
mcpm.sh
CLI MCP package manager & registry for all platforms and all clients. Search & configure MCP servers. Advanced Router & Profile features.
Stars: 735

MCPM is an open source CLI tool for managing MCP servers, providing a simplified global configuration approach to install servers once, organize them with profiles, and integrate them into any MCP client. Features include server discovery, direct execution, sharing capabilities, and client integration tools. It eliminates the complexity of v1's target-based system in favor of a clean global workspace model. The tool is designed to be AI agent friendly with comprehensive automation support and a rich CLI interface.
README:
English | 简体中文
Open Source. Forever Free.
Built with ❤️ by Path Integral Institute
MCPM is an open source CLI tool for managing MCP servers. It provides a simplified global configuration approach where you install servers once and organize them with profiles, then integrate them into any MCP client. Features include server discovery through a central registry, direct execution, sharing capabilities, and client integration tools.
Demo is showing outdated v1 commands, new demo is baking ...

💡 Grow the MCP ecosystem! We welcome contributions to our MCP Registry. Add your own servers, improve documentation, or suggest features. Open source thrives with community participation!
curl -sSL https://mcpm.sh/install | bashOr choose other installation methods like brew, pipx, uv etc.
MCPM v2.0 provides a simplified approach to managing MCP servers with a global configuration model. Key features include:
- ✨ Global Server Management: Install servers once, use everywhere
- 📋 Virtual Profiles: Organize servers with tags for different workflows
- 🔍 Server Discovery: Browse and install from the MCP Registry
- 🚀 Direct Execution: Run servers over stdio or HTTP for testing
- 🌐 Public Sharing: Share servers through secure tunnels
- 🎛️ Client Integration: Manage configurations for Claude Desktop, Cursor, Windsurf, and more
- 🤖 AI Agent Friendly: Non-interactive CLI with comprehensive automation support and llm.txt guide
- 💻 Beautiful CLI: Rich formatting and interactive interfaces
- 📊 Usage Analytics: Monitor server usage and performance
MCPM v2.0 eliminates the complexity of v1's target-based system in favor of a clean global workspace model.
MCPM will support managing MCP servers for the following clients:
- 🤖 Claude Desktop (Anthropic)
- ⌨️ Cursor
- 🏄 Windsurf
- 🧩 Vscode
- 📝 Cline
- ➡️ Continue
- 🦢 Goose
- 🔥 5ire
- 🦘 Roo Code
- ✨ More clients coming soon...
MCPM provides a comprehensive CLI with a clean, organized interface. The v2.0 architecture uses a global configuration model where servers are installed once and can be organized with profiles, then integrated into specific MCP clients as needed.
mcpm --help # Display help information and available commands
mcpm --version # Display the current version of MCPMGlobal server installation and management commands:
# 🔍 Search and Install
mcpm search [QUERY] # Search the MCP Registry for available servers
mcpm info SERVER_NAME # Display detailed information about a server
mcpm install SERVER_NAME # Install a server from registry to global configuration
mcpm uninstall SERVER_NAME # Remove a server from global configuration
# 📋 List and Inspect
mcpm ls # List all installed servers and their profile assignments
mcpm edit SERVER_NAME # Edit a server configuration
mcpm inspect SERVER_NAME # Launch MCP Inspector to test/debug a serverExecute servers directly for testing or integration:
mcpm run SERVER_NAME # Execute a server directly over stdio
mcpm run SERVER_NAME --http # Execute a server over HTTP for testing
mcpm share SERVER_NAME # Share a server through secure tunnel for remote access
mcpm usage # Display comprehensive analytics and usage dataProfiles are virtual tags that organize servers into logical groups for different workflows:
# 🔄 Profile Operations
mcpm profile ls # List all profiles and their tagged servers
mcpm profile create PROFILE # Create a new profile
mcpm profile rm PROFILE # Remove a profile (servers remain installed)
mcpm profile edit PROFILE # Interactive server selection for profile
# 🚀 Profile Execution
mcpm profile run PROFILE # Execute all servers in a profile over stdio or HTTP
mcpm profile share PROFILE # Share all servers in a profile through secure tunnel
mcpm profile inspect PROFILE # Launch MCP Inspector for all servers in profileManage MCP client configurations (Claude Desktop, Cursor, Windsurf, etc.):
mcpm client ls # List all supported MCP clients and their status
mcpm client edit CLIENT_NAME # Interactive server enable/disable for a client
mcpm client edit CLIENT_NAME -e # Open client config in external editor
mcpm client import CLIENT_NAME # Import server configurations from a clientmcpm doctor # Check system health and server status
mcpm config # Manage MCPM configuration and settings
mcpm migrate # Migrate from v1 to v2 configurationThe MCP Registry is a central repository of available MCP servers that can be installed using MCPM. The registry is available at mcpm.sh/registry.
MCPM is designed to be AI agent friendly with comprehensive automation support. Every interactive command has a non-interactive alternative using CLI parameters and environment variables.
Set environment variables to enable full automation:
export MCPM_NON_INTERACTIVE=true # Disable all interactive prompts
export MCPM_FORCE=true # Skip confirmations
export MCPM_JSON_OUTPUT=true # JSON output for parsingThe llm.txt file provides comprehensive documentation specifically designed for AI agents, including:
- Complete command reference with parameters and examples
- Environment variable usage patterns
- Best practices for automation
- Error handling and troubleshooting
- Batch operation patterns
The llm.txt file is automatically generated from the CLI structure and kept up-to-date with each release.
- Add the server to MCPM
mcpm new [MY_SERVER_NAME] --type stdio --command "[COMMAND]" --args "[ARG_1] [ARG_2] ..."(Add --force arg to bypass the confirmation interaction)
Verify it appears in your installed servers:
mcpm lsYou should see [MY_SERVER_NAME] in the list.
- Serve it over HTTP
mcpm run [MY_SERVER_NAME] --httpMCPM prints the server URL, for example:
URL: http://127.0.0.1:6276/mcp/
- Expose it on your network (optional)
mcpm run [MY_SERVER_NAME] --http --host 0.0.0.0Tip: add --port <PORT> to choose a different port.
- Add the servers to MCPM
# Stdio server
mcpm new [SERVER_A] --type stdio --command "[COMMAND]" --args "[ARG_1] [ARG_2] ..." --force
# Remote HTTP/SSE server
mcpm new [SERVER_B] --type remote --url "http://SERVER_ADDR/mcp/" --force- Create a profile and add the servers Interactive:
mcpm profile create [PROFILE_NAME]
mcpm profile edit [PROFILE_NAME]MCPM would list out all installed servers, you can use arrows to navigate, space to select/deselect, type to search, and Enter to confirm.
Verify:
mcpm profile lsYou should see your profile with the selected servers.
- Run the profile
# Stdio
mcpm profile run [PROFILE_NAME]
# HTTP
mcpm profile run [PROFILE_NAME] --http
# Optional: host and port
mcpm profile run [PROFILE_NAME] --http --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8080# Server management
mcpm new myserver --type stdio --command "python -m server" --force
mcpm edit myserver --env "API_KEY=secret" --force
# Profile management
mcpm profile edit web-dev --add-server myserver --force
mcpm profile run web-dev --port 8080
# Client integration
mcpm client edit cursor --add-profile web-dev --force- [x] Global server configuration model
- [x] Profile-based server tagging and organization
- [x] Interactive command interfaces
- [x] Client integration management (
mcpm client edit) - [x] Modern CLI with consistent UX
- [x] Registry integration and server discovery
- [x] Direct server execution and sharing
- [x] Import from existing client configurations
- [x] Additional client support (gemini-cli, codex, etc.)
- [ ] Advanced Server access monitoring and analytics
- [ ] Execution in docker
- [ ] Expose MCPM functionality as an MCP server (search, install, profile management etc.)
- [ ] TUI interface for MCP inspect
- [ ] TUI interface for MCP & profile management
brew install mcpmpipx install mcpmuv tool install mcpmpip install mcpmIf you are a user of x-cmd, you can run:
x install mcpm.shThis repository contains the CLI and service components for MCP Manager, built with Python and Click following modern package development practices.
- 🐍 Python 3.10+
- 🚀 uv (for virtual environment and dependency management)
- 🖱️ Click framework for CLI
- ✨ Rich for enhanced console output
- 🌐 Requests for API interactions
The project follows the modern src-based layout:
mcpm.sh/
├── src/ # Source package directory
│ └── mcpm/ # Main package code
├── tests/ # Test directory
├── test_cli.py # Development CLI runner
├── pyproject.toml # Project configuration
├── pages/ # Website content
│ └── registry/ # Registry website
├── mcp-registry/ # MCP Registry data
└── README.md # Documentation
-
Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/pathintegral-institute/mcpm.sh.git cd mcpm.sh -
Set up a virtual environment with uv
uv venv --seed source .venv/bin/activate # On Unix/Mac -
Install dependencies in development mode
uv pip install -e . -
Run the CLI directly during development
# Either use the installed package mcpm --help # Or use the development script ./test_cli.py --help -
Run tests
pytest tests/
- 📁 Use the src-based directory structure to prevent import confusion
- 🔧 Develop with an editable install using
uv pip install -e . - 🧩 Keep commands modular in the
src/mcpm/commands/directory - 🧪 Add tests for new functionality in the
tests/directory - 💻 Use the
test_cli.pyscript for quick development testing
MCP uses a single source of truth pattern for version management to ensure consistency across all components.
- 📍 The canonical version is defined in
version.pyat the project root - 📥
src/mcpm/__init__.pyimports this version - 📄
pyproject.tomluses dynamic versioning to read fromversion.py - 🏷️ Git tags are created with the same version number prefixed with 'v' (e.g., v1.0.0)
When releasing a new version:
-
Use the provided version bump script
./bump_version.sh NEW_VERSION # Example: ./bump_version.sh 1.1.0 -
Push the changes and tags
git push && git push --tags -
Create a GitHub release matching the new version
This process ensures that the version is consistent in all places: code, package metadata, and git tags. PyPI release is handled by the CI/CD pipeline and will be triggered automatically.
MIT
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for mcpm.sh
Similar Open Source Tools

mcpm.sh
MCPM is an open source CLI tool for managing MCP servers, providing a simplified global configuration approach to install servers once, organize them with profiles, and integrate them into any MCP client. Features include server discovery, direct execution, sharing capabilities, and client integration tools. It eliminates the complexity of v1's target-based system in favor of a clean global workspace model. The tool is designed to be AI agent friendly with comprehensive automation support and a rich CLI interface.
Shellsage
Shell Sage is an intelligent terminal companion and AI-powered terminal assistant that enhances the terminal experience with features like local and cloud AI support, context-aware error diagnosis, natural language to command translation, and safe command execution workflows. It offers interactive workflows, supports various API providers, and allows for custom model selection. Users can configure the tool for local or API mode, select specific models, and switch between modes easily. Currently in alpha development, Shell Sage has known limitations like limited Windows support and occasional false positives in error detection. The roadmap includes improvements like better context awareness, Windows PowerShell integration, Tmux integration, and CI/CD error pattern database.
NextChat
NextChat is a well-designed cross-platform ChatGPT web UI tool that supports Claude, GPT4, and Gemini Pro. It offers a compact client for Linux, Windows, and MacOS, with features like self-deployed LLMs compatibility, privacy-first data storage, markdown support, responsive design, and fast loading speed. Users can create, share, and debug chat tools with prompt templates, access various prompts, compress chat history, and use multiple languages. The tool also supports enterprise-level privatization and customization deployment, with features like brand customization, resource integration, permission control, knowledge integration, security auditing, private deployment, and continuous updates.
Pixelle-MCP
Pixelle-MCP is a multi-channel publishing tool designed to streamline the process of publishing content across various social media platforms. It allows users to create, schedule, and publish posts simultaneously on platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram. With a user-friendly interface and advanced scheduling features, Pixelle-MCP helps users save time and effort in managing their social media presence. The tool also provides analytics and insights to track the performance of posts and optimize content strategy. Whether you are a social media manager, content creator, or digital marketer, Pixelle-MCP is a valuable tool to enhance your online presence and engage with your audience effectively.
chunkr
Chunkr is an open-source document intelligence API that provides a production-ready service for document layout analysis, OCR, and semantic chunking. It allows users to convert PDFs, PPTs, Word docs, and images into RAG/LLM-ready chunks. The API offers features such as layout analysis, OCR with bounding boxes, structured HTML and markdown output, and VLM processing controls. Users can interact with Chunkr through a Python SDK, enabling them to upload documents, process them, and export results in various formats. The tool also supports self-hosted deployment options using Docker Compose or Kubernetes, with configurations for different AI models like OpenAI, Google AI Studio, and OpenRouter. Chunkr is dual-licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License v3.0 (AGPL-3.0) and a commercial license, providing flexibility for different usage scenarios.
markpdfdown
MarkPDFDown is a powerful tool that leverages multimodal large language models to transcribe PDF files into Markdown format. It simplifies the process of converting PDF documents into clean, editable Markdown text by accurately extracting text, preserving formatting, and handling complex document structures including tables, formulas, and diagrams.
markpdfdown
MarkPDFDown is a powerful tool that leverages multimodal large language models to transcribe PDF files into Markdown format. It simplifies the process of converting PDF documents into clean, editable Markdown text by accurately extracting text, preserving formatting, and handling complex document structures including tables, formulas, and diagrams.
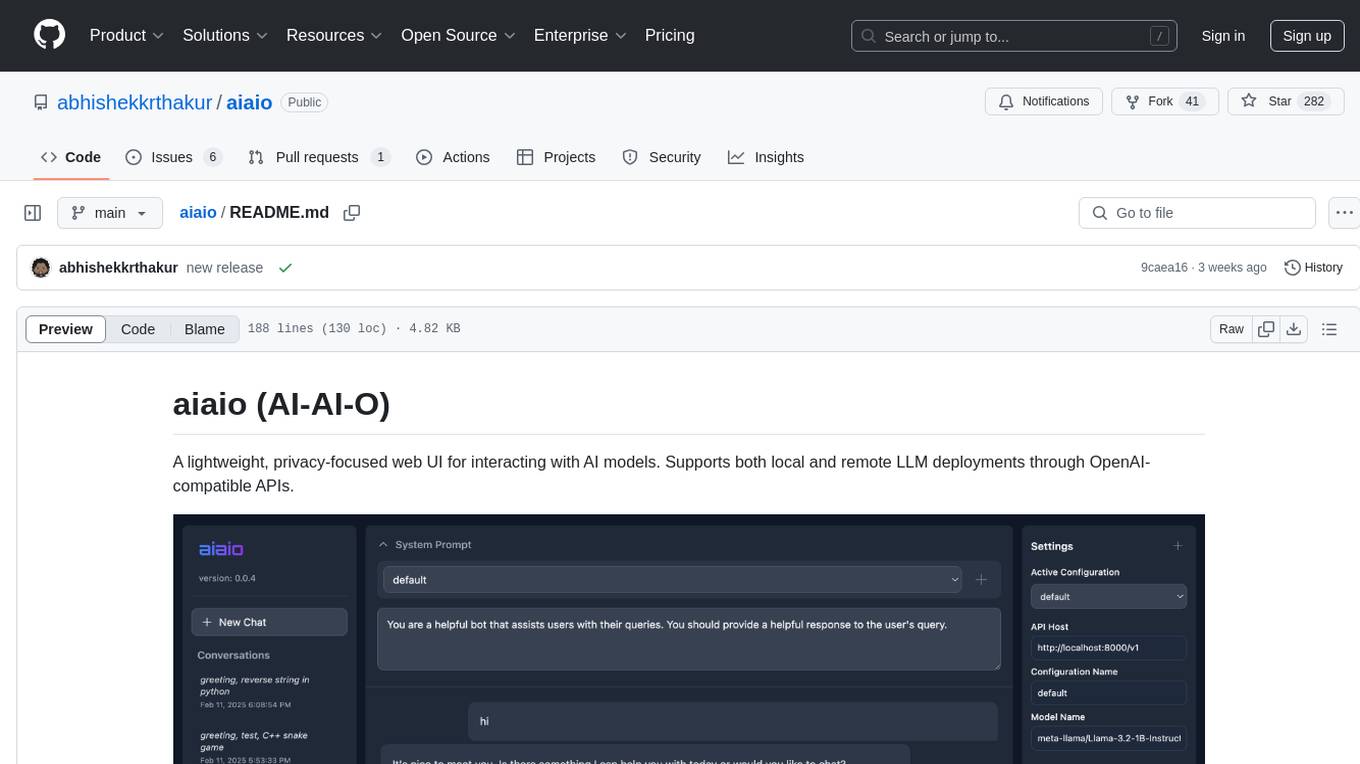
aiaio
aiaio (AI-AI-O) is a lightweight, privacy-focused web UI for interacting with AI models. It supports both local and remote LLM deployments through OpenAI-compatible APIs. The tool provides features such as dark/light mode support, local SQLite database for conversation storage, file upload and processing, configurable model parameters through UI, privacy-focused design, responsive design for mobile/desktop, syntax highlighting for code blocks, real-time conversation updates, automatic conversation summarization, customizable system prompts, WebSocket support for real-time updates, Docker support for deployment, multiple API endpoint support, and multiple system prompt support. Users can configure model parameters and API settings through the UI, handle file uploads, manage conversations, and use keyboard shortcuts for efficient interaction. The tool uses SQLite for storage with tables for conversations, messages, attachments, and settings. Contributions to the project are welcome under the Apache License 2.0.
moling
MoLing is a computer-use and browser-use MCP Server that implements system interaction through operating system APIs, enabling file system operations such as reading, writing, merging, statistics, and aggregation, as well as the ability to execute system commands. It is a dependency-free local office automation assistant. Requiring no installation of any dependencies, MoLing can be run directly and is compatible with multiple operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and macOS. This eliminates the hassle of dealing with environment conflicts involving Node.js, Python, Docker, and other development environments. Command-line operations are dangerous and should be used with caution. MoLing supports features like file system operations, command-line terminal execution, browser control powered by 'github.com/chromedp/chromedp', and future plans for personal PC data organization, document writing assistance, schedule planning, and life assistant features. MoLing has been tested on macOS but may have issues on other operating systems.
aigne-doc-smith
AIGNE DocSmith is a powerful AI-driven documentation generation tool that automates the creation of detailed, structured, and multi-language documentation directly from source code. It intelligently analyzes codebase to generate a comprehensive document structure, populates content with high-quality AI-powered generation, supports seamless translation into 12+ languages, integrates with AIGNE Hub for large language models, offers Discuss Kit publishing, automatically updates documentation with source code changes, and allows for individual document optimization.
aiogram_bot_template
Aiogram bot template is a boilerplate for creating Telegram bots using Aiogram framework. It provides a solid foundation for building robust and scalable bots with a focus on code organization, database integration, and localization.
y-gui
y-gui is a web-based graphical interface for AI chat interactions with support for multiple AI models and powerful MCP integrations. It provides interactive chat capabilities with AI models, supports multiple bot configurations, and integrates with Gmail, Google Calendar, and image generation services. The tool offers a comprehensive MCP integration system, secure authentication with Auth0 and Google login, dark/light theme support, real-time updates, and responsive design for all devices. The architecture consists of a frontend React application and a backend Cloudflare Workers with D1 storage. It allows users to manage emails, create calendar events, and generate images directly within chat conversations.
flock
Flock is a workflow-based low-code platform that enables rapid development of chatbots, RAG applications, and coordination of multi-agent teams. It offers a flexible, low-code solution for orchestrating collaborative agents, supporting various node types for specific tasks, such as input processing, text generation, knowledge retrieval, tool execution, intent recognition, answer generation, and more. Flock integrates LangChain and LangGraph to provide offline operation capabilities and supports future nodes like Conditional Branch, File Upload, and Parameter Extraction for creating complex workflows. Inspired by StreetLamb, Lobe-chat, Dify, and fastgpt projects, Flock introduces new features and directions while leveraging open-source models and multi-tenancy support.
comfyui-web-viewer
The ComfyUI Web Viewer by vrch.ai is a real-time AI-generated interactive art framework that integrates realtime streaming into ComfyUI workflows. It supports keyboard control nodes, OSC control nodes, sound input nodes, and more, accessible from any device with a web browser. It enables real-time interaction with AI-generated content, ideal for interactive visual projects and enhancing ComfyUI workflows with efficient content management and display.
fast-mcp
Fast MCP is a Ruby gem that simplifies the integration of AI models with your Ruby applications. It provides a clean implementation of the Model Context Protocol, eliminating complex communication protocols, integration challenges, and compatibility issues. With Fast MCP, you can easily connect AI models to your servers, share data resources, choose from multiple transports, integrate with frameworks like Rails and Sinatra, and secure your AI-powered endpoints. The gem also offers real-time updates and authentication support, making AI integration a seamless experience for developers.
orra
Orra is a tool for building production-ready multi-agent applications that handle complex real-world interactions. It coordinates tasks across existing stack, agents, and tools run as services using intelligent reasoning. With features like smart pre-evaluated execution plans, domain grounding, durable execution, and automatic service health monitoring, Orra enables users to go fast with tools as services and revert state to handle failures. It provides real-time status tracking and webhook result delivery, making it ideal for developers looking to move beyond simple crews and agents.
For similar tasks

mcpm.sh
MCPM is an open source CLI tool for managing MCP servers, providing a simplified global configuration approach to install servers once, organize them with profiles, and integrate them into any MCP client. Features include server discovery, direct execution, sharing capabilities, and client integration tools. It eliminates the complexity of v1's target-based system in favor of a clean global workspace model. The tool is designed to be AI agent friendly with comprehensive automation support and a rich CLI interface.
For similar jobs

AirGo
AirGo is a front and rear end separation, multi user, multi protocol proxy service management system, simple and easy to use. It supports vless, vmess, shadowsocks, and hysteria2.
mosec
Mosec is a high-performance and flexible model serving framework for building ML model-enabled backend and microservices. It bridges the gap between any machine learning models you just trained and the efficient online service API. * **Highly performant** : web layer and task coordination built with Rust 🦀, which offers blazing speed in addition to efficient CPU utilization powered by async I/O * **Ease of use** : user interface purely in Python 🐍, by which users can serve their models in an ML framework-agnostic manner using the same code as they do for offline testing * **Dynamic batching** : aggregate requests from different users for batched inference and distribute results back * **Pipelined stages** : spawn multiple processes for pipelined stages to handle CPU/GPU/IO mixed workloads * **Cloud friendly** : designed to run in the cloud, with the model warmup, graceful shutdown, and Prometheus monitoring metrics, easily managed by Kubernetes or any container orchestration systems * **Do one thing well** : focus on the online serving part, users can pay attention to the model optimization and business logic
llm-code-interpreter
The 'llm-code-interpreter' repository is a deprecated plugin that provides a code interpreter on steroids for ChatGPT by E2B. It gives ChatGPT access to a sandboxed cloud environment with capabilities like running any code, accessing Linux OS, installing programs, using filesystem, running processes, and accessing the internet. The plugin exposes commands to run shell commands, read files, and write files, enabling various possibilities such as running different languages, installing programs, starting servers, deploying websites, and more. It is powered by the E2B API and is designed for agents to freely experiment within a sandboxed environment.

pezzo
Pezzo is a fully cloud-native and open-source LLMOps platform that allows users to observe and monitor AI operations, troubleshoot issues, save costs and latency, collaborate, manage prompts, and deliver AI changes instantly. It supports various clients for prompt management, observability, and caching. Users can run the full Pezzo stack locally using Docker Compose, with prerequisites including Node.js 18+, Docker, and a GraphQL Language Feature Support VSCode Extension. Contributions are welcome, and the source code is available under the Apache 2.0 License.
learn-generative-ai
Learn Cloud Applied Generative AI Engineering (GenEng) is a course focusing on the application of generative AI technologies in various industries. The course covers topics such as the economic impact of generative AI, the role of developers in adopting and integrating generative AI technologies, and the future trends in generative AI. Students will learn about tools like OpenAI API, LangChain, and Pinecone, and how to build and deploy Large Language Models (LLMs) for different applications. The course also explores the convergence of generative AI with Web 3.0 and its potential implications for decentralized intelligence.
gcloud-aio
This repository contains shared codebase for two projects: gcloud-aio and gcloud-rest. gcloud-aio is built for Python 3's asyncio, while gcloud-rest is a threadsafe requests-based implementation. It provides clients for Google Cloud services like Auth, BigQuery, Datastore, KMS, PubSub, Storage, and Task Queue. Users can install the library using pip and refer to the documentation for usage details. Developers can contribute to the project by following the contribution guide.
fluid
Fluid is an open source Kubernetes-native Distributed Dataset Orchestrator and Accelerator for data-intensive applications, such as big data and AI applications. It implements dataset abstraction, scalable cache runtime, automated data operations, elasticity and scheduling, and is runtime platform agnostic. Key concepts include Dataset and Runtime. Prerequisites include Kubernetes version > 1.16, Golang 1.18+, and Helm 3. The tool offers features like accelerating remote file accessing, machine learning, accelerating PVC, preloading dataset, and on-the-fly dataset cache scaling. Contributions are welcomed, and the project is under the Apache 2.0 license with a vendor-neutral approach.
aiges
AIGES is a core component of the Athena Serving Framework, designed as a universal encapsulation tool for AI developers to deploy AI algorithm models and engines quickly. By integrating AIGES, you can deploy AI algorithm models and engines rapidly and host them on the Athena Serving Framework, utilizing supporting auxiliary systems for networking, distribution strategies, data processing, etc. The Athena Serving Framework aims to accelerate the cloud service of AI algorithm models and engines, providing multiple guarantees for cloud service stability through cloud-native architecture. You can efficiently and securely deploy, upgrade, scale, operate, and monitor models and engines without focusing on underlying infrastructure and service-related development, governance, and operations.






