
1.5-Pints
A compact LLM pretrained in 9 days by using high quality data
Stars: 230

1.5-Pints is a repository that provides a recipe to pre-train models in 9 days, aiming to create AI assistants comparable to Apple OpenELM and Microsoft Phi. It includes model architecture, training scripts, and utilities for 1.5-Pints and 0.12-Pint developed by Pints.AI. The initiative encourages replication, experimentation, and open-source development of Pint by sharing the model's codebase and architecture. The repository offers installation instructions, dataset preparation scripts, model training guidelines, and tools for model evaluation and usage. Users can also find information on finetuning models, converting lit models to HuggingFace models, and running Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) post-finetuning. Additionally, the repository includes tests to ensure code modifications do not disrupt the existing functionality.
README:
A recipe to pre-train models in 9 days, to become comparable AI assistants to the likes of Apple OpenELM and Microsoft Phi.
This repo contains the model architecture, training scripts, and utilities of 1.5-Pints and 0.12-Pint, developed by Pints.AI. By providing access to the model's codebase and architecture, this initiative seeks to facilitate the replication, experimentation, and further open-source development of Pint.
Join us at Discord: https://discord.com/invite/RSHk22Z29j
@misc{tan202415pintstechnicalreportpretraining,
title={1.5-Pints Technical Report: Pretraining in Days, Not Months -- Your Language Model Thrives on Quality Data},
author={Calvin Tan and Jerome Wang},
year={2024},
eprint={2408.03506},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2408.03506},
}Typically just stick to Ubuntu 22.04 LTS x86-64. Debian 12 has been tested to work as well.
GOTCHA1: Dont use arm64 / aarch64. xformers does not support ARM64 processors.
GOTCHA2: We should not install system-wide CUDA using apt. It is best to constrain the CUDA installation to within the conda environment, so that different projects can use different CUDA versions.
wget https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh && \
sh Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.shSource just to be sure conda cli will be available:
source ~/.bashrcSometimes if you still face conda: command cannot be found, you can find the installation and source it:
Note: This path assumes you took up the default installation settings. Otherwise, find where you installed it.
source ~/miniconda3/etc/profile.d/conda.shgit clone https://github.com/Pints-AI/1.5-Pints.git && \
cd 1.5-Pintsconda create --prefix ./.conda python=3.10 && \
conda activate ./.condaNote: Stick to Python 3.10. 3.12 breaks a lot of things as of now (23 Feb 2024), and 3.11 has not been tested.
conda install nvidia/label/cuda-12.1.1::cuda-toolkitpip install -r requirements.txt && \
pip install flash-attn --no-build-isolation && \
pip install -r pretrain/requirements.txtNote: The pip install for dropout_layer_norm can take up ~30 minutes to build depending on the machine.
curl -s https://packagecloud.io/install/repositories/github/git-lfs/script.deb.sh | sudo bash
sudo apt-get install git-lfscd /path/to/dataset_dir
git clone https://huggingface.co/datasets/pints-ai/Expository-Prose-V1python -m prepare_dataset.standard_parquet \
--source_path /path/to/dataset_dir \
--train_val_split_ratio 0.9 \
--max_cores 60 \
--destination_path /path/to/output_dirRefer to prepare_dataset folder for the dataset preparation scripts.
max_cores is not required if you don't OOM on high core machines.
fabric run model \
--accelerator=cuda \
--devices=8 \
pretrain/main.py \
--data_dir data/output \
--out_dir ../1.5-pints \
--gpus 8 \
--global_batch_size 512 \
--learning_rate 4e-4 \
--micro_batch_size 8 \
--max_step 96180 \
--warmup_steps 2000 \
--weight_decay 0.1 \
--beta1 0.9 \
--beta2 0.95 \
--grad_clip 1.0 \
--min_lr 4e-5 \
--model_name 1.5-Pints-2k \
--wandb_name <run_name> \
--wandb_project <project_name> \
--tokenizer_dir tokenizer/pintsNote1: --devices and --gpus must be the same. See pretrain.py's setup arguments for all parameters that you can adjust.
Note2: Select the architecture (layers/dimensions/heads) configuration using --model_name. This must be in lit_gpt/config.py.
Note3: Select a micro_batch_size to optimize GPU memory. So far once started, it remains stable, even during validation. micro_batch_size need not be a number that batch_size is divisible by. batch_size is derived from global_batch_size / devices.
Note4: Modify TRAIN_DATA_CONFIG in pretrain/main.py to decide on the datasets used for training. Ensure that the dataset is prepared beforehand.
If you are asked for the wandb API key, you can login and get from: https://wandb.ai/authorize
cd finetune && \
pip install -r requirements.txtBefore you start finetuning, you need to convert the pretrain weights:
python convert/convert_pretrained_checkpoint.py --checkpoint_dir path/to/checkpoint --output_dir path/to/outputlightning run \
--accelerator=cuda \
--devices=8 \
finetune/full.py \
--checkpoint_dir <path to lit_model.pth> \
--out_dir ~/1.5-pints-2k/ep2/step-00045000/finetuned \
--model_name 1.5-Pints-2k \
--gpus 8 \
--train.save_interval 6000 \
--train.global_batch_size 512 \
--train.micro_batch_size 8 \
--train.lr_warmup_steps 1125 \
--train.epoch 5 \
--train.learning_rate 2e-5 \
--train.max_seq_length 2048 \
--train.beta1 0.9 \
--train.beta2 0.95 \
--train.weight_decay 0.1 \
--logger_name wandb \
--tokenizer_dir tokenizer/pints \
--known_data_max_seq_length 2048 \
--wandb_project <project name>DPO is opted for use post-finetuning. See here for the execution process.
See here
python convert_lit_to_hf.py \
--checkpoint_name lit_model.pth \
--directory ../models/1.5-pints \
--model_name 1.5-Pints-2k \
--output_config=True \
--safetensors=True \
--delete_pytorch_model=TrueNote: We found better success using the safetensors file. Therefore it's recommended to use it instead of pytorch_model.bin.
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("/model/path")
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("/model/path")
prompt = '''<|im_start|>user
Do not go gentle into that good night.<|im_end|>
<|im_start|>assistant
'''
tokenized_input = tokenizer.encode(prompt)
tokenized_output = model.generate(tokenized_input)
print(tokenizer.decode(tokenized_output))This codebase comes with tests. If you need to make modifications, you can run the tests to ensure your modifications did not disrupt the existing code.
Install test requirements:
pip install -r requirements.test.txtRun pytest:
python -m pytest --verboseFor Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for 1.5-Pints
Similar Open Source Tools

1.5-Pints
1.5-Pints is a repository that provides a recipe to pre-train models in 9 days, aiming to create AI assistants comparable to Apple OpenELM and Microsoft Phi. It includes model architecture, training scripts, and utilities for 1.5-Pints and 0.12-Pint developed by Pints.AI. The initiative encourages replication, experimentation, and open-source development of Pint by sharing the model's codebase and architecture. The repository offers installation instructions, dataset preparation scripts, model training guidelines, and tools for model evaluation and usage. Users can also find information on finetuning models, converting lit models to HuggingFace models, and running Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) post-finetuning. Additionally, the repository includes tests to ensure code modifications do not disrupt the existing functionality.
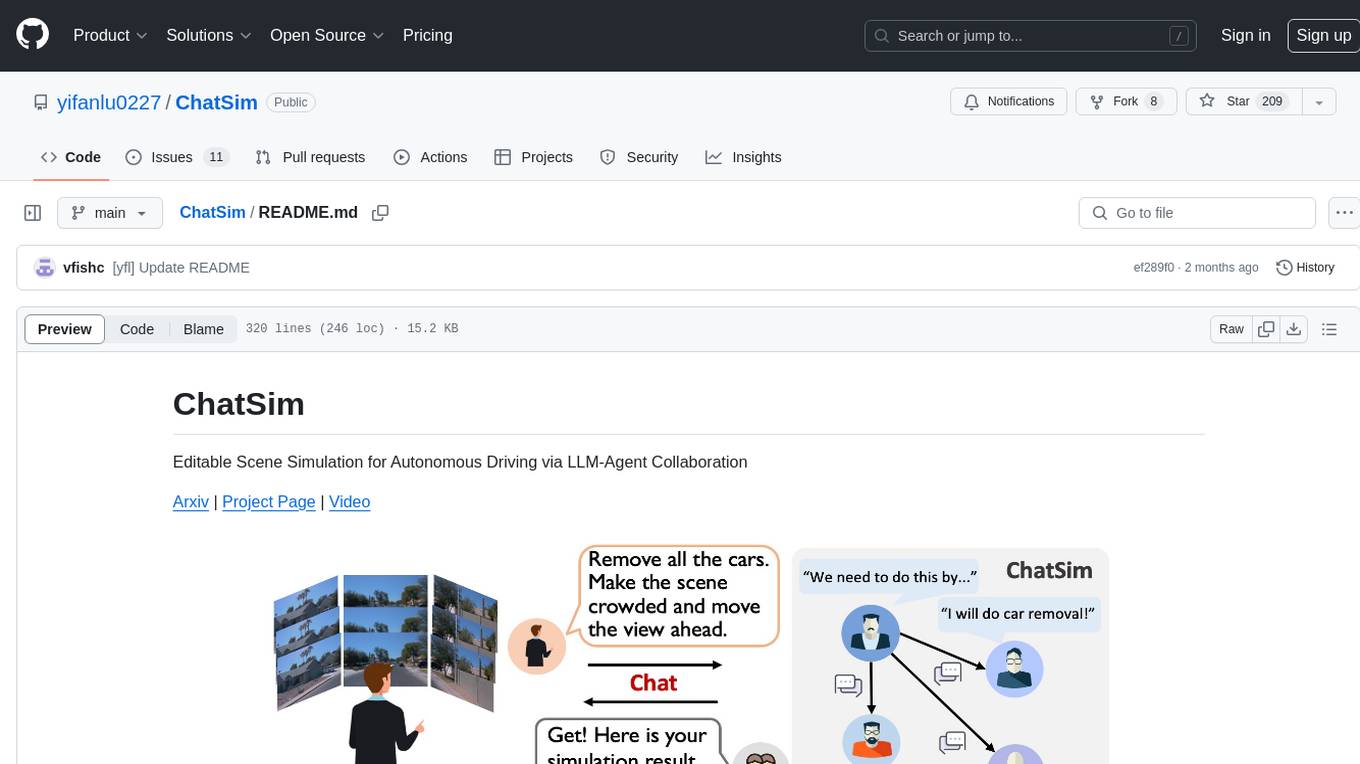
ChatSim
ChatSim is a tool designed for editable scene simulation for autonomous driving via LLM-Agent collaboration. It provides functionalities for setting up the environment, installing necessary dependencies like McNeRF and Inpainting tools, and preparing data for simulation. Users can train models, simulate scenes, and track trajectories for smoother and more realistic results. The tool integrates with Blender software and offers options for training McNeRF models and McLight's skydome estimation network. It also includes a trajectory tracking module for improved trajectory tracking. ChatSim aims to facilitate the simulation of autonomous driving scenarios with collaborative LLM-Agents.
air
Air is a live-reloading command line utility for developing Go applications. It provides colorful log output, customizable build or any command, support for excluding subdirectories, and allows watching new directories after Air started. Users can overwrite specific configuration from arguments and pass runtime arguments for running the built binary. Air can be installed via `go install`, `install.sh`, or `goblin.run`, and can also be used with Docker/Podman. It supports debugging, Docker Compose, and provides a Q&A section for common issues. The tool requires Go 1.16+ for development and welcomes pull requests. Air is released under the GNU General Public License v3.0.
llm-rankers
llm-rankers is a repository that provides implementations for Pointwise, Listwise, Pairwise, and Setwise Document Ranking using Large Language Models. It includes various methods for reranking documents retrieved by a first-stage retriever, such as BM25. The repository offers examples and code snippets for using LLMs to improve document ranking performance in information retrieval tasks. Additionally, it introduces a new setwise reranker called Rank-R1 with reasoning ability.

air
Air is a live-reloading command line utility for developing Go applications. It provides colorful log output, allows customization of build or any command, supports excluding subdirectories, and allows watching new directories after Air has started. Air can be installed via `go install`, `install.sh`, `goblin.run`, or Docker/Podman. To use Air, simply run `air` in your project root directory and leave it alone to focus on your code. Air has nothing to do with hot-deploy for production.
shell-pilot
Shell-pilot is a simple, lightweight shell script designed to interact with various AI models such as OpenAI, Ollama, Mistral AI, LocalAI, ZhipuAI, Anthropic, Moonshot, and Novita AI from the terminal. It enhances intelligent system management without any dependencies, offering features like setting up a local LLM repository, using official models and APIs, viewing history and session persistence, passing input prompts with pipe/redirector, listing available models, setting request parameters, generating and running commands in the terminal, easy configuration setup, system package version checking, and managing system aliases.
CosyVoice
CosyVoice is a tool designed for speech synthesis, offering pretrained models for zero-shot, sft, instruct inference. It provides a web demo for easy usage and supports advanced users with train and inference scripts. The tool can be deployed using grpc for service deployment. Users can download pretrained models and resources for immediate use or train their own models from scratch. CosyVoice is suitable for researchers, developers, linguists, AI engineers, and speech technology enthusiasts.
llm-detect-ai
This repository contains code and configurations for the LLM - Detect AI Generated Text competition. It includes setup instructions for hardware, software, dependencies, and datasets. The training section covers scripts and configurations for training LLM models, DeBERTa ranking models, and an embedding model. Text generation section details fine-tuning LLMs using the CLM objective on the PERSUADE corpus to generate student-like essays.
paxml
Pax is a framework to configure and run machine learning experiments on top of Jax.
cheating-based-prompt-engine
This is a vulnerability mining engine purely based on GPT, requiring no prior knowledge base, no fine-tuning, yet its effectiveness can overwhelmingly surpass most of the current related research. The core idea revolves around being task-driven, not question-driven, driven by prompts, not by code, and focused on prompt design, not model design. The essence is encapsulated in one word: deception. It is a type of code understanding logic vulnerability mining that fully stimulates the capabilities of GPT, suitable for real actual projects.
trickPrompt-engine
This repository contains a vulnerability mining engine based on GPT technology. The engine is designed to identify logic vulnerabilities in code by utilizing task-driven prompts. It does not require prior knowledge or fine-tuning and focuses on prompt design rather than model design. The tool is effective in real-world projects and should not be used for academic vulnerability testing. It supports scanning projects in various languages, with current support for Solidity. The engine is configured through prompts and environment settings, enabling users to scan for vulnerabilities in their codebase. Future updates aim to optimize code structure, add more language support, and enhance usability through command line mode. The tool has received a significant audit bounty of $50,000+ as of May 2024.
ethereum-etl-airflow
This repository contains Airflow DAGs for extracting, transforming, and loading (ETL) data from the Ethereum blockchain into BigQuery. The DAGs use the Google Cloud Platform (GCP) services, including BigQuery, Cloud Storage, and Cloud Composer, to automate the ETL process. The repository also includes scripts for setting up the GCP environment and running the DAGs locally.
friendly-stable-audio-tools
This repository is a refactored and updated version of `stable-audio-tools`, an open-source code for audio/music generative models originally by Stability AI. It contains refactored codes for improved readability and usability, useful scripts for evaluating and playing with trained models, and instructions on how to train models such as `Stable Audio 2.0`. The repository does not contain any pretrained checkpoints. Requirements include PyTorch 2.0 or later for Flash Attention support and Python 3.8.10 or later for development. The repository provides guidance on installing, building a training environment using Docker or Singularity, logging with Weights & Biases, training configurations, and stages for VAE-GAN and Diffusion Transformer (DiT) training.
k8sgpt
K8sGPT is a tool for scanning your Kubernetes clusters, diagnosing, and triaging issues in simple English. It has SRE experience codified into its analyzers and helps to pull out the most relevant information to enrich it with AI.
jupyter-quant
Jupyter Quant is a dockerized environment tailored for quantitative research, equipped with essential tools like statsmodels, pymc, arch, py_vollib, zipline-reloaded, PyPortfolioOpt, numpy, pandas, sci-py, scikit-learn, yellowbricks, shap, optuna, and more. It provides Interactive Broker connectivity via ib_async and includes major Python packages for statistical and time series analysis. The image is optimized for size, includes jedi language server, jupyterlab-lsp, and common command line utilities. Users can install new packages with sudo, leverage apt cache, and bring their own dot files and SSH keys. The tool is designed for ephemeral containers, ensuring data persistence and flexibility for quantitative analysis tasks.
DeepPavlov
DeepPavlov is an open-source conversational AI library built on PyTorch. It is designed for the development of production-ready chatbots and complex conversational systems, as well as for research in the area of NLP and dialog systems. The library offers a wide range of models for tasks such as Named Entity Recognition, Intent/Sentence Classification, Question Answering, Sentence Similarity/Ranking, Syntactic Parsing, and more. DeepPavlov also provides embeddings like BERT, ELMo, and FastText for various languages, along with AutoML capabilities and integrations with REST API, Socket API, and Amazon AWS.
For similar tasks

1.5-Pints
1.5-Pints is a repository that provides a recipe to pre-train models in 9 days, aiming to create AI assistants comparable to Apple OpenELM and Microsoft Phi. It includes model architecture, training scripts, and utilities for 1.5-Pints and 0.12-Pint developed by Pints.AI. The initiative encourages replication, experimentation, and open-source development of Pint by sharing the model's codebase and architecture. The repository offers installation instructions, dataset preparation scripts, model training guidelines, and tools for model evaluation and usage. Users can also find information on finetuning models, converting lit models to HuggingFace models, and running Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) post-finetuning. Additionally, the repository includes tests to ensure code modifications do not disrupt the existing functionality.
ComputerGYM
Optexity is a framework for training foundation models using human demonstrations of computer tasks. It enables recording, processing, and utilizing demonstrations to train AI agents for web-based tasks. The tool also plans to incorporate training through self-exploration, software documentations, and YouTube videos in the future.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.

