lfai-landscape
🌄 Open Source AI & Data Landscape - provides overview of top tier projects in the open source AI and Data ecosystem, shows projects through GitHub data, funding or market cap, first and last commits, contributor count and much other information.
Stars: 322
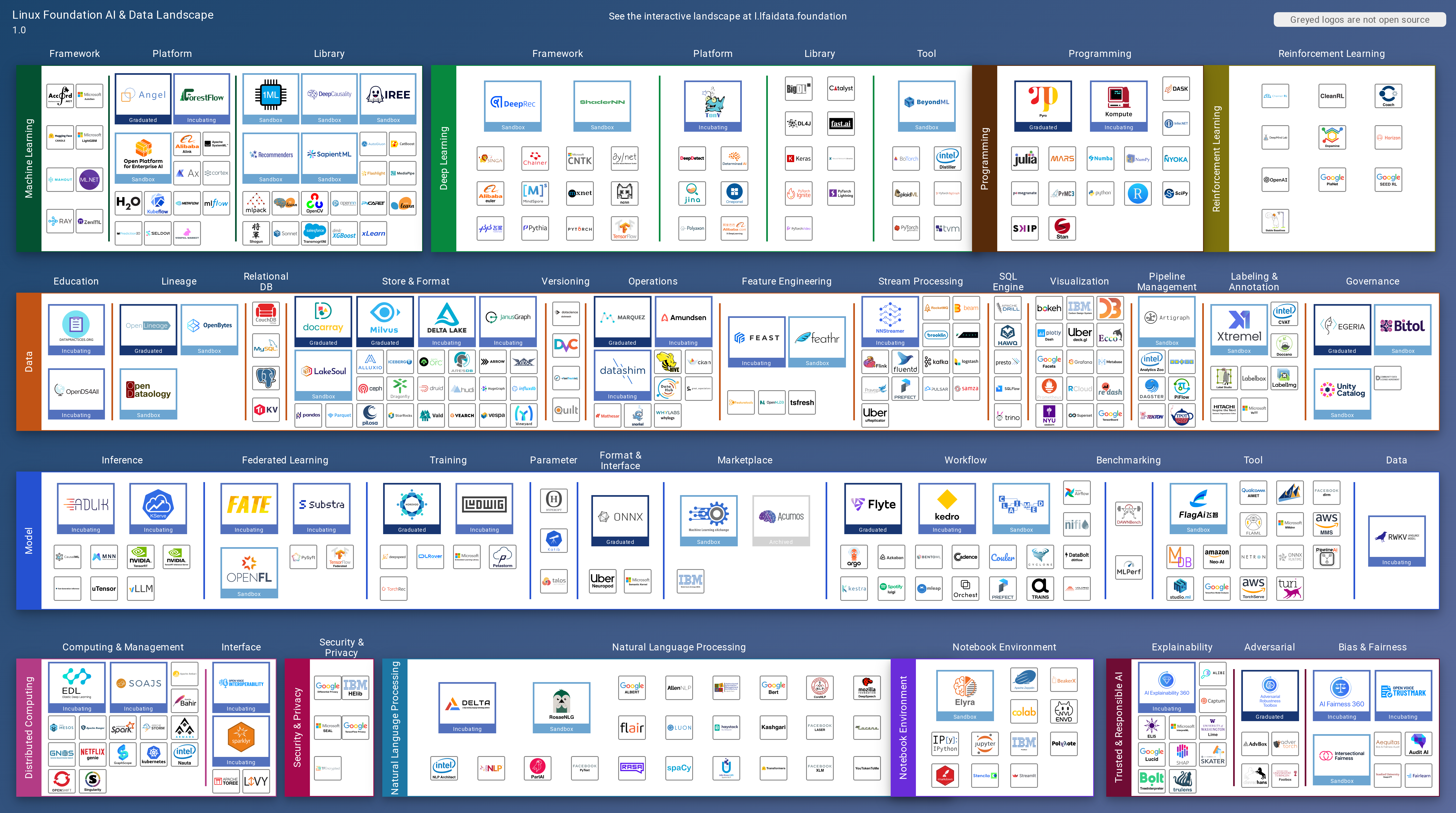
LF AI & Data Landscape is a map to explore open source projects in the AI & Data domains, highlighting companies that are members of LF AI & Data. It showcases members of the Foundation and is modelled after the Cloud Native Computing Foundation landscape. The landscape includes current version, interactive version, new entries, logos, proper SVGs, corrections, external data, best practices badge, non-updated items, license, formats, installation, vulnerability reporting, and adjusting the landscape view.
README:
This landscape is intended as a map to explore open source projects in the AI & Data domains, highlights companies that are member of LF AI & Data, and also showcases members of the Foundation. It is modelled after the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) landscape and based on the same open source code.
Please see landscape.lfaidata.foundation.
- Projects must be open source and hosted on or mirrored to GitHub.
- AI, ML, and DL projects with at least 300 GitHub stars that clearly fit in an existing category are generally included. Put the project in the single category where it best fits.
- We are unlikely to create a new category for projects as we'd rather find the best home with the current options.
- Your project or company needs a logo and the logo needs to include the name.
- Crunchbase organization should be the company or organization that controls the software. That is normally the owner of the trademark, whether or not a trademark has been formally filed.
If you think your project should be included, please open a pull request to add it to landscape.yml. For the logo, you can either upload an SVG to the hosted_logos directory or put a URL as the value, and it will be fetched.
Netlify will generate a staging server for you to preview your updates. Please check that the logo and information appear correctly and then add LGTM to the pull request confirming your review and requesting a merge.
The following rules will produce the most readable and attractive logos:
- We require SVGs, as they are smaller, display correctly at any scale, and work on all modern browsers. If you only have the logo in another vector format (like AI or EPS), please open an issue and we'll convert it to an SVG for you, or you can often do it yourself at https://cloudconvert.com/. Note that you may need to zip your file to attach it to a GitHub issue. Please note that we require pure SVGs and will reject SVGs that contain embedded PNGs since they have the same problems of being bigger and not scaling seamlessly. We also require that SVGs convert fonts to outlines so that they will render correctly whether or not a font is installed. See Proper SVGs below.
- When multiple variants exist, use stacked (not horizontal) logos. For example, we use the second column (stacked), not the first (horizontal), of CNCF project logos.
- Don't use reversed logos (i.e., with a non-white, non-transparent background color). If you only have a reversed logo, create an issue with it attached and we'll produce a non-reversed version for you.
- Logos must include the company, product or project name in English. It's fine to also include words from another language. If you don't have a version of your logo with the name in it, please open an issue and we'll create one for you (and please specify the font).
- Match the item name to the English words in the logos. So an Acme Rocket logo that shows "Rocket" should have product name "Rocket", while if the logo shows "Acme Rocket", the product name should be "Acme Rocket". Otherwise, logos looks out of place when you sort alphabetically.
- Google images is often the best way to find a good version of the logo (but ensure it's the up-to-date version). Search for grpc logo filetype:svg but substitute your project or product name for grpc.
- You can either upload an SVG to the
hosted_logosdirectory or put a URL as the value, and it will be fetched.
SVGs need to not rely on external fonts so that they will render correctly in any web browser, whether or not the correct fonts are installed. If you have the original AI file, here are the steps in Illustrator to create a proper SVG:
- Open file in Illustrator
- Select all text
- With the text selected, go to Object > Expand in the top menu
- Export file by going to File > Export > Export As in top menu
- Select SVG from the format drop down and make sure that "Use Artboards" is checked
- This will open a SVG options box, make sure to set Decimal to 5 (that is the highest possible, so to ensure that sufficient detail is preserved)
- Click Okay to export
Please open a pull request with edits to landscape.yml. The file processed_landscape.yml is generated and so should never be edited directly.
If the error is with data from Crunchbase you should open an account there and edit the data. If you don't like a project description, edit it in GitHub. If your project isn't showing the license correctly, you may need to paste the unmodified text of the license into a LICENSE file at the root of your project in GitHub, in order for GitHub to serve the license information correctly.
The canonical source for all data is landscape.yml. Once a day, we download data for projects and companies from the following sources:
- Project info from GitHub
- Funding info from Crunchbase
- Market cap data from Yahoo Finance
- CII Best Practices Badge data
The update server enhances the source data with the fetched data and saves the result in processed_landscape.yml. The app loads a JSON representation of processed_landscape.yml to display data.
As explained at https://bestpractices.coreinfrastructure.org/:
The Linux Foundation (LF) Core Infrastructure Initiative (CII) Best Practices badge is a way for Free/Libre and Open Source Software (FLOSS) projects to show that they follow best practices. Projects can voluntarily self-certify, at no cost, by using this web application to explain how they follow each best practice. The CII Best Practices Badge is inspired by the many badges available to projects on GitHub. Consumers of the badge can quickly assess which FLOSS projects are following best practices and as a result are more likely to produce higher-quality secure software.
The interactive landscape displays the status (or non-existence) of a badge for each open-source project. There's also a feature not available through the filter bar to see all items with and without badges. Note that a passing badge is a requirement for projects to graduate in the CNCF.
We generally remove open source projects that have not had a commit in over 3 months. Note that for projects not hosted on GitHub, we need them to mirror to GitHub to fetch updates, and we try to work with projects when their mirrors are broken. Here is view of projects sorted by last update: https://landscape.lfai.foundation/grouping=no&license=open-source&sort=latest-commit
We generally remove closed source products when they have not tweeted in over 3 months. This doesn't apply to Chinese companies without Twitter accounts, since Twitter is blocked there. Here is a view of products sorted by last tweet: https://landscape.lfai.foundation/grouping=no&license=not-open-source&sort=latest-tweet
Items that have been removed can apply to be re-added using the regular New Entries criteria above.
This repository contains data received from Crunchbase. This data is not licensed pursuant to the Apache License. It is subject to Crunchbase’s Data Access Terms, available at https://data.crunchbase.com/v3.1/docs/terms, and is only permitted to be used with this Landscape Project which is hosted by the Linux Foundation.
Everything else is under the Apache License, Version 2.0, except for project and product logos, which are generally copyrighted by the company that created them, and are simply cached here for reliability. The trail map, static landscape, serverless landscape, and landscape.yml file are alternatively available under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 license.
The LF AI & Data Landscape is available in these formats:
You can install and run locally with the install directions. It's not necessary to install locally if you just want to edit landscape.yml. You can do so via the GitHub web interface.
Please open an issue or, for sensitive information, email [email protected].
The file src/components/MainContent2.js describes the key elements of a landscape big picture. It specifies where to put these sections: App Definition and Development, Orchesteration & Management, Runtime, Provisioning, Cloud, Platform, Observability and Analyzis, Special. Also it specifies where to locate the link to the serverless preview and an info with a QR code.
All these elements should have top, left, width and height properties to
position them. rows and cols specify how much columns or rows we expect in a
given horizontal or vertical section.
When we see that those elements can not fit the sections, we need to either increase the width of all the horizontal sections, or increase height and amount of rows in a single horitzontal section and adjust the position of sections below.
Beside that, we have to adjust the width of a parent div (1620), the width in a
src/components/BigPicture/FullscreenLandscape.js (1640) and the width in a
tools/renderLandscape.js (6560, because of x4 zoom and margins)
Sometimes the total height is changed too, then we need to adjust the height the same way as we adjust the width.
We have an experimental fitWidth property, it is good when you want to get rid of
an extra space on the right of a section.
The best way to test that layout is ok, is to visit /landscape, and if it looks ok, run PORT=3000 babel-node tools/renderLandscape and see the rendered png files, they are in src/images folder.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for lfai-landscape
Similar Open Source Tools

lfai-landscape
LF AI & Data Landscape is a map to explore open source projects in the AI & Data domains, highlighting companies that are members of LF AI & Data. It showcases members of the Foundation and is modelled after the Cloud Native Computing Foundation landscape. The landscape includes current version, interactive version, new entries, logos, proper SVGs, corrections, external data, best practices badge, non-updated items, license, formats, installation, vulnerability reporting, and adjusting the landscape view.
Airports
This repository contains raw airport files intended as a starting point to create new airport files for the game Endless ATC. Users can contribute by customizing airport files and submitting pull requests. The repository also welcomes markdown files with gameplay and development tips. Contributors are encouraged to join the Discord server for assistance and information.
gpdb
Greenplum Database (GPDB) is an advanced, fully featured, open source data warehouse, based on PostgreSQL. It provides powerful and rapid analytics on petabyte scale data volumes. Uniquely geared toward big data analytics, Greenplum Database is powered by the world’s most advanced cost-based query optimizer delivering high analytical query performance on large data volumes.
modelbench
ModelBench is a tool for running safety benchmarks against AI models and generating detailed reports. It is part of the MLCommons project and is designed as a proof of concept to aggregate measures, relate them to specific harms, create benchmarks, and produce reports. The tool requires LlamaGuard for evaluating responses and a TogetherAI account for running benchmarks. Users can install ModelBench from GitHub or PyPI, run tests using Poetry, and create benchmarks by providing necessary API keys. The tool generates static HTML pages displaying benchmark scores and allows users to dump raw scores and manage cache for faster runs. ModelBench is aimed at enabling users to test their own models and create tests and benchmarks.
lumigator
Lumigator is an open-source platform developed by Mozilla.ai to help users select the most suitable language model for their specific needs. It supports the evaluation of summarization tasks using sequence-to-sequence models such as BART and BERT, as well as causal models like GPT and Mistral. The platform aims to make model selection transparent, efficient, and empowering by providing a framework for comparing LLMs using task-specific metrics to evaluate how well a model fits a project's needs. Lumigator is in the early stages of development and plans to expand support to additional machine learning tasks and use cases in the future.
WilmerAI
WilmerAI is a middleware system designed to process prompts before sending them to Large Language Models (LLMs). It categorizes prompts, routes them to appropriate workflows, and generates manageable prompts for local models. It acts as an intermediary between the user interface and LLM APIs, supporting multiple backend LLMs simultaneously. WilmerAI provides API endpoints compatible with OpenAI API, supports prompt templates, and offers flexible connections to various LLM APIs. The project is under heavy development and may contain bugs or incomplete code.
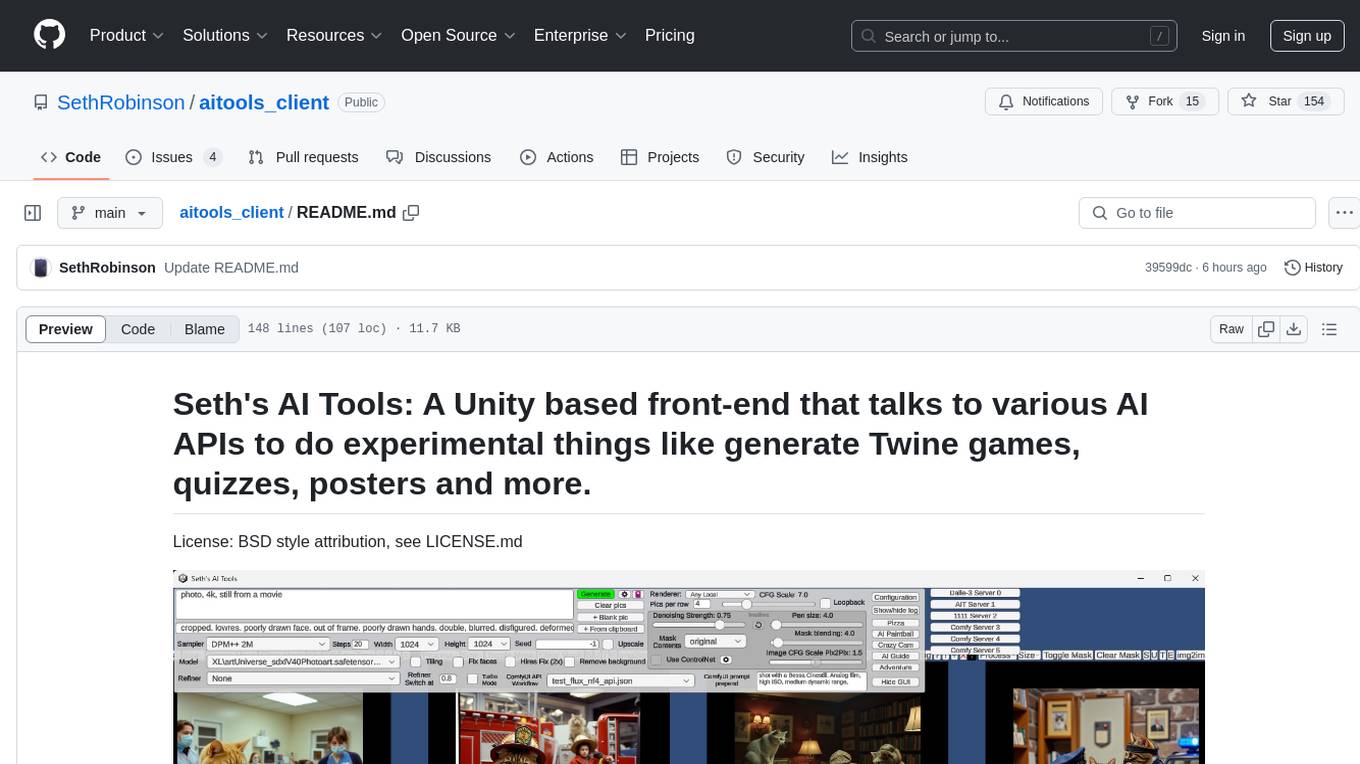
aitools_client
Seth's AI Tools is a Unity-based front-end that interfaces with various AI APIs to perform tasks such as generating Twine games, quizzes, posters, and more. The tool is a native Windows application that supports features like live update integration with image editors, text-to-image conversion, image processing, mask painting, and more. It allows users to connect to multiple servers for fast generation using GPUs and offers a neat workflow for evolving images in real-time. The tool respects user privacy by operating locally and includes built-in games and apps to test AI/SD capabilities. Additionally, it features an AI Guide for creating motivational posters and illustrated stories, as well as an Adventure mode with presets for generating web quizzes and Twine game projects.
roam-extension-live-ai-assistant
Live AI is an AI Assistant tailor-made for Roam, providing access to the latest LLMs directly in Roam blocks. Users can interact with AI to extend their thinking, explore their graph, and chat with structured responses. The tool leverages Roam's features to write prompts, query graph parts, and chat with content. Users can dictate, translate, transform, and enrich content easily. Live AI supports various tasks like audio and video analysis, PDF reading, image generation, and web search. The tool offers features like Chat panel, Live AI context menu, and Ask Your Graph agent for versatile usage. Users can control privacy levels, compare AI models, create custom prompts, and apply styles for response formatting. Security concerns are addressed by allowing users to control data sent to LLMs.
chronon
Chronon is a platform that simplifies and improves ML workflows by providing a central place to define features, ensuring point-in-time correctness for backfills, simplifying orchestration for batch and streaming pipelines, offering easy endpoints for feature fetching, and guaranteeing and measuring consistency. It offers benefits over other approaches by enabling the use of a broad set of data for training, handling large aggregations and other computationally intensive transformations, and abstracting away the infrastructure complexity of data plumbing.
deep-seek
DeepSeek is a new experimental architecture for a large language model (LLM) powered internet-scale retrieval engine. Unlike current research agents designed as answer engines, DeepSeek aims to process a vast amount of sources to collect a comprehensive list of entities and enrich them with additional relevant data. The end result is a table with retrieved entities and enriched columns, providing a comprehensive overview of the topic. DeepSeek utilizes both standard keyword search and neural search to find relevant content, and employs an LLM to extract specific entities and their associated contents. It also includes a smaller answer agent to enrich the retrieved data, ensuring thoroughness. DeepSeek has the potential to revolutionize research and information gathering by providing a comprehensive and structured way to access information from the vastness of the internet.

local-chat
LocalChat is a simple, easy-to-set-up, and open-source local AI chat tool that allows users to interact with generative language models on their own computers without transmitting data to a cloud server. It provides a chat-like interface for users to experience ChatGPT-like behavior locally, ensuring GDPR compliance and data privacy. Users can download LocalChat for macOS, Windows, or Linux to chat with open-weight generative language models.
sorcery
Sorcery is a SillyTavern extension that allows AI characters to interact with the real world by executing user-defined scripts at specific events in the chat. It is easy to use and does not require a specially trained function calling model. Sorcery can be used to control smart home appliances, interact with virtual characters, and perform various tasks in the chat environment. It works by injecting instructions into the system prompt and intercepting markers to run associated scripts, providing a seamless user experience.
pearai-master
PearAI is an inventory that curates cutting-edge AI tools in one place, offering a unified interface for seamless tool integration. The repository serves as the conglomeration of all PearAI project repositories, including VSCode fork, AI chat functionalities, landing page, documentation, and server. Contributions are welcome through quests and issue tackling, with the project stack including TypeScript/Electron.js, Next.js/React, Python FastAPI, and Axiom for logging/telemetry.
aiohomekit
aiohomekit is a Python library that implements the HomeKit protocol for controlling HomeKit accessories using asyncio. It is primarily used with Home Assistant, targeting the same versions of Python and following their code standards. The library is still under development and does not offer API guarantees yet. It aims to match the behavior of real HAP controllers, even when not strictly specified, and works around issues like JSON formatting, boolean encoding, header sensitivity, and TCP packet splitting. aiohomekit is primarily tested with Phillips Hue and Eve Extend bridges via Home Assistant, but is known to work with many more devices. It does not support BLE accessories and is intended for client-side use only.
AIlice
AIlice is a fully autonomous, general-purpose AI agent that aims to create a standalone artificial intelligence assistant, similar to JARVIS, based on the open-source LLM. AIlice achieves this goal by building a "text computer" that uses a Large Language Model (LLM) as its core processor. Currently, AIlice demonstrates proficiency in a range of tasks, including thematic research, coding, system management, literature reviews, and complex hybrid tasks that go beyond these basic capabilities. AIlice has reached near-perfect performance in everyday tasks using GPT-4 and is making strides towards practical application with the latest open-source models. We will ultimately achieve self-evolution of AI agents. That is, AI agents will autonomously build their own feature expansions and new types of agents, unleashing LLM's knowledge and reasoning capabilities into the real world seamlessly.
ClipboardConqueror
Clipboard Conqueror is a multi-platform omnipresent copilot alternative. Currently requiring a kobold united or openAI compatible back end, this software brings powerful LLM based tools to any text field, the universal copilot you deserve. It simply works anywhere. No need to sign in, no required key. Provided you are using local AI, CC is a data secure alternative integration provided you trust whatever backend you use. *Special thank you to the creators of KoboldAi, KoboldCPP, llamma, openAi, and the communities that made all this possible to figure out.
For similar tasks

lfai-landscape
LF AI & Data Landscape is a map to explore open source projects in the AI & Data domains, highlighting companies that are members of LF AI & Data. It showcases members of the Foundation and is modelled after the Cloud Native Computing Foundation landscape. The landscape includes current version, interactive version, new entries, logos, proper SVGs, corrections, external data, best practices badge, non-updated items, license, formats, installation, vulnerability reporting, and adjusting the landscape view.
python-weekly
Python Trending Weekly is a curated newsletter by Python猫 that selects the most valuable articles, tutorials, open-source projects, software tools, podcasts, videos, and hot topics from over 250 English and Chinese sources. The newsletter aims to help readers improve their Python skills and increase their income from both professional and side projects. It offers paid subscription options and is available on various platforms like GitHub, WeChat, blogs, email, Telegram, and Twitter. Each issue shares a collection of articles, open-source projects, videos, and books related to Python and technology.
WilliamButcherBot
WilliamButcherBot is a Telegram Group Manager Bot and Userbot written in Python using Pyrogram. It provides features for managing Telegram groups and users, with ready-to-use methods available. The bot requires Python 3.9, Telegram API Key, Telegram Bot Token, and MongoDB URI. Users can install it locally or on a VPS, run it directly, generate Pyrogram session for Heroku, or use Docker for deployment. Additionally, users can write new modules to extend the bot's functionality by adding them to the wbb/modules/ directory.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.