
cog-comfyui
Run ComfyUI with an API
Stars: 604
Cog-comfyui allows users to run ComfyUI workflows on Replicate. ComfyUI is a visual programming tool for creating and sharing generative art workflows. With cog-comfyui, users can access a variety of pre-trained models and custom nodes to create their own unique artworks. The tool is easy to use and does not require any coding experience. Users simply need to upload their API JSON file and any necessary input files, and then click the "Run" button. Cog-comfyui will then generate the output image or video file.
README:
Run ComfyUI workflows on Replicate:
- https://replicate.com/fofr/any-comfyui-workflow
- https://replicate.com/fofr/any-comfyui-workflow-a100
We recommend:
- trying it on the website with your favorite workflow and making sure it works
- using your own instance to run your workflow quickly and efficiently on Replicate (see the guide below)
- using the production ready Replicate API to integrate your workflow into your own app or website
We've tried to include many of the most popular model weights and custom nodes:
Raise an issue to request more custom nodes or models, or use the train tab on Replicate to use your own weights (see below).
You’ll need the API version of your ComfyUI workflow. This is different to the commonly shared JSON version, it does not included visual information about nodes, etc.
To get your API JSON:
- Turn on the "Enable Dev mode Options" from the ComfyUI settings (via the settings icon)
- Load your workflow into ComfyUI
- Export your API JSON using the "Save (API format)" button
If your model takes inputs, like images for img2img or controlnet, you have 3 options:
Modify your API JSON file to point at a URL:
- "image": "/your-path-to/image.jpg",
+ "image": "https://example.com/image.jpg",You can also upload a single input file when running the model.
This file will be saved as input.[extension] – for example input.jpg. It'll be placed in the ComfyUI input directory, so you can reference in your workflow with:
- "image": "/your-path-to/image.jpg",
+ "image": "image.jpg",These will be downloaded and extracted to the input directory. You can then reference them in your workflow based on their relative paths.
So a zip file containing:
- my_img.png
- references/my_reference_01.jpg
- references/my_reference_02.jpg
Might be used in the workflow like:
"image": "my_img.png",
...
"directory": "references",
You can use LoRAs directly from CivitAI, HuggingFace, or any other URL in two ways:
Use the direct download URL as the lora_name:
{
"inputs": {
"lora_name": "https://huggingface.co/username/model/resolve/main/lora.safetensors",
...
},
"class_type": "LoraLoader"
}
Alternatively, use the dedicated LoraLoaderFromURL node from ComfyUI-GlifNodes:
{
"inputs": {
"url": "https://civitai.com/api/download/models/1163532",
// ...
},
"class_type": "LoraLoaderFromURL"
}
Both methods work the same way - the standard LoraLoader will automatically switch to use LoraLoaderFromURL when it detects a URL in the lora_name field.
With all your inputs updated, you can now run your workflow.
Some workflows save temporary files, for example pre-processed controlnet images. You can also return these by enabling the return_temp_files option.
The any-comfyui-workflow model on Replicate is a shared public model. This means many users will be sending workflows to it that might be quite different to yours. The effect of this will be that the internal ComfyUI server may need to swap models in and out of memory, this can slow down your prediction time.
ComfyUI and it's custom nodes are also continually being updated. While this means the newest versions are usually running, if there are breaking changes to custom nodes then your workflow may stop working.
If you have your own dedicated instance you will:
- fix the code and custom nodes to a known working version
- have a faster prediction time by keeping just your models in memory
- benefit from ComfyUI’s own internal optimisations when running the same workflow repeatedly
To get the best performance from the model you should run a dedicated instance. You have 3 choices:
- Create a private deployment (simplest, but you'll need to pay for setup and idle time)
- Create and deploy a fork using Cog (most powerful but most complex)
- Create a new model from the train tab (simple, your model can be public or private and you can bring your own weights)
Go to:
https://replicate.com/deployments/create
Select fofr/any-comfyui-workflow as the model you'd like to deploy. Pick your hardware and min and max instances, and you're ready to go. You'll be pinned to the version you deploy from. When any-comfyui-workflow is updated, you can test your workflow with it, and then deploy again using the new version.
You can read more about deployments in the Replicate docs:
https://replicate.com/docs/deployments
You can use this repository as a template to create your own model. This gives you complete control over the ComfyUI version, custom nodes, and the API you'll use to run the model.
You'll need to be familiar with Python, and you'll also need a GPU to push your model using Cog. Replicate has a good getting started guide: https://replicate.com/docs/guides/push-a-model
The kolors model on Replicate is a good example to follow:
- https://replicate.com/fofr/kolors (The model with it’s customised API)
- https://github.com/fofr/cog-comfyui-kolors (The new repo)
It was created from this repo, and then deployed using Cog. You can step through the commits of that repo to see what was changed and how, but broadly:
- this repository is used as a template
- the script
scripts/prepare_template.pyis run first, to remove examples and unnecessary boilerplate -
custom_nodes.jsonis modified to add or remove custom nodes you need, making sure to also add or remove their dependencies fromcog.yaml - run
./scripts/install_custom_nodes.pyto install the custom nodes (or./scripts/reset.pyto reinstall ComfyUI and all custom nodes) - the workflow is added as
workflow_api.json -
predict.pyis updated with a new API and theupdate_workflowmethod is changed so that it modifies the right parts of the JSON - the model is tested using
cog predict -i option_name=option_value -i another_option_name=another_option_valueon a GPU - the model is pushed to Replicate using
cog push r8.im/your-username/your-model-name
Visit the train tab on Replicate:
https://replicate.com/fofr/any-comfyui-workflow/train
Here you can give public or private URLs to weights on HuggingFace and CivitAI. If URLs are private or need authentication, make sure to include an API key or access token.
Check the training logs to see what filenames to use in your workflow JSON. For example:
Downloading from HuggingFace:
...
Size of the tar file: 217.88 MB
====================================
When using your new model, use these filenames in your JSON workflow:
araminta_k_midsommar_cartoon.safetensors
After running the training, you'll have your own ComfyUI model with your customised weights loaded during model setup. To prevent others from using it, you can make it private. Private models are billed differently to public models on Replicate.
Clone this repository:
git clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/fofr/cog-comfyui.gitRun the following script to install all the custom nodes:
./scripts/install_custom_nodes.pyYou can view the list of nodes in custom_nodes.json
- GPU Machine: Start the Cog container and expose port 8188:
sudo cog run -p 8188 bashRunning this command starts up the Cog container and let's you access it
- Inside Cog Container: Now that we have access to the Cog container, we start the server, binding to all network interfaces:
cd ComfyUI/
python main.py --listen 0.0.0.0-
Local Machine: Access the server using the GPU machine's IP and the exposed port (8188):
http://<gpu-machines-ip>:8188
When you goto http://<gpu-machines-ip>:8188 you'll see the classic ComfyUI web form!
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for cog-comfyui
Similar Open Source Tools

cog-comfyui
Cog-comfyui allows users to run ComfyUI workflows on Replicate. ComfyUI is a visual programming tool for creating and sharing generative art workflows. With cog-comfyui, users can access a variety of pre-trained models and custom nodes to create their own unique artworks. The tool is easy to use and does not require any coding experience. Users simply need to upload their API JSON file and any necessary input files, and then click the "Run" button. Cog-comfyui will then generate the output image or video file.

cog-comfyui
Cog-ComfyUI is a tool designed to run ComfyUI workflows on Replicate. It allows users to easily integrate their own workflows into their app or website using the Replicate API. The tool includes popular model weights and custom nodes, with the option to request more custom nodes or models. Users can get their API JSON, gather input files, and use custom LoRAs from CivitAI or HuggingFace. Additionally, users can run their workflows and set up their own dedicated instances for better performance and control. The tool provides options for private deployments, forking using Cog, or creating new models from the train tab on Replicate. It also offers guidance on developing locally and running the Web UI from a Cog container.
ray-llm
RayLLM (formerly known as Aviary) is an LLM serving solution that makes it easy to deploy and manage a variety of open source LLMs, built on Ray Serve. It provides an extensive suite of pre-configured open source LLMs, with defaults that work out of the box. RayLLM supports Transformer models hosted on Hugging Face Hub or present on local disk. It simplifies the deployment of multiple LLMs, the addition of new LLMs, and offers unique autoscaling support, including scale-to-zero. RayLLM fully supports multi-GPU & multi-node model deployments and offers high performance features like continuous batching, quantization and streaming. It provides a REST API that is similar to OpenAI's to make it easy to migrate and cross test them. RayLLM supports multiple LLM backends out of the box, including vLLM and TensorRT-LLM.
civitai
Civitai is a platform where people can share their stable diffusion models (textual inversions, hypernetworks, aesthetic gradients, VAEs, and any other crazy stuff people do to customize their AI generations), collaborate with others to improve them, and learn from each other's work. The platform allows users to create an account, upload their models, and browse models that have been shared by others. Users can also leave comments and feedback on each other's models to facilitate collaboration and knowledge sharing.
openui
OpenUI is a tool designed to simplify the process of building UI components by allowing users to describe UI using their imagination and see it rendered live. It supports converting HTML to React, Svelte, Web Components, etc. The tool is open source and aims to make UI development fun, fast, and flexible. It integrates with various AI services like OpenAI, Groq, Gemini, Anthropic, Cohere, and Mistral, providing users with the flexibility to use different models. OpenUI also supports LiteLLM for connecting to various LLM services and allows users to create custom proxy configs. The tool can be run locally using Docker or Python, and it offers a development environment for quick setup and testing.
langgraph-studio
LangGraph Studio is a specialized agent IDE that enables visualization, interaction, and debugging of complex agentic applications. It offers visual graphs and state editing to better understand agent workflows and iterate faster. Users can collaborate with teammates using LangSmith to debug failure modes. The tool integrates with LangSmith and requires Docker installed. Users can create and edit threads, configure graph runs, add interrupts, and support human-in-the-loop workflows. LangGraph Studio allows interactive modification of project config and graph code, with live sync to the interactive graph for easier iteration on long-running agents.
CLI
Bito CLI provides a command line interface to the Bito AI chat functionality, allowing users to interact with the AI through commands. It supports complex automation and workflows, with features like long prompts and slash commands. Users can install Bito CLI on Mac, Linux, and Windows systems using various methods. The tool also offers configuration options for AI model type, access key management, and output language customization. Bito CLI is designed to enhance user experience in querying AI models and automating tasks through the command line interface.
vectara-answer
Vectara Answer is a sample app for Vectara-powered Summarized Semantic Search (or question-answering) with advanced configuration options. For examples of what you can build with Vectara Answer, check out Ask News, LegalAid, or any of the other demo applications.
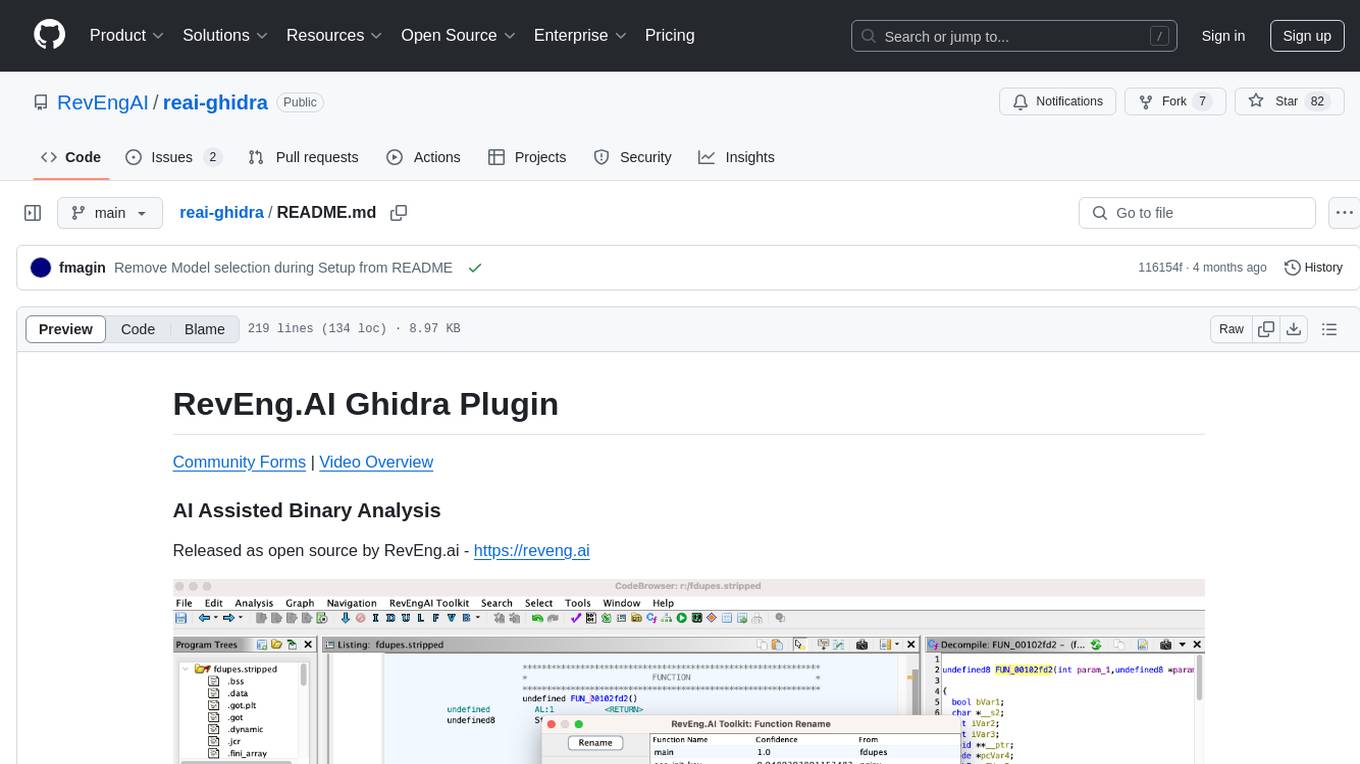
reai-ghidra
The RevEng.AI Ghidra Plugin by RevEng.ai allows users to interact with their API within Ghidra for Binary Code Similarity analysis to aid in Reverse Engineering stripped binaries. Users can upload binaries, rename functions above a confidence threshold, and view similar functions for a selected function.
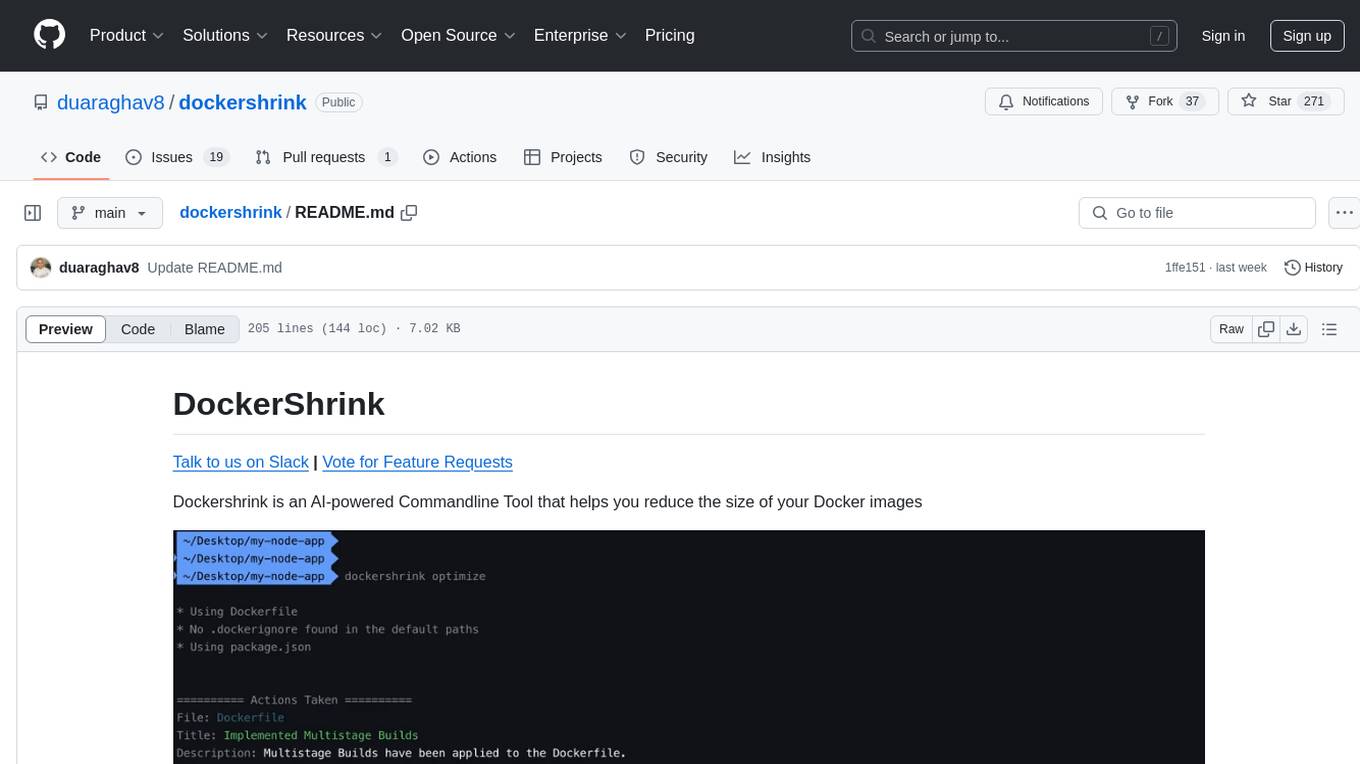
dockershrink
Dockershrink is an AI-powered Commandline Tool designed to help reduce the size of Docker images. It combines traditional Rule-based analysis with Generative AI techniques to optimize Image configurations. The tool supports NodeJS applications and aims to save costs on storage, data transfer, and build times while increasing developer productivity. By automatically applying advanced optimization techniques, Dockershrink simplifies the process for engineers and organizations, resulting in significant savings and efficiency improvements.

airbyte_serverless
AirbyteServerless is a lightweight tool designed to simplify the management of Airbyte connectors. It offers a serverless mode for running connectors, allowing users to easily move data from any source to their data warehouse. Unlike the full Airbyte-Open-Source-Platform, AirbyteServerless focuses solely on the Extract-Load process without a UI, database, or transform layer. It provides a CLI tool, 'abs', for managing connectors, creating connections, running jobs, selecting specific data streams, handling secrets securely, and scheduling remote runs. The tool is scalable, allowing independent deployment of multiple connectors. It aims to streamline the connector management process and provide a more agile alternative to the comprehensive Airbyte platform.
llm-subtrans
LLM-Subtrans is an open source subtitle translator that utilizes LLMs as a translation service. It supports translating subtitles between any language pairs supported by the language model. The application offers multiple subtitle formats support through a pluggable system, including .srt, .ssa/.ass, and .vtt files. Users can choose to use the packaged release for easy usage or install from source for more control over the setup. The tool requires an active internet connection as subtitles are sent to translation service providers' servers for translation.
gpt-subtrans
GPT-Subtrans is an open-source subtitle translator that utilizes large language models (LLMs) as translation services. It supports translation between any language pairs that the language model supports. Note that GPT-Subtrans requires an active internet connection, as subtitles are sent to the provider's servers for translation, and their privacy policy applies.

fasttrackml
FastTrackML is an experiment tracking server focused on speed and scalability, fully compatible with MLFlow. It provides a user-friendly interface to track and visualize your machine learning experiments, making it easy to compare different models and identify the best performing ones. FastTrackML is open source and can be easily installed and run with pip or Docker. It is also compatible with the MLFlow Python package, making it easy to integrate with your existing MLFlow workflows.

Mapperatorinator
Mapperatorinator is a multi-model framework that uses spectrogram inputs to generate fully featured osu! beatmaps for all gamemodes and assist modding beatmaps. The project aims to automatically generate rankable quality osu! beatmaps from any song with a high degree of customizability. The tool is built upon osuT5 and osu-diffusion, utilizing GPU compute and instances on vast.ai for development. Users can responsibly use AI in their beatmaps with this tool, ensuring disclosure of AI usage. Installation instructions include cloning the repository, creating a virtual environment, and installing dependencies. The tool offers a Web GUI for user-friendly experience and a Command-Line Inference option for advanced configurations. Additionally, an Interactive CLI script is available for terminal-based workflow with guided setup. The tool provides generation tips and features MaiMod, an AI-driven modding tool for osu! beatmaps. Mapperatorinator tokenizes beatmaps, utilizes a model architecture based on HF Transformers Whisper model, and offers multitask training format for conditional generation. The tool ensures seamless long generation, refines coordinates with diffusion, and performs post-processing for improved beatmap quality. Super timing generator enhances timing accuracy, and LoRA fine-tuning allows adaptation to specific styles or gamemodes. The project acknowledges credits and related works in the osu! community.
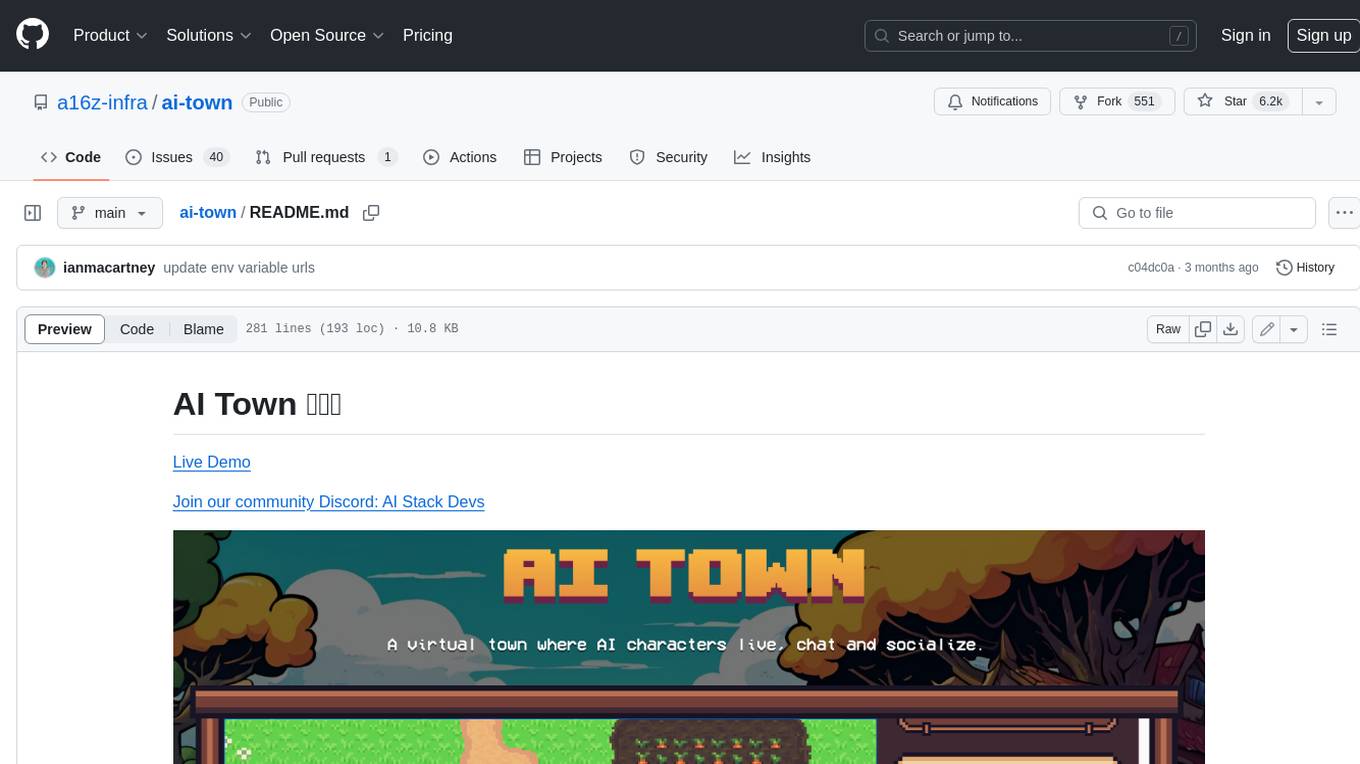
ai-town
AI Town is a virtual town where AI characters live, chat, and socialize. This project provides a deployable starter kit for building and customizing your own version of AI Town. It features a game engine, database, vector search, auth, text model, deployment, pixel art generation, background music generation, and local inference. You can customize your own simulation by creating characters and stories, updating spritesheets, changing the background, and modifying the background music.
For similar tasks

cog-comfyui
Cog-comfyui allows users to run ComfyUI workflows on Replicate. ComfyUI is a visual programming tool for creating and sharing generative art workflows. With cog-comfyui, users can access a variety of pre-trained models and custom nodes to create their own unique artworks. The tool is easy to use and does not require any coding experience. Users simply need to upload their API JSON file and any necessary input files, and then click the "Run" button. Cog-comfyui will then generate the output image or video file.
deforum-comfy-nodes
Deforum for ComfyUI is an integration tool designed to enhance the user experience of using ComfyUI. It provides custom nodes that can be added to ComfyUI to improve functionality and workflow. Users can easily install Deforum for ComfyUI by cloning the repository and following the provided instructions. The tool is compatible with Python v3.10 and is recommended to be used within a virtual environment. Contributions to the tool are welcome, and users can join the Discord community for support and discussions.
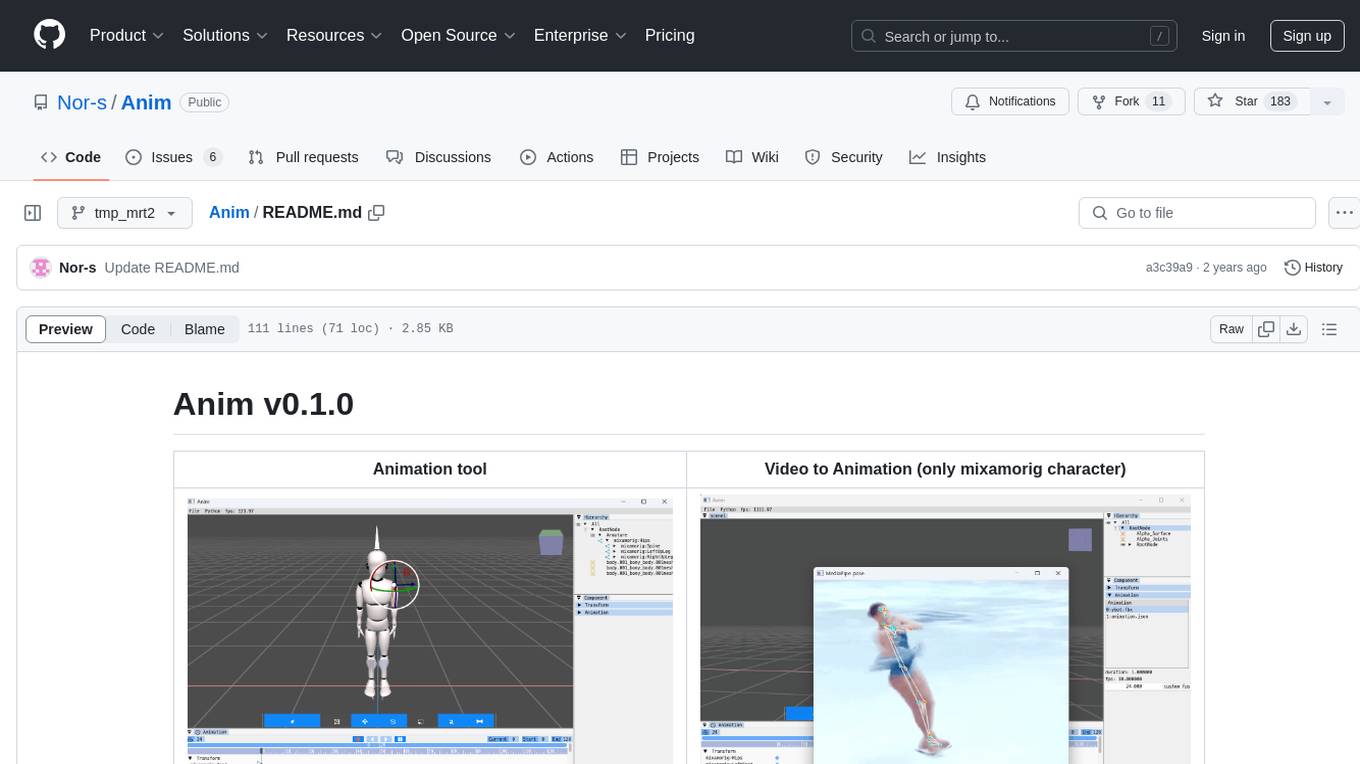
Anim
Anim v0.1.0 is an animation tool that allows users to convert videos to animations using mixamorig characters. It features FK animation editing, object selection, embedded Python support (only on Windows), and the ability to export to glTF and FBX formats. Users can also utilize Mediapipe to create animations. The tool is designed to assist users in creating animations with ease and flexibility.
next-money
Next Money Stripe Starter is a SaaS Starter project that empowers your next project with a stack of Next.js, Prisma, Supabase, Clerk Auth, Resend, React Email, Shadcn/ui, and Stripe. It seamlessly integrates these technologies to accelerate your development and SaaS journey. The project includes frameworks, platforms, UI components, hooks and utilities, code quality tools, and miscellaneous features to enhance the development experience. Created by @koyaguo in 2023 and released under the MIT license.
aitviewer
A set of tools to visualize and interact with sequences of 3D data with cross-platform support on Windows, Linux, and macOS. It provides a native Python interface for loading and displaying SMPL[-H/-X], MANO, FLAME, STAR, and SUPR sequences in an interactive viewer. Users can render 3D data on top of images, edit SMPL sequences and poses, export screenshots and videos, and utilize a high-performance ModernGL-based rendering pipeline. The tool is designed for easy use and hacking, with features like headless mode, remote mode, animatable camera paths, and a built-in extensible GUI.
twick
Twick is a comprehensive video editing toolkit built with modern web technologies. It is a monorepo containing multiple packages for video and image manipulation. The repository includes core utilities for media handling, a React-based canvas library for video and image editing, a video visualization and animation toolkit, a React component for video playback and control, timeline management and editing capabilities, a React-based video editor, and example implementations and usage demonstrations. Twick provides detailed API documentation and module information for developers. It offers easy integration with existing projects and allows users to build videos using the Twick Studio. The project follows a comprehensive style guide for naming conventions and code style across all packages.
NanoBanana-AI-Pose-Transfer
NanoBanana-AI-Pose-Transfer is a lightweight tool for transferring poses between images using artificial intelligence. It leverages advanced AI algorithms to accurately map and transfer poses from a source image to a target image. This tool is designed to be user-friendly and efficient, allowing users to easily manipulate and transfer poses for various applications such as image editing, animation, and virtual reality. With NanoBanana-AI-Pose-Transfer, users can seamlessly transfer poses between images with high precision and quality.
generative-ai
This repository contains notebooks, code samples, sample apps, and other resources that demonstrate how to use, develop and manage generative AI workflows using Generative AI on Google Cloud, powered by Vertex AI. For more Vertex AI samples, please visit the Vertex AI samples Github repository.
For similar jobs

ap-plugin
AP-PLUGIN is an AI drawing plugin for the Yunzai series robot framework, allowing you to have a convenient AI drawing experience in the input box. It uses the open source Stable Diffusion web UI as the backend, deploys it for free, and generates a variety of images with richer functions.

cog-comfyui
Cog-comfyui allows users to run ComfyUI workflows on Replicate. ComfyUI is a visual programming tool for creating and sharing generative art workflows. With cog-comfyui, users can access a variety of pre-trained models and custom nodes to create their own unique artworks. The tool is easy to use and does not require any coding experience. Users simply need to upload their API JSON file and any necessary input files, and then click the "Run" button. Cog-comfyui will then generate the output image or video file.
Adobe-Photoshop-AI-Crack
Adobe Photoshop 2024 is the latest version of the program for processing raster graphics. It supports a variety of graphic formats and allows both the creation and editing of images. It is used for creating photorealistic images, working with color scanned images, retouching, color correction, collaging, graphic transformation, color separation, and more. Adobe Photoshop encompasses all methods of working with bitmap images, utilizes layers, and contours. The program is an undisputed leader among professional graphic editors due to its extensive capabilities, high efficiency, and speed. Adobe Photoshop provides all the necessary tools for correction, editing, preparing images for printing, and high-quality output.
IOPaint
IOPaint is a free and open-source inpainting & outpainting tool powered by SOTA AI model. It supports various AI models to perform erase, inpainting, or outpainting tasks. Users can remove unwanted objects, defects, watermarks, or people from images using erase models. Additionally, diffusion models can replace objects or perform outpainting. The tool also offers plugins for interactive object segmentation, background removal, anime segmentation, super resolution, face restoration, and file management. IOPaint provides a web UI for easy access to the latest AI models and supports batch processing of images through the command line. Developers can contribute to the project by installing front-end dependencies, setting up the backend, and starting the development environment for both front-end and back-end components.
adobe-photoshopCRCK
Adobe PhotoshopCRCK is a tool designed to provide users with the latest version of Adobe Photoshop for free on Windows. It allows users to access advanced photo editing features and functionalities without the need for a paid subscription. The tool is intended for individuals looking to explore professional photo editing capabilities without incurring additional costs. With Adobe PhotoshopCRCK, users can enhance their images, create stunning graphics, and unleash their creativity through a wide range of editing tools and options.
DeepNude-AI-List
DeepNude AI List is a compilation of various NSFW AI tools that are designed for generating nude or suggestive content. The list includes tools like Dreampaint.net, Nudify.me, NoDress.io, Undress Her, and more. These tools utilize artificial intelligence algorithms to manipulate images and create provocative visuals. Users should exercise caution and responsibility when using such tools, as they may raise ethical and privacy concerns.
generative-ai-js
Generative AI JS is a JavaScript library that provides tools for creating generative art and music using artificial intelligence techniques. It allows users to generate unique and creative content by leveraging machine learning models. The library includes functions for generating images, music, and text based on user input and preferences. With Generative AI JS, users can explore the intersection of art and technology, experiment with different creative processes, and create dynamic and interactive content for various applications.
comfyui-photoshop
ComfyUI for Photoshop is a plugin that integrates with an AI-powered image generation system to enhance the Photoshop experience with features like unlimited generative fill, customizable back-end, AI-powered artistry, and one-click transformation. The plugin requires a minimum of 6GB graphics memory and 12GB RAM. Users can install the plugin and set up the ComfyUI workflow using provided links and files. Additionally, specific files like Check points, Loras, and Detailer Lora are required for different functionalities. Support and contributions are encouraged through GitHub.