
Generative_AI_For_Science
None
Stars: 58
Generative AI for Science is a comprehensive, hands-on guide for researchers, students, and practitioners who want to apply cutting-edge AI techniques to scientific discovery. The book bridges the gap between AI/ML expertise and domain science, providing practical implementations across chemistry, biology, physics, geoscience, and beyond. It covers key AI architectures like Transformers, Diffusion Models, VAEs, and GNNs, and teaches how to apply generative models to problems in climate science, drug discovery, genomics, materials science, and more. The book also emphasizes best practices around ethics, reproducibility, and deployment, helping readers develop the intuition to know when and how to apply AI to scientific research.
README:
500+ pages • 13 chapters • 50+ runnable notebooks • Zero setup required
By Dr. J. Paul Liu
📢 Updated regularly based on student & reader feedback
Check the sample chapters
| The Revolution | The Impact |
|---|---|
| 🧪 AI-designed drugs | 80-90% Phase I success vs traditional 40-65% |
| 🧬 AlphaFold protein prediction | 2024 Nobel Prize in Chemistry |
| 🌍 GenCast weather AI | Outperforms best models in 97% of scenarios |
| ⚡ Neural surrogates | Simulations 1000x faster than traditional methods |
This book teaches you HOW to start and build educational-similar systems yourself.
| In 30 Minutes | You'll Create | Using |
|---|---|---|
| 🧪 Drug Discovery | Design molecules with target properties | GNNs + Diffusion |
| 🧬 Protein Engineering | Predict 3D structure from sequence | ESMFold |
| 🌍 Climate Science | Fast weather/climate emulators | Neural Surrogates |
| ⚛️ Physics Simulation | Solve PDEs with neural networks | PINNs |
| 📚 Literature Mining | Extract insights from papers | RAG + LLMs |
Generative AI for Science is a comprehensive, hands-on guide for researchers, students, and practitioners who want to apply cutting-edge AI techniques to scientific discovery. This book bridges the gap between AI/ML expertise and domain science, providing practical implementations across chemistry, biology, physics, geoscience, and beyond.
"Generative AI does not replace the scientific method—it enhances it. It expands the space of hypotheses we can explore, sharpens experimental design, and reveals patterns hidden in complexity."
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| 🔬 Theory Meets Practice | Every concept is paired with ready-to-run code |
| 💻 Interactive Learning | All examples provided as Google Colab notebooks—no installation required |
| 🧪 Real Scientific Problems | Examples from authentic research across multiple domains |
| 📊 Accessible Yet Rigorous | Suitable for domain scientists exploring AI and ML experts entering scientific applications |
| You Are... | You'll Get... |
|---|---|
| 🔬 Domain Scientist | AI skills to accelerate your research |
| 💻 ML Engineer | Scientific applications for your expertise |
| 🎓 Graduate Student | Complete curriculum with hands-on projects |
| 👔 Industry Practitioner | Production-ready code and best practices |
By the end of this book, you will:
- ✅ Understand key AI architectures: Transformers, Diffusion Models, VAEs, and GNNs
- ✅ Represent scientific data types effectively for AI models
- ✅ Apply generative models to problems in climate science, drug discovery, genomics, materials science, and more
- ✅ Follow best practices around ethics, reproducibility, and deployment
- ✅ Stay current with emerging methods and future directions
- ✅ Develop the intuition to know when and how to apply AI to scientific research
| Chapter | Title | Topics |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Generative AI: A New Frontier for Scientific Discovery | AI revolution in science, core technologies, cross-cutting capabilities |
| 2 | Generative AI Fundamentals | Transformers, LLMs, Diffusion Models, VAEs, GANs, attention mechanisms |
| 3 | Scientific Data & Workflows | Data challenges, FAIR principles, data preparation, workflow automation |
| 4 | Text, Code & Knowledge Generation | Literature synthesis, RAG, hypothesis generation, code generation, scientific writing |
| Chapter | Title | Topics |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | Data-to-Data Models | Missing data imputation, synthetic data with GANs, VAEs, Gaussian processes, time series |
| 6 | Physics-Informed AI and Simulation | PINNs, neural surrogates, code optimization, automated testing |
| Chapter | Title | Topics |
|---|---|---|
| 7 | Domain Applications | Chemistry & Materials, Biology & Biomedicine, Physics & Engineering, Geoscience & Climate |
📂 Chapter 7 Detailed Breakdown (click to expand)
Part I: Chemistry & Materials Science
- Molecular Graph Learning (GNNs)
- Molecular Generation with Diffusion Models
- Crystal Structure Prediction
- Reaction Outcome Prediction with Transformers
Part II: Biology & Biomedicine
- Protein Structure Prediction (ESMFold, AlphaFold2)
- Protein Sequence Generation (ProteinMPNN, RFDiffusion)
- Genomic Variant Analysis
- Clinical Trial Optimization
Part III: Physics & Engineering
- Particle Physics Applications
- Quantum Systems
- Materials Characterization
Part IV: Geoscience & Climate
- Ocean Forecasting
- Hurricane Prediction
- Climate Modeling
- Weather AI (GenCast, Aurora)
Part V: Cross-Cutting Applications
- Transfer Learning
- Multi-task Learning
- Foundation Models
| Chapter | Title | Topics |
|---|---|---|
| 8 | Fine-Tuning & Domain Adaptation | LoRA, PEFT, domain-specific training, evaluation strategies |
| 9 | Multimodal Generative AI | Vision-language models, graph-text models, multimodal fusion |
| 10 | Evaluation, Validation & Benchmarking | Metrics, validation strategies, uncertainty quantification, robustness testing |
| 11 | Ethics & Responsible AI | Reproducibility, bias & fairness, environmental impact, dual-use, data privacy |
| 12 | Deployment & MLOps | Experiment tracking, data versioning, model lifecycle, continuous training |
| 13 | Future Directions & Conclusion | Emerging architectures, foundation models, AI reasoning, open challenges |
✅ Basic Python (functions, loops, data structures)
✅ Undergraduate statistics (helpful but not required)
✅ A web browser + curiosity
❌ No prior deep learning experience needed
-
📖 Get the 500-page book
-
📥 Pick up a chapter
- Read the chapter and open that chapter's Colab Notebook
-
▶️ Open any notebook in Google Colab- Click the "Open in Colab" badge in each notebook
- Or upload directly to colab.research.google.com
- GPU runtime recommended for deep learning examples
Generative_AI_For_Science/
├── 📁 Chapter01_Introduction/
│ └── 📓 Ch01_AI_Scientific_Discovery.ipynb
├── 📁 Chapter02_Fundamentals/
│ ├── 📓 Ch02_Transformers.ipynb
│ ├── 📓 Ch02_Diffusion_Models.ipynb
│ └── 📓 Ch02_VAEs_GANs.ipynb
├── 📁 Chapter03_Data_Workflows/
│ └── 📓 Ch03_Scientific_Data.ipynb
├── 📁 Chapter04_Text_Code_Knowledge/
│ ├── 📓 Ch04_RAG_Literature.ipynb
│ └── 📓 Ch04_Code_Generation.ipynb
├── 📁 Chapter05_Data_to_Data/
│ ├── 📓 Ch05_Autoencoders.ipynb
│ ├── 📓 Ch05_GANs.ipynb
│ ├── 📓 Ch05_VAEs.ipynb
│ └── 📓 Ch05_Time_Series.ipynb
├── 📁 Chapter06_Physics_Informed/
│ ├── 📓 Ch06_PINNs.ipynb
│ └── 📓 Ch06_Neural_Surrogates.ipynb
├── 📁 Chapter07_Domain_Applications/
│ ├── 📓 Ch07_Chemistry_GNNs.ipynb
│ ├── 📓 Ch07_Molecular_Diffusion.ipynb
│ ├── 📓 Ch07_Protein_Structure.ipynb
│ ├── 📓 Ch07_Genomics.ipynb
│ └── 📓 Ch07_Climate_AI.ipynb
├── 📁 Chapter08_FineTuning/
│ └── 📓 Ch08_LoRA_PEFT.ipynb
├── 📁 Chapter09_Multimodal/
│ └── 📓 Ch09_Vision_Language.ipynb
├── 📁 Chapter10_Evaluation/
│ └── 📓 Ch10_Metrics_Validation.ipynb
├── 📁 Chapter11_Ethics/
│ └── 📓 Ch11_Responsible_AI.ipynb
├── 📁 Chapter12_Deployment/
│ └── 📓 Ch12_MLOps.ipynb
├── 📁 slides/
│ └── 📊 PowerPoint slides for each chapter
├── 📁 assets/
│ └── 🖼️ Figures and images
└── 📄 README.md
| Use Case | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| 📖 As a course text | Follow chapters sequentially for structured introduction |
| 🔍 As a reference | Jump directly to sections relevant to your research domain |
| 💻 As a hands-on guide | Open Colab notebooks alongside each chapter, run and modify code |
| 🚀 As a research launchpad | Use provided implementations as starting points for your projects |
- Molecular Property Prediction with Graph Neural Networks
- Drug Design with Diffusion Models
- Crystal Structure Prediction with AI
- Reaction Prediction with Transformers
- Protein Structure Prediction (ESMFold, AlphaFold2)
- Protein Design (ProteinMPNN, RFDiffusion)
- Variant Effect Prediction for genomics
- Clinical Trial Optimization
- Weather Forecasting with GenCast
- Ocean Dynamics modeling
- Climate Projection with surrogates
- Extreme Event Prediction
- Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs)
- Neural Network Surrogates for simulations
- Uncertainty Quantification
| Architecture | Use Cases | Scientific Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Transformers & LLMs | Text, code, sequences | Literature synthesis, protein sequences, code generation |
| Diffusion Models | Structured outputs, images | Molecular structures, protein folding, climate data |
| VAEs & GANs | Latent space learning | Synthetic data, anomaly detection, compression |
| Graph Neural Networks | Molecular graphs | Property prediction, reaction prediction |
| Physics-Informed NNs | PDEs, conservation laws | Fluid dynamics, heat transfer, wave propagation |
While all notebooks run in Google Colab, you can also set up locally:
# Create virtual environment
python -m venv genai-science
source genai-science/bin/activate # Linux/Mac
# or: genai-science\Scripts\activate # Windows
# Install dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txttorch>=2.0
transformers>=4.30
rdkit
numpy
pandas
matplotlib
scikit-learn
| Model Type | GPU Memory | Recommended Platform |
|---|---|---|
| Small models (GNNs, VAEs) | < 4 GB | Colab Free Tier |
| Medium models (Diffusion) | 4-8 GB | Colab Pro |
| Large models (LLMs, ESMFold) | 16+ GB | Colab Pro+, A100 |
We welcome contributions! Please see our Contributing Guidelines for details.
- 🐛 Report bugs or issues
- 💡 Suggest new examples or applications
- 📝 Improve documentation
- 🔧 Submit code improvements
- 🌍 Translate content
If you use this book or code in your research, please cite:
@book{liu2026generativeai,
title = {Generative AI for Science},
author = {Liu, J. Paul},
year = {2026},
publisher = {Leanpub},
url = {https://leanpub.com/generativeaiforscience}
}Or simply:
J. Paul Liu, 2026. Generative AI for Science. Leanpub, https://leanpub.com/generativeaiforscience
| Platform | Link |
|---|---|
| Contact through Leanpub | |
| 🐦 Twitter / X | @jpliu168 — follow for updates |
| Paul Liu — connect for professional updates | |
| 💬 Discussions | Use GitHub Discussions for Q&A |
| 🐛 Issues | Report bugs via GitHub Issues |
This book was developed through:
- Graduate courses at the Data Science and AI Academy
- Bioinformatics Research Center workshops
- Cross-campus AI for Research training programs
- Research Triangle AI Society–LLM intensive bootcamps
- Collaborations in oceanography, materials science, protein engineering, and literature mining
Special thanks to all students and colleagues who provided feedback and helped refine the material.
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.
The book content is © 2026 J. Paul Liu. Code examples are provided under MIT License for educational use.
If you find this resource helpful:
- ⭐ Star this repository to help others discover it
- 🐦 Share on Twitter/LinkedIn to spread the word
- 📖 Get the book to support continued development
- 💬 Leave feedback to help improve future editions
🚀 Ready to accelerate your scientific discovery with AI?


"Combine human creativity with machine assistance, and new discoveries become possible."
— Dr. J. Paul Liu
Other related book:
How to Build and Fine-Tune a Small Language Model:

https://leanpub.com/howtobuildandfine-tuneasmalllanguagemodel
https://www.amazon.com/dp/B0G3MYWTJK
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Generative_AI_For_Science
Similar Open Source Tools

Generative_AI_For_Science
Generative AI for Science is a comprehensive, hands-on guide for researchers, students, and practitioners who want to apply cutting-edge AI techniques to scientific discovery. The book bridges the gap between AI/ML expertise and domain science, providing practical implementations across chemistry, biology, physics, geoscience, and beyond. It covers key AI architectures like Transformers, Diffusion Models, VAEs, and GNNs, and teaches how to apply generative models to problems in climate science, drug discovery, genomics, materials science, and more. The book also emphasizes best practices around ethics, reproducibility, and deployment, helping readers develop the intuition to know when and how to apply AI to scientific research.

AI-LLM-ML-CS-Quant-Readings
AI-LLM-ML-CS-Quant-Readings is a repository dedicated to taking notes on Artificial Intelligence, Large Language Models, Machine Learning, Computer Science, and Quantitative Finance. It contains a wide range of resources, including theory, applications, conferences, essentials, foundations, system design, computer systems, finance, and job interview questions. The repository covers topics such as AI systems, multi-agent systems, deep learning theory and applications, system design interviews, C++ design patterns, high-frequency finance, algorithmic trading, stochastic volatility modeling, and quantitative investing. It is a comprehensive collection of materials for individuals interested in these fields.
awesome-ai-efficiency
Awesome AI Efficiency is a curated list of resources dedicated to enhancing efficiency in AI systems. The repository covers various topics essential for optimizing AI models and processes, aiming to make AI faster, cheaper, smaller, and greener. It includes topics like quantization, pruning, caching, distillation, factorization, compilation, parameter-efficient fine-tuning, speculative decoding, hardware optimization, training techniques, inference optimization, sustainability strategies, and scalability approaches.
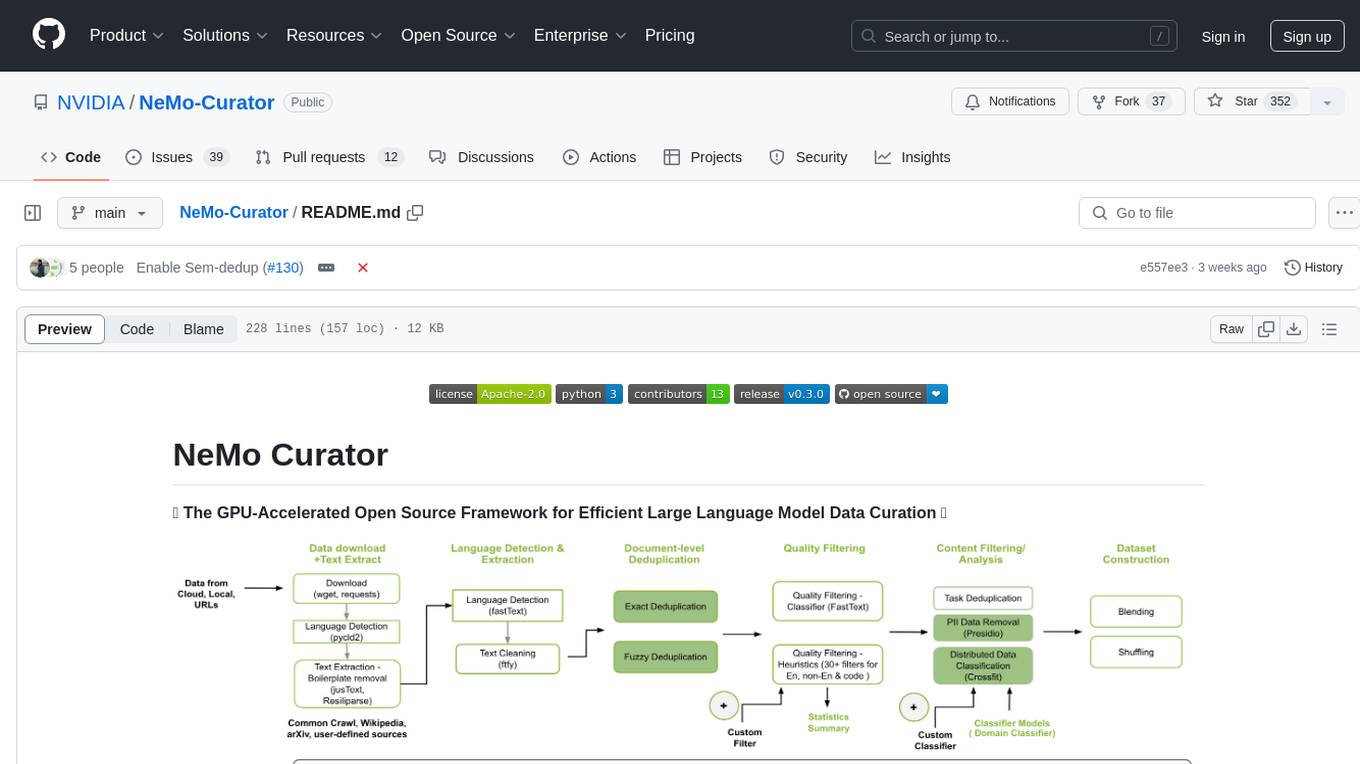
Curator
NeMo Curator is a Python library designed for fast and scalable data processing and curation for generative AI use cases. It accelerates data processing by leveraging GPUs with Dask and RAPIDS, providing customizable pipelines for text and image curation. The library offers pre-built pipelines for synthetic data generation, enabling users to train and customize generative AI models such as LLMs, VLMs, and WFMs.
Documents-Parsing-Lab
A curated collection of Jupyter notebooks for experimenting with state-of-the-art OCR, document parsing, table extraction, and chart understanding techniques. This repository enables easy benchmarking and practical usage of the latest open-source and cloud-based solutions for document image processing.
ALwrity
ALwrity is a lightweight and user-friendly text analysis tool designed for developers and data scientists. It provides various functionalities for analyzing and processing text data, including sentiment analysis, keyword extraction, and text summarization. With ALwrity, users can easily gain insights from their text data and make informed decisions based on the analysis results. The tool is highly customizable and can be integrated into existing workflows seamlessly, making it a valuable asset for anyone working with text data in their projects.
claude-code-ultimate-guide
The Claude Code Ultimate Guide is an exhaustive documentation resource that takes users from beginner to power user in using Claude Code. It includes production-ready templates, workflow guides, a quiz, and a cheatsheet for daily use. The guide covers educational depth, methodologies, and practical examples to help users understand concepts and workflows. It also provides interactive onboarding, a repository structure overview, and learning paths for different user levels. The guide is regularly updated and offers a unique 257-question quiz for comprehensive assessment. Users can also find information on agent teams coverage, methodologies, annotated templates, resource evaluations, and learning paths for different roles like junior developer, senior developer, power user, and product manager/devops/designer.

handit.ai
Handit.ai is an autonomous engineer tool designed to fix AI failures 24/7. It catches failures, writes fixes, tests them, and ships PRs automatically. It monitors AI applications, detects issues, generates fixes, tests them against real data, and ships them as pull requests—all automatically. Users can write JavaScript, TypeScript, Python, and more, and the tool automates what used to require manual debugging and firefighting.

prism-insight
PRISM-INSIGHT is a comprehensive stock analysis and trading simulation system based on AI agents. It automatically captures daily surging stocks via Telegram channel, generates expert-level analyst reports, and performs trading simulations. The system utilizes OpenAI GPT-4.1 for in-depth stock analysis and GPT-5 for investment strategy simulation. It also interacts with users via Anthropic Claude for Telegram conversations. The system architecture includes AI analysis agents, stock tracking, PDF conversion, and Telegram bot functionalities. Users can customize criteria for identifying surging stocks, modify AI prompts, and adjust chart styles. The project is open-source under the MIT license, and all investment decisions based on the analysis are the responsibility of the user.
AutoAgents
AutoAgents is a cutting-edge multi-agent framework built in Rust that enables the creation of intelligent, autonomous agents powered by Large Language Models (LLMs) and Ractor. Designed for performance, safety, and scalability. AutoAgents provides a robust foundation for building complex AI systems that can reason, act, and collaborate. With AutoAgents you can create Cloud Native Agents, Edge Native Agents and Hybrid Models as well. It is so extensible that other ML Models can be used to create complex pipelines using Actor Framework.
Video-ChatGPT
Video-ChatGPT is a video conversation model that aims to generate meaningful conversations about videos by combining large language models with a pretrained visual encoder adapted for spatiotemporal video representation. It introduces high-quality video-instruction pairs, a quantitative evaluation framework for video conversation models, and a unique multimodal capability for video understanding and language generation. The tool is designed to excel in tasks related to video reasoning, creativity, spatial and temporal understanding, and action recognition.
Foundations-of-LLMs
Foundations-of-LLMs is a comprehensive book aimed at readers interested in large language models, providing systematic explanations of foundational knowledge and introducing cutting-edge technologies. The book covers traditional language models, evolution of large language model architectures, prompt engineering, parameter-efficient fine-tuning, model editing, and retrieval-enhanced generation. Each chapter uses an animal as a theme to explain specific technologies, enhancing readability. The content is based on the author team's exploration and understanding of the field, with continuous monthly updates planned. The book includes a 'Paper List' for each chapter to track the latest advancements in related technologies.
AI-LLM-ML-CS-Quant-Overview
AI-LLM-ML-CS-Quant-Overview is a repository providing overview notes on AI, Large Language Models (LLM), Machine Learning (ML), Computer Science (CS), and Quantitative Finance. It covers various topics such as LangGraph & Cursor AI, DeepSeek, MoE (Mixture of Experts), NVIDIA GTC, LLM Essentials, System Design, Computer Systems, Big Data and AI in Finance, Econometrics and Statistics Conference, C++ Design Patterns and Derivatives Pricing, High-Frequency Finance, Machine Learning for Algorithmic Trading, Stochastic Volatility Modeling, Quant Job Interview Questions, Distributed Systems, Language Models, Designing Machine Learning Systems, Designing Data-Intensive Applications (DDIA), Distributed Machine Learning, and The Elements of Quantitative Investing.

rivet
Rivet is a desktop application for creating complex AI agents and prompt chaining, and embedding it in your application. Rivet currently has LLM support for OpenAI GPT-3.5 and GPT-4, Anthropic Claude Instant and Claude 2, [Anthropic Claude 3 Haiku, Sonnet, and Opus](https://www.anthropic.com/news/claude-3-family), and AssemblyAI LeMUR framework for voice data. Rivet has embedding/vector database support for OpenAI Embeddings and Pinecone. Rivet also supports these additional integrations: Audio Transcription from AssemblyAI. Rivet core is a TypeScript library for running graphs created in Rivet. It is used by the Rivet application, but can also be used in your own applications, so that Rivet can call into your own application's code, and your application can call into Rivet graphs.
ToolUniverse
ToolUniverse is a collection of 211 biomedical tools designed for Agentic AI, providing access to biomedical knowledge for solving therapeutic reasoning tasks. The tools cover various aspects of drugs and diseases, linked to trusted sources like US FDA-approved drugs since 1939, Open Targets, and Monarch Initiative.
END-TO-END-GENERATIVE-AI-PROJECTS
The 'END TO END GENERATIVE AI PROJECTS' repository is a collection of awesome industry projects utilizing Large Language Models (LLM) for various tasks such as chat applications with PDFs, image to speech generation, video transcribing and summarizing, resume tracking, text to SQL conversion, invoice extraction, medical chatbot, financial stock analysis, and more. The projects showcase the deployment of LLM models like Google Gemini Pro, HuggingFace Models, OpenAI GPT, and technologies such as Langchain, Streamlit, LLaMA2, LLaMAindex, and more. The repository aims to provide end-to-end solutions for different AI applications.
For similar tasks

Generative_AI_For_Science
Generative AI for Science is a comprehensive, hands-on guide for researchers, students, and practitioners who want to apply cutting-edge AI techniques to scientific discovery. The book bridges the gap between AI/ML expertise and domain science, providing practical implementations across chemistry, biology, physics, geoscience, and beyond. It covers key AI architectures like Transformers, Diffusion Models, VAEs, and GNNs, and teaches how to apply generative models to problems in climate science, drug discovery, genomics, materials science, and more. The book also emphasizes best practices around ethics, reproducibility, and deployment, helping readers develop the intuition to know when and how to apply AI to scientific research.
REINVENT4
REINVENT is a molecular design tool for de novo design, scaffold hopping, R-group replacement, linker design, molecule optimization, and other small molecule design tasks. It uses a Reinforcement Learning (RL) algorithm to generate optimized molecules compliant with a user-defined property profile defined as a multi-component score. Transfer Learning (TL) can be used to create or pre-train a model that generates molecules closer to a set of input molecules.
awesome-AI4MolConformation-MD
The 'awesome-AI4MolConformation-MD' repository focuses on protein conformations and molecular dynamics using generative artificial intelligence and deep learning. It provides resources, reviews, datasets, packages, and tools related to AI-driven molecular dynamics simulations. The repository covers a wide range of topics such as neural networks potentials, force fields, AI engines/frameworks, trajectory analysis, visualization tools, and various AI-based models for protein conformational sampling. It serves as a comprehensive guide for researchers and practitioners interested in leveraging AI for studying molecular structures and dynamics.
For similar jobs
grand-challenge.org
Grand Challenge is a platform that provides access to large amounts of annotated training data, objective comparisons of state-of-the-art machine learning solutions, and clinical validation using real-world data. It assists researchers, data scientists, and clinicians in collaborating to develop robust machine learning solutions to problems in biomedical imaging.
Detection-and-Classification-of-Alzheimers-Disease
This tool is designed to detect and classify Alzheimer's Disease using Deep Learning and Machine Learning algorithms on an early basis, which is further optimized using the Crow Search Algorithm (CSA). Alzheimer's is a fatal disease, and early detection is crucial for patients to predetermine their condition and prevent its progression. By analyzing MRI scanned images using Artificial Intelligence technology, this tool can classify patients who may or may not develop AD in the future. The CSA algorithm, combined with ML algorithms, has proven to be the most effective approach for this purpose.
OpenCRISPR
OpenCRISPR is a set of free and open gene editing systems designed by Profluent Bio. The OpenCRISPR-1 protein maintains the prototypical architecture of a Type II Cas9 nuclease but is hundreds of mutations away from SpCas9 or any other known natural CRISPR-associated protein. You can view OpenCRISPR-1 as a drop-in replacement for many protocols that need a cas9-like protein with an NGG PAM and you can even use it with canonical SpCas9 gRNAs. OpenCRISPR-1 can be fused in a deactivated or nickase format for next generation gene editing techniques like base, prime, or epigenome editing.
AlphaFold3
AlphaFold3 is an implementation of the Alpha Fold 3 model in PyTorch for accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions. It includes modules for genetic diffusion and full model examples for forward pass computations. The tool allows users to generate random pair and single representations, operate on atomic coordinates, and perform structure predictions based on input tensors. The implementation also provides functionalities for training and evaluating the model.

fuse-med-ml
FuseMedML is a Python framework designed to accelerate machine learning-based discovery in the medical field by promoting code reuse. It provides a flexible design concept where data is stored in a nested dictionary, allowing easy handling of multi-modality information. The framework includes components for creating custom models, loss functions, metrics, and data processing operators. Additionally, FuseMedML offers 'batteries included' key components such as fuse.data for data processing, fuse.eval for model evaluation, and fuse.dl for reusable deep learning components. It supports PyTorch and PyTorch Lightning libraries and encourages the creation of domain extensions for specific medical domains.
hi-ml
The Microsoft Health Intelligence Machine Learning Toolbox is a repository that provides low-level and high-level building blocks for Machine Learning / AI researchers and practitioners. It simplifies and streamlines work on deep learning models for healthcare and life sciences by offering tested components such as data loaders, pre-processing tools, deep learning models, and cloud integration utilities. The repository includes two Python packages, 'hi-ml-azure' for helper functions in AzureML, 'hi-ml' for ML components, and 'hi-ml-cpath' for models and workflows related to histopathology images.
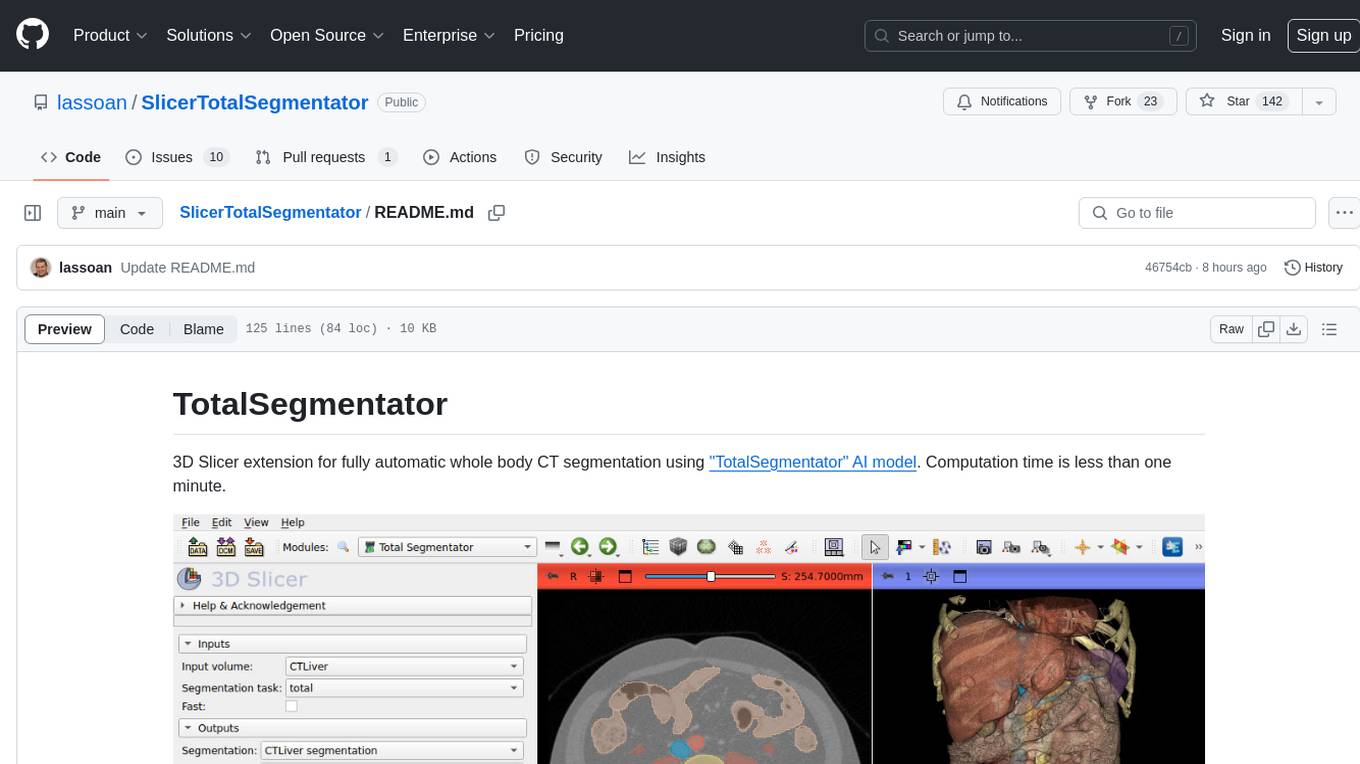
SlicerTotalSegmentator
TotalSegmentator is a 3D Slicer extension designed for fully automatic whole body CT segmentation using the 'TotalSegmentator' AI model. The computation time is less than one minute, making it efficient for research purposes. Users can set up GPU acceleration for faster segmentation. The tool provides a user-friendly interface for loading CT images, creating segmentations, and displaying results in 3D. Troubleshooting steps are available for common issues such as failed computation, GPU errors, and inaccurate segmentations. Contributions to the extension are welcome, following 3D Slicer contribution guidelines.
md-agent
MD-Agent is a LLM-agent based toolset for Molecular Dynamics. It uses Langchain and a collection of tools to set up and execute molecular dynamics simulations, particularly in OpenMM. The tool assists in environment setup, installation, and usage by providing detailed steps. It also requires API keys for certain functionalities, such as OpenAI and paper-qa for literature searches. Contributions to the project are welcome, with a detailed Contributor's Guide available for interested individuals.



