
burr
Build applications that make decisions (chatbots, agents, simulations, etc...). Monitor, trace, persist, and execute on your own infrastructure.
Stars: 1509
Burr is a Python library and UI that makes it easy to develop applications that make decisions based on state (chatbots, agents, simulations, etc...). Burr includes a UI that can track/monitor those decisions in real time.
README:
Burr makes it easy to develop applications that make decisions (chatbots, agents, simulations, etc...) from simple python building blocks.
Burr works well for any application that uses LLMs, and can integrate with any of your favorite frameworks. Burr includes a UI that can track/monitor/trace your system in real time, along with pluggable persisters (e.g. for memory) to save & load application state.
Link to documentation. Quick (<3min) video intro here. Longer video intro & walkthrough. Blog post here. Join discord for help/questions here.
Install from pypi:
pip install "burr[start]"(see the docs if you're using poetry)
Then run the UI server:
burrThis will open up Burr's telemetry UI. It comes loaded with some default data so you can click around.
It also has a demo chat application to help demonstrate what the UI captures enabling you too see things changing in
real-time. Hit the "Demos" side bar on the left and select chatbot. To chat it requires the OPENAI_API_KEY
environment variable to be set, but you can still see how it works if you don't have an API key set.
Next, start coding / running examples:
git clone https://github.com/dagworks-inc/burr && cd burr/examples/hello-world-counter
python application.pyYou'll see the counter example running in the terminal, along with the trace being tracked in the UI. See if you can find it.
For more details see the getting started guide.
With Burr you express your application as a state machine (i.e. a graph/flowchart). You can (and should!) use it for anything in which you have to manage state, track complex decisions, add human feedback, or dictate an idempotent, self-persisting workflow.
The core API is simple -- the Burr hello-world looks like this (plug in your own LLM, or copy from the docs for gpt-X)
from burr.core import action, State, ApplicationBuilder
@action(reads=[], writes=["prompt", "chat_history"])
def human_input(state: State, prompt: str) -> State:
# your code -- write what you want here, for example
chat_item = {"role" : "user", "content" : prompt}
return state.update(prompt=prompt).append(chat_history=chat_item)
@action(reads=["chat_history"], writes=["response", "chat_history"])
def ai_response(state: State) -> State:
# query the LLM however you want (or don't use an LLM, up to you...)
response = _query_llm(state["chat_history"]) # Burr doesn't care how you use LLMs!
chat_item = {"role" : "system", "content" : response}
return state.update(response=content).append(chat_history=chat_item)
app = (
ApplicationBuilder()
.with_actions(human_input, ai_response)
.with_transitions(
("human_input", "ai_response"),
("ai_response", "human_input")
).with_state(chat_history=[])
.with_entrypoint("human_input")
.build()
)
*_, state = app.run(halt_after=["ai_response"], inputs={"prompt": "Who was Aaron Burr, sir?"})
print("answer:", app.state["response"])Burr includes:
- A (dependency-free) low-abstraction python library that enables you to build and manage state machines with simple python functions
- A UI you can use view execution telemetry for introspection and debugging
- A set of integrations to make it easier to persist state, connect to telemetry, and integrate with other systems
Burr can be used to power a variety of applications, including:
- A simple gpt-like chatbot
- A stateful RAG-based chatbot
- An LLM-based adventure game
- An interactive assistant for writing emails
As well as a variety of (non-LLM) use-cases, including a time-series forecasting simulation, and hyperparameter tuning.
And a lot more!
Using hooks and other integrations you can (a) integrate with any of your favorite vendors (LLM observability, storage, etc...), and (b) build custom actions that delegate to your favorite libraries (like Hamilton).
Burr will not tell you how to build your models, how to query APIs, or how to manage your data. It will help you tie all these together in a way that scales with your needs and makes following the logic of your system easy. Burr comes out of the box with a host of integrations including tooling to build a UI in streamlit and watch your state machine execute.
See the documentation for getting started, and follow the example. Then read through some of the concepts and write your own application!
While Burr is attempting something (somewhat) unique, there are a variety of tools that occupy similar spaces:
| Criteria | Burr | Langgraph | temporal | Langchain | Superagent | Hamilton |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Explicitly models a state machine | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Framework-agnostic | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
| Asynchronous event-based orchestration | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Built for core web-service logic | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Open-source user-interface for monitoring/tracing | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
| Works with non-LLM use-cases | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
Burr is named after Aaron Burr, founding father, third VP of the United States, and murderer/arch-nemesis of Alexander Hamilton. What's the connection with Hamilton? This is DAGWorks' second open-source library release after the Hamilton library We imagine a world in which Burr and Hamilton lived in harmony and saw through their differences to better the union. We originally built Burr as a harness to handle state between executions of Hamilton DAGs (because DAGs don't have cycles), but realized that it has a wide array of applications and decided to release it more broadly.
"After evaluating several other obfuscating LLM frameworks, their elegant yet comprehensive state management solution proved to be the powerful answer to rolling out robots driven by AI decision-making."
Ashish Ghosh CTO, Peanut Robotics
"Of course, you can use it [LangChain], but whether it's really production-ready and improves the time from 'code-to-prod' [...], we've been doing LLM apps for two years, and the answer is no [...] All these 'all-in-one' libs suffer from this [...]. Honestly, take a look at Burr. Thank me later."
Reddit user cyan2k LocalLlama, Subreddit
"Using Burr is a no-brainer if you want to build a modular AI application. It is so easy to build with, and I especially love their UI which makes debugging a piece of cake. And the always-ready-to-help team is the cherry on top."
Ishita Founder, Watto.ai
"I just came across Burr and I'm like WOW, this seems like you guys predicted this exact need when building this. No weird esoteric concepts just because it's AI."
Matthew Rideout Staff Software Engineer, Paxton AI
"Burr's state management part is really helpful for creating state snapshots and building debugging, replaying, and even evaluation cases around that."
Rinat Gareev Senior Solutions Architect, Provectus
"I have been using Burr over the past few months, and compared to many agentic LLM platforms out there (e.g. LangChain, CrewAi, AutoGen, Agency Swarm, etc), Burr provides a more robust framework for designing complex behaviors."
Hadi Nayebi Co-founder, CognitiveGraphs
"Moving from LangChain to Burr was a game-changer!
- Time-Saving: It took me just a few hours to get started with Burr, compared to the days and weeks I spent trying to navigate LangChain.
- Cleaner Implementation: With Burr, I could finally have a cleaner, more sophisticated, and stable implementation. No more wrestling with complex codebases.
- Team Adoption: I pitched Burr to my teammates, and we pivoted our entire codebase to it. It's been a smooth ride ever since."
Aditya K. DS Architect, TaskHuman
While Burr is stable and well-tested, we have quite a few tools/features on our roadmap!
- FastAPI integration + hosted deployment -- make it really easy to get Burr in an app in production without thinking about REST APIs
- Various efficiency/usability improvements for the core library (see planned capabilities for more details). This includes:
- First-class support for retries + exception management
- More integration with popular frameworks (LCEL, LLamaIndex, Hamilton, etc...)
- Capturing & surfacing extra metadata, e.g. annotations for particular point in time, that you can then pull out for fine-tuning, etc.
- Improvements to the pydantic-based typing system
- Tooling for hosted execution of state machines, integrating with your infrastructure (Ray, modal, FastAPI + EC2, etc...)
- Additional storage integrations. More integrations with technologies like MySQL, S3, etc. so you can run Burr on top of what you have available.
If you want to avoid self-hosting the above solutions we're building Burr Cloud. To let us know you're interested sign up here for the waitlist to get access.
We welcome contributors! To get started on developing, see the developer-facing docs.
Users who have contributed core functionality, integrations, or examples.
Users who have contributed small docs fixes, design suggestions, and found bugs
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for burr
Similar Open Source Tools

burr
Burr is a Python library and UI that makes it easy to develop applications that make decisions based on state (chatbots, agents, simulations, etc...). Burr includes a UI that can track/monitor those decisions in real time.
oh-my-opencode
OhMyOpenCode is a free and open-source tool that enhances coding productivity by providing an agent harness for orchestrating multiple models and tools. It offers features like background agents, LSP/AST tools, curated MCPs, and compatibility with various agents like Claude Code. The tool aims to boost productivity, automate tasks, and streamline the coding process for users. It is highly extensible and customizable, catering to both hackers and non-hackers alike, with a focus on enhancing the development experience and performance.
OpenHands
OpenDevin is a platform for autonomous software engineers powered by AI and LLMs. It allows human developers to collaborate with agents to write code, fix bugs, and ship features. The tool operates in a secured docker sandbox and provides access to different LLM providers for advanced configuration options. Users can contribute to the project through code contributions, research and evaluation of LLMs in software engineering, and providing feedback and testing. OpenDevin is community-driven and welcomes contributions from developers, researchers, and enthusiasts looking to advance software engineering with AI.
12-factor-agents
12-Factor Agents is a project focused on building reliable LLM-powered software by outlining 12 core engineering principles. The project aims to provide guidance on creating production-ready customer-facing agents that leverage AI technology effectively. It emphasizes the importance of software design, context management, tool integration, and control flow in developing high-quality AI agents. The project offers insights, design patterns, and practical advice for software engineers looking to enhance their AI applications with agent-based approaches.
uptrain
UpTrain is an open-source unified platform to evaluate and improve Generative AI applications. We provide grades for 20+ preconfigured evaluations (covering language, code, embedding use cases), perform root cause analysis on failure cases and give insights on how to resolve them.
raycast-g4f
Raycast-G4F is a free extension that allows users to leverage powerful AI models such as GPT-4 and Llama-3 within the Raycast app without the need for an API key. The extension offers features like streaming support, diverse commands, chat interaction with AI, web search capabilities, file upload functionality, image generation, and custom AI commands. Users can easily install the extension from the source code and benefit from frequent updates and a user-friendly interface. Raycast-G4F supports various providers and models, each with different capabilities and performance ratings, ensuring a versatile AI experience for users.
searchGPT
searchGPT is an open-source project that aims to build a search engine based on Large Language Model (LLM) technology to provide natural language answers. It supports web search with real-time results, file content search, and semantic search from sources like the Internet. The tool integrates LLM technologies such as OpenAI and GooseAI, and offers an easy-to-use frontend user interface. The project is designed to provide grounded answers by referencing real-time factual information, addressing the limitations of LLM's training data. Contributions, especially from frontend developers, are welcome under the MIT License.
AgentLab
AgentLab is an open, easy-to-use, and extensible framework designed to accelerate web agent research. It provides features for developing and evaluating agents on various benchmarks supported by BrowserGym. The framework allows for large-scale parallel agent experiments using ray, building blocks for creating agents over BrowserGym, and a unified LLM API for OpenRouter, OpenAI, Azure, or self-hosted using TGI. AgentLab also offers reproducibility features, a unified LeaderBoard, and supports multiple benchmarks like WebArena, WorkArena, WebLinx, VisualWebArena, AssistantBench, GAIA, Mind2Web-live, and MiniWoB.

edenai-apis
Eden AI aims to simplify the use and deployment of AI technologies by providing a unique API that connects to all the best AI engines. With the rise of **AI as a Service** , a lot of companies provide off-the-shelf trained models that you can access directly through an API. These companies are either the tech giants (Google, Microsoft , Amazon) or other smaller, more specialized companies, and there are hundreds of them. Some of the most known are : DeepL (translation), OpenAI (text and image analysis), AssemblyAI (speech analysis). There are **hundreds of companies** doing that. We're regrouping the best ones **in one place** !
yuna-ai
Yuna AI is a unique AI companion designed to form a genuine connection with users. It runs exclusively on the local machine, ensuring privacy and security. The project offers features like text generation, language translation, creative content writing, roleplaying, and informal question answering. The repository provides comprehensive setup and usage guides for Yuna AI, along with additional resources and tools to enhance the user experience.
obsidian-chat-cbt-plugin
ChatCBT is an AI-powered journaling assistant for Obsidian, inspired by cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT). It helps users reframe negative thoughts and rewire reactions to distressful situations. The tool provides kind and objective responses to uncover negative thinking patterns, store conversations privately, and summarize reframed thoughts. Users can choose between a cloud-based AI service (OpenAI) or a local and private service (Ollama) for handling data. ChatCBT is not a replacement for therapy but serves as a journaling assistant to help users gain perspective on their problems.
OpenDevin
OpenDevin is an open-source project aiming to replicate Devin, an autonomous AI software engineer capable of executing complex engineering tasks and collaborating actively with users on software development projects. The project aspires to enhance and innovate upon Devin through the power of the open-source community. Users can contribute to the project by developing core functionalities, frontend interface, or sandboxing solutions, participating in research and evaluation of LLMs in software engineering, and providing feedback and testing on the OpenDevin toolset.

second-brain-ai-assistant-course
This open-source course teaches how to build an advanced RAG and LLM system using LLMOps and ML systems best practices. It helps you create an AI assistant that leverages your personal knowledge base to answer questions, summarize documents, and provide insights. The course covers topics such as LLM system architecture, pipeline orchestration, large-scale web crawling, model fine-tuning, and advanced RAG features. It is suitable for ML/AI engineers and data/software engineers & data scientists looking to level up to production AI systems. The course is free, with minimal costs for tools like OpenAI's API and Hugging Face's Dedicated Endpoints. Participants will build two separate Python applications for offline ML pipelines and online inference pipeline.
leon
Leon is an open-source personal assistant who can live on your server. He does stuff when you ask him to. You can talk to him and he can talk to you. You can also text him and he can also text you. If you want to, Leon can communicate with you by being offline to protect your privacy.

Follow
Follow is a content organization tool that creates a noise-free timeline for users, allowing them to share lists, explore collections, and browse distraction-free. It offers features like subscribing to feeds, AI-powered browsing, dynamic content support, an ownership economy with $POWER tipping, and a community-driven experience. Follow is under active development and welcomes feedback from users and developers. It can be accessed via web app or desktop client and offers installation methods for different operating systems. The tool aims to provide a customized information hub, AI-powered browsing experience, and support for various types of content, while fostering a community-driven and open-source environment.
thread
Thread is an AI-powered Jupyter alternative that integrates an AI copilot into your editing experience. It offers a familiar Jupyter Notebook editing experience with features like natural language code edits, generating cells to answer questions, context-aware chat sidebar, and automatic error explanations or fixes. The tool aims to enhance code editing and data exploration by providing a more interactive and intuitive experience for users. Thread can be used for free with Ollama or your own API key, and it runs locally for convenience and privacy.
For similar tasks

burr
Burr is a Python library and UI that makes it easy to develop applications that make decisions based on state (chatbots, agents, simulations, etc...). Burr includes a UI that can track/monitor those decisions in real time.
llama_deploy
llama_deploy is an async-first framework for deploying, scaling, and productionizing agentic multi-service systems based on workflows from llama_index. It allows building workflows in llama_index and deploying them seamlessly with minimal changes to code. The system includes services endlessly processing tasks, a control plane managing state and services, an orchestrator deciding task handling, and fault tolerance mechanisms. It is designed for high-concurrency scenarios, enabling real-time and high-throughput applications.
pipecat-flows
Pipecat Flows is a framework designed for building structured conversations in AI applications. It allows users to create both predefined conversation paths and dynamically generated flows, handling state management and LLM interactions. The framework includes a Python module for building conversation flows and a visual editor for designing and exporting flow configurations. Pipecat Flows is suitable for scenarios such as customer service scripts, intake forms, personalized experiences, and complex decision trees.
agentscript
AgentScript is an open-source framework for building AI agents that think in code. It prompts a language model to generate JavaScript code, which is then executed in a dedicated runtime with resumability, state persistence, and interactivity. The framework allows for abstract task execution without needing to know all the data beforehand, making it flexible and efficient. AgentScript supports tools, deterministic functions, and LLM-enabled functions, enabling dynamic data processing and decision-making. It also provides state management and human-in-the-loop capabilities, allowing for pausing, serialization, and resumption of execution.
agents
Cloudflare Agents is a framework for building intelligent, stateful agents that persist, think, and evolve at the edge of the network. It allows for maintaining persistent state and memory, real-time communication, processing and learning from interactions, autonomous operation at global scale, and hibernating when idle. The project is actively evolving with focus on core agent framework, WebSocket communication, HTTP endpoints, React integration, and basic AI chat capabilities. Future developments include advanced memory systems, WebRTC for audio/video, email integration, evaluation framework, enhanced observability, and self-hosting guide.
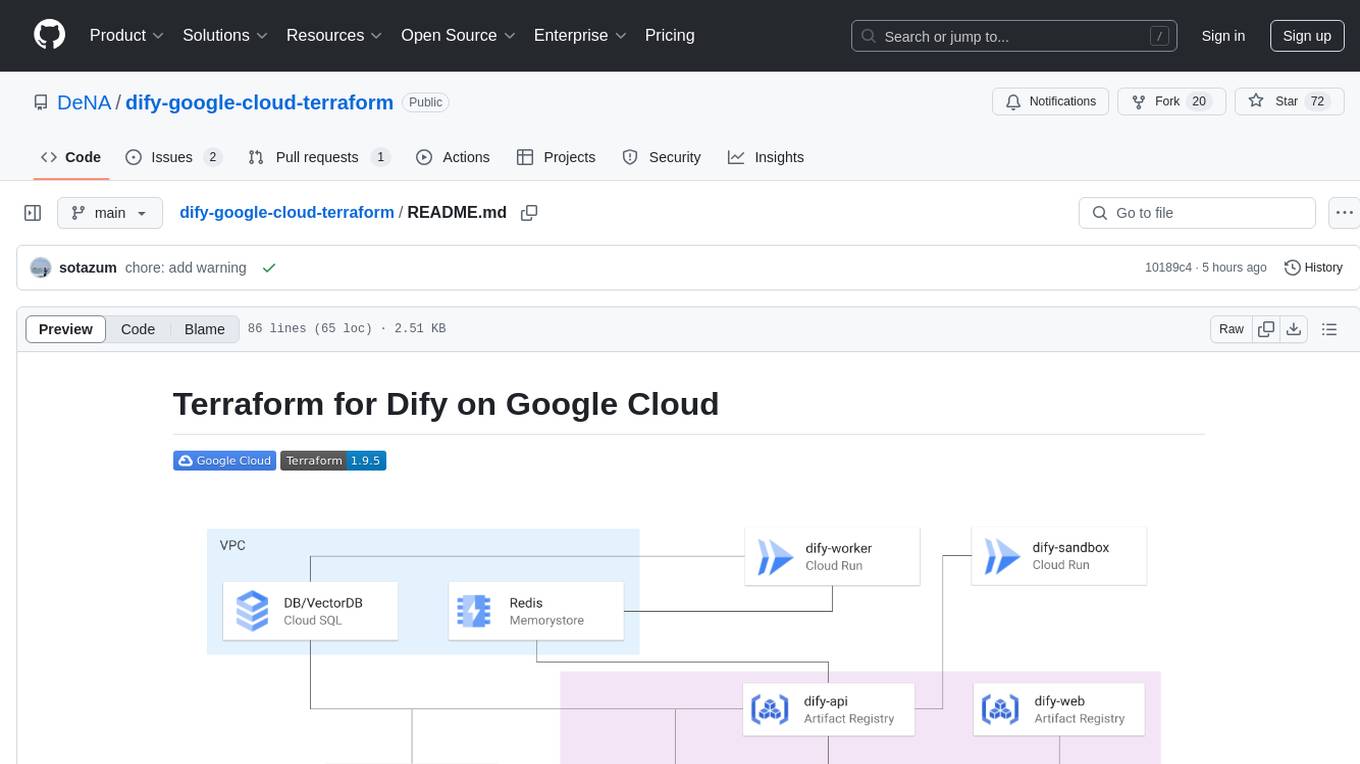
dify-google-cloud-terraform
This repository provides Terraform configurations to automatically set up Google Cloud resources and deploy Dify in a highly available configuration. It includes features such as serverless hosting, auto-scaling, and data persistence. Users need a Google Cloud account, Terraform, and gcloud CLI installed to use this tool. The configuration involves setting environment-specific values and creating a GCS bucket for managing Terraform state. The tool allows users to initialize Terraform, create Artifact Registry repository, build and push container images, plan and apply Terraform changes, and cleanup resources when needed.

exospherehost
Exosphere is an open source infrastructure designed to run AI agents at scale for large data and long running flows. It allows developers to define plug and playable nodes that can be run on a reliable backbone in the form of a workflow, with features like dynamic state creation at runtime, infinite parallel agents, persistent state management, and failure handling. This enables the deployment of production agents that can scale beautifully to build robust autonomous AI workflows.

xpander.ai
xpander.ai is a Backend-as-a-Service for autonomous agents that abstracts the ops layer, allowing AI engineers to focus on behavior and outcomes. It provides managed agent hosting with version control and CI/CD, a fully managed PostgreSQL memory layer, and a library of 2,000+ functions. The platform features an AI native triggering system that processes inputs from various sources and delivers unified messages to agents. With support for any agent framework or SDK, including Agno and OpenAI, xpander.ai enables users to build intelligent, production-ready AI agents without dealing with infrastructure complexity.
For similar jobs

burr
Burr is a Python library and UI that makes it easy to develop applications that make decisions based on state (chatbots, agents, simulations, etc...). Burr includes a UI that can track/monitor those decisions in real time.
ChatFAQ
ChatFAQ is an open-source comprehensive platform for creating a wide variety of chatbots: generic ones, business-trained, or even capable of redirecting requests to human operators. It includes a specialized NLP/NLG engine based on a RAG architecture and customized chat widgets, ensuring a tailored experience for users and avoiding vendor lock-in.

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.
anything-llm
AnythingLLM is a full-stack application that enables you to turn any document, resource, or piece of content into context that any LLM can use as references during chatting. This application allows you to pick and choose which LLM or Vector Database you want to use as well as supporting multi-user management and permissions.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.

glide
Glide is a cloud-native LLM gateway that provides a unified REST API for accessing various large language models (LLMs) from different providers. It handles LLMOps tasks such as model failover, caching, key management, and more, making it easy to integrate LLMs into applications. Glide supports popular LLM providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI, AWS Bedrock (Titan), Cohere, Google Gemini, OctoML, and Ollama. It offers high availability, performance, and observability, and provides SDKs for Python and NodeJS to simplify integration.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.








