
ubicloud
Open source alternative to AWS. Elastic compute, block storage (non replicated), firewall and load balancer, managed Postgres, K8s, AI inference, and IAM services.
Stars: 11849

Ubicloud is an open source cloud platform that provides Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) features on bare metal providers like Hetzner, Leaseweb, and AWS Bare Metal. Users can either set it up themselves on these providers or use the managed service offered by Ubicloud. The platform allows users to cloudify bare metal Linux machines, provision and manage cloud resources, and offers an open source alternative to traditional cloud providers, reducing costs and returning control of infrastructure to the users.
README:
Ubicloud is an open source cloud that can run anywhere. Think of it as an open alternative to cloud providers, like what Linux is to proprietary operating systems.
Ubicloud provides IaaS cloud features on bare metal providers, such as Hetzner, Leaseweb, and AWS Bare Metal. You can set it up yourself on these providers or you can use our managed service.
You can use Ubicloud without installing anything. When you do this, we pass along the underlying provider's benefits to you, such as price or location.
You can also build your own cloud. To do this, start up Ubicloud's control plane and connect to its cloud console.
git clone [email protected]:ubicloud/ubicloud.git
# Generate secrets for demo
./demo/generate_env
# Run containers: db-migrator, app (web & respirate), postgresql
docker-compose -f demo/docker-compose.yml up
# Visit localhost:3000
The control plane is responsible for cloudifying bare metal Linux machines. The easiest way to build your own cloud is to lease instances from one of those providers. For example: https://www.hetzner.com/sb
Once you lease instance(s), update the .env file with the following environment
variables:
HETZNER_USERHETZNER_PASSWORDHETZNER_SSH_PUBLIC_KEYHETZNER_SSH_PRIVATE_KEY
To get the user credentials, create a user according to these instructions. The SSH key is the one you set when you created the robot server.
The first thing to make sure is you use the hetzner robot rescue system to install ubuntu 24.04.
Then, run the following script for each instance to cloudify it. Currently, the script cloudifies bare metal instances leased from Hetzner. After you cloudify your instances, you can provision and manage cloud resources on these machines.
# Enter hostname/IP and provider
docker exec -it ubicloud-app ./demo/cloudify_server
Later when you create VMs, Ubicloud will assign them IPv6 addresses. If your ISP doesn't support IPv6, please use a VPN or tunnel broker such as Mullvad or Hurricane Electric's https://tunnelbroker.net/ to connect. Alternatively, you could lease IPv4 addresses from your provider and add them to your control plane.
Public cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud have made life easier for start-ups and enterprises. But they are closed source, have you rent computers at a huge premium, and lock you in. Ubicloud offers an open source alternative, reduces your costs, and returns control of your infrastructure back to you. All without sacrificing the cloud's convenience.
Today, AWS offers about two hundred cloud services. Ultimately, we will implement 10% of the cloud services that make up 80% of that consumption.
Example workloads and reasons to use Ubicloud today include:
-
You have an ephemeral workload like a CI/CD pipeline (we're integrating with GitHub Actions), or you'd like to run compute/memory heavy tests. Our managed cloud is ~3x cheaper than AWS, so you save on costs.
-
You want a portable and simple app deployment service like Kamal. We're moving Ubicloud's control plane from Heroku to Kamal; and we want to provide open and portable services for Kamal's dependencies in the process.
-
You have bare metal machines sitting somewhere. You'd like to build your own cloud for portability, security, or compliance reasons.
You can provide us your feedback, get help, or ask us questions regarding your Ubicloud installations in the Community Forum.
We follow an established architectural pattern in building public cloud services. A control plane manages a data plane, where the data plane leverages open source software. You can find our current cloud components / services below.
-
Elastic Compute: Our control plane communicates with Linux bare metal servers using SSH. We use Cloud Hypervisor as our virtual machine monitor (VMM); and each instance of the VMM is contained within Linux namespaces for further isolation / security.
-
Networking: We use IPsec tunneling to establish an encrypted and private network environment. We support IPv4 and IPv6 in a dual-stack setup and provide both public and private networking. For security, each customer’s VMs operate in their own networking namespace. For firewalls and load balancers, we use Linux nftables.
-
Block Storage, non replicated: We use Storage Performance Development Toolkit (SPDK) to provide virtualized block storage to VMs. SPDK enables us to add enterprise features such as snapshot and replication in the future. We follow security best practices and encrypt the data encryption key itself.
-
Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC): With ABAC, you can define attributes, roles, and permissions for users and give them fine-grained access to resources. You can read more about our ABAC design here.
-
What's Next?: We're planning to work on a managed K8s or metrics/monitoring service next. If you have a workload that would benefit from a specific cloud service, please get in touch with us through our Community Forum.
-
Control plane: Manages data plane services and resources. This is a Ruby program that stores its data in Postgres. We use the Roda framework to serve HTTP requests and Sequel to access the database. We manage web authentication with Rodauth. We communicate with data plane servers using SSH, via the library net-ssh. For our tests, we use RSpec.
-
Cloud console: Server-side web app served by the Roda framework. For the visual design, we use Tailwind CSS with components from Tailwind UI. We also use jQuery for interactivity.
If you’d like to start hacking with Ubicloud, any method of obtaining
Ruby and Postgres versions is acceptable. If you have no opinion on
this, our development team uses mise as documented here in
detail.
Greptile provides an AI/LLM that indexes Ubicloud's source code can answer questions about it.
Our founding team comes from Azure; and worked at Amazon and Heroku before that. We also have start-up experience. We were co-founders and founding team members at Citus Data, which got acquired by Microsoft.
We see three differences. First, Ubicloud is available as a managed service (vs boxed software). This way, you can get started in minutes rather than weeks. Since Ubicloud is designed for multi-tenancy, it comes with built-in features such as encryption at rest and in transit, virtual networking, secrets rotation, etc.
Second, we're initially targeting developers. This -we hope- will give us fast feedback cycles and enable us to have 6 key services in GA form in the next two years. OpenStack is still primarily used for 3 cloud services.
Last, we're designing for simplicity. With OpenStack, you pick between 10 hypervisors, 10 S3 implementations, and 5 block storage implementations. The software needs to work in a way where all of these implementations are compatible with each other. That leads to consultant-ware. We'll take a more opinionated approach with Ubicloud.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for ubicloud
Similar Open Source Tools

ubicloud
Ubicloud is an open source cloud platform that provides Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) features on bare metal providers like Hetzner, Leaseweb, and AWS Bare Metal. Users can either set it up themselves on these providers or use the managed service offered by Ubicloud. The platform allows users to cloudify bare metal Linux machines, provision and manage cloud resources, and offers an open source alternative to traditional cloud providers, reducing costs and returning control of infrastructure to the users.
tau
Tau is a framework for building low maintenance & highly scalable cloud computing platforms that software developers will love. It aims to solve the high cost and time required to build, deploy, and scale software by providing a developer-friendly platform that offers autonomy and flexibility. Tau simplifies the process of building and maintaining a cloud computing platform, enabling developers to achieve 'Local Coding Equals Global Production' effortlessly. With features like auto-discovery, content-addressing, and support for WebAssembly, Tau empowers users to create serverless computing environments, host frontends, manage databases, and more. The platform also supports E2E testing and can be extended using a plugin system called orbit.
Heat
Heat is an open source native iOS and macOS client for interacting with the most popular LLM services. A sister project, Swift GenKit, attempts to abstract away all the differences across each service including OpenAI, Mistral, Perplexity, Anthropic and all the models available with Ollama which you can run locally.
paddler
Paddler is an open-source LLM load balancer and serving platform designed for digital products and users who prioritize privacy, reliability, cost control, and independence from closed-source model providers. It allows running inference, deploying, and scaling LLMs on personal infrastructure, offering a seamless developer experience. Key features include inference through llama.cpp engine, LLM-specific load balancing, dynamic model swapping, request buffering, and built-in web admin panel for management and monitoring. Paddler is suitable for product teams needing LLM inference, DevOps/LLMOps teams deploying LLMs at scale, organizations handling sensitive data, and product leaders aiming for predictable LLM costs and reliable model performance.
foundationallm
FoundationaLLM is a platform designed for deploying, scaling, securing, and governing generative AI in enterprises. It allows users to create AI agents grounded in enterprise data, integrate REST APIs, experiment with large language models, centrally manage AI agents and assets, deploy scalable vectorization data pipelines, enable non-developer users to create their own AI agents, control access with role-based access controls, and harness capabilities from Azure AI and Azure OpenAI. The platform simplifies integration with enterprise data sources, provides fine-grain security controls, load balances across multiple endpoints, and is extensible to new data sources and orchestrators. FoundationaLLM addresses the need for customized copilots or AI agents that are secure, licensed, flexible, and suitable for enterprise-scale production.
foundationallm
FoundationaLLM is a platform designed for deploying, scaling, securing, and governing generative AI in enterprises. It allows users to create AI agents grounded in enterprise data, integrate REST APIs, experiment with various large language models, centrally manage AI agents and their assets, deploy scalable vectorization data pipelines, enable non-developer users to create their own AI agents, control access with role-based access controls, and harness capabilities from Azure AI and Azure OpenAI. The platform simplifies integration with enterprise data sources, provides fine-grain security controls, scalability, extensibility, and addresses the challenges of delivering enterprise copilots or AI agents.
cedana-cli
Cedana is a framework for the democritization and commodification of compute. It leverages checkpoint/restore to migrate work across machines, clouds, and beyond. The repo contains a CLI tool for developers to experiment with the system.
wandb
Weights & Biases (W&B) is a platform that helps users build better machine learning models faster by tracking and visualizing all components of the machine learning pipeline, from datasets to production models. It offers tools for tracking, debugging, evaluating, and monitoring machine learning applications. W&B provides integrations with popular frameworks like PyTorch, TensorFlow/Keras, Hugging Face Transformers, PyTorch Lightning, XGBoost, and Sci-Kit Learn. Users can easily log metrics, visualize performance, and compare experiments using W&B. The platform also supports hosting options in the cloud or on private infrastructure, making it versatile for various deployment needs.
chat-with-your-data-solution-accelerator
Chat with your data using OpenAI and AI Search. This solution accelerator uses an Azure OpenAI GPT model and an Azure AI Search index generated from your data, which is integrated into a web application to provide a natural language interface, including speech-to-text functionality, for search queries. Users can drag and drop files, point to storage, and take care of technical setup to transform documents. There is a web app that users can create in their own subscription with security and authentication.
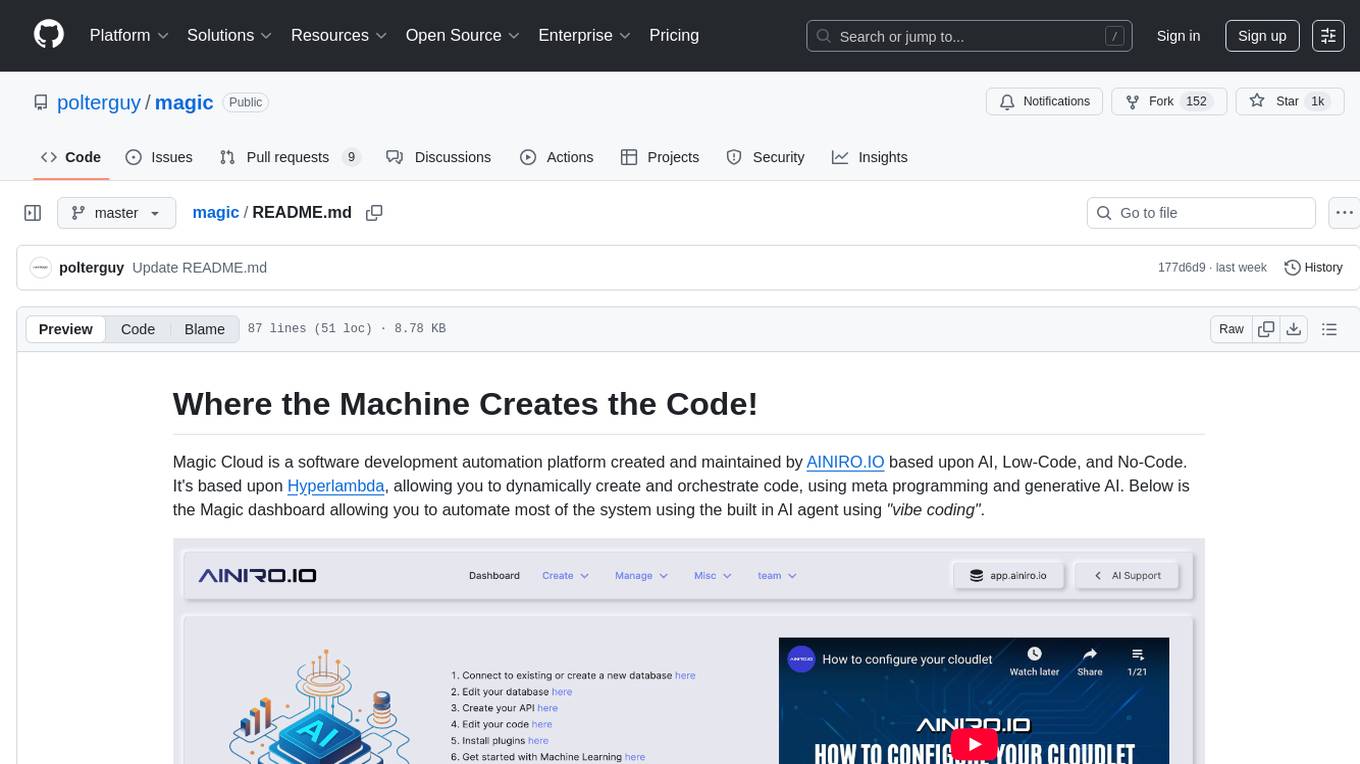
magic
Magic Cloud is a software development automation platform based on AI, Low-Code, and No-Code. It allows dynamic code creation and orchestration using Hyperlambda, generative AI, and meta programming. The platform includes features like CRUD generation, No-Code AI, Hyperlambda programming language, AI agents creation, and various components for software development. Magic is suitable for backend development, AI-related tasks, and creating AI chatbots. It offers high-level programming capabilities, productivity gains, and reduced technical debt.
autoMate
autoMate is an AI-powered local automation tool designed to help users automate repetitive tasks and reclaim their time. It leverages AI and RPA technology to operate computer interfaces, understand screen content, make autonomous decisions, and support local deployment for data security. With natural language task descriptions, users can easily automate complex workflows without the need for programming knowledge. The tool aims to transform work by freeing users from mundane activities and allowing them to focus on tasks that truly create value, enhancing efficiency and liberating creativity.
tiledesk
Tiledesk is an Open Source Live Chat platform with integrated Chatbots written in NodeJs and Express. It provides a multi-channel platform for Web, Android, and iOS, offering out-of-the-box chatbots that work alongside humans. Users can automate conversations using native chatbot technology powered by AI, connect applications via APIs or Webhooks, deploy visual applications within conversations, and enable applications to interact with chatbots or end-users. Tiledesk is multichannel, allowing chatbot scripts with images and buttons to run on various channels like Whatsapp, Facebook Messenger, and Telegram. The project includes Tiledesk Server, Dashboard, Design Studio, Chat21 ionic, Web Widget, Server, Http Server, MongoDB, and a proxy. It offers Helm charts for Kubernetes deployment, but customization is recommended for production environments, such as integrating with external MongoDB or monitoring/logging tools. Enterprise customers can request private Docker images by contacting [email protected].
materialize
Materialize is a real-time data integration platform that creates and continually updates consistent views of transactional data from across your organization. Its SQL interface democratizes the ability to serve and access live data. Materialize can be deployed anywhere your infrastructure runs. Use Materialize to deliver fresh context for AI/RAG pipelines, power operational dashboards, and create more dynamic customer experiences without building time-consuming custom data pipelines. Materialize focuses on providing correct and consistent answers with minimal latency, and does not ask you to accept either approximate answers or eventual consistency. Materialize answers a query with the correct result on a specific version of your data. Materialize recasts SQL queries as dataflows, which can react efficiently to changes in your data as they happen. Materialize supports a large fraction of PostgreSQL features and is actively expanding support for more built-in PostgreSQL functions. Materialize can read data directly from PostgreSQL or MySQL replication stream, from Kafka, or from SaaS applications via webhooks. Once data is in, define views and perform reads via the PostgreSQL protocol. Materialize supports a comprehensive variety of SQL features, all using the PostgreSQL dialect and protocol. Materialize can incrementally maintain views in the presence of arbitrary inserts, updates, and deletes. Materialize supports recursion that enables incrementally updating tree and graph structures. Materialize is primarily written in Rust.
TagUI
TagUI is an open-source RPA tool that allows users to automate repetitive tasks on their computer, including tasks on websites, desktop apps, and the command line. It supports multiple languages and offers features like interacting with identifiers, automating data collection, moving data between TagUI and Excel, and sending Telegram notifications. Users can create RPA robots using MS Office Plug-ins or text editors, run TagUI on the cloud, and integrate with other RPA tools. TagUI prioritizes enterprise security by running on users' computers and not storing data. It offers detailed logs, enterprise installation guides, and support for centralised reporting.
lumigator
Lumigator is an open-source platform developed by Mozilla.ai to help users select the most suitable language model for their specific needs. It supports the evaluation of summarization tasks using sequence-to-sequence models such as BART and BERT, as well as causal models like GPT and Mistral. The platform aims to make model selection transparent, efficient, and empowering by providing a framework for comparing LLMs using task-specific metrics to evaluate how well a model fits a project's needs. Lumigator is in the early stages of development and plans to expand support to additional machine learning tasks and use cases in the future.
cymbal-air-toolbox-demo
Cymbal Air Toolbox Demo is a project that provides a production-quality reference implementation for building Agentic applications using Agents and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) to query and interact with data stored in Google Cloud Databases. The demo showcases a customer service assistant for a fictional airline, Cymbal Air, assisting travelers with flight management and providing information about San Francisco International Airport (SFO). It utilizes techniques like Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) and Agent-based Orchestration to enhance responses and handle a wide variety of queries. The architecture includes components like the user-facing application, MCP Toolbox middleware server, and a database, offering advantages such as better security, scalability, and recall for agents.
For similar tasks

ubicloud
Ubicloud is an open source cloud platform that provides Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) features on bare metal providers like Hetzner, Leaseweb, and AWS Bare Metal. Users can either set it up themselves on these providers or use the managed service offered by Ubicloud. The platform allows users to cloudify bare metal Linux machines, provision and manage cloud resources, and offers an open source alternative to traditional cloud providers, reducing costs and returning control of infrastructure to the users.
open-saas
Open SaaS is a free and open-source React and Node.js template for building SaaS applications. It comes with a variety of features out of the box, including authentication, payments, analytics, and more. Open SaaS is built on top of the Wasp framework, which provides a number of features to make it easy to build SaaS applications, such as full-stack authentication, end-to-end type safety, jobs, and one-command deploy.

airbroke
Airbroke is an open-source error catcher tool designed for modern web applications. It provides a PostgreSQL-based backend with an Airbrake-compatible HTTP collector endpoint and a React-based frontend for error management. The tool focuses on simplicity, maintaining a small database footprint even under heavy data ingestion. Users can ask AI about issues, replay HTTP exceptions, and save/manage bookmarks for important occurrences. Airbroke supports multiple OAuth providers for secure user authentication and offers occurrence charts for better insights into error occurrences. The tool can be deployed in various ways, including building from source, using Docker images, deploying on Vercel, Render.com, Kubernetes with Helm, or Docker Compose. It requires Node.js, PostgreSQL, and specific system resources for deployment.
llmops-promptflow-template
LLMOps with Prompt flow is a template and guidance for building LLM-infused apps using Prompt flow. It provides centralized code hosting, lifecycle management, variant and hyperparameter experimentation, A/B deployment, many-to-many dataset/flow relationships, multiple deployment targets, comprehensive reporting, BYOF capabilities, configuration-based development, local prompt experimentation and evaluation, endpoint testing, and optional Human-in-loop validation. The tool is customizable to suit various application needs.
cheat-sheet-pdf
The Cheat-Sheet Collection for DevOps, Engineers, IT professionals, and more is a curated list of cheat sheets for various tools and technologies commonly used in the software development and IT industry. It includes cheat sheets for Nginx, Docker, Ansible, Python, Go (Golang), Git, Regular Expressions (Regex), PowerShell, VIM, Jenkins, CI/CD, Kubernetes, Linux, Redis, Slack, Puppet, Google Cloud Developer, AI, Neural Networks, Machine Learning, Deep Learning & Data Science, PostgreSQL, Ajax, AWS, Infrastructure as Code (IaC), System Design, and Cyber Security.
awesome-production-llm
This repository is a curated list of open-source libraries for production large language models. It includes tools for data preprocessing, training/finetuning, evaluation/benchmarking, serving/inference, application/RAG, testing/monitoring, and guardrails/security. The repository also provides a new category called LLM Cookbook/Examples for showcasing examples and guides on using various LLM APIs.
generative-ai-on-aws
Generative AI on AWS by O'Reilly Media provides a comprehensive guide on leveraging generative AI models on the AWS platform. The book covers various topics such as generative AI use cases, prompt engineering, large-language models, fine-tuning techniques, optimization, deployment, and more. Authors Chris Fregly, Antje Barth, and Shelbee Eigenbrode offer insights into cutting-edge AI technologies and practical applications in the field. The book is a valuable resource for data scientists, AI enthusiasts, and professionals looking to explore generative AI capabilities on AWS.
palico-ai
Palico AI is a tech stack designed for rapid iteration of LLM applications. It allows users to preview changes instantly, improve performance through experiments, debug issues with logs and tracing, deploy applications behind a REST API, and manage applications with a UI control panel. Users have complete flexibility in building their applications with Palico, integrating with various tools and libraries. The tool enables users to swap models, prompts, and logic easily using AppConfig. It also facilitates performance improvement through experiments and provides options for deploying applications to cloud providers or using managed hosting. Contributions to the project are welcomed, with easy ways to get involved by picking issues labeled as 'good first issue'.
For similar jobs

minio
MinIO is a High Performance Object Storage released under GNU Affero General Public License v3.0. It is API compatible with Amazon S3 cloud storage service. Use MinIO to build high performance infrastructure for machine learning, analytics and application data workloads.

ai-on-gke
This repository contains assets related to AI/ML workloads on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). Run optimized AI/ML workloads with Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) platform orchestration capabilities. A robust AI/ML platform considers the following layers: Infrastructure orchestration that support GPUs and TPUs for training and serving workloads at scale Flexible integration with distributed computing and data processing frameworks Support for multiple teams on the same infrastructure to maximize utilization of resources

kong
Kong, or Kong API Gateway, is a cloud-native, platform-agnostic, scalable API Gateway distinguished for its high performance and extensibility via plugins. It also provides advanced AI capabilities with multi-LLM support. By providing functionality for proxying, routing, load balancing, health checking, authentication (and more), Kong serves as the central layer for orchestrating microservices or conventional API traffic with ease. Kong runs natively on Kubernetes thanks to its official Kubernetes Ingress Controller.
AI-in-a-Box
AI-in-a-Box is a curated collection of solution accelerators that can help engineers establish their AI/ML environments and solutions rapidly and with minimal friction, while maintaining the highest standards of quality and efficiency. It provides essential guidance on the responsible use of AI and LLM technologies, specific security guidance for Generative AI (GenAI) applications, and best practices for scaling OpenAI applications within Azure. The available accelerators include: Azure ML Operationalization in-a-box, Edge AI in-a-box, Doc Intelligence in-a-box, Image and Video Analysis in-a-box, Cognitive Services Landing Zone in-a-box, Semantic Kernel Bot in-a-box, NLP to SQL in-a-box, Assistants API in-a-box, and Assistants API Bot in-a-box.
awsome-distributed-training
This repository contains reference architectures and test cases for distributed model training with Amazon SageMaker Hyperpod, AWS ParallelCluster, AWS Batch, and Amazon EKS. The test cases cover different types and sizes of models as well as different frameworks and parallel optimizations (Pytorch DDP/FSDP, MegatronLM, NemoMegatron...).
generative-ai-cdk-constructs
The AWS Generative AI Constructs Library is an open-source extension of the AWS Cloud Development Kit (AWS CDK) that provides multi-service, well-architected patterns for quickly defining solutions in code to create predictable and repeatable infrastructure, called constructs. The goal of AWS Generative AI CDK Constructs is to help developers build generative AI solutions using pattern-based definitions for their architecture. The patterns defined in AWS Generative AI CDK Constructs are high level, multi-service abstractions of AWS CDK constructs that have default configurations based on well-architected best practices. The library is organized into logical modules using object-oriented techniques to create each architectural pattern model.
model_server
OpenVINO™ Model Server (OVMS) is a high-performance system for serving models. Implemented in C++ for scalability and optimized for deployment on Intel architectures, the model server uses the same architecture and API as TensorFlow Serving and KServe while applying OpenVINO for inference execution. Inference service is provided via gRPC or REST API, making deploying new algorithms and AI experiments easy.
dify-helm
Deploy langgenius/dify, an LLM based chat bot app on kubernetes with helm chart.
