langtest
Deliver safe & effective language models
Stars: 539

Langtest is a tool designed for testing and analyzing programming languages. It provides a platform for users to write code snippets in various languages and run them to see the output. The tool supports multiple programming languages and offers features like syntax highlighting, code execution, and result comparison. Users can use Langtest to quickly test code snippets, compare language syntax, and evaluate language performance. It is a useful tool for students, developers, and language enthusiasts to experiment with different programming languages in a convenient and efficient manner.
README:
Project's Website • Key Features • How To Use • Benchmark Datasets • Community Support • Contributing • Mission • License
Take a look at our official page for user documentation and examples: langtest.org
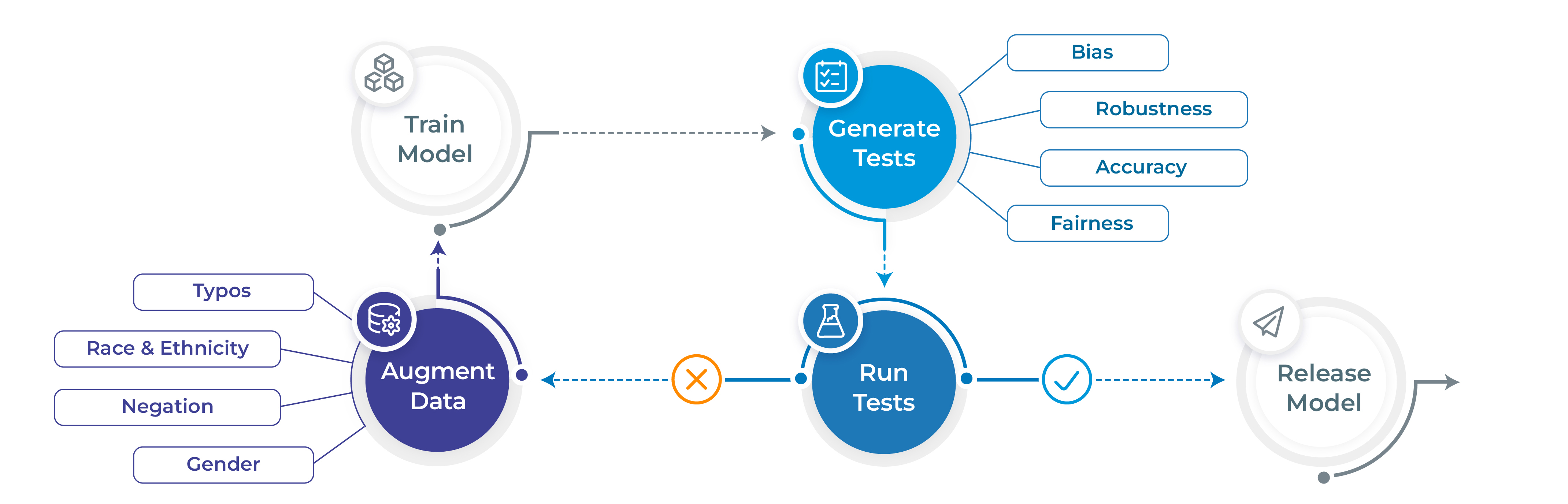
- Generate and execute more than 60 distinct types of tests only with 1 line of code
- Test all aspects of model quality: robustness, bias, representation, fairness and accuracy.
- Automatically augment training data based on test results (for select models)
- Support for popular NLP frameworks for NER, Translation and Text-Classifcation: Spark NLP, Hugging Face & Transformers.
- Support for testing LLMS ( OpenAI, Cohere, AI21, Hugging Face Inference API and Azure-OpenAI LLMs) for question answering, toxicity, clinical-tests, legal-support, factuality, sycophancy, summarization and other popular tests.
LangTest comes with different datasets to test your models, covering a wide range of use cases and evaluation scenarios. You can explore all the benchmark datasets available here, each meticulously curated to challenge and enhance your language models. Whether you're focused on Question-Answering, text summarization etc, LangTest ensures you have the right data to push your models to their limits and achieve peak performance in diverse linguistic tasks.
# Install langtest
!pip install langtest[transformers]
# Import and create a Harness object
from langtest import Harness
h = Harness(task='ner', model={"model":'dslim/bert-base-NER', "hub":'huggingface'})
# Generate test cases, run them and view a report
h.generate().run().report()Note For more extended examples of usage and documentation, head over to langtest.org
You can check out the following LangTest articles:
| Blog | Description |
|---|---|
| Automatically Testing for Demographic Bias in Clinical Treatment Plans Generated by Large Language Models | Helps in understanding and testing demographic bias in clinical treatment plans generated by LLM. |
| LangTest: Unveiling & Fixing Biases with End-to-End NLP Pipelines | The end-to-end language pipeline in LangTest empowers NLP practitioners to tackle biases in language models with a comprehensive, data-driven, and iterative approach. |
| Beyond Accuracy: Robustness Testing of Named Entity Recognition Models with LangTest | While accuracy is undoubtedly crucial, robustness testing takes natural language processing (NLP) models evaluation to the next level by ensuring that models can perform reliably and consistently across a wide array of real-world conditions. |
| Elevate Your NLP Models with Automated Data Augmentation for Enhanced Performance | In this article, we discuss how automated data augmentation may supercharge your NLP models and improve their performance and how we do that using LangTest. |
| Mitigating Gender-Occupational Stereotypes in AI: Evaluating Models with the Wino Bias Test through Langtest Library | In this article, we discuss how we can test the "Wino Bias” using LangTest. It specifically refers to testing biases arising from gender-occupational stereotypes. |
| Automating Responsible AI: Integrating Hugging Face and LangTest for More Robust Models | In this article, we have explored the integration between Hugging Face, your go-to source for state-of-the-art NLP models and datasets, and LangTest, your NLP pipeline’s secret weapon for testing and optimization. |
| Detecting and Evaluating Sycophancy Bias: An Analysis of LLM and AI Solutions | In this blog post, we discuss the pervasive issue of sycophantic AI behavior and the challenges it presents in the world of artificial intelligence. We explore how language models sometimes prioritize agreement over authenticity, hindering meaningful and unbiased conversations. Furthermore, we unveil a potential game-changing solution to this problem, synthetic data, which promises to revolutionize the way AI companions engage in discussions, making them more reliable and accurate across various real-world conditions. |
| Unmasking Language Model Sensitivity in Negation and Toxicity Evaluations | In this blog post, we delve into Language Model Sensitivity, examining how models handle negations and toxicity in language. Through these tests, we gain insights into the models' adaptability and responsiveness, emphasizing the continuous need for improvement in NLP models. |
| Unveiling Bias in Language Models: Gender, Race, Disability, and Socioeconomic Perspectives | In this blog post, we explore bias in Language Models, focusing on gender, race, disability, and socioeconomic factors. We assess this bias using the CrowS-Pairs dataset, designed to measure stereotypical biases. To address these biases, we discuss the importance of tools like LangTest in promoting fairness in NLP systems. |
| Unmasking the Biases Within AI: How Gender, Ethnicity, Religion, and Economics Shape NLP and Beyond | In this blog post, we tackle AI bias on how Gender, Ethnicity, Religion, and Economics Shape NLP systems. We discussed strategies for reducing bias and promoting fairness in AI systems. |
| Evaluating Large Language Models on Gender-Occupational Stereotypes Using the Wino Bias Test | In this blog post, we dive into testing the WinoBias dataset on LLMs, examining language models’ handling of gender and occupational roles, evaluation metrics, and the wider implications. Let’s explore the evaluation of language models with LangTest on the WinoBias dataset and confront the challenges of addressing bias in AI. |
| Streamlining ML Workflows: Integrating MLFlow Tracking with LangTest for Enhanced Model Evaluations | In this blog post, we dive into the growing need for transparent, systematic, and comprehensive tracking of models. Enter MLFlow and LangTest: two tools that, when combined, create a revolutionary approach to ML development. |
| Testing the Question Answering Capabilities of Large Language Models | In this blog post, we dive into enhancing the QA evaluation capabilities using LangTest library. Explore about different evaluation methods that LangTest offers to address the complexities of evaluating Question Answering (QA) tasks. |
| Evaluating Stereotype Bias with LangTest | In this blog post, we are focusing on using the StereoSet dataset to assess bias related to gender, profession, and race. |
| Testing the Robustness of LSTM-Based Sentiment Analysis Models | Explore the robustness of custom models with LangTest Insights. |
| LangTest Insights: A Deep Dive into LLM Robustness on OpenBookQA | Explore the robustness of Language Models (LLMs) on the OpenBookQA dataset with LangTest Insights. |
| LangTest: A Secret Weapon for Improving the Robustness of Your Transformers Language Models | Explore the robustness of Transformers Language Models with LangTest Insights. |
| Mastering Model Evaluation: Introducing the Comprehensive Ranking & Leaderboard System in LangTest | The Model Ranking & Leaderboard system by John Snow Labs' LangTest offers a systematic approach to evaluating AI models with comprehensive ranking, historical comparisons, and dataset-specific insights, empowering researchers and data scientists to make data-driven decisions on model performance. |
| Evaluating Long-Form Responses with Prometheus-Eval and Langtest | Prometheus-Eval and LangTest unite to offer an open-source, reliable, and cost-effective solution for evaluating long-form responses, combining Prometheus's GPT-4-level performance and LangTest's robust testing framework to provide detailed, interpretable feedback and high accuracy in assessments. |
| Ensuring Precision of LLMs in Medical Domain: The Challenge of Drug Name Swapping | Accurate drug name identification is crucial for patient safety. Testing GPT-4o with LangTest's drug_generic_to_brand conversion test revealed potential errors in predicting drug names when brand names are replaced by ingredients, highlighting the need for ongoing refinement and rigorous testing to ensure medical LLM accuracy and reliability. |
Note To check all blogs, head over to Blogs
-
Slack For live discussion with the LangTest community, join the
#langtestchannel - GitHub For bug reports, feature requests, and contributions
- Discussions To engage with other community members, share ideas, and show off how you use LangTest!
While there is a lot of talk about the need to train AI models that are safe, robust, and fair - few tools have been made available to data scientists to meet these goals. As a result, the front line of NLP models in production systems reflects a sorry state of affairs.
We propose here an early stage open-source community project that aims to fill this gap, and would love for you to join us on this mission. We aim to build on the foundation laid by previous research such as Ribeiro et al. (2020), Song et al. (2020), Parrish et al. (2021), van Aken et al. (2021) and many others.
John Snow Labs has a full development team allocated to the project and is committed to improving the library for years, as we do with other open-source libraries. Expect frequent releases with new test types, tasks, languages, and platforms to be added regularly. We look forward to working together to make safe, reliable, and responsible NLP an everyday reality.
Note For usage and documentation, head over to langtest.org
We welcome all sorts of contributions:
A detailed overview of contributing can be found in the contributing guide.
If you are looking to start working with the LangTest codebase, navigate to the GitHub "issues" tab and start looking through interesting issues. There are a number of issues listed under where you could start out. Or maybe through using LangTest you have an idea of your own or are looking for something in the documentation and thinking ‘This can be improved’...you can do something about it!
Feel free to ask questions on the Q&A discussions.
As contributors and maintainers to this project, you are expected to abide by LangTest's code of conduct. More information can be found at: Contributor Code of Conduct
We have published a paper that you can cite for the LangTest library:
@article{nazir2024langtest,
title={LangTest: A comprehensive evaluation library for custom LLM and NLP models},
author={Arshaan Nazir, Thadaka Kalyan Chakravarthy, David Amore Cecchini, Rakshit Khajuria, Prikshit Sharma, Ali Tarik Mirik, Veysel Kocaman and David Talby},
journal={Software Impacts},
pages={100619},
year={2024},
publisher={Elsevier}
}We would like to acknowledge all contributors of this open-source community project.
LangTest is released under the Apache License 2.0, which guarantees commercial use, modification, distribution, patent use, private use and sets limitations on trademark use, liability and warranty.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for langtest
Similar Open Source Tools

langtest
Langtest is a tool designed for testing and analyzing programming languages. It provides a platform for users to write code snippets in various languages and run them to see the output. The tool supports multiple programming languages and offers features like syntax highlighting, code execution, and result comparison. Users can use Langtest to quickly test code snippets, compare language syntax, and evaluate language performance. It is a useful tool for students, developers, and language enthusiasts to experiment with different programming languages in a convenient and efficient manner.
coderunner
Coderunner is a versatile tool designed for running code snippets in various programming languages. It provides an interactive environment for testing and debugging code without the need for a full-fledged IDE. With support for multiple languages and quick execution times, Coderunner is ideal for beginners learning to code, experienced developers prototyping algorithms, educators creating coding exercises, interview candidates practicing coding challenges, and professionals testing small code snippets.
nanocoder
Nanocoder is a versatile code editor designed for beginners and experienced programmers alike. It provides a user-friendly interface with features such as syntax highlighting, code completion, and error checking. With Nanocoder, you can easily write and debug code in various programming languages, making it an ideal tool for learning, practicing, and developing software projects. Whether you are a student, hobbyist, or professional developer, Nanocoder offers a seamless coding experience to boost your productivity and creativity.
evalica
Evalica is a powerful tool for evaluating code quality and performance in software projects. It provides detailed insights and metrics to help developers identify areas for improvement and optimize their code. With support for multiple programming languages and frameworks, Evalica offers a comprehensive solution for code analysis and optimization. Whether you are a beginner looking to learn best practices or an experienced developer aiming to enhance your code quality, Evalica is the perfect tool for you.
DelhiLM
DelhiLM is a natural language processing tool for building and training language models. It provides a user-friendly interface for text processing tasks such as tokenization, lemmatization, and language model training. With DelhiLM, users can easily preprocess text data and train custom language models for various NLP applications. The tool supports different languages and allows for fine-tuning pre-trained models to suit specific needs. DelhiLM is designed to be flexible, efficient, and easy to use for both beginners and experienced NLP practitioners.
mdream
Mdream is a lightweight and user-friendly markdown editor designed for developers and writers. It provides a simple and intuitive interface for creating and editing markdown files with real-time preview. The tool offers syntax highlighting, markdown formatting options, and the ability to export files in various formats. Mdream aims to streamline the writing process and enhance productivity for individuals working with markdown documents.
promptl
Promptl is a versatile command-line tool designed to streamline the process of creating and managing prompts for user input in various programming projects. It offers a simple and efficient way to prompt users for information, validate their input, and handle different scenarios based on their responses. With Promptl, developers can easily integrate interactive prompts into their scripts, applications, and automation workflows, enhancing user experience and improving overall usability. The tool provides a range of customization options and features, making it suitable for a wide range of use cases across different programming languages and environments.
BentoVLLM
BentoVLLM is an example project demonstrating how to serve and deploy open-source Large Language Models using vLLM, a high-throughput and memory-efficient inference engine. It provides a basis for advanced code customization, such as custom models, inference logic, or vLLM options. The project allows for simple LLM hosting with OpenAI compatible endpoints without the need to write any code. Users can interact with the server using Swagger UI or other methods, and the service can be deployed to BentoCloud for better management and scalability. Additionally, the repository includes integration examples for different LLM models and tools.
LocalLLMClient
LocalLLMClient is a Swift package designed to interact with local Large Language Models (LLMs) on Apple platforms. It supports GGUF, MLX models, and the FoundationModels framework, providing streaming API, multimodal capabilities, and tool calling functionalities. Users can easily integrate this tool to work with various models for text generation and processing. The package also includes advanced features for low-level API control and multimodal image processing. LocalLLMClient is experimental and subject to API changes, offering support for iOS, macOS, and Linux platforms.
VectorCode
VectorCode is a code repository indexing tool that helps users write better prompts for coding LLMs by providing information about the code repository being worked on. It includes a neovim plugin and supports multiple embedding engines. The tool enhances completion results by providing project context and improves understanding of close-source or cutting edge projects.
verl-tool
The verl-tool is a versatile command-line utility designed to streamline various tasks related to version control and code management. It provides a simple yet powerful interface for managing branches, merging changes, resolving conflicts, and more. With verl-tool, users can easily track changes, collaborate with team members, and ensure code quality throughout the development process. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced developer, verl-tool offers a seamless experience for version control operations.

LightLLM
LightLLM is a lightweight library for linear and logistic regression models. It provides a simple and efficient way to train and deploy machine learning models for regression tasks. The library is designed to be easy to use and integrate into existing projects, making it suitable for both beginners and experienced data scientists. With LightLLM, users can quickly build and evaluate regression models using a variety of algorithms and hyperparameters. The library also supports feature engineering and model interpretation, allowing users to gain insights from their data and make informed decisions based on the model predictions.

SpecForge
SpecForge is a powerful tool for generating API specifications from code. It helps developers to easily create and maintain accurate API documentation by extracting information directly from the codebase. With SpecForge, users can streamline the process of documenting APIs, ensuring consistency and reducing manual effort. The tool supports various programming languages and frameworks, making it versatile and adaptable to different development environments. By automating the generation of API specifications, SpecForge enhances collaboration between developers and stakeholders, improving overall project efficiency and quality.
nvim-aider
Nvim-aider is a plugin for Neovim that provides additional functionality and key mappings to enhance the user's editing experience. It offers features such as code navigation, quick access to commonly used commands, and improved text manipulation tools. With Nvim-aider, users can streamline their workflow and increase productivity while working with Neovim.
vivaria
Vivaria is a web application tool designed for running evaluations and conducting agent elicitation research. Users can interact with Vivaria using a web UI and a command-line interface. It allows users to start task environments based on METR Task Standard definitions, run AI agents, perform agent elicitation research, view API requests and responses, add tags and comments to runs, store results in a PostgreSQL database, sync data to Airtable, test prompts against LLMs, and authenticate using Auth0.
ai21-python
The AI21 Labs Python SDK is a comprehensive tool for interacting with the AI21 API. It provides functionalities for chat completions, conversational RAG, token counting, error handling, and support for various cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Vertex. The SDK offers both synchronous and asynchronous usage, along with detailed examples and documentation. Users can quickly get started with the SDK to leverage AI21's powerful models for various natural language processing tasks.
For similar tasks
Awesome-LLM4EDA
LLM4EDA is a repository dedicated to showcasing the emerging progress in utilizing Large Language Models for Electronic Design Automation. The repository includes resources, papers, and tools that leverage LLMs to solve problems in EDA. It covers a wide range of applications such as knowledge acquisition, code generation, code analysis, verification, and large circuit models. The goal is to provide a comprehensive understanding of how LLMs can revolutionize the EDA industry by offering innovative solutions and new interaction paradigms.
DeGPT
DeGPT is a tool designed to optimize decompiler output using Large Language Models (LLM). It requires manual installation of specific packages and setting up API key for OpenAI. The tool provides functionality to perform optimization on decompiler output by running specific scripts.
code2prompt
Code2Prompt is a powerful command-line tool that generates comprehensive prompts from codebases, designed to streamline interactions between developers and Large Language Models (LLMs) for code analysis, documentation, and improvement tasks. It bridges the gap between codebases and LLMs by converting projects into AI-friendly prompts, enabling users to leverage AI for various software development tasks. The tool offers features like holistic codebase representation, intelligent source tree generation, customizable prompt templates, smart token management, Gitignore integration, flexible file handling, clipboard-ready output, multiple output options, and enhanced code readability.
SinkFinder
SinkFinder + LLM is a closed-source semi-automatic vulnerability discovery tool that performs static code analysis on jar/war/zip files. It enhances the capability of LLM large models to verify path reachability and assess the trustworthiness score of the path based on the contextual code environment. Users can customize class and jar exclusions, depth of recursive search, and other parameters through command-line arguments. The tool generates rule.json configuration file after each run and requires configuration of the DASHSCOPE_API_KEY for LLM capabilities. The tool provides detailed logs on high-risk paths, LLM results, and other findings. Rules.json file contains sink rules for various vulnerability types with severity levels and corresponding sink methods.
open-repo-wiki
OpenRepoWiki is a tool designed to automatically generate a comprehensive wiki page for any GitHub repository. It simplifies the process of understanding the purpose, functionality, and core components of a repository by analyzing its code structure, identifying key files and functions, and providing explanations. The tool aims to assist individuals who want to learn how to build various projects by providing a summarized overview of the repository's contents. OpenRepoWiki requires certain dependencies such as Google AI Studio or Deepseek API Key, PostgreSQL for storing repository information, Github API Key for accessing repository data, and Amazon S3 for optional usage. Users can configure the tool by setting up environment variables, installing dependencies, building the server, and running the application. It is recommended to consider the token usage and opt for cost-effective options when utilizing the tool.

CodebaseToPrompt
CodebaseToPrompt is a simple tool that converts a local directory into a structured prompt for Large Language Models (LLMs). It allows users to select specific files for code review, analysis, or documentation by exploring and filtering through the file tree in a browser-based interface. The tool generates a formatted output that can be directly used with AI tools, provides token count estimates, and supports local storage for saving selections. Users can easily copy the selected files in the desired format for further use.
air
air is an R formatter and language server written in Rust. It is currently in alpha stage, so users should expect breaking changes in both the API and formatting results. The tool draws inspiration from various sources like roslyn, swift, rust-analyzer, prettier, biome, and ruff. It provides formatters and language servers, influenced by design decisions from these tools. Users can install air using standalone installers for macOS, Linux, and Windows, which automatically add air to the PATH. Developers can also install the dev version of the air CLI and VS Code extension for further customization and development.
code-graph
Code-graph is a tool composed of FalkorDB Graph DB, Code-Graph-Backend, and Code-Graph-Frontend. It allows users to store and query graphs, manage backend logic, and interact with the website. Users can run the components locally by setting up environment variables and installing dependencies. The tool supports analyzing C & Python source files with plans to add support for more languages in the future. It provides a local repository analysis feature and a live demo accessible through a web browser.
For similar jobs
yet-another-applied-llm-benchmark
Yet Another Applied LLM Benchmark is a collection of diverse tests designed to evaluate the capabilities of language models in performing real-world tasks. The benchmark includes tests such as converting code, decompiling bytecode, explaining minified JavaScript, identifying encoding formats, writing parsers, and generating SQL queries. It features a dataflow domain-specific language for easily adding new tests and has nearly 100 tests based on actual scenarios encountered when working with language models. The benchmark aims to assess whether models can effectively handle tasks that users genuinely care about.
BadukMegapack
BadukMegapack is an installer for various AI Baduk (Go) programs, designed for baduk players who want to easily access and use a variety of baduk AI programs without complex installations. The megapack includes popular programs like Lizzie, KaTrain, Sabaki, KataGo, LeelaZero, and more, along with weight files for different AI models. Users can update their graphics card drivers before installation for optimal performance.
Halite-III
Halite III is an AI programming competition hosted by Two Sigma. Contestants write bots to play a turn-based strategy game on a square grid. Bots navigate the sea collecting halite in this resource management game. The competition offers players the opportunity to develop bots with various strategies and in multiple programming languages.

OmniSteward
OmniSteward is an AI-powered steward system based on large language models that can interact with users through voice or text to help control smart home devices and computer programs. It supports multi-turn dialogue, tool calling for complex tasks, multiple LLM models, voice recognition, smart home control, computer program management, online information retrieval, command line operations, and file management. The system is highly extensible, allowing users to customize and share their own tools.
cs-books
CS Books is a curated collection of computer science resources organized by topics and real-world applications. It provides a dual academic/practical focus for students, researchers, and industry professionals. The repository contains a variety of books covering topics such as computer architecture, computer programming, artificial intelligence, data science, cloud computing, edge computing, embedded systems, signal processing, automotive, cybersecurity, game development, healthcare, and robotics. Each section includes a curated list of books with reference links to their Google Drive folders, allowing users to access valuable resources in these fields.

langtest
Langtest is a tool designed for testing and analyzing programming languages. It provides a platform for users to write code snippets in various languages and run them to see the output. The tool supports multiple programming languages and offers features like syntax highlighting, code execution, and result comparison. Users can use Langtest to quickly test code snippets, compare language syntax, and evaluate language performance. It is a useful tool for students, developers, and language enthusiasts to experiment with different programming languages in a convenient and efficient manner.

nanocoder
Nanocoder is a versatile code editor designed for beginners and experienced programmers alike. It provides a user-friendly interface with features such as syntax highlighting, code completion, and error checking. With Nanocoder, you can easily write and debug code in various programming languages, making it an ideal tool for learning, practicing, and developing software projects. Whether you are a student, hobbyist, or professional developer, Nanocoder offers a seamless coding experience to boost your productivity and creativity.
mage
XMage is an open-source, cross-platform application that allows users to play the collectible card game Magic: The Gathering online against other players or computer opponents. It supports over 25,000 unique cards and more than 65,000 reprints from different editions, including custom sets like Star Wars. XMage supports single matches and tournaments with dozens of game modes, including duel, multiplayer, standard, modern, commander, pauper, oathbreaker, historic, freeform, and richman. It also features a deck editor, a player rating system, and support for special formats like Commander, Oathbreaker, Cube, Tiny Leaders, Super Standard, and Historic Standard.