
pgedge-postgres-mcp
pgEdge MCP Server. A PostgreSQL MCP server with a Natural Language Agent CLI and Web UI. BETA CODE - DO NOT USE FOR PRODUCTION!
Stars: 55
The pgedge-postgres-mcp repository contains a set of tools and scripts for managing and monitoring PostgreSQL databases in an edge computing environment. It provides functionalities for automating database tasks, monitoring database performance, and ensuring data integrity in edge computing scenarios. The tools are designed to be lightweight and efficient, making them suitable for resource-constrained edge devices. With pgedge-postgres-mcp, users can easily deploy and manage PostgreSQL databases in edge computing environments with minimal overhead.
README:
- Introduction
- Installing the MCP Server
- Configuring the MCP Server
- Specifying Configuration Preferences
- Using Environment Variables to Specify Options
- Including Provider Embeddings in a Configuration File
- Configuring the Agent for Multiple Databases
- Configuring Supporting Services; HTTP, systemd, and nginx
- Using an Encryption Secret File
- Enabling or Disabling Features
- Configuring and Using Client Applications
- Authentication and Security
- Reference
- Advanced Topics
- For Developers
- Building Chat Clients
- Contributing
- Troubleshooting
- pgEdge Postgres MCP Server and Natural Language Agent Release Notes
- Licence
The pgEdge Postgres Model Context Protocol (MCP) server enables SQL queries against PostgreSQL databases through MCP-compatible clients like Claude Desktop. The Natural Language Agent provides supporting functionality that allows you to use natural language to form SQL queries.
🚧 WARNING: This code is in pre-release status and MUST NOT be put into production without thorough testing!
⚠️ NOT FOR PUBLIC-FACING APPLICATIONS: This MCP server provides LLMs with read access to your entire database schema and data. It should only be used for internal tools, developer workflows, or environments where all users are trusted. For public-facing applications, consider the pgEdge RAG Server instead. See the Choosing the Right Solution guide for details.
- 🔒 Read-Only Protection - All queries run in read-only transactions
- 📊 Resources - Access PostgreSQL statistics and more
- 🛠️ Tools - Query execution, schema analysis, advanced hybrid search (BM25+MMR), embedding generation, resource reading, and more
- 🧠 Prompts - Guided workflows for semantic search setup, database exploration, query diagnostics, and more
- 💬 Production Chat Client - Full-featured Go client with Anthropic prompt caching (90% cost reduction)
- 🌐 HTTP/HTTPS Mode - Direct API access with token authentication
- 🖥️ Web Interface - Modern React-based UI with AI-powered chat for natural language database interaction
- 🐳 Docker Support - Complete containerized deployment with Docker Compose
- 🔐 Secure - TLS support, token auth, read-only enforcement
- 🔄 Hot Reload - Automatic reload of authentication files without server restart
git clone <repository-url>
cd pgedge-postgres-mcp
make buildClaude Code: .mcp.json in each of your project directories
Claude Desktop on macOS: ~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json
Claude Desktop on Windows: %APPDATA%\\Claude\\claude_desktop_config.json
{
"mcpServers": {
"pgedge": {
"command": "/absolute/path/to/bin/pgedge-postgres-mcp"
}
}
}Update your Claude Code and/or Claude Desktop configuration to include database connection parameters:
{
"mcpServers": {
"pgedge": {
"command": "/absolute/path/to/bin/pgedge-postgres-mcp",
"env": {
"PGHOST": "localhost",
"PGPORT": "5432",
"PGDATABASE": "mydb",
"PGUSER": "myuser",
"PGPASSWORD": "mypass"
}
}
}
}Alternatively, use a .pgpass file for password management (recommended for
security):
# ~/.pgpass
localhost:5432:mydb:myuser:mypassThen, provide connection details (except PGPASSWORD) in the configuration file:
{
"mcpServers": {
"pgedge": {
"command": "/absolute/path/to/bin/pgedge-postgres-mcp",
"env": {
"PGHOST": "localhost",
"PGPORT": "5432",
"PGDATABASE": "mydb",
"PGUSER": "myuser"
}
}
}
}Note: The server connects to the database at startup using standard PostgreSQL environment variables (PG*) or PGEDGE_DB_* variables. You can store passwords securely in the
.pgpassfile.
The MCP client (like Claude Desktop) can translate natural language to SQL, which is then executed by this server.
Schema Discovery:
- Request schema information using the
get_schema_infotool - Execute SQL:
SELECT table_name FROM information_schema.tables WHERE table_schema = 'public';
Data Analysis:
- Execute SQL:
SELECT customer_id, SUM(order_total) FROM orders GROUP BY customer_id ORDER BY SUM(order_total) DESC LIMIT 10; - Execute SQL:
SELECT * FROM orders WHERE shipping_time > INTERVAL '7 days';
System Monitoring:
- Use the
pg://stat/activityresource for current connections - Execute SQL:
SELECT schemaname, tablename, n_dead_tup FROM pg_stat_user_tables ORDER BY n_dead_tup DESC; - Execute SQL:
SELECT sum(heap_blks_hit) / (sum(heap_blks_hit) + sum(heap_blks_read)) as cache_hit_ratio FROM pg_statio_user_tables;
Run as a standalone HTTP server for direct API access:
# HTTP without authentication (development only)
./bin/pgedge-postgres-mcp -http -no-auth
# HTTP with token authentication (recommended)
./bin/pgedge-postgres-mcp -http -token-file tokens.json
# HTTPS with TLS and authentication
./bin/pgedge-postgres-mcp -http -tls \
-cert server.crt \
-key server.key \
-token-file tokens.jsonNote: Authentication is enabled by default in HTTP mode. Use
-no-authto disable it for local development, or provide an authentication token file with-token-file. See the Authentication Guide for token setup.
API Endpoint: POST http://localhost:8080/mcp/v1
Example request (with authentication):
curl -X POST http://localhost:8080/mcp/v1 \
-H "Authorization: Bearer your-token" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"method": "tools/call",
"params": {
"name": "query_database",
"arguments": {
"query": "SELECT * FROM users LIMIT 10"
}
}
}'Example request (without authentication):
curl -X POST http://localhost:8080/mcp/v1 \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"method": "tools/call",
"params": {
"name": "query_database",
"arguments": {
"query": "SELECT * FROM users LIMIT 10"
}
}
}'A production-ready, full-featured command-line chat interface is available for interacting with your PostgreSQL database using natural language:
# Stdio mode setup (MCP server as subprocess)
cp examples/pgedge-postgres-mcp-stdio.yaml.example bin/pgedge-postgres-mcp-stdio.yaml
cp examples/pgedge-nla-cli-stdio.yaml.example bin/pgedge-nla-cli-stdio.yaml
# Edit config files with your database settings, then:
./start_cli_stdio.sh
# HTTP mode setup (MCP server via HTTP with auth)
# First set up web client config (see Web Client section), then:
cp examples/pgedge-nla-cli-http.yaml.example bin/pgedge-nla-cli-http.yaml
./start_cli_http.shFeatures:
- 💬 Natural language database queries powered by Claude, GPT, or Ollama
- 🔧 Dual mode support (stdio subprocess or HTTP API)
- 💰 Anthropic prompt caching (90% cost reduction on repeated queries)
- ⚡ Runtime configuration with slash commands
- 📝 Persistent command history with readline support
- 🎨 PostgreSQL-themed UI with animations
Example queries:
- What tables are in my database?
- Show me the 10 most recent orders
- Which customers have placed more than 5 orders?
- Find documents similar to 'PostgreSQL performance tuning'
API Key Configuration:
The CLI client supports three ways to provide LLM API keys (in priority order):
-
Environment variables (recommended for development):
export ANTHROPIC_API_KEY="sk-ant-..." export OPENAI_API_KEY="sk-proj-..."
-
API key files (recommended for production):
echo "sk-ant-..." > ~/.anthropic-api-key chmod 600 ~/.anthropic-api-key
-
Configuration file values (not recommended - use env vars or files instead)
See Using the CLI Client for detailed documentation.
A web-based management interface is available for monitoring and interacting with the MCP server:
# 1. Copy example config files
cp examples/pgedge-postgres-mcp-http.yaml.example bin/pgedge-postgres-mcp-http.yaml
cp examples/pgedge-postgres-mcp-users.yaml.example bin/pgedge-postgres-mcp-users.yaml
cp examples/pgedge-postgres-mcp-tokens.yaml.example bin/pgedge-postgres-mcp-tokens.yaml
# 2. Edit config with your database and LLM settings
nano bin/pgedge-postgres-mcp-http.yaml
# 3. Create a user for web login
./bin/pgedge-postgres-mcp -add-user -username myuser -user-note "My User"
# 4. Start the web client (starts both MCP server and web interface)
./start_web_client.shFeatures:
- 🔐 Secure authentication using MCP server credentials
- 📊 Real-time PostgreSQL system information
- 🌓 Light/dark theme support
- 📱 Responsive design for desktop and mobile
Access:
- Web Interface: http://localhost:5173
- MCP Server API: http://localhost:8080
See web/README.md for detailed documentation.
Deploy the entire stack with Docker Compose for production or development:
# 1. Copy the example environment file
cp .env.example .env
# 2. Edit .env with your configuration
nano .env # Add your database connection, API keys, etc.
# 3. Build and start all services
docker-compose up -dWhat gets deployed:
- 🐘 MCP Server - Backend service on port 8080
- 🌐 Web Client - Browser interface on port 8081
- 🔐 Authentication - Token or user-based auth from config
- 💾 Persistent Storage - User and token data in Docker volumes
Quick Access:
- Web Interface: http://localhost:8081
- MCP API: http://localhost:8080
See Deploying on Docker for complete documentation including:
- Individual container builds
- Production deployment with reverse proxy
- Security hardening
- Resource limits and monitoring
- Troubleshooting
- Configure - Set database connection parameters via environment variables, config file, or command-line flags
- Start - Server starts and connects to PostgreSQL, extracting schema metadata
- Query - You provide SQL queries via Claude Desktop or API
- Execute - SQL runs in a read-only transaction
- Return - Results formatted and returned to the client
Read-Only Protection: All queries run in read-only mode - no INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, or DDL operations allowed.
Natural Language Support: The MCP client (like Claude Desktop with an LLM) can translate your natural language questions into SQL queries that are then executed by this server.
- Go 1.21 or higher
- PostgreSQL (for testing)
- golangci-lint v1.x (for linting)
The project uses golangci-lint v1.x. Install it with:
go install github.com/golangci/golangci-lint/cmd/golangci-lint@latestNote: The configuration file .golangci.yml is compatible
with golangci-lint v1.x (not v2).
# Run tests (uses TEST_PGEDGE_POSTGRES_CONNECTION_STRING)
export TEST_PGEDGE_POSTGRES_CONNECTION_STRING=\
"postgres://localhost/postgres?sslmode=disable"
go test ./...
# Run with coverage
go test -v -cover ./...
# Run linting
make lint
# or directly:
golangci-lint run
# Run locally (configure database connection via environment variables or
# config file)
./bin/pgedge-postgres-mcpThe web UI has a comprehensive test suite. See web/TEST_SUMMARY.md for details.
cd web
npm test # Run all tests
npm run test:watch # Watch mode
npm run test:coverage # With coverage- ✅ Read-only transaction enforcement
- ✅ API token authentication with expiration
- ✅ TLS/HTTPS support
- ✅ SHA256 token hashing
- ✅ File permission enforcement (0600)
- ✅ Input validation and sanitization
See Security Guide for comprehensive security documentation.
Tools not visible in Claude Desktop?
- Use absolute paths in config
- Restart Claude Desktop completely
- Check JSON syntax
Database connection errors?
- Ensure database connection is configured before starting the server (via environment variables, config file, or command-line flags)
- Verify PostgreSQL is running:
pg_isready - Check connection parameters are correct (host, port, database, user, password)
See Troubleshooting Guide for detailed solutions.
This software is released under the PostgreSQL License.
- 📖 Documentation: docs/index.md
- 🐛 Issues: GitHub Issues
- 💡 Examples: Query Examples
- Model Context Protocol - MCP specification
- Claude Desktop - Anthropic's Claude AI assistant
- PostgreSQL - The world's most advanced open source database
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for pgedge-postgres-mcp
Similar Open Source Tools

pgedge-postgres-mcp
The pgedge-postgres-mcp repository contains a set of tools and scripts for managing and monitoring PostgreSQL databases in an edge computing environment. It provides functionalities for automating database tasks, monitoring database performance, and ensuring data integrity in edge computing scenarios. The tools are designed to be lightweight and efficient, making them suitable for resource-constrained edge devices. With pgedge-postgres-mcp, users can easily deploy and manage PostgreSQL databases in edge computing environments with minimal overhead.
MCP-PostgreSQL-Ops
MCP-PostgreSQL-Ops is a repository containing scripts and tools for managing and optimizing PostgreSQL databases. It provides a set of utilities to automate common database administration tasks, such as backup and restore, performance tuning, and monitoring. The scripts are designed to simplify the operational aspects of running PostgreSQL databases, making it easier for administrators to maintain and optimize their database instances. With MCP-PostgreSQL-Ops, users can streamline their database management processes and improve the overall performance and reliability of their PostgreSQL deployments.
SQLBot
SQLBot is a versatile tool for executing SQL queries and managing databases. It provides a user-friendly interface for interacting with databases, allowing users to easily query, insert, update, and delete data. SQLBot supports various database systems such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQLite, making it a valuable tool for developers, data analysts, and database administrators. With SQLBot, users can streamline their database management tasks and improve their productivity by quickly accessing and manipulating data without the need for complex SQL commands.

hyper-mcp
hyper-mcp is a fast and secure MCP server that enables adding AI capabilities to applications through WebAssembly plugins. It supports writing plugins in various languages, distributing them via standard OCI registries, and running them in resource-constrained environments. The tool offers sandboxing with WASM for limiting access, cross-platform compatibility, and deployment flexibility. Security features include sandboxed plugins, memory-safe execution, secure plugin distribution, and fine-grained access control. Users can configure the tool for global or project-specific use, start the server with different transport options, and utilize available plugins for tasks like time calculations, QR code generation, hash generation, IP retrieval, and webpage fetching.
mcp-server-mysql
The MCP Server for MySQL based on NodeJS is a Model Context Protocol server that provides access to MySQL databases. It enables users to inspect database schemas and execute SQL queries. The server offers tools for executing SQL queries, providing comprehensive database information, security features like SQL injection prevention, performance optimizations, monitoring, and debugging capabilities. Users can configure the server using environment variables and advanced options. The server supports multi-DB mode, schema-specific permissions, and includes troubleshooting guidelines for common issues. Contributions are welcome, and the project roadmap includes enhancing query capabilities, security features, performance optimizations, monitoring, and expanding schema information.

gaia
Gaia is a powerful open-source tool for managing infrastructure as code. It allows users to define and provision cloud resources using simple configuration files. With Gaia, you can automate the deployment and scaling of your applications, ensuring consistency and reliability across your infrastructure. The tool supports multiple cloud providers and offers a user-friendly interface for managing your resources efficiently. Gaia simplifies the process of infrastructure management, making it easier for teams to collaborate and deploy applications seamlessly.

spiceai
Spice is a portable runtime written in Rust that offers developers a unified SQL interface to materialize, accelerate, and query data from any database, data warehouse, or data lake. It connects, fuses, and delivers data to applications, machine-learning models, and AI-backends, functioning as an application-specific, tier-optimized Database CDN. Built with industry-leading technologies such as Apache DataFusion, Apache Arrow, Apache Arrow Flight, SQLite, and DuckDB. Spice makes it fast and easy to query data from one or more sources using SQL, co-locating a managed dataset with applications or machine learning models, and accelerating it with Arrow in-memory, SQLite/DuckDB, or attached PostgreSQL for fast, high-concurrency, low-latency queries.
redb-open
reDB Node is a distributed, policy-driven data mesh platform that enables True Data Portability across various databases, warehouses, clouds, and environments. It unifies data access, data mobility, and schema transformation into one open platform. Built for developers, architects, and AI systems, reDB addresses the challenges of fragmented data ecosystems in modern enterprises by providing multi-database interoperability, automated schema versioning, zero-downtime migration, real-time developer data environments with obfuscation, quantum-resistant encryption, and policy-based access control. The project aims to build a foundation for future-proof data infrastructure.
tools
Strands Agents Tools is a community-driven project that provides a powerful set of tools for your agents to use. It bridges the gap between large language models and practical applications by offering ready-to-use tools for file operations, system execution, API interactions, mathematical operations, and more. The tools cover a wide range of functionalities including file operations, shell integration, memory storage, web infrastructure, HTTP client, Slack client, Python execution, mathematical tools, AWS integration, image and video processing, audio output, environment management, task scheduling, advanced reasoning, swarm intelligence, dynamic MCP client, parallel tool execution, browser automation, diagram creation, RSS feed management, and computer automation.

mcp-server-chart
mcp-server-chart is a Helm chart for deploying a Minecraft server on Kubernetes. It simplifies the process of setting up and managing a Minecraft server in a Kubernetes environment. The chart includes configurations for specifying server settings, resource limits, and persistent storage options. With mcp-server-chart, users can easily deploy and scale Minecraft servers on Kubernetes clusters, ensuring high availability and performance for multiplayer gaming experiences.
orchestkit
OrchestKit is a powerful and flexible orchestration tool designed to streamline and automate complex workflows. It provides a user-friendly interface for defining and managing orchestration tasks, allowing users to easily create, schedule, and monitor workflows. With support for various integrations and plugins, OrchestKit enables seamless automation of tasks across different systems and applications. Whether you are a developer looking to automate deployment processes or a system administrator managing complex IT operations, OrchestKit offers a comprehensive solution to simplify and optimize your workflow management.
koog
Koog is a Kotlin-based framework for building and running AI agents entirely in idiomatic Kotlin. It allows users to create agents that interact with tools, handle complex workflows, and communicate with users. Key features include pure Kotlin implementation, MCP integration, embedding capabilities, custom tool creation, ready-to-use components, intelligent history compression, powerful streaming API, persistent agent memory, comprehensive tracing, flexible graph workflows, modular feature system, scalable architecture, and multiplatform support.
edge-ai-libraries
The Edge AI Libraries project is a collection of libraries, microservices, and tools for Edge application development. It includes sample applications showcasing generic AI use cases. Key components include Anomalib, Dataset Management Framework, Deep Learning Streamer, ECAT EnableKit, EtherCAT Masterstack, FLANN, OpenVINO toolkit, Audio Analyzer, ORB Extractor, PCL, PLCopen Servo, Real-time Data Agent, RTmotion, Audio Intelligence, Deep Learning Streamer Pipeline Server, Document Ingestion, Model Registry, Multimodal Embedding Serving, Time Series Analytics, Vector Retriever, Visual-Data Preparation, VLM Inference Serving, Intel Geti, Intel SceneScape, Visual Pipeline and Platform Evaluation Tool, Chat Question and Answer, Document Summarization, PLCopen Benchmark, PLCopen Databus, Video Search and Summarization, Isolation Forest Classifier, Random Forest Microservices. Visit sub-directories for instructions and guides.
falkordb-browser
FalkorDB Browser is a user-friendly web application for browsing and managing databases. It provides an intuitive interface for users to interact with their databases, allowing them to view, edit, and query data easily. With FalkorDB Browser, users can perform various database operations without the need for complex commands or scripts, making database management more accessible and efficient.

python-sdk
Python SDK is a software development kit that provides tools and resources for developers to interact with Python programming language. It simplifies the process of integrating Python code into applications and services, offering a wide range of functionalities and libraries to streamline development workflows. With Python SDK, developers can easily access and manipulate data, create automation scripts, build web applications, and perform various tasks efficiently. It is designed to enhance the productivity and flexibility of Python developers by providing a comprehensive set of tools and utilities for software development.
DB-GPT
DB-GPT is an open source AI native data app development framework with AWEL(Agentic Workflow Expression Language) and agents. It aims to build infrastructure in the field of large models, through the development of multiple technical capabilities such as multi-model management (SMMF), Text2SQL effect optimization, RAG framework and optimization, Multi-Agents framework collaboration, AWEL (agent workflow orchestration), etc. Which makes large model applications with data simpler and more convenient.
For similar tasks

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.

danswer
Danswer is an open-source Gen-AI Chat and Unified Search tool that connects to your company's docs, apps, and people. It provides a Chat interface and plugs into any LLM of your choice. Danswer can be deployed anywhere and for any scale - on a laptop, on-premise, or to cloud. Since you own the deployment, your user data and chats are fully in your own control. Danswer is MIT licensed and designed to be modular and easily extensible. The system also comes fully ready for production usage with user authentication, role management (admin/basic users), chat persistence, and a UI for configuring Personas (AI Assistants) and their Prompts. Danswer also serves as a Unified Search across all common workplace tools such as Slack, Google Drive, Confluence, etc. By combining LLMs and team specific knowledge, Danswer becomes a subject matter expert for the team. Imagine ChatGPT if it had access to your team's unique knowledge! It enables questions such as "A customer wants feature X, is this already supported?" or "Where's the pull request for feature Y?"
semantic-kernel
Semantic Kernel is an SDK that integrates Large Language Models (LLMs) like OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, and Hugging Face with conventional programming languages like C#, Python, and Java. Semantic Kernel achieves this by allowing you to define plugins that can be chained together in just a few lines of code. What makes Semantic Kernel _special_ , however, is its ability to _automatically_ orchestrate plugins with AI. With Semantic Kernel planners, you can ask an LLM to generate a plan that achieves a user's unique goal. Afterwards, Semantic Kernel will execute the plan for the user.
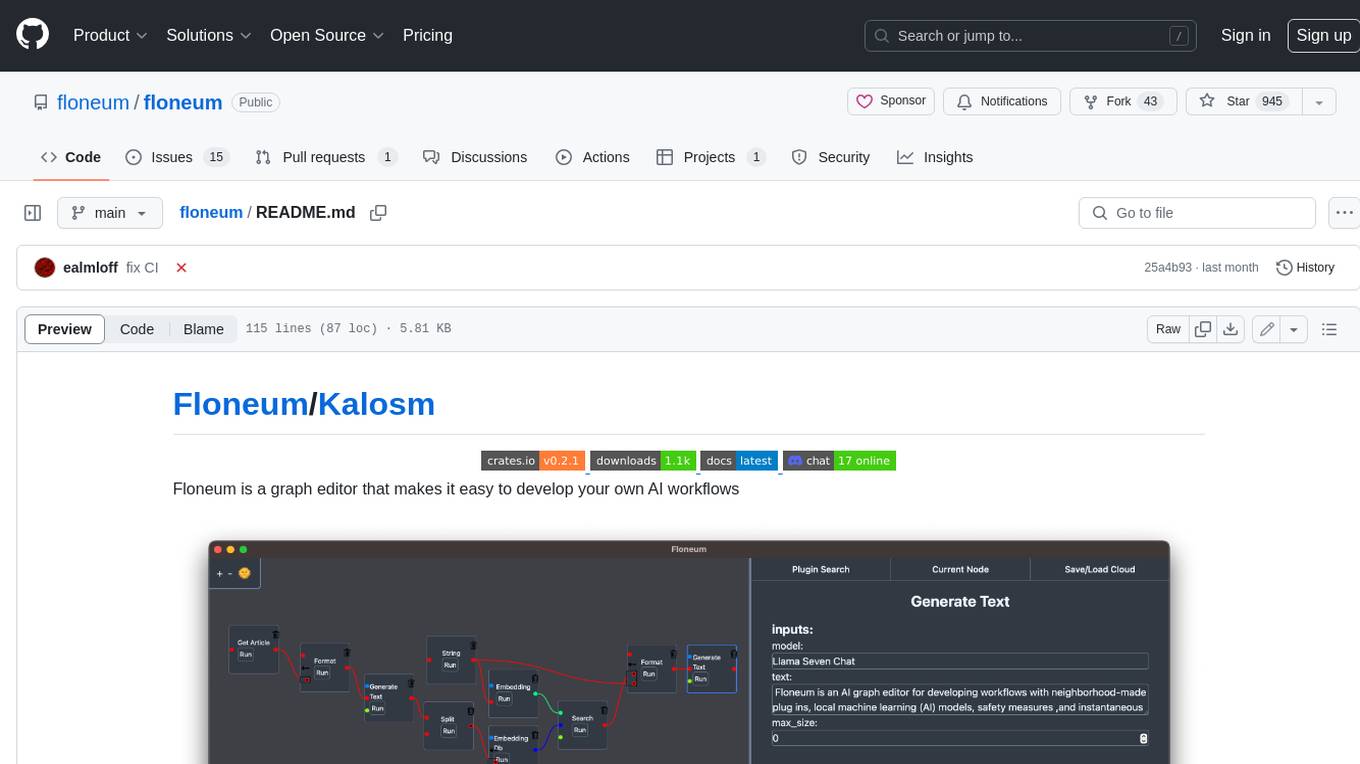
floneum
Floneum is a graph editor that makes it easy to develop your own AI workflows. It uses large language models (LLMs) to run AI models locally, without any external dependencies or even a GPU. This makes it easy to use LLMs with your own data, without worrying about privacy. Floneum also has a plugin system that allows you to improve the performance of LLMs and make them work better for your specific use case. Plugins can be used in any language that supports web assembly, and they can control the output of LLMs with a process similar to JSONformer or guidance.

mindsdb
MindsDB is a platform for customizing AI from enterprise data. You can create, serve, and fine-tune models in real-time from your database, vector store, and application data. MindsDB "enhances" SQL syntax with AI capabilities to make it accessible for developers worldwide. With MindsDB’s nearly 200 integrations, any developer can create AI customized for their purpose, faster and more securely. Their AI systems will constantly improve themselves — using companies’ own data, in real-time.
aiscript
AiScript is a lightweight scripting language that runs on JavaScript. It supports arrays, objects, and functions as first-class citizens, and is easy to write without the need for semicolons or commas. AiScript runs in a secure sandbox environment, preventing infinite loops from freezing the host. It also allows for easy provision of variables and functions from the host.
activepieces
Activepieces is an open source replacement for Zapier, designed to be extensible through a type-safe pieces framework written in Typescript. It features a user-friendly Workflow Builder with support for Branches, Loops, and Drag and Drop. Activepieces integrates with Google Sheets, OpenAI, Discord, and RSS, along with 80+ other integrations. The list of supported integrations continues to grow rapidly, thanks to valuable contributions from the community. Activepieces is an open ecosystem; all piece source code is available in the repository, and they are versioned and published directly to npmjs.com upon contributions. If you cannot find a specific piece on the pieces roadmap, please submit a request by visiting the following link: Request Piece Alternatively, if you are a developer, you can quickly build your own piece using our TypeScript framework. For guidance, please refer to the following guide: Contributor's Guide
superagent-js
Superagent is an open source framework that enables any developer to integrate production ready AI Assistants into any application in a matter of minutes.
For similar jobs

minio
MinIO is a High Performance Object Storage released under GNU Affero General Public License v3.0. It is API compatible with Amazon S3 cloud storage service. Use MinIO to build high performance infrastructure for machine learning, analytics and application data workloads.

ai-on-gke
This repository contains assets related to AI/ML workloads on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE). Run optimized AI/ML workloads with Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) platform orchestration capabilities. A robust AI/ML platform considers the following layers: Infrastructure orchestration that support GPUs and TPUs for training and serving workloads at scale Flexible integration with distributed computing and data processing frameworks Support for multiple teams on the same infrastructure to maximize utilization of resources

kong
Kong, or Kong API Gateway, is a cloud-native, platform-agnostic, scalable API Gateway distinguished for its high performance and extensibility via plugins. It also provides advanced AI capabilities with multi-LLM support. By providing functionality for proxying, routing, load balancing, health checking, authentication (and more), Kong serves as the central layer for orchestrating microservices or conventional API traffic with ease. Kong runs natively on Kubernetes thanks to its official Kubernetes Ingress Controller.
AI-in-a-Box
AI-in-a-Box is a curated collection of solution accelerators that can help engineers establish their AI/ML environments and solutions rapidly and with minimal friction, while maintaining the highest standards of quality and efficiency. It provides essential guidance on the responsible use of AI and LLM technologies, specific security guidance for Generative AI (GenAI) applications, and best practices for scaling OpenAI applications within Azure. The available accelerators include: Azure ML Operationalization in-a-box, Edge AI in-a-box, Doc Intelligence in-a-box, Image and Video Analysis in-a-box, Cognitive Services Landing Zone in-a-box, Semantic Kernel Bot in-a-box, NLP to SQL in-a-box, Assistants API in-a-box, and Assistants API Bot in-a-box.
awsome-distributed-training
This repository contains reference architectures and test cases for distributed model training with Amazon SageMaker Hyperpod, AWS ParallelCluster, AWS Batch, and Amazon EKS. The test cases cover different types and sizes of models as well as different frameworks and parallel optimizations (Pytorch DDP/FSDP, MegatronLM, NemoMegatron...).
generative-ai-cdk-constructs
The AWS Generative AI Constructs Library is an open-source extension of the AWS Cloud Development Kit (AWS CDK) that provides multi-service, well-architected patterns for quickly defining solutions in code to create predictable and repeatable infrastructure, called constructs. The goal of AWS Generative AI CDK Constructs is to help developers build generative AI solutions using pattern-based definitions for their architecture. The patterns defined in AWS Generative AI CDK Constructs are high level, multi-service abstractions of AWS CDK constructs that have default configurations based on well-architected best practices. The library is organized into logical modules using object-oriented techniques to create each architectural pattern model.
model_server
OpenVINO™ Model Server (OVMS) is a high-performance system for serving models. Implemented in C++ for scalability and optimized for deployment on Intel architectures, the model server uses the same architecture and API as TensorFlow Serving and KServe while applying OpenVINO for inference execution. Inference service is provided via gRPC or REST API, making deploying new algorithms and AI experiments easy.
dify-helm
Deploy langgenius/dify, an LLM based chat bot app on kubernetes with helm chart.