
interpreto
🪄 Interpreto is an interpretability toolbox for LLMs
Stars: 142

Interpreto is an interpretability toolkit for large language models (LLMs) that provides a modular framework encompassing attribution methods, concept-based methods, and evaluation metrics. It includes various inference-based and gradient-based attribution methods for both classification and generation tasks. The toolkit also offers concept-based explanations to provide high-level interpretations of latent model representations through steps like concept discovery, interpretation, and concept-to-output attribution. Interpreto aims to enhance model interpretability and facilitate understanding of model decisions and outputs.
README:
The library is available on PyPI, try pip install interpreto to install it.
Checkout the tutorials to get started:
- Attributions walkthrough (both classification and generation)
- Classification concept-based explanations
- Generation concept-based explanations
Interpreto 🪄 provides a modular framework encompassing Attribution Methods, Concept-Based Methods, and Evaluation Metrics.
Interpreto includes both inference-based and gradient-based attribution methods.
They all work seamlessly for both classification (...ForSequenceClassification) and generation (...ForCausalLM)
Inference-based Methods:
-
KernelShap— Lundberg and Lee, 2017 -
LIME— Ribeiro et al., 2013 -
Occlusion— Zeiler and Fergus, 2014 -
Sobol— Fel et al., 2021
Gradient-based methods:
-
GradientShap— Lundberg and Lee, 2017 -
InputxGradient— Simonyan et al., 2013 -
Integrated Gradient— Sundararajan et al., 2017 -
Saliency— Simonyan et al., 2013 -
SmoothGrad— Smilkov et al., 2017 -
SquareGrad— Hooker et al., 2019 -
VarGrad— Richter et al., 2020
Concept-based explanations aim to provide high-level interpretations of latent model representations.
Interpreto generalizes these methods through four core steps:
- Split a model in two and obtain a dataset of activations
- Concept Discovery (e.g., from latent embeddings)
- Concept Interpretation (mapping discovered concepts to human-understandable elements)
- Concept-to-Output Attribution (assessing concept relevance to model outputs)
1. Split a model in two and obtain a dataset of activations: (mainly via nnsight):
Choose any layer in any HuggingFace language model with our ModelWithSplitPoints based on nnsight. Then pass a dataset through it to obtain a dataset of activations.
2. Dictionary Learning for Concept Discovery (mainly via overcomplete):
- Interpret neurons directly via
NeuronsAsConcepts -
NMF,Semi-NMF,ConvexNMF -
ICA,SVD,PCA,KMeans - SAE variants:
Vanilla SAE,TopK SAE,JumpReLU SAE,BatchTopK SAE
3. Available Concept Interpretation Techniques:
- Top-k tokens from tokenizer vocabulary via
TopKInputsanduse_vocab=True - Top-k tokens/words/sentences/samples from specific datasets via
TopKInputs - Label concepts via LLMs with
LLMLabels(Bills et al. 2023)
Concept Interpretation Techniques Added in the future:
- Input-to-concept attribution from dataset examples (Jourdan et al. 2023)
- Theme prediction via LLMs from top-k tokens/sentences
- Aligning concepts with human labels (Sajjad et al. 2022)
- Word cloud visualizations of concepts (Dalvi et al. 2022)
- VocabProj & TokenChange (Gur-Arieh et al. 2025)
4. Concept-to-Output Attribution:
Estimate the contribution of each concept to the model output.
Can be obtained with any concept-based explainer via MethodConcepts.concept_output_gradient().
Papers available in the future:
Thanks to this generalization encompassing all concept-based methods and our highly flexible architecture, we can easily obtain a large number of concept-based methods:
- CAV and TCAV: Kim et al. 2018, Interpretability Beyond Feature Attribution: Quantitative Testing with Concept Activation Vectors (TCAV)
- ConceptSHAP: Yeh et al. 2020, On Completeness-aware Concept-Based Explanations in Deep Neural Networks
- COCKATIEL: Jourdan et al. 2023, COCKATIEL: COntinuous Concept ranKed ATtribution with Interpretable ELements for explaining neural net classifiers on NLP
- Yun et al. 2021, Transformer visualization via dictionary learning: contextualized embedding as a linear superposition of transformer factors
- FFN values interpretation: Geva et al. 2022, Transformer Feed-Forward Layers Build Predictions by Promoting Concepts in the Vocabulary Space
- SparseCoding: Cunningham et al. 2023, Sparse Autoencoders Find Highly Interpretable Features in Language Models
- Parameter Interpretation: Dar et al. 2023, Analyzing Transformers in Embedding Space
Evaluation Metrics for Attribution
To evaluate attribution methods faithfulness, there are the Insertion and Deletion metrics.
Evaluation Metrics for Concepts
Concept-based methods have several steps that can be evaluated together via ConSim.
Or independently:
- Concept-space (dictionary learning evaluation)
- faithfulness:
MSE,FID, andReconstructionError - complexity:
Sparsity,SparsityRatio,SparsityRatio - stability:
Stability
- faithfulness:
- Concepts interpretations
- No metric yet, will be included soon.
- Concept-to-Output attribution
- No metric yet, will be included soon.
Feel free to propose your ideas or come and contribute with us on the Interpreto 🪄 toolbox! We have a specific document where we describe in a simple way how to make your first pull request.
More from the DEEL project:
- Xplique a Python library dedicated to explaining neural networks (Images, Time Series, Tabular data) on TensorFlow.
- Puncc a Python library for predictive uncertainty quantification using conformal prediction.
- oodeel a Python library that performs post-hoc deep Out-of-Distribution (OOD) detection on already trained neural network image classifiers.
- deel-lip a Python library for training k-Lipschitz neural networks on TensorFlow.
- deel-torchlip a Python library for training k-Lipschitz neural networks on PyTorch.
- Influenciae a Python library dedicated to computing influence values for the discovery of potentially problematic samples in a dataset.
- DEEL White paper a summary of the DEEL team on the challenges of certifiable AI and the role of data quality, representativity and explainability for this purpose.
This project received funding from the French ”Investing for the Future – PIA3” program within the Artificial and Natural Intelligence Toulouse Institute (ANITI). The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of the DEEL and the FOR projects.
Interpreto 🪄 is a project of the FOR and the DEEL teams at the IRT Saint-Exupéry in Toulouse, France.
If you use Interpreto 🪄 as part of your workflow in a scientific publication, please consider citing 🗞️ our paper:
@article{poche2025interpreto,
title = {Interpreto: An Explainability Library for Transformers},
author = {Poch{\'e}, Antonin and Mullor, Thomas and Sarti, Gabriele and Boisnard, Fr{\'e}d{\'e}ric and Friedrich, Corentin and Claye, Charlotte and Hoofd, Fran{\c{c}}ois and Bernas, Raphael and Hudelot, C{\'e}line and Jourdan, Fanny},
journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2512.09730},
year = {2025}
}The package is released under MIT license.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for interpreto
Similar Open Source Tools

interpreto
Interpreto is an interpretability toolkit for large language models (LLMs) that provides a modular framework encompassing attribution methods, concept-based methods, and evaluation metrics. It includes various inference-based and gradient-based attribution methods for both classification and generation tasks. The toolkit also offers concept-based explanations to provide high-level interpretations of latent model representations through steps like concept discovery, interpretation, and concept-to-output attribution. Interpreto aims to enhance model interpretability and facilitate understanding of model decisions and outputs.
Quantus
Quantus is a toolkit designed for the evaluation of neural network explanations. It offers more than 30 metrics in 6 categories for eXplainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) evaluation. The toolkit supports different data types (image, time-series, tabular, NLP) and models (PyTorch, TensorFlow). It provides built-in support for explanation methods like captum, tf-explain, and zennit. Quantus is under active development and aims to provide a comprehensive set of quantitative evaluation metrics for XAI methods.
MathCoder
MathCoder is a repository focused on enhancing mathematical reasoning by fine-tuning open-source language models to use code for modeling and deriving math equations. It introduces MathCodeInstruct dataset with solutions interleaving natural language, code, and execution results. The repository provides MathCoder models capable of generating code-based solutions for challenging math problems, achieving state-of-the-art scores on MATH and GSM8K datasets. It offers tools for model deployment, inference, and evaluation, along with a citation for referencing the work.
LLM-as-HH
LLM-as-HH is a codebase that accompanies the paper ReEvo: Large Language Models as Hyper-Heuristics with Reflective Evolution. It introduces Language Hyper-Heuristics (LHHs) that leverage LLMs for heuristic generation with minimal manual intervention and open-ended heuristic spaces. Reflective Evolution (ReEvo) is presented as a searching framework that emulates the reflective design approach of human experts while surpassing human capabilities with scalable LLM inference, Internet-scale domain knowledge, and powerful evolutionary search. The tool can improve various algorithms on problems like Traveling Salesman Problem, Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem, Orienteering Problem, Multiple Knapsack Problems, Bin Packing Problem, and Decap Placement Problem in both black-box and white-box settings.

langfair
LangFair is a Python library for bias and fairness assessments of large language models (LLMs). It offers a comprehensive framework for choosing bias and fairness metrics, demo notebooks, and a technical playbook. Users can tailor evaluations to their use cases with a Bring Your Own Prompts approach. The focus is on output-based metrics practical for governance audits and real-world testing.
GOLEM
GOLEM is an open-source AI framework focused on optimization and learning of structured graph-based models using meta-heuristic methods. It emphasizes the potential of meta-heuristics in complex problem spaces where gradient-based methods are not suitable, and the importance of structured models in various problem domains. The framework offers features like structured model optimization, metaheuristic methods, multi-objective optimization, constrained optimization, extensibility, interpretability, and reproducibility. It can be applied to optimization problems represented as directed graphs with defined fitness functions. GOLEM has applications in areas like AutoML, Bayesian network structure search, differential equation discovery, geometric design, and neural architecture search. The project structure includes packages for core functionalities, adapters, graph representation, optimizers, genetic algorithms, utilities, serialization, visualization, examples, and testing. Contributions are welcome, and the project is supported by ITMO University's Research Center Strong Artificial Intelligence in Industry.
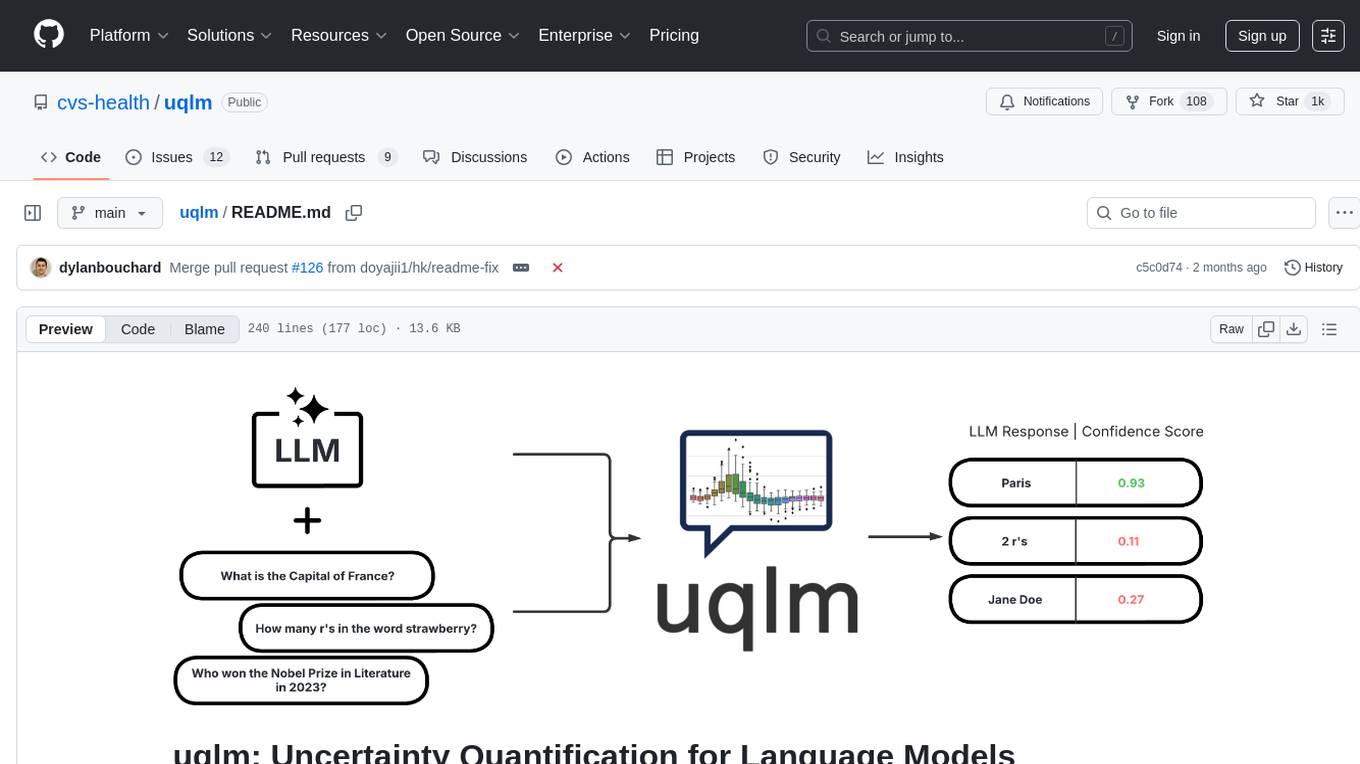
uqlm
UQLM is a Python library for Large Language Model (LLM) hallucination detection using state-of-the-art uncertainty quantification techniques. It provides response-level scorers for quantifying uncertainty of LLM outputs, categorized into four main types: Black-Box Scorers, White-Box Scorers, LLM-as-a-Judge Scorers, and Ensemble Scorers. Users can leverage different scorers to assess uncertainty in generated responses, with options for off-the-shelf usage or customization. The library offers illustrative code snippets and detailed information on available scorers for each type, along with example usage for conducting hallucination detection. Additionally, UQLM includes documentation, example notebooks, and associated research for further exploration and understanding.
Adaptive-MT-LLM-Fine-tuning
The repository Adaptive-MT-LLM-Fine-tuning contains code and data for the paper 'Fine-tuning Large Language Models for Adaptive Machine Translation'. It focuses on enhancing Mistral 7B, a large language model, for real-time adaptive machine translation in the medical domain. The fine-tuning process involves using zero-shot and one-shot translation prompts to improve terminology and style adherence. The repository includes training and test data, data processing code, fuzzy match retrieval techniques, fine-tuning methods, conversion to CTranslate2 format, tokenizers, translation codes, and evaluation metrics.
baal
Baal is an active learning library that supports both industrial applications and research use cases. It provides a framework for Bayesian active learning methods such as Monte-Carlo Dropout, MCDropConnect, Deep ensembles, and Semi-supervised learning. Baal helps in labeling the most uncertain items in the dataset pool to improve model performance and reduce annotation effort. The library is actively maintained by a dedicated team and has been used in various research papers for production and experimentation.

fuse-med-ml
FuseMedML is a Python framework designed to accelerate machine learning-based discovery in the medical field by promoting code reuse. It provides a flexible design concept where data is stored in a nested dictionary, allowing easy handling of multi-modality information. The framework includes components for creating custom models, loss functions, metrics, and data processing operators. Additionally, FuseMedML offers 'batteries included' key components such as fuse.data for data processing, fuse.eval for model evaluation, and fuse.dl for reusable deep learning components. It supports PyTorch and PyTorch Lightning libraries and encourages the creation of domain extensions for specific medical domains.
InstructGraph
InstructGraph is a framework designed to enhance large language models (LLMs) for graph-centric tasks by utilizing graph instruction tuning and preference alignment. The tool collects and decomposes 29 standard graph datasets into four groups, enabling LLMs to better understand and generate graph data. It introduces a structured format verbalizer to transform graph data into a code-like format, facilitating code understanding and generation. Additionally, it addresses hallucination problems in graph reasoning and generation through direct preference optimization (DPO). The tool aims to bridge the gap between textual LLMs and graph data, offering a comprehensive solution for graph-related tasks.
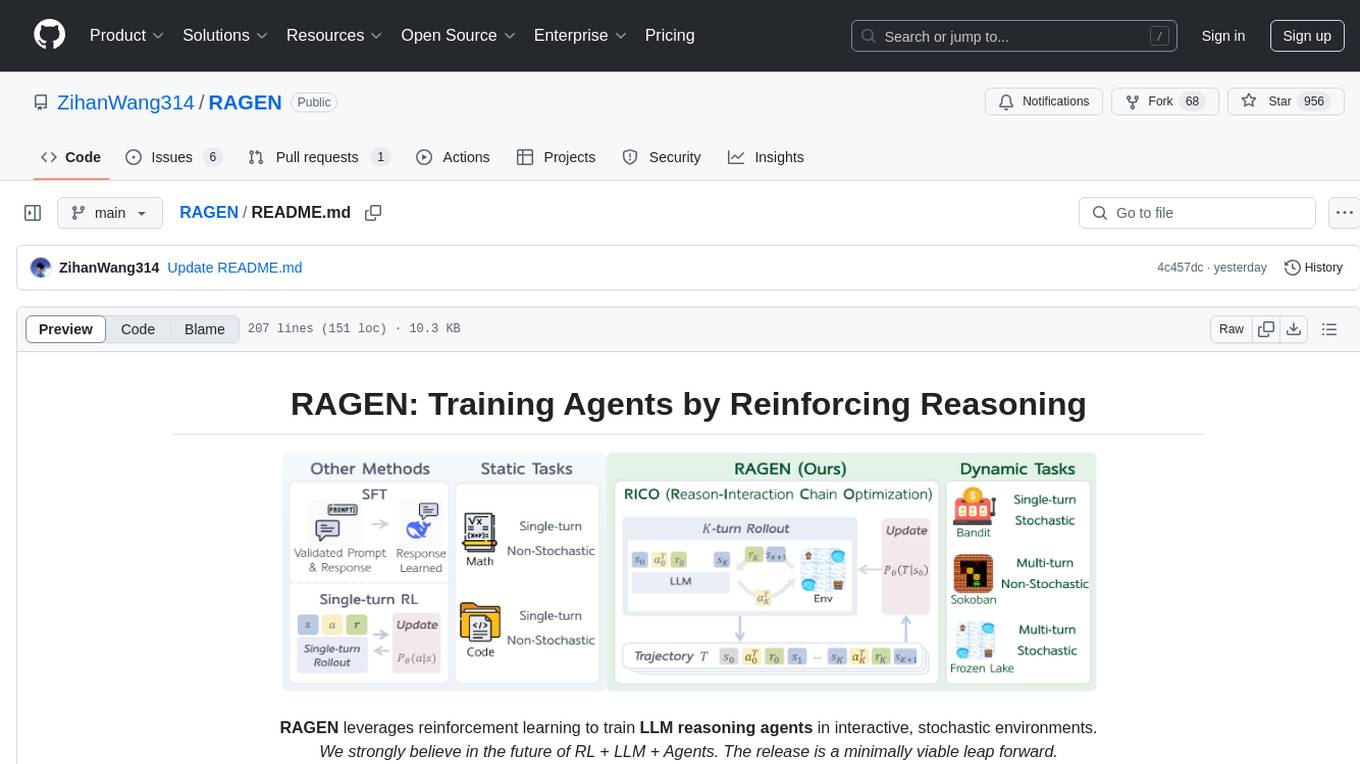
RAGEN
RAGEN is a reinforcement learning framework designed to train reasoning-capable large language model (LLM) agents in interactive, stochastic environments. It addresses challenges such as multi-turn interactions and stochastic environments through a Markov Decision Process (MDP) formulation, Reason-Interaction Chain Optimization (RICO) algorithm, and progressive reward normalization strategies. The framework enables LLMs to reason and interact with the environment, optimizing entire trajectories for long-horizon reasoning while maintaining computational efficiency.

AutoMathText
AutoMathText is an extensive dataset of around 200 GB of mathematical texts autonomously selected by the language model Qwen-72B. It aims to facilitate research in mathematics and artificial intelligence, serve as an educational tool for learning complex mathematical concepts, and provide a foundation for developing AI models specialized in processing mathematical content.

raga-llm-hub
Raga LLM Hub is a comprehensive evaluation toolkit for Language and Learning Models (LLMs) with over 100 meticulously designed metrics. It allows developers and organizations to evaluate and compare LLMs effectively, establishing guardrails for LLMs and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) applications. The platform assesses aspects like Relevance & Understanding, Content Quality, Hallucination, Safety & Bias, Context Relevance, Guardrails, and Vulnerability scanning, along with Metric-Based Tests for quantitative analysis. It helps teams identify and fix issues throughout the LLM lifecycle, revolutionizing reliability and trustworthiness.
LongCite
LongCite is a tool that enables Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate fine-grained citations in long-context Question Answering (QA) scenarios. It provides models trained on GLM-4-9B and Meta-Llama-3.1-8B, supporting up to 128K context. Users can deploy LongCite chatbots, generate accurate responses, and obtain precise sentence-level citations. The tool includes components for model deployment, Coarse to Fine (CoF) pipeline for data construction, model training using LongCite-45k dataset, evaluation with LongBench-Cite benchmark, and citation generation.
llm-analysis
llm-analysis is a tool designed for Latency and Memory Analysis of Transformer Models for Training and Inference. It automates the calculation of training or inference latency and memory usage for Large Language Models (LLMs) or Transformers based on specified model, GPU, data type, and parallelism configurations. The tool helps users to experiment with different setups theoretically, understand system performance, and optimize training/inference scenarios. It supports various parallelism schemes, communication methods, activation recomputation options, data types, and fine-tuning strategies. Users can integrate llm-analysis in their code using the `LLMAnalysis` class or use the provided entry point functions for command line interface. The tool provides lower-bound estimations of memory usage and latency, and aims to assist in achieving feasible and optimal setups for training or inference.
For similar tasks
LLM-Finetuning-Toolkit
LLM Finetuning toolkit is a config-based CLI tool for launching a series of LLM fine-tuning experiments on your data and gathering their results. It allows users to control all elements of a typical experimentation pipeline - prompts, open-source LLMs, optimization strategy, and LLM testing - through a single YAML configuration file. The toolkit supports basic, intermediate, and advanced usage scenarios, enabling users to run custom experiments, conduct ablation studies, and automate fine-tuning workflows. It provides features for data ingestion, model definition, training, inference, quality assurance, and artifact outputs, making it a comprehensive tool for fine-tuning large language models.

interpreto
Interpreto is an interpretability toolkit for large language models (LLMs) that provides a modular framework encompassing attribution methods, concept-based methods, and evaluation metrics. It includes various inference-based and gradient-based attribution methods for both classification and generation tasks. The toolkit also offers concept-based explanations to provide high-level interpretations of latent model representations through steps like concept discovery, interpretation, and concept-to-output attribution. Interpreto aims to enhance model interpretability and facilitate understanding of model decisions and outputs.
ExplainableAI.jl
ExplainableAI.jl is a Julia package that implements interpretability methods for black-box classifiers, focusing on local explanations and attribution maps in input space. The package requires models to be differentiable with Zygote.jl. It is similar to Captum and Zennit for PyTorch and iNNvestigate for Keras models. Users can analyze and visualize explanations for model predictions, with support for different XAI methods and customization. The package aims to provide transparency and insights into model decision-making processes, making it a valuable tool for understanding and validating machine learning models.
context-cite
ContextCite is a tool for attributing statements generated by LLMs back to specific parts of the context. It allows users to analyze and understand the sources of information used by language models in generating responses. By providing attributions, users can gain insights into how the model makes decisions and where the information comes from.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.





