
browser-copilot
Browser extension and framework to use and build AI assistants for any web application
Stars: 123
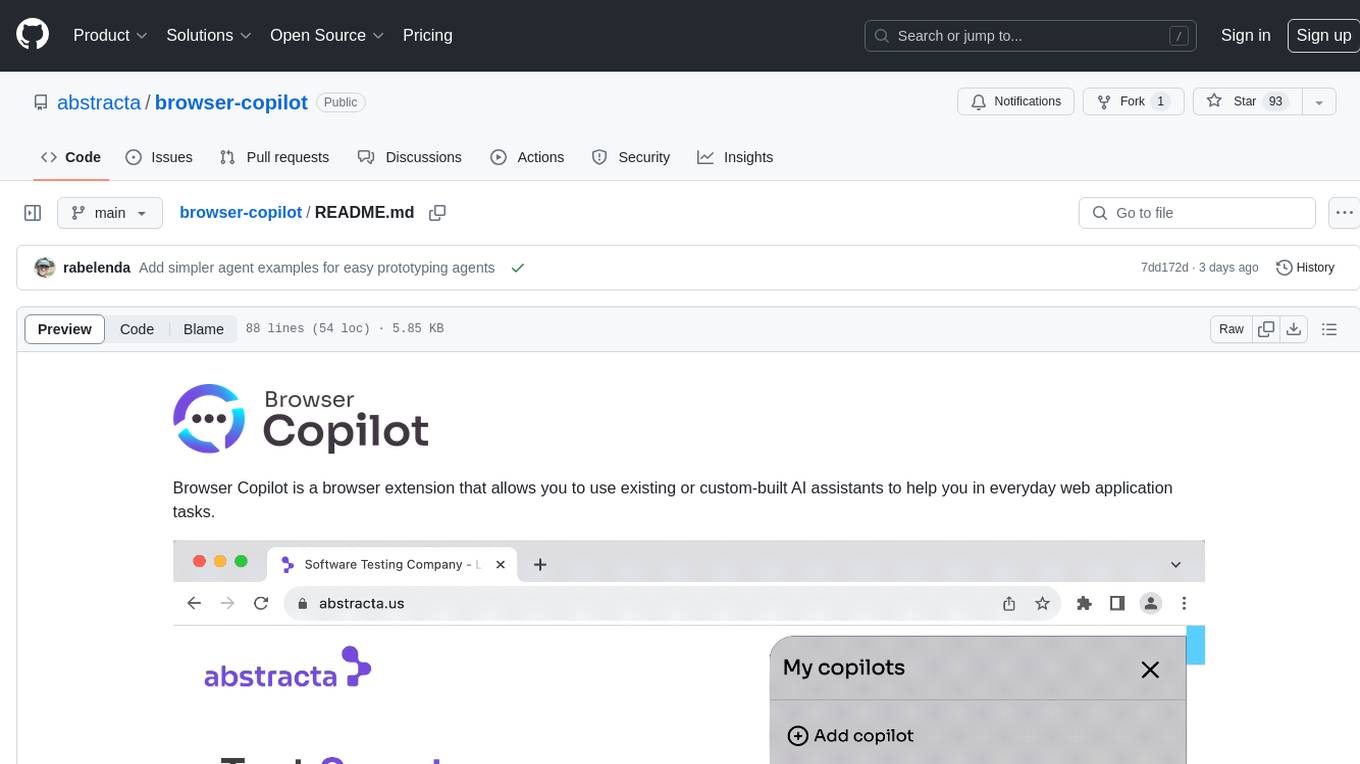
Browser Copilot is a browser extension that enables users to utilize AI assistants for various web application tasks. It provides a versatile UI and framework to implement copilots that can automate tasks, extract information, interact with web applications, and utilize service APIs. Users can easily install copilots, start chats, save prompts, and toggle the copilot on or off. The project also includes a sample copilot implementation for testing purposes and encourages community contributions to expand the catalog of copilots.
README:
Browser Copilot is a browser extension that allows you to use existing or custom-built AI assistants to help you in everyday web application tasks.
The goal is to provide a versatile UI and simple framework to implement and use an ever-increasing set of copilots (AI assistants). These copilots can help in a wide range of tasks by taking advantage of browser extension capabilities.
Here are a few examples of what these copilots can do:
- 🤖 Automatically activate copilots that are relevant to specific web applications. For instance, a Mail Copilot can activate when a Mail web app is loaded in a browser tab.
- 🔍 Extract information from the current web application. For example, the copilot could extract current mail content, from a Mail web app, and provide a summarization of the mail, or users may ask questions about the mail contents.
- ⚙️ Interact with web applications. A copilot could generate mail bodies based on user requests. It could also fill web app form fields with appropriate test data.
- 🔌 Use any service API to extract additional information or automate web app processes. For example, the copilot could retrieve valid examples from the web app backend to populate frontend forms.
- 💡 Many other ideas and capabilities can be explored by combining the browser extension with AI and LLM capabilities.
- Install the extension in your browser by downloading the latest version from the releases. To install an extension from a zip file you need to go to your browser "Manage Extension" screen, enable developer mode, and drag and drop the extension zip file.
- Open the extension by clicking on its icon and add a new copilot by providing its base URL. The base URL should correspond to the location of
manifest.jsonandlogo.png, for example:http://localhost:8000if your agent is running locally. - Start a new chat by clicking on a configured copilot, or, if the copilot has automatic activation, just use your browser and the copilot chat will automatically appear when the copilot activates.
- Save your preferred prompts directly from the chat. To quickly access them later, simply type '/' in the chat input.
At any point, you can close the copilot to later resume the conversation by the extension icon or right-clicking on the page and selecting Toggle Browser Copilot.
If you don't know any copilot URLs, this project includes a simple copilot implementation in agent folder. You can start it by copying agent/sample.env to agent/.env, changing the environment variables on it, and running docker-compose up (docker is required for this). Once started, you can configure your extension to use it by adding a copilot with the URL http://localhost:8000.
When you activate the copilot (click on the copilots list), it will request some credentials. Use test user and test password to login.
In the future, we plan to add a catalog of copilots contributed by the community. Therefore, if you create new copilots, please let us know so we can include them in the initial catalog.
To develop a new agent, you can refer to the agent-mock, agent-simple or agent-extended folders. The later is the most complete one with proper documentation on endpoints and manifest.json.
For the development environment, this project uses devbox and direnv.
To install all required dependencies (after installing devbox and direnv), run the following command:
devbox run installNext, set appropriate environment variables in agent-extended/.env.
To speed up development, you can comment out the Keycloak section, so you don't need to authenticate every time you want to try your copilot in the extension. If you don't comment out the Keycloak section, then you need to run
devbox run keycloakto spin up Keycloak for authentication and usetesttestcredentials for login (when requested by the browser extension).
To run the agent in dev mode, enabling automatic hot-reloading whenever any changes are detected in the agent source files, execute the following command:
devbox run agentIf you want to debug the agent, you can start the agent with your preferred IDE, pointing to the relevant virtual environment created by devbox, and using IDE's debugger capabilities to run the main script.
For more details about the agent, please refer to its readme.
If you plan to contribute changes to the browser extension, refer to the browser-extension folder.
To launch a Chrome browser with hot-reload capabilities, use the following command:
devbox run browserTo modify the default browser settings, consult browser-extension/vite.config.ts.
To build the final distribution of the extension, execute the following command:
devbox run buildWe welcome all kinds of contributions!
- ⭐ Give this project a star to make it more visible to the entire community. It lets us know that you are interested in this project, motivating us to invest more effort into it.
- 📢 Spread the word about this project. If you make any publications (tweets, StackOverflow mentions, LinkedIn posts, Medium articles, etc.) about it, please let us know. We plan to add references to such publications in the future.
- 🙋 Ask questions and request improvements by creating issues or opening discussions in the repository.
- 🧑💻 If you enjoy coding, you can build new agents, helping us implement browser extension features or general improvements.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for browser-copilot
Similar Open Source Tools

browser-copilot
Browser Copilot is a browser extension that enables users to utilize AI assistants for various web application tasks. It provides a versatile UI and framework to implement copilots that can automate tasks, extract information, interact with web applications, and utilize service APIs. Users can easily install copilots, start chats, save prompts, and toggle the copilot on or off. The project also includes a sample copilot implementation for testing purposes and encourages community contributions to expand the catalog of copilots.
fuji-web
Fuji-Web is an intelligent AI partner designed for full browser automation. It autonomously navigates websites and performs tasks on behalf of the user while providing explanations for each action step. Users can easily install the extension in their browser, access the Fuji icon to input tasks, and interact with the tool to streamline web browsing tasks. The tool aims to enhance user productivity by automating repetitive web actions and providing a seamless browsing experience.
reverse-engineering-assistant
ReVA (Reverse Engineering Assistant) is a project aimed at building a disassembler agnostic AI assistant for reverse engineering tasks. It utilizes a tool-driven approach, providing small tools to the user to empower them in completing complex tasks. The assistant is designed to accept various inputs, guide the user in correcting mistakes, and provide additional context to encourage exploration. Users can ask questions, perform tasks like decompilation, class diagram generation, variable renaming, and more. ReVA supports different language models for online and local inference, with easy configuration options. The workflow involves opening the RE tool and program, then starting a chat session to interact with the assistant. Installation includes setting up the Python component, running the chat tool, and configuring the Ghidra extension for seamless integration. ReVA aims to enhance the reverse engineering process by breaking down actions into small parts, including the user's thoughts in the output, and providing support for monitoring and adjusting prompts.
lumigator
Lumigator is an open-source platform developed by Mozilla.ai to help users select the most suitable language model for their specific needs. It supports the evaluation of summarization tasks using sequence-to-sequence models such as BART and BERT, as well as causal models like GPT and Mistral. The platform aims to make model selection transparent, efficient, and empowering by providing a framework for comparing LLMs using task-specific metrics to evaluate how well a model fits a project's needs. Lumigator is in the early stages of development and plans to expand support to additional machine learning tasks and use cases in the future.
concierge
Concierge is a versatile automation tool designed to streamline repetitive tasks and workflows. It provides a user-friendly interface for creating custom automation scripts without the need for extensive coding knowledge. With Concierge, users can automate various tasks across different platforms and applications, increasing efficiency and productivity. The tool offers a wide range of pre-built automation templates and allows users to customize and schedule their automation processes. Concierge is suitable for individuals and businesses looking to automate routine tasks and improve overall workflow efficiency.
dialog
Dialog is an API-focused tool designed to simplify the deployment of Large Language Models (LLMs) for programmers interested in AI. It allows users to deploy any LLM based on the structure provided by dialog-lib, enabling them to spend less time coding and more time training their models. The tool aims to humanize Retrieval-Augmented Generative Models (RAGs) and offers features for better RAG deployment and maintenance. Dialog requires a knowledge base in CSV format and a prompt configuration in TOML format to function effectively. It provides functionalities for loading data into the database, processing conversations, and connecting to the LLM, with options to customize prompts and parameters. The tool also requires specific environment variables for setup and configuration.
CustomSuggestionServiceForCopilotForXcode
This repository provides a custom suggestion service for Copilot for Xcode, allowing users to enhance code suggestions using chat models. It supports different suggestion services and strategies for generating code suggestions. Users can customize prompt formats and utilize local models for code completion.

raggenie
RAGGENIE is a low-code RAG builder tool designed to simplify the creation of conversational AI applications. It offers out-of-the-box plugins for connecting to various data sources and building conversational AI on top of them, including integration with pre-built agents for actions. The tool is open-source under the MIT license, with a current focus on making it easy to build RAG applications and future plans for maintenance, monitoring, and transitioning applications from pilots to production.
amazon-transcribe-live-call-analytics
The Amazon Transcribe Live Call Analytics (LCA) with Agent Assist Sample Solution is designed to help contact centers assess and optimize caller experiences in real time. It leverages Amazon machine learning services like Amazon Transcribe, Amazon Comprehend, and Amazon SageMaker to transcribe and extract insights from contact center audio. The solution provides real-time supervisor and agent assist features, integrates with existing contact centers, and offers a scalable, cost-effective approach to improve customer interactions. The end-to-end architecture includes features like live call transcription, call summarization, AI-powered agent assistance, and real-time analytics. The solution is event-driven, ensuring low latency and seamless processing flow from ingested speech to live webpage updates.
obsidian-companion
Companion is an Obsidian plugin that adds an AI-powered autocomplete feature to your note-taking and personal knowledge management platform. With Companion, you can write notes more quickly and easily by receiving suggestions for completing words, phrases, and even entire sentences based on the context of your writing. The autocomplete feature uses OpenAI's state-of-the-art GPT-3 and GPT-3.5, including ChatGPT, and locally hosted Ollama models, among others, to generate smart suggestions that are tailored to your specific writing style and preferences. Support for more models is planned, too.
cymbal-air-toolbox-demo
Cymbal Air Toolbox Demo is a project that provides a production-quality reference implementation for building Agentic applications using Agents and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) to query and interact with data stored in Google Cloud Databases. The demo showcases a customer service assistant for a fictional airline, Cymbal Air, assisting travelers with flight management and providing information about San Francisco International Airport (SFO). It utilizes techniques like Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) and Agent-based Orchestration to enhance responses and handle a wide variety of queries. The architecture includes components like the user-facing application, MCP Toolbox middleware server, and a database, offering advantages such as better security, scalability, and recall for agents.
testdriverai
TestDriver.ai is a unique test framework that acts as an OS Agent for QA, utilizing AI vision, mouse, and keyboard emulation to control the desktop. It simplifies testing setup, requires less maintenance, and offers more power to test any application and control any OS setting. Users can automate testing of user flows on websites, desktop apps, browser windows, popups, HTML elements, file uploads, chrome extensions, and application integrations. The tool allows users to instruct TestDriver in natural language, generate test scripts, execute tests, and deploy tests using GitHub Actions for continuous integration.
python-whatsapp-bot
This repository provides a comprehensive guide on building AI WhatsApp bots using Python and Flask. It covers setting up a Meta developer account, integrating webhook events for real-time message reception, and using OpenAI for AI responses. The tutorial includes steps for selecting phone numbers, sending messages with the API, configuring webhooks, integrating AI into the application, and adding a phone number. It also explains the process of creating a system user, obtaining access tokens, and validating verification requests and payloads for webhook security. The repository aims to help users create intelligent WhatsApp bots with Python and AI capabilities.
ChatGPT_Model_Switcher
ChatGPT Model Switcher is a user script that enables users to utilize the GPT-4 Mobile model on the ChatGPT web interface and switch to other models for added flexibility. It ensures compatibility with multiple mirror sites and hides inaccessible models for non-subscribers. However, recent updates have introduced stricter limitations due to enhanced authentication mechanisms and personal constraints, potentially affecting the project's ability to override usage limits. Users are encouraged to contribute to the project if capable.
Minimalistic-Comfy-Wrapper-WebUI
Minimalistic Comfy Wrapper WebUI is a user interface extension for ComfyUI that provides an additional inference-focused UI. It dynamically adapts to workflows, allowing users to change node titles and refresh the UI. The tool ensures stability by storing data in the browser's local storage, supports working with the same workflows in Comfy and the webui, offers better queues management, prompt presets, batch support, a minimalist image editor, and mobile-friendly UI. Users can install it from the ComfyUI manager and customize node titles for input and output nodes. The tool is designed for users who prefer a simpler interface for inference tasks and want to work with ComfyUI workflows from a different perspective.
atomic_agents
Atomic Agents is a modular and extensible framework designed for creating powerful applications. It follows the principles of Atomic Design, emphasizing small and single-purpose components. Leveraging Pydantic for data validation and serialization, the framework offers a set of tools and agents that can be combined to build AI applications. It depends on the Instructor package and supports various APIs like OpenAI, Cohere, Anthropic, and Gemini. Atomic Agents is suitable for developers looking to create AI agents with a focus on modularity and flexibility.
For similar tasks

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.

danswer
Danswer is an open-source Gen-AI Chat and Unified Search tool that connects to your company's docs, apps, and people. It provides a Chat interface and plugs into any LLM of your choice. Danswer can be deployed anywhere and for any scale - on a laptop, on-premise, or to cloud. Since you own the deployment, your user data and chats are fully in your own control. Danswer is MIT licensed and designed to be modular and easily extensible. The system also comes fully ready for production usage with user authentication, role management (admin/basic users), chat persistence, and a UI for configuring Personas (AI Assistants) and their Prompts. Danswer also serves as a Unified Search across all common workplace tools such as Slack, Google Drive, Confluence, etc. By combining LLMs and team specific knowledge, Danswer becomes a subject matter expert for the team. Imagine ChatGPT if it had access to your team's unique knowledge! It enables questions such as "A customer wants feature X, is this already supported?" or "Where's the pull request for feature Y?"
semantic-kernel
Semantic Kernel is an SDK that integrates Large Language Models (LLMs) like OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, and Hugging Face with conventional programming languages like C#, Python, and Java. Semantic Kernel achieves this by allowing you to define plugins that can be chained together in just a few lines of code. What makes Semantic Kernel _special_ , however, is its ability to _automatically_ orchestrate plugins with AI. With Semantic Kernel planners, you can ask an LLM to generate a plan that achieves a user's unique goal. Afterwards, Semantic Kernel will execute the plan for the user.
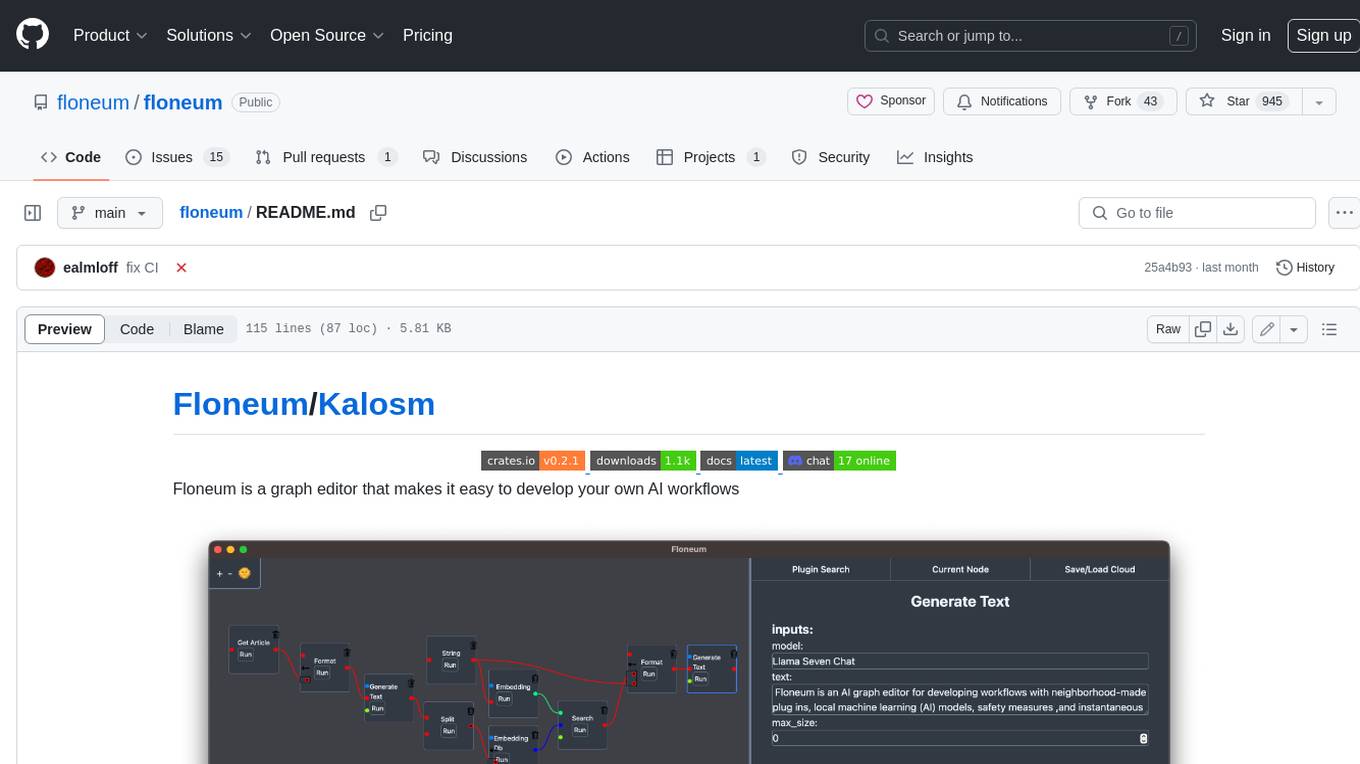
floneum
Floneum is a graph editor that makes it easy to develop your own AI workflows. It uses large language models (LLMs) to run AI models locally, without any external dependencies or even a GPU. This makes it easy to use LLMs with your own data, without worrying about privacy. Floneum also has a plugin system that allows you to improve the performance of LLMs and make them work better for your specific use case. Plugins can be used in any language that supports web assembly, and they can control the output of LLMs with a process similar to JSONformer or guidance.

mindsdb
MindsDB is a platform for customizing AI from enterprise data. You can create, serve, and fine-tune models in real-time from your database, vector store, and application data. MindsDB "enhances" SQL syntax with AI capabilities to make it accessible for developers worldwide. With MindsDB’s nearly 200 integrations, any developer can create AI customized for their purpose, faster and more securely. Their AI systems will constantly improve themselves — using companies’ own data, in real-time.
aiscript
AiScript is a lightweight scripting language that runs on JavaScript. It supports arrays, objects, and functions as first-class citizens, and is easy to write without the need for semicolons or commas. AiScript runs in a secure sandbox environment, preventing infinite loops from freezing the host. It also allows for easy provision of variables and functions from the host.
activepieces
Activepieces is an open source replacement for Zapier, designed to be extensible through a type-safe pieces framework written in Typescript. It features a user-friendly Workflow Builder with support for Branches, Loops, and Drag and Drop. Activepieces integrates with Google Sheets, OpenAI, Discord, and RSS, along with 80+ other integrations. The list of supported integrations continues to grow rapidly, thanks to valuable contributions from the community. Activepieces is an open ecosystem; all piece source code is available in the repository, and they are versioned and published directly to npmjs.com upon contributions. If you cannot find a specific piece on the pieces roadmap, please submit a request by visiting the following link: Request Piece Alternatively, if you are a developer, you can quickly build your own piece using our TypeScript framework. For guidance, please refer to the following guide: Contributor's Guide
superagent-js
Superagent is an open source framework that enables any developer to integrate production ready AI Assistants into any application in a matter of minutes.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.

