
Co-LLM-Agents
[ICLR 2024] Source codes for the paper "Building Cooperative Embodied Agents Modularly with Large Language Models"
Stars: 245
Co-LLM-Agents is a repository containing codes for the paper 'Building Cooperative Embodied Agents Modularly with Large Language Models'. The project focuses on developing cooperative embodied agents using large language models, with a specific emphasis on the ThreeDWorld Multi-Agent Transport environment. The repository provides implementations, installation instructions, and example scripts for running experiments with the CoELA model. It extends the ThreeDWorld Transport Challenge into a multi-agent setting, enabling agents to transport target objects using containers and communicate with each other. Additionally, it includes the Communicative Watch-And-Help challenge, where agents can send messages to each other while performing tasks such as preparing meals, washing dishes, and setting up dinner tables.
README:
This repo contains codes for the following paper:
Hongxin Zhang*, Weihua Du*, Jiaming Shan, Qinhong Zhou, Yilun Du, Joshua B. Tenenbaum, Tianmin Shu, Chuang Gan: Building Cooperative Embodied Agents Modularly with Large Language Models
Paper: Arxiv
Project Website: Co-LLM-Agents
[8/25/2024]: Updates on the navigation module of agents on the ThreeDWorld Multi-Agent Transport environment to fix the navigation issues.
[9/4/2023]: ThreeDWorld Multi-Agent Transport no longer provides ground truth segmentation mask in default. We implement a vision detection module with a fine-tuned Mask-RCNN model. For more details, please read README in tdw_mat.
[8/1/2023]: We provide the VirtualHome Simulator executable we used here. If you met XDG_RUNTIME_DIR not set in the environment error previously, please check if you are using the new version we provided.
For detailed instructions on the installation of the two embodied multi-agent environments Communicative Watch-And-Help and ThreeDWorld Multi-Agent Transport, please refer to the Setup sections in cwah/README.md and tdw_mat/README.md respectively.
Run the following commands step by step to set up the environments:
cd tdw_mat
conda create -n tdw_mat python=3.9
conda activate tdw_mat
pip install -e .If you're running TDW on a remote Linux server, follow the TDW Installation Document to configure the X server.
After that, you can run the demo scene to verify your setup:
python demo/demo_scene.pyStep 1: Get the VirtualHome Simulator and API and put it at the same level as the cwah folder.
Clone the VirtualHome API repository:
git clone --branch wah https://github.com/xavierpuigf/virtualhome.gitDownload the Simulator (Linux x86-64 version), and unzip it.
gdown https://drive.google.com/uc?id=1L79SxE07Jt-8-_uCvNnkwz5Kf6AjtaGp
unzip executable.zip
chmod +x executable/linux_exec.v2.3.0.x86_64The files should be organized as follows:
|--cwah/
|--virtualhome/
|--executable/Step 2: Install Requirements
cd cwah
conda create --name cwah python=3.8
conda activate cwah
pip install -r requirements.txtThe main implementation code of our CoELA is in tdw_mat/LLM and tdw_mat/tdw_gym/lm_agent.py.
We also prepare example scripts to run experiments with HP baseline and our CoELA under the folder tdw_mat/scripts.
For example, to run experiments with two CoELA on ThreeDWorld Multi-Agent Transport, run the following command in folder tdw_mat.
./scripts/test_LMs-gpt-4.sh
We extend the ThreeDWorld Transport Challenge into a multi-agent setting with more types of objects and containers, more realistic object placements, and support communication between agents, named ThreeDWorld Multi-Agent Transport (TDW-MAT), built on top of the TDW platform.
The agents are tasked to transport as many target objects as possible to the goal position with the help of containers as tools. One container can carry most three objects, and without containers, the agent can transport only two objects at a time. The agents have the ego-centric visual observation and action space as before with a new communication action added.
We selected $6$ scenes from the TDW-House dataset and sampled $2$ types of tasks and $2$ settings in each of the scenes, making a test set of $24$ episodes. Every scene has $6$ to $8$ rooms, $10$ objects, and a few containers. An episode is terminated if all the target objects have been transported to the goal position or the maximum number of frames ($3000$) is reached.
The tasks are named food task and stuff task. Containers for the food task can be found in both the kitchen and living room, while containers for the stuff task can be found in the living room and office.
The configuration and distribution of containers vary based on two distinct settings: the Enough Container Setting and the Rare Container Setting. In the Enough Container Setting, the ratio of containers to objects stands at $1:2$, and containers associated with a specific task are located in no more than two rooms. On the other hand, in the Rare Container Setting, the container-to-object ratio decreases to $1:5$. This distribution differs from the "Enough Container Setting" as containers in the Rare Container Setting are strictly localized to a single room.
One example of scenes, target objects, and containers is shown in the following image:
- Transport Rate (TR): The fraction of the target objects successfully transported to the goal position.
- Efficiency Improvements (EI): The efficiency improvements of cooperating with base agents.
Communicative Watch-And-Help(C-WAH) is an extension of the Watch-And-Help challenge, which enables agents to send messages to each other. Sending messages, alongside other actions, takes one timestep and has an upper limit on message length.
Five types of tasks are available in C-WAH, named Prepare afternoon tea, Wash dishes, Prepare a meal, Put groceries, and Set up a dinner table. These tasks include a range of housework, and each task contains a few subgoals, which are described by predicates. A predicate is in ON/IN(x, y) format, that is, Put x ON/IN y. The detailed descriptions of tasks are listed in the following table:
| Task Name | Predicate Set |
|---|---|
| Prepare afternoon tea | ON(cupcake,coffeetable), ON(pudding,coffeetable), ON(apple,coffeetable), ON(juice,coffeetable), ON(wine,coffeetable) |
| Wash dishes | IN(plate,dishwasher), IN(fork,dishwasher) |
| Prepare a meal | ON(coffeepot,dinnertable),ON(cupcake,dinnertable), ON(pancake,dinnertable), ON(poundcake,dinnertable), ON(pudding,dinnertable), ON(apple,dinnertable), ON(juice,dinnertable), ON(wine,dinnertable) |
| Put groceries | IN(cupcake,fridge), IN(pancake,fridge), IN(poundcake,fridge), IN(pudding,fridge), IN(apple,fridge), IN(juice,fridge), IN(wine,fridge) |
| Set up a dinner table | ON(plate,dinnertable), ON(fork,dinnertable) |
The task goal is to satisfy all the given subgoals within $250$ time steps, and the number of subgoals in each task ranges from $3$ to $5$.
- Average Steps (L): Number of steps to finish the task;
- Efficiency Improvement (EI): The efficiency improvements of cooperating with base agents.
We noticed many interesting agents' behaviors exhibited in our experiments and identified several cooperative behaviors.
There are more interesting cases and demos on our website!
If you find our work useful, please consider citing:
@article{zhang2024building,
title={Building Cooperative Embodied Agents Modularly with Large Language Models},
author={Zhang, Hongxin and Du, Weihua and Shan, Jiaming and Zhou, Qinhong and Du, Yilun and Tenenbaum, Joshua B and Shu, Tianmin and Gan, Chuang},
journal={ICLR},
year={2024}
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Co-LLM-Agents
Similar Open Source Tools

Co-LLM-Agents
Co-LLM-Agents is a repository containing codes for the paper 'Building Cooperative Embodied Agents Modularly with Large Language Models'. The project focuses on developing cooperative embodied agents using large language models, with a specific emphasis on the ThreeDWorld Multi-Agent Transport environment. The repository provides implementations, installation instructions, and example scripts for running experiments with the CoELA model. It extends the ThreeDWorld Transport Challenge into a multi-agent setting, enabling agents to transport target objects using containers and communicate with each other. Additionally, it includes the Communicative Watch-And-Help challenge, where agents can send messages to each other while performing tasks such as preparing meals, washing dishes, and setting up dinner tables.
Co-LLM-Agents
This repository contains code for building cooperative embodied agents modularly with large language models. The agents are trained to perform tasks in two different environments: ThreeDWorld Multi-Agent Transport (TDW-MAT) and Communicative Watch-And-Help (C-WAH). TDW-MAT is a multi-agent environment where agents must transport objects to a goal position using containers. C-WAH is an extension of the Watch-And-Help challenge, which enables agents to send messages to each other. The code in this repository can be used to train agents to perform tasks in both of these environments.
CogAgent
CogAgent is an advanced intelligent agent model designed for automating operations on graphical interfaces across various computing devices. It supports platforms like Windows, macOS, and Android, enabling users to issue commands, capture device screenshots, and perform automated operations. The model requires a minimum of 29GB of GPU memory for inference at BF16 precision and offers capabilities for executing tasks like sending Christmas greetings and sending emails. Users can interact with the model by providing task descriptions, platform specifications, and desired output formats.
mentals-ai
Mentals AI is a tool designed for creating and operating agents that feature loops, memory, and various tools, all through straightforward markdown syntax. This tool enables you to concentrate solely on the agent’s logic, eliminating the necessity to compose underlying code in Python or any other language. It redefines the foundational frameworks for future AI applications by allowing the creation of agents with recursive decision-making processes, integration of reasoning frameworks, and control flow expressed in natural language. Key concepts include instructions with prompts and references, working memory for context, short-term memory for storing intermediate results, and control flow from strings to algorithms. The tool provides a set of native tools for message output, user input, file handling, Python interpreter, Bash commands, and short-term memory. The roadmap includes features like a web UI, vector database tools, agent's experience, and tools for image generation and browsing. The idea behind Mentals AI originated from studies on psychoanalysis executive functions and aims to integrate 'System 1' (cognitive executor) with 'System 2' (central executive) to create more sophisticated agents.
matsciml
The Open MatSci ML Toolkit is a flexible framework for machine learning in materials science. It provides a unified interface to a variety of materials science datasets, as well as a set of tools for data preprocessing, model training, and evaluation. The toolkit is designed to be easy to use for both beginners and experienced researchers, and it can be used to train models for a wide range of tasks, including property prediction, materials discovery, and materials design.

llm-reasoners
LLM Reasoners is a library that enables LLMs to conduct complex reasoning, with advanced reasoning algorithms. It approaches multi-step reasoning as planning and searches for the optimal reasoning chain, which achieves the best balance of exploration vs exploitation with the idea of "World Model" and "Reward". Given any reasoning problem, simply define the reward function and an optional world model (explained below), and let LLM reasoners take care of the rest, including Reasoning Algorithms, Visualization, LLM calling, and more!
kafka-ml
Kafka-ML is a framework designed to manage the pipeline of Tensorflow/Keras and PyTorch machine learning models on Kubernetes. It enables the design, training, and inference of ML models with datasets fed through Apache Kafka, connecting them directly to data streams like those from IoT devices. The Web UI allows easy definition of ML models without external libraries, catering to both experts and non-experts in ML/AI.

pydantic-ai
PydanticAI is a Python agent framework designed to make it less painful to build production grade applications with Generative AI. It is built by the Pydantic Team and supports various AI models like OpenAI, Anthropic, Gemini, Ollama, Groq, and Mistral. PydanticAI seamlessly integrates with Pydantic Logfire for real-time debugging, performance monitoring, and behavior tracking of LLM-powered applications. It is type-safe, Python-centric, and offers structured responses, dependency injection system, and streamed responses. PydanticAI is in early beta, offering a Python-centric design to apply standard Python best practices in AI-driven projects.

MegatronApp
MegatronApp is a toolchain built around the Megatron-LM training framework, offering performance tuning, slow-node detection, and training-process visualization. It includes modules like MegaScan for anomaly detection, MegaFBD for forward-backward decoupling, MegaDPP for dynamic pipeline planning, and MegaScope for visualization. The tool aims to enhance large-scale distributed training by providing valuable capabilities and insights.

zshot
Zshot is a highly customizable framework for performing Zero and Few shot named entity and relationships recognition. It can be used for mentions extraction, wikification, zero and few shot named entity recognition, zero and few shot named relationship recognition, and visualization of zero-shot NER and RE extraction. The framework consists of two main components: the mentions extractor and the linker. There are multiple mentions extractors and linkers available, each serving a specific purpose. Zshot also includes a relations extractor and a knowledge extractor for extracting relations among entities and performing entity classification. The tool requires Python 3.6+ and dependencies like spacy, torch, transformers, evaluate, and datasets for evaluation over datasets like OntoNotes. Optional dependencies include flair and blink for additional functionalities. Zshot provides examples, tutorials, and evaluation methods to assess the performance of the components.
ygo-agent
YGO Agent is a project focused on using deep learning to master the Yu-Gi-Oh! trading card game. It utilizes reinforcement learning and large language models to develop advanced AI agents that aim to surpass human expert play. The project provides a platform for researchers and players to explore AI in complex, strategic game environments.
storm
STORM is a LLM system that writes Wikipedia-like articles from scratch based on Internet search. While the system cannot produce publication-ready articles that often require a significant number of edits, experienced Wikipedia editors have found it helpful in their pre-writing stage. **Try out our [live research preview](https://storm.genie.stanford.edu/) to see how STORM can help your knowledge exploration journey and please provide feedback to help us improve the system 🙏!**
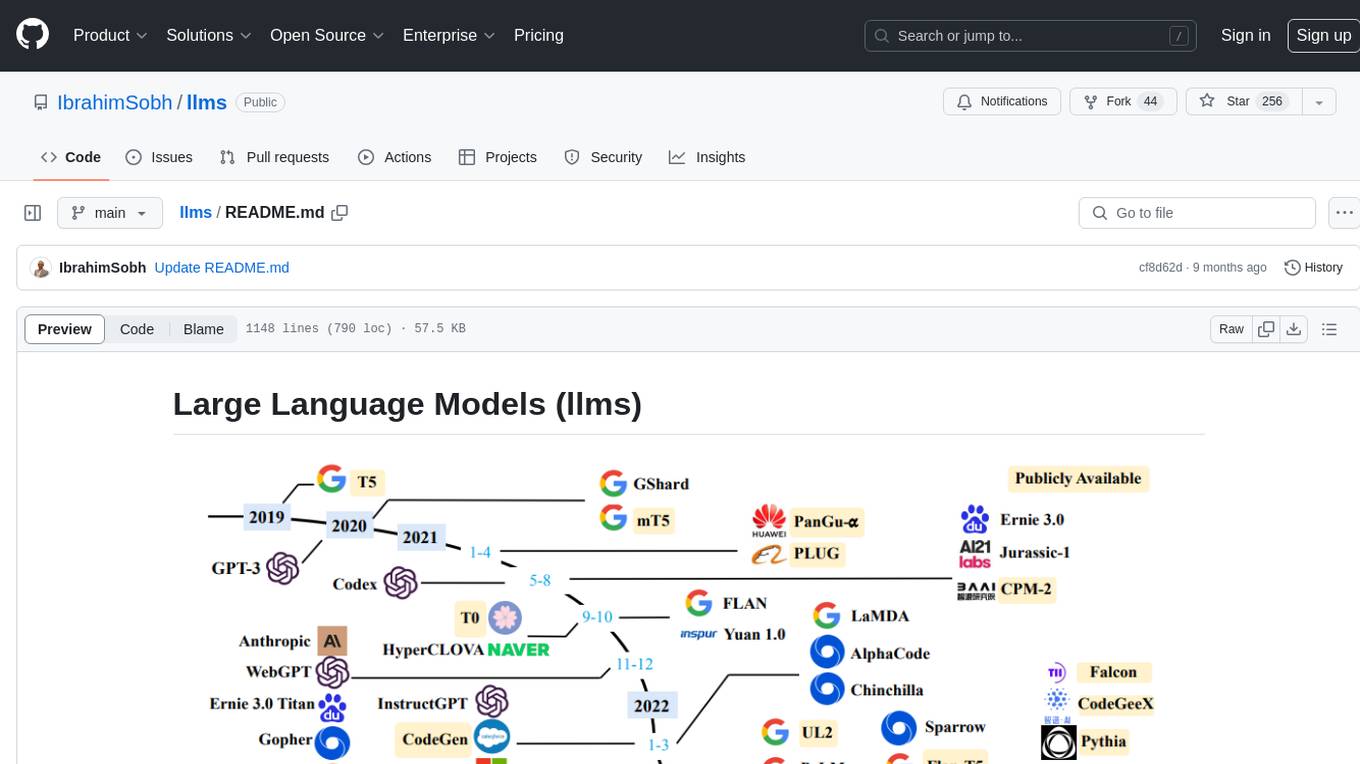
llms
The 'llms' repository is a comprehensive guide on Large Language Models (LLMs), covering topics such as language modeling, applications of LLMs, statistical language modeling, neural language models, conditional language models, evaluation methods, transformer-based language models, practical LLMs like GPT and BERT, prompt engineering, fine-tuning LLMs, retrieval augmented generation, AI agents, and LLMs for computer vision. The repository provides detailed explanations, examples, and tools for working with LLMs.
mosec
Mosec is a high-performance and flexible model serving framework for building ML model-enabled backend and microservices. It bridges the gap between any machine learning models you just trained and the efficient online service API. * **Highly performant** : web layer and task coordination built with Rust 🦀, which offers blazing speed in addition to efficient CPU utilization powered by async I/O * **Ease of use** : user interface purely in Python 🐍, by which users can serve their models in an ML framework-agnostic manner using the same code as they do for offline testing * **Dynamic batching** : aggregate requests from different users for batched inference and distribute results back * **Pipelined stages** : spawn multiple processes for pipelined stages to handle CPU/GPU/IO mixed workloads * **Cloud friendly** : designed to run in the cloud, with the model warmup, graceful shutdown, and Prometheus monitoring metrics, easily managed by Kubernetes or any container orchestration systems * **Do one thing well** : focus on the online serving part, users can pay attention to the model optimization and business logic
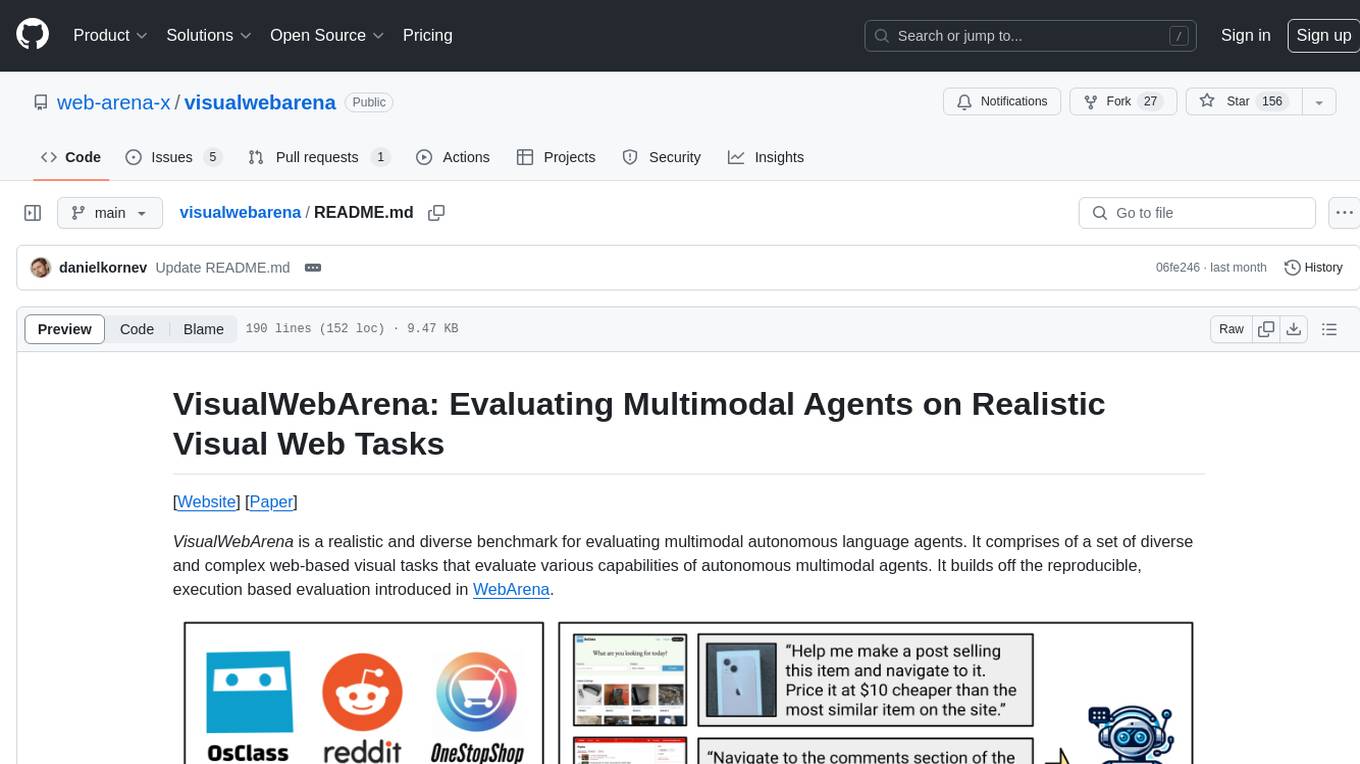
visualwebarena
VisualWebArena is a benchmark for evaluating multimodal autonomous language agents through diverse and complex web-based visual tasks. It builds on the reproducible evaluation introduced in WebArena. The repository provides scripts for end-to-end training, demos to run multimodal agents on webpages, and tools for setting up environments for evaluation. It includes trajectories of the GPT-4V + SoM agent on VWA tasks, along with human evaluations on 233 tasks. The environment supports OpenAI models and Gemini models for evaluation.
SheetCopilot
SheetCopilot is an assistant agent that manipulates spreadsheets by following user commands. It leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to interact with spreadsheets like a human expert, enabling non-expert users to complete tasks on complex software such as Google Sheets and Excel via a language interface. The tool observes spreadsheet states, polishes generated solutions based on external action documents and error feedback, and aims to improve success rate and efficiency. SheetCopilot offers a dataset with diverse task categories and operations, supporting operations like entry & manipulation, management, formatting, charts, and pivot tables. Users can interact with SheetCopilot in Excel or Google Sheets, executing tasks like calculating revenue, creating pivot tables, and plotting charts. The tool's evaluation includes performance comparisons with leading LLMs and VBA-based methods on specific datasets, showcasing its capabilities in controlling various aspects of a spreadsheet.
For similar tasks

Co-LLM-Agents
Co-LLM-Agents is a repository containing codes for the paper 'Building Cooperative Embodied Agents Modularly with Large Language Models'. The project focuses on developing cooperative embodied agents using large language models, with a specific emphasis on the ThreeDWorld Multi-Agent Transport environment. The repository provides implementations, installation instructions, and example scripts for running experiments with the CoELA model. It extends the ThreeDWorld Transport Challenge into a multi-agent setting, enabling agents to transport target objects using containers and communicate with each other. Additionally, it includes the Communicative Watch-And-Help challenge, where agents can send messages to each other while performing tasks such as preparing meals, washing dishes, and setting up dinner tables.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.


