
LLM101n
LLM101n: Let's build a Storyteller
Stars: 24377
LLM101n is a course focused on building a Storyteller AI Large Language Model (LLM) from scratch in Python, C, and CUDA. The course covers various topics such as language modeling, machine learning, attention mechanisms, tokenization, optimization, device usage, precision training, distributed optimization, datasets, inference, finetuning, deployment, and multimodal applications. Participants will gain a deep understanding of AI, LLMs, and deep learning through hands-on projects and practical examples.
README:
What I cannot create, I do not understand. -Richard Feynman
In this course we will build a Storyteller AI Large Language Model (LLM). Hand in hand, you'll be able create, refine and illustrate little stories with the AI. We are going to build everything end-to-end from basics to a functioning web app similar to ChatGPT, from scratch in Python, C and CUDA, and with minimal computer science prerequisits. By the end you should have a relatively deep understanding of AI, LLMs, and deep learning more generally.
Syllabus
- Chapter 01 Bigram Language Model (language modeling)
- Chapter 02 Micrograd (machine learning, backpropagation)
- Chapter 03 N-gram model (multi-layer perceptron, matmul, gelu)
- Chapter 04 Attention (attention, softmax, positional encoder)
- Chapter 05 Transformer (transformer, residual, layernorm, GPT-2)
- Chapter 06 Tokenization (minBPE, byte pair encoding)
- Chapter 07 Optimization (initialization, optimization, AdamW)
- Chapter 08 Need for Speed I: Device (device, CPU, GPU, ...)
- Chapter 09 Need for Speed II: Precision (mixed precision training, fp16, bf16, fp8, ...)
- Chapter 10 Need for Speed III: Distributed (distributed optimization, DDP, ZeRO)
- Chapter 11 Datasets (datasets, data loading, synthetic data generation)
- Chapter 12 Inference I: kv-cache (kv-cache)
- Chapter 13 Inference II: Quantization (quantization)
- Chapter 14 Finetuning I: SFT (supervised finetuning SFT, PEFT, LoRA, chat)
- Chapter 15 Finetuning II: RL (reinforcement learning, RLHF, PPO, DPO)
- Chapter 16 Deployment (API, web app)
- Chapter 17 Multimodal (VQVAE, diffusion transformer)
Appendix
Further topics to work into the progression above:
- Programming languages: Assembly, C, Python
- Data types: Integer, Float, String (ASCII, Unicode, UTF-8)
- Tensor: shapes, views, strides, contiguous, ...
- Deep Learning frameowrks: PyTorch, JAX
- Neural Net Architecture: GPT (1,2,3,4), Llama (RoPE, RMSNorm, GQA), MoE, ...
- Multimodal: Images, Audio, Video, VQVAE, VQGAN, diffusion
Update June 25. To clarify, the course will take some time to build. There is no specific timeline. Thank you for your interest but please do not submit Issues/PRs.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for LLM101n
Similar Open Source Tools

LLM101n
LLM101n is a course focused on building a Storyteller AI Large Language Model (LLM) from scratch in Python, C, and CUDA. The course covers various topics such as language modeling, machine learning, attention mechanisms, tokenization, optimization, device usage, precision training, distributed optimization, datasets, inference, finetuning, deployment, and multimodal applications. Participants will gain a deep understanding of AI, LLMs, and deep learning through hands-on projects and practical examples.
LibreChat
LibreChat is an all-in-one AI conversation platform that integrates multiple AI models, including ChatGPT, into a user-friendly interface. It offers a wide range of features, including multimodal chat, multilingual UI, AI model selection, custom presets, conversation branching, message export, search, plugins, multi-user support, and extensive configuration options. LibreChat is open-source and community-driven, with a focus on providing a free and accessible alternative to ChatGPT Plus. It is designed to enhance productivity, creativity, and communication through advanced AI capabilities.
kornia
Kornia is a differentiable computer vision library for PyTorch. It consists of a set of routines and differentiable modules to solve generic computer vision problems. At its core, the package uses PyTorch as its main backend both for efficiency and to take advantage of the reverse-mode auto-differentiation to define and compute the gradient of complex functions.
veScale
veScale is a PyTorch Native LLM Training Framework. It provides a set of tools and components to facilitate the training of large language models (LLMs) using PyTorch. veScale includes features such as 4D parallelism, fast checkpointing, and a CUDA event monitor. It is designed to be scalable and efficient, and it can be used to train LLMs on a variety of hardware platforms.
AI-PhD-S25
AI-PhD-S25 is a mono-repo for the DOTE 6635 course on AI for Business Research at CUHK Business School. The course aims to provide a fundamental understanding of ML/AI concepts and methods relevant to business research, explore applications of ML/AI in business research, and discover cutting-edge AI/ML technologies. The course resources include Google CoLab for code distribution, Jupyter Notebooks, Google Sheets for group tasks, Overleaf template for lecture notes, replication projects, and access to HPC Server compute resource. The course covers topics like AI/ML in business research, deep learning basics, attention mechanisms, transformer models, LLM pretraining, posttraining, causal inference fundamentals, and more.
AI-PhD-S24
AI-PhD-S24 is a mono-repo for the PhD course 'AI for Business Research' at CUHK Business School in Spring 2024. The course aims to provide a basic understanding of machine learning and artificial intelligence concepts/methods used in business research, showcase how ML/AI is utilized in business research, and introduce state-of-the-art AI/ML technologies. The course includes scribed lecture notes, class recordings, and covers topics like AI/ML fundamentals, DL, NLP, CV, unsupervised learning, and diffusion models.
llms-interview-questions
This repository contains a comprehensive collection of 63 must-know Large Language Models (LLMs) interview questions. It covers topics such as the architecture of LLMs, transformer models, attention mechanisms, training processes, encoder-decoder frameworks, differences between LLMs and traditional statistical language models, handling context and long-term dependencies, transformers for parallelization, applications of LLMs, sentiment analysis, language translation, conversation AI, chatbots, and more. The readme provides detailed explanations, code examples, and insights into utilizing LLMs for various tasks.
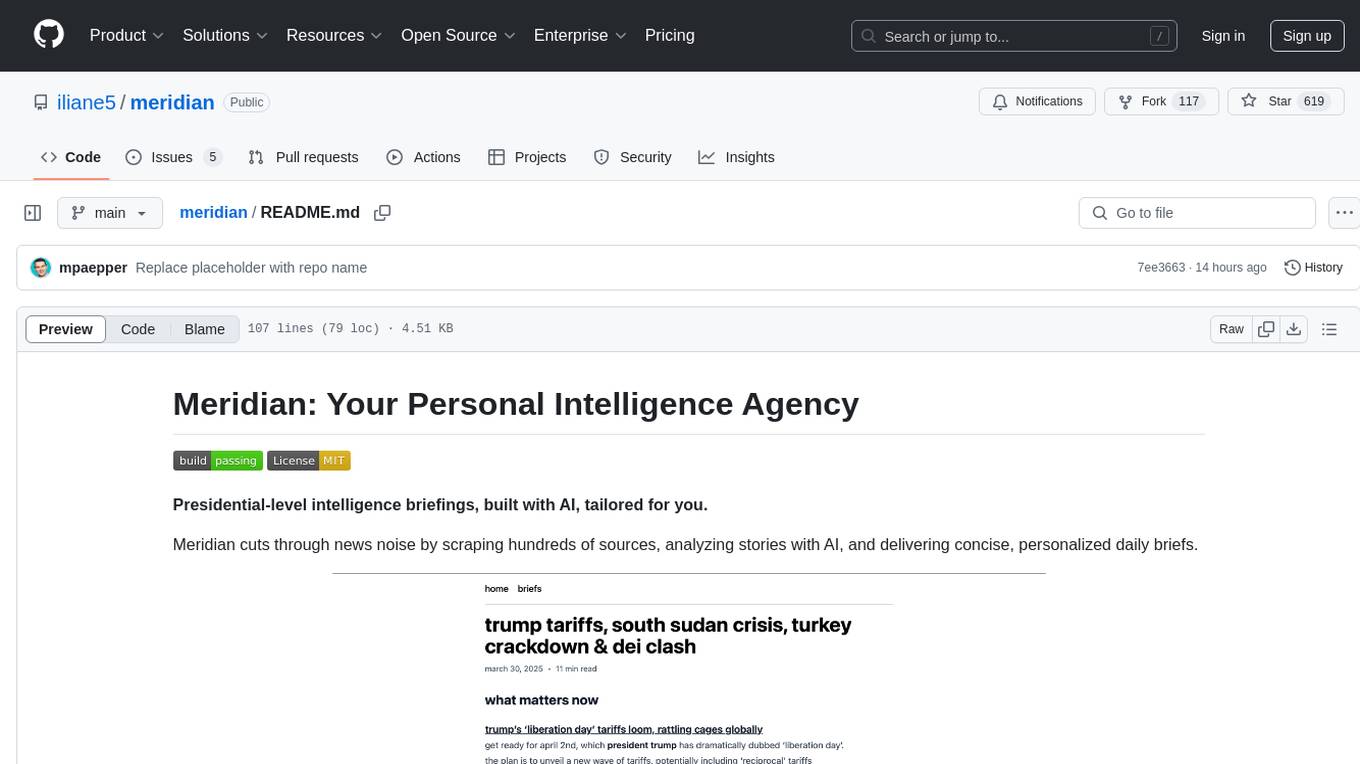
meridian
Meridian is a tool that provides personalized daily intelligence briefings by scraping news from hundreds of sources, analyzing stories with AI, and delivering concise briefs. It offers key global events, context, implications analysis, and open-source transparency. Built for the curious who seek in-depth news beyond headlines without spending too much time. The tool uses multi-stage LLM processing for article and cluster analysis, smart clustering techniques to group related articles, and a web interface powered by Nuxt 3. The workflow involves scraping RSS feeds, processing articles with Gemini for relevance, clustering articles, and generating a final brief. The project leverages AI models like Gemini, multilingual embeddings, UMAP, and HDBSCAN for analysis. The tech stack includes Turborepo, Cloudflare services, TypeScript, PostgreSQL, and Nuxt 3 with Vue 3 and Tailwind for the frontend.
zuckerman
Zuckerman is an ultra-minimal personal AI agent that self-modifies its code live, adapts to user needs by writing code and features, and shares improvements with other agents. It aims to build a self-growing intelligence that can add tools, rewrite behavior, and extend core logic by editing its own files with almost no external code required. Zuckerman offers a collaborative ecosystem where agents propose and publish capabilities to a shared contribution site for others to discover, adopt, and evolve further.
PINNeAPPle
Pinneaple is an open-source Python platform that unifies physical data, geometry, numerical solvers, and machine learning models for Physics-Informed AI. It emphasizes physical consistency, scalability, auditability, and interoperability with CFD/CAD/scientific data formats. It provides tools for unified physical dataset representation, data pipelines, geometry and mesh operations, a model zoo, physics loss factory, solvers, synthetic data generation, training and evaluation. The platform is designed for physics AI researchers, CFD/FEA/climate ML teams, industrial R&D groups, scientific ML practitioners, and anyone building surrogates, inverse models, or hybrid solvers.
flower
Flower is a framework for building federated learning systems. It is designed to be customizable, extensible, framework-agnostic, and understandable. Flower can be used with any machine learning framework, for example, PyTorch, TensorFlow, Hugging Face Transformers, PyTorch Lightning, scikit-learn, JAX, TFLite, MONAI, fastai, MLX, XGBoost, Pandas for federated analytics, or even raw NumPy for users who enjoy computing gradients by hand.
learn-low-code-agentic-ai
This repository is dedicated to learning about Low-Code Full-Stack Agentic AI Development. It provides material for building modern AI-powered applications using a low-code full-stack approach. The main tools covered are UXPilot for UI/UX mockups, Lovable.dev for frontend applications, n8n for AI agents and workflows, Supabase for backend data storage, authentication, and vector search, and Model Context Protocol (MCP) for integration. The focus is on prompt and context engineering as the foundation for working with AI systems, enabling users to design, develop, and deploy AI-driven full-stack applications faster, smarter, and more reliably.
Fueling-Ambitions-Via-Book-Discoveries
Fueling-Ambitions-Via-Book-Discoveries is an Advanced Machine Learning & AI Course designed for students, professionals, and AI researchers. The course integrates rigorous theoretical foundations with practical coding exercises, ensuring learners develop a deep understanding of AI algorithms and their applications in finance, healthcare, robotics, NLP, cybersecurity, and more. Inspired by MIT, Stanford, and Harvard’s AI programs, it combines academic research rigor with industry-standard practices used by AI engineers at companies like Google, OpenAI, Facebook AI, DeepMind, and Tesla. Learners can learn 50+ AI techniques from top Machine Learning & Deep Learning books, code from scratch with real-world datasets, projects, and case studies, and focus on ML Engineering & AI Deployment using Django & Streamlit. The course also offers industry-relevant projects to build a strong AI portfolio.
tensorzero
TensorZero is an open-source platform that helps LLM applications graduate from API wrappers into defensible AI products. It enables a data & learning flywheel for LLMs by unifying inference, observability, optimization, and experimentation. The platform includes a high-performance model gateway, structured schema-based inference, observability, experimentation, and data warehouse for analytics. TensorZero Recipes optimize prompts and models, and the platform supports experimentation features and GitOps orchestration for deployment.
kserve
KServe provides a Kubernetes Custom Resource Definition for serving predictive and generative machine learning (ML) models. It encapsulates the complexity of autoscaling, networking, health checking, and server configuration to bring cutting edge serving features like GPU Autoscaling, Scale to Zero, and Canary Rollouts to ML deployments. KServe enables a simple, pluggable, and complete story for Production ML Serving including prediction, pre-processing, post-processing, and explainability. It is a standard, cloud agnostic Model Inference Platform for serving predictive and generative AI models on Kubernetes, built for highly scalable use cases.
ToolUniverse
ToolUniverse is a collection of 211 biomedical tools designed for Agentic AI, providing access to biomedical knowledge for solving therapeutic reasoning tasks. The tools cover various aspects of drugs and diseases, linked to trusted sources like US FDA-approved drugs since 1939, Open Targets, and Monarch Initiative.
For similar tasks

LLM101n
LLM101n is a course focused on building a Storyteller AI Large Language Model (LLM) from scratch in Python, C, and CUDA. The course covers various topics such as language modeling, machine learning, attention mechanisms, tokenization, optimization, device usage, precision training, distributed optimization, datasets, inference, finetuning, deployment, and multimodal applications. Participants will gain a deep understanding of AI, LLMs, and deep learning through hands-on projects and practical examples.

dstack
Dstack is an open-source orchestration engine for running AI workloads in any cloud. It supports a wide range of cloud providers (such as AWS, GCP, Azure, Lambda, TensorDock, Vast.ai, CUDO, RunPod, etc.) as well as on-premises infrastructure. With Dstack, you can easily set up and manage dev environments, tasks, services, and pools for your AI workloads.
one-click-llms
The one-click-llms repository provides templates for quickly setting up an API for language models. It includes advanced inferencing scripts for function calling and offers various models for text generation and fine-tuning tasks. Users can choose between Runpod and Vast.AI for different GPU configurations, with recommendations for optimal performance. The repository also supports Trelis Research and offers templates for different model sizes and types, including multi-modal APIs and chat models.

starcoder2-self-align
StarCoder2-Instruct is an open-source pipeline that introduces StarCoder2-15B-Instruct-v0.1, a self-aligned code Large Language Model (LLM) trained with a fully permissive and transparent pipeline. It generates instruction-response pairs to fine-tune StarCoder-15B without human annotations or data from proprietary LLMs. The tool is primarily finetuned for Python code generation tasks that can be verified through execution, with potential biases and limitations. Users can provide response prefixes or one-shot examples to guide the model's output. The model may have limitations with other programming languages and out-of-domain coding tasks.
enhance_llm
The enhance_llm repository contains three main parts: 1. Vector model domain fine-tuning based on llama_index and qwen fine-tuning BGE vector model. 2. Large model domain fine-tuning based on PEFT fine-tuning qwen1.5-7b-chat, with sft and dpo. 3. High-order retrieval enhanced generation (RAG) system based on the above domain work, implementing a two-stage RAG system. It includes query rewriting, recall reordering, retrieval reordering, multi-turn dialogue, and more. The repository also provides hardware and environment configurations along with star history and licensing information.
fms-fsdp
The 'fms-fsdp' repository is a companion to the Foundation Model Stack, providing a (pre)training example to efficiently train FMS models, specifically Llama2, using native PyTorch features like FSDP for training and SDPA implementation of Flash attention v2. It focuses on leveraging FSDP for training efficiently, not as an end-to-end framework. The repo benchmarks training throughput on different GPUs, shares strategies, and provides installation and training instructions. It trained a model on IBM curated data achieving high efficiency and performance metrics.

CogVLM2
CogVLM2 is a new generation of open source models that offer significant improvements in benchmarks such as TextVQA and DocVQA. It supports 8K content length, image resolution up to 1344 * 1344, and both Chinese and English languages. The project provides basic calling methods, fine-tuning examples, and OpenAI API format calling examples to help developers quickly get started with the model.
liboai
liboai is a simple C++17 library for the OpenAI API, providing developers with access to OpenAI endpoints through a collection of methods and classes. It serves as a spiritual port of OpenAI's Python library, 'openai', with similar structure and features. The library supports various functionalities such as ChatGPT, Audio, Azure, Functions, Image DALL·E, Models, Completions, Edit, Embeddings, Files, Fine-tunes, Moderation, and Asynchronous Support. Users can easily integrate the library into their C++ projects to interact with OpenAI services.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.
