OpenSpec
Spec-driven development for AI coding assistants.
Stars: 195
OpenSpec is a tool for spec-driven development, aligning humans and AI coding assistants to agree on what to build before any code is written. It adds a lightweight specification workflow that ensures deterministic, reviewable outputs without the need for API keys. With OpenSpec, stakeholders can draft change proposals, review and align with AI assistants, implement tasks based on agreed specs, and archive completed changes for merging back into the source-of-truth specs. It works seamlessly with existing AI tools, offering shared visibility into proposed, active, or archived work.
README:
Spec-driven development for AI coding assistants.
Follow @0xTab on X for updates · Join the OpenSpec Discord for help and questions.
OpenSpec aligns humans and AI coding assistants with spec-driven development so you agree on what to build before any code is written. No API keys required.
AI coding assistants are powerful but unpredictable when requirements live in chat history. OpenSpec adds a lightweight specification workflow that locks intent before implementation, giving you deterministic, reviewable outputs.
Key outcomes:
- Human and AI stakeholders agree on specs before work begins.
- Structured change folders (proposals, tasks, and spec updates) keep scope explicit and auditable.
- Shared visibility into what's proposed, active, or archived.
- Works with the AI tools you already use: custom slash commands where supported, context rules everywhere else.
┌────────────────────┐
│ Draft Change │
│ Proposal │
└────────┬───────────┘
│ share intent with your AI
▼
┌────────────────────┐
│ Review & Align │
│ (edit specs/tasks) │◀──── feedback loop ──────┐
└────────┬───────────┘ │
│ approved plan │
▼ │
┌────────────────────┐ │
│ Implement Tasks │──────────────────────────┘
│ (AI writes code) │
└────────┬───────────┘
│ ship the change
▼
┌────────────────────┐
│ Archive & Update │
│ Specs (source) │
└────────────────────┘
1. Draft a change proposal that captures the spec updates you want.
2. Review the proposal with your AI assistant until everyone agrees.
3. Implement tasks that reference the agreed specs.
4. Archive the change to merge the approved updates back into the source-of-truth specs.
These tools have built-in OpenSpec commands. Select the OpenSpec integration when prompted.
| Tool | Commands |
|---|---|
| Claude Code |
/openspec:proposal, /openspec:apply, /openspec:archive
|
| Cursor |
/openspec-proposal, /openspec-apply, /openspec-archive
|
| OpenCode |
/openspec-proposal, /openspec-apply, /openspec-archive
|
These tools automatically read workflow instructions from openspec/AGENTS.md. Ask them to follow the OpenSpec workflow if they need a reminder. Learn more about the AGENTS.md convention.
| Tools |
|---|
| Codex • Amp • Jules • Gemini CLI • GitHub Copilot • Others |
-
Node.js >= 20.19.0 - Check your version with
node --version
npm install -g @fission-ai/openspec@latestVerify installation:
openspec --versionNavigate to your project directory:
cd my-projectRun the initialization:
openspec initWhat happens during initialization:
- You'll be prompted to select your AI tool (Claude Code, Cursor, etc.)
- OpenSpec automatically configures slash commands or
AGENTS.mdbased on your selection - A new
openspec/directory structure is created in your project
After setup:
- Primary AI tools can trigger
/openspecworkflows without additional configuration - Run
openspec listto verify the setup and view any active changes
Here's a real example showing the complete OpenSpec workflow. This works with any AI tool. Those with native slash commands will recognize the shortcuts automatically.
Start by asking your AI to create a change proposal:
You: Create an OpenSpec change proposal for adding profile search filters by role and team
(Shortcut for tools with slash commands: /openspec:proposal Add profile search filters)
AI: I'll create an OpenSpec change proposal for profile filters.
*Scaffolds openspec/changes/add-profile-filters/ with proposal.md, tasks.md, spec deltas.*
Check that the change was created correctly and review the proposal:
$ openspec list # Confirm the change folder exists
$ openspec validate add-profile-filters # Validate spec formatting
$ openspec show add-profile-filters # Review proposal, tasks, and spec deltaIterate on the specifications until they match your needs:
You: Can you add acceptance criteria for the role and team filters?
AI: I'll update the spec delta with scenarios for role and team filters.
*Edits openspec/changes/add-profile-filters/specs/profile/spec.md and tasks.md.*
Once specs look good, start implementation:
You: The specs look good. Let's implement this change.
(Shortcut for tools with slash commands: /openspec:apply add-profile-filters)
AI: I'll work through the tasks in the add-profile-filters change.
*Implements tasks from openspec/changes/add-profile-filters/tasks.md*
*Marks tasks complete: Task 1.1 ✓, Task 1.2 ✓, Task 2.1 ✓...*
After implementation is complete, archive the change:
AI: All tasks are complete. The implementation is ready.
You: Please archive the change
(Shortcut for tools with slash commands: /openspec:archive add-profile-filters)
AI: I'll archive the add-profile-filters change.
*Runs: openspec archive add-profile-filters*
✓ Change archived successfully. Specs updated. Ready for the next feature!
Or run the command yourself in terminal:
$ openspec archive add-profile-filters # Archive the completed changeNote: Tools with native slash commands (Claude Code, Cursor) can use the shortcuts shown. All other tools work with natural language requests to "create an OpenSpec proposal", "apply the OpenSpec change", or "archive the change".
openspec list # View active change folders
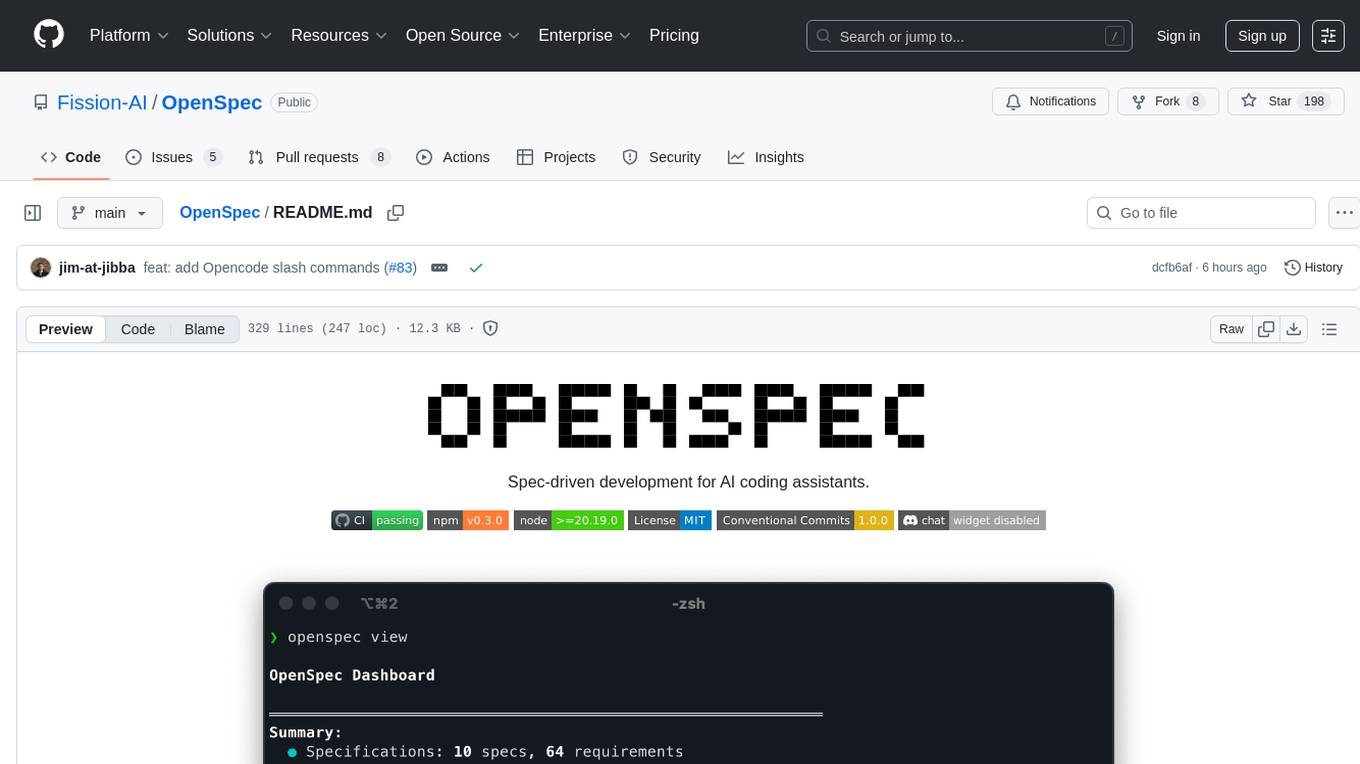
openspec view # Interactive dashboard of specs and changes
openspec show <change> # Display change details (proposal, tasks, spec updates)
openspec validate <change> # Check spec formatting and structure
openspec archive <change> # Move a completed change into archive/When you ask your AI assistant to "add two-factor authentication", it creates:
openspec/
├── specs/
│ └── auth/
│ └── spec.md # Current auth spec (if exists)
└── changes/
└── add-2fa/ # AI creates this entire structure
├── proposal.md # Why and what changes
├── tasks.md # Implementation checklist
├── design.md # Technical decisions (optional)
└── specs/
└── auth/
└── spec.md # Delta showing additions
# Auth Specification
## Purpose
Authentication and session management.
## Requirements
### Requirement: User Authentication
The system SHALL issue a JWT on successful login.
#### Scenario: Valid credentials
- WHEN a user submits valid credentials
- THEN a JWT is returned# Delta for Auth
## ADDED Requirements
### Requirement: Two-Factor Authentication
The system MUST require a second factor during login.
#### Scenario: OTP required
- WHEN a user submits valid credentials
- THEN an OTP challenge is required## 1. Database Setup
- [ ] 1.1 Add OTP secret column to users table
- [ ] 1.2 Create OTP verification logs table
## 2. Backend Implementation
- [ ] 2.1 Add OTP generation endpoint
- [ ] 2.2 Modify login flow to require OTP
- [ ] 2.3 Add OTP verification endpoint
## 3. Frontend Updates
- [ ] 3.1 Create OTP input component
- [ ] 3.2 Update login flow UIImportant: You don't create these files manually. Your AI assistant generates them based on your requirements and the existing codebase.
Deltas are "patches" that show how specs change:
-
## ADDED Requirements- New capabilities -
## MODIFIED Requirements- Changed behavior (include complete updated text) -
## REMOVED Requirements- Deprecated features
Format requirements:
- Use
### Requirement: <name>for headers - Every requirement needs at least one
#### Scenario:block - Use SHALL/MUST in requirement text
OpenSpec groups every change for a feature in one folder (openspec/changes/feature-name/), making it easy to track related specs, tasks, and designs together. Kiro spreads updates across multiple spec folders, which can make feature tracking harder.
Without specs, AI coding assistants generate code from vague prompts, often missing requirements or adding unwanted features. OpenSpec brings predictability by agreeing on the desired behavior before any code is written.
-
Initialize OpenSpec – Run
openspec initin your repo. - Start with new features – Ask your AI to capture upcoming work as change proposals.
- Grow incrementally – Each change archives into living specs that document your system.
- Stay flexible – Different teammates can use Claude Code, Cursor, or any AGENTS.md-compatible tool while sharing the same specs.
Run openspec update whenever someone switches tools so your agents pick up the latest instructions and slash-command bindings.
-
Upgrade the package
npm install -g @fission-ai/openspec@latest
-
Refresh agent instructions
- Run
openspec updateinside each project to regenerate AI guidance and ensure the latest slash commands are active.
- Run
- Install dependencies:
pnpm install - Build:
pnpm run build - Test:
pnpm test - Develop CLI locally:
pnpm run devorpnpm run dev:cli - Conventional commits (one-line):
type(scope): subject
MIT
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for OpenSpec
Similar Open Source Tools

OpenSpec
OpenSpec is a tool for spec-driven development, aligning humans and AI coding assistants to agree on what to build before any code is written. It adds a lightweight specification workflow that ensures deterministic, reviewable outputs without the need for API keys. With OpenSpec, stakeholders can draft change proposals, review and align with AI assistants, implement tasks based on agreed specs, and archive completed changes for merging back into the source-of-truth specs. It works seamlessly with existing AI tools, offering shared visibility into proposed, active, or archived work.
Archon
Archon is an AI meta-agent designed to autonomously build, refine, and optimize other AI agents. It serves as a practical tool for developers and an educational framework showcasing the evolution of agentic systems. Through iterative development, Archon demonstrates the power of planning, feedback loops, and domain-specific knowledge in creating robust AI agents.
tambourine-voice
Tambourine is a personal voice interface tool that allows users to speak naturally and have their words appear wherever the cursor is. It is powered by customizable AI voice dictation, providing a universal voice-to-text interface for emails, messages, documents, code editors, and terminals. Users can capture ideas quickly, type at the speed of thought, and benefit from AI formatting that cleans up speech, adds punctuation, and applies personal dictionaries. Tambourine offers full control and transparency, with the ability to customize AI providers, formatting, and extensions. The tool supports dual-mode recording, real-time speech-to-text, LLM text formatting, context-aware formatting, customizable prompts, and more, making it a versatile solution for dictation and transcription tasks.
multi-agent-shogun
multi-agent-shogun is a system that runs multiple AI coding CLI instances simultaneously, orchestrating them like a feudal Japanese army. It supports Claude Code, OpenAI Codex, GitHub Copilot, and Kimi Code. The system allows you to command your AI army with zero coordination cost, enabling parallel execution, non-blocking workflow, cross-session memory, event-driven communication, and full transparency. It also features skills discovery, phone notifications, pane border task display, shout mode, and multi-CLI support.
LangGraph-Expense-Tracker
LangGraph Expense tracker is a small project that explores the possibilities of LangGraph. It allows users to send pictures of invoices, which are then structured and categorized into expenses and stored in a database. The project includes functionalities for invoice extraction, database setup, and API configuration. It consists of various modules for categorizing expenses, creating database tables, and running the API. The database schema includes tables for categories, payment methods, and expenses, each with specific columns to track transaction details. The API documentation is available for reference, and the project utilizes LangChain for processing expense data.

vibe-remote
Vibe Remote is a tool that allows developers to code using AI agents through Slack or Discord, eliminating the need for a laptop or IDE. It provides a seamless experience for coding tasks, enabling users to interact with AI agents in real-time, delegate tasks, and monitor progress. The tool supports multiple coding agents, offers a setup wizard for easy installation, and ensures security by running locally on the user's machine. Vibe Remote enhances productivity by reducing context-switching and enabling parallel task execution within isolated workspaces.
marvin
Marvin is a lightweight AI toolkit for building natural language interfaces that are reliable, scalable, and easy to trust. Each of Marvin's tools is simple and self-documenting, using AI to solve common but complex challenges like entity extraction, classification, and generating synthetic data. Each tool is independent and incrementally adoptable, so you can use them on their own or in combination with any other library. Marvin is also multi-modal, supporting both image and audio generation as well using images as inputs for extraction and classification. Marvin is for developers who care more about _using_ AI than _building_ AI, and we are focused on creating an exceptional developer experience. Marvin users should feel empowered to bring tightly-scoped "AI magic" into any traditional software project with just a few extra lines of code. Marvin aims to merge the best practices for building dependable, observable software with the best practices for building with generative AI into a single, easy-to-use library. It's a serious tool, but we hope you have fun with it. Marvin is open-source, free to use, and made with 💙 by the team at Prefect.
one
ONE is a modern web and AI agent development toolkit that empowers developers to build AI-powered applications with high performance, beautiful UI, AI integration, responsive design, type safety, and great developer experience. It is perfect for building modern web applications, from simple landing pages to complex AI-powered platforms.
OpenManus
OpenManus is an open-source project aiming to replicate the capabilities of the Manus AI agent, known for autonomously executing complex tasks like travel planning and stock analysis. The project provides a modular, containerized framework using Docker, Python, and JavaScript, allowing developers to build, deploy, and experiment with a multi-agent AI system. Features include collaborative AI agents, Dockerized environment, task execution support, tool integration, modular design, and community-driven development. Users can interact with OpenManus via CLI, API, or web UI, and the project welcomes contributions to enhance its capabilities.
shannon
Shannon is an AI pentester that delivers actual exploits, not just alerts. It autonomously hunts for attack vectors in your code, then uses its built-in browser to execute real exploits, such as injection attacks, and auth bypass, to prove the vulnerability is actually exploitable. Shannon closes the security gap by acting as your on-demand whitebox pentester, providing concrete proof of vulnerabilities to let you ship with confidence. It is a core component of the Keygraph Security and Compliance Platform, automating penetration testing and compliance journey. Shannon Lite achieves a 96.15% success rate on a hint-free, source-aware XBOW benchmark.

rlama
RLAMA is a powerful AI-driven question-answering tool that seamlessly integrates with local Ollama models. It enables users to create, manage, and interact with Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems tailored to their documentation needs. RLAMA follows a clean architecture pattern with clear separation of concerns, focusing on lightweight and portable RAG capabilities with minimal dependencies. The tool processes documents, generates embeddings, stores RAG systems locally, and provides contextually-informed responses to user queries. Supported document formats include text, code, and various document types, with troubleshooting steps available for common issues like Ollama accessibility, text extraction problems, and relevance of answers.
claude-container
Claude Container is a Docker container pre-installed with Claude Code, providing an isolated environment for running Claude Code with optional API request logging in a local SQLite database. It includes three images: main container with Claude Code CLI, optional HTTP proxy for logging requests, and a web UI for visualizing and querying logs. The tool offers compatibility with different versions of Claude Code, quick start guides using a helper script or Docker Compose, authentication process, integration with existing projects, API request logging proxy setup, and data visualization with Datasette.
aiconfigurator
The `aiconfigurator` tool assists in finding a strong starting configuration for disaggregated serving in AI deployments. It helps optimize throughput at a given latency by evaluating thousands of configurations based on model, GPU count, and GPU type. The tool models LLM inference using collected data for a target machine and framework, running via CLI and web app. It generates configuration files for deployment with Dynamo, offering features like customized configuration, all-in-one automation, and tuning with advanced features. The tool estimates performance by breaking down LLM inference into operations, collecting operation execution times, and searching for strong configurations. Supported features include models like GPT and operations like attention, KV cache, GEMM, AllReduce, embedding, P2P, element-wise, MoE, MLA BMM, TRTLLM versions, and parallel modes like tensor-parallel and pipeline-parallel.
tangent
Tangent is a canvas for exploring AI conversations, allowing users to resurrect and continue conversations, branch and explore different ideas, organize conversations by topics, and support archive data exports. It aims to provide a visual/textual/audio exploration experience with AI assistants, offering a 'thoughts workbench' for experimenting freely, reviving old threads, and diving into tangents. The project structure includes a modular backend with components for API routes, background task management, data processing, and more. Prerequisites for setup include Whisper.cpp, Ollama, and exported archive data from Claude or ChatGPT. Users can initialize the environment, install Python packages, set up Ollama, configure local models, and start the backend and frontend to interact with the tool.
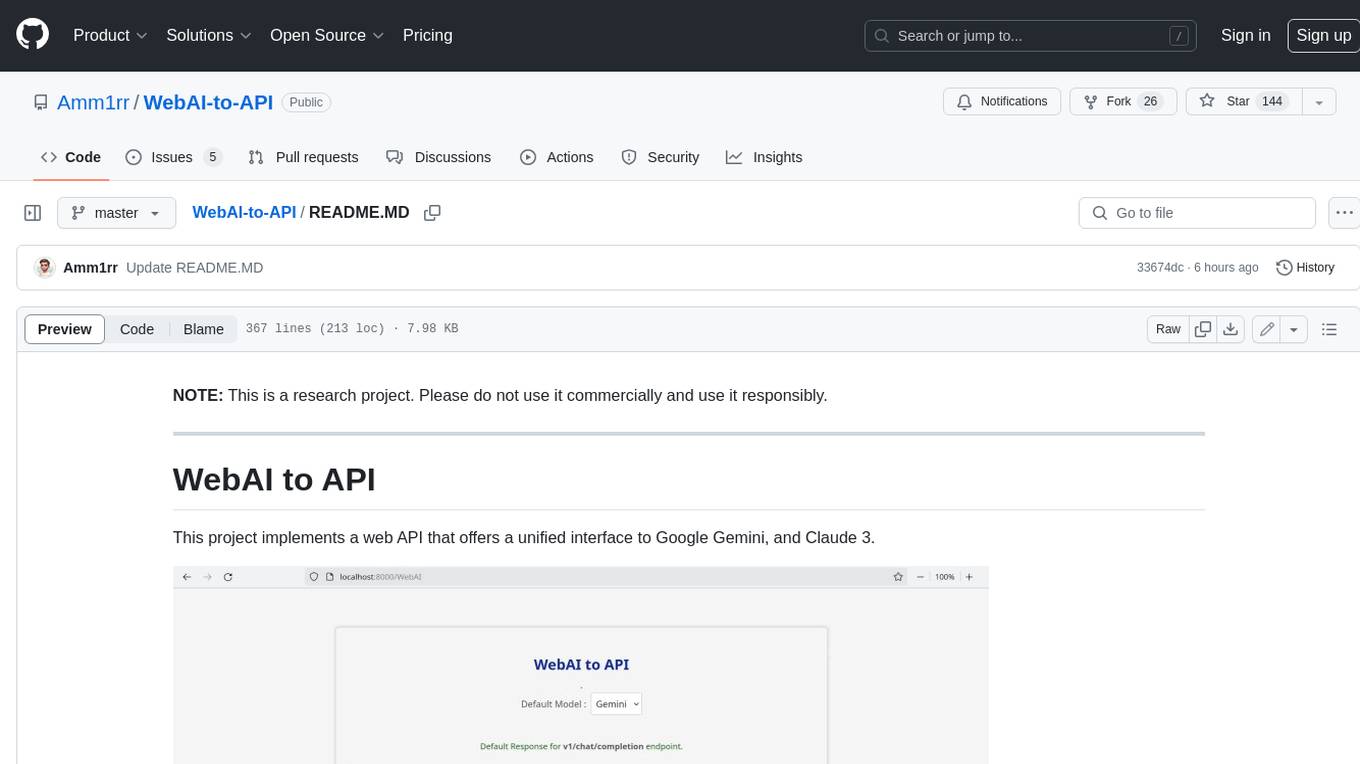
WebAI-to-API
This project implements a web API that offers a unified interface to Google Gemini and Claude 3. It provides a self-hosted, lightweight, and scalable solution for accessing these AI models through a streaming API. The API supports both Claude and Gemini models, allowing users to interact with them in real-time. The project includes a user-friendly web UI for configuration and documentation, making it easy to get started and explore the capabilities of the API.
For similar tasks

OpenSpec
OpenSpec is a tool for spec-driven development, aligning humans and AI coding assistants to agree on what to build before any code is written. It adds a lightweight specification workflow that ensures deterministic, reviewable outputs without the need for API keys. With OpenSpec, stakeholders can draft change proposals, review and align with AI assistants, implement tasks based on agreed specs, and archive completed changes for merging back into the source-of-truth specs. It works seamlessly with existing AI tools, offering shared visibility into proposed, active, or archived work.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.