Documents-Parsing-Lab
Jupyter notebooks testing different OCR models for document parsing (Dolphin, MonkeyOCR, Marker, Nanonets, ...)
Stars: 63
A curated collection of Jupyter notebooks for experimenting with state-of-the-art OCR, document parsing, table extraction, and chart understanding techniques. This repository enables easy benchmarking and practical usage of the latest open-source and cloud-based solutions for document image processing.
README:
A curated collection of Jupyter notebooks for experimenting with state-of-the-art OCR, document parsing, table extraction, and chart understanding techniques. This repository enables easy benchmarking and practical usage of the latest open-source and cloud-based solutions for document image processing.
| Notebook | Description |
|---|---|
| bytedance-dolphin-image-parsing.ipynb | Document page parsing with Dolphin by ByteDance |
| Llama-3.1-Nemotron-Nano-VL-8B-V1_parsing_documents.ipynb | Testing the performance of document parsing with Llama-3.1-Nemotron-Nano-VL-8B-V1 |
| docling-documents-parsing-and-tables-extraction.ipynb | Parsing and table extraction with Docling |
| typhoon-ocr-7b-docs-pages-parser.ipynb | Evaluating Typhoon_ocr_7b Document Parsing Capabilities Across Various Use Cases |
| florence-2-large-ocr-documents-pages.ipynb | OCR of document pages using Florence 2 Large |
| florence-2-large-ocr-images-real-life-scenarios.ipynb | Real-life scenario OCR with Florence 2 Large |
| got-ocr2-0-docs-parsing.ipynb | Document pages parsing with GOT-OCR2.0 and Gemini 2.5 Flash |
| marker-docs-parsing.ipynb | Marker-based document parsing experiments |
| mistralocr-docs-parsing.ipynb | Document parsing using MistralOCR |
| monkeyocr-docs-pages-parsing.ipynb | Document parsing with MonkeyOCR |
| nanonets-OCR-s_docs_parsing.ipynb | Advanced document parsing using Nanonets-OCR-s |
| ollama-llama3-2-vision-usage.ipynb | Using Llama3-2 Vision for document parsing |
| paddleocr-3-0-docs-parsing.ipynb | Parsing with PaddleOCR 3.0 PP-StructureV3 |
| pix2text-docs-pages-parsing.ipynb | Document parsing using Pix2Text |
| smoldocling-documents-understanding.ipynb | Document understanding with SmolDocling |
| zerox-pdf-parsing.ipynb | PDF parsing experiments with Zerox |
| qwen2-vl-2b-docs-parsing.ipynb | Documents pages parsing with Qwen2-VL-2B |
| OCRFlux_3B_Docs_Parsing.ipynb | Document parsing with OCRFlux-3B on Lightning AI |
| granite-docling-258m-document-parsing-review.ipynb | Evaluating IBM Granite DocLing 258M for document parsing and layout understanding |
This section includes notebooks focused on table and chart detection, structure recognition, and extraction from documents. It covers various open-source approaches and benchmarks for understanding table and chart layouts and content.
| Notebook | Description |
|---|---|
| unitable-testing-for-table-structure-recognition.ipynb | Testing table detection and structure recognition with UniTable |
| deepdoctection-tables-recognition.ipynb | Evaluating Deepdoctection for table extraction across varied structures |
| gemini-2-5-pro-on-chart-and-table-extraction.ipynb | Chart/table extraction using Gemini 2.5 Pro |
| deplot-plots-to-tables-converter.ipynb | Converting Charts into Tables with DePlot |
| cohere-command-a-vision-charts-understanding.ipynb | Cohere Command A Vision for Charts Understanding |
| cohere-command-a-vision-tables-recognition.ipynb | Cohere Command A Vision for Tables Recognition |
| moondream2-charts-tables-interpretation.ipynb | Moondream2 for Charts and Tables understanding |
This section covers the structured data extraction phase, detailing methods to extract specific data from documents or images. It includes steps like OCR preprocessing, table extraction, named entity recognition (NER), and conversion to structured formats.
| Notebook | Description |
|---|---|
| NuExtract-2-8b-structured-data-extraction | NuExtract-2.0-8B for Structured Data Extraction |
- Benchmark different OCR/document parsing models on real documents.
- Demonstrate table, chart, and text extraction workflows.
- Compare open-source and commercial solutions.
- Provide ready-to-use code snippets for rapid prototyping.
-
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/AdemBoukhris457/Docs_Parsing_Techniques.git
-
Install dependencies as needed for each notebook (see the first cells of each
.ipynbfor requirements). -
Launch Jupyter Notebook or JupyterLab and open any notebook of interest.
-
Run the cells and adapt the code for your documents.
- Some notebooks require model weights or API keys, check comments in each notebook for details.
- Results, insights, and sample outputs are provided inline.
📂 You can find more notebooks, experiments, and datasets related to document parsing and OCR on my Kaggle profile: 👉 https://www.kaggle.com/ademboukhris/code
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Documents-Parsing-Lab
Similar Open Source Tools

Documents-Parsing-Lab
A curated collection of Jupyter notebooks for experimenting with state-of-the-art OCR, document parsing, table extraction, and chart understanding techniques. This repository enables easy benchmarking and practical usage of the latest open-source and cloud-based solutions for document image processing.
Curator
NeMo Curator is a Python library designed for fast and scalable data processing and curation for generative AI use cases. It accelerates data processing by leveraging GPUs with Dask and RAPIDS, providing customizable pipelines for text and image curation. The library offers pre-built pipelines for synthetic data generation, enabling users to train and customize generative AI models such as LLMs, VLMs, and WFMs.
auto-dev
AutoDev Xiuper is an AI-native, multi-agent development platform built on Kotlin Multiplatform. It covers all seven phases of the software development lifecycle and runs on 8+ platforms. The platform provides a unified architecture for writing code once and running it anywhere, with specialized agents for each phase of development. It supports various devices including IntelliJ IDEA, VS Code, CLI, Web, Desktop, Android, iOS, and Server. The platform also offers features like Multi-LLM support, DevIns language for workflow automation, MCP Protocol for extensible tool ecosystem, and code intelligence for multiple programming languages.
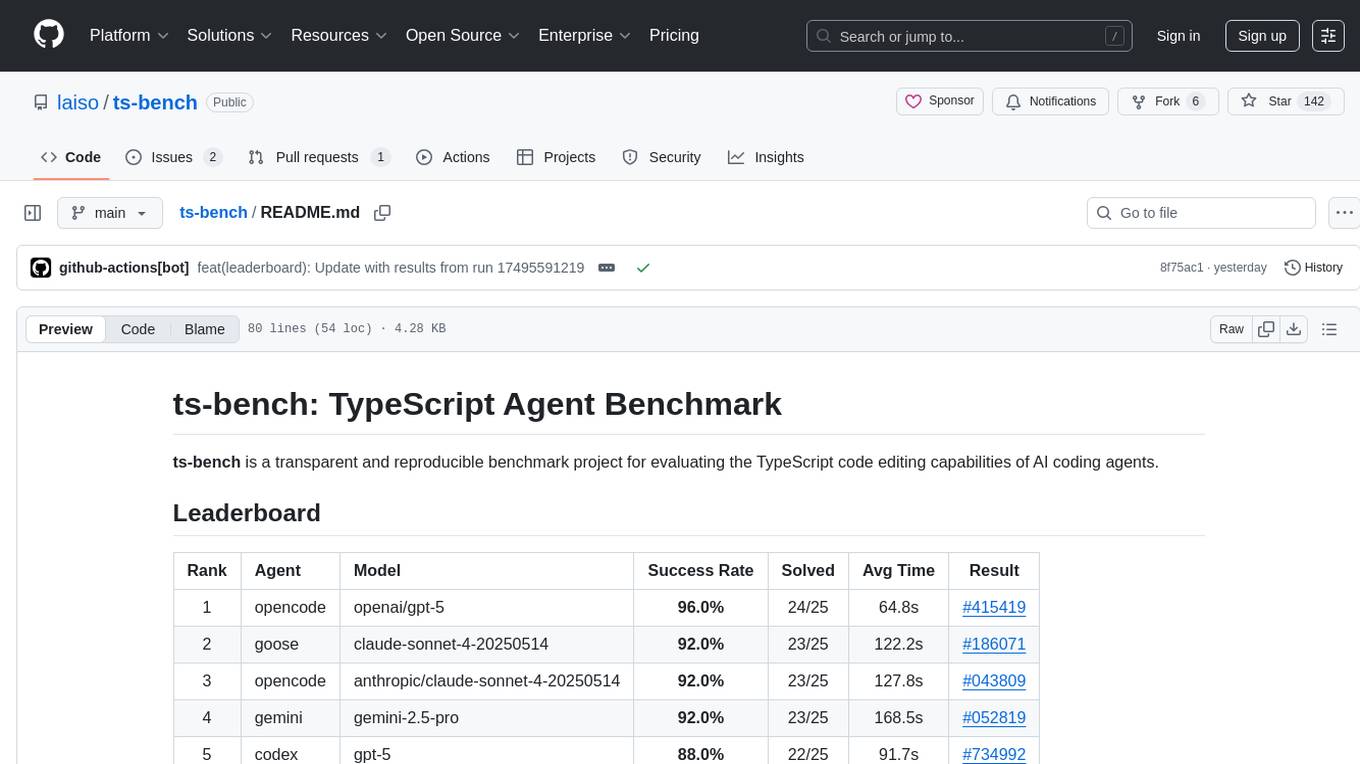
ts-bench
TS-Bench is a performance benchmarking tool for TypeScript projects. It provides detailed insights into the performance of TypeScript code, helping developers optimize their projects. With TS-Bench, users can measure and compare the execution time of different code snippets, functions, or modules. The tool offers a user-friendly interface for running benchmarks and analyzing the results. TS-Bench is a valuable asset for developers looking to enhance the performance of their TypeScript applications.
sktime
sktime is a Python library for time series analysis that provides a unified interface for various time series learning tasks such as classification, regression, clustering, annotation, and forecasting. It offers time series algorithms and tools compatible with scikit-learn for building, tuning, and validating time series models. sktime aims to enhance the interoperability and usability of the time series analysis ecosystem by empowering users to apply algorithms across different tasks and providing interfaces to related libraries like scikit-learn, statsmodels, tsfresh, PyOD, and fbprophet.
AReaL
AReaL (Ant Reasoning RL) is an open-source reinforcement learning system developed at the RL Lab, Ant Research. It is designed for training Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) in a fully open and inclusive manner. AReaL provides reproducible experiments for 1.5B and 7B LRMs, showcasing its scalability and performance across diverse computational budgets. The system follows an iterative training process to enhance model performance, with a focus on mathematical reasoning tasks. AReaL is equipped to adapt to different computational resource settings, enabling users to easily configure and launch training trials. Future plans include support for advanced models, optimizations for distributed training, and exploring research topics to enhance LRMs' reasoning capabilities.

motia
Motia is an AI agent framework designed for software engineers to create, test, and deploy production-ready AI agents quickly. It provides a code-first approach, allowing developers to write agent logic in familiar languages and visualize execution in real-time. With Motia, developers can focus on business logic rather than infrastructure, offering zero infrastructure headaches, multi-language support, composable steps, built-in observability, instant APIs, and full control over AI logic. Ideal for building sophisticated agents and intelligent automations, Motia's event-driven architecture and modular steps enable the creation of GenAI-powered workflows, decision-making systems, and data processing pipelines.

deepfabric
DeepFabric is a CLI tool and SDK designed for researchers and developers to generate high-quality synthetic datasets at scale using large language models. It leverages a graph and tree-based architecture to create diverse and domain-specific datasets while minimizing redundancy. The tool supports generating Chain of Thought datasets for step-by-step reasoning tasks and offers multi-provider support for using different language models. DeepFabric also allows for automatic dataset upload to Hugging Face Hub and uses YAML configuration files for flexibility in dataset generation.
pai-opencode
PAI-OpenCode is a complete port of Daniel Miessler's Personal AI Infrastructure (PAI) to OpenCode, an open-source, provider-agnostic AI coding assistant. It brings modular capabilities, dynamic multi-agent orchestration, session history, and lifecycle automation to personalize AI assistants for users. With support for 75+ AI providers, PAI-OpenCode offers dynamic per-task model routing, full PAI infrastructure, real-time session sharing, and multiple client options. The tool optimizes cost and quality with a 3-tier model strategy and a 3-tier research system, allowing users to switch presets for different routing strategies. PAI-OpenCode's architecture preserves PAI's design while adapting to OpenCode, documented through Architecture Decision Records (ADRs).
Generative_AI_For_Science
Generative AI for Science is a comprehensive, hands-on guide for researchers, students, and practitioners who want to apply cutting-edge AI techniques to scientific discovery. The book bridges the gap between AI/ML expertise and domain science, providing practical implementations across chemistry, biology, physics, geoscience, and beyond. It covers key AI architectures like Transformers, Diffusion Models, VAEs, and GNNs, and teaches how to apply generative models to problems in climate science, drug discovery, genomics, materials science, and more. The book also emphasizes best practices around ethics, reproducibility, and deployment, helping readers develop the intuition to know when and how to apply AI to scientific research.
UniCoT
Uni-CoT is a unified reasoning framework that extends Chain-of-Thought (CoT) principles to the multimodal domain, enabling Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to perform interpretable, step-by-step reasoning across both text and vision. It decomposes complex multimodal tasks into structured, manageable steps that can be executed sequentially or in parallel, allowing for more scalable and systematic reasoning.
LlamaV-o1
LlamaV-o1 is a Large Multimodal Model designed for spontaneous reasoning tasks. It outperforms various existing models on multimodal reasoning benchmarks. The project includes a Step-by-Step Visual Reasoning Benchmark, a novel evaluation metric, and a combined Multi-Step Curriculum Learning and Beam Search Approach. The model achieves superior performance in complex multi-step visual reasoning tasks in terms of accuracy and efficiency.
rag-web-ui
RAG Web UI is an intelligent dialogue system based on RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) technology. It helps enterprises and individuals build intelligent Q&A systems based on their own knowledge bases. By combining document retrieval and large language models, it delivers accurate and reliable knowledge-based question-answering services. The system is designed with features like intelligent document management, advanced dialogue engine, and a robust architecture. It supports multiple document formats, async document processing, multi-turn contextual dialogue, and reference citations in conversations. The architecture includes a backend stack with Python FastAPI, MySQL + ChromaDB, MinIO, Langchain, JWT + OAuth2 for authentication, and a frontend stack with Next.js, TypeScript, Tailwind CSS, Shadcn/UI, and Vercel AI SDK for AI integration. Performance optimization includes incremental document processing, streaming responses, vector database performance tuning, and distributed task processing. The project is licensed under the Apache-2.0 License and is intended for learning and sharing RAG knowledge only, not for commercial purposes.
axonhub
AxonHub is an all-in-one AI development platform that serves as an AI gateway allowing users to switch between model providers without changing any code. It provides features like vendor lock-in prevention, integration simplification, observability enhancement, and cost control. Users can access any model using any SDK with zero code changes. The platform offers full request tracing, enterprise RBAC, smart load balancing, and real-time cost tracking. AxonHub supports multiple databases, provides a unified API gateway, and offers flexible model management and API key creation for authentication. It also integrates with various AI coding tools and SDKs for seamless usage.
spark-nlp
Spark NLP is a state-of-the-art Natural Language Processing library built on top of Apache Spark. It provides simple, performant, and accurate NLP annotations for machine learning pipelines that scale easily in a distributed environment. Spark NLP comes with 36000+ pretrained pipelines and models in more than 200+ languages. It offers tasks such as Tokenization, Word Segmentation, Part-of-Speech Tagging, Named Entity Recognition, Dependency Parsing, Spell Checking, Text Classification, Sentiment Analysis, Token Classification, Machine Translation, Summarization, Question Answering, Table Question Answering, Text Generation, Image Classification, Image to Text (captioning), Automatic Speech Recognition, Zero-Shot Learning, and many more NLP tasks. Spark NLP is the only open-source NLP library in production that offers state-of-the-art transformers such as BERT, CamemBERT, ALBERT, ELECTRA, XLNet, DistilBERT, RoBERTa, DeBERTa, XLM-RoBERTa, Longformer, ELMO, Universal Sentence Encoder, Llama-2, M2M100, BART, Instructor, E5, Google T5, MarianMT, OpenAI GPT2, Vision Transformers (ViT), OpenAI Whisper, and many more not only to Python and R, but also to JVM ecosystem (Java, Scala, and Kotlin) at scale by extending Apache Spark natively.
For similar tasks

Documents-Parsing-Lab
A curated collection of Jupyter notebooks for experimenting with state-of-the-art OCR, document parsing, table extraction, and chart understanding techniques. This repository enables easy benchmarking and practical usage of the latest open-source and cloud-based solutions for document image processing.
extractor
Extractor is an AI-powered data extraction library for Laravel that leverages OpenAI's capabilities to effortlessly extract structured data from various sources, including images, PDFs, and emails. It features a convenient wrapper around OpenAI Chat and Completion endpoints, supports multiple input formats, includes a flexible Field Extractor for arbitrary data extraction, and integrates with Textract for OCR functionality. Extractor utilizes JSON Mode from the latest GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 models, providing accurate and efficient data extraction.
NeMo-Guardrails
NeMo Guardrails is an open-source toolkit for easily adding _programmable guardrails_ to LLM-based conversational applications. Guardrails (or "rails" for short) are specific ways of controlling the output of a large language model, such as not talking about politics, responding in a particular way to specific user requests, following a predefined dialog path, using a particular language style, extracting structured data, and more.
kor
Kor is a prototype tool designed to help users extract structured data from text using Language Models (LLMs). It generates prompts, sends them to specified LLMs, and parses the output. The tool works with the parsing approach and is integrated with the LangChain framework. Kor is compatible with pydantic v2 and v1, and schema is typed checked using pydantic. It is primarily used for extracting information from text based on provided reference examples and schema documentation. Kor is designed to work with all good-enough LLMs regardless of their support for function/tool calling or JSON modes.
awesome-llm-json
This repository is an awesome list dedicated to resources for using Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate JSON or other structured outputs. It includes terminology explanations, hosted and local models, Python libraries, blog articles, videos, Jupyter notebooks, and leaderboards related to LLMs and JSON generation. The repository covers various aspects such as function calling, JSON mode, guided generation, and tool usage with different providers and models.
tensorzero
TensorZero is an open-source platform that helps LLM applications graduate from API wrappers into defensible AI products. It enables a data & learning flywheel for LLMs by unifying inference, observability, optimization, and experimentation. The platform includes a high-performance model gateway, structured schema-based inference, observability, experimentation, and data warehouse for analytics. TensorZero Recipes optimize prompts and models, and the platform supports experimentation features and GitOps orchestration for deployment.
stagehand
Stagehand is an AI web browsing framework that simplifies and extends web automation using three simple APIs: act, extract, and observe. It aims to provide a lightweight, configurable framework without complex abstractions, allowing users to automate web tasks reliably. The tool generates Playwright code based on atomic instructions provided by the user, enabling natural language-driven web automation. Stagehand is open source, maintained by the Browserbase team, and supports different models and model providers for flexibility in automation tasks.
azure-ai-document-processing-samples
This repository contains a collection of code samples that demonstrate how to use various Azure AI capabilities to process documents. The samples help engineering teams establish techniques with Azure AI Foundry, Azure OpenAI, Azure AI Document Intelligence, and Azure AI Language services to build solutions for extracting structured data, classifying, and analyzing documents. The techniques simplify custom model training, improve reliability in document processing, and simplify document processing workflows by providing reusable code and patterns that can be easily modified and evaluated for most use cases.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.