
fast-mcp
A Ruby Implementation of the Model Context Protocol
Stars: 1010
Fast MCP is a Ruby gem that simplifies the integration of AI models with your Ruby applications. It provides a clean implementation of the Model Context Protocol, eliminating complex communication protocols, integration challenges, and compatibility issues. With Fast MCP, you can easily connect AI models to your servers, share data resources, choose from multiple transports, integrate with frameworks like Rails and Sinatra, and secure your AI-powered endpoints. The gem also offers real-time updates and authentication support, making AI integration a seamless experience for developers.
README:
No complex protocols, no integration headaches, no compatibility issues – just beautiful, expressive Ruby code.
AI models are powerful, but they need to interact with your applications to be truly useful. Traditional approaches mean wrestling with:
- 🔄 Complex communication protocols and custom JSON formats
- 🔌 Integration challenges with different model providers
- 🧩 Compatibility issues between your app and AI tools
- 🧠 Managing the state between AI interactions and your data
Fast MCP solves all these problems by providing a clean, Ruby-focused implementation of the Model Context Protocol, making AI integration a joy, not a chore.
- 🛠️ Tools API - Let AI models call your Ruby functions securely, with in-depth argument validation through Dry-Schema.
- 📚 Resources API - Share data between your app and AI models
- 🔄 Multiple Transports - Choose from STDIO, HTTP, or SSE based on your needs
- 🧩 Framework Integration - Works seamlessly with Rails, Sinatra or any Rack app.
- 🔒 Authentication Support - Secure your AI-powered endpoints with ease
- 🚀 Real-time Updates - Subscribe to changes for interactive applications
- 🎯 Dynamic Filtering - Control tool/resource access based on request context (permissions, API versions, etc.)
# Define tools for AI models to use
server = FastMcp::Server.new(name: 'popular-users', version: '1.0.0')
# Define a tool by inheriting from FastMcp::Tool
class CreateUserTool < FastMcp::Tool
description "Create a user"
# These arguments will generate the needed JSON to be presented to the MCP Client
# And they will be validated at run time.
# The validation is based off Dry-Schema, with the addition of the description.
arguments do
required(:first_name).filled(:string).description("First name of the user")
optional(:age).filled(:integer).description("Age of the user")
required(:address).description("The shipping address").hash do
required(:street).filled(:string).description("Street address")
optional(:city).filled(:string).description("City name")
optional(:zipcode).maybe(:string).description("Postal code")
end
end
def call(first_name:, age: nil, address: {})
User.create!(first_name:, age:, address:)
end
end
# Register the tool with the server
server.register_tool(CreateUserTool)
# Share data resources with AI models by inheriting from FastMcp::Resource
class PopularUsers < FastMcp::Resource
uri "myapp:///users/popular"
resource_name "Popular Users"
mime_type "application/json"
def content
JSON.generate(User.popular.limit(5).as_json)
end
end
class User < FastMcp::Resource
uri "myapp:///users/{id}" # This is a resource template
resource_name "user"
mime_type "application/json"
def content
id = params[:id] # params are computed from the uri pattern
JSON.generate(User.find(id).as_json)
end
end
# Register the resource with the server
server.register_resources(PopularUsers, User)
# Accessing the resource through the server
server.read_resource(PopularUsers.uri)
# Notify the resource content has been updated to clients
server.notify_resource_updated(PopularUsers.variabilized_uri)
# Notifiy the content of a resource from a template has been updated to clients
server.notify_resource_updated(User.variabilized_uri(id: 1))Control which tools and resources are available based on request context:
# Tag your tools for easy filtering
class AdminTool < FastMcp::Tool
tags :admin, :dangerous
description "Perform admin operations"
def call
# Admin only functionality
end
end
# Filter tools based on user permissions
server.filter_tools do |request, tools|
user_role = request.params['role']
case user_role
when 'admin'
tools # Admins see all tools
when 'user'
tools.reject { |t| t.tags.include?(:admin) }
else
tools.select { |t| t.tags.include?(:public) }
end
endbundle add fast-mcp
bin/rails generate fast_mcp:installThis will add a configurable fast_mcp.rb initializer
require 'fast_mcp'
FastMcp.mount_in_rails(
Rails.application,
name: Rails.application.class.module_parent_name.underscore.dasherize,
version: '1.0.0',
path_prefix: '/mcp', # This is the default path prefix
messages_route: 'messages', # This is the default route for the messages endpoint
sse_route: 'sse', # This is the default route for the SSE endpoint
# Add allowed origins below, it defaults to Rails.application.config.hosts
# allowed_origins: ['localhost', '127.0.0.1', 'example.com', /.*\.example\.com/],
# localhost_only: true, # Set to false to allow connections from other hosts
# whitelist specific ips to if you want to run on localhost and allow connections from other IPs
# allowed_ips: ['127.0.0.1', '::1']
# authenticate: true, # Uncomment to enable authentication
# auth_token: 'your-token' # Required if authenticate: true
) do |server|
Rails.application.config.after_initialize do
# FastMcp will automatically discover and register:
# - All classes that inherit from ApplicationTool (which uses ActionTool::Base)
# - All classes that inherit from ApplicationResource (which uses ActionResource::Base)
server.register_tools(*ApplicationTool.descendants)
server.register_resources(*ApplicationResource.descendants)
# alternatively, you can register tools and resources manually:
# server.register_tool(MyTool)
# server.register_resource(MyResource)
end
endThe install script will also:
- add app/resources folder
- add app/tools folder
- add app/tools/sample_tool.rb
- add app/resources/sample_resource.rb
- add ApplicationTool to inherit from
- add ApplicationResource to inherit from as well
For Rails applications, FastMCP provides Rails-style class names to better fit with Rails conventions:
-
ActionTool::Base- An alias forFastMcp::Tool -
ActionResource::Base- An alias forFastMcp::Resource
These are automatically set up in Rails applications. You can use either naming convention in your code:
# Using Rails-style naming:
class MyTool < ActionTool::Base
description "My awesome tool"
arguments do
required(:input).filled(:string)
end
def call(input:)
# Your implementation
end
end
# Using standard FastMcp naming:
class AnotherTool < FastMcp::Tool
# Both styles work interchangeably in Rails apps
endWhen creating new tools or resources, the generators will use the Rails naming convention by default:
# app/tools/application_tool.rb
class ApplicationTool < ActionTool::Base
# Base methods for all tools
end
# app/resources/application_resource.rb
class ApplicationResource < ActionResource::Base
# Base methods for all resources
endI'll let you check out the dedicated sinatra integration docs.
require 'fast_mcp'
# Create an MCP server
server = FastMcp::Server.new(name: 'my-ai-server', version: '1.0.0')
# Define a tool by inheriting from FastMcp::Tool
class SummarizeTool < FastMcp::Tool
description "Summarize a given text"
arguments do
required(:text).filled(:string).description("Text to summarize")
optional(:max_length).filled(:integer).description("Maximum length of summary")
end
def call(text:, max_length: 100)
# Your summarization logic here
text.split('.').first(3).join('.') + '...'
end
end
# Register the tool with the server
server.register_tool(SummarizeTool)
# Create a resource by inheriting from FastMcp::Resource
class StatisticsResource < FastMcp::Resource
uri "data/statistics"
resource_name "Usage Statistics"
description "Current system statistics"
mime_type "application/json"
def content
JSON.generate({
users_online: 120,
queries_per_minute: 250,
popular_topics: ["Ruby", "AI", "WebDev"]
})
end
end
# Register the resource with the server
server.register_resource(StatisticsResource)
# Start the server
server.startMCP has developed a very useful inspector. You can use it to validate your implementation. I suggest you use the examples I provided with this project as an easy boilerplate. Clone this project, then give it a go !
npx @modelcontextprotocol/inspector examples/server_with_stdio_transport.rbOr to test with an SSE transport using a rack middleware:
npx @modelcontextprotocol/inspector examples/rack_middleware.rbOr to test over SSE with an authenticated rack middleware:
npx @modelcontextprotocol/inspector examples/authenticated_rack_middleware.rbYou can test your custom implementation with the official MCP inspector by using:
# Test with a stdio transport:
npx @modelcontextprotocol/inspector path/to/your_ruby_file.rb
# Test with an HTTP / SSE server. In the UI select SSE and input your address.
npx @modelcontextprotocol/inspector# app.rb
require 'sinatra'
require 'fast_mcp'
use FastMcp::RackMiddleware.new(name: 'my-ai-server', version: '1.0.0') do |server|
# Register tools and resources here
server.register_tool(SummarizeTool)
end
get '/' do
'Hello World!'
endAdd your server to your Claude Desktop configuration at:
- macOS:
~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json - Windows:
%APPDATA%\Claude\claude_desktop_config.json
{
"mcpServers": {
"my-great-server": {
"command": "ruby",
"args": ["/Users/path/to/your/awesome/fast-mcp/server.rb"]
}
}
}Please refer to configuring_mcp_clients
| Feature | Status |
|---|---|
| ✅ JSON-RPC 2.0 | Full implementation for communication |
| ✅ Tool Definition & Calling | Define and call tools with rich argument types |
| ✅ Resource & Resource Templates Management | Create, read, update, and subscribe to resources |
| ✅ Transport Options | STDIO, HTTP, and SSE for flexible integration |
| ✅ Framework Integration | Rails, Sinatra, Hanami, and any Rack-compatible framework |
| ✅ Authentication | Secure your AI endpoints with token authentication |
| ✅ Schema Support | Full JSON Schema for tool arguments with validation |
- 🤖 AI-powered Applications: Connect LLMs to your Ruby app's functionality
- 📊 Real-time Dashboards: Build dashboards with live AI-generated insights
- 🔗 Microservice Communication: Use MCP as a clean protocol between services
- 📚 Interactive Documentation: Create AI-enhanced API documentation
- 💬 Chatbots and Assistants: Build AI assistants with access to your app's data
Fast MCP includes built-in security features to protect your applications:
The HTTP/SSE transport validates the Origin header on all incoming connections to prevent DNS rebinding attacks, which could allow malicious websites to interact with local MCP servers.
# Configure allowed origins (defaults to ['localhost', '127.0.0.1'])
FastMcp.rack_middleware(app,
allowed_origins: ['localhost', '127.0.0.1', 'your-domain.com', /.*\.your-domain\.com/],
localhost_only: false,
allowed_ips: ['192.168.1.1', '10.0.0.1'],
# other options...
)Fast MCP supports token-based authentication for all connections:
# Enable authentication
FastMcp.authenticated_rack_middleware(app,
auth_token: 'your-secret-token',
# other options...
)- 🚀 Getting Started Guide
- 🧩 Integration Guide
- 🛤️ Rails Integration
- 🌐 Sinatra Integration
- 📚 Resources
- 🛠️ Tools
- 🔒 Security
- 🎯 Dynamic Filtering
Check out the examples directory for more detailed examples:
-
🔨 Basic Examples:
-
🌐 Web Integration:
- Ruby 3.2+
We welcome contributions to Fast MCP! Here's how you can help:
- Fork the repository
- Create your feature branch (
git checkout -b my-new-feature) - Commit your changes (
git commit -am 'Add some feature') - Push to the branch (
git push origin my-new-feature) - Create a new Pull Request
Please read our Contributing Guide for more details.
This project is available as open source under the terms of the MIT License.
- The Model Context Protocol team for creating the specification
- The Dry-Schema team for the argument validation.
- All contributors to this project
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for fast-mcp
Similar Open Source Tools

fast-mcp
Fast MCP is a Ruby gem that simplifies the integration of AI models with your Ruby applications. It provides a clean implementation of the Model Context Protocol, eliminating complex communication protocols, integration challenges, and compatibility issues. With Fast MCP, you can easily connect AI models to your servers, share data resources, choose from multiple transports, integrate with frameworks like Rails and Sinatra, and secure your AI-powered endpoints. The gem also offers real-time updates and authentication support, making AI integration a seamless experience for developers.
action_mcp
Action MCP is a powerful tool for managing and automating your cloud infrastructure. It provides a user-friendly interface to easily create, update, and delete resources on popular cloud platforms. With Action MCP, you can streamline your deployment process, reduce manual errors, and improve overall efficiency. The tool supports various cloud providers and offers a wide range of features to meet your infrastructure management needs. Whether you are a developer, system administrator, or DevOps engineer, Action MCP can help you simplify and optimize your cloud operations.
open-responses
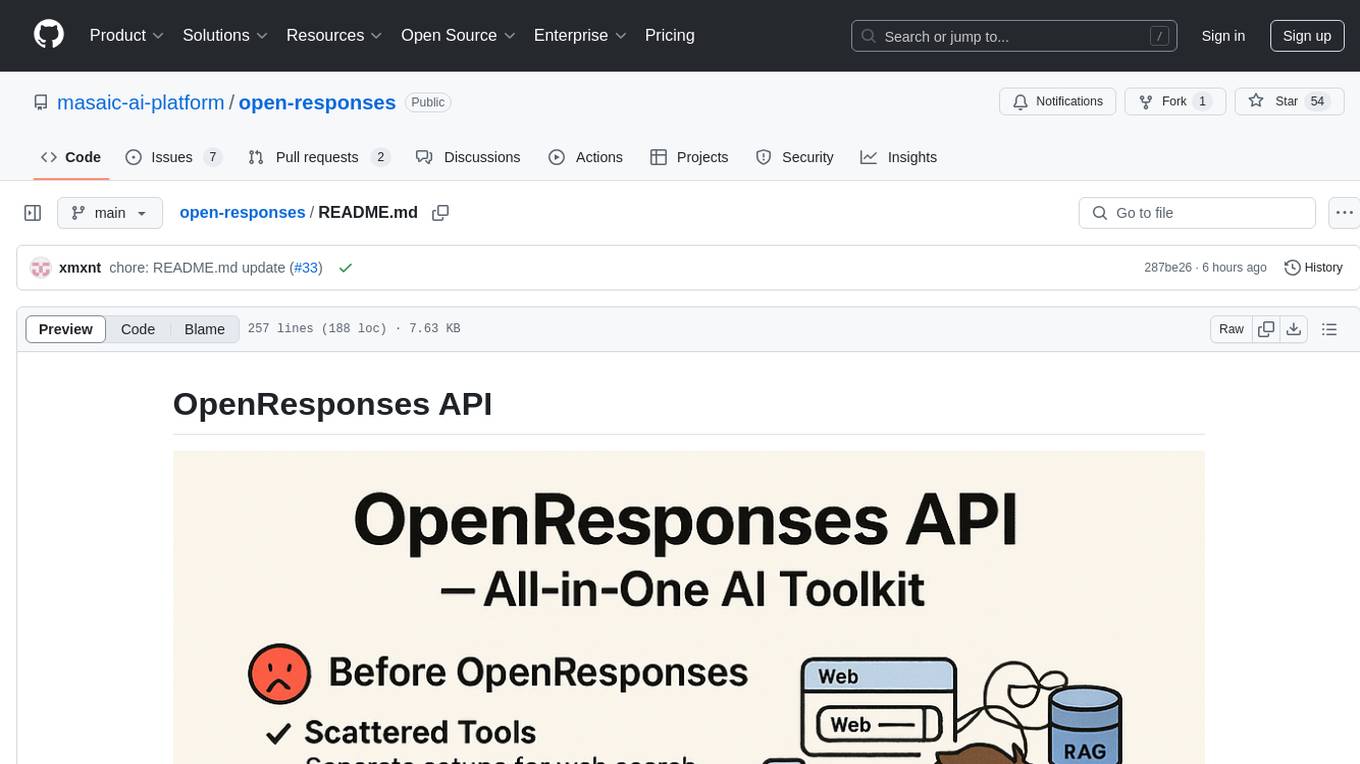
OpenResponses API provides enterprise-grade AI capabilities through a powerful API, simplifying development and deployment while ensuring complete data control. It offers automated tracing, integrated RAG for contextual information retrieval, pre-built tool integrations, self-hosted architecture, and an OpenAI-compatible interface. The toolkit addresses development challenges like feature gaps and integration complexity, as well as operational concerns such as data privacy and operational control. Engineering teams can benefit from improved productivity, production readiness, compliance confidence, and simplified architecture by choosing OpenResponses.
agentpress
AgentPress is a collection of simple but powerful utilities that serve as building blocks for creating AI agents. It includes core components for managing threads, registering tools, processing responses, state management, and utilizing LLMs. The tool provides a modular architecture for handling messages, LLM API calls, response processing, tool execution, and results management. Users can easily set up the environment, create custom tools with OpenAPI or XML schema, and manage conversation threads with real-time interaction. AgentPress aims to be agnostic, simple, and flexible, allowing users to customize and extend functionalities as needed.
context7
Context7 is a powerful tool for analyzing and visualizing data in various formats. It provides a user-friendly interface for exploring datasets, generating insights, and creating interactive visualizations. With advanced features such as data filtering, aggregation, and customization, Context7 is suitable for both beginners and experienced data analysts. The tool supports a wide range of data sources and formats, making it versatile for different use cases. Whether you are working on exploratory data analysis, data visualization, or data storytelling, Context7 can help you uncover valuable insights and communicate your findings effectively.
recommendarr
Recommendarr is a tool that generates personalized TV show and movie recommendations based on your Sonarr, Radarr, Plex, and Jellyfin libraries using AI. It offers AI-powered recommendations, media server integration, flexible AI support, watch history analysis, customization options, and dark/light mode toggle. Users can connect their media libraries and watch history services, configure AI service settings, and get personalized recommendations based on genre, language, and mood/vibe preferences. The tool works with any OpenAI-compatible API and offers various recommended models for different cost options and performance levels. It provides personalized suggestions, detailed information, filter options, watch history analysis, and one-click adding of recommended content to Sonarr/Radarr.
ai-dial-sdk
AI DIAL Python SDK is a framework designed to create applications and model adapters for AI DIAL API, which is based on Azure OpenAI API. It provides a user-friendly interface for routing requests to applications. The SDK includes features for chat completions, response generation, and API interactions. Developers can easily build and deploy AI-powered applications using this SDK, ensuring compatibility with the AI DIAL platform.
ai-gateway
LangDB AI Gateway is an open-source enterprise AI gateway built in Rust. It provides a unified interface to all LLMs using the OpenAI API format, focusing on high performance, enterprise readiness, and data control. The gateway offers features like comprehensive usage analytics, cost tracking, rate limiting, data ownership, and detailed logging. It supports various LLM providers and provides OpenAI-compatible endpoints for chat completions, model listing, embeddings generation, and image generation. Users can configure advanced settings, such as rate limiting, cost control, dynamic model routing, and observability with OpenTelemetry tracing. The gateway can be run with Docker Compose and integrated with MCP tools for server communication.

LEANN
LEANN is an innovative vector database that democratizes personal AI, transforming your laptop into a powerful RAG system that can index and search through millions of documents using 97% less storage than traditional solutions without accuracy loss. It achieves this through graph-based selective recomputation and high-degree preserving pruning, computing embeddings on-demand instead of storing them all. LEANN allows semantic search of file system, emails, browser history, chat history, codebase, or external knowledge bases on your laptop with zero cloud costs and complete privacy. It is a drop-in semantic search MCP service fully compatible with Claude Code, enabling intelligent retrieval without changing your workflow.
openai-kotlin
OpenAI Kotlin API client is a Kotlin client for OpenAI's API with multiplatform and coroutines capabilities. It allows users to interact with OpenAI's API using Kotlin programming language. The client supports various features such as models, chat, images, embeddings, files, fine-tuning, moderations, audio, assistants, threads, messages, and runs. It also provides guides on getting started, chat & function call, file source guide, and assistants. Sample apps are available for reference, and troubleshooting guides are provided for common issues. The project is open-source and licensed under the MIT license, allowing contributions from the community.

langserve
LangServe helps developers deploy `LangChain` runnables and chains as a REST API. This library is integrated with FastAPI and uses pydantic for data validation. In addition, it provides a client that can be used to call into runnables deployed on a server. A JavaScript client is available in LangChain.js.

golf
Golf is a simple command-line tool for calculating the distance between two geographic coordinates. It uses the Haversine formula to accurately determine the distance between two points on the Earth's surface. This tool is useful for developers working on location-based applications or projects that require distance calculations. With Golf, users can easily input latitude and longitude coordinates and get the precise distance in kilometers or miles. The tool is lightweight, easy to use, and can be integrated into various programming workflows.
orra
Orra is a tool for building production-ready multi-agent applications that handle complex real-world interactions. It coordinates tasks across existing stack, agents, and tools run as services using intelligent reasoning. With features like smart pre-evaluated execution plans, domain grounding, durable execution, and automatic service health monitoring, Orra enables users to go fast with tools as services and revert state to handle failures. It provides real-time status tracking and webhook result delivery, making it ideal for developers looking to move beyond simple crews and agents.
fraim
Fraim is an AI-powered toolkit designed for security engineers to enhance their workflows by leveraging AI capabilities. It offers solutions to find, detect, fix, and flag vulnerabilities throughout the development lifecycle. The toolkit includes features like Risk Flagger for identifying risks in code changes, Code Security Analysis for context-aware vulnerability detection, and Infrastructure as Code Analysis for spotting misconfigurations in cloud environments. Fraim can be run as a CLI tool or integrated into Github Actions, making it a versatile solution for security teams and organizations looking to enhance their security practices with AI technology.
graphiti
Graphiti is a framework for building and querying temporally-aware knowledge graphs, tailored for AI agents in dynamic environments. It continuously integrates user interactions, structured and unstructured data, and external information into a coherent, queryable graph. The framework supports incremental data updates, efficient retrieval, and precise historical queries without complete graph recomputation, making it suitable for developing interactive, context-aware AI applications.
Scrapling
Scrapling is a high-performance, intelligent web scraping library for Python that automatically adapts to website changes while significantly outperforming popular alternatives. For both beginners and experts, Scrapling provides powerful features while maintaining simplicity. It offers features like fast and stealthy HTTP requests, adaptive scraping with smart element tracking and flexible selection, high performance with lightning-fast speed and memory efficiency, and developer-friendly navigation API and rich text processing. It also includes advanced parsing features like smart navigation, content-based selection, handling structural changes, and finding similar elements. Scrapling is designed to handle anti-bot protections and website changes effectively, making it a versatile tool for web scraping tasks.
For similar tasks

fast-mcp
Fast MCP is a Ruby gem that simplifies the integration of AI models with your Ruby applications. It provides a clean implementation of the Model Context Protocol, eliminating complex communication protocols, integration challenges, and compatibility issues. With Fast MCP, you can easily connect AI models to your servers, share data resources, choose from multiple transports, integrate with frameworks like Rails and Sinatra, and secure your AI-powered endpoints. The gem also offers real-time updates and authentication support, making AI integration a seamless experience for developers.
flute
FLUTE (Flexible Lookup Table Engine for LUT-quantized LLMs) is a tool designed for uniform quantization and lookup table quantization of weights in lower-precision intervals. It offers flexibility in mapping intervals to arbitrary values through a lookup table. FLUTE supports various quantization formats such as int4, int3, int2, fp4, fp3, fp2, nf4, nf3, nf2, and even custom tables. The tool also introduces new quantization algorithms like Learned Normal Float (NFL) for improved performance and calibration data learning. FLUTE provides benchmarks, model zoo, and integration with frameworks like vLLM and HuggingFace for easy deployment and usage.
KernelBench
KernelBench is a benchmark tool designed to evaluate Large Language Models' (LLMs) ability to generate GPU kernels. It focuses on transpiling operators from PyTorch to CUDA kernels at different levels of granularity. The tool categorizes problems into four levels, ranging from single-kernel operators to full model architectures, and assesses solutions based on compilation, correctness, and speed. The repository provides a structured directory layout, setup instructions, usage examples for running single or multiple problems, and upcoming roadmap features like additional GPU platform support and integration with other frameworks.
frontman
Frontman is a framework-integrated AI coding agent that allows users to edit their frontend directly in the browser. It enables users to point at any element in their running app, describe the change they want, and Frontman edits the source code for them without the need for copy-pasting or context switching. The tool supports popular frameworks like Next.js, Astro, and Vite, providing features such as point-and-click editing, real-time streaming of AI-generated edits, and framework-aware context. Frontman also offers an open protocol layer for decoupled and extensible client, server, and framework adapters.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.

