
LLMs-Planning
An extensible benchmark for evaluating large language models on planning
Stars: 329
This repository contains code for three papers related to evaluating large language models on planning and reasoning about change. It includes benchmarking tools and analysis for assessing the planning abilities of large language models. The latest addition evaluates and enhances the planning and scheduling capabilities of a specific language reasoning model. The repository provides a static test set leaderboard showcasing model performance on various tasks with natural language and planning domain prompts.
README:
This repo has the code for three papers:
- The code in 'plan-bench' subdirectory belongs to the paper "PlanBench: An Extensible Benchmark for Evaluating Large Language Models on Planning and Reasoning about Change"
- The code in 'llm_planning_analysis' subdirectory belongs to the paper "On the Planning Abilities of Large Language Models--A Critical Investigation"
- NEW: 'llm_planning_analysis' subdirectory also contains the code for the paper "Planning in Strawberry Fields: Evaluating and Improving the Planning and Scheduling Capabilities of LRM o1"
The leaderboard below shows the performance of the models on the PlanBench static test set with zero-shot prompting. Check out llm_planning_analysis/results/ folder for the detailed files. For Blocksworld Hard, the results are included in results/backprompting/ folder.
| Model Name | Model Type | Blocksworld - NL - 600 instances | Mystery Blocksworld - NL - 600 instances | Randomized Mystery Blocksworld - NL - 600 instances | Blocksworld Hard - PDDL - 110 instances |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deepseek R1 | LRM | 99.1% | 54.1% | 25.8% | 53.6% |
| o1-mini | LRM | 56.6% | 19.1% | 3.5% | 10% |
| o1-preview | LRM | 97.8% | 52.8% | 37.3% | 23.65% |
| Claude-3.5 Sonnet | LLM | 54.8% | 0% | - | - |
| GPT-4o | LLM | 35.5% | 0% | - | - |
| LLaMA-3.1 405B | LLM | 62.6% | 0.8% | - | - |
| Claude 3 Opus | LLM | 59.3% | 0% | - | - |
| LLaMA-3 70B | LLM | 34.16% | 0% | - | - |
| GPT-4 | LLM | 34.6% | 0% | - | - |
| Gemini 1.5 Pro | LLM | 23.8% | - | - | - |
Note: LLM = Large Language Model, LRM = Language Reasoning Model, NL = Natural Language Prompting, PDDL = Planning Domain Definition Language Prompting
Kindly submit results of any new models by submitting a pull request with the result file and the leaderboard will be updated.
PlanBench - NeurIPS 2023 Datasets and Benchmarks Track:
@article{valmeekam2023planbench,
title={Planbench: An extensible benchmark for evaluating large language models on planning and reasoning about change},
author={Valmeekam, Karthik and Marquez, Matthew and Olmo, Alberto and Sreedharan, Sarath and Kambhampati, Subbarao},
journal={Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems},
volume={36},
pages={38975--38987},
year={2023}
}
On the Planning Abilities of Large Language Models - NeurIPS 2023 Spotlight:
@article{valmeekam2023planning,
title={On the planning abilities of large language models-a critical investigation},
author={Valmeekam, Karthik and Marquez, Matthew and Sreedharan, Sarath and Kambhampati, Subbarao},
journal={Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems},
volume={36},
pages={75993--76005},
year={2023}
}
Planning in Strawberry Fields - A version to appear in TMLR:
@article{valmeekam2024planning,
title={Planning in Strawberry Fields: Evaluating and Improving the Planning and Scheduling Capabilities of LRM o1},
author={Valmeekam, Karthik and Stechly, Kaya and Gundawar, Atharva and Kambhampati, Subbarao},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2410.02162},
year={2024}
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for LLMs-Planning
Similar Open Source Tools

LLMs-Planning
This repository contains code for three papers related to evaluating large language models on planning and reasoning about change. It includes benchmarking tools and analysis for assessing the planning abilities of large language models. The latest addition evaluates and enhances the planning and scheduling capabilities of a specific language reasoning model. The repository provides a static test set leaderboard showcasing model performance on various tasks with natural language and planning domain prompts.
LLM-PowerHouse-A-Curated-Guide-for-Large-Language-Models-with-Custom-Training-and-Inferencing
LLM-PowerHouse is a comprehensive and curated guide designed to empower developers, researchers, and enthusiasts to harness the true capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) and build intelligent applications that push the boundaries of natural language understanding. This GitHub repository provides in-depth articles, codebase mastery, LLM PlayLab, and resources for cost analysis and network visualization. It covers various aspects of LLMs, including NLP, models, training, evaluation metrics, open LLMs, and more. The repository also includes a collection of code examples and tutorials to help users build and deploy LLM-based applications.
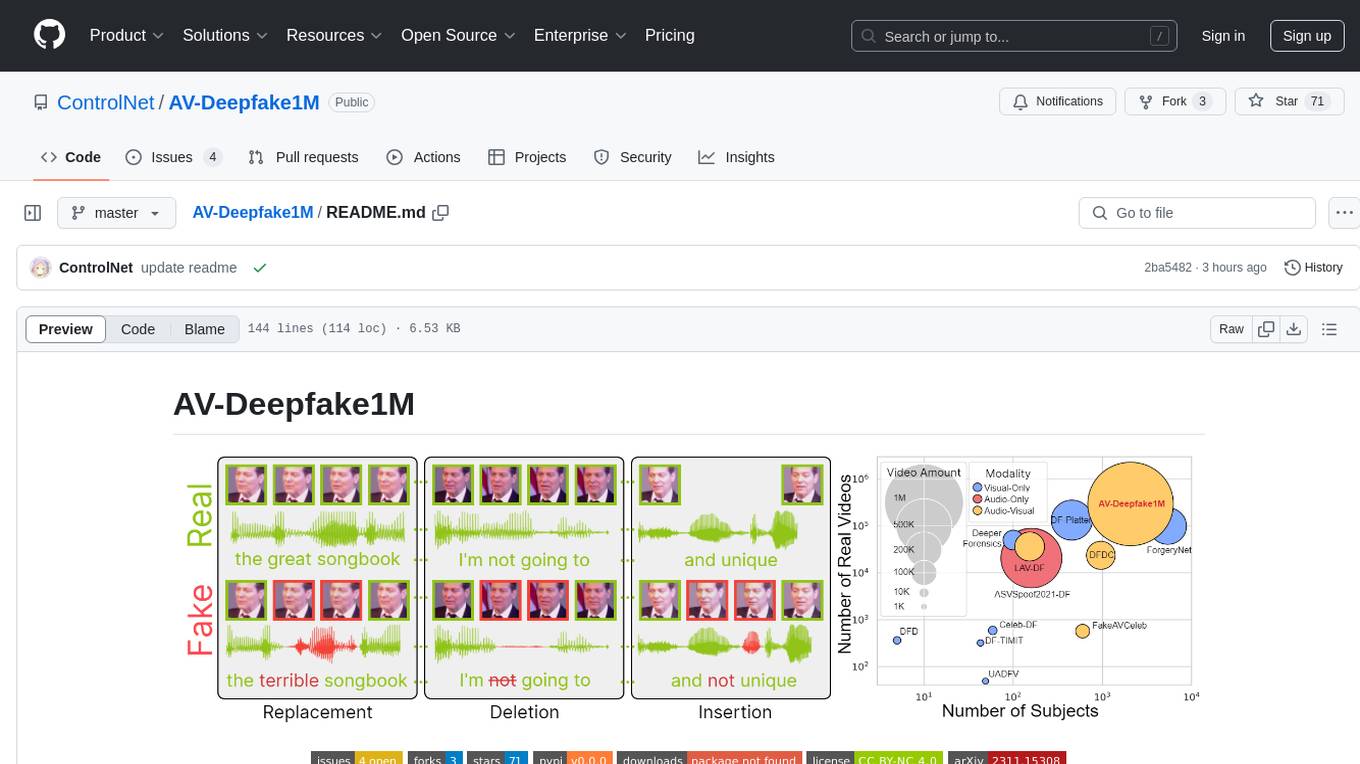
AV-Deepfake1M
The AV-Deepfake1M repository is the official repository for the paper AV-Deepfake1M: A Large-Scale LLM-Driven Audio-Visual Deepfake Dataset. It addresses the challenge of detecting and localizing deepfake audio-visual content by proposing a dataset containing video manipulations, audio manipulations, and audio-visual manipulations for over 2K subjects resulting in more than 1M videos. The dataset is crucial for developing next-generation deepfake localization methods.
llm-compression-intelligence
This repository presents the findings of the paper "Compression Represents Intelligence Linearly". The study reveals a strong linear correlation between the intelligence of LLMs, as measured by benchmark scores, and their ability to compress external text corpora. Compression efficiency, derived from raw text corpora, serves as a reliable evaluation metric that is linearly associated with model capabilities. The repository includes the compression corpora used in the paper, code for computing compression efficiency, and data collection and processing pipelines.
Awesome-LLM-Large-Language-Models-Notes
Awesome-LLM-Large-Language-Models-Notes is a repository that provides a comprehensive collection of information on various Large Language Models (LLMs) classified by year, size, and name. It includes details on known LLM models, their papers, implementations, and specific characteristics. The repository also covers LLM models classified by architecture, must-read papers, blog articles, tutorials, and implementations from scratch. It serves as a valuable resource for individuals interested in understanding and working with LLMs in the field of Natural Language Processing (NLP).
llm-datasets
LLM Datasets is a repository containing high-quality datasets, tools, and concepts for LLM fine-tuning. It provides datasets with characteristics like accuracy, diversity, and complexity to train large language models for various tasks. The repository includes datasets for general-purpose, math & logic, code, conversation & role-play, and agent & function calling domains. It also offers guidance on creating high-quality datasets through data deduplication, data quality assessment, data exploration, and data generation techniques.
aideml
AIDE is a machine learning code generation agent that can generate solutions for machine learning tasks from natural language descriptions. It has the following features: 1. **Instruct with Natural Language**: Describe your problem or additional requirements and expert insights, all in natural language. 2. **Deliver Solution in Source Code**: AIDE will generate Python scripts for the **tested** machine learning pipeline. Enjoy full transparency, reproducibility, and the freedom to further improve the source code! 3. **Iterative Optimization**: AIDE iteratively runs, debugs, evaluates, and improves the ML code, all by itself. 4. **Visualization**: We also provide tools to visualize the solution tree produced by AIDE for a better understanding of its experimentation process. This gives you insights not only about what works but also what doesn't. AIDE has been benchmarked on over 60 Kaggle data science competitions and has demonstrated impressive performance, surpassing 50% of Kaggle participants on average. It is particularly well-suited for tasks that require complex data preprocessing, feature engineering, and model selection.

RobustVLM
This repository contains code for the paper 'Robust CLIP: Unsupervised Adversarial Fine-Tuning of Vision Embeddings for Robust Large Vision-Language Models'. It focuses on fine-tuning CLIP in an unsupervised manner to enhance its robustness against visual adversarial attacks. By replacing the vision encoder of large vision-language models with the fine-tuned CLIP models, it achieves state-of-the-art adversarial robustness on various vision-language tasks. The repository provides adversarially fine-tuned ViT-L/14 CLIP models and offers insights into zero-shot classification settings and clean accuracy improvements.
LLaVA-MORE
LLaVA-MORE is a new family of Multimodal Language Models (MLLMs) that integrates recent language models with diverse visual backbones. The repository provides a unified training protocol for fair comparisons across all architectures and releases training code and scripts for distributed training. It aims to enhance Multimodal LLM performance and offers various models for different tasks. Users can explore different visual backbones like SigLIP and methods for managing image resolutions (S2) to improve the connection between images and language. The repository is a starting point for expanding the study of Multimodal LLMs and enhancing new features in the field.
amber-train
Amber is the first model in the LLM360 family, an initiative for comprehensive and fully open-sourced LLMs. It is a 7B English language model with the LLaMA architecture. The model type is a language model with the same architecture as LLaMA-7B. It is licensed under Apache 2.0. The resources available include training code, data preparation, metrics, and fully processed Amber pretraining data. The model has been trained on various datasets like Arxiv, Book, C4, Refined-Web, StarCoder, StackExchange, and Wikipedia. The hyperparameters include a total of 6.7B parameters, hidden size of 4096, intermediate size of 11008, 32 attention heads, 32 hidden layers, RMSNorm ε of 1e^-6, max sequence length of 2048, and a vocabulary size of 32000.
MathEval
MathEval is a benchmark designed for evaluating the mathematical capabilities of large models. It includes over 20 evaluation datasets covering various mathematical domains with more than 30,000 math problems. The goal is to assess the performance of large models across different difficulty levels and mathematical subfields. MathEval serves as a reliable reference for comparing mathematical abilities among large models and offers guidance on enhancing their mathematical capabilities in the future.
jailbreak_llms
This is the official repository for the ACM CCS 2024 paper 'Do Anything Now': Characterizing and Evaluating In-The-Wild Jailbreak Prompts on Large Language Models. The project employs a new framework called JailbreakHub to conduct the first measurement study on jailbreak prompts in the wild, collecting 15,140 prompts from December 2022 to December 2023, including 1,405 jailbreak prompts. The dataset serves as the largest collection of in-the-wild jailbreak prompts. The repository contains examples of harmful language and is intended for research purposes only.
TableLLM
TableLLM is a large language model designed for efficient tabular data manipulation tasks in real office scenarios. It can generate code solutions or direct text answers for tasks like insert, delete, update, query, merge, and chart operations on tables embedded in spreadsheets or documents. The model has been fine-tuned based on CodeLlama-7B and 13B, offering two scales: TableLLM-7B and TableLLM-13B. Evaluation results show its performance on benchmarks like WikiSQL, Spider, and self-created table operation benchmark. Users can use TableLLM for code and text generation tasks on tabular data.
dl_model_infer
This project is a c++ version of the AI reasoning library that supports the reasoning of tensorrt models. It provides accelerated deployment cases of deep learning CV popular models and supports dynamic-batch image processing, inference, decode, and NMS. The project has been updated with various models and provides tutorials for model exports. It also includes a producer-consumer inference model for specific tasks. The project directory includes implementations for model inference applications, backend reasoning classes, post-processing, pre-processing, and target detection and tracking. Speed tests have been conducted on various models, and onnx downloads are available for different models.
imodels
Python package for concise, transparent, and accurate predictive modeling. All sklearn-compatible and easy to use. _For interpretability in NLP, check out our new package:imodelsX _
PredictorLLM
PredictorLLM is an advanced trading agent framework that utilizes large language models to automate trading in financial markets. It includes a profiling module to establish agent characteristics, a layered memory module for retaining and prioritizing financial data, and a decision-making module to convert insights into trading strategies. The framework mimics professional traders' behavior, surpassing human limitations in data processing and continuously evolving to adapt to market conditions for superior investment outcomes.
For similar tasks

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.

sorrentum
Sorrentum is an open-source project that aims to combine open-source development, startups, and brilliant students to build machine learning, AI, and Web3 / DeFi protocols geared towards finance and economics. The project provides opportunities for internships, research assistantships, and development grants, as well as the chance to work on cutting-edge problems, learn about startups, write academic papers, and get internships and full-time positions at companies working on Sorrentum applications.

tidb
TiDB is an open-source distributed SQL database that supports Hybrid Transactional and Analytical Processing (HTAP) workloads. It is MySQL compatible and features horizontal scalability, strong consistency, and high availability.

zep-python
Zep is an open-source platform for building and deploying large language model (LLM) applications. It provides a suite of tools and services that make it easy to integrate LLMs into your applications, including chat history memory, embedding, vector search, and data enrichment. Zep is designed to be scalable, reliable, and easy to use, making it a great choice for developers who want to build LLM-powered applications quickly and easily.

telemetry-airflow
This repository codifies the Airflow cluster that is deployed at workflow.telemetry.mozilla.org (behind SSO) and commonly referred to as "WTMO" or simply "Airflow". Some links relevant to users and developers of WTMO: * The `dags` directory in this repository contains some custom DAG definitions * Many of the DAGs registered with WTMO don't live in this repository, but are instead generated from ETL task definitions in bigquery-etl * The Data SRE team maintains a WTMO Developer Guide (behind SSO)

mojo
Mojo is a new programming language that bridges the gap between research and production by combining Python syntax and ecosystem with systems programming and metaprogramming features. Mojo is still young, but it is designed to become a superset of Python over time.

pandas-ai
PandasAI is a Python library that makes it easy to ask questions to your data in natural language. It helps you to explore, clean, and analyze your data using generative AI.

databend
Databend is an open-source cloud data warehouse that serves as a cost-effective alternative to Snowflake. With its focus on fast query execution and data ingestion, it's designed for complex analysis of the world's largest datasets.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.