
AwesomeResponsibleAI
A curated list of awesome academic research, books, code of ethics, data sets, institutes, maturity models, newsletters, principles, podcasts, reports, tools, regulations and standards related to Responsible, Trustworthy, and Human-Centered AI.
Stars: 66
Awesome Responsible AI is a curated list of academic research, books, code of ethics, courses, data sets, frameworks, institutes, newsletters, principles, podcasts, reports, tools, regulations, and standards related to Responsible, Trustworthy, and Human-Centered AI. It covers various concepts such as Responsible AI, Trustworthy AI, Human-Centered AI, Responsible AI frameworks, AI Governance, and more. The repository provides a comprehensive collection of resources for individuals interested in ethical, transparent, and accountable AI development and deployment.
README:
A curated list of awesome academic research, books, code of ethics, courses, data sets, frameworks, institutes, maturity models, newsletters, principles, podcasts, reports, tools, regulations and standards related to Responsible, Trustworthy, and Human-Centered AI.
AI governance is a system of rules, processes, frameworks, and tools within an organization to ensure the ethical and responsible development of AI.
Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence (HCAI) is an approach to AI development that prioritizes human users' needs, experiences, and well-being.
When we refer to a “system,” we are speaking both broadly about a fully functional structure and its discrete structural elements. To be considered Open Source, the requirements are the same, whether applied to a system, a model, weights and parameters, or other structural elements.
An Open Source AI is an AI system made available under terms and in a way that grant the freedoms1 to:
- Use the system for any purpose and without having to ask for permission.
- Study how the system works and inspect its components.
- Modify the system for any purpose, including to change its output.
- Share the system for others to use with or without modifications, for any purpose.
Responsible AI (RAI) refers to the development, deployment, and use of artificial intelligence (AI) systems in ways that are ethical, transparent, accountable, and aligned with human values.
Responsible AI frameworks often encompass guidelines, principles, and practices that prioritize fairness, safety, and respect for individual rights.
Trustworthy AI (TAI) refers to artificial intelligence systems designed and deployed to be transparent, robust and respectful of data privacy.
AI is a transformative technology prone to reshape industries, yet it requires careful governance to balance the benefits of automation and insight with protections against unintended social, economic, and security impacts. You can read more about the current wave here.
- Academic Research
- Books
- Code of Ethics
- Courses
- Data Sets
- Frameworks
- Institutes
- Maturity Models
- Newsletters
- Principles
- Podcasts
- Reports
- Tools
- Regulations
- Standards
- Citing this repository
- Oprea, A., & Vassilev, A. (2023). Adversarial machine learning: A taxonomy and terminology of attacks and mitigations. National Institute of Standards and Technology. Article
- Schwartz, R., et al. (2022). Towards a standard for identifying and managing bias in artificial intelligence (Vol. 3, p. 00). US Department of Commerce, National Institute of Standards and Technology. Article
NIST
- D'Amour, A., et al. (2022). Underspecification presents challenges for credibility in modern machine learning. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 23(226), 1-61. Article
Google
- Ackerman, S., et al. (2021, June). Machine learning model drift detection via weak data slices. In 2021 IEEE/ACM Third International Workshop on Deep Learning for Testing and Testing for Deep Learning (DeepTest) (pp. 1-8). IEEE. Article
IBM - Ackerman, S., Raz, O., & Zalmanovici, M. (2020, February). FreaAI: Automated extraction of data slices to test machine learning models. In International Workshop on Engineering Dependable and Secure Machine Learning Systems (pp. 67-83). Cham: Springer International Publishing. Article
IBM
- Dhurandhar, A., Chen, P. Y., Luss, R., Tu, C. C., Ting, P., Shanmugam, K., & Das, P. (2018). Explanations based on the missing: Towards contrastive explanations with pertinent negatives. Advances in neural information processing systems, 31. Article
University of MichiganIBM Research - Dhurandhar, A., Shanmugam, K., Luss, R., & Olsen, P. A. (2018). Improving simple models with confidence profiles. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 31. Article
IBM Research - Gurumoorthy, K. S., Dhurandhar, A., Cecchi, G., & Aggarwal, C. (2019, November). Efficient data representation by selecting prototypes with importance weights. In 2019 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM) (pp. 260-269). IEEE. Article
Amazon Development CenterIBM Research - Hind, M., Wei, D., Campbell, M., Codella, N. C., Dhurandhar, A., Mojsilović, A., ... & Varshney, K. R. (2019, January). TED: Teaching AI to explain its decisions. In Proceedings of the 2019 AAAI/ACM Conference on AI, Ethics, and Society (pp. 123-129)Article
IBM Research - Lundberg, S. M., & Lee, S. I. (2017). A unified approach to interpreting model predictions. Advances in neural information processing systems, 30. Article, Github
University of Washington - Luss, R., Chen, P. Y., Dhurandhar, A., Sattigeri, P., Zhang, Y., Shanmugam, K., & Tu, C. C. (2021, August). Leveraging latent features for local explanations. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM SIGKDD conference on knowledge discovery & data mining (pp. 1139-1149). Article
IBM ResearchUniversity of Michigan - Ribeiro, M. T., Singh, S., & Guestrin, C. (2016, August). "Why should i trust you?" Explaining the predictions of any classifier. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining (pp. 1135-1144). Article, Github
University of Washington - Wei, D., Dash, S., Gao, T., & Gunluk, O. (2019, May). Generalized linear rule models. In International conference on machine learning (pp. 6687-6696). PMLR. Article
IBM Research - Contrastive Explanations Method with Monotonic Attribute Functions (Luss et al., 2019)
- Boolean Decision Rules via Column Generation (Light Edition) (Dash et al., 2018)
IBM Research - Towards Robust Interpretability with Self-Explaining Neural Networks (Alvarez-Melis et al., 2018)
MIT
An interesting curated collection of articules (updated until 2021) A Living and Curated Collection of Explainable AI Methods.
- Gebru, T., Morgenstern, J., Vecchione, B., Vaughan, J. W., Wallach, H., Iii, H. D., & Crawford, K. (2021). Datasheets for datasets. Communications of the ACM, 64(12), 86-92. Article
Google - Mitchell, M., Wu, S., Zaldivar, A., Barnes, P., Vasserman, L., Hutchinson, B., ... & Gebru, T. (2019, January). Model cards for model reporting. In Proceedings of the conference on fairness, accountability, and transparency (pp. 220-229). Article
Google - Pushkarna, M., Zaldivar, A., & Kjartansson, O. (2022, June). Data cards: Purposeful and transparent dataset documentation for responsible ai. In Proceedings of the 2022 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency (pp. 1776-1826). Article
Google - Rostamzadeh, N., Mincu, D., Roy, S., Smart, A., Wilcox, L., Pushkarna, M., ... & Heller, K. (2022, June). Healthsheet: development of a transparency artifact for health datasets. In Proceedings of the 2022 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency (pp. 1943-1961). Article
Google - Saint-Jacques, G., Sepehri, A., Li, N., & Perisic, I. (2020). Fairness through Experimentation: Inequality in A/B testing as an approach to responsible design. arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.05819. Article
LinkedIn
- Agarwal, C., et al. (2022). Openxai: Towards a transparent evaluation of model explanations. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 35, 15784-15799. Article
- Liesenfeld, A., and Dingemanse, M. (2024). Rethinking Open Source Generative AI: Open-Washing and the EU AI Act. In The 2024 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency (FAccT ’24). Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: ACM. Article Benchmark
- Caton, S., & Haas, C. (2024). Fairness in machine learning: A survey. ACM Computing Surveys, 56(7), 1-38. Article
- Chouldechova, A. (2017). Fair prediction with disparate impact: A study of bias in recidivism prediction instruments. Big data, 5(2), 153-163. Article
- Coston, A., Mishler, A., Kennedy, E. H., & Chouldechova, A. (2020, January). Counterfactual risk assessments, evaluation, and fairness. In Proceedings of the 2020 conference on fairness, accountability, and transparency (pp. 582-593). Article
- Jesus, S., Saleiro, P., Jorge, B. M., Ribeiro, R. P., Gama, J., Bizarro, P., & Ghani, R. (2024). Aequitas Flow: Streamlining Fair ML Experimentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.05809. Article
- Saleiro, P., Kuester, B., Hinkson, L., London, J., Stevens, A., Anisfeld, A., ... & Ghani, R. (2018). Aequitas: A bias and fairness audit toolkit. arXiv preprint arXiv:1811.05577. Article
- Vasudevan, S., & Kenthapadi, K. (2020, October). Lift: A scalable framework for measuring fairness in ml applications. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM international conference on information & knowledge management (pp. 2773-2780). Article
LinkedIn
- Wasil, A. R., Reed, T., Miller, J. W., & Barnett, P. (2024). Verification methods for international AI agreements. arXiv preprint arXiv:2408.16074. Article
- Slattery, P., et al. (2024). The ai risk repository: A comprehensive meta-review, database, and taxonomy of risks from artificial intelligence. arXiv preprint arXiv:2408.12622. Article
- Lacoste, A., Luccioni, A., Schmidt, V., & Dandres, T. (2019). Quantifying the carbon emissions of machine learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.09700. Article
- P. Li, J. Yang, M. A. Islam, S. Ren, (2023) Making AI Less “Thirsty”: Uncovering and Addressing the Secret Water Footprint of AI Models. arXiv:2304.03271 Article
- Parcollet, T., & Ravanelli, M. (2021). The energy and carbon footprint of training end-to-end speech recognizers. Article
- Patterson, D., Gonzalez, J., Le, Q., Liang, C., Munguia, L.M., Rothchild, D., So, D., Texier, M. and Dean, J. (2021). Carbon emissions and large neural network training. arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.10350. Article
- Sculley, D., Holt, G., Golovin, D., Davydov, E., Phillips, T., Ebner, D., ... & Dennison, D. (2015). Hidden technical debt in machine learning systems. Advances in neural information processing systems, 28. Article
Google - Sculley, D., Holt, G., Golovin, D., Davydov, E., Phillips, T., Ebner, D., ... & Young, M. (2014, December). Machine learning: The high interest credit card of technical debt. In SE4ML: software engineering for machine learning (NIPS 2014 Workshop) (Vol. 111, p. 112). Article
Google - Strubell, E., Ganesh, A., & McCallum, A. (2019). Energy and policy considerations for deep learning in NLP. arXiv preprint arXiv:1906.02243. Article
- Sustainable AI: AI for sustainability and the sustainability of AI (van Wynsberghe, A. 2021). AI and Ethics, 1-6
- Green Algorithms: Quantifying the carbon emissions of computation (Lannelongue, L. et al. 2020)
- C.-J. Wu, R. Raghavendra, U. Gupta, B. Acun, N. Ardalani, K. Maeng, G. Chang, F. Aga, J. Huang, C. Bai, M. Gschwind, A. Gupta, M. Ott, A. Melnikov, S. Candido, D. Brooks, G. Chauhan, B. Lee, H.-H. Lee, K. Hazelwood, Sustainable AI: Environmental implications, challenges and opportunities. Proceedings of the 5th Conference on Machine Learning and Systems (MLSys) (2022) vol. 4, pp. 795–813. Article
- Google Research on Responsible AI: https://research.google/pubs/?collection=responsible-ai
Google - Pipeline-Aware Fairness: http://fairpipe.dssg.io
Computational reproducibility (when the results in a paper can be replicated using the exact code and dataset provided by the authors) is becoming a significant problem not only for academic but for practitionars who want to implement AI in their organizations and aim to resuse ideas from academia. Read more about this problem here.
- Barocas, S., Hardt, M., & Narayanan, A. (2023). Fairness and machine learning: Limitations and opportunities. MIT press. Book
- Barrett, M., Gerke, T. & D’Agostino McGowa, L. (2024). Causal Inference in R Book
Causal InferenceR - Biecek, P., & Burzykowski, T. (2021). Explanatory model analysis: explore, explain, and examine predictive models. Chapman and Hall/CRC. Book
ExplainabilityInterpretabilityTransparencyR - Biecek, P. (2024). Adversarial Model Analysis. Book
SafetyRed Teaming - Cunningham, Scott. (2021) Causal inference: The mixtape. Yale university press. Book
Causal Inference - Fourrier, C. and et all. (2024) LLM Evaluation Guidebook. Github Repository. Web
LLM Evaluation - Freiesleben, T. & Molnar, C. (2024). Supervised Machine Learning for Science: How to stop worrying and love your black box. Book
- Matloff, N et al. (2204) Data Science Looks at Discrimination Book
FairnessR - Molnar, C. (2020). Interpretable Machine Learning. Lulu.com. Book
ExplainabilityInterpretabilityTransparencyR - Huntington-Klein, Nick. (2012) The effect: An introduction to research design and causality. Chapman and Hall/CRC. Book
Causal Inference
- Trust in Machine Learning (Varshney, K., 2022)
SafetyPrivacyDriftFairnessInterpretabilityExplainability - Interpretable AI (Thampi, A., 2022)
ExplainabilityFairnessInterpretability - AI Fairness (Mahoney, T., Varshney, K.R., Hind, M., 2020
ReportFairness - Practical Fairness (Nielsen, A., 2021)
Fairness - Hands-On Explainable AI (XAI) with Python (Rothman, D., 2020)
Explainability - AI and the Law (Kilroy, K., 2021)
ReportTrustLaw - Responsible Machine Learning (Hall, P., Gill, N., Cox, B., 2020)
ReportLawComplianceSafetyPrivacy - Privacy-Preserving Machine Learning
- Human-In-The-Loop Machine Learning: Active Learning and Annotation for Human-Centered AI
- Interpretable Machine Learning With Python: Learn to Build Interpretable High-Performance Models With Hands-On Real-World Examples
- Responsible AI (Hall, P., Chowdhury, R., 2023)
GovernanceSafetyDrift - Marcus, G., and Davis, E. (2019). Rebooting AI: Building artificial intelligence we can trust. Vintage. Book
- Marcus, G. F. (2024). Taming Silicon Valley: How We Can Ensure That AI Works for Us. MIT Press. Book
- Yampolskiy, R. V. (2024) AI: Unexplainable, Unpredictable, Uncontrollable. 2024. CRC Press Book
- ACS Code of Professional Conduct by Australian ICT (Information and Communication Technology)
- AI Standards Hub
- Association for Computer Machinery's Code of Ethics and Professional Conduct
- IEEE Global Initiative for Ethical Considerations in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Autonomous Systems (AS)
- ISO/IEC's Standards for Artificial Intelligence
-
AI Alignment
BlueDot Impact -
AI Fast-Track
BlueDot Impact
-
AI Governance
BlueDot Impact -
AI Ethics & Governance (AEG)
The Alan Turing Institute
-
Explainable Artificial Intelligence
Harvard University
-
CS594 - Causal Inference and Learning
University of Illinois at Chicago
-
Introduction to AI Ethics
Kaggle - Modern-Day Oracles or Bullshit Machines?
-
Practical Data Ethics
Fast.ai -
Public Engagement of Data Science and AI (PED)
The Alan Turing Institute
-
Data Justice (DJ)
The Alan Turing Institute
-
CS7880 - Rigorous Approaches to Data Privacy
Northeastern University -
CS860 - Algorithms for Private Data Analysis
University of Waterloo
-
CIS 4230/5230 - Ethical Algorithm Design
University of Pennsylvania -
Responsible Research and Innovation (RRI)
The Alan Turing Institute
-
AI Safety, Ethics and Society
Center for AI Safety -
Introduction to ML Safety
Center for AI Safety
-
AI Risk Database
MITRE -
AI Risk Repository
MIT - ARC AGI
- Common Corpus
- An ImageNet replacement for self-supervised pretraining without humans
- Huggingface Data Sets
- The Stack
-
A Framework for Ethical Decision Making
Markkula Center for Applied Ethics -
Data Ethics Canvas
Open Data Institute -
Deon
PythonDrivendata - Ethics & Algorithms Toolkit
-
RAI Toolkit
US Department of Defense
-
Beijing AISI
China -
Canada AISI
Canada -
EU AI Office
Europe -
Korea AISI
South Korea -
Singapore AISI
Singapore
-
UK AISI
United Kingdom
| Code | Title | Description | Status | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI Safety Evaluation v1.0.1 | A guide to red teaming techniques for AI safety | Presents basic concepts that those involved in the development and provision of AI systems can refer to when conducting AI Safety evaluations | Published | Source |
| AI Safety RT v1.0.0 | Guide to Red Teaming Methodology on AI Safety | Intended to help developers and providers of AI systems to evaluate the basic considerations of red teaming methodologies for AI systems from the viewpoint of attackers | Published | Source |
| Code | Title | Description | Status | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NIST AI 800-1 | Managing Misuse Risk for Dual-Use Foundation Models | Outlines voluntary best practices for identifying, measuring, and mitigating risks to public safety and national security across the AI lifecycle | Draft (second Version) | Source |
-
Ada Lovelace Institute
United Kingdom -
Centre pour la Securité de l'IA, CeSIA
France - European Centre for Algorithmic Transparency
-
Center for Human-Compatible AI
UC BerkeleyUnited States of America -
Center for Responsible AI
New York UniversityUnited States of America -
Montreal AI Ethics Institute
Canada -
Munich Center for Technology in Society (IEAI)
TUM School of Social Sciences and TechnologyGermany -
National AI Centre's Responsible AI Network
Australia -
Open Data Institute
United Kingdom -
Stanford University Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence (HAI)
United States of America - The Institute for Ethical AI & Machine Learning
-
UNESCO Chair in AI Ethics & Governance
IE UniversitySpain -
University of Oxford Institute for Ethics in AI
University of OxfordUnited Kingdom - Australian Government-funded AI Adopt Centres:
- Future of Life Institute: Focused on reducing existential risks, this institute brings together experts to ensure AI benefits humanity.
- International Panel on the Information Environment: A global network of scholars and practitioners working to improve public understanding of our evolving information landscape, including the role of AI.
- Center for AI Safety: This organization researches the challenges of AI safety and develops strategies to mitigate potential risks in AI development.
- Distributed AI Research Institute -DAIR-: DAIR advocates for decentralized and transparent AI research, emphasizing open collaboration for safe technological progress.
- International Association for Safe and Ethical AI: Dedicated to advancing safe and ethical AI practices, this association provides a platform for stakeholders to share guidelines and best practices.
- Partnership on AI: Bringing together industry, academia, and civil society, this partnership promotes responsible AI development and broad benefits for all.
- AI Now Institute: An interdisciplinary research center that examines the social implications of AI and advocates for greater accountability in AI systems.
- Centre for the Governance of AI: Based at the University of Oxford, this centre researches policy and governance frameworks to manage the challenges of AI technologies.
- Future of Humanity Institute: An interdisciplinary research center that explores global challenges and the long-term impacts of AI on society and humanity.
- Machine Intelligence Research Institute -MIRI-: MIRI focuses on developing theoretical tools to ensure that advanced AI systems are aligned with human values and remain safe.
- AI Policy Perspectives
- AI Policy Weekly
- AI Safety in China
- AI Safety Newsletter
- AI Snake Oil
- Import AI
- Marcus on AI
- ML Safety Newsletter
- Navigating AI Risks
- One Useful Thing
- The AI Ethics Brief
- The AI Evaluation Substack
- The EU AI Act Newsletter
- The Machine Learning Engineer
- Turing Post
-
Allianz's Principles for a responsible usage of AI
Allianz - Asilomar AI principles
- European Commission's Guidelines for Trustworthy AI
-
Google's AI Principles
Google -
IEEE's Ethically Aligned Design
IEEE -
Microsoft's AI principles
Microsoft -
OECD's AI principles
OECD -
Telefonica's AI principles
Telefonica - The Institute for Ethical AI & Machine Learning: The Responsible Machine Learning Principles
Additional:
-
FAIR Principles
FindabilityAccessibilityInteroperabilityReuse
- Araujo, R. 2024. Understanding the First Wave of AI Safety Institutes: Characteristics, Functions, and Challenges. Institute for AI Policy and Strategy (IAPS) Article
- Buchanan, B. 2020. The AI triad and what it means for national security strategy. Center for Security and Emerging Technology. Article
- Corrigan, J. et al. 2023. The Policy Playbook: Building a Systems-Oriented Approach to Technology and National Security Policy. CSET (Center for Security and Emerging Technology) Article
- Curto, J. 2024. How Can Spain Remain Internationally Competitive in AI under EU Legislation? Article
- CSIS. 2024 The AI Safety Institute International Network: Next Steps and Recommendations. CSIS (Center for Strategic and International Studies) Article
- Gupta, Ritwik, et al. (2024). Data-Centric AI Governance: Addressing the Limitations of Model-Focused Policies. arXiv preprint arXiv:2409.17216 (Article)[https://arxiv.org/pdf/2409.17216]
- Hendrycks, D. et al. 2023. An overview of catastrophic AI risks. Center of AI Safety. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.12001. Article
- Janjeva, A., et al. (2023). Strengthening Resilience to AI Risk. A guide for UK policymakers. CETaS (Centre for Emerging Technology and Security) Article
- Piattini, M. and Fernández C.M. 2024. Marco Confiable. Revista SIC 162 Article
- Sastry, G., et al. 2024. Computing Power and the Governance of Artificial Intelligence. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.08797. Article
- AIAAIC
- AI Badness: An open catalog of generative AI badness
- AI Incident Database
-
AI Incident Tracker
MIT - AI Vulnerability Database (AVID)
- George Washington University Law School's AI Litigation Database
- Merging AI Incidents Research with Political Misinformation Research: Introducing the Political Deepfakes Incidents Database
- OECD AI Incidents Monitor
- Verica Open Incident Database (VOID)
-
International AI Safety Report
AI Action Summit
-
Copyright and Artificial Intelligence
US Copyright Office
-
AI Safety Index - 2024 -
Future of Life - Global Index for AI Safety
- State of AI - from 2018 up to now -
-
The AI Index Report - from 2017 up to now -
Stanford Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence
-
Four Principles of Explainable Artificial Intelligence
NISTExplainability -
Psychological Foundations of Explainability and Interpretability in Artificial Intelligence
NISTExplainability -
Inferring Concept Drift Without Labeled Data, 2021
Drift -
Interpretability, Fast Forward Labs, 2020
Interpretability -
Towards a Standard for Identifying and Managing Bias in Artificial Intelligence (NIST Special Publication 1270)
NISTBias -
Auditing machine learning algorithms
Auditing
-
balance
PythonFacebook -
smclafify
PythonAmazon -
SolasAI
Python -
TRAK (Attributing Model Behaviour at Scale) Article
Python
-
CausalAI
PythonSalesforce -
CausalNex
Python -
CausalImpact
R -
Causalinference
Python -
Causal Inference 360
Python -
CausalPy
Python -
CIMTx: Causal Inference for Multiple Treatments with a Binary Outcome
R -
dagitty
R -
DoWhy
PythonMicrosoft -
mediation: Causal Mediation Analysis
R -
MRPC
R
-
Alibi Detect
Python -
Deepchecks
Python -
drifter
R -
Evidently
Python -
nannyML
Python -
phoenix
Python
-
Aequitas' Bias & Fairness Audit Toolkit
Python -
AI360 Toolkit
PythonRIBM -
dsld: Data Science Looks at Discrimination
R -
EDFfair: Explicitly Deweighted Features
R -
EquiPy
Python -
Fairlearn
PythonMicrosoft -
Fairmodels
RUniversity of California -
fairness
R -
Fairness Indicators
PythonGoogle -
FairRankTune
Python -
FairPAN - Fair Predictive Adversarial Network
R -
OxonFair
PythonOxford Internet Institute -
Themis ML
Python -
What-If Tool
PythonGoogle
-
Butterfree
Python -
Featureform
Python -
Feathr
Python -
Feast
Python -
Hopsworks
Python
-
Alibi Explain
Python -
Automated interpretability
PythonOpenAI -
AI360 Toolkit
PythonRIBM -
aorsf: Accelerated Oblique Random Survival Forests
R -
breakDown: Model Agnostic Explainers for Individual Predictions
R -
captum
PythonPyTorch -
ceterisParibus: Ceteris Paribus Profiles
R -
DALEX: moDel Agnostic Language for Exploration and eXplanation
PythonR -
DALEXtra: extension for DALEX
PythonR -
Dianna
Python -
Diverse Counterfactual Explanations (DiCE)
PythonMicrosoft -
dtreeviz
Python -
ecco article
Python -
effectplots
R -
eli5
Python -
explabox
PythonNational Police Lab AI -
eXplainability Toolbox
Python -
ExplainaBoard
PythonCarnegie Mellon University -
ExplainerHub in github
Python -
fastshap
R -
fasttreeshap
PythonLinkedIn -
FAT Forensics
Python -
ferret
Python -
flashlight
R -
Human Learn
Python -
hstats
R -
innvestigate
PythonNeural Networks -
Inseq
Python -
intepretML
Python -
interactions: Comprehensive, User-Friendly Toolkit for Probing Interactions
R -
kernelshap: Kernel SHAP
R -
Learning Interpretability Tool
PythonGoogle -
lime: Local Interpretable Model-Agnostic Explanations
R -
Network Dissection
PythonNeural NetworksMIT -
OmniXAI
PythonSalesforce -
Shap
Python -
Shapash
Python -
shapper
R -
shapviz
R -
Skater
PythonOracle -
survex
R -
teller
Python -
TCAV (Testing with Concept Activation Vectors)
Python -
Transformer Debugger
PythonOpenAI -
truelens
PythonTruera -
truelens-eval
PythonTruera -
pre: Prediction Rule Ensembles
R -
Vetiver
RPythonPosit -
vip
R -
vivid
R -
XAI - An eXplainability toolbox for machine learning
PythonThe Institute for Ethical Machine Learning -
xplique
Python -
XAIoGraphs
PythonTelefonica -
XAITK
PythonDARPA -
Zennit
Python
-
imodels
Python -
imodelsX
Python -
interpretML
PythonMicrosoftR -
PiML Toolbox
Python -
Tensorflow Lattice
PythonGoogle
-
COMPL-AI
PythonETH ZurichInsaitLaticeFlow AI
- AIluminate
- AlignEval: Making Evals Easy, Fun, and Semi-Automated Motivation
-
AlpacaEval
Python -
ARES
PythonStandorf Future Data Systems -
Azure AI Evaluation
PythonMicrosoft -
Banana-lyzer
Python -
BALROG
Python -
BIG-Bench Extra Hard
PythonDeepmind -
DeepEval
Python -
evals
PythonOpenAI -
EvalScope
Python -
FMBench
PythonAmazon -
FlagEval
PythonBAAI -
FBI: Finding Blindspots in LLM Evaluations with Interpretable Checklists
Python - FrontierMath
- Geekbench AI
-
Giskard
Python -
HAL Harness
PythonPLI -
HELM
Python -
Humanity's Last Exam
Scale AICenter for AI Safety -
Inspect
UK AISIPython -
Jailbreakbench
Python -
LightEval
HuggingFacePython -
LiveBench: A Challenging, Contamination-Free LLM Benchmark
Contamination free -
LM Evaluation Harness
Python -
lmms-eval
Python -
MixEval
Python - ML Commons Safety Benchmark for general purpose AI chat model
-
MLGym
PythonFacebookAgents -
MLPerf Training Benchmark
Training -
MMMU
ApplePython -
Moonshoot
AI Verify FoundationPython -
NaturalBench
Python -
OffsetBias: Leveraging Debiased Data for Tuning Evaluators
Python -
opik
CometPython -
Phoenix
Arize AIPython -
Prometheus
Python -
Promptfoo
Python -
ragas
Python -
RewardBench: Evaluating Reward Models
PythonAi2 -
Rouge
Python -
SALAD-BENCH Article
Python -
Selene Mini
PythonAtla -
simple evals
PythonOpenAI -
StrongREJECT jailbreak benchmark
Python -
τ-bench: A Benchmark for Tool-Agent-User Interaction in Real-World Domains
Python -
Yet Another Applied LLM Benchmark
Python -
Verdict
Python -
VLMEvalKit
Python -
WindowsAgentArena
PythonMicrosoft
Additional benchmarks can be found here.
-
auditor
R -
automl: Deep Learning with Metaheuristic
R -
AutoKeras
Python -
Auto-Sklearn
Python -
DataPerf
PythonGoogle -
deepchecks
Python -
EloML
R -
Featuretools
Python -
LOFO Importance
Python -
forester
R -
metrica: Prediction performance metrics
R -
MLmetrics
R -
model-diagnostics
Python -
NNI: Neural Network Intelligence
PythonMicrosoft -
performance
R -
rliable
PythonGoogle -
SLmetrics
R -
TensorFlow Model Analysis
PythonGoogle -
TPOT
Python -
Unleash
Python -
yardstick
R -
Yellowbrick
Python -
WeightWatcher (Examples)
Python
-
Copyright Traps for Large Language Models
Python -
Nightshade
University of ChicagoTool -
Glaze
University of ChicagoTool -
Fawkes
University of ChicagoTool
-
BackPACK
Python -
diffpriv
R -
Diffprivlib
PythonIBM -
Discrete Gaussian for Differential Privacy
PythonIBM -
Opacus
PythonFacebook -
Privacy Meter
PythonNational University of Singapore -
PyVacy: Privacy Algorithms for PyTorch
Python -
SEAL
PythonMicrosoft -
Tensorflow Privacy
PythonGoogle
-
BELLS (Benchmark for the Evaluation of LLM Safeguards)
PythonCeSIA - Centre pour la Sécurité de l'IA - BetterBench Database
-
openXAI
Python
-
Adversarial Robustness Toolbox (ART)
Python -
BackdoorBench
Python -
Factool
Python -
Foolbox
Python -
Guardrails
Python -
NeMo Guardrails
PythonAmazon
-
AIxploit
Python -
Bandit
Python -
Diotra
PythonNIST -
Garak
PythonNvidia -
Safety CLI
Python
-
Counterfit
PythonMicrosoft -
detect-secrets
Python -
Modelscan
Python -
NB Defense
Python -
PyRIT
PythonMicrosoft -
Rebuff Playground
Python -
Turing Data Safe Haven
PythonThe Alan Turing Institute
For consumers:
- Curator
-
DataSynthesizer: Privacy-Preserving Synthetic Datasets
PythonDrexel UniversityUniversity of Washington -
Gretel Synthetics
Python -
SmartNoise
PythonOpenDP -
SDV
Python -
Snorkel
Python -
YData Synthetic
Python
-
Azure Sustainability Calculator
Microsoft -
Carbon Tracker Website
Python -
CodeCarbon Website
Python - Computer Progress
-
Impact Framework
API
-
Deepchecks
Python -
Dr. Why
RWarsaw University of Technology -
Mercury
PythonBBVA -
Responsible AI Toolbox
PythonMicrosoft -
Responsible AI Widgets
RMicrosoft -
The Data Cards Playbook
PythonGoogle -
Zeno Hub
Python
-
AudioSeal: Proactive Localized Watermarking
PythonFacebook -
MarkLLM: An Open-Source Toolkit for LLM Watermarking
Python -
SynthID Text
PythonGoogle
What are regulations?
Regulations are requirements established by governments.
-
Data Protection and Privacy Legislation Worldwide
UNCTAD - Data Protection Laws of the Word
- Digital Policy Alert
- ETO Agora
- GDPR Comparison
- Global AI Regulation
- National AI policies & strategies
- Policy Database
- SCL Artificial Intelligence Contractual Clauses
- Algorithmic Impact Assessment tool
- Directive on Automated Decision-Making
- Directive on Privacy Practices
- Directive on Security Management
- Directive on Service and Digital
- Policy on Government Security
- Policy on Service and Digital
- Privacy Act
- Pan-Canadian Artificial Intelligence Strategy
- Artificial Intelligence and Data Act (Bill C-27)
- Voluntary Code of Conduct on the Responsible Development and Management of Advanced Generative AI Systems
- Guidelines for secure AI system development
| Short Name | Code | Description | Status | Website | Legal text |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cyber Resilience Act (CRA) - horizontal cybersecurity requirements for products with digital elements | 2022/0272(COD) | It introduces mandatory cybersecurity requirements for hardware and software products, throughout their whole lifecycle. | Proposal | Website | Source |
| Data Act | EU/2023/2854 | It enables a fair distribution of the value of data by establishing clear and fair rules for accessing and using data within the European data economy. | Published | Website | Source |
| Data Governance Act | EU/2022/868 | It supports the setup and development of Common European Data Spaces in strategic domains, involving both private and public players, in sectors such as health, environment, energy, agriculture, mobility, finance, manufacturing, public administration and skills. | Published | Website | Source |
| Digital Market Act | EU/2022/1925 | It establishes a set of clearly defined objective criteria to identify “gatekeepers”. Gatekeepers are large digital platforms providing so called core platform services, such as for example online search engines, app stores, messenger services. Gatekeepers will have to comply with the do’s (i.e. obligations) and don’ts (i.e. prohibitions) listed in the DMA. | Published | Website | Source |
| Digital Services Act | EU/2022/2026 | It regulates online intermediaries and platforms such as marketplaces, social networks, content-sharing platforms, app stores, and online travel and accommodation platforms. Its main goal is to prevent illegal and harmful activities online and the spread of disinformation. It ensures user safety, protects fundamental rights, and creates a fair and open online platform environment. | Published | Website | Source |
| DMS Directive | EU/2019/790 | It is intended to ensure a well-functioning marketplace for copyright. | Published | Website | Source |
| Energy Efficiency Directive | EU/2023/1791 | It establishes ‘energy efficiency first’ as a fundamental principle of EU energy policy, giving it legal-standing for the first time. In practical terms, this means that energy efficiency must be considered by EU countries in all relevant policy and major investment decisions taken in the energy and non-energy sectors. | Published | Website | Source |
| EU AI ACT | EU/2024/1689 | It assigns applications of AI to three risk categories. First, applications and systems that create an unacceptable risk are banned. Second, high-risk applications are subject to specific legal requirements. Lastly, applications not explicitly banned or listed as high-risk are largely left unregulated. | Published | Website | Source |
| General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) | EU/2016/679 | It strengthens individuals' fundamental rights in the digital age and facilitate business by clarifying rules for companies and public bodies in the digital single market. | Published | Website | Source |
| NIS2 Directive | EU/2022/2555 | It provides legal measures to boost the overall level of cybersecurity in the EU by ensuring preparedness, cooperation and security cultere across the Member States. | Published | Website | Source |
- State laws: California (CCPA and its amendment, CPRA), Virginia (VCDPA), Colorado (ColoPA - Colorado SB21-190 and Colorado SB21-169: Regulation prohibiting unfair discrimination in insurance) and New York NYC Local Law 144: Mandatory bias audits for automated employment decision tools.
- Specific and limited privacy data laws: HIPAA, FCRA, FERPA, GLBA, ECPA, COPPA, VPPA and FTC.
- EU-U.S. and Swiss-U.S. Privacy Shield Frameworks - The EU-U.S. and Swiss-U.S. Privacy Shield Frameworks were designed by the U.S. Department of Commerce and the European Commission and Swiss Administration to provide companies on both sides of the Atlantic with a mechanism to comply with data protection requirements when transferring personal data from the European Union and Switzerland to the United States in support of transatlantic commerce.
- REMOVING BARRIERS TO AMERICAN LEADERSHIP IN ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE - Official mandate by the President of the US to position the country at the forefront of AI innovation.
- Privacy Act of 1974 - The privacy act of 1974 which establishes a code of fair information practices that governs the collection, maintenance, use and dissemination of information about individuals that is maintained in systems of records by federal agencies.
- Privacy Protection Act of 1980 - The Privacy Protection Act of 1980 protects journalists from being required to turn over to law enforcement any work product and documentary materials, including sources, before it is disseminated to the public.
What are standards?
Standards are voluntary, consensus solutions. They document an agreement on how a material, product, process, or service should be specified, performed or delivered. They keep people safe and ensure things work. They create confidence and provide security for investment.
Standards can be understood as formal specifications of best practices as well. There is a growing number of standards related to AI. You can search for the latest in the Standards Database from AI Standards Hub.
The European Committee for Standardization is one of three European Standardization Organizations (together with CENELEC and ETSI) that have been officially recognized by the European Union and by the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) as being responsible for developing and defining voluntary standards at European level.
| Domain | Standard | Status | URL |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data governance and quality for AI within the European context | CEN/CLC/TR 18115:2024 | Published | Source |
CEN AI Work programme can be found here.
| Domain | Standard | Status | URL |
|---|---|---|---|
| IEEE Guide for an Architectural Framework for Explainable Artificial Intelligence | IEEE 2894-2024 | Published | Source |
| IEEE Recommended Practice for the Quality Management of Datasets for Medical Artificial Intelligence | IEEE 2801-2022 | Published | Source |
| IEEE Standard for Ethical Considerations in Emulated Empathy in Autonomous and Intelligent Systems | IEEE 7014-2024 | Published | Source |
| IEEE Standard for Robustness Testing and Evaluation of Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based Image Recognition Service | IEEE 3129-2023 | Published | Source |
| IEEE Standard for Performance Benchmarking for Artificial Intelligence Server Systems | IEEE 2937-2022 | Published | Source |
UNE is Spain's only Standardisation Organisation, designated by the Spanish Ministry of Economy, Industry and Competitiveness to the European Commission. It helps Spanish organizations to keep up-to-date on all aspects related to standardisation:
- Discover the new regulatory developments;
- Take part in developing standards;
- Learn how to integrate standardisation in your R&D&i project;
| Domain | Standard | Status | URL |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calidad del dato | UNE 0079:2023 | Published | Source |
| Gestión del dato | UNE 0078:2023 | Published | Source |
| Gobierno del dato | UNE 0077:2023 | Published | Source |
| Guía de evaluación de la Calidad de un Conjunto de Datos. | UNE 0081:2023 | Published | Source |
| Guía de evaluación del Gobierno, Gestión y Gestión de la Calidad del Dato. | UNE 0080:2023 | Published | Source |
Additional translations in Spanish can be found here.
| Domain | Standard | Status | URL |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI Concepts and Terminology | ISO/IEC 22989:2022 Information technology — Artificial intelligence — Artificial intelligence concepts and terminology | Published | https://www.iso.org/standard/74296.html |
| AI Risk Management | ISO/IEC 23894:2023 Information technology - Artificial intelligence - Guidance on risk management | Published | https://www.iso.org/standard/77304.html |
| AI Management System | ISO/IEC DIS 42001 Information technology — Artificial intelligence — Management system | Published | https://www.iso.org/standard/81230.html |
| Biases in AI | ISO/IEC TR 24027:2021 Information technology — Artificial intelligence (AI) — Bias in AI systems and AI aided decision making | Published | https://www.iso.org/standard/77607.html |
| AI Performance | ISO/IEC TS 4213:2022 Information technology — Artificial intelligence — Assessment of machine learning classification performance | Published | https://www.iso.org/standard/79799.html |
| Ethical and societal concerns | ISO/IEC TR 24368:2022 Information technology — Artificial intelligence — Overview of ethical and societal concerns | Published | https://www.iso.org/standard/78507.html |
| Explainability | ISO/IEC AWI TS 6254 Information technology — Artificial intelligence — Objectives and approaches for explainability of ML models and AI systems | Under Development | https://www.iso.org/standard/82148.html |
| AI Sustainability | ISO/IEC AWI TR 20226 Information technology — Artificial intelligence — Environmental sustainability aspects of AI systems | Under Development | https://www.iso.org/standard/86177.html |
| AI Verification and Validation | ISO/IEC AWI TS 17847 Information technology — Artificial intelligence — Verification and validation analysis of AI systems | Under Development | https://www.iso.org/standard/85072.html |
| AI Controllabitlity | ISO/IEC CD TS 8200 Information technology — Artificial intelligence — Controllability of automated artificial intelligence systems | Published | https://www.iso.org/standard/83012.html |
| Biases in AI | ISO/IEC CD TS 12791 Information technology — Artificial intelligence — Treatment of unwanted bias in classification and regression machine learning tasks | Published | https://www.iso.org/standard/84110.html |
| AI Impact Assessment | ISO/IEC AWI 42005 Information technology — Artificial intelligence — AI system impact assessment | Under Development | https://www.iso.org/standard/44545.html |
| Data Quality for AI/ML | ISO/IEC DIS 5259 Artificial intelligence — Data quality for analytics and machine learning (ML) (1 to 6) | Published | https://www.iso.org/standard/81088.html |
| Data Lifecycle | ISO/IEC FDIS 8183 Information technology — Artificial intelligence — Data life cycle framework | Published | https://www.iso.org/standard/83002.html |
| Audit and Certification | ISO/IEC CD 42006 Information technology — Artificial intelligence — Requirements for bodies providing audit and certification of artificial intelligence management systems | Under Development | https://www.iso.org/standard/44546.html |
| Transparency | ISO/IEC AWI 12792 Information technology — Artificial intelligence — Transparency taxonomy of AI systems | Under Development | https://www.iso.org/standard/84111.html |
| AI Quality | ISO/IEC AWI TR 42106 Information technology — Artificial intelligence — Overview of differentiated benchmarking of AI system quality characteristics | Under Development | https://www.iso.org/standard/86903.html |
| Trustworthy AI | ISO/IEC TR 24028:2020 Information technology — Artificial intelligence — Overview of trustworthiness in artificial intelligence | Published | https://www.iso.org/standard/77608.html |
| Synthetic Data | ISO/IEC AWI TR 42103 Information technology — Artificial intelligence — Overview of synthetic data in the context of AI systems | Under Development | https://www.iso.org/standard/86899.html |
| AI Security | ISO/IEC AWI 27090 Cybersecurity — Artificial Intelligence — Guidance for addressing security threats and failures in artificial intelligence systems | Under Development | https://www.iso.org/standard/56581.html |
| AI Privacy | ISO/IEC AWI 27091 Cybersecurity and Privacy — Artificial Intelligence — Privacy protection | Under Development | https://www.iso.org/standard/56582.html |
| AI Governance | ISO/IEC 38507:2022 Information technology — Governance of IT — Governance implications of the use of artificial intelligence by organizations | Published | https://www.iso.org/standard/56641.html |
| AI Safety | ISO/IEC CD TR 5469 Artificial intelligence — Functional safety and AI systems | Published | https://www.iso.org/standard/81283.html |
| Beneficial AI Systems | ISO/IEC AWI TR 21221 Information technology – Artificial intelligence – Beneficial AI systems | Under Development | https://www.iso.org/standard/86690.html |
| Resource | Description | Source |
|---|---|---|
| AI RMF (Risk Management Framework) | The AI Risk Management Framework (AI RMF) is intended for voluntary use and to improve the ability to incorporate trustworthiness considerations into the design, development, use, and evaluation of AI products, services, and systems. | Source |
| AI RMF Playbook | The Playbook provides suggested actions for achieving the outcomes laid out in the AI Risk Management Framework (AI RMF) Core (Tables 1 – 4 in AI RMF 1.0). Suggestions are aligned to each sub-category within the four AI RMF functions (Govern, Map, Measure, Manage). | Source |
| AI RMF Glossary | This glossary seeks to promote a shared understanding and improve communication among individuals and organizations seeking to operationalize trustworthy and responsible AI through approaches such as the NIST AI Risk Management Framework (AI RMF). | Source |
Additional standards can be found using the Standards Database and we recommend to review NIST Assessing Risks and Impacts of AI (ARIA) as well.
Contributors with over 50 edits can be named coauthors in the citation of visible names. Otherwise, all contributors with fewer than 50 edits are included under "et al."
@misc{arai_repo,
author={Josep Curto et al.},
title={Awesome Responsible Artificial Intelligence},
year={2025},
note={\url{https://github.com/AthenaCore/AwesomeResponsibleAI}}
}
ACM (Association for Computing Machinery)
Curto, J., et al. 2025. Awesome Responsible Artificial Intelligence. GitHub. https://github.com/AthenaCore/AwesomeResponsibleAI.
APA (American Psychological Association) 7th Edition
Curto, J., et al. (2025). Awesome Responsible Artificial Intelligence. GitHub. https://github.com/AthenaCore/AwesomeResponsibleAI.
Chicago Manual of Style 17th Edition
Curto, J., et al. "Awesome Responsible Artificial Intelligence." GitHub. Last modified 2025. https://github.com/AthenaCore/AwesomeResponsibleAI.
MLA (Modern Language Association) 9th Edition
Curto, J., et al. "Awesome Responsible Artificial Intelligence". GitHub, 2025, https://github.com/AthenaCore/AwesomeResponsibleAI. Accessed 07 Feb 2025.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for AwesomeResponsibleAI
Similar Open Source Tools

AwesomeResponsibleAI
Awesome Responsible AI is a curated list of academic research, books, code of ethics, courses, data sets, frameworks, institutes, newsletters, principles, podcasts, reports, tools, regulations, and standards related to Responsible, Trustworthy, and Human-Centered AI. It covers various concepts such as Responsible AI, Trustworthy AI, Human-Centered AI, Responsible AI frameworks, AI Governance, and more. The repository provides a comprehensive collection of resources for individuals interested in ethical, transparent, and accountable AI development and deployment.
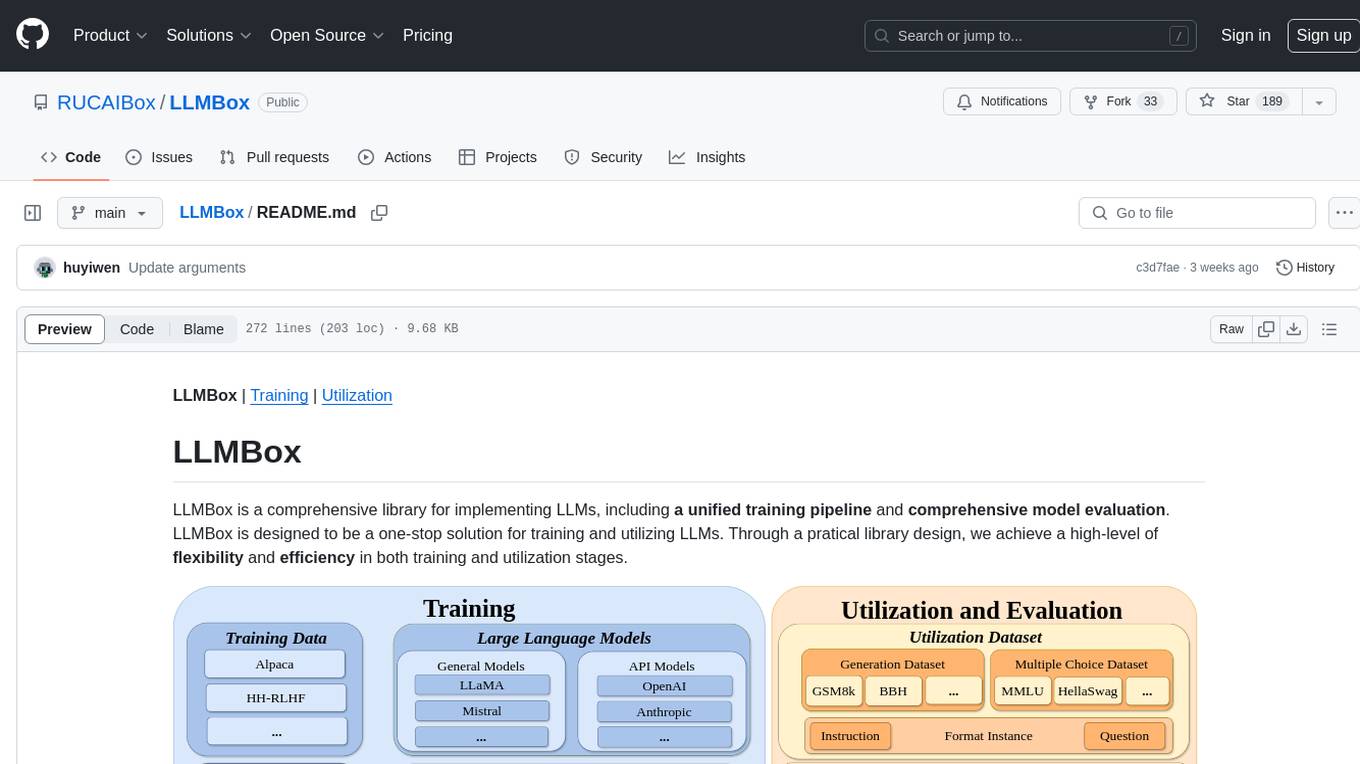
LLMBox
LLMBox is a comprehensive library designed for implementing Large Language Models (LLMs) with a focus on a unified training pipeline and comprehensive model evaluation. It serves as a one-stop solution for training and utilizing LLMs, offering flexibility and efficiency in both training and utilization stages. The library supports diverse training strategies, comprehensive datasets, tokenizer vocabulary merging, data construction strategies, parameter efficient fine-tuning, and efficient training methods. For utilization, LLMBox provides comprehensive evaluation on various datasets, in-context learning strategies, chain-of-thought evaluation, evaluation methods, prefix caching for faster inference, support for specific LLM models like vLLM and Flash Attention, and quantization options. The tool is suitable for researchers and developers working with LLMs for natural language processing tasks.

interpreto
Interpreto is an interpretability toolkit for large language models (LLMs) that provides a modular framework encompassing attribution methods, concept-based methods, and evaluation metrics. It includes various inference-based and gradient-based attribution methods for both classification and generation tasks. The toolkit also offers concept-based explanations to provide high-level interpretations of latent model representations through steps like concept discovery, interpretation, and concept-to-output attribution. Interpreto aims to enhance model interpretability and facilitate understanding of model decisions and outputs.
sec-code-bench
SecCodeBench is a benchmark suite for evaluating the security of AI-generated code, specifically designed for modern Agentic Coding Tools. It addresses challenges in existing security benchmarks by ensuring test case quality, employing precise evaluation methods, and covering Agentic Coding Tools. The suite includes 98 test cases across 5 programming languages, focusing on functionality-first evaluation and dynamic execution-based validation. It offers a highly extensible testing framework for end-to-end automated evaluation of agentic coding tools, generating comprehensive reports and logs for analysis and improvement.
LLM-as-HH
LLM-as-HH is a codebase that accompanies the paper ReEvo: Large Language Models as Hyper-Heuristics with Reflective Evolution. It introduces Language Hyper-Heuristics (LHHs) that leverage LLMs for heuristic generation with minimal manual intervention and open-ended heuristic spaces. Reflective Evolution (ReEvo) is presented as a searching framework that emulates the reflective design approach of human experts while surpassing human capabilities with scalable LLM inference, Internet-scale domain knowledge, and powerful evolutionary search. The tool can improve various algorithms on problems like Traveling Salesman Problem, Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem, Orienteering Problem, Multiple Knapsack Problems, Bin Packing Problem, and Decap Placement Problem in both black-box and white-box settings.
SpargeAttn
SpargeAttn is an official implementation designed for accelerating any model inference by providing accurate sparse attention. It offers a significant speedup in model performance while maintaining quality. The tool is based on SageAttention and SageAttention2, providing options for different levels of optimization. Users can easily install the package and utilize the available APIs for their specific needs. SpargeAttn is particularly useful for tasks requiring efficient attention mechanisms in deep learning models.
evolving-agents
A toolkit for agent autonomy, evolution, and governance enabling agents to learn from experience, collaborate, communicate, and build new tools within governance guardrails. It focuses on autonomous evolution, agent self-discovery, governance firmware, self-building systems, and agent-centric architecture. The toolkit leverages existing frameworks to enable agent autonomy and self-governance, moving towards truly autonomous AI systems.
distilabel
Distilabel is a framework for synthetic data and AI feedback for AI engineers that require high-quality outputs, full data ownership, and overall efficiency. It helps you synthesize data and provide AI feedback to improve the quality of your AI models. With Distilabel, you can: * **Synthesize data:** Generate synthetic data to train your AI models. This can help you to overcome the challenges of data scarcity and bias. * **Provide AI feedback:** Get feedback from AI models on your data. This can help you to identify errors and improve the quality of your data. * **Improve your AI output quality:** By using Distilabel to synthesize data and provide AI feedback, you can improve the quality of your AI models and get better results.
basiclingua-LLM-Based-NLP
BasicLingua is a Python library that provides functionalities for linguistic tasks such as tokenization, stemming, lemmatization, and many others. It is based on the Gemini Language Model, which has demonstrated promising results in dealing with text data. BasicLingua can be used as an API or through a web demo. It is available under the MIT license and can be used in various projects.
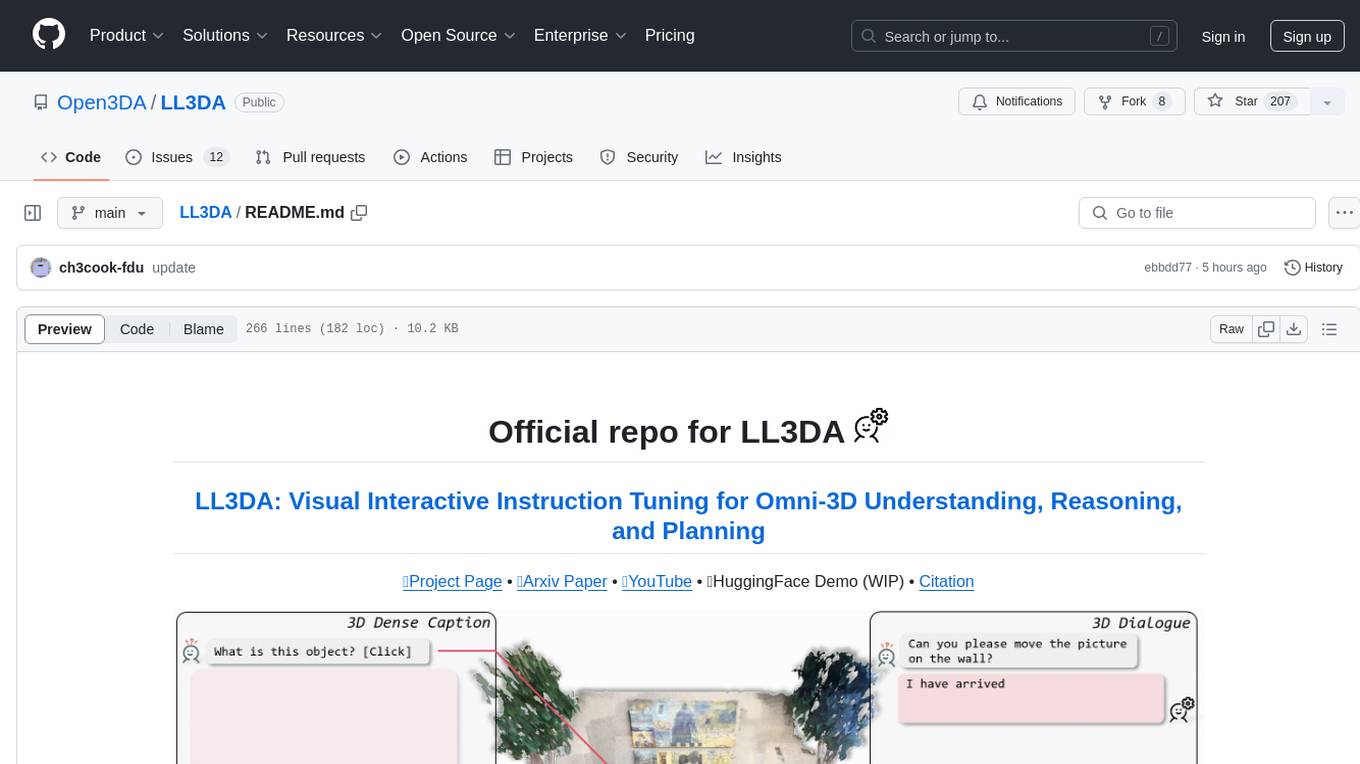
LL3DA
LL3DA is a Large Language 3D Assistant that responds to both visual and textual interactions within complex 3D environments. It aims to help Large Multimodal Models (LMM) comprehend, reason, and plan in diverse 3D scenes by directly taking point cloud input and responding to textual instructions and visual prompts. LL3DA achieves remarkable results in 3D Dense Captioning and 3D Question Answering, surpassing various 3D vision-language models. The code is fully released, allowing users to train customized models and work with pre-trained weights. The tool supports training with different LLM backends and provides scripts for tuning and evaluating models on various tasks.
LongCite
LongCite is a tool that enables Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate fine-grained citations in long-context Question Answering (QA) scenarios. It provides models trained on GLM-4-9B and Meta-Llama-3.1-8B, supporting up to 128K context. Users can deploy LongCite chatbots, generate accurate responses, and obtain precise sentence-level citations. The tool includes components for model deployment, Coarse to Fine (CoF) pipeline for data construction, model training using LongCite-45k dataset, evaluation with LongBench-Cite benchmark, and citation generation.
KnowAgent
KnowAgent is a tool designed for Knowledge-Augmented Planning for LLM-Based Agents. It involves creating an action knowledge base, converting action knowledge into text for model understanding, and a knowledgeable self-learning phase to continually improve the model's planning abilities. The tool aims to enhance agents' potential for application in complex situations by leveraging external reservoirs of information and iterative processes.
evidently
Evidently is an open-source Python library designed for evaluating, testing, and monitoring machine learning (ML) and large language model (LLM) powered systems. It offers a wide range of functionalities, including working with tabular, text data, and embeddings, supporting predictive and generative systems, providing over 100 built-in metrics for data drift detection and LLM evaluation, allowing for custom metrics and tests, enabling both offline evaluations and live monitoring, and offering an open architecture for easy data export and integration with existing tools. Users can utilize Evidently for one-off evaluations using Reports or Test Suites in Python, or opt for real-time monitoring through the Dashboard service.
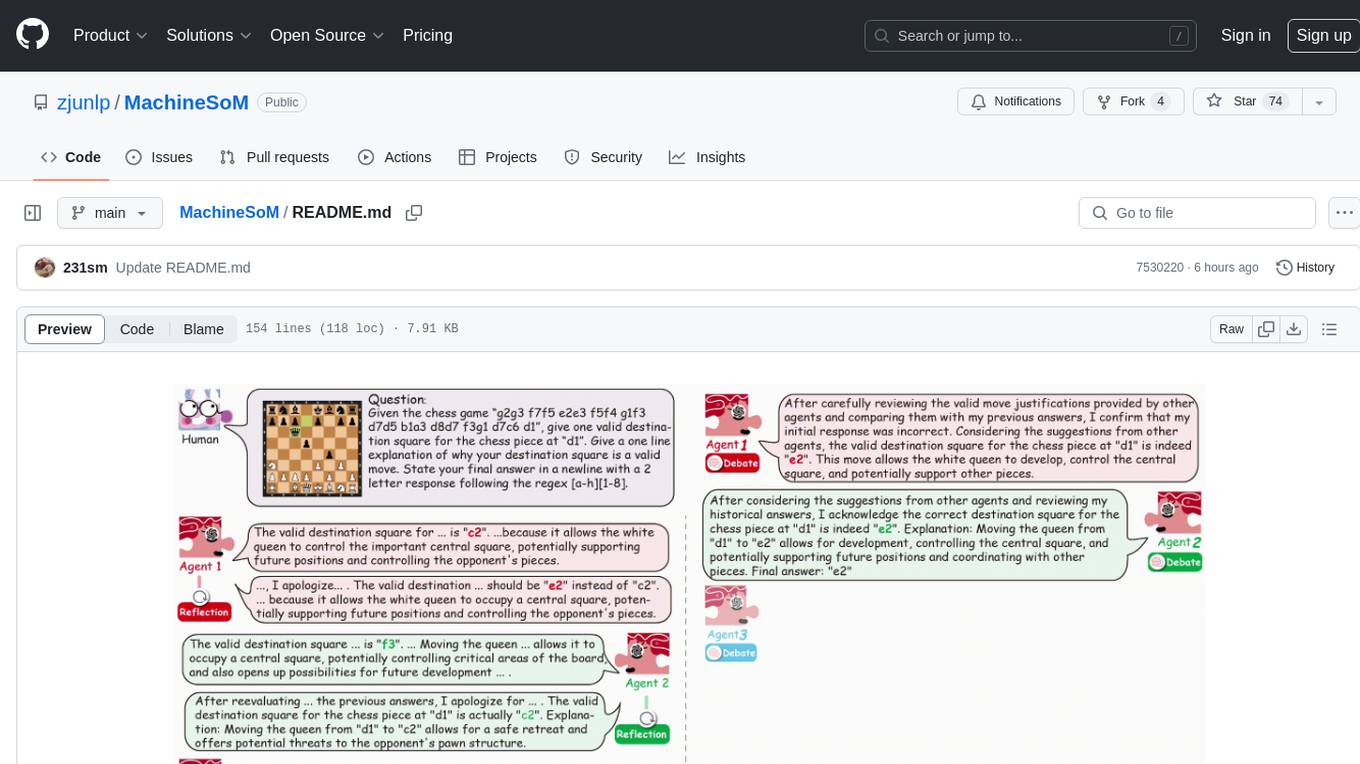
MachineSoM
MachineSoM is a code repository for the paper 'Exploring Collaboration Mechanisms for LLM Agents: A Social Psychology View'. It focuses on the emergence of intelligence from collaborative and communicative computational modules, enabling effective completion of complex tasks. The repository includes code for societies of LLM agents with different traits, collaboration processes such as debate and self-reflection, and interaction strategies for determining when and with whom to interact. It provides a coding framework compatible with various inference services like Replicate, OpenAI, Dashscope, and Anyscale, supporting models like Qwen and GPT. Users can run experiments, evaluate results, and draw figures based on the paper's content, with available datasets for MMLU, Math, and Chess Move Validity.
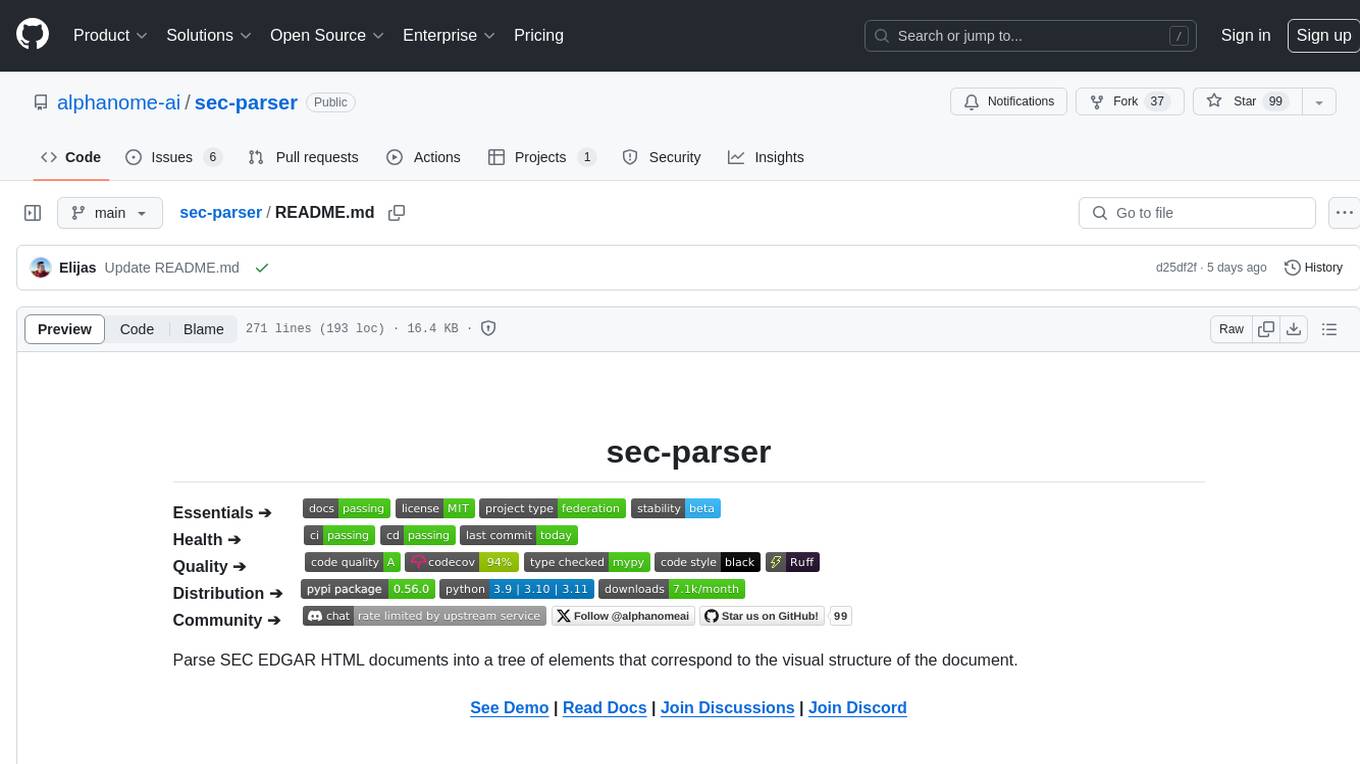
sec-parser
The `sec-parser` project simplifies extracting meaningful information from SEC EDGAR HTML documents by organizing them into semantic elements and a tree structure. It helps in parsing SEC filings for financial and regulatory analysis, analytics and data science, AI and machine learning, causal AI, and large language models. The tool is especially beneficial for AI, ML, and LLM applications by streamlining data pre-processing and feature extraction.
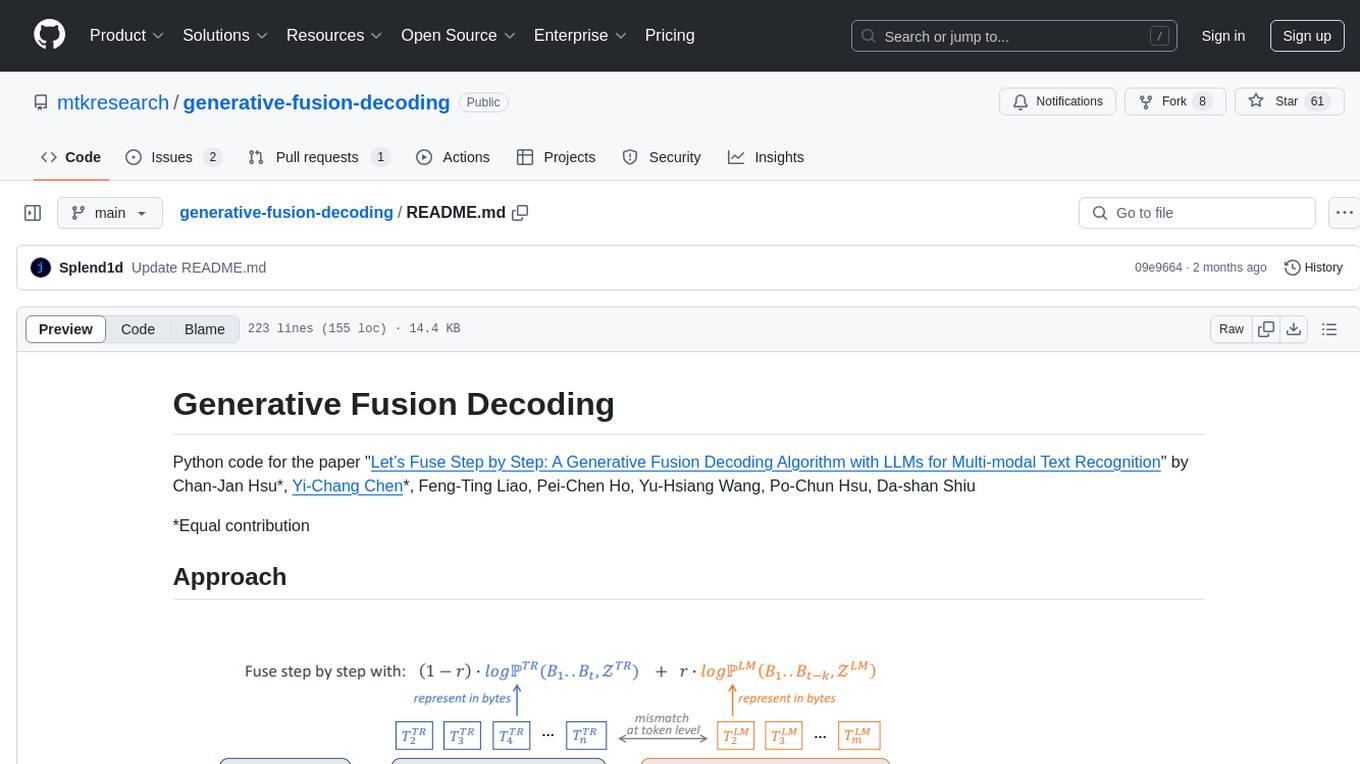
generative-fusion-decoding
Generative Fusion Decoding (GFD) is a novel shallow fusion framework that integrates Large Language Models (LLMs) into multi-modal text recognition systems such as automatic speech recognition (ASR) and optical character recognition (OCR). GFD operates across mismatched token spaces of different models by mapping text token space to byte token space, enabling seamless fusion during the decoding process. It simplifies the complexity of aligning different model sample spaces, allows LLMs to correct errors in tandem with the recognition model, increases robustness in long-form speech recognition, and enables fusing recognition models deficient in Chinese text recognition with LLMs extensively trained on Chinese. GFD significantly improves performance in ASR and OCR tasks, offering a unified solution for leveraging existing pre-trained models through step-by-step fusion.
For similar tasks

AwesomeResponsibleAI
Awesome Responsible AI is a curated list of academic research, books, code of ethics, courses, data sets, frameworks, institutes, newsletters, principles, podcasts, reports, tools, regulations, and standards related to Responsible, Trustworthy, and Human-Centered AI. It covers various concepts such as Responsible AI, Trustworthy AI, Human-Centered AI, Responsible AI frameworks, AI Governance, and more. The repository provides a comprehensive collection of resources for individuals interested in ethical, transparent, and accountable AI development and deployment.
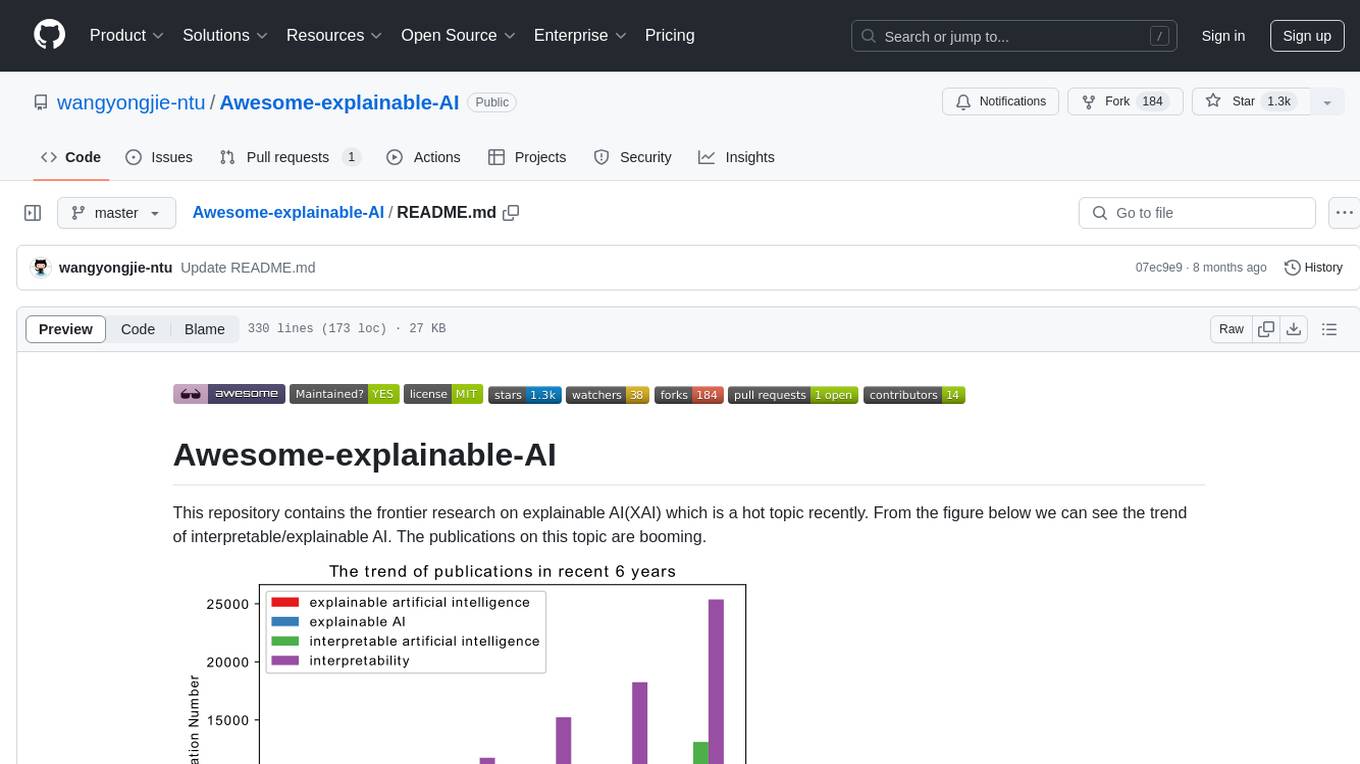
Awesome-explainable-AI
This repository contains frontier research on explainable AI (XAI), a hot topic in the field of artificial intelligence. It includes trends, use cases, survey papers, books, open courses, papers, and Python libraries related to XAI. The repository aims to organize and categorize publications on XAI, provide evaluation methods, and list various Python libraries for explainable AI.
pytorch-grad-cam
This repository provides advanced AI explainability for PyTorch, offering state-of-the-art methods for Explainable AI in computer vision. It includes a comprehensive collection of Pixel Attribution methods for various tasks like Classification, Object Detection, Semantic Segmentation, and more. The package supports high performance with full batch image support and includes metrics for evaluating and tuning explanations. Users can visualize and interpret model predictions, making it suitable for both production and model development scenarios.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.




