voltagent
AI Agent Engineering Platform built on an Open Source TypeScript AI Agent Framework
Stars: 5875
VoltAgent is an open-source TypeScript framework designed for building and orchestrating AI agents. It simplifies the development of AI agent applications by providing modular building blocks, standardized patterns, and abstractions. Whether you're creating chatbots, virtual assistants, automated workflows, or complex multi-agent systems, VoltAgent handles the underlying complexity, allowing developers to focus on defining their agents' capabilities and logic. The framework offers ready-made building blocks, such as the Core Engine, Multi-Agent Systems, Workflow Engine, Extensible Packages, Tooling & Integrations, Data Retrieval & RAG, Memory management, LLM Compatibility, and a Developer Ecosystem. VoltAgent empowers developers to build sophisticated AI applications faster and more reliably, avoiding repetitive setup and the limitations of simpler tools.
README:
VoltAgent is an end-to-end AI Agent Engineering Platform that consists of two main parts:
- Open-Source TypeScript Framework – Memory, RAG, Guardrails, Tools, MCP, Voice, Workflow, and more.
-
VoltOps Console
CloudSelf-Hosted– Observability, Automation, Deployment, Evals, Guardrails, Prompts, and more.
Build agents with full code control and ship them with production-ready visibility and operations.
With the open-source framework, you can build intelligent agents with memory, tools, and multi-step workflows while connecting to any AI provider. Create sophisticated multi-agent systems where specialized agents work together under supervisor coordination.
-
Core Runtime (
@voltagent/core): Define agents with typed roles, tools, memory, and model providers in one place so everything stays organized. - Workflow Engine: Describe multi-step automations declaratively rather than stitching together custom control flow.
- Supervisors & Sub-Agents: Run teams of specialized agents under a supervisor runtime that routes tasks and keeps them in sync.
- Tool Registry & MCP: Ship Zod-typed tools with lifecycle hooks and cancellation, and connect to Model Context Protocol servers without extra glue code.
- LLM Compatibility: Swap between OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, or other providers by changing config, not rewriting agent logic.
- Memory: Attach durable memory adapters so agents remember important context across runs.
- Resumable Streaming: Let clients reconnect to in-flight streams after refresh and continue receiving the same response.
- Retrieval & RAG: Plug in retriever agents to pull facts from your data sources and ground responses (RAG) before the model answers.
- VoltAgent Knowledge Base: Use the managed RAG service for document ingestion, chunking, embeddings, and search.
- Voice: Add text-to-speech and speech-to-text capabilities with OpenAI, ElevenLabs, or custom voice providers.
- Guardrails: Intercept and validate agent input or output at runtime to enforce content policies and safety rules.
- Evals: Run agent eval suites alongside your workflows to measure and improve agent behavior.
You can use the MCP server @voltagent/mcp-docs-server to teach your LLM how to use VoltAgent for AI-powered coding assistants like Claude, Cursor, or Windsurf. This allows AI assistants to access VoltAgent documentation, examples, and changelogs directly while you code.
📖 How to setup MCP docs server
Create a new VoltAgent project in seconds using the create-voltagent-app CLI tool:
npm create voltagent-app@latestThis command guides you through setup.
You'll see the starter code in src/index.ts, which now registers both an agent and a comprehensive workflow example found in src/workflows/index.ts.
import { VoltAgent, Agent, Memory } from "@voltagent/core";
import { LibSQLMemoryAdapter } from "@voltagent/libsql";
import { createPinoLogger } from "@voltagent/logger";
import { honoServer } from "@voltagent/server-hono";
import { openai } from "@ai-sdk/openai";
import { expenseApprovalWorkflow } from "./workflows";
import { weatherTool } from "./tools";
// Create a logger instance
const logger = createPinoLogger({
name: "my-agent-app",
level: "info",
});
// Optional persistent memory (remove to use default in-memory)
const memory = new Memory({
storage: new LibSQLMemoryAdapter({ url: "file:./.voltagent/memory.db" }),
});
// A simple, general-purpose agent for the project.
const agent = new Agent({
name: "my-agent",
instructions: "A helpful assistant that can check weather and help with various tasks",
model: openai("gpt-4o-mini"),
tools: [weatherTool],
memory,
});
// Initialize VoltAgent with your agent(s) and workflow(s)
new VoltAgent({
agents: {
agent,
},
workflows: {
expenseApprovalWorkflow,
},
server: honoServer(),
logger,
});Afterwards, navigate to your project and run:
npm run devWhen you run the dev command, tsx will compile and run your code. You should see the VoltAgent server startup message in your terminal:
══════════════════════════════════════════════════
VOLTAGENT SERVER STARTED SUCCESSFULLY
══════════════════════════════════════════════════
✓ HTTP Server: http://localhost:3141
Test your agents with VoltOps Console: https://console.voltagent.dev
══════════════════════════════════════════════════
Your agent is now running! To interact with it:
- Open the Console: Click the VoltOps LLM Observability Platform link in your terminal output (or copy-paste it into your browser).
- Find Your Agent: On the VoltOps LLM Observability Platform page, you should see your agent listed (e.g., "my-agent").
- Open Agent Details: Click on your agent's name.
- Start Chatting: On the agent detail page, click the chat icon in the bottom right corner to open the chat window.
- Send a Message: Type a message like "Hello" and press Enter.
Your new project also includes a powerful workflow engine.
The expense approval workflow demonstrates human-in-the-loop automation with suspend/resume capabilities:
import { createWorkflowChain } from "@voltagent/core";
import { z } from "zod";
export const expenseApprovalWorkflow = createWorkflowChain({
id: "expense-approval",
name: "Expense Approval Workflow",
purpose: "Process expense reports with manager approval for high amounts",
input: z.object({
employeeId: z.string(),
amount: z.number(),
category: z.string(),
description: z.string(),
}),
result: z.object({
status: z.enum(["approved", "rejected"]),
approvedBy: z.string(),
finalAmount: z.number(),
}),
})
// Step 1: Validate expense and check if approval needed
.andThen({
id: "check-approval-needed",
resumeSchema: z.object({
approved: z.boolean(),
managerId: z.string(),
comments: z.string().optional(),
adjustedAmount: z.number().optional(),
}),
execute: async ({ data, suspend, resumeData }) => {
// If we're resuming with manager's decision
if (resumeData) {
return {
...data,
approved: resumeData.approved,
approvedBy: resumeData.managerId,
finalAmount: resumeData.adjustedAmount || data.amount,
};
}
// Check if manager approval is needed (expenses over $500)
if (data.amount > 500) {
await suspend("Manager approval required", {
employeeId: data.employeeId,
requestedAmount: data.amount,
});
}
// Auto-approve small expenses
return {
...data,
approved: true,
approvedBy: "system",
finalAmount: data.amount,
};
},
})
// Step 2: Process the final decision
.andThen({
id: "process-decision",
execute: async ({ data }) => {
return {
status: data.approved ? "approved" : "rejected",
approvedBy: data.approvedBy,
finalAmount: data.finalAmount,
};
},
});You can test the pre-built expenseApprovalWorkflow directly from the VoltOps console:
- Go to the Workflows Page: After starting your server, go directly to the Workflows page.
- Select Your Project: Use the project selector to choose your project (e.g., "my-agent-app").
- Find and Run: You will see "Expense Approval Workflow" listed. Click it, then click the "Run" button.
-
Provide Input: The workflow expects a JSON object with expense details. Try a small expense for automatic approval:
{ "employeeId": "EMP-123", "amount": 250, "category": "office-supplies", "description": "New laptop mouse and keyboard" } - View the Results: After execution, you can inspect the detailed logs for each step and see the final output directly in the console.
For more examples, visit our examples repository.
- Airtable Agent - React to new records and write updates back into Airtable with VoltOps actions.
- Slack Agent - Respond to channel messages and reply via VoltOps Slack actions.
- ChatGPT App With VoltAgent - Deploy VoltAgent over MCP and connect to ChatGPT Apps.
- WhatsApp Order Agent - Build a WhatsApp chatbot that handles food orders through natural conversation. (Source)
- YouTube to Blog Agent - Convert YouTube videos into Markdown blog posts using a supervisor agent with MCP tools. (Source)
- AI Ads Generator Agent - Generate Instagram ads using BrowserBase Stagehand and Google Gemini AI. (Source)
- AI Recipe Generator Agent - Create personalized cooking suggestions based on ingredients and preferences. (Source | Video)
- AI Research Assistant Agent - Multi-agent research workflow for generating comprehensive reports. (Source | Video)
VoltOps Console is the platform side of VoltAgent, providing observability, automation, and deployment so you can monitor and debug agents in production with real-time execution traces, performance metrics, and visual dashboards.
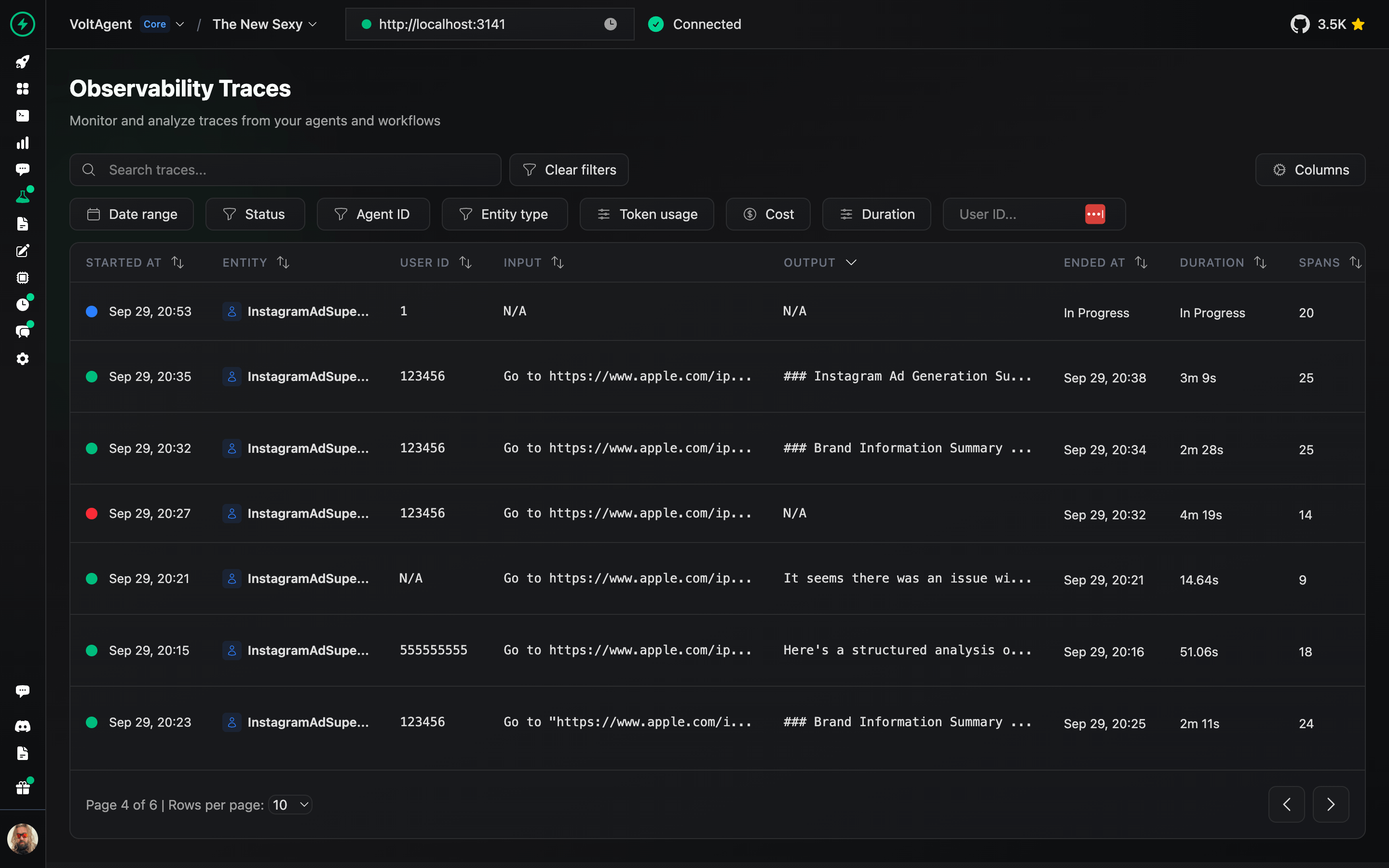
Deep dive into agent execution flow with detailed traces and performance metrics.
Get a comprehensive overview of all your agents, workflows, and system performance metrics.
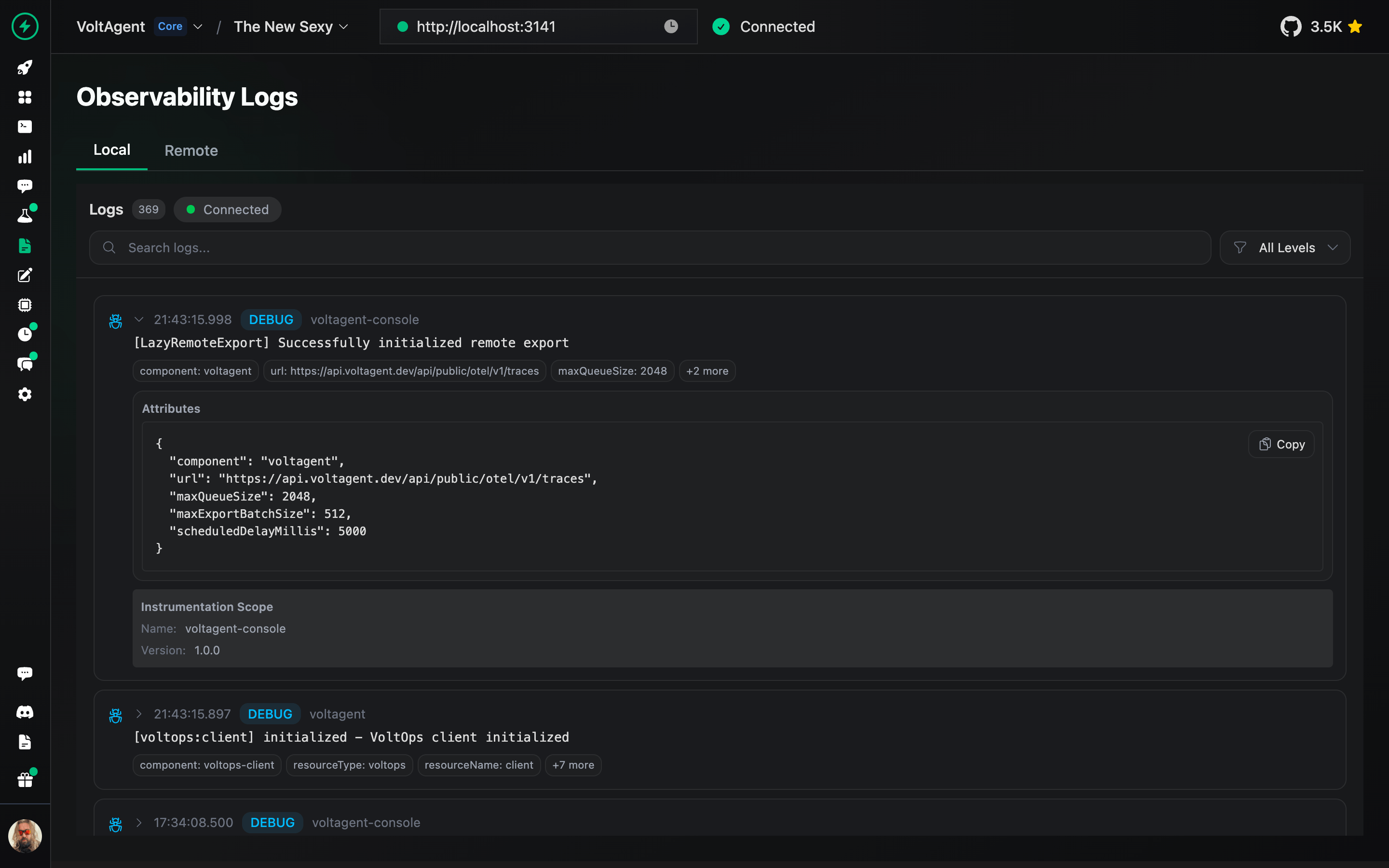
Track detailed execution logs for every agent interaction and workflow step.
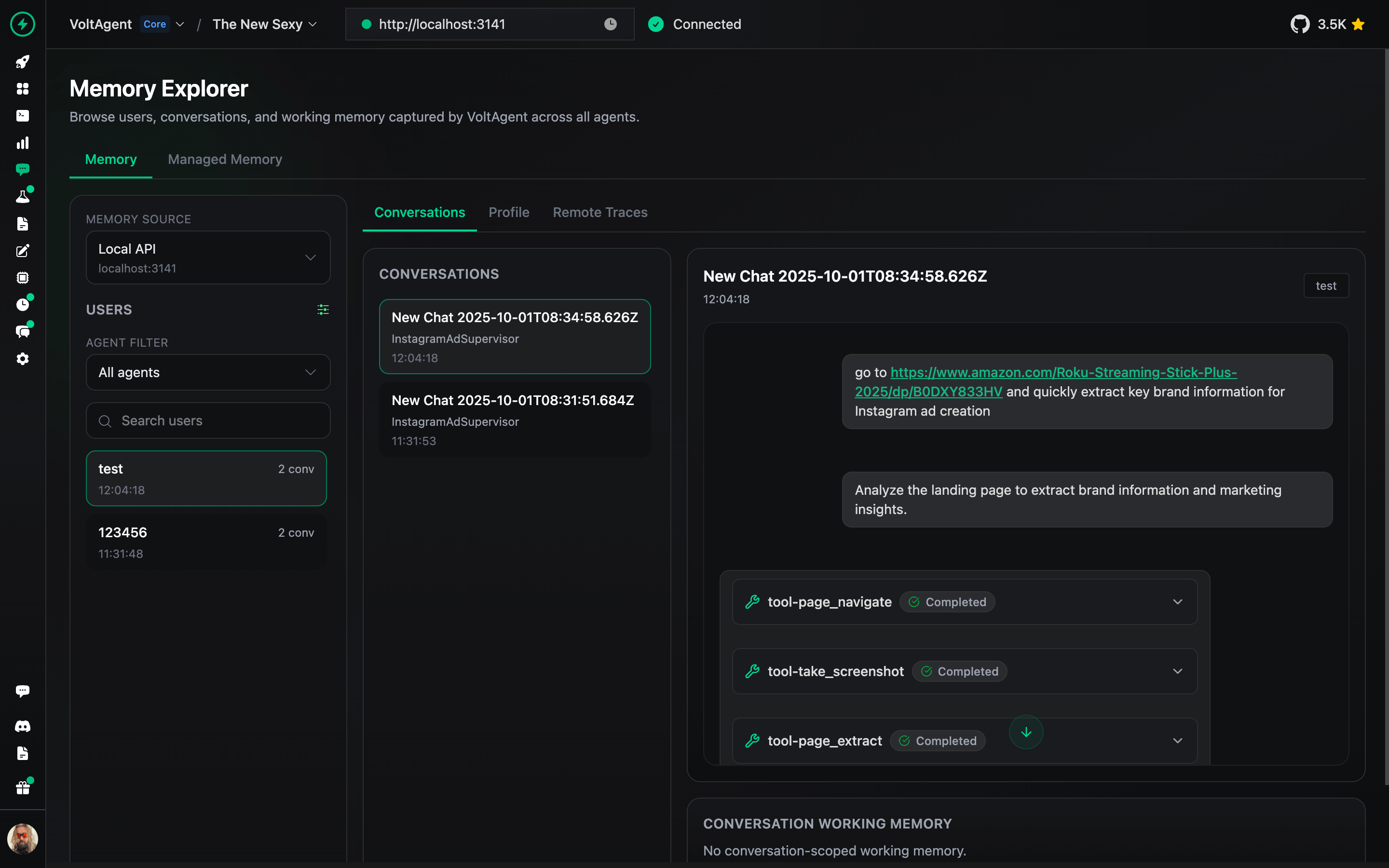
Inspect and manage agent memory, context, and conversation history.
Analyze complete execution traces to understand agent behavior and optimize performance.
Design, test, and refine prompts directly in the console.
Deploy your agents to production with one-click GitHub integration and managed infrastructure.
📖 VoltOps Deploy Documentation
Automate agent workflows with webhooks, schedules, and custom triggers to react to external events.
Monitor agent health, performance metrics, and resource usage across your entire system.
Set up safety boundaries and content filters to ensure agents operate within defined parameters.
Run evaluation suites to test agent behavior, accuracy, and performance against benchmarks.
Connect your agents to knowledge sources with built-in retrieval-augmented generation capabilities.
- Start with interactive tutorial to learn the fundamentals building AI Agents.
- Documentation: Dive into guides, concepts, and tutorials.
- Examples: Explore practical implementations.
- Blog: Read more about technical insights, and best practices.
We welcome contributions! Please refer to the contribution guidelines (link needed if available). Join our Discord server for questions and discussions.
Big thanks to everyone who's been part of the VoltAgent journey, whether you've built a plugin, opened an issue, dropped a pull request, or just helped someone out on Discord or GitHub Discussions.
VoltAgent is a community effort, and it keeps getting better because of people like you.
Licensed under the MIT License, Copyright © 2026-present VoltAgent.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for voltagent
Similar Open Source Tools

voltagent
VoltAgent is an open-source TypeScript framework designed for building and orchestrating AI agents. It simplifies the development of AI agent applications by providing modular building blocks, standardized patterns, and abstractions. Whether you're creating chatbots, virtual assistants, automated workflows, or complex multi-agent systems, VoltAgent handles the underlying complexity, allowing developers to focus on defining their agents' capabilities and logic. The framework offers ready-made building blocks, such as the Core Engine, Multi-Agent Systems, Workflow Engine, Extensible Packages, Tooling & Integrations, Data Retrieval & RAG, Memory management, LLM Compatibility, and a Developer Ecosystem. VoltAgent empowers developers to build sophisticated AI applications faster and more reliably, avoiding repetitive setup and the limitations of simpler tools.
Roo-Code
Roo Code is an AI-powered development tool that integrates with your code editor to help you generate code from natural language descriptions and specifications, refactor and debug existing code, write and update documentation, answer questions about your codebase, automate repetitive tasks, and utilize MCP servers. It offers different modes such as Code, Architect, Ask, Debug, and Custom Modes to adapt to various tasks and workflows. Roo Code provides tutorial and feature videos, documentation, a YouTube channel, a Discord server, a Reddit community, GitHub issues tracking, and a feature request platform. Users can set up and develop Roo Code locally by cloning the repository, installing dependencies, and running the extension in development mode or by automated/manual VSIX installation. The tool uses changesets for versioning and publishing. Please note that Roo Code, Inc. does not make any representations or warranties regarding the tools provided, and users assume all risks associated with their use.
pyspur
PySpur is a graph-based editor designed for LLM (Large Language Models) workflows. It offers modular building blocks, node-level debugging, and performance evaluation. The tool is easy to hack, supports JSON configs for workflow graphs, and is lightweight with minimal dependencies. Users can quickly set up PySpur by cloning the repository, creating a .env file, starting docker services, and accessing the portal. PySpur can also work with local models served using Ollama, with steps provided for configuration. The roadmap includes features like canvas, async/batch execution, support for Ollama, new nodes, pipeline optimization, templates, code compilation, multimodal support, and more.
GPTSwarm
GPTSwarm is a graph-based framework for LLM-based agents that enables the creation of LLM-based agents from graphs and facilitates the customized and automatic self-organization of agent swarms with self-improvement capabilities. The library includes components for domain-specific operations, graph-related functions, LLM backend selection, memory management, and optimization algorithms to enhance agent performance and swarm efficiency. Users can quickly run predefined swarms or utilize tools like the file analyzer. GPTSwarm supports local LM inference via LM Studio, allowing users to run with a local LLM model. The framework has been accepted by ICML2024 and offers advanced features for experimentation and customization.
unify
The Unify Python Package provides access to the Unify REST API, allowing users to query Large Language Models (LLMs) from any Python 3.7.1+ application. It includes Synchronous and Asynchronous clients with Streaming responses support. Users can easily use any endpoint with a single key, route to the best endpoint for optimal throughput, cost, or latency, and customize prompts to interact with the models. The package also supports dynamic routing to automatically direct requests to the top-performing provider. Additionally, users can enable streaming responses and interact with the models asynchronously for handling multiple user requests simultaneously.
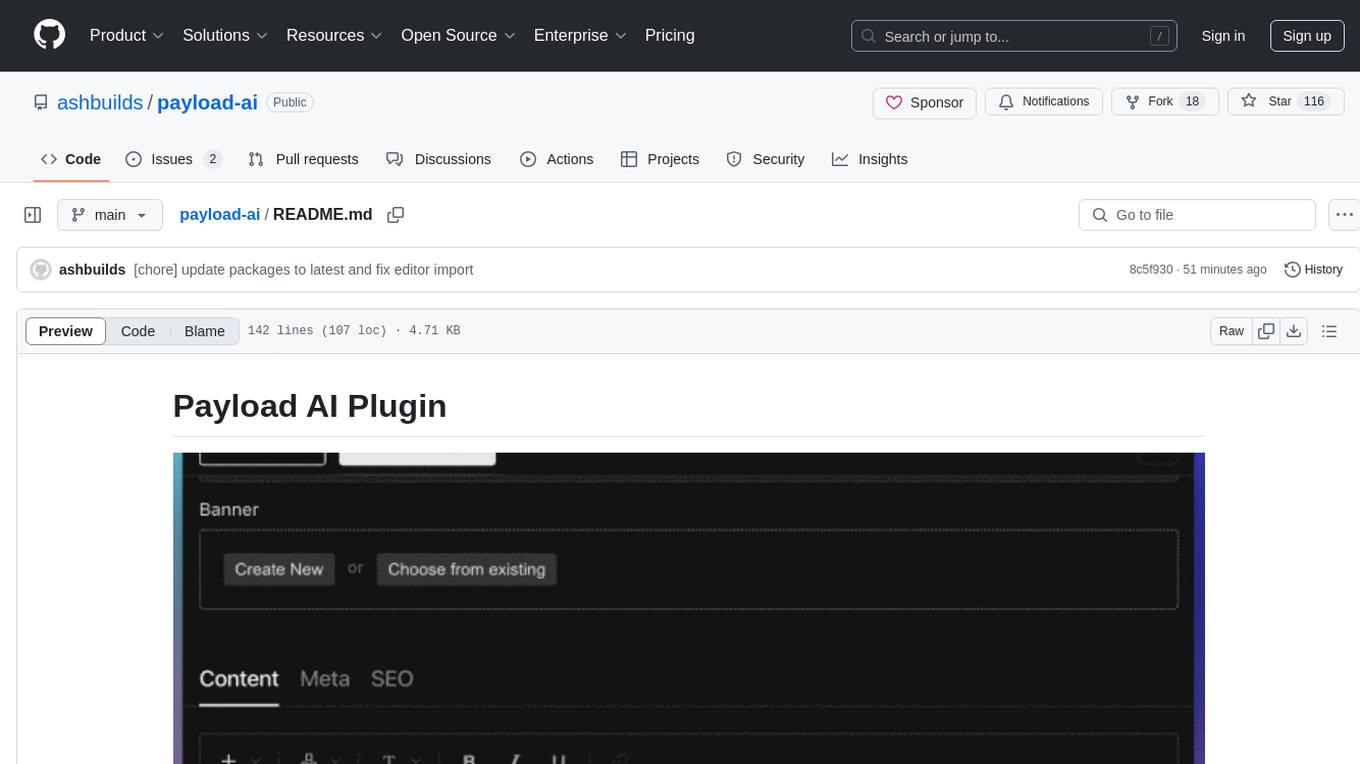
payload-ai
The Payload AI Plugin is an advanced extension that integrates modern AI capabilities into your Payload CMS, streamlining content creation and management. It offers features like text generation, voice and image generation, field-level prompt customization, prompt editor, document analyzer, fact checking, automated content workflows, internationalization support, editor AI suggestions, and AI chat support. Users can personalize and configure the plugin by setting environment variables. The plugin is actively developed and tested with Payload version v3.2.1, with regular updates expected.
eliza
Eliza is a versatile AI agent operating system designed to support various models and connectors, enabling users to create chatbots, autonomous agents, handle business processes, create video game NPCs, and engage in trading. It offers multi-agent and room support, document ingestion and interaction, retrievable memory and document store, and extensibility to create custom actions and clients. Eliza is easy to use and provides a comprehensive solution for AI agent development.
TaskingAI
TaskingAI brings Firebase's simplicity to **AI-native app development**. The platform enables the creation of GPTs-like multi-tenant applications using a wide range of LLMs from various providers. It features distinct, modular functions such as Inference, Retrieval, Assistant, and Tool, seamlessly integrated to enhance the development process. TaskingAI’s cohesive design ensures an efficient, intelligent, and user-friendly experience in AI application development.
pocketpaw
PocketPaw is a lightweight and user-friendly tool designed for managing and organizing your digital assets. It provides a simple interface for users to easily categorize, tag, and search for files across different platforms. With PocketPaw, you can efficiently organize your photos, documents, and other files in a centralized location, making it easier to access and share them. Whether you are a student looking to organize your study materials, a professional managing project files, or a casual user wanting to declutter your digital space, PocketPaw is the perfect solution for all your file management needs.
mem0
Mem0 is a tool that provides a smart, self-improving memory layer for Large Language Models, enabling personalized AI experiences across applications. It offers persistent memory for users, sessions, and agents, self-improving personalization, a simple API for easy integration, and cross-platform consistency. Users can store memories, retrieve memories, search for related memories, update memories, get the history of a memory, and delete memories using Mem0. It is designed to enhance AI experiences by enabling long-term memory storage and retrieval.

InsForge
InsForge is a backend development platform designed for AI coding agents and AI code editors. It serves as a semantic layer that enables agents to interact with backend primitives such as databases, authentication, storage, and functions in a meaningful way. The platform allows agents to fetch backend context, configure primitives, and inspect backend state through structured schemas. InsForge facilitates backend context engineering for AI coding agents to understand, operate, and monitor backend systems effectively.
WebMasterLog
WebMasterLog is a comprehensive repository showcasing various web development projects built with front-end and back-end technologies. It highlights interactive user interfaces, dynamic web applications, and a spectrum of web development solutions. The repository encourages contributions in areas such as adding new projects, improving existing projects, updating documentation, fixing bugs, implementing responsive design, enhancing code readability, and optimizing project functionalities. Contributors are guided to follow specific guidelines for project submissions, including directory naming conventions, README file inclusion, project screenshots, and commit practices. Pull requests are reviewed based on criteria such as proper PR template completion, originality of work, code comments for clarity, and sharing screenshots for frontend updates. The repository also participates in various open-source programs like JWOC, GSSoC, Hacktoberfest, KWOC, 24 Pull Requests, IWOC, SWOC, and DWOC, welcoming valuable contributors.
packmind
Packmind is an engineering playbook tool that helps AI-native engineers to centralize and manage their team's coding standards, commands, and skills. It addresses the challenges of storing standards in various formats and locations, and automates the generation of instruction files for AI tools like GitHub Copilot, Claude Code, and Cursor. With Packmind, users can create a real engineering playbook to ensure AI agents code according to their team's standards.
DriveLM
DriveLM is a multimodal AI model that enables autonomous driving by combining computer vision and natural language processing. It is designed to understand and respond to complex driving scenarios using visual and textual information. DriveLM can perform various tasks related to driving, such as object detection, lane keeping, and decision-making. It is trained on a massive dataset of images and text, which allows it to learn the relationships between visual cues and driving actions. DriveLM is a powerful tool that can help to improve the safety and efficiency of autonomous vehicles.
DevoxxGenieIDEAPlugin
Devoxx Genie is a Java-based IntelliJ IDEA plugin that integrates with local and cloud-based LLM providers to aid in reviewing, testing, and explaining project code. It supports features like code highlighting, chat conversations, and adding files/code snippets to context. Users can modify REST endpoints and LLM parameters in settings, including support for cloud-based LLMs. The plugin requires IntelliJ version 2023.3.4 and JDK 17. Building and publishing the plugin is done using Gradle tasks. Users can select an LLM provider, choose code, and use commands like review, explain, or generate unit tests for code analysis.
memU
MemU is an open-source memory framework designed for AI companions, offering high accuracy, fast retrieval, and cost-effectiveness. It serves as an intelligent 'memory folder' that adapts to various AI companion scenarios. With MemU, users can create AI companions that remember them, learn their preferences, and evolve through interactions. The framework provides advanced retrieval strategies, 24/7 support, and is specialized for AI companions. MemU offers cloud, enterprise, and self-hosting options, with features like memory organization, interconnected knowledge graph, continuous self-improvement, and adaptive forgetting mechanism. It boasts high memory accuracy, fast retrieval, and low cost, making it suitable for building intelligent agents with persistent memory capabilities.
For similar tasks

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.

zep-python
Zep is an open-source platform for building and deploying large language model (LLM) applications. It provides a suite of tools and services that make it easy to integrate LLMs into your applications, including chat history memory, embedding, vector search, and data enrichment. Zep is designed to be scalable, reliable, and easy to use, making it a great choice for developers who want to build LLM-powered applications quickly and easily.
lollms
LoLLMs Server is a text generation server based on large language models. It provides a Flask-based API for generating text using various pre-trained language models. This server is designed to be easy to install and use, allowing developers to integrate powerful text generation capabilities into their applications.
LlamaIndexTS
LlamaIndex.TS is a data framework for your LLM application. Use your own data with large language models (LLMs, OpenAI ChatGPT and others) in Typescript and Javascript.
semantic-kernel
Semantic Kernel is an SDK that integrates Large Language Models (LLMs) like OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, and Hugging Face with conventional programming languages like C#, Python, and Java. Semantic Kernel achieves this by allowing you to define plugins that can be chained together in just a few lines of code. What makes Semantic Kernel _special_ , however, is its ability to _automatically_ orchestrate plugins with AI. With Semantic Kernel planners, you can ask an LLM to generate a plan that achieves a user's unique goal. Afterwards, Semantic Kernel will execute the plan for the user.
botpress
Botpress is a platform for building next-generation chatbots and assistants powered by OpenAI. It provides a range of tools and integrations to help developers quickly and easily create and deploy chatbots for various use cases.
BotSharp
BotSharp is an open-source machine learning framework for building AI bot platforms. It provides a comprehensive set of tools and components for developing and deploying intelligent virtual assistants. BotSharp is designed to be modular and extensible, allowing developers to easily integrate it with their existing systems and applications. With BotSharp, you can quickly and easily create AI-powered chatbots, virtual assistants, and other conversational AI applications.

qdrant
Qdrant is a vector similarity search engine and vector database. It is written in Rust, which makes it fast and reliable even under high load. Qdrant can be used for a variety of applications, including: * Semantic search * Image search * Product recommendations * Chatbots * Anomaly detection Qdrant offers a variety of features, including: * Payload storage and filtering * Hybrid search with sparse vectors * Vector quantization and on-disk storage * Distributed deployment * Highlighted features such as query planning, payload indexes, SIMD hardware acceleration, async I/O, and write-ahead logging Qdrant is available as a fully managed cloud service or as an open-source software that can be deployed on-premises.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.