
LLM-RGB
LLM Reasoning and Generation Benchmark. Evaluate LLMs in complex scenarios systematically.
Stars: 138
LLM-RGB is a repository containing a collection of detailed test cases designed to evaluate the reasoning and generation capabilities of Language Learning Models (LLMs) in complex scenarios. The benchmark assesses LLMs' performance in understanding context, complying with instructions, and handling challenges like long context lengths, multi-step reasoning, and specific response formats. Each test case evaluates an LLM's output based on context length difficulty, reasoning depth difficulty, and instruction compliance difficulty, with a final score calculated for each test case. The repository provides a score table, evaluation details, and quick start guide for running evaluations using promptfoo testing tools.
README:
This repository contains a collection of detailed test cases (prompts) designed to evaluate the reasoning and generation capabilities of Language Learning Models (LLMs) in complex scenarios. It's important to note that this benchmark is not intended to be a comprehensive test for LLMs. The project was initially developed as an internal project at babel.cloud, with the aim of assessing the performance of LLMs in understanding context and complying with instructions.
Complex scenarios present three main challenges compared to chat or simple generations:
- Context Length: A single prompt may contain more than 10K tokens (approximately 30K characters).
- Reasoning Depth: The generation of an answer may require multi-step reasoning.
- Instruction Compliance: The LLM may need to generate a response in a specific format, rather than in natural language.
Each test case is a generation task for an LLM, without involving multi-turn conversations. The complexity of each test case is assessed based on the following dimensions:
The value is 1 if the prompt contains 2000 characters or less. If the number of characters is between 2000 and 5000 (inclusive), the value is 2. If it's more than 5000, the value is 3. The model's actual performance in this dimension depends on the result of each task and the task's context length difficulty. It's not accurate to rate a model's ability in different context lengths solely based on the maximum context length that the model can handle.
The value is 1 if the answer can be inferred directly from the context, such as a knowledge base. If the answer requires reasoning, the value is 2, for example, "Who is considered the father of the iPhone and what is the last digit of his birth year?". If the answer requires reasoning with the provided context, the value is 4, such as writing a program using the provided context syntax.
The value is 1 if the expected response is in natural language without any special requirements. If the expected response should be in a specific style such as "YES or NO", "Shell command only", the value is 2. If the expected response requires a structural format such as JSON, YAML, the value is 3.
The difficulty of each test case (Dn) is the sum of the three difficulties. Each test case includes a set of assertions to evaluate the LLM's output. The result of the assertion (Rn) is a decimal between [0, 1]. The final score of the test case (Sn) is calculated as Rn x Dn. "n" is the test case number. The total score for each LLM is the sum of all test case scores (S1...Sn).
The following tables show the evaluation results, executed on Oct. 11th, 2024. We ran the evaluation 10 times and take the average scores. The full score of all 15 testcases is 100. You can check experiments/2024-10-11T22-43-25-810Z for the detailed results.
The testing tools used in this project are provided by promptfoo.
cp promptfooconfig.yaml.example promptfooconfig.yamlTo run evaluations, you need to fill in the LLM configurations in promptfooconfig.yaml. You should comment out any providers and test cases that you don't want to use. You can also add LLM providers according to promptfoo documents https://www.promptfoo.dev/docs/providers/ .
npm installnpm run start --repeat=10 --concurrency=8You should change the repeat and concurrency settings as needed. If these values are not specified, the default value of repeat is 1 and concurrency is 8.
Some of the test cases requires python to execute. Make sure you have python installed. If you have python3 installed, you can run the following command to create a symlink.
sudo ln -s $(which python3) /usr/local/bin/pythonYou can check the history results in the experiments folder. Each experiment subfolder contains the evaluation results of the LLMs. You can use following command to render the results in a human-readable table.
ts-node utils/render.ts "path to the folder, eg. experiments/2024-10-11T22-43-25-810Z"We welcome contributions of test cases that can evaluate the reasoning and generation abilities of LLMs. Please refer to the existing test cases for the required files and formats.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for LLM-RGB
Similar Open Source Tools

LLM-RGB
LLM-RGB is a repository containing a collection of detailed test cases designed to evaluate the reasoning and generation capabilities of Language Learning Models (LLMs) in complex scenarios. The benchmark assesses LLMs' performance in understanding context, complying with instructions, and handling challenges like long context lengths, multi-step reasoning, and specific response formats. Each test case evaluates an LLM's output based on context length difficulty, reasoning depth difficulty, and instruction compliance difficulty, with a final score calculated for each test case. The repository provides a score table, evaluation details, and quick start guide for running evaluations using promptfoo testing tools.
PromptAgent
PromptAgent is a repository for a novel automatic prompt optimization method that crafts expert-level prompts using language models. It provides a principled framework for prompt optimization by unifying prompt sampling and rewarding using MCTS algorithm. The tool supports different models like openai, palm, and huggingface models. Users can run PromptAgent to optimize prompts for specific tasks by strategically sampling model errors, generating error feedbacks, simulating future rewards, and searching for high-reward paths leading to expert prompts.
llama3_interpretability_sae
This project focuses on implementing Sparse Autoencoders (SAEs) for mechanistic interpretability in Large Language Models (LLMs) like Llama 3.2-3B. The SAEs aim to untangle superimposed representations in LLMs into separate, interpretable features for each neuron activation. The project provides an end-to-end pipeline for capturing training data, training the SAEs, analyzing learned features, and verifying results experimentally. It includes comprehensive logging, visualization, and checkpointing of SAE training, interpretability analysis tools, and a pure PyTorch implementation of Llama 3.1/3.2 chat and text completion. The project is designed for scalability, efficiency, and maintainability.
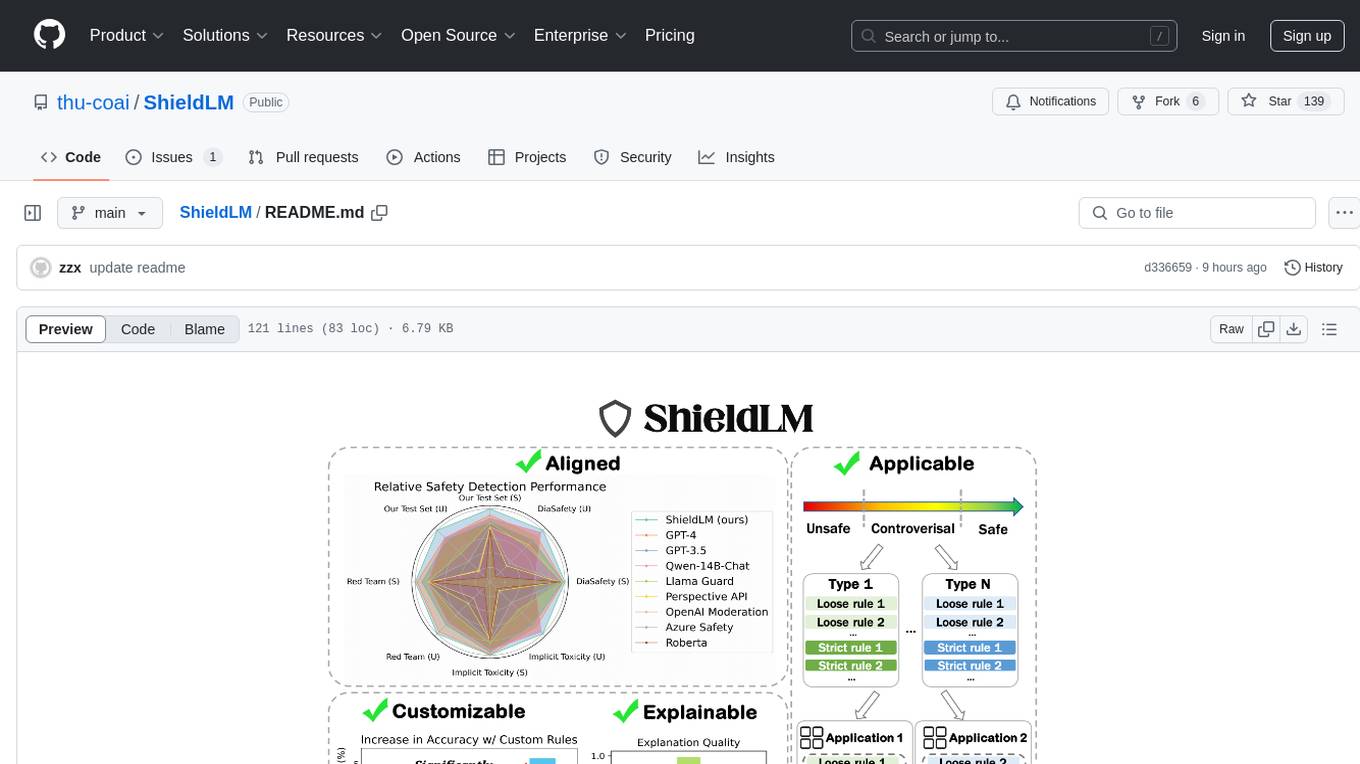
ShieldLM
ShieldLM is a bilingual safety detector designed to detect safety issues in LLMs' generations. It aligns with human safety standards, supports customizable detection rules, and provides explanations for decisions. Outperforming strong baselines, ShieldLM is impressive across 4 test sets.
SciMLBenchmarks.jl
SciMLBenchmarks.jl holds webpages, pdfs, and notebooks showing the benchmarks for the SciML Scientific Machine Learning Software ecosystem, including: * Benchmarks of equation solver implementations * Speed and robustness comparisons of methods for parameter estimation / inverse problems * Training universal differential equations (and subsets like neural ODEs) * Training of physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) * Surrogate comparisons, including radial basis functions, neural operators (DeepONets, Fourier Neural Operators), and more The SciML Bench suite is made to be a comprehensive open source benchmark from the ground up, covering the methods of computational science and scientific computing all the way to AI for science.
uncheatable_eval
Uncheatable Eval is a tool designed to assess the language modeling capabilities of LLMs on real-time, newly generated data from the internet. It aims to provide a reliable evaluation method that is immune to data leaks and cannot be gamed. The tool supports the evaluation of Hugging Face AutoModelForCausalLM models and RWKV models by calculating the sum of negative log probabilities on new texts from various sources such as recent papers on arXiv, new projects on GitHub, news articles, and more. Uncheatable Eval ensures that the evaluation data is not included in the training sets of publicly released models, thus offering a fair assessment of the models' performance.

eureka-ml-insights
The Eureka ML Insights Framework is a repository containing code designed to help researchers and practitioners run reproducible evaluations of generative models efficiently. Users can define custom pipelines for data processing, inference, and evaluation, as well as utilize pre-defined evaluation pipelines for key benchmarks. The framework provides a structured approach to conducting experiments and analyzing model performance across various tasks and modalities.
raft
RAFT (Retrieval-Augmented Fine-Tuning) is a method for creating conversational agents that realistically emulate specific human targets. It involves a dual-phase process of fine-tuning and retrieval-based augmentation to generate nuanced and personalized dialogue. The tool is designed to combine interview transcripts with memories from past writings to enhance language model responses. RAFT has the potential to advance the field of personalized, context-sensitive conversational agents.
LLMs-World-Models-for-Planning
This repository provides a Python implementation of a method that leverages pre-trained large language models to construct and utilize world models for model-based task planning. It includes scripts to generate domain models using natural language descriptions, correct domain models based on feedback, and support plan generation for tasks in different domains. The code has been refactored for better readability and includes tools for validating PDDL syntax and handling corrective feedback.
FigStep
FigStep is a black-box jailbreaking algorithm against large vision-language models (VLMs). It feeds harmful instructions through the image channel and uses benign text prompts to induce VLMs to output contents that violate common AI safety policies. The tool highlights the vulnerability of VLMs to jailbreaking attacks, emphasizing the need for safety alignments between visual and textual modalities.
AIlice
AIlice is a fully autonomous, general-purpose AI agent that aims to create a standalone artificial intelligence assistant, similar to JARVIS, based on the open-source LLM. AIlice achieves this goal by building a "text computer" that uses a Large Language Model (LLM) as its core processor. Currently, AIlice demonstrates proficiency in a range of tasks, including thematic research, coding, system management, literature reviews, and complex hybrid tasks that go beyond these basic capabilities. AIlice has reached near-perfect performance in everyday tasks using GPT-4 and is making strides towards practical application with the latest open-source models. We will ultimately achieve self-evolution of AI agents. That is, AI agents will autonomously build their own feature expansions and new types of agents, unleashing LLM's knowledge and reasoning capabilities into the real world seamlessly.
chronon
Chronon is a platform that simplifies and improves ML workflows by providing a central place to define features, ensuring point-in-time correctness for backfills, simplifying orchestration for batch and streaming pipelines, offering easy endpoints for feature fetching, and guaranteeing and measuring consistency. It offers benefits over other approaches by enabling the use of a broad set of data for training, handling large aggregations and other computationally intensive transformations, and abstracting away the infrastructure complexity of data plumbing.
ChatAFL
ChatAFL is a protocol fuzzer guided by large language models (LLMs) that extracts machine-readable grammar for protocol mutation, increases message diversity, and breaks coverage plateaus. It integrates with ProfuzzBench for stateful fuzzing of network protocols, providing smooth integration. The artifact includes modified versions of AFLNet and ProfuzzBench, source code for ChatAFL with proposed strategies, and scripts for setup, execution, analysis, and cleanup. Users can analyze data, construct plots, examine LLM-generated grammars, enriched seeds, and state-stall responses, and reproduce results with downsized experiments. Customization options include modifying fuzzers, tuning parameters, adding new subjects, troubleshooting, and working on GPT-4. Limitations include interaction with OpenAI's Large Language Models and a hard limit of 150,000 tokens per minute.
LLM-Geo
LLM-Geo is an AI-powered geographic information system (GIS) that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) for automatic spatial data collection, analysis, and visualization. By adopting LLM as the reasoning core, it addresses spatial problems with self-generating, self-organizing, self-verifying, self-executing, and self-growing capabilities. The tool aims to make spatial analysis easier, faster, and more accessible by reducing manual operation time and delivering accurate results through case studies. It uses GPT-4 API in a Python environment and advocates for further research and development in autonomous GIS.
ai-rag-chat-evaluator
This repository contains scripts and tools for evaluating a chat app that uses the RAG architecture. It provides parameters to assess the quality and style of answers generated by the chat app, including system prompt, search parameters, and GPT model parameters. The tools facilitate running evaluations, with examples of evaluations on a sample chat app. The repo also offers guidance on cost estimation, setting up the project, deploying a GPT-4 model, generating ground truth data, running evaluations, and measuring the app's ability to say 'I don't know'. Users can customize evaluations, view results, and compare runs using provided tools.
LiveBench
LiveBench is a benchmark tool designed for Language Model Models (LLMs) with a focus on limiting contamination through monthly new questions based on recent datasets, arXiv papers, news articles, and IMDb movie synopses. It provides verifiable, objective ground-truth answers for accurate scoring without an LLM judge. The tool offers 18 diverse tasks across 6 categories and promises to release more challenging tasks over time. LiveBench is built on FastChat's llm_judge module and incorporates code from LiveCodeBench and IFEval.
For similar tasks

LLM-RGB
LLM-RGB is a repository containing a collection of detailed test cases designed to evaluate the reasoning and generation capabilities of Language Learning Models (LLMs) in complex scenarios. The benchmark assesses LLMs' performance in understanding context, complying with instructions, and handling challenges like long context lengths, multi-step reasoning, and specific response formats. Each test case evaluates an LLM's output based on context length difficulty, reasoning depth difficulty, and instruction compliance difficulty, with a final score calculated for each test case. The repository provides a score table, evaluation details, and quick start guide for running evaluations using promptfoo testing tools.
MMC
This repository, MMC, focuses on advancing multimodal chart understanding through large-scale instruction tuning. It introduces a dataset supporting various tasks and chart types, a benchmark for evaluating reasoning capabilities over charts, and an assistant achieving state-of-the-art performance on chart QA benchmarks. The repository provides data for chart-text alignment, benchmarking, and instruction tuning, along with existing datasets used in experiments. Additionally, it offers a Gradio demo for the MMCA model.

ai-rag-chat-evaluator
This repository contains scripts and tools for evaluating a chat app that uses the RAG architecture. It provides parameters to assess the quality and style of answers generated by the chat app, including system prompt, search parameters, and GPT model parameters. The tools facilitate running evaluations, with examples of evaluations on a sample chat app. The repo also offers guidance on cost estimation, setting up the project, deploying a GPT-4 model, generating ground truth data, running evaluations, and measuring the app's ability to say 'I don't know'. Users can customize evaluations, view results, and compare runs using provided tools.
mastra
Mastra is an opinionated Typescript framework designed to help users quickly build AI applications and features. It provides primitives such as workflows, agents, RAG, integrations, syncs, and evals. Users can run Mastra locally or deploy it to a serverless cloud. The framework supports various LLM providers, offers tools for building language models, workflows, and accessing knowledge bases. It includes features like durable graph-based state machines, retrieval-augmented generation, integrations, syncs, and automated tests for evaluating LLM outputs.
seer
Seer is a service that provides AI capabilities to Sentry by running inference on Sentry issues and providing user insights. It is currently in early development and not yet compatible with self-hosted Sentry instances. The tool requires access to internal Sentry resources and is intended for internal Sentry employees. Users can set up the environment, download model artifacts, integrate with local Sentry, run evaluations for Autofix AI agent, and deploy to a sandbox staging environment. Development commands include applying database migrations, creating new migrations, running tests, and more. The tool also supports VCRs for recording and replaying HTTP requests.
SWELancer-Benchmark
SWE-Lancer is a benchmark repository containing datasets and code for the paper 'SWE-Lancer: Can Frontier LLMs Earn $1 Million from Real-World Freelance Software Engineering?'. It provides instructions for package management, building Docker images, configuring environment variables, and running evaluations. Users can use this tool to assess the performance of language models in real-world freelance software engineering tasks.

inspect_evals
Inspect Evals is a repository of community-contributed LLM evaluations for Inspect AI, created in collaboration by the UK AISI, Arcadia Impact, and the Vector Institute. It supports many model providers including OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, Mistral, Azure AI, AWS Bedrock, Together AI, Groq, Hugging Face, vLLM, and Ollama. Users can contribute evaluations, install necessary dependencies, and run evaluations for various models. The repository covers a wide range of evaluation tasks across different domains such as coding, assistants, cybersecurity, safeguards, mathematics, reasoning, knowledge, scheming, multimodal tasks, bias evaluation, personality assessment, and writing tasks.
codemie-code
Unified AI Coding Assistant CLI for managing multiple AI agents like Claude Code, Google Gemini, OpenCode, and custom AI agents. Supports OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, AWS Bedrock, LiteLLM, Ollama, and Enterprise SSO. Features built-in LangGraph agent with file operations, command execution, and planning tools. Cross-platform support for Windows, Linux, and macOS. Ideal for developers seeking a powerful alternative to GitHub Copilot or Cursor.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.