Awesome-Audio-LLM
Audio Large Language Models
Stars: 424
Awesome-Audio-LLM is a repository dedicated to various models and methods related to audio and language processing. It includes a wide range of research papers and models developed by different institutions and authors. The repository covers topics such as bridging audio and language, speech emotion recognition, voice assistants, and more. It serves as a comprehensive resource for those interested in the intersection of audio and language processing.
README:
We thank the following contributors for their valuable contributions! zwenyu, Yuan-ManX, chaoweihuang, Liu-Tianchi, Sakshi113, hbwu-ntu, potsawee, czwxian, marianasignal, and You!
- OSUM
- Step-Audio
- Audio-CoT
- UltraEval-Audio
- LUCY
- MinMo
- ADU-Bench
- TalkArena
- Typhoon2-Audio
- MERaLiON-AudioLLM
- ADU-Bench
- Taiwanese AudioLLM
- WavChat-Survey
- Dynamic-SUPERB Phase-2
- VoiceBench
- MMAU
- SPIRIT LM
- SpeechLLM-Survey
- SpeechEmotionLlama
- SPIRIT LM
- SpeechLM-Survey
- DiVA
- AudioBERT
- Ultravox
- LLaMA-Omni
- SALMon
- DeSTA2
- ASRCompare
- MoWE-Audio
- Moshi
- EMOVA
- MuChoMusic
- Mini-Omni
- MooER
- Typhoon-Audio
- Qwen2-Audio
- LLaST
- Decoder-only LLMs for STT
- AudioEntailment
- GAMA
- FunAudioLLM
- CompA
- Speech ReaLLM
- Audio Hallucination
- AudioBench
- DeSTA
- CodecFake
- SD-Eval
- AIR-Bench
- Audio Flamingo
- VoiceJailbreak
- LibriSQA
- SALMONN
- SpokenWOZ
- WavLLM
- SLAM-LLM
- AudioLM-Survey
- Pengi
- Qwen-Audio
- CoDi-2
- UniAudio
- Dynamic-SUPERB
- LLaSM
- Segment-level Q-Former
- Prompting LLMs with Speech Recognition
- Macaw-LLM
- SpeechGPT
- AudioGPT
-
【2024-04】-【LibriSQA】-【Shanghai Jiao Tong University】-【Type: Dataset Resource】- LibriSQA: A Novel Dataset and Framework for Spoken Question Answering with Large Language Models
- Author(s): Zihan Zhao, Yiyang Jiang, Heyang Liu, Yanfeng Wang, Yu Wang
- Paper
-
【2025-02】-【OSUM】-【ASLP@NPU】-【Type: Model】- OSUM: Advancing Open Speech Understanding Models with Limited Resources in Academia
- Author(s): Xuelong Geng, Kun Wei, Qijie Shao, Shuiyun Liu, Zhennan Lin, Zhixian Zhao, Guojian Li, Wenjie Tian, Peikun Chen, Yangze Li, Pengcheng Guo, Mingchen Shao, Shuiyuan Wang, Yuang Cao, Chengyou Wang, Tianyi Xu, Yuhang Dai, Xinfa Zhu, Yue Li, Li Zhang, Lei Xie
- Paper / Hugging Face Model
-
【2025-02】-【Step-Audio】-【Step-Audio Team, StepFun】-【Type: Model】- Step-Audio: Unified Understanding and Generation in Intelligent Speech Interaction
- Author(s): Ailin Huang, Boyong Wu, Bruce Wang, Chao Yan, Chen Hu, Chengli Feng, Fei Tian, Feiyu Shen, Jingbei Li, Mingrui Chen, Peng Liu, Ruihang Miao, Wang You, Xi Chen, Xuerui Yang, Yechang Huang, Yuxiang Zhang, Zheng Gong, Zixin Zhang, Hongyu Zhou, Jianjian Sun, Brian Li, Chengting Feng, Changyi Wan, Hanpeng Hu, Jianchang Wu, Jiangjie Zhen, Ranchen Ming, Song Yuan, Xuelin Zhang, Yu Zhou, Bingxin Li, Buyun Ma, Hongyuan Wang, Kang An, Wei Ji, Wen Li, Xuan Wen, Xiangwen Kong, Yuankai Ma, Yuanwei Liang, Yun Mou, Bahtiyar Ahmidi, Bin Wang, Bo Li, Changxin Miao, Chen Xu, Chenrun Wang, Dapeng Shi, Deshan Sun, Dingyuan Hu, Dula Sai, Enle Liu, Guanzhe Huang, Gulin Yan, Heng Wang, Haonan Jia, Haoyang Zhang, Jiahao Gong, Junjing Guo, Jiashuai Liu, Jiahong Liu, Jie Feng, Jie Wu, Jiaoren Wu, Jie Yang, Jinguo Wang, Jingyang Zhang, Junzhe Lin, Kaixiang Li, Lei Xia, Li Zhou, Liang Zhao, Longlong Gu, Mei Chen, Menglin Wu, Ming Li, Mingxiao Li, Mingliang Li, Mingyao Liang, Na Wang, Nie Hao, Qiling Wu, Qinyuan Tan, Ran Sun, Shuai Shuai, Shaoliang Pang, Shiliang Yang, Shuli Gao, Shanshan Yuan, Siqi Liu, Shihong Deng, Shilei Jiang, Sitong Liu, Tiancheng Cao, Tianyu Wang, Wenjin Deng, Wuxun Xie, Weipeng Ming, Wenqing He , Wen Sun, Xin Han, Xin Huang, Xiaomin Deng, Xiaojia Liu, Xin Wu, Xu Zhao, Yanan Wei, Yanbo Yu, Yang Cao, Yangguang Li, Yangzhen Ma, Yanming Xu, Yaoyu Wang, Yaqiang Shi, Yilei Wang, Yizhuang Zhou, Yinmin Zhong, Yang Zhang, Yaoben Wei, Yu Luo, Yuanwei Lu, Yuhe Yin, Yuchu Luo, Yuanhao Ding, Yuting Yan, Yaqi Dai, Yuxiang Yang, Zhe Xie, Zheng Ge, Zheng Sun, Zhewei Huang, Zhichao Chang, Zhisheng Guan, Zidong Yang, Zili Zhang, Binxing Jiao, Daxin Jiang, Heung-Yeung Shum, Jiansheng Chen, Jing Li, Shuchang Zhou, Xiangyu Zhang, Xinhao Zhang, Yibo Zhu
- Paper / Hugging Face Model
-
【2025-01】-【Audio-CoT】-【Nanyang Technological University, Singapore】-【Type: Model】- Audio-CoT: Exploring Chain-of-Thought Reasoning in Large Audio Language Model
- Author(s): Ziyang Ma, Zhuo Chen, Yuping Wang, Eng Siong Chng, Xie Chen
- Paper
-
【2025-01】-【LUCY】-【Tencent】-【Type: Model】- LUCY: Linguistic Understanding and Control Yielding Early Stage of Her
- Author(s): Heting Gao, Hang Shao, Xiong Wang, Chaofan Qiu, Yunhang Shen, Siqi Cai, Yuchen Shi, Zihan Xu, Zuwei Long, Yike Zhang, Shaoqi Dong, Chaoyou Fu, Ke Li, Long Ma, Xing Sun
- Paper
-
【2024-12】-【Typhoon2-Audio】-【SCB 10X】-【Type: Multimodal Language Model】- Typhoon2-Audio: A Thai Multimodal Language Model for Speech and Text Processing
- Author(s): Kunat Pipatanakul, Potsawee Manakul, Natapong Nitarach, Warit Sirichotedumrong, Surapon Nonesung, Teetouch Jaknamon, Parinthapat Pengpun, Pittawat Taveekitworachai, Adisai Na-Thalang, Sittipong Sripaisarnmongkol, Krisanapong Jirayoot, Kasima Tharnpipitchai
- Paper / Hugging Face Model / Demo
-
【2024-12】-【MERaLiON-AudioLLM】-【I2R, A*STAR, Singapore】-【Type: Model】- MERaLiON-AudioLLM: Bridging Audio and Language with Large Language Models
- Author(s): Yingxu He, Zhuohan Liu, Shuo Sun, Bin Wang, Wenyu Zhang, Xunlong Zou, Nancy F. Chen, Ai Ti Aw
- Paper / Hugging Face Model / Demo
-
【2024-11】-【Taiwanese AudioLLM】-【National Taiwan University】-【Type: Model】- Building a Taiwanese Mandarin Spoken Language Model: A First Attempt
- Author(s): Chih-Kai Yang, Yu-Kuan Fu, Chen-An Li, Yi-Cheng Lin, Yu-Xiang Lin, Wei-Chih Chen, Ho Lam Chung, Chun-Yi Kuan, Wei-Ping Huang, Ke-Han Lu, Tzu-Quan Lin, Hsiu-Hsuan Wang, En-Pei Hu, Chan-Jan Hsu, Liang-Hsuan Tseng, I-Hsiang Chiu, Ulin Sanga, Xuanjun Chen, Po-chun Hsu, Shu-wen Yang, Hung-yi Lee
- Paper
-
【2024-10】-【SPIRIT LM】-【Meta】-【Type: Model】- SPIRIT LM: Interleaved Spoken and Written Language Model
- Author(s): Tu Anh Nguyen, Benjamin Muller, Bokai Yu, Marta R. Costa-jussa, Maha Elbayad, Sravya Popuri, Christophe Ropers, Paul-Ambroise Duquenne, Robin Algayres, Ruslan Mavlyutov, Itai Gat, Mary Williamson, Gabriel Synnaeve, Juan Pino, Benoit Sagot, Emmanuel Dupoux
- Paper / Other Link
-
【2024-10】-【SpeechEmotionLlama】-【MIT, Meta】-【Type: Model】- Frozen Large Language Models Can Perceive Paralinguistic Aspects of Speech
- Author(s): Wonjune Kang, Junteng Jia, Chunyang Wu, Wei Zhou, Egor Lakomkin, Yashesh Gaur, Leda Sari, Suyoun Kim, Ke Li, Jay Mahadeokar, Ozlem Kalinli
- Paper
-
【2024-10】-【SPIRIT LM】-【Meta】-【Type: Model】- SPIRIT LM: Interleaved Spoken and Written Language Model
- Author(s): Tu Anh Nguyen, Benjamin Muller, Bokai Yu, Marta R. Costa-jussa, Maha Elbayad, Sravya Popuri, Paul-Ambroise Duquenne, Robin Algayres, Ruslan Mavlyutov, Itai Gat, Gabriel Synnaeve, Juan Pino, Benoît Sagot, Emmanuel Dupoux
- Paper / Demo
-
【2024-10】-【DiVA】-【Georgia Tech, Stanford】-【Type: Model】 -
【2024-09】-【AudioBERT】-【POSTECH, Inha University】-【Type: Model】- AudioBERT: Audio Knowledge Augmented Language Model
- Author(s): Hyunjong Ok, Suho Yoo, Jaeho Lee
- Paper
-
【2024-09】-【Ultravox】-【Fixie.ai】-【Type: Model】 -
【2024-09】-【LLaMA-Omni】-【Institute of Computing Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (ICT/CAS)】-【Type: Model】- LLaMA-Omni: Seamless Speech Interaction with Large Language Models
- Author(s): Qingkai Fang, Shoutao Guo, Yan Zhou, Zhengrui Ma, Shaolei Zhang, Yang Feng
- Paper
-
【2024-09】-【DeSTA2】-【National Taiwan University, NVIDIA】-【Type: Model】- Developing Instruction-Following Speech Language Model Without Speech Instruction-Tuning Data
- Author(s): Ke-Han Lu, Zhehuai Chen, Szu-Wei Fu, Chao-Han Huck Yang, Jagadeesh Balam, Boris Ginsburg, Yu-Chiang Frank Wang, Hung-yi Lee
- Paper
-
【2024-09】-【ASRCompare】-【Tsinghua University, Tencent AI Lab】-【Type: Model】- Comparing Discrete and Continuous Space LLMs for Speech Recognition
- Author(s): Yaoxun Xu, Shi-Xiong Zhang, Jianwei Yu, Zhiyong Wu, Dong Yu
- Paper
-
【2024-09】-【MoWE-Audio】-【A*STAR】-【Type: Model】- MoWE-Audio: Multitask AudioLLMs with Mixture of Weak Encoders
- Author(s): Wenyu Zhang, Shuo Sun, Bin Wang, Xunlong Zou, Zhuohan Liu, Yingxu He, Geyu Lin, Nancy F. Chen, Ai Ti Aw
- Paper
-
【2024-09】-【Moshi】-【Kyutai】-【Type: Model】- Moshi: a speech-text foundation model for real-time dialogue
- Author(s): Alexandre Défossez, Laurent Mazaré, Manu Orsini, Amélie Royer, Patrick Pérez, Hervé Jégou, Edouard Grave, Neil Zeghidour
- Paper
-
【2024-08】-【Mini-Omni】-【Tsinghua University】-【Type: Model】- Mini-Omni: Language Models Can Hear, Talk While Thinking in Streaming
- Author(s): Zhifei Xie, Changqiao Wu
- Paper
-
【2024-08】-【MooER】-【Moore Threads】-【Type: Model】- MooER: LLM-based Speech Recognition and Translation Models from Moore Threads
- Author(s): Zhenlin Liang, Junhao Xu, Yi Liu, Yichao Hu, Jian Li, Yajun Zheng, Meng Cai, Hua Wang
- Paper
-
【2024-08】-【Typhoon-Audio】-【SCB 10X】-【Type: Multimodal Language Model】- Typhoon-Audio: Enhancing Low-Resource Language and Instruction Following Capabilities of Audio Language Models
- Author(s): Potsawee Manakul, Guangzhi Sun, Warit Sirichotedumrong, Kasima Tharnpipitchai, Kunat Pipatanakul
- Paper / Hugging Face Model
-
【2024-07】-【Qwen2-Audio】-【Alibaba Group】-【Type: Model】- Qwen2-Audio Technical Report
- Author(s): Yunfei Chu, Jin Xu, Qian Yang, Haojie Wei, Xipin Wei, Zhifang Guo, Yichong Leng, Yuanjun Lv, Jinzheng He, Junyang Lin, Chang Zhou, Jingren Zhou
- Paper
-
【2024-07】-【LLaST】-【The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shenzhen; Shanghai AI Laboratory; Nara Institute of Science and Technology, Japan】-【Type: Model】- LLaST: Improved End-to-end Speech Translation System Leveraged by Large Language Models
- Author(s): Xi Chen, Songyang Zhang, Qibing Bai, Kai Chen, Satoshi Nakamura
- Paper
-
【2024-07】-【Decoder-only LLMs for STT】-【NTU-Taiwan, Meta】-【Type: Research】- Investigating Decoder-only Large Language Models for Speech-to-text Translation
- Author(s): Authors not specified in the provided information
- Paper
-
【2024-07】-【GAMA】-【University of Maryland, College Park】-【Type: Model】 -
【2024-07】-【FunAudioLLM】-【Alibaba】-【Type: Model】 -
【2024-07】-【CompA】-【University of Maryland, College Park; Adobe, USA; NVIDIA, Bangalore, India】-【Type: Model】 -
【2024-06】-【Speech ReaLLM】-【Meta】-【Type: Model】- Speech ReaLLM – Real-time Streaming Speech Recognition with Multimodal LLMs by Teaching the Flow of Time
- Author(s): Authors not specified in the provided information
- Paper
-
【2024-06】-【DeSTA】-【NTU-Taiwan, Nvidia】-【Type: Model】- DeSTA: Enhancing Speech Language Models through Descriptive Speech-Text Alignment
- Author(s): Authors not specified in the provided information
- Paper
-
【2024-05】-【Audio Flamingo】-【Nvidia】-【Type: Model】- Audio Flamingo: A Novel Audio Language Model with Few-Shot Learning and Dialogue Abilities
- Author(s): Authors not specified in the provided information
- Paper
-
【2024-04】-【SALMONN】-【Tsinghua】-【Type: Model】 -
【2024-03】-【WavLLM】-【CUHK】-【Type: Model】- WavLLM: Towards Robust and Adaptive Speech Large Language Model
- Author(s): Authors not specified in the provided information
- Paper
-
【2024-02】-【SLAM-LLM】-【Shanghai Jiao Tong University (SJTU)】-【Type: Model】- An Embarrassingly Simple Approach for LLM with Strong ASR Capacity
- Author(s): Authors not specified in the provided information
- Paper
-
【2024-01】-【Pengi】-【Microsoft】-【Type: Model】- Pengi: An Audio Language Model for Audio Tasks
- Author(s): Authors not specified in the provided information
- Paper
-
【2023-12】-【Qwen-Audio】-【Alibaba】-【Type: Model】 -
【2023-10】-【UniAudio】-【Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK)】-【Type: Model】 -
【2023-09】-【LLaSM】-【LinkSoul.AI】-【Type: Model】- LLaSM: Large Language and Speech Model
- Author(s): Authors not specified in the provided information
- Paper
-
【2023-09】-【Segment-level Q-Former】-【Tsinghua University, ByteDance】-【Type: Model】- Connecting Speech Encoder and Large Language Model for ASR
- Author(s): Wenyi Yu, Changli Tang, Guangzhi Sun, Xianzhao Chen, Tian Tan, Wei Li, Lu Lu, Zejun Ma, Chao Zhang
- Paper
-
【2023-07】-【Prompting LLMs with Speech Recognition】-【Meta】-【Type: Model】- Prompting Large Language Models with Speech Recognition Abilities
- Author(s): Yassir Fathullah, Chunyang Wu, Egor Lakomkin, Junteng Jia, Yuan Shangguan, Ke Li, Jinxi Guo, Wenhan Xiong, Jay Mahadeokar, Ozlem Kalinli, Christian Fuegen, Mike Seltzer
- Paper
-
【2023-05】-【SpeechGPT】-【Fudan University】-【Type: Model】 -
【2023-04】-【AudioGPT】-【Zhejiang University】-【Type: Model】- AudioGPT: Understanding and Generating Speech, Music, Sound, and Talking Head
- Author(s): Rongjie Huang, Mingze Li, Dongchao Yang, Jiatong Shi, Xuankai Chang, Zhenhui Ye, Yuning Wu, Zhiqing Hong, Jiawei Huang, Jinglin Liu, Yi Ren, Zhou Zhao, Shinji Watanabe
- Paper
-
【2025-01】-【UltraEval-Audio】-【OpenBMB】-【Type: Benchmark】 -
【2024-12】-【ADU-Bench】-【Tsinghua University, University of Oxford】-【Type: Benchmark】- Benchmarking Open-ended Audio Dialogue Understanding for Large Audio-Language Models
- Author(s): Kuofeng Gao, Shu-Tao Xia, Ke Xu, Philip Torr, Jindong Gu
- Paper
-
【2024-12】-【TalkArena】-【Stanford University, SCB 10X】-【Type: Interactive Benchmarking Tool】- TalkArena: Interactive Evaluation of Large Audio Models
- Author(s): Ella Minzhi Li*, Will Held*, Michael J. Ryan, Kunat Pipatanakul, Potsawee Manakul, Hao Zhu, Diyi Yang (*Equal Contribution)
- Demo / Other Link
-
【2024-12】-【ADU-Bench】-【Tsinghua University, University of Oxford】-【Type: Benchmark】- Benchmarking Open-ended Audio Dialogue Understanding for Large Audio-Language Models
- Author(s): Kuofeng Gao, Shu-Tao Xia, Ke Xu, Philip Torr, Jindong Gu
- Paper
-
【2024-11】-【Dynamic-SUPERB Phase-2】-【National Taiwan University, University of Texas at Austin, Carnegie Mellon University, Nanyang Technological University, Toyota Technological Institute of Chicago, Université du Québec (INRS-EMT), NVIDIA, ASAPP, Renmin University of China】-【Type: Evaluation Framework】- Dynamic-SUPERB Phase-2: A Collaboratively Expanding Benchmark for Measuring the Capabilities of Spoken Language Models with 180 Tasks
- Author(s): Chien-yu Huang, Wei-Chih Chen, Shu-wen Yang, Andy T. Liu, Chen-An Li, Yu-Xiang Lin, Wei-Cheng Tseng, Anuj Diwan, Yi-Jen Shih, Jiatong Shi, William Chen, Xuanjun Chen, Chi-Yuan Hsiao, Puyuan Peng, Shih-Heng Wang, Chun-Yi Kuan, Haibin Wu, Siddhant Arora, Kai-Wei Chang, Yifan Peng, Roshan Sharma, Shinji Watanabe, Bhiksha Ramakrishnan, Shady Shehata, Hung-yi Lee
- Paper / Other Link
-
【2024-10】-【VoiceBench】-【National University of Singapore】-【Type: Benchmark】- VoiceBench: Benchmarking LLM-Based Voice Assistants
- Author(s): Yiming Chen, Xianghu Yue, Chen Zhang, Xiaoxue Gao, Robby T. Tan, Haizhou Li
- Paper
-
【2024-10】-【MMAU】-【University of Maryland】-【Type: Benchmark】- MMAU: A Massive Multi-Task Audio Understanding and Reasoning Benchmark
- Author(s): S Sakshi, Utkarsh Tyagi, Sonal Kumar, Ashish Seth, Ramaneswaran Selvakumar, Oriol Nieto, Ramani Duraiswami, Sreyan Ghosh, Dinesh Manocha
- Paper / Other Link
-
【2024-09】-【SALMon】-【Hebrew University of Jerusalem】-【Type: Benchmark】 -
【2024-08】-【MuChoMusic】-【UPF, QMUL, UMG】-【Type: Benchmark】- MuChoMusic: Evaluating Music Understanding in Multimodal Audio-Language Models
- Author(s): Benno Weck, Ilaria Manco, Emmanouil Benetos, Elio Quinton, George Fazekas, Dmitry Bogdanov
- Paper
-
【2024-07】-【AudioEntailment】-【CMU, Microsoft】-【Type: Benchmark】- Audio Entailment: Assessing Deductive Reasoning for Audio Understanding
- Author(s): Soham Deshmukh, Shuo Han, Hazim Bukhari, Benjamin Elizalde, Hannes Gamper, Rita Singh, Bhiksha Raj
- Paper
-
【2024-06】-【AudioBench】-【A*STAR, Singapore】-【Type: Benchmark】 -
【2024-06】-【SD-Eval】-【CUHK, Bytedance】-【Type: Benchmark】- SD-Eval: A Benchmark Dataset for Spoken Dialogue Understanding Beyond Words
- Author(s): Junyi Ao, Yuancheng Wang, Xiaohai Tian, Dekun Chen, Jun Zhang, Lu Lu, Yuxuan Wang, Haizhou Li, Zhizheng Wu
- Paper
-
【2024-05】-【AIR-Bench】-【ZJU, Alibaba】-【Type: Benchmark】- AIR-Bench: Benchmarking Large Audio-Language Models via Generative Comprehension
- Author(s): Qian Yang, Jin Xu, Wenrui Liu, Yunfei Chu, Ziyue Jiang, Xiaohuan Zhou, Yichong Leng, Yuanjun Lv, Zhou Zhao, Chang Zhou, Jingren Zhou
- Paper
-
【2024-03】-【SpokenWOZ】-【Tencent】-【Type: Benchmark】 -
【2023-09】-【Dynamic-SUPERB】-【NTU-Taiwan, etc.】-【Type: Benchmark】- Dynamic-SUPERB: Towards A Dynamic, Collaborative, and Comprehensive Instruction-Tuning Benchmark for Speech
- Author(s): Chien-yu Huang, Ke-Han Lu, Shih-Heng Wang, Chi-Yuan Hsiao, Chun-Yi Kuan, Haibin Wu, Siddhant Arora, Kai-Wei Chang, Jiatong Shi, Yifan Peng, Roshan Sharma, Shinji Watanabe, Bhiksha Ramakrishnan, Shady Shehata, Hung-yi Lee
- Paper
-
【2024-11】-【WavChat-Survey】-【Zhejiang University】-【Type: Survey】- WavChat: A Survey of Spoken Dialogue Models
- Author(s): Shengpeng Ji, Yifu Chen, Minghui Fang, Jialong Zuo, Jingyu Lu, Hanting Wang, Ziyue Jiang, Long Zhou, Shujie Liu, Xize Cheng, Xiaoda Yang, Zehan Wang, Qian Yang, Jian Li, Yidi Jiang, Jingzhen He, Yunfei Chu, Jin Xu, Zhou Zhao
- Paper
-
【2024-10】-【SpeechLLM-Survey】-【SJTU, AISpeech】-【Type: Survey】- A Survey on Speech Large Language Models
- Author(s): Jing Peng, Yucheng Wang, Yu Xi, Xu Li, Xizhuo Zhang, Kai Yu
- Paper
-
【2024-10】-【SpeechLM-Survey】-【CUHK, Tencent】-【Type: Survey】- Recent Advances in Speech Language Models: A Survey
- Author(s): Wenqian Cui, Dianzhi Yu, Xiaoqi Jiao, Ziqiao Meng, Guangyan Zhang, Qichao Wang, Yiwen Guo, Irwin King
- Paper
-
【2024-02】-【AudioLM-Survey】-【National Taiwan University, MIT】-【Type: Survey】- Towards audio language modeling -- an overview
- Author(s): Haibin Wu, Xuanjun Chen, Yi-Cheng Lin, Kai-wei Chang, Ho-Lam Chung, Alexander H. Liu, Hung-yi Lee
- Paper
-
【2024-09】-【EMOVA】-【HKUST】-【Type: Model】- EMOVA: Empowering Language Models to See, Hear and Speak with Vivid Emotions
- Author(s): Kai Chen, Yunhao Gou, Runhui Huang, Zhili Liu, Daxin Tan, Jing Xu, Chunwei Wang, Yi Zhu, Yihan Zeng, Kuo Yang, Dingdong Wang, Kun Xiang, Haoyuan Li, Haoli Bai, Jianhua Han, Xiaohui Li, Weike Jin, Nian Xie, Yu Zhang, James T. Kwok, Hengshuang Zhao, Xiaodan Liang, Dit-Yan Yeung, Xiao Chen, Zhenguo Li, Wei Zhang, Qun Liu, Jun Yao, Lanqing Hong, Lu Hou, Hang Xu
- Paper / Demo
-
【2023-11】-【CoDi-2】-【UC Berkeley】-【Type: Model】 -
【2023-06】-【Macaw-LLM】-【Tencent】-【Type: Model】- Macaw-LLM: Multi-Modal Language Modeling with Image, Video, Audio, and Text Integration
- Author(s): Chenyang Lyu, Minghao Wu, Longyue Wang, Xinting Huang, Bingshuai Liu, Zefeng Du, Shuming Shi, Zhaopeng Tu
- Paper
-
【2024-06】-【Audio Hallucination】-【NTU-Taiwan】-【Type: Research】- Understanding Sounds, Missing the Questions: The Challenge of Object Hallucination in Large Audio-Language Models
- Author(s): Chun-Yi Kuan, Wei-Ping Huang, Hung-yi Lee
- Paper
-
【2024-06】-【CodecFake】-【National Taiwan University】-【Type: Safety】- CodecFake: Enhancing Anti-Spoofing Models Against Deepfake Audios from Codec-Based Speech Synthesis Systems
- Author(s): Haibin Wu, Yuan Tseng, Hung-yi Lee
- Paper / Other Link
-
【2024-05】-【VoiceJailbreak】-【CISPA】-【Type: Method】- Voice Jailbreak Attacks Against GPT-4o
- Author(s): Xinyue Shen, Yixin Wu, Michael Backes, Yang Zhang
- Paper
-
【2025-01】-【MinMo】-【FunAudioLLM Team, Tongyi Lab, Alibaba Group】-【Type: Multimodal Large Language Model】- MinMo: A Multimodal Large Language Model for Seamless Voice Interaction
- Author(s): Qian Chen, Yafeng Chen, Yanni Chen, Mengzhe Chen, Yingda Chen, Chong Deng, Zhihao Du, Ruize Gao, Changfeng Gao, Zhifu Gao, Yabin Li, Xiang Lv, Jiaqing Liu, Haoneng Luo, Bin Ma, Chongjia Ni, Xian Shi, Jialong Tang, Hui Wang, Hao Wang, Wen Wang, Yuxuan Wang, Yunlan Xu, Fan Yu, Zhijie Yan, Yexin Yang, Baosong Yang, Xian Yang, Guanrou Yang, Tianyu Zhao, Qinglin Zhang, Shiliang Zhang, Nan Zhao, Pei Zhang, Chong Zhang, Jinren Zhou
- Paper / Other Link
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Awesome-Audio-LLM
Similar Open Source Tools

Awesome-Audio-LLM
Awesome-Audio-LLM is a repository dedicated to various models and methods related to audio and language processing. It includes a wide range of research papers and models developed by different institutions and authors. The repository covers topics such as bridging audio and language, speech emotion recognition, voice assistants, and more. It serves as a comprehensive resource for those interested in the intersection of audio and language processing.
awesome-llm-unlearning
This repository tracks the latest research on machine unlearning in large language models (LLMs). It offers a comprehensive list of papers, datasets, and resources relevant to the topic.
awesome-llm-role-playing-with-persona
Awesome-llm-role-playing-with-persona is a curated list of resources for large language models for role-playing with assigned personas. It includes papers and resources related to persona-based dialogue systems, personalized response generation, psychology of LLMs, biases in LLMs, and more. The repository aims to provide a comprehensive collection of research papers and tools for exploring role-playing abilities of large language models in various contexts.
LLM-as-a-Judge
LLM-as-a-Judge is a repository that includes papers discussed in a survey paper titled 'A Survey on LLM-as-a-Judge'. The repository covers various aspects of using Large Language Models (LLMs) as judges for tasks such as evaluation, reasoning, and decision-making. It provides insights into evaluation pipelines, improvement strategies, and specific tasks related to LLMs. The papers included in the repository explore different methodologies, applications, and future research directions for leveraging LLMs as evaluators in various domains.
Awesome-LLM-Reasoning-Openai-o1-Survey
The repository 'Awesome LLM Reasoning Openai-o1 Survey' provides a collection of survey papers and related works on OpenAI o1, focusing on topics such as LLM reasoning, self-play reinforcement learning, complex logic reasoning, and scaling law. It includes papers from various institutions and researchers, showcasing advancements in reasoning bootstrapping, reasoning scaling law, self-play learning, step-wise and process-based optimization, and applications beyond math. The repository serves as a valuable resource for researchers interested in exploring the intersection of language models and reasoning techniques.
Awesome-Multimodal-LLM-for-Code
This repository contains papers, methods, benchmarks, and evaluations for code generation under multimodal scenarios. It covers UI code generation, scientific code generation, slide code generation, visually rich programming, logo generation, program repair, UML code generation, and general benchmarks.
Awesome-LLM-Preference-Learning
The repository 'Awesome-LLM-Preference-Learning' is the official repository of a survey paper titled 'Towards a Unified View of Preference Learning for Large Language Models: A Survey'. It contains a curated list of papers related to preference learning for Large Language Models (LLMs). The repository covers various aspects of preference learning, including on-policy and off-policy methods, feedback mechanisms, reward models, algorithms, evaluation techniques, and more. The papers included in the repository explore different approaches to aligning LLMs with human preferences, improving mathematical reasoning in LLMs, enhancing code generation, and optimizing language model performance.
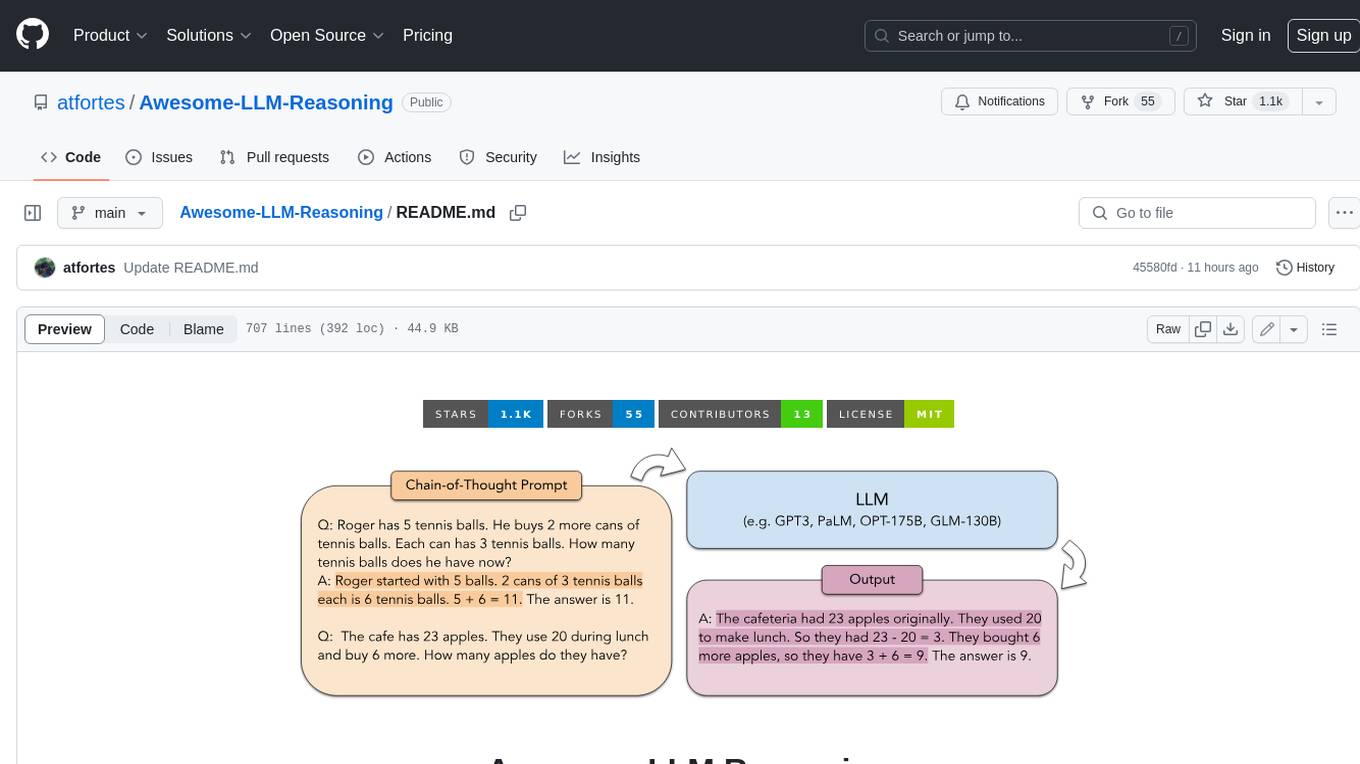
Awesome-LLM-Reasoning
**Curated collection of papers and resources on how to unlock the reasoning ability of LLMs and MLLMs.** **Description in less than 400 words, no line breaks and quotation marks.** Large Language Models (LLMs) have revolutionized the NLP landscape, showing improved performance and sample efficiency over smaller models. However, increasing model size alone has not proved sufficient for high performance on challenging reasoning tasks, such as solving arithmetic or commonsense problems. This curated collection of papers and resources presents the latest advancements in unlocking the reasoning abilities of LLMs and Multimodal LLMs (MLLMs). It covers various techniques, benchmarks, and applications, providing a comprehensive overview of the field. **5 jobs suitable for this tool, in lowercase letters.** - content writer - researcher - data analyst - software engineer - product manager **Keywords of the tool, in lowercase letters.** - llm - reasoning - multimodal - chain-of-thought - prompt engineering **5 specific tasks user can use this tool to do, in less than 3 words, Verb + noun form, in daily spoken language.** - write a story - answer a question - translate a language - generate code - summarize a document
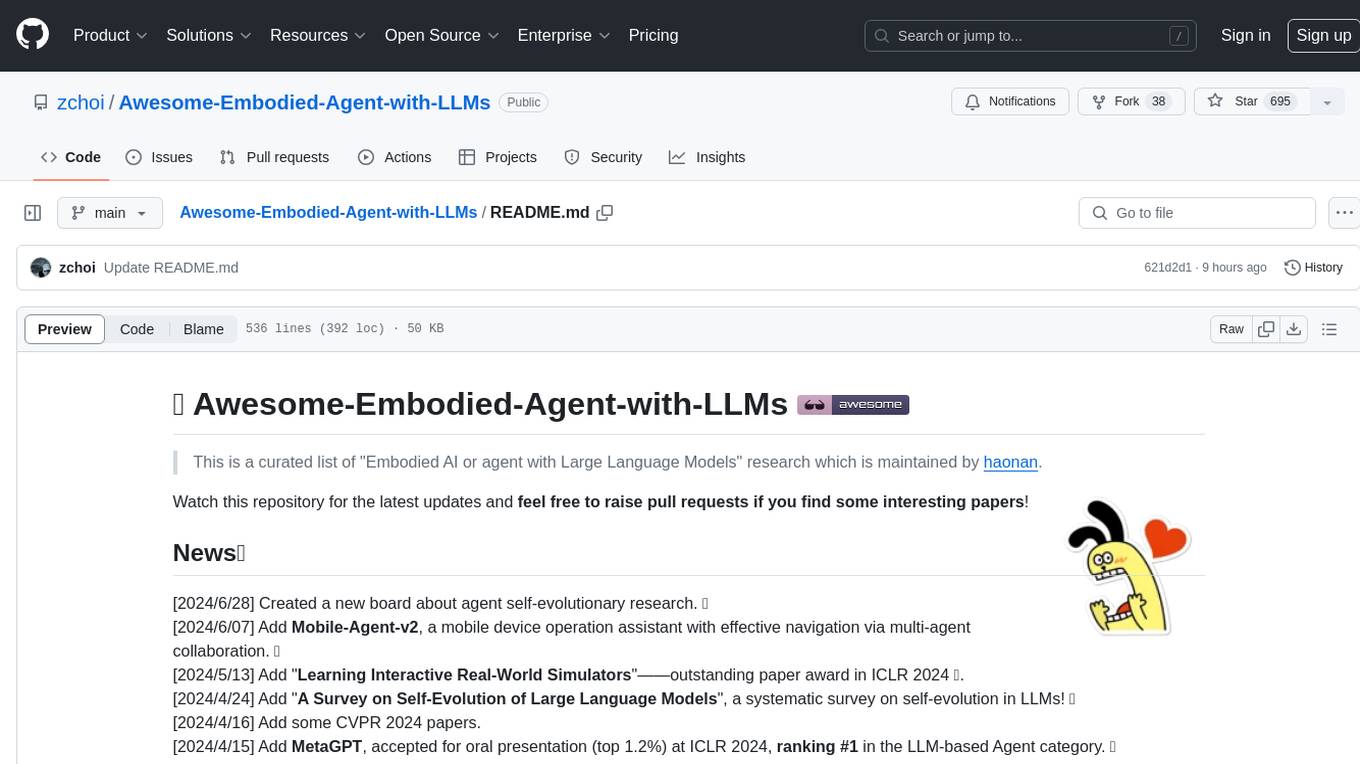
Awesome-Embodied-Agent-with-LLMs
This repository, named Awesome-Embodied-Agent-with-LLMs, is a curated list of research related to Embodied AI or agents with Large Language Models. It includes various papers, surveys, and projects focusing on topics such as self-evolving agents, advanced agent applications, LLMs with RL or world models, planning and manipulation, multi-agent learning and coordination, vision and language navigation, detection, 3D grounding, interactive embodied learning, rearrangement, benchmarks, simulators, and more. The repository provides a comprehensive collection of resources for individuals interested in exploring the intersection of embodied agents and large language models.
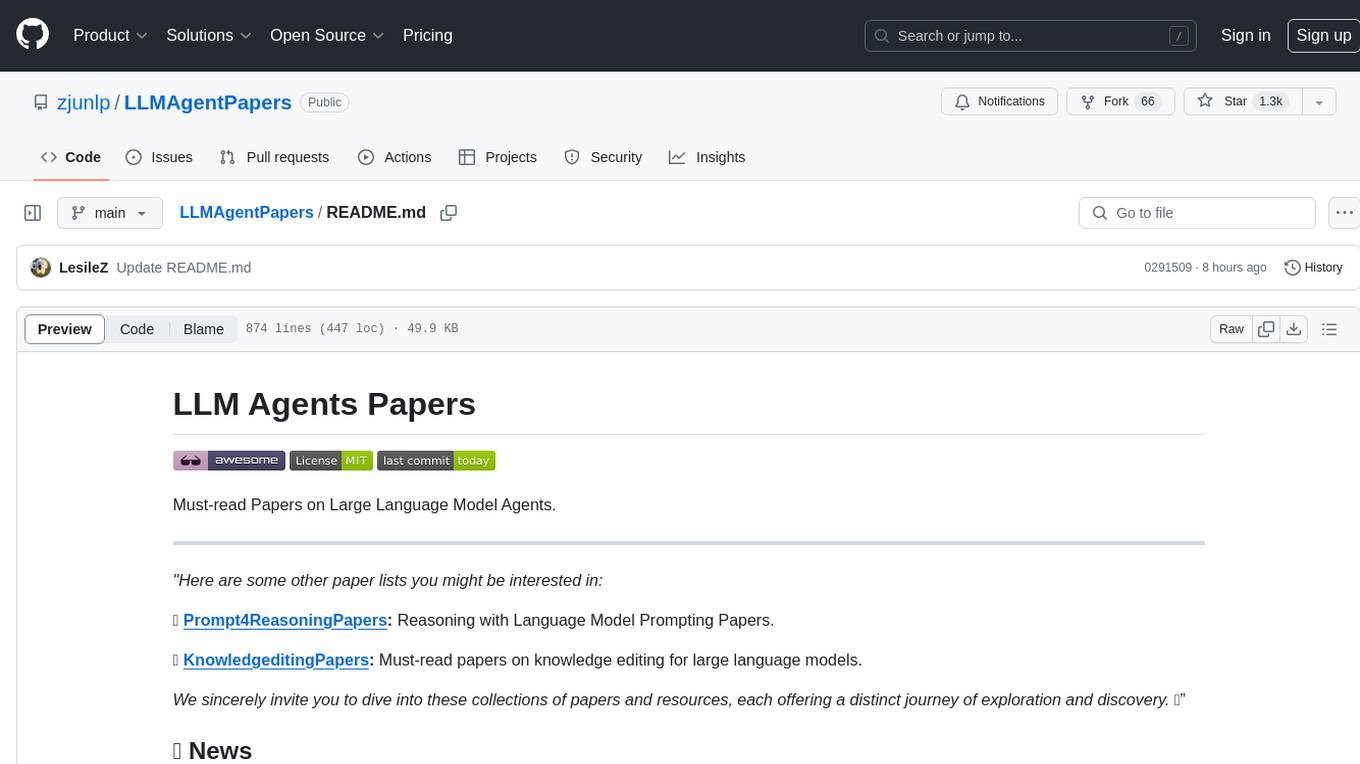
LLMAgentPapers
LLM Agents Papers is a repository containing must-read papers on Large Language Model Agents. It covers a wide range of topics related to language model agents, including interactive natural language processing, large language model-based autonomous agents, personality traits in large language models, memory enhancements, planning capabilities, tool use, multi-agent communication, and more. The repository also provides resources such as benchmarks, types of tools, and a tool list for building and evaluating language model agents. Contributors are encouraged to add important works to the repository.
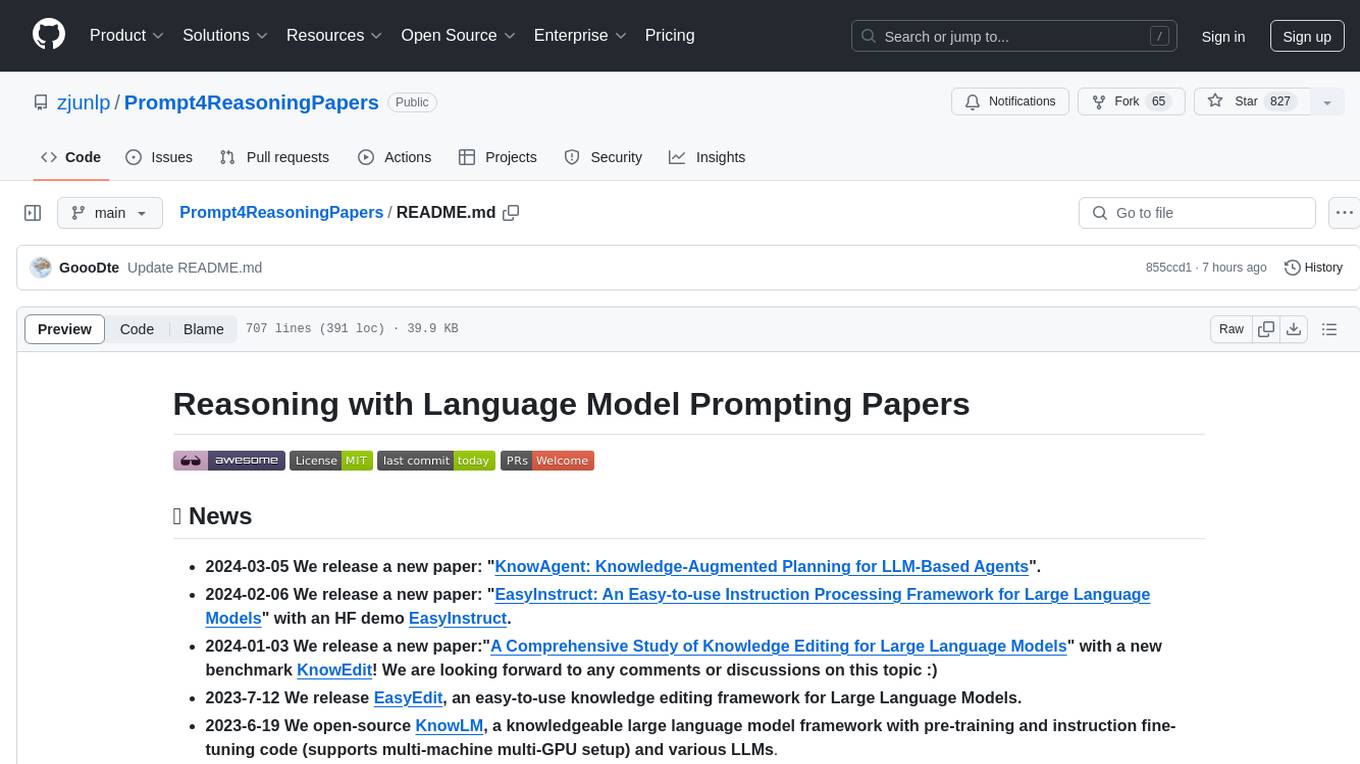
Prompt4ReasoningPapers
Prompt4ReasoningPapers is a repository dedicated to reasoning with language model prompting. It provides a comprehensive survey of cutting-edge research on reasoning abilities with language models. The repository includes papers, methods, analysis, resources, and tools related to reasoning tasks. It aims to support various real-world applications such as medical diagnosis, negotiation, etc.
Awesome-LLM-RAG
This repository, Awesome-LLM-RAG, aims to record advanced papers on Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) in Large Language Models (LLMs). It serves as a resource hub for researchers interested in promoting their work related to LLM RAG by updating paper information through pull requests. The repository covers various topics such as workshops, tutorials, papers, surveys, benchmarks, retrieval-enhanced LLMs, RAG instruction tuning, RAG in-context learning, RAG embeddings, RAG simulators, RAG search, RAG long-text and memory, RAG evaluation, RAG optimization, and RAG applications.
Awesome-Latent-CoT
This repository contains a regularly updated paper list for Large Language Models (LLMs) reasoning in latent space. Reasoning in latent space allows for more flexible and efficient thought representation beyond language tokens, bringing AI closer to human-like cognition. The repository covers various aspects of LLMs, including pre-training, supervised finetuning, analysis, interpretability, multimodal reasoning, and applications. It aims to showcase the advancements in reasoning with latent thoughts and continuous concepts in AI models.

awesome-generative-information-retrieval
This repository contains a curated list of resources on generative information retrieval, including research papers, datasets, tools, and applications. Generative information retrieval is a subfield of information retrieval that uses generative models to generate new documents or passages of text that are relevant to a given query. This can be useful for a variety of tasks, such as question answering, summarization, and document generation. The resources in this repository are intended to help researchers and practitioners stay up-to-date on the latest advances in generative information retrieval.
For similar tasks

Awesome-Audio-LLM
Awesome-Audio-LLM is a repository dedicated to various models and methods related to audio and language processing. It includes a wide range of research papers and models developed by different institutions and authors. The repository covers topics such as bridging audio and language, speech emotion recognition, voice assistants, and more. It serves as a comprehensive resource for those interested in the intersection of audio and language processing.
vocode-python
Vocode is an open source library that enables users to easily build voice-based LLM (Large Language Model) apps. With Vocode, users can create real-time streaming conversations with LLMs and deploy them for phone calls, Zoom meetings, and more. The library offers abstractions and integrations for transcription services, LLMs, and synthesis services, making it a comprehensive tool for voice-based applications.

ultravox
Ultravox is a fast multimodal Language Model (LLM) that can understand both text and human speech in real-time without the need for a separate Audio Speech Recognition (ASR) stage. By extending Meta's Llama 3 model with a multimodal projector, Ultravox converts audio directly into a high-dimensional space used by Llama 3, enabling quick responses and potential understanding of paralinguistic cues like timing and emotion in human speech. The current version (v0.3) has impressive speed metrics and aims for further enhancements. Ultravox currently converts audio to streaming text and plans to emit speech tokens for direct audio conversion. The tool is open for collaboration to enhance this functionality.
For similar jobs

Awesome-Audio-LLM
Awesome-Audio-LLM is a repository dedicated to various models and methods related to audio and language processing. It includes a wide range of research papers and models developed by different institutions and authors. The repository covers topics such as bridging audio and language, speech emotion recognition, voice assistants, and more. It serves as a comprehensive resource for those interested in the intersection of audio and language processing.
LLMVoX
LLMVoX is a lightweight 30M-parameter, LLM-agnostic, autoregressive streaming Text-to-Speech (TTS) system designed to convert text outputs from Large Language Models into high-fidelity streaming speech with low latency. It achieves significantly lower Word Error Rate compared to speech-enabled LLMs while operating at comparable latency and speech quality. Key features include being lightweight & fast with only 30M parameters, LLM-agnostic for easy integration with existing models, multi-queue streaming for continuous speech generation, and multilingual support for easy adaptation to new languages.

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.

oss-fuzz-gen
This framework generates fuzz targets for real-world `C`/`C++` projects with various Large Language Models (LLM) and benchmarks them via the `OSS-Fuzz` platform. It manages to successfully leverage LLMs to generate valid fuzz targets (which generate non-zero coverage increase) for 160 C/C++ projects. The maximum line coverage increase is 29% from the existing human-written targets.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.