users, providing a seamless experience within VS Code for utilizing different language models.
slidev-mcp
slidev-mcp is an intelligent slide generation tool based on Slidev that integrates large language model technology, allowing users to automatically generate professional online PPT presentations with simple descriptions. It dramatically lowers the barrier to using Slidev, provides natural language interactive slide creation, and offers automated generation of professional presentations. The tool also includes various features for environment and project management, slide content management, and utility tools to enhance the slide creation process.

langchain_dart
LangChain.dart is a Dart port of the popular LangChain Python framework created by Harrison Chase. LangChain provides a set of ready-to-use components for working with language models and a standard interface for chaining them together to formulate more advanced use cases (e.g. chatbots, Q&A with RAG, agents, summarization, extraction, etc.). The components can be grouped into a few core modules: * **Model I/O:** LangChain offers a unified API for interacting with various LLM providers (e.g. OpenAI, Google, Mistral, Ollama, etc.), allowing developers to switch between them with ease. Additionally, it provides tools for managing model inputs (prompt templates and example selectors) and parsing the resulting model outputs (output parsers). * **Retrieval:** assists in loading user data (via document loaders), transforming it (with text splitters), extracting its meaning (using embedding models), storing (in vector stores) and retrieving it (through retrievers) so that it can be used to ground the model's responses (i.e. Retrieval-Augmented Generation or RAG). * **Agents:** "bots" that leverage LLMs to make informed decisions about which available tools (such as web search, calculators, database lookup, etc.) to use to accomplish the designated task. The different components can be composed together using the LangChain Expression Language (LCEL).
TableLLM
TableLLM is a large language model designed for efficient tabular data manipulation tasks in real office scenarios. It can generate code solutions or direct text answers for tasks like insert, delete, update, query, merge, and chart operations on tables embedded in spreadsheets or documents. The model has been fine-tuned based on CodeLlama-7B and 13B, offering two scales: TableLLM-7B and TableLLM-13B. Evaluation results show its performance on benchmarks like WikiSQL, Spider, and self-created table operation benchmark. Users can use TableLLM for code and text generation tasks on tabular data.
llm-structured-output-benchmarks
Benchmark various LLM Structured Output frameworks like Instructor, Mirascope, Langchain, LlamaIndex, Fructose, Marvin, Outlines, LMFormatEnforcer, etc on tasks like multi-label classification, named entity recognition, synthetic data generation. The tool provides benchmark results, methodology, instructions to run the benchmark, add new data, and add a new framework. It also includes a roadmap for framework-related tasks, contribution guidelines, citation information, and feedback request.
SemanticFinder
SemanticFinder is a frontend-only live semantic search tool that calculates embeddings and cosine similarity client-side using transformers.js and SOTA embedding models from Huggingface. It allows users to search through large texts like books with pre-indexed examples, customize search parameters, and offers data privacy by keeping input text in the browser. The tool can be used for basic search tasks, analyzing texts for recurring themes, and has potential integrations with various applications like wikis, chat apps, and personal history search. It also provides options for building browser extensions and future ideas for further enhancements and integrations.
AI-Toolbox
AI-Toolbox is a C++ library aimed at representing and solving common AI problems, with a focus on MDPs, POMDPs, and related algorithms. It provides an easy-to-use interface that is extensible to many problems while maintaining readable code. The toolbox includes tutorials for beginners in reinforcement learning and offers Python bindings for seamless integration. It features utilities for combinatorics, polytopes, linear programming, sampling, distributions, statistics, belief updating, data structures, logging, seeding, and more. Additionally, it supports bandit/normal games, single agent MDP/stochastic games, single agent POMDP, and factored/joint multi-agent scenarios.
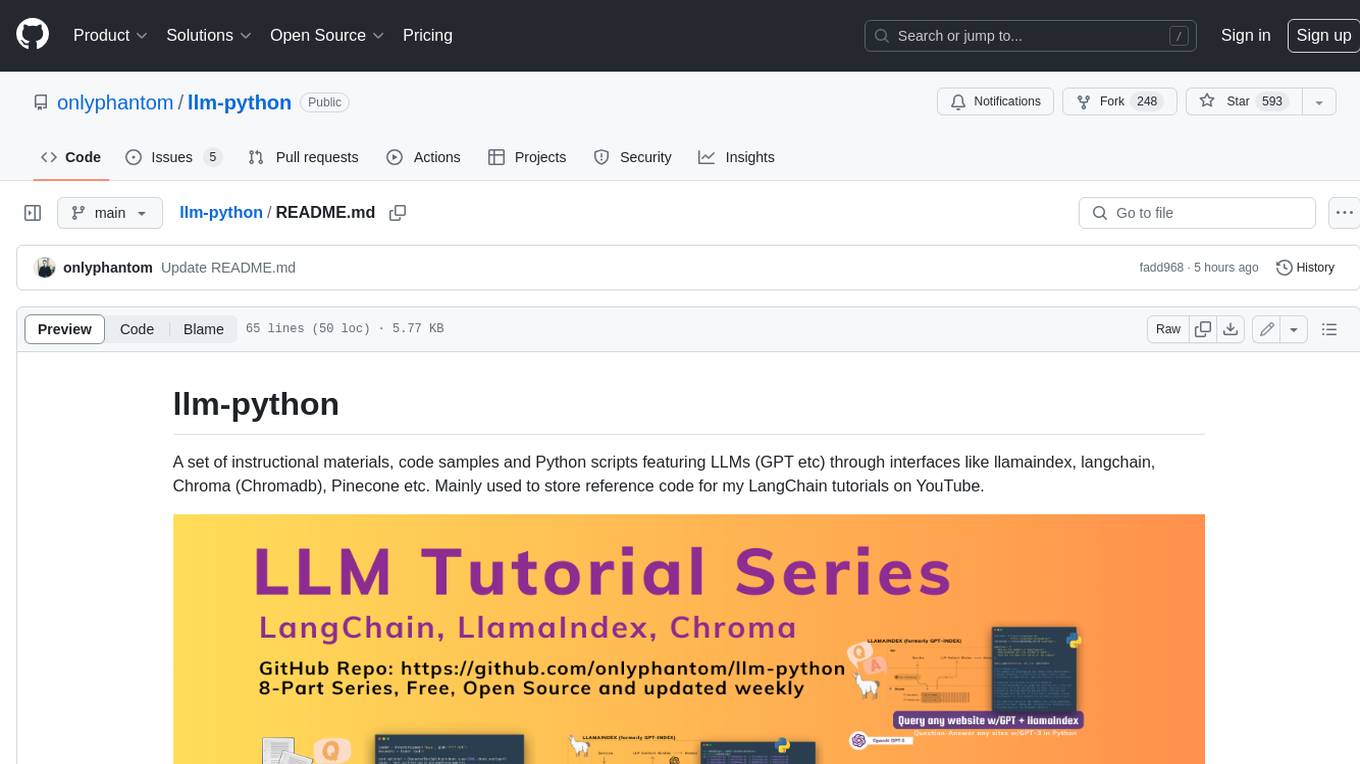
llm-python
A set of instructional materials, code samples and Python scripts featuring LLMs (GPT etc) through interfaces like llamaindex, langchain, Chroma (Chromadb), Pinecone etc. Mainly used to store reference code for my LangChain tutorials on YouTube.
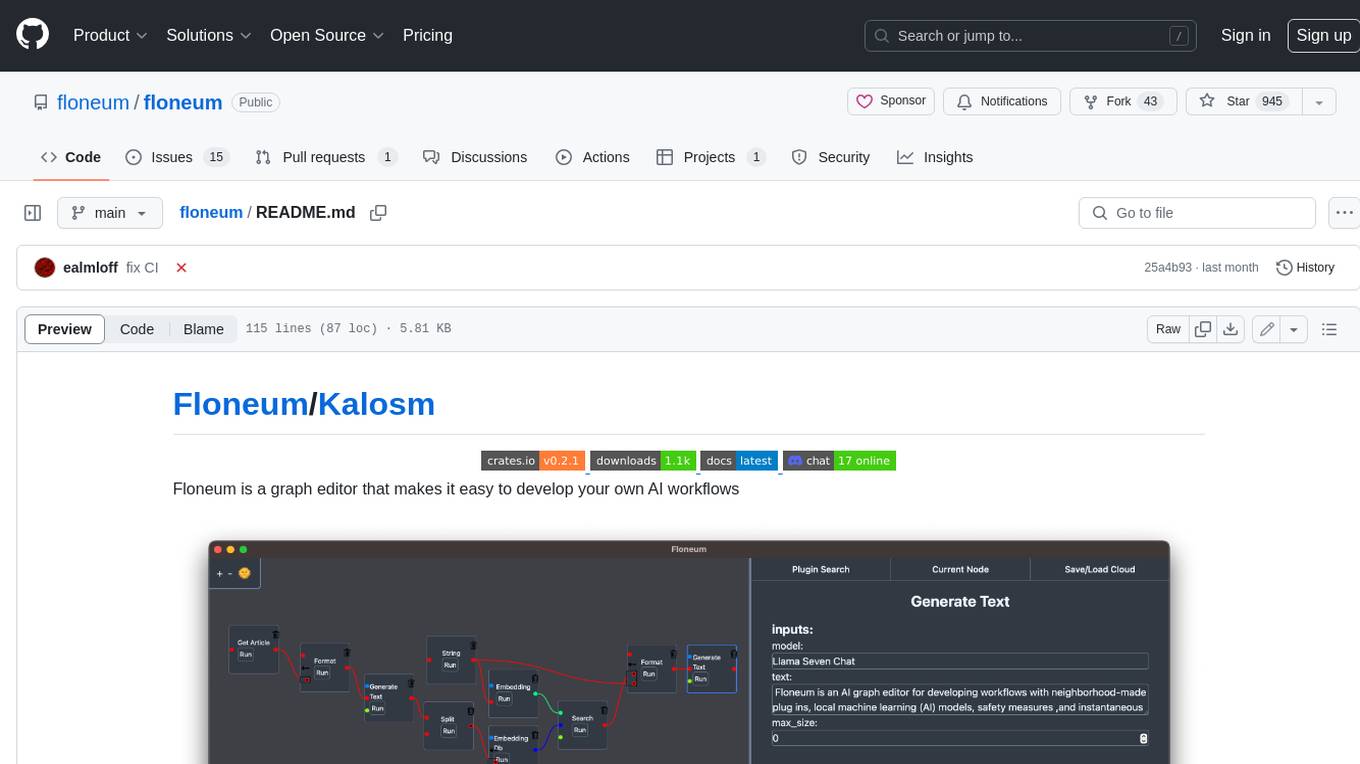
floneum
Floneum is a graph editor that makes it easy to develop your own AI workflows. It uses large language models (LLMs) to run AI models locally, without any external dependencies or even a GPU. This makes it easy to use LLMs with your own data, without worrying about privacy. Floneum also has a plugin system that allows you to improve the performance of LLMs and make them work better for your specific use case. Plugins can be used in any language that supports web assembly, and they can control the output of LLMs with a process similar to JSONformer or guidance.
PredictorLLM
PredictorLLM is an advanced trading agent framework that utilizes large language models to automate trading in financial markets. It includes a profiling module to establish agent characteristics, a layered memory module for retaining and prioritizing financial data, and a decision-making module to convert insights into trading strategies. The framework mimics professional traders' behavior, surpassing human limitations in data processing and continuously evolving to adapt to market conditions for superior investment outcomes.

llmvision-card
LLM Vision Timeline Card is a custom card designed to display the LLM Vision Timeline on your Home Assistant Dashboard. It requires LLM Vision set up in Home Assistant, Timeline provider set up in LLM Vision, and Blueprint or Automation to add events to the timeline. The card allows users to show events that occurred within a specified number of hours and customize the display based on categories and colors. It supports multiple languages for UI and icon generation.
terraform-genai-doc-summarization
This solution showcases how to summarize a large corpus of documents using Generative AI. It provides an end-to-end demonstration of document summarization going all the way from raw documents, detecting text in the documents and summarizing the documents on-demand using Vertex AI LLM APIs, Cloud Vision Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and BigQuery.

FFAIVideo
FFAIVideo is a lightweight node.js project that utilizes popular AI LLM to intelligently generate short videos. It supports multiple AI LLM models such as OpenAI, Moonshot, Azure, g4f, Google Gemini, etc. Users can input text to automatically synthesize exciting video content with subtitles, background music, and customizable settings. The project integrates Microsoft Edge's online text-to-speech service for voice options and uses Pexels website for video resources. Installation of FFmpeg is essential for smooth operation. Inspired by MoneyPrinterTurbo, MoneyPrinter, and MsEdgeTTS, FFAIVideo is designed for front-end developers with minimal dependencies and simple usage.
For similar tasks
langfuse-docs
Langfuse Docs is a repository for langfuse.com, built on Nextra. It provides guidelines for contributing to the documentation using GitHub Codespaces and local development setup. The repository includes Python cookbooks in Jupyter notebooks format, which are converted to markdown for rendering on the site. It also covers media management for images, videos, and gifs. The stack includes Nextra, Next.js, shadcn/ui, and Tailwind CSS. Additionally, there is a bundle analysis feature to analyze the production build bundle size using @next/bundle-analyzer.

docs
The TiDB Documentation repository contains the source files for TiDB Docs in English and Chinese. Users can contribute by creating issues or pull requests to improve the documentation. It also provides guidance on customizing and generating PDF versions of the documentation. The repository maintains various versions of TiDB documentation in different branches, including development milestone releases and long-term support versions. Contributors can refer to the Contributing Guide to become a part of the project. The documentation is licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0.
For similar jobs
MaxKB
MaxKB is a knowledge base Q&A system based on the LLM large language model. MaxKB = Max Knowledge Base, which aims to become the most powerful brain of the enterprise.
crewAI
crewAI is a cutting-edge framework for orchestrating role-playing, autonomous AI agents. By fostering collaborative intelligence, CrewAI empowers agents to work together seamlessly, tackling complex tasks. It provides a flexible and structured approach to AI collaboration, enabling users to define agents with specific roles, goals, and tools, and assign them tasks within a customizable process. crewAI supports integration with various LLMs, including OpenAI, and offers features such as autonomous task delegation, flexible task management, and output parsing. It is open-source and welcomes contributions, with a focus on improving the library based on usage data collected through anonymous telemetry.
documentation
Vespa documentation is served using GitHub Project pages with Jekyll. To edit documentation, check out and work off the master branch in this repository. Documentation is written in HTML or Markdown. Use a single Jekyll template _layouts/default.html to add header, footer and layout. Install bundler, then $ bundle install $ bundle exec jekyll serve --incremental --drafts --trace to set up a local server at localhost:4000 to see the pages as they will look when served. If you get strange errors on bundle install try $ export PATH=“/usr/local/opt/[email protected]/bin:$PATH” $ export LDFLAGS=“-L/usr/local/opt/[email protected]/lib” $ export CPPFLAGS=“-I/usr/local/opt/[email protected]/include” $ export PKG_CONFIG_PATH=“/usr/local/opt/[email protected]/lib/pkgconfig” The output will highlight rendering/other problems when starting serving. Alternatively, use the docker image `jekyll/jekyll` to run the local server on Mac $ docker run -ti --rm --name doc \ --publish 4000:4000 -e JEKYLL_UID=$UID -v $(pwd):/srv/jekyll \ jekyll/jekyll jekyll serve or RHEL 8 $ podman run -it --rm --name doc -p 4000:4000 -e JEKYLL_ROOTLESS=true \ -v "$PWD":/srv/jekyll:Z docker.io/jekyll/jekyll jekyll serve The layout is written in denali.design, see _layouts/default.html for usage. Please do not add custom style sheets, as it is harder to maintain.
deep-seek
DeepSeek is a new experimental architecture for a large language model (LLM) powered internet-scale retrieval engine. Unlike current research agents designed as answer engines, DeepSeek aims to process a vast amount of sources to collect a comprehensive list of entities and enrich them with additional relevant data. The end result is a table with retrieved entities and enriched columns, providing a comprehensive overview of the topic. DeepSeek utilizes both standard keyword search and neural search to find relevant content, and employs an LLM to extract specific entities and their associated contents. It also includes a smaller answer agent to enrich the retrieved data, ensuring thoroughness. DeepSeek has the potential to revolutionize research and information gathering by providing a comprehensive and structured way to access information from the vastness of the internet.
basehub
JavaScript / TypeScript SDK for BaseHub, the first AI-native content hub. **Features:** * ✨ Infers types from your BaseHub repository... _meaning IDE autocompletion works great._ * 🏎️ No dependency on graphql... _meaning your bundle is more lightweight._ * 🌐 Works everywhere `fetch` is supported... _meaning you can use it anywhere._
discourse-chatbot
The discourse-chatbot is an original AI chatbot for Discourse forums that allows users to converse with the bot in posts or chat channels. Users can customize the character of the bot, enable RAG mode for expert answers, search Wikipedia, news, and Google, provide market data, perform accurate math calculations, and experiment with vision support. The bot uses cutting-edge Open AI API and supports Azure and proxy server connections. It includes a quota system for access management and can be used in RAG mode or basic bot mode. The setup involves creating embeddings to make the bot aware of forum content and setting up bot access permissions based on trust levels. Users must obtain an API token from Open AI and configure group quotas to interact with the bot. The plugin is extensible to support other cloud bots and content search beyond the provided set.

crewAI
CrewAI is a cutting-edge framework designed to orchestrate role-playing autonomous AI agents. By fostering collaborative intelligence, CrewAI empowers agents to work together seamlessly, tackling complex tasks. It enables AI agents to assume roles, share goals, and operate in a cohesive unit, much like a well-oiled crew. Whether you're building a smart assistant platform, an automated customer service ensemble, or a multi-agent research team, CrewAI provides the backbone for sophisticated multi-agent interactions. With features like role-based agent design, autonomous inter-agent delegation, flexible task management, and support for various LLMs, CrewAI offers a dynamic and adaptable solution for both development and production workflows.
KB-Builder
KB Builder is an open-source knowledge base generation system based on the LLM large language model. It utilizes the RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) data generation enhancement method to provide users with the ability to enhance knowledge generation and quickly build knowledge bases based on RAG. It aims to be the central hub for knowledge construction in enterprises, offering platform-based intelligent dialogue services and document knowledge base management functionality. Users can upload docx, pdf, txt, and md format documents and generate high-quality knowledge base question-answer pairs by invoking large models through the 'Parse Document' feature.
