
AixLib
A Modelica model library for building performance simulations
Stars: 187
AixLib is a Modelica model library for building performance simulations developed at RWTH Aachen University, E.ON Energy Research Center, Institute for Energy Efficient Buildings and Indoor Climate (EBC) in Aachen, Germany. It contains models of HVAC systems as well as high and reduced order building models. The name AixLib is derived from the city's French name Aix-la-Chapelle, following a local tradition. The library is continuously improved and offers citable papers for reference. Contributions to the development can be made via Issues section or Pull Requests, following the workflow described in the Wiki. AixLib is released under a 3-clause BSD-license with acknowledgements to public funded projects and financial support by BMWi (German Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy).
README:
AixLib is a Modelica model library for building performance simulations.
The library contains models of HVAC systems as well as high and reduced order building models.
It is being developed at RWTH Aachen University, E.ON Energy Research Center, Institute for Energy Efficient Buildings and Indoor Climate (EBC) in Aachen, Germany.
As the library is developed at RWTH Aachen University's EBC, the library's name AixLib is derived from the city's French name Aix-la-Chapelle, which the people of Aachen are very fond of and use a lot. With the name AixLib we follow this local tradition.
If you have any questions regarding AixLib, feel free to contact us at [email protected].
- To clone the repository for the first time run:
git clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/RWTH-EBC/AixLib.git - If you have already cloned the repository, run:
git submodule update --init --recursive - The default branch of AixLib is the
mainbranch. This means that after cloning the repository, you always checked out themainbranch.
The latest version is always available on the release page and defined in AixLib's package.mo.
We continuously improve AixLib and try to keep the community up-to-date with citable papers. Please use the following article for citations when using or enhancing AixLib.
@article{doi:10.1080/19401493.2023.2250521,
author = {Laura Maier and David Jansen and Fabian Wüllhorst and Martin Kremer and Alexander Kümpel and Tobias Blacha and Dirk Müller},
title = {AixLib: an open-source Modelica library for compound building energy systems from component to district level with automated quality management},
journal = {Journal of Building Performance Simulation},
volume = {17},
number = {2},
pages = {196-219},
year = {2023},
publisher = {Taylor & Francis},
doi = {10.1080/19401493.2023.2250521},
URL = {https://doi.org/10.1080/19401493.2023.2250521 },
eprint = {https://doi.org/10.1080/19401493.2023.2250521 }
}Please see the publications list
You are invited to contribute to the development of AixLib. Issues can be reported using this site's Issues section. Furthermore, you are welcome to contribute via Pull Requests. The workflow for changes is described in our Wiki.
The AixLib Library is released by RWTH Aachen University, E.ON Energy Research Center, Institute for Energy Efficient Buildings and Indoor Climate and is available under a 3-clause BSD-license. See AixLib Library license.
Parts of AixLib have been developed within public funded projects and with financial support by BMWi (German Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy).
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for AixLib
Similar Open Source Tools

AixLib
AixLib is a Modelica model library for building performance simulations developed at RWTH Aachen University, E.ON Energy Research Center, Institute for Energy Efficient Buildings and Indoor Climate (EBC) in Aachen, Germany. It contains models of HVAC systems as well as high and reduced order building models. The name AixLib is derived from the city's French name Aix-la-Chapelle, following a local tradition. The library is continuously improved and offers citable papers for reference. Contributions to the development can be made via Issues section or Pull Requests, following the workflow described in the Wiki. AixLib is released under a 3-clause BSD-license with acknowledgements to public funded projects and financial support by BMWi (German Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy).
baal
Baal is an active learning library that supports both industrial applications and research use cases. It provides a framework for Bayesian active learning methods such as Monte-Carlo Dropout, MCDropConnect, Deep ensembles, and Semi-supervised learning. Baal helps in labeling the most uncertain items in the dataset pool to improve model performance and reduce annotation effort. The library is actively maintained by a dedicated team and has been used in various research papers for production and experimentation.
opening-up-chatgpt.github.io
This repository provides a curated list of open-source projects that implement instruction-tuned large language models (LLMs) with reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF). The projects are evaluated in terms of their openness across a predefined set of criteria in the areas of Availability, Documentation, and Access. The goal of this repository is to promote transparency and accountability in the development and deployment of LLMs.

zshot
Zshot is a highly customizable framework for performing Zero and Few shot named entity and relationships recognition. It can be used for mentions extraction, wikification, zero and few shot named entity recognition, zero and few shot named relationship recognition, and visualization of zero-shot NER and RE extraction. The framework consists of two main components: the mentions extractor and the linker. There are multiple mentions extractors and linkers available, each serving a specific purpose. Zshot also includes a relations extractor and a knowledge extractor for extracting relations among entities and performing entity classification. The tool requires Python 3.6+ and dependencies like spacy, torch, transformers, evaluate, and datasets for evaluation over datasets like OntoNotes. Optional dependencies include flair and blink for additional functionalities. Zshot provides examples, tutorials, and evaluation methods to assess the performance of the components.
LLMLingua
LLMLingua is a tool that utilizes a compact, well-trained language model to identify and remove non-essential tokens in prompts. This approach enables efficient inference with large language models, achieving up to 20x compression with minimal performance loss. The tool includes LLMLingua, LongLLMLingua, and LLMLingua-2, each offering different levels of prompt compression and performance improvements for tasks involving large language models.
k2
K2 (GeoLLaMA) is a large language model for geoscience, trained on geoscience literature and fine-tuned with knowledge-intensive instruction data. It outperforms baseline models on objective and subjective tasks. The repository provides K2 weights, core data of GeoSignal, GeoBench benchmark, and code for further pretraining and instruction tuning. The model is available on Hugging Face for use. The project aims to create larger and more powerful geoscience language models in the future.

asreview
The ASReview project implements active learning for systematic reviews, utilizing AI-aided pipelines to assist in finding relevant texts for search tasks. It accelerates the screening of textual data with minimal human input, saving time and increasing output quality. The software offers three modes: Oracle for interactive screening, Exploration for teaching purposes, and Simulation for evaluating active learning models. ASReview LAB is designed to support decision-making in any discipline or industry by improving efficiency and transparency in screening large amounts of textual data.
ChatDev
ChatDev is a virtual software company powered by intelligent agents like CEO, CPO, CTO, programmer, reviewer, tester, and art designer. These agents collaborate to revolutionize the digital world through programming. The platform offers an easy-to-use, highly customizable, and extendable framework based on large language models, ideal for studying collective intelligence. ChatDev introduces innovative methods like Iterative Experience Refinement and Experiential Co-Learning to enhance software development efficiency. It supports features like incremental development, Docker integration, Git mode, and Human-Agent-Interaction mode. Users can customize ChatChain, Phase, and Role settings, and share their software creations easily. The project is open-source under the Apache 2.0 License and utilizes data licensed under CC BY-NC 4.0.
Docs2KG
Docs2KG is a tool designed for constructing a unified knowledge graph from heterogeneous documents. It addresses the challenges of digitizing diverse unstructured documents and constructing a high-quality knowledge graph with less effort. The tool combines bottom-up and top-down approaches, utilizing a human-LLM collaborative interface to enhance the generated knowledge graph. It organizes the knowledge graph into MetaKG, LayoutKG, and SemanticKG, providing a comprehensive view of document content. Docs2KG aims to streamline the process of knowledge graph construction and offers metrics for evaluating the quality of automatic construction.
MathPile
MathPile is a generative AI tool designed for math, offering a diverse and high-quality math-centric corpus comprising about 9.5 billion tokens. It draws from various sources such as textbooks, arXiv, Wikipedia, ProofWiki, StackExchange, and web pages, catering to different educational levels and math competitions. The corpus is meticulously processed to ensure data quality, with extensive documentation and data contamination detection. MathPile aims to enhance mathematical reasoning abilities of language models.
OpenNARS-for-Applications
OpenNARS-for-Applications is an implementation of a Non-Axiomatic Reasoning System, a general-purpose reasoner that adapts under the Assumption of Insufficient Knowledge and Resources. The system combines the logic and conceptual ideas of OpenNARS, event handling and procedure learning capabilities of ANSNA and 20NAR1, and the control model from ALANN. It is written in C, offers improved reasoning performance, and has been compared with Reinforcement Learning and means-end reasoning approaches. The system has been used in real-world applications such as assisting first responders, real-time traffic surveillance, and experiments with autonomous robots. It has been developed with a pragmatic mindset focusing on effective implementation of existing theory.
matsciml
The Open MatSci ML Toolkit is a flexible framework for machine learning in materials science. It provides a unified interface to a variety of materials science datasets, as well as a set of tools for data preprocessing, model training, and evaluation. The toolkit is designed to be easy to use for both beginners and experienced researchers, and it can be used to train models for a wide range of tasks, including property prediction, materials discovery, and materials design.
merlin
Merlin is a groundbreaking model capable of generating natural language responses intricately linked with object trajectories of multiple images. It excels in predicting and reasoning about future events based on initial observations, showcasing unprecedented capability in future prediction and reasoning. Merlin achieves state-of-the-art performance on the Future Reasoning Benchmark and multiple existing multimodal language models benchmarks, demonstrating powerful multi-modal general ability and foresight minds.

fuse-med-ml
FuseMedML is a Python framework designed to accelerate machine learning-based discovery in the medical field by promoting code reuse. It provides a flexible design concept where data is stored in a nested dictionary, allowing easy handling of multi-modality information. The framework includes components for creating custom models, loss functions, metrics, and data processing operators. Additionally, FuseMedML offers 'batteries included' key components such as fuse.data for data processing, fuse.eval for model evaluation, and fuse.dl for reusable deep learning components. It supports PyTorch and PyTorch Lightning libraries and encourages the creation of domain extensions for specific medical domains.
ml-engineering
This repository provides a comprehensive collection of methodologies, tools, and step-by-step instructions for successful training of large language models (LLMs) and multi-modal models. It is a technical resource suitable for LLM/VLM training engineers and operators, containing numerous scripts and copy-n-paste commands to facilitate quick problem-solving. The repository is an ongoing compilation of the author's experiences training BLOOM-176B and IDEFICS-80B models, and currently focuses on the development and training of Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) models at Contextual.AI. The content is organized into six parts: Insights, Hardware, Orchestration, Training, Development, and Miscellaneous. It includes key comparison tables for high-end accelerators and networks, as well as shortcuts to frequently needed tools and guides. The repository is open to contributions and discussions, and is licensed under Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International.
aligner
Aligner is a model-agnostic alignment tool designed to efficiently correct responses from large language models. It redistributes initial answers to align with human intentions, improving performance across various LLMs. The tool can be applied with minimal training, enhancing upstream models and reducing hallucination. Aligner's 'copy and correct' method preserves the base structure while enhancing responses. It achieves significant performance improvements in helpfulness, harmlessness, and honesty dimensions, with notable success in boosting Win Rates on evaluation leaderboards.
For similar tasks

AixLib
AixLib is a Modelica model library for building performance simulations developed at RWTH Aachen University, E.ON Energy Research Center, Institute for Energy Efficient Buildings and Indoor Climate (EBC) in Aachen, Germany. It contains models of HVAC systems as well as high and reduced order building models. The name AixLib is derived from the city's French name Aix-la-Chapelle, following a local tradition. The library is continuously improved and offers citable papers for reference. Contributions to the development can be made via Issues section or Pull Requests, following the workflow described in the Wiki. AixLib is released under a 3-clause BSD-license with acknowledgements to public funded projects and financial support by BMWi (German Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy).
For similar jobs

AixLib
AixLib is a Modelica model library for building performance simulations developed at RWTH Aachen University, E.ON Energy Research Center, Institute for Energy Efficient Buildings and Indoor Climate (EBC) in Aachen, Germany. It contains models of HVAC systems as well as high and reduced order building models. The name AixLib is derived from the city's French name Aix-la-Chapelle, following a local tradition. The library is continuously improved and offers citable papers for reference. Contributions to the development can be made via Issues section or Pull Requests, following the workflow described in the Wiki. AixLib is released under a 3-clause BSD-license with acknowledgements to public funded projects and financial support by BMWi (German Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy).

sorrentum
Sorrentum is an open-source project that aims to combine open-source development, startups, and brilliant students to build machine learning, AI, and Web3 / DeFi protocols geared towards finance and economics. The project provides opportunities for internships, research assistantships, and development grants, as well as the chance to work on cutting-edge problems, learn about startups, write academic papers, and get internships and full-time positions at companies working on Sorrentum applications.
quivr
Quivr is a personal assistant powered by Generative AI, designed to be a second brain for users. It offers fast and efficient access to data, ensuring security and compatibility with various file formats. Quivr is open source and free to use, allowing users to share their brains publicly or keep them private. The marketplace feature enables users to share and utilize brains created by others, boosting productivity. Quivr's offline mode provides anytime, anywhere access to data. Key features include speed, security, OS compatibility, file compatibility, open source nature, public/private sharing options, a marketplace, and offline mode.
chatgpt-web
ChatGPT Web is a web application that provides access to the ChatGPT API. It offers two non-official methods to interact with ChatGPT: through the ChatGPTAPI (using the `gpt-3.5-turbo-0301` model) or through the ChatGPTUnofficialProxyAPI (using a web access token). The ChatGPTAPI method is more reliable but requires an OpenAI API key, while the ChatGPTUnofficialProxyAPI method is free but less reliable. The application includes features such as user registration and login, synchronization of conversation history, customization of API keys and sensitive words, and management of users and keys. It also provides a user interface for interacting with ChatGPT and supports multiple languages and themes.
speechless
Speechless.AI is committed to integrating the superior language processing and deep reasoning capabilities of large language models into practical business applications. By enhancing the model's language understanding, knowledge accumulation, and text creation abilities, and introducing long-term memory, external tool integration, and local deployment, our aim is to establish an intelligent collaborative partner that can independently interact, continuously evolve, and closely align with various business scenarios.
extractor
Extractor is an AI-powered data extraction library for Laravel that leverages OpenAI's capabilities to effortlessly extract structured data from various sources, including images, PDFs, and emails. It features a convenient wrapper around OpenAI Chat and Completion endpoints, supports multiple input formats, includes a flexible Field Extractor for arbitrary data extraction, and integrates with Textract for OCR functionality. Extractor utilizes JSON Mode from the latest GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 models, providing accurate and efficient data extraction.

duckduckgpt
DuckDuckGPT brings the magic of ChatGPT to DDG (powered by GPT-4!). DuckDuckGPT is a browser extension that allows you to use ChatGPT within DuckDuckGo. This means you can ask ChatGPT questions, get help with tasks, and generate creative content, all without leaving DuckDuckGo. DuckDuckGPT is easy to use. Once you have installed the extension, simply type your question into the DuckDuckGo search bar and hit enter. ChatGPT will then generate a response that will appear below the search results. DuckDuckGPT is a powerful tool that can help you with a wide variety of tasks. Here are just a few examples of what you can use it for: * Get help with research * Write essays and other creative content * Translate languages * Get coding help * Answer trivia questions * And much more! DuckDuckGPT is still in development, but it is already a very powerful tool. As GPT-4 continues to improve, DuckDuckGPT will only get better. So if you are looking for a way to make your DuckDuckGo searches more productive, be sure to give DuckDuckGPT a try.
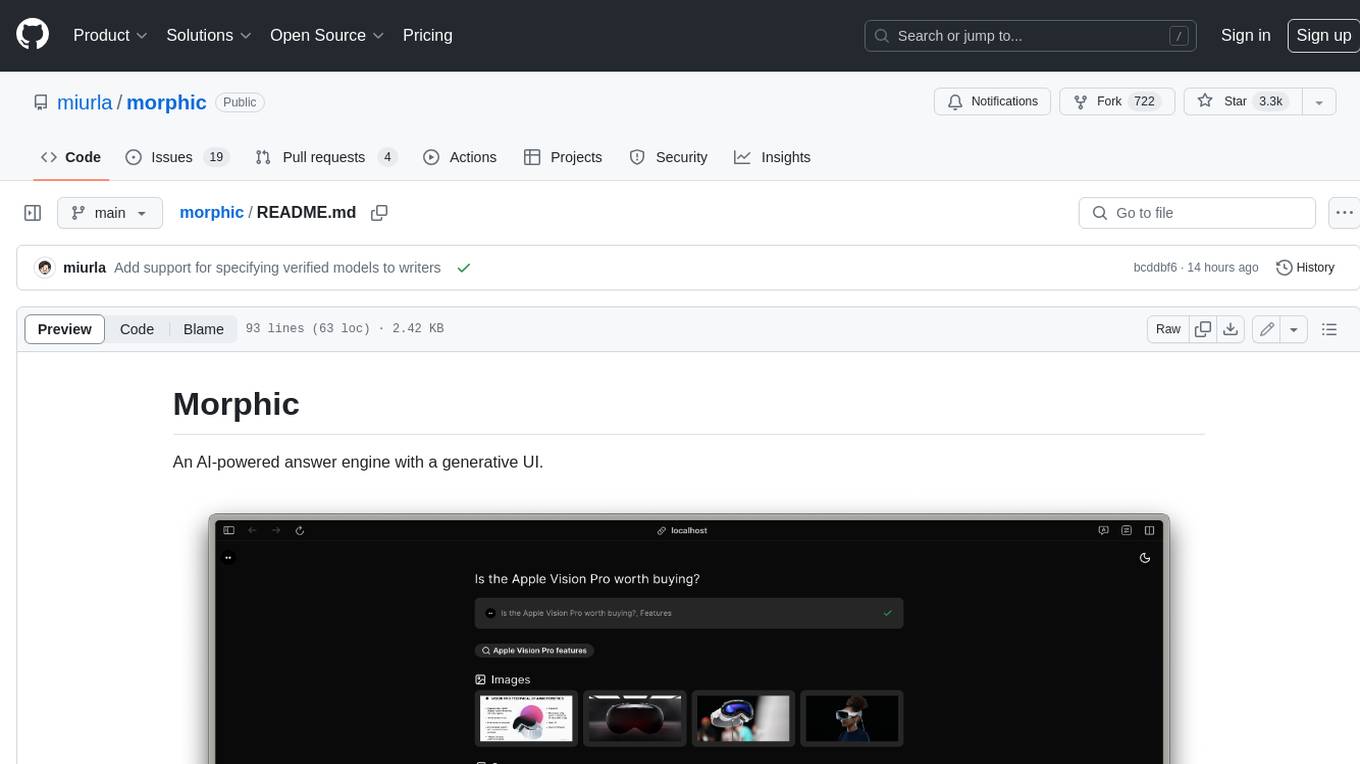
morphic
Morphic is an AI-powered answer engine with a generative UI. It utilizes a stack of Next.js, Vercel AI SDK, OpenAI, Tavily AI, shadcn/ui, Radix UI, and Tailwind CSS. To get started, fork and clone the repo, install dependencies, fill out secrets in the .env.local file, and run the app locally using 'bun dev'. You can also deploy your own live version of Morphic with Vercel. Verified models that can be specified to writers include Groq, LLaMA3 8b, and LLaMA3 70b.
