
llm
LLM을 활용한 실전 AI 애플리케이션 개발
Stars: 144
This repository provides practical guidance on developing real-world AI applications using LLM, covering topics from the basics of LLM architecture to creating RAG, a representative application of LLM. It explains how to tame LLM to meet application requirements, lightweight it to operate smoothly in limited computing environments, and gradually create RAG. The book also addresses challenges encountered in the operational process, advanced topics such as multimodal and agents, and essential development knowledge for the LLM era from both theoretical and practical perspectives.
README:
★ 정오사항 확인: https://www.onlybook.co.kr/entry/llm-errata
이 책에서는 LLM의 기본 아키텍처에서 출발해 애플리케이션의 요구사항에 맞춰 LLM을 길들이고 제한된 컴퓨팅 환경에서 동작하게 경량화해서 원활하게 서빙하게끔 기초를 다진 다음에 RAG라는 LLM의 대표적인 애플리케이션을 만드는 방법을 차근차근 설명한다. 또한, 실제 운영과정에서 부딪히는 어려움을 해소하는 방법과 멀티 모달과 더불어 에이전트와 같은 고급 주제까지 다룬다. LLM 시대를 맞이해 필수적으로 갖춰야 하는 개발 지식을 이론과 실무 양쪽 관점에서 설명하므로, 새로운 패러다임에 적응하고자 하는 개발자들에게 가뭄의 단비와도 같을 책이다.
실습 코드는 책의 깃허브 저장소(https://github.com/onlybooks/llm)에서 확인할 수 있습니다. 깃허브의 코드는 구글 코랩에서 두 가지 방법으로 활용할 수 있다.
- 로컬에서 업로드하기: 깃허브의 코드를 로컬 환경에 클론하거나 압축 파일 형태로 내려받은 후 진행하려는 실습 폴더의 노트북 파일(ipynb)을 구글 코랩에서 열어 실습을 진행할 수 있다.
- 깃허브 URL로 열기: 구글 코랩에서 노트 열기(Ctrl+O)를 선택하면 다양한 노트 열기 방식 중 깃허브GitHub 탭에서 코드의 URL을 통해 실습 노트북을 열 수 있다.
이 책의 실습은 구글 코랩에서 실행한다. 구글 코랩은 구글에서 제공하는 노트북 실행 환경으로, 파이썬의 주피터 노트북과 유사한 UI로 브라우저에서 실행할 수 있다. 또 구글 코랩에서는 무료로 T4 GPU(16GB)를 사용할 수 있도록 제공한다. 구글 코랩의 무료 버전은 12시간의 런타임 제한이 있으며, 장시간 사용하지 않으면 연결이 끊길 수 있다.
서울대학교 기계항공공학부를 졸업하고 롯데면세점 빅데이터팀 데이터 분석가를 거쳐 현재는 프리랜서 마켓 크몽에서 AI 엔지니어로 일하고 있다. 『파이토치 라이트닝으로 시작하는 딥러닝』을 번역했으며, 최근에는 LLM을 활용한 어시스턴트(에이전트) 개발에 관심이 많다.
1.1 딥러닝과 언어 모델링
__1.1.1 데이터의 특징을 스스로 추출하는 딥러닝
__1.1.2 임베딩: 딥러닝 모델이 데이터를 표현하는 방식
__1.1.3 언어 모델링: 딥러닝 모델의 언어 학습법
1.2 언어 모델이 챗GPT가 되기까지
__1.2.1 RNN에서 트랜스포머 아키텍처로
__1.2.2 GPT 시리즈로 보는 모델 크기와 성능의 관계
__1.2.3 챗GPT의 등장
1.3 LLM 애플리케이션의 시대가 열리다
__1.3.1 지식 사용법을 획기적으로 바꾼 LLM
__1.3.2 sLLM: 더 작고 효율적인 모델 만들기
__1.3.3 더 효율적인 학습과 추론을 위한 기술
__1.3.4 LLM의 환각 현상을 대처하는 검색 증강 생성(RAG) 기술
1.4 LLM의 미래: 인식과 행동의 확장
1.5 정리
2.1 트랜스포머 아키텍처란
2.2 텍스트를 임베딩으로 변환하기
__2.2.1 토큰화
__2.2.2 토큰 임베딩으로 변환하기
__2.2.3 위치 인코딩
2.3 어텐션 이해하기
__2.3.1 사람이 글을 읽는 방법과 어텐션
__2.3.2 쿼리, 키, 값 이해하기
__2.3.3 코드로 보는 어텐션
__2.3.4 멀티 헤드 어텐션
2.4 정규화와 피드 포워드 층
__2.4.1 층 정규화 이해하기
__2.4.2 피드 포워드 층
2.5 인코더
2.6 디코더
2.7 BERT, GPT, T5 등 트랜스포머를 활용한 아키텍처
__2.7.1 인코더를 활용한 BERT
__2.7.2 디코더를 활용한 GPT
__2.7.3 인코더와 디코더를 모두 사용하는 BART, T5
2.8 주요 사전 학습 메커니즘
__2.8.1 인과적 언어 모델링
__2.8.2 마스크 언어 모델링
2.9 정리
3.1 허깅페이스 트랜스포머란
3.2 허깅페이스 허브 탐색하기
__3.2.1 모델 허브
__3.2.2 데이터셋 허브
__3.2.3 모델 데모를 공개하고 사용할 수 있는 스페이스
3.3 허깅페이스 라이브러리 사용법 익히기
__3.3.1 모델 활용하기
__3.3.2 토크나이저 활용하기
__3.3.3 데이터셋 활용하기
3.4 모델 학습시키기
__3.4.1 데이터 준비
__3.4.2 트레이너 API를 사용해 학습하기
__3.4.3 트레이너 API를 사용하지 않고 학습하기
__3.4.4 학습한 모델 업로드하기
3.5 모델 추론하기
__3.5.1 파이프라인을 활용한 추론
__3.5.2 직접 추론하기
3.6 정리
4.1 코딩 테스트 통과하기: 사전 학습과 지도 미세 조정
__4.1.1 코딩 개념 익히기: LLM의 사전 학습
__4.1.2 연습문제 풀어보기: 지도 미세 조정
__4.1.3 좋은 지시 데이터셋이 갖춰야 할 조건
4.2 채점 모델로 코드 가독성 높이기
__4.2.1 선호 데이터셋을 사용한 채점 모델 만들기
__4.2.2 강화 학습: 높은 코드 가독성 점수를 향해
__4.2.3 PPO: 보상 해킹 피하기
__4.2.4 RLHF: 멋지지만 피할 수 있다면…
4.3 강화 학습이 꼭 필요할까?
__4.3.1 기각 샘플링: 단순히 가장 점수가 높은 데이터를 사용한다면?
__4.3.2 DPO: 선호 데이터셋을 직접 학습하기
__4.3.3 DPO를 사용해 학습한 모델들
4.4 정리
5.1 GPU에 올라가는 데이터 살펴보기
__5.1.1 딥러닝 모델의 데이터 타입
__5.1.2 양자화로 모델 용량 줄이기
__5.1.3 GPU 메모리 분해하기
5.2 단일 GPU 효율적으로 활용하기
__5.2.1 그레이디언트 누적
__5.2.2 그레이디언트 체크포인팅
5.3 분산 학습과 ZeRO
__5.3.1 분산 학습
__5.3.2 데이터 병렬화에서 중복 저장 줄이기(ZeRO)
5.4 효율적인 학습 방법(PEFT): LoRA
__5.4.1 모델 파라미터의 일부만 재구성해 학습하는 LoRA
__5.4.2 LoRA 설정 살펴보기
__5.4.3 코드로 LoRA 학습 사용하기
5.5 효율적인 학습 방법(PEFT): QLoRA
__5.5.1 4비트 양자화와 2차 양자화
__5.5.2 페이지 옵티마이저
__5.5.3 코드로 QLoRA 모델 활용하기
5.6 정리
6.1 Text2SQL 데이터셋
__6.1.1 대표적인 Text2SQL 데이터셋
__6.1.2 한국어 데이터셋
__6.1.3 합성 데이터 활용
6.2 성능 평가 파이프라인 준비하기
__6.2.1 Text2SQL 평가 방식
__6.2.2 평가 데이터셋 구축
__6.2.3 SQL 생성 프롬프트
__6.2.4 GPT-4 평가 프롬프트와 코드 준비
6.3 실습: 미세 조정 수행하기
__6.3.1 기초 모델 평가하기
__6.3.2 미세 조정 수행
__6.3.3 학습 데이터 정제와 미세 조정
__6.3.4 기초 모델 변경
__6.3.5 모델 성능 비교
6.4 정리
7.1 언어 모델 추론 이해하기
__7.1.1 언어 모델이 언어를 생성하는 방법
__7.1.2 중복 연산을 줄이는 KV 캐시
__7.1.3 GPU 구조와 최적의 배치 크기
__7.1.4 KV 캐시 메모리 줄이기
7.2 양자화로 모델 용량 줄이기
__7.2.1 비츠앤바이츠
__7.2.2 GPTQ
__7.2.3 AWQ
7.3 지식 증류 활용하기
7.4 정리
8.1 효율적인 배치 전략
__8.1.1 일반 배치(정적 배치)
__8.1.2 동적 배치
__8.1.3 연속 배치
8.2 효율적인 트랜스포머 연산
__8.2.1 플래시어텐션
__8.2.2 플래시어텐션 2
__8.2.3 상대적 위치 인코딩
8.3 효율적인 추론 전략
__8.3.1 커널 퓨전
__8.3.2 페이지어텐션
__8.3.3 추측 디코딩
8.4 실습: LLM 서빙 프레임워크
__8.4.1 오프라인 서빙
__8.4.2 온라인 서빙
8.5 정리
9.1 검색 증강 생성(RAG)
__9.1.1 데이터 저장
__9.1.2 프롬프트에 검색 결과 통합
__9.1.3 실습: 라마인덱스로 RAG 구현하기
9.2 LLM 캐시
__9.2.1 LLM 캐시 작동 원리
__9.2.2 실습: OpenAI API 캐시 구현
9.3 데이터 검증
__9.3.1 데이터 검증 방식
__9.3.2 데이터 검증 실습
9.4 데이터 로깅
__9.4.1 OpenAI API 로깅
__9.4.2 라마인덱스 로깅
9.5 정리
10.1 텍스트 임베딩 이해하기
__10.1.1 문장 임베딩 방식의 장점
__10.1.2 원핫 인코딩
__10.1.3 백오브워즈
__10.1.4 TF-IDF
__10.1.5 워드투벡
10.2 문장 임베딩 방식
__10.2.1 문장 사이의 관계를 계산하는 두 가지 방법
__10.2.2 바이 인코더 모델 구조
__10.2.3 Sentence-Transformers로 텍스트와 이미지 임베딩 생성해 보기
__10.2.4 오픈소스와 상업용 임베딩 모델 비교하기
10.3 실습: 의미 검색 구현하기
__10.3.1 의미 검색 구현하기
__10.3.2 라마인덱스에서 Sentence-Transformers 모델 사용하기
10.4 검색 방식을 조합해 성능 높이기
__10.4.1 키워드 검색 방식: BM25
__10.4.2 상호 순위 조합 이해하기
10.5 실습: 하이브리드 검색 구현하기
__10.5.1 BM25 구현하기
__10.5.2 상호 순위 조합 구현하기
__10.5.3 하이브리드 검색 구현하기
10.6 정리
11.1 검색 성능을 높이기 위한 두 가지 방법
11.2 언어 모델을 임베딩 모델로 만들기
__11.2.1 대조 학습
__11.2.2 실습: 학습 준비하기
__11.2.3 실습: 유사한 문장 데이터로 임베딩 모델 학습하기
11.3 임베딩 모델 미세 조정하기
__11.3.1 실습: 학습 준비
__11.3.2 MNR 손실을 활용해 미세 조정하기
11.4 검색 품질을 높이는 순위 재정렬
11.5 바이 인코더와 교차 인코더로 개선된 RAG 구현하기
__11.5.1 기본 임베딩 모델로 검색하기
__11.5.2 미세 조정한 임베딩 모델로 검색하기
__11.5.3 미세 조정한 임베딩 모델과 교차 인코더 조합하기
11.6 정리
12.1 벡터 데이터베이스란
__12.1.1 딥러닝과 벡터 데이터베이스
__12.1.2 벡터 데이터베이스 지형 파악하기
12.2 벡터 데이터베이스 작동 원리
__12.2.1 KNN 검색과 그 한계
__12.2.2 ANN 검색이란
__12.2.3 탐색 가능한 작은 세계(NSW)
__12.2.4 계층 구조
12.3 실습: HNSW 인덱스의 핵심 파라미터 이해하기
__12.3.1 파라미터 m 이해하기
__12.3.2 파라미터 ef_construction 이해하기
__12.3.3 파라미터 ef_search 이해하기
12.4 실습: 파인콘으로 벡터 검색 구현하기
__12.4.1 파인콘 클라이언트 사용법
__12.4.2 라마인덱스에서 벡터 데이터베이스 변경하기
12.5 실습: 파인콘을 활용해 멀티 모달 검색 구현하기
__12.5.1 데이터셋
__12.5.2 실습 흐름
__12.5.3 GPT-4o로 이미지 설명 생성하기
__12.5.4 프롬프트 저장
__12.5.5 이미지 임베딩 검색
__12.5.6 DALL-E 3로 이미지 생성
12.6 정리
13.1 MLOps
__13.1.1 데이터 관리
__13.1.2 실험 관리
__13.1.3 모델 저장소
__13.1.4 모델 모니터링
13.2 LLMOps는 무엇이 다를까?
__13.2.1 상업용 모델과 오픈소스 모델 선택하기
__13.2.2 모델 최적화 방법의 변화
__13.2.3 LLM 평가의 어려움
13.3 LLM 평가하기
__13.3.1 정량적 지표
__13.3.2 벤치마크 데이터셋을 활용한 평가
__13.3.3 사람이 직접 평가하는 방식
__13.3.4 LLM을 통한 평가
__13.3.4 RAG 평가
13.4 정리
LLM 14.1 멀티 모달 LLM이란
__14.1.1 멀티 모달 LLM의 구성요소
__14.1.2 멀티 모달 LLM 학습 과정
14.2 이미지와 텍스트를 연결하는 모델: CLIP
__14.2.1 CLIP 모델이란
__14.2.2 CLIP 모델의 학습 방법
__14.2.3 CLIP 모델의 활용과 뛰어난 성능
__14.2.4 CLIP 모델 직접 활용하기
14.3 텍스트로 이미지를 생성하는 모델: DALL-E
__14.3.1 디퓨전 모델 원리
__14.3.2 DALL-E 모델
14.4 LLaVA
__14.4.1 LLaVA의 학습 데이터
__14.4.2 LLaVA 모델 구조
__14.4.3 LLaVA 1.5
__14.4.4 LLaVA NeXT
14.5 정리
15.1 에이전트란 __15.1.1 에이전트의 구성요소 __15.1.2 에이전트의 두뇌 __15.1.3 에이전트의 감각 __15.1.4 에이전트의 행동 15.2 에이전트 시스템의 형태 __15.2.1 단일 에이전트 __15.2.2 사용자와 에이전트의 상호작용 __15.2.3 멀티 에이전트 15.3 에이전트 평가하기 15.4 실습: 에이전트 구현 __15.4.1 AutoGen 기본 사용법 __15.4.2 RAG 에이전트 __15.4.3 멀티 모달 에이전트 15.5 정리
16.1 기존 아키텍처의 장단점
16.2 SSM
__16.2.1 S4
16.3 선택 메커니즘
16.4 맘바
__16.4.1 맘바의 성능
__16.4.2 기존 아키텍처와의 비교
16.5 코드로 보는 맘바
A.1 구글 코랩 사용법
A.2 허깅페이스 토큰
A.3 OpenAI 토큰
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for llm
Similar Open Source Tools

llm
This repository provides practical guidance on developing real-world AI applications using LLM, covering topics from the basics of LLM architecture to creating RAG, a representative application of LLM. It explains how to tame LLM to meet application requirements, lightweight it to operate smoothly in limited computing environments, and gradually create RAG. The book also addresses challenges encountered in the operational process, advanced topics such as multimodal and agents, and essential development knowledge for the LLM era from both theoretical and practical perspectives.
LangChain-SearXNG
LangChain-SearXNG is an open-source AI search engine built on LangChain and SearXNG. It supports faster and more accurate search and question-answering functionalities. Users can deploy SearXNG and set up Python environment to run LangChain-SearXNG. The tool integrates AI models like OpenAI and ZhipuAI for search queries. It offers two search modes: Searxng and ZhipuWebSearch, allowing users to control the search workflow based on input parameters. LangChain-SearXNG v2 version enhances response speed and content quality compared to the previous version, providing a detailed configuration guide and showcasing the effectiveness of different search modes through comparisons.
ai-trend-publish
AI TrendPublish is an AI-based trend discovery and content publishing system that supports multi-source data collection, intelligent summarization, and automatic publishing to WeChat official accounts. It features data collection from various sources, AI-powered content processing using DeepseekAI Together, key information extraction, intelligent title generation, automatic article publishing to WeChat official accounts with custom templates and scheduled tasks, notification system integration with Bark for task status updates and error alerts. The tool offers multiple templates for content customization and is built using Node.js + TypeScript with AI services from DeepseekAI Together, data sources including Twitter/X API and FireCrawl, and uses node-cron for scheduling tasks and EJS as the template engine.
aid
Aid2 is a tool designed to authorize iOS devices and install apps similar to iTools. After authorizing with Aid2, the IPA files can be installed without entering the app ID and password. This second version of Aid supports both Windows and Mac systems, although the Mac system has not been fully tested yet. Version 2.1 added the functionality to install IPA files. Version 2.5 streamlined the authorization process, executing it on each device using a single thread to reduce code complexity and improve authorization speed. The tool requires a compilation environment with Vcpkg, gRPC, Protobuf, and OpenSSL, and users need to have access to a VPN for successful configuration.
rime_wanxiang_pro
Rime Wanxiang Pro is an enhanced version of Wanxiang, supporting the 9, 14, and 18-key layouts. It features a pinyin library with optimized word and language models, supporting accurate sentence output with tones. The tool also allows for mixed Chinese and English input, offering various usage scenarios. Users can customize their input method by selecting different decoding and auxiliary code rules, enabling flexible combinations of pinyin and auxiliary codes. The tool simplifies the complex configuration of Rime and provides a unified word library for multiple input methods, enhancing input efficiency and user experience.
CareGPT
CareGPT is a medical large language model (LLM) that explores medical data, training, and deployment related research work. It integrates resources, open-source models, rich data, and efficient deployment methods. It supports various medical tasks, including patient diagnosis, medical dialogue, and medical knowledge integration. The model has been fine-tuned on diverse medical datasets to enhance its performance in the healthcare domain.
langchain4j-aideepin-web
The langchain4j-aideepin-web repository is the frontend project of langchain4j-aideepin, an open-source, offline deployable retrieval enhancement generation (RAG) project based on large language models such as ChatGPT and application frameworks such as Langchain4j. It includes features like registration & login, multi-sessions (multi-roles), image generation (text-to-image, image editing, image-to-image), suggestions, quota control, knowledge base (RAG) based on large models, model switching, and search engine switching.
llm-jp-eval
LLM-jp-eval is a tool designed to automatically evaluate Japanese large language models across multiple datasets. It provides functionalities such as converting existing Japanese evaluation data to text generation task evaluation datasets, executing evaluations of large language models across multiple datasets, and generating instruction data (jaster) in the format of evaluation data prompts. Users can manage the evaluation settings through a config file and use Hydra to load them. The tool supports saving evaluation results and logs using wandb. Users can add new evaluation datasets by following specific steps and guidelines provided in the tool's documentation. It is important to note that using jaster for instruction tuning can lead to artificially high evaluation scores, so caution is advised when interpreting the results.
fastllm
FastLLM is a high-performance large model inference library implemented in pure C++ with no third-party dependencies. Models of 6-7B size can run smoothly on Android devices. Deployment communication QQ group: 831641348
DocTranslator
DocTranslator is a document translation tool that supports various file formats, compatible with OpenAI format API, and offers batch operations and multi-threading support. Whether for individual users or enterprise teams, DocTranslator helps efficiently complete document translation tasks. It supports formats like txt, markdown, word, csv, excel, pdf (non-scanned), and ppt for AI translation. The tool is deployed using Docker for easy setup and usage.
PersonalExam
PersonalExam is a personalized question generation system based on LLM and knowledge graph collaboration. It utilizes the BKT algorithm, RAG engine, and OpenPangu model to achieve personalized intelligent question generation and recommendation. The system features adaptive question recommendation, fine-grained knowledge tracking, AI answer evaluation, student profiling, visual reports, interactive knowledge graph, user management, and system monitoring.
aipan-netdisk-search
Aipan-Netdisk-Search is a free and open-source web project for searching netdisk resources. It utilizes third-party APIs with IP access restrictions, suggesting self-deployment. The project can be easily deployed on Vercel and provides instructions for manual deployment. Users can clone the project, install dependencies, run it in the browser, and access it at localhost:3001. The project also includes documentation for deploying on personal servers using NUXT.JS. Additionally, there are options for donations and communication via WeChat.
meet-libai
The 'meet-libai' project aims to promote and popularize the cultural heritage of the Chinese poet Li Bai by constructing a knowledge graph of Li Bai and training a professional AI intelligent body using large models. The project includes features such as data preprocessing, knowledge graph construction, question-answering system development, and visualization exploration of the graph structure. It also provides code implementations for large models and RAG retrieval enhancement.
OpenClawChineseTranslation
OpenClaw Chinese Translation is a localization project that provides a fully Chinese interface for the OpenClaw open-source personal AI assistant platform. It allows users to interact with their AI assistant through chat applications like WhatsApp, Telegram, and Discord to manage daily tasks such as emails, calendars, and files. The project includes both CLI command-line and dashboard web interface fully translated into Chinese.

AstrBot
AstrBot is an open-source one-stop Agentic chatbot platform and development framework. It supports large model conversations, multiple messaging platforms, Agent capabilities, plugin extensions, and WebUI for visual configuration and management of the chatbot.
For similar tasks

zep-python
Zep is an open-source platform for building and deploying large language model (LLM) applications. It provides a suite of tools and services that make it easy to integrate LLMs into your applications, including chat history memory, embedding, vector search, and data enrichment. Zep is designed to be scalable, reliable, and easy to use, making it a great choice for developers who want to build LLM-powered applications quickly and easily.
E2B
E2B Sandbox is a secure sandboxed cloud environment made for AI agents and AI apps. Sandboxes allow AI agents and apps to have long running cloud secure environments. In these environments, large language models can use the same tools as humans do. For example: * Cloud browsers * GitHub repositories and CLIs * Coding tools like linters, autocomplete, "go-to defintion" * Running LLM generated code * Audio & video editing The E2B sandbox can be connected to any LLM and any AI agent or app.
LlamaIndexTS
LlamaIndex.TS is a data framework for your LLM application. Use your own data with large language models (LLMs, OpenAI ChatGPT and others) in Typescript and Javascript.
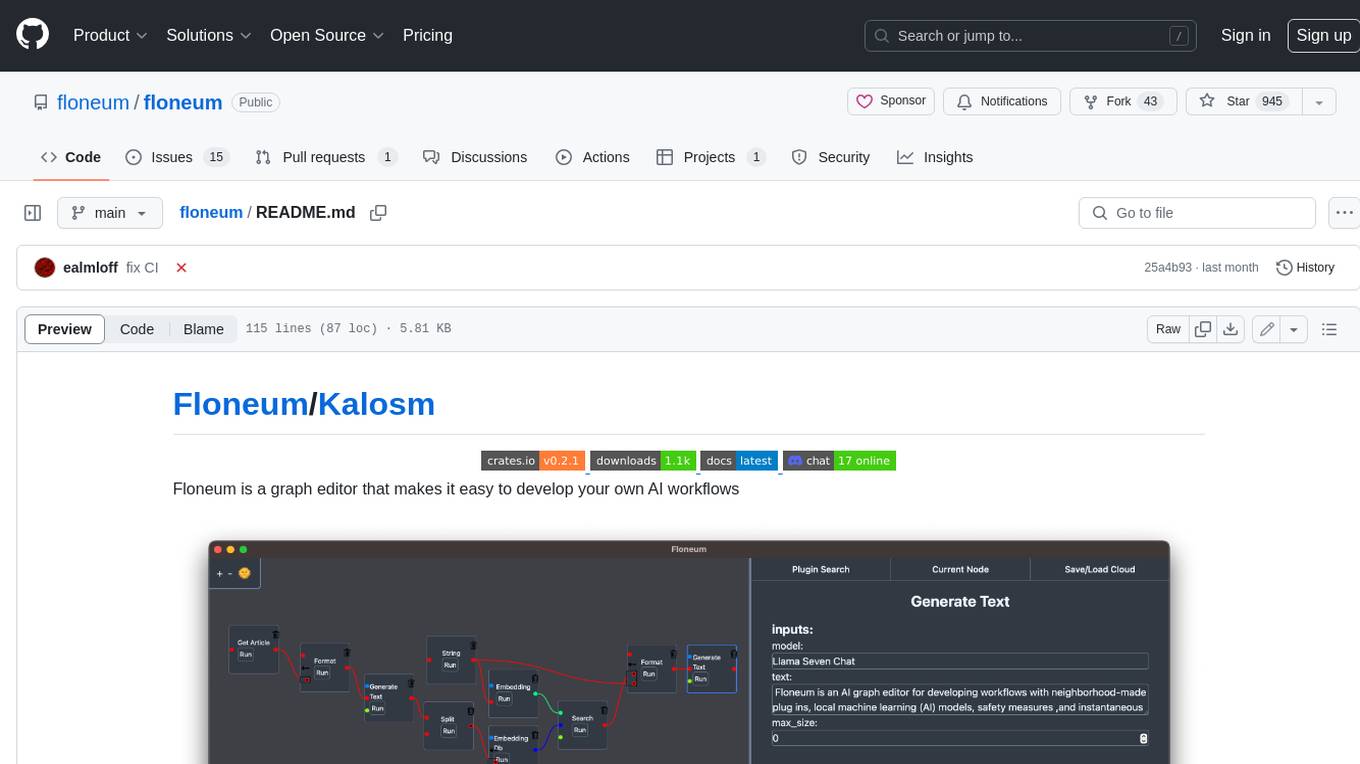
floneum
Floneum is a graph editor that makes it easy to develop your own AI workflows. It uses large language models (LLMs) to run AI models locally, without any external dependencies or even a GPU. This makes it easy to use LLMs with your own data, without worrying about privacy. Floneum also has a plugin system that allows you to improve the performance of LLMs and make them work better for your specific use case. Plugins can be used in any language that supports web assembly, and they can control the output of LLMs with a process similar to JSONformer or guidance.
generative-ai-for-beginners
This course has 18 lessons. Each lesson covers its own topic so start wherever you like! Lessons are labeled either "Learn" lessons explaining a Generative AI concept or "Build" lessons that explain a concept and code examples in both **Python** and **TypeScript** when possible. Each lesson also includes a "Keep Learning" section with additional learning tools. **What You Need** * Access to the Azure OpenAI Service **OR** OpenAI API - _Only required to complete coding lessons_ * Basic knowledge of Python or Typescript is helpful - *For absolute beginners check out these Python and TypeScript courses. * A Github account to fork this entire repo to your own GitHub account We have created a **Course Setup** lesson to help you with setting up your development environment. Don't forget to star (🌟) this repo to find it easier later. ## 🧠 Ready to Deploy? If you are looking for more advanced code samples, check out our collection of Generative AI Code Samples in both **Python** and **TypeScript**. ## 🗣️ Meet Other Learners, Get Support Join our official AI Discord server to meet and network with other learners taking this course and get support. ## 🚀 Building a Startup? Sign up for Microsoft for Startups Founders Hub to receive **free OpenAI credits** and up to **$150k towards Azure credits to access OpenAI models through Azure OpenAI Services**. ## 🙏 Want to help? Do you have suggestions or found spelling or code errors? Raise an issue or Create a pull request ## 📂 Each lesson includes: * A short video introduction to the topic * A written lesson located in the README * Python and TypeScript code samples supporting Azure OpenAI and OpenAI API * Links to extra resources to continue your learning ## 🗃️ Lessons | | Lesson Link | Description | Additional Learning | | :-: | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | | 00 | Course Setup | **Learn:** How to Setup Your Development Environment | Learn More | | 01 | Introduction to Generative AI and LLMs | **Learn:** Understanding what Generative AI is and how Large Language Models (LLMs) work. | Learn More | | 02 | Exploring and comparing different LLMs | **Learn:** How to select the right model for your use case | Learn More | | 03 | Using Generative AI Responsibly | **Learn:** How to build Generative AI Applications responsibly | Learn More | | 04 | Understanding Prompt Engineering Fundamentals | **Learn:** Hands-on Prompt Engineering Best Practices | Learn More | | 05 | Creating Advanced Prompts | **Learn:** How to apply prompt engineering techniques that improve the outcome of your prompts. | Learn More | | 06 | Building Text Generation Applications | **Build:** A text generation app using Azure OpenAI | Learn More | | 07 | Building Chat Applications | **Build:** Techniques for efficiently building and integrating chat applications. | Learn More | | 08 | Building Search Apps Vector Databases | **Build:** A search application that uses Embeddings to search for data. | Learn More | | 09 | Building Image Generation Applications | **Build:** A image generation application | Learn More | | 10 | Building Low Code AI Applications | **Build:** A Generative AI application using Low Code tools | Learn More | | 11 | Integrating External Applications with Function Calling | **Build:** What is function calling and its use cases for applications | Learn More | | 12 | Designing UX for AI Applications | **Learn:** How to apply UX design principles when developing Generative AI Applications | Learn More | | 13 | Securing Your Generative AI Applications | **Learn:** The threats and risks to AI systems and methods to secure these systems. | Learn More | | 14 | The Generative AI Application Lifecycle | **Learn:** The tools and metrics to manage the LLM Lifecycle and LLMOps | Learn More | | 15 | Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) and Vector Databases | **Build:** An application using a RAG Framework to retrieve embeddings from a Vector Databases | Learn More | | 16 | Open Source Models and Hugging Face | **Build:** An application using open source models available on Hugging Face | Learn More | | 17 | AI Agents | **Build:** An application using an AI Agent Framework | Learn More | | 18 | Fine-Tuning LLMs | **Learn:** The what, why and how of fine-tuning LLMs | Learn More |

carrot
The 'carrot' repository on GitHub provides a list of free and user-friendly ChatGPT mirror sites for easy access. The repository includes sponsored sites offering various GPT models and services. Users can find and share sites, report errors, and access stable and recommended sites for ChatGPT usage. The repository also includes a detailed list of ChatGPT sites, their features, and accessibility options, making it a valuable resource for ChatGPT users seeking free and unlimited GPT services.
pyAIML
PyAIML is a Python implementation of the AIML (Artificial Intelligence Markup Language) interpreter. It aims to be a simple, standards-compliant interpreter for AIML 1.0.1. PyAIML is currently in pre-alpha development, so use it at your own risk. For more information on PyAIML, see the CHANGES.txt and SUPPORTED_TAGS.txt files.
PythonPark
PythonPark is a paradise for learning Python, providing babysitter-level tutorials on AI labs, treasure videos, data structures, study guides, machine learning practicals, deep learning practicals, Python basics, web scraping, big company interview experiences, programming life, and resource sharing. Original articles are published at least twice a week, with the latest articles being first released on WeChat and videos on Bilibili. Join the WeChat group for technical discussions or to provide feedback. Continuously improving and outputting content!
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.

