
CS7320-AI
Examples for an AI course following the textbook Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach by Russell and Norvig.
Stars: 81
CS7320-AI is a repository containing lecture materials, simple Python code examples, and assignments for the course CS 5/7320 Artificial Intelligence. The code examples cover various chapters of the textbook 'Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach' by Russell and Norvig. The repository focuses on basic AI concepts rather than advanced implementation techniques. It includes HOWTO guides for installing Python, working on assignments, and using AI with Python.
README:
This repository contains lecture material, simple Python code examples, and assignments for the course CS 5/7320 Artificial Intelligence taught by Michael Hahsler at the Department of Computer Science at SMU.
The code examples cover several chapters of the textbook Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach (AIMA) by Russell and Norvig. The code in this repository is intended to be simple to focus more on the basic AI concepts and less on the use of advanced implementation techniques (e.g., object-oriented design and flexibility). More complex code examples accompanying the textbook can be found at the GitHub repository aimacode.
Studying the material requires
- advanced Python programming skills.
- practical knowledge of how to implement data structures (Big-O notation, search trees).
- a working knowledge of probability theory and combinatorics.
| Module | Chapter | Lecture Slides | Code |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1: Introduction to AI (+ 27 Ethics and Safety) | PDF, PowerPoint | - |
| 2 | 2: Intelligent Agents | PDF, PowerPoint | Code |
| 3 | 3: Solving Problems by Search | PDF, PowerPoint | Code |
| 4 | 4.1-4.2: Search in Complex Environments: Local Search | PDF, PowerPoint | Code |
| 5 | 4.3-4.5: Search in Complex Environments: Search with Uncertainty | PDF, PowerPoint | Code |
| 6 | 5: Adversarial Search and Games | PDF, PowerPoint | Code |
| 7 | 6: Constraint Satisfaction Problem | PDF, PowerPoint | Code |
| 8 | 7-10: Knowledge-Based Agents + LLMs and Agentic AI | PDF, PowerPoint | Code |
| 9 | 11: Automated Planning: Hierarchical Planning and Monitoring | PDF, PowerPoint | - |
| 10 | 12: Quantifying Uncertainty: Bayesian Decision-Making | PDF,PowerPoint | Code |
| 11 | 13: Probabilistic Reasoning: Bayesian Networks | PDF, PowerPoint | Code |
| 12 | 16: Making Simple Decision: Decision Networks | PDF, PowerPoint | - |
| 13 | 19: Learning from Examples: Supervised Machine Learning | PDF, PowerPoint | Code |
| - | 22+17: Reinforcement Learning and MDPs | PDF, PowerPoint | Code |
 Ask the AIMA Scholar (GPT) a question about the content of the textbook.
Ask the AIMA Scholar (GPT) a question about the content of the textbook.
- HOWTO install and use Python and Jupyter Notebooks
- HOWTO work on assignments
- HOWTOs for AI with Python with code examples
All code and documents in this repository are provided under Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-SA 4.0) License.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for CS7320-AI
Similar Open Source Tools

CS7320-AI
CS7320-AI is a repository containing lecture materials, simple Python code examples, and assignments for the course CS 5/7320 Artificial Intelligence. The code examples cover various chapters of the textbook 'Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach' by Russell and Norvig. The repository focuses on basic AI concepts rather than advanced implementation techniques. It includes HOWTO guides for installing Python, working on assignments, and using AI with Python.
tamingLLMs
The 'Taming LLMs' repository provides a practical guide to the pitfalls and challenges associated with Large Language Models (LLMs) when building applications. It focuses on key limitations and implementation pitfalls, offering practical Python examples and open source solutions to help engineers and technical leaders navigate these challenges. The repository aims to equip readers with the knowledge to harness the power of LLMs while avoiding their inherent limitations.
LLM-PowerHouse-A-Curated-Guide-for-Large-Language-Models-with-Custom-Training-and-Inferencing
LLM-PowerHouse is a comprehensive and curated guide designed to empower developers, researchers, and enthusiasts to harness the true capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) and build intelligent applications that push the boundaries of natural language understanding. This GitHub repository provides in-depth articles, codebase mastery, LLM PlayLab, and resources for cost analysis and network visualization. It covers various aspects of LLMs, including NLP, models, training, evaluation metrics, open LLMs, and more. The repository also includes a collection of code examples and tutorials to help users build and deploy LLM-based applications.
llm-datasets
LLM Datasets is a repository containing high-quality datasets, tools, and concepts for LLM fine-tuning. It provides datasets with characteristics like accuracy, diversity, and complexity to train large language models for various tasks. The repository includes datasets for general-purpose, math & logic, code, conversation & role-play, and agent & function calling domains. It also offers guidance on creating high-quality datasets through data deduplication, data quality assessment, data exploration, and data generation techniques.
data-prep-kit
Data Prep Kit is a community project aimed at democratizing and speeding up unstructured data preparation for LLM app developers. It provides high-level APIs and modules for transforming data (code, language, speech, visual) to optimize LLM performance across different use cases. The toolkit supports Python, Ray, Spark, and Kubeflow Pipelines runtimes, offering scalability from laptop to datacenter-scale processing. Developers can contribute new custom modules and leverage the data processing library for building data pipelines. Automation features include workflow automation with Kubeflow Pipelines for transform execution.
Awesome-LLM-Large-Language-Models-Notes
Awesome-LLM-Large-Language-Models-Notes is a repository that provides a comprehensive collection of information on various Large Language Models (LLMs) classified by year, size, and name. It includes details on known LLM models, their papers, implementations, and specific characteristics. The repository also covers LLM models classified by architecture, must-read papers, blog articles, tutorials, and implementations from scratch. It serves as a valuable resource for individuals interested in understanding and working with LLMs in the field of Natural Language Processing (NLP).
data-prep-kit
Data Prep Kit accelerates unstructured data preparation for LLM app developers. It allows developers to cleanse, transform, and enrich unstructured data for pre-training, fine-tuning, instruct-tuning LLMs, or building RAG applications. The kit provides modules for Python, Ray, and Spark runtimes, supporting Natural Language and Code data modalities. It offers a framework for custom transforms and uses Kubeflow Pipelines for workflow automation. Users can install the kit via PyPi and access a variety of transforms for data processing pipelines.
AI-For-Beginners
AI-For-Beginners is a comprehensive 12-week, 24-lesson curriculum designed by experts at Microsoft to introduce beginners to the world of Artificial Intelligence (AI). The curriculum covers various topics such as Symbolic AI, Neural Networks, Computer Vision, Natural Language Processing, Genetic Algorithms, and Multi-Agent Systems. It includes hands-on lessons, quizzes, and labs using popular frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch. The focus is on providing a foundational understanding of AI concepts and principles, making it an ideal starting point for individuals interested in AI.
ai-samples
AI Samples for .NET is a repository containing various samples demonstrating how to use AI in .NET applications. It provides quickstarts using Semantic Kernel and Azure OpenAI SDK, covers LLM Core Concepts, End to End Examples, Local Models, Local Embedding Models, Tokenizers, Vector Databases, and Reference Examples. The repository showcases different AI-related projects and tools for developers to explore and learn from.
SLR-FC
This repository provides a comprehensive collection of AI tools and resources to enhance literature reviews. It includes a curated list of AI tools for various tasks, such as identifying research gaps, discovering relevant papers, visualizing paper content, and summarizing text. Additionally, the repository offers materials on generative AI, effective prompts, copywriting, image creation, and showcases of AI capabilities. By leveraging these tools and resources, researchers can streamline their literature review process, gain deeper insights from scholarly literature, and improve the quality of their research outputs.
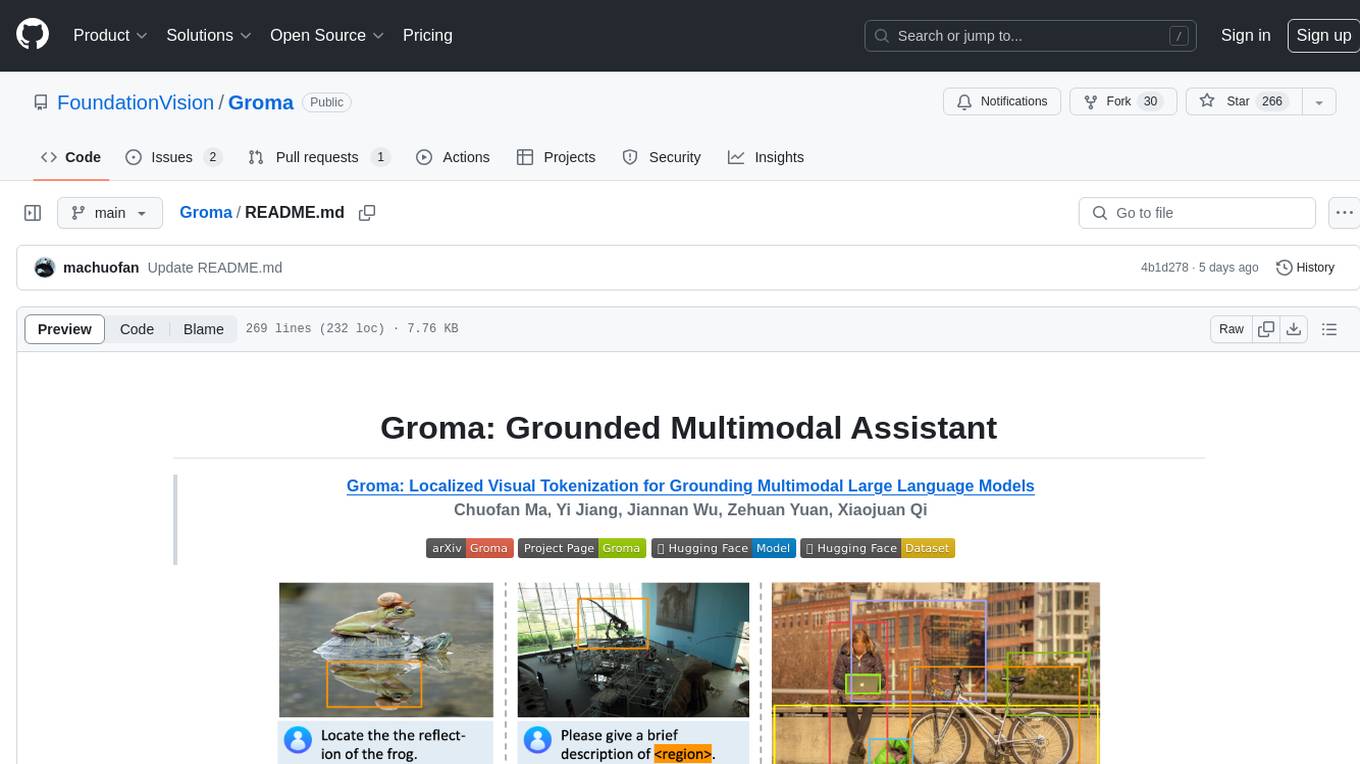
Groma
Groma is a grounded multimodal assistant that excels in region understanding and visual grounding. It can process user-defined region inputs and generate contextually grounded long-form responses. The tool presents a unique paradigm for multimodal large language models, focusing on visual tokenization for localization. Groma achieves state-of-the-art performance in referring expression comprehension benchmarks. The tool provides pretrained model weights and instructions for data preparation, training, inference, and evaluation. Users can customize training by starting from intermediate checkpoints. Groma is designed to handle tasks related to detection pretraining, alignment pretraining, instruction finetuning, instruction following, and more.
ai-hands-on
A complete, hands-on guide to becoming an AI Engineer. This repository is designed to help you learn AI from first principles, build real neural networks, and understand modern LLM systems end-to-end. Progress through math, PyTorch, deep learning, transformers, RAG, and OCR with clean, intuitive Jupyter notebooks guiding you at every step. Suitable for beginners and engineers leveling up, providing clarity, structure, and intuition to build real AI systems.
amber-train
Amber is the first model in the LLM360 family, an initiative for comprehensive and fully open-sourced LLMs. It is a 7B English language model with the LLaMA architecture. The model type is a language model with the same architecture as LLaMA-7B. It is licensed under Apache 2.0. The resources available include training code, data preparation, metrics, and fully processed Amber pretraining data. The model has been trained on various datasets like Arxiv, Book, C4, Refined-Web, StarCoder, StackExchange, and Wikipedia. The hyperparameters include a total of 6.7B parameters, hidden size of 4096, intermediate size of 11008, 32 attention heads, 32 hidden layers, RMSNorm ε of 1e^-6, max sequence length of 2048, and a vocabulary size of 32000.
LLMs-Planning
This repository contains code for three papers related to evaluating large language models on planning and reasoning about change. It includes benchmarking tools and analysis for assessing the planning abilities of large language models. The latest addition evaluates and enhances the planning and scheduling capabilities of a specific language reasoning model. The repository provides a static test set leaderboard showcasing model performance on various tasks with natural language and planning domain prompts.
redis-ai-resources
A curated repository of code recipes, demos, and resources for basic and advanced Redis use cases in the AI ecosystem. It includes demos for ArxivChatGuru, Redis VSS, Vertex AI & Redis, Agentic RAG, ArXiv Search, and Product Search. Recipes cover topics like Getting started with RAG, Semantic Cache, Advanced RAG, and Recommendation systems. The repository also provides integrations/tools like RedisVL, AWS Bedrock, LangChain Python, LangChain JS, LlamaIndex, Semantic Kernel, RelevanceAI, and DocArray. Additional content includes blog posts, talks, reviews, and documentation related to Vector Similarity Search, AI-Powered Document Search, Vector Databases, Real-Time Product Recommendations, and more. Benchmarks compare Redis against other Vector Databases and ANN benchmarks. Documentation includes QuickStart guides, official literature for Vector Similarity Search, Redis-py client library docs, Redis Stack documentation, and Redis client list.

together-cookbook
The Together Cookbook is a collection of code and guides designed to help developers build with open source models using Together AI. The recipes provide examples on how to chain multiple LLM calls, create agents that route tasks to specialized models, run multiple LLMs in parallel, break down tasks into parallel subtasks, build agents that iteratively improve responses, perform LoRA fine-tuning and inference, fine-tune LLMs for repetition, improve summarization capabilities, fine-tune LLMs on multi-step conversations, implement retrieval-augmented generation, conduct multimodal search and conditional image generation, visualize vector embeddings, improve search results with rerankers, implement vector search with embedding models, extract structured text from images, summarize and evaluate outputs with LLMs, generate podcasts from PDF content, and get LLMs to generate knowledge graphs.
For similar tasks

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.

sorrentum
Sorrentum is an open-source project that aims to combine open-source development, startups, and brilliant students to build machine learning, AI, and Web3 / DeFi protocols geared towards finance and economics. The project provides opportunities for internships, research assistantships, and development grants, as well as the chance to work on cutting-edge problems, learn about startups, write academic papers, and get internships and full-time positions at companies working on Sorrentum applications.

tidb
TiDB is an open-source distributed SQL database that supports Hybrid Transactional and Analytical Processing (HTAP) workloads. It is MySQL compatible and features horizontal scalability, strong consistency, and high availability.

zep-python
Zep is an open-source platform for building and deploying large language model (LLM) applications. It provides a suite of tools and services that make it easy to integrate LLMs into your applications, including chat history memory, embedding, vector search, and data enrichment. Zep is designed to be scalable, reliable, and easy to use, making it a great choice for developers who want to build LLM-powered applications quickly and easily.

telemetry-airflow
This repository codifies the Airflow cluster that is deployed at workflow.telemetry.mozilla.org (behind SSO) and commonly referred to as "WTMO" or simply "Airflow". Some links relevant to users and developers of WTMO: * The `dags` directory in this repository contains some custom DAG definitions * Many of the DAGs registered with WTMO don't live in this repository, but are instead generated from ETL task definitions in bigquery-etl * The Data SRE team maintains a WTMO Developer Guide (behind SSO)

mojo
Mojo is a new programming language that bridges the gap between research and production by combining Python syntax and ecosystem with systems programming and metaprogramming features. Mojo is still young, but it is designed to become a superset of Python over time.

pandas-ai
PandasAI is a Python library that makes it easy to ask questions to your data in natural language. It helps you to explore, clean, and analyze your data using generative AI.

databend
Databend is an open-source cloud data warehouse that serves as a cost-effective alternative to Snowflake. With its focus on fast query execution and data ingestion, it's designed for complex analysis of the world's largest datasets.
For similar jobs
NanoLLM
NanoLLM is a tool designed for optimized local inference for Large Language Models (LLMs) using HuggingFace-like APIs. It supports quantization, vision/language models, multimodal agents, speech, vector DB, and RAG. The tool aims to provide efficient and effective processing for LLMs on local devices, enhancing performance and usability for various AI applications.
mslearn-ai-fundamentals
This repository contains materials for the Microsoft Learn AI Fundamentals module. It covers the basics of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data science. The content includes hands-on labs, interactive learning modules, and assessments to help learners understand key concepts and techniques in AI. Whether you are new to AI or looking to expand your knowledge, this module provides a comprehensive introduction to the fundamentals of AI.

awesome-ai-tools
Awesome AI Tools is a curated list of popular tools and resources for artificial intelligence enthusiasts. It includes a wide range of tools such as machine learning libraries, deep learning frameworks, data visualization tools, and natural language processing resources. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced AI practitioner, this repository aims to provide you with a comprehensive collection of tools to enhance your AI projects and research. Explore the list to discover new tools, stay updated with the latest advancements in AI technology, and find the right resources to support your AI endeavors.
go2coding.github.io
The go2coding.github.io repository is a collection of resources for AI enthusiasts, providing information on AI products, open-source projects, AI learning websites, and AI learning frameworks. It aims to help users stay updated on industry trends, learn from community projects, access learning resources, and understand and choose AI frameworks. The repository also includes instructions for local and external deployment of the project as a static website, with details on domain registration, hosting services, uploading static web pages, configuring domain resolution, and a visual guide to the AI tool navigation website. Additionally, it offers a platform for AI knowledge exchange through a QQ group and promotes AI tools through a WeChat public account.
AI-Notes
AI-Notes is a repository dedicated to practical applications of artificial intelligence and deep learning. It covers concepts such as data mining, machine learning, natural language processing, and AI. The repository contains Jupyter Notebook examples for hands-on learning and experimentation. It explores the development stages of AI, from narrow artificial intelligence to general artificial intelligence and superintelligence. The content delves into machine learning algorithms, deep learning techniques, and the impact of AI on various industries like autonomous driving and healthcare. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of AI technologies and their real-world applications.
promptpanel
Prompt Panel is a tool designed to accelerate the adoption of AI agents by providing a platform where users can run large language models across any inference provider, create custom agent plugins, and use their own data safely. The tool allows users to break free from walled-gardens and have full control over their models, conversations, and logic. With Prompt Panel, users can pair their data with any language model, online or offline, and customize the system to meet their unique business needs without any restrictions.
ai-demos
The 'ai-demos' repository is a collection of example code from presentations focusing on building with AI and LLMs. It serves as a resource for developers looking to explore practical applications of artificial intelligence in their projects. The code snippets showcase various techniques and approaches to leverage AI technologies effectively. The repository aims to inspire and educate developers on integrating AI solutions into their applications.
ai_summer
AI Summer is a repository focused on providing workshops and resources for developing foundational skills in generative AI models and transformer models. The repository offers practical applications for inferencing and training, with a specific emphasis on understanding and utilizing advanced AI chat models like BingGPT. Participants are encouraged to engage in interactive programming environments, decide on projects to work on, and actively participate in discussions and breakout rooms. The workshops cover topics such as generative AI models, retrieval-augmented generation, building AI solutions, and fine-tuning models. The goal is to equip individuals with the necessary skills to work with AI technologies effectively and securely, both locally and in the cloud.

